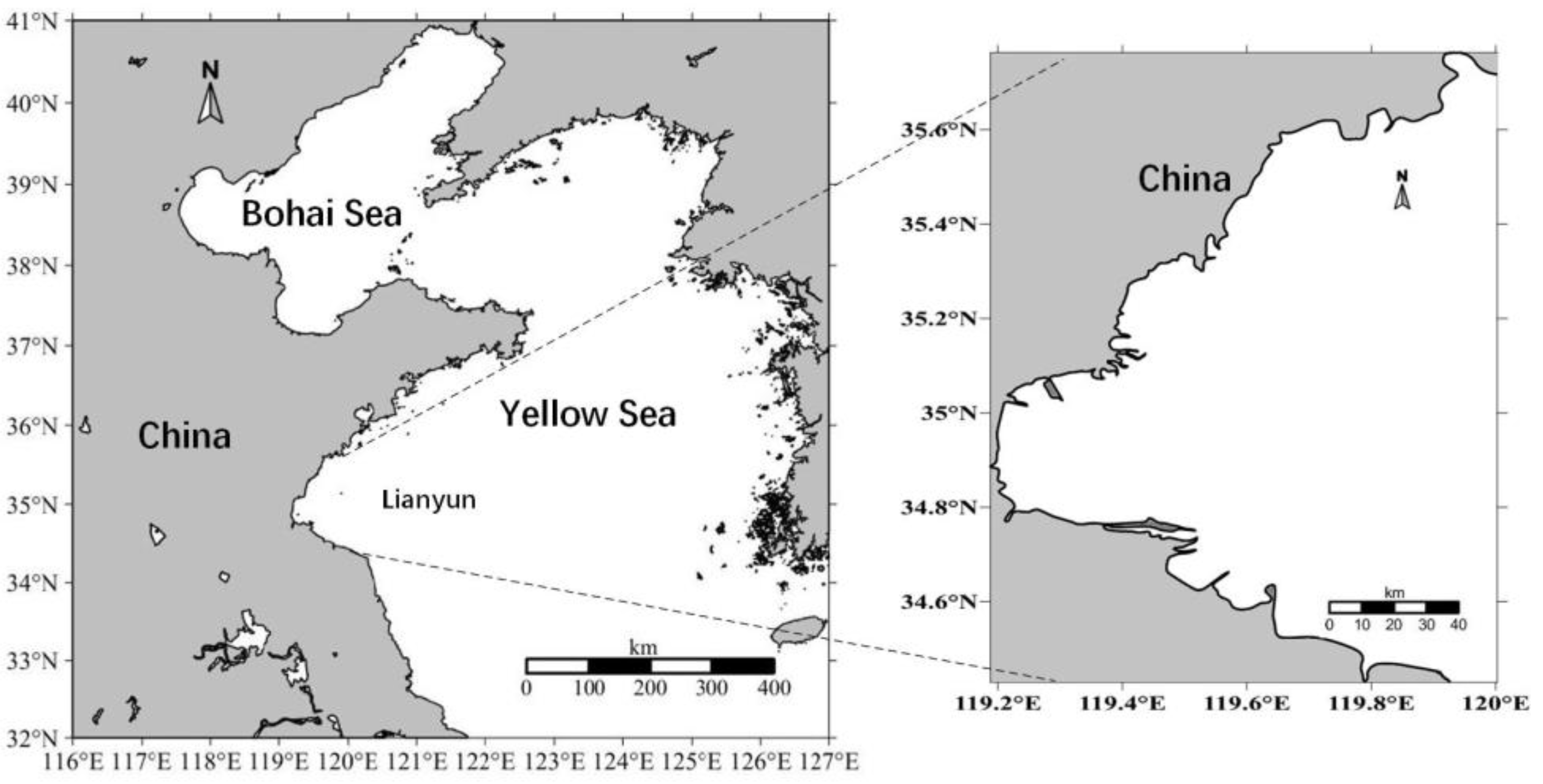
The Impact of Tides and Monsoons on Tritium Migration and Diffusion in Coastal Harbours: A Simulation Study in Lianyungang Haizhou Bay, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modelling and Numerical Experimental Design
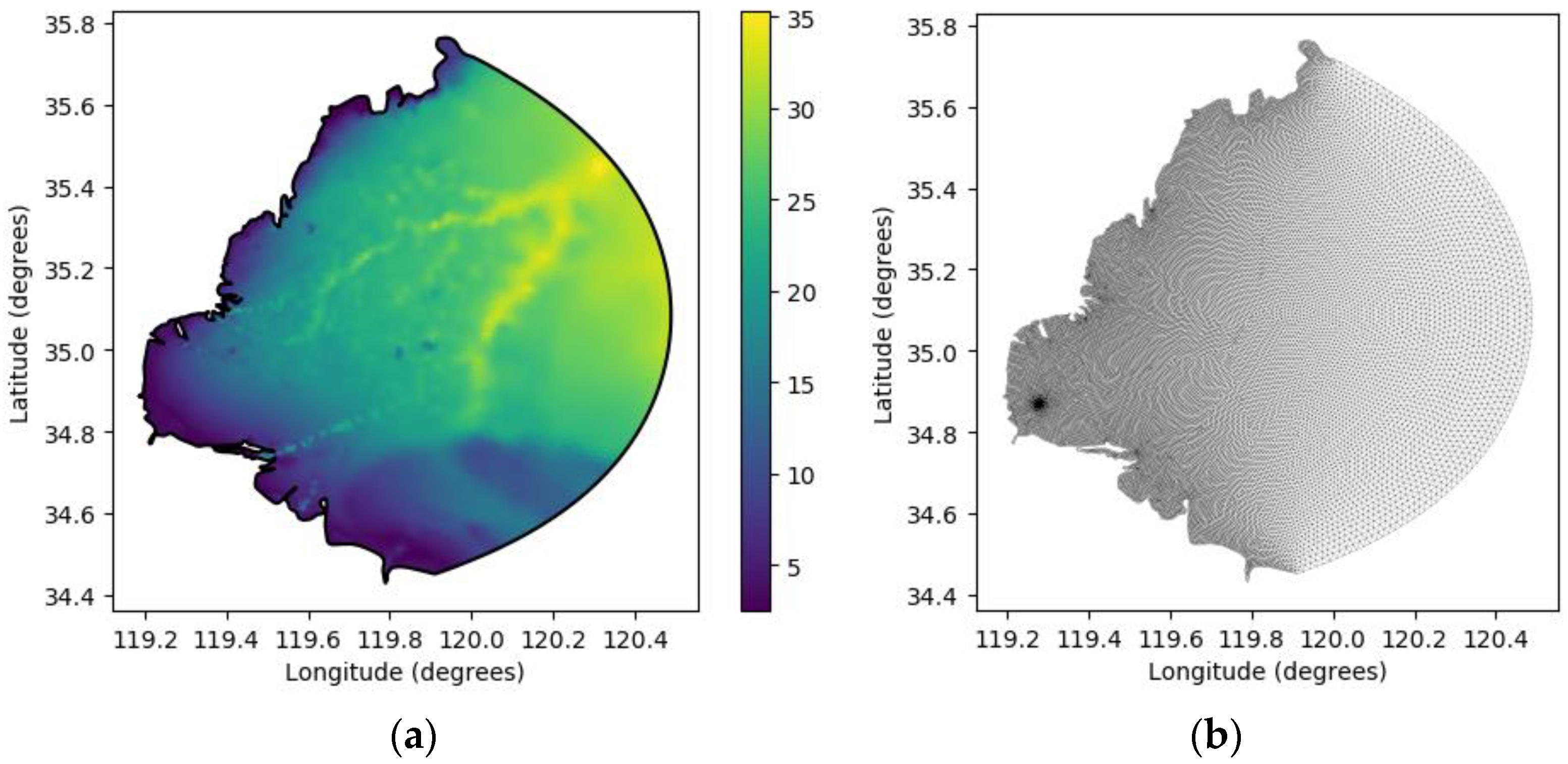
2.1. Model Description
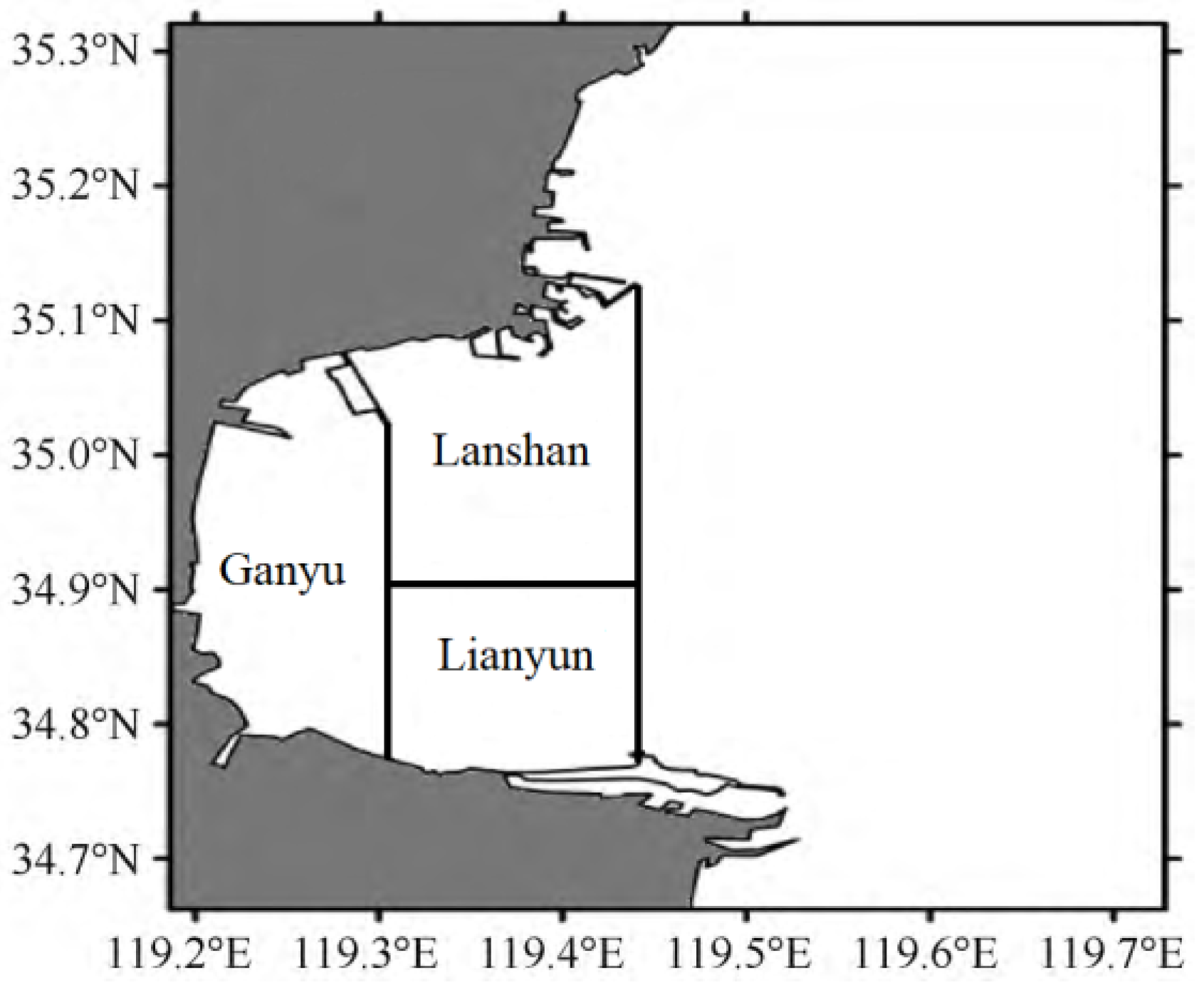
2.2. Numerical Experiment Design
2.3. Initial Condition Setting
3. Hydrodynamic Simulation Results and Discussion
3.1. Model Description
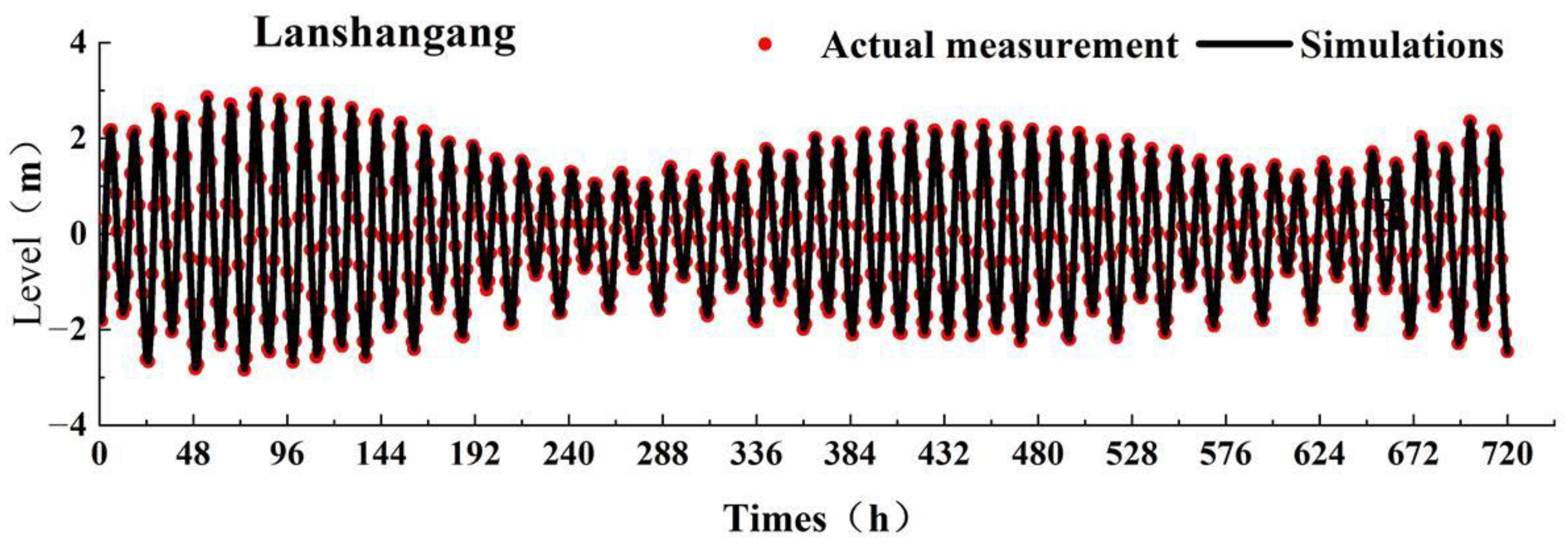
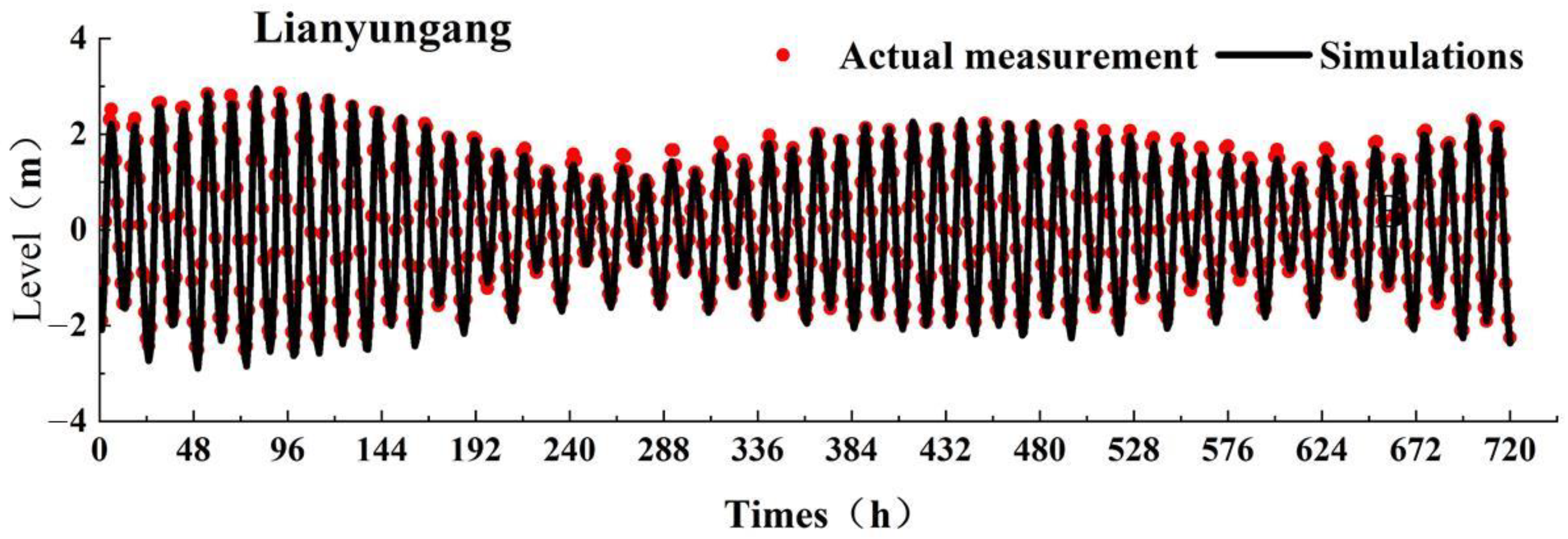
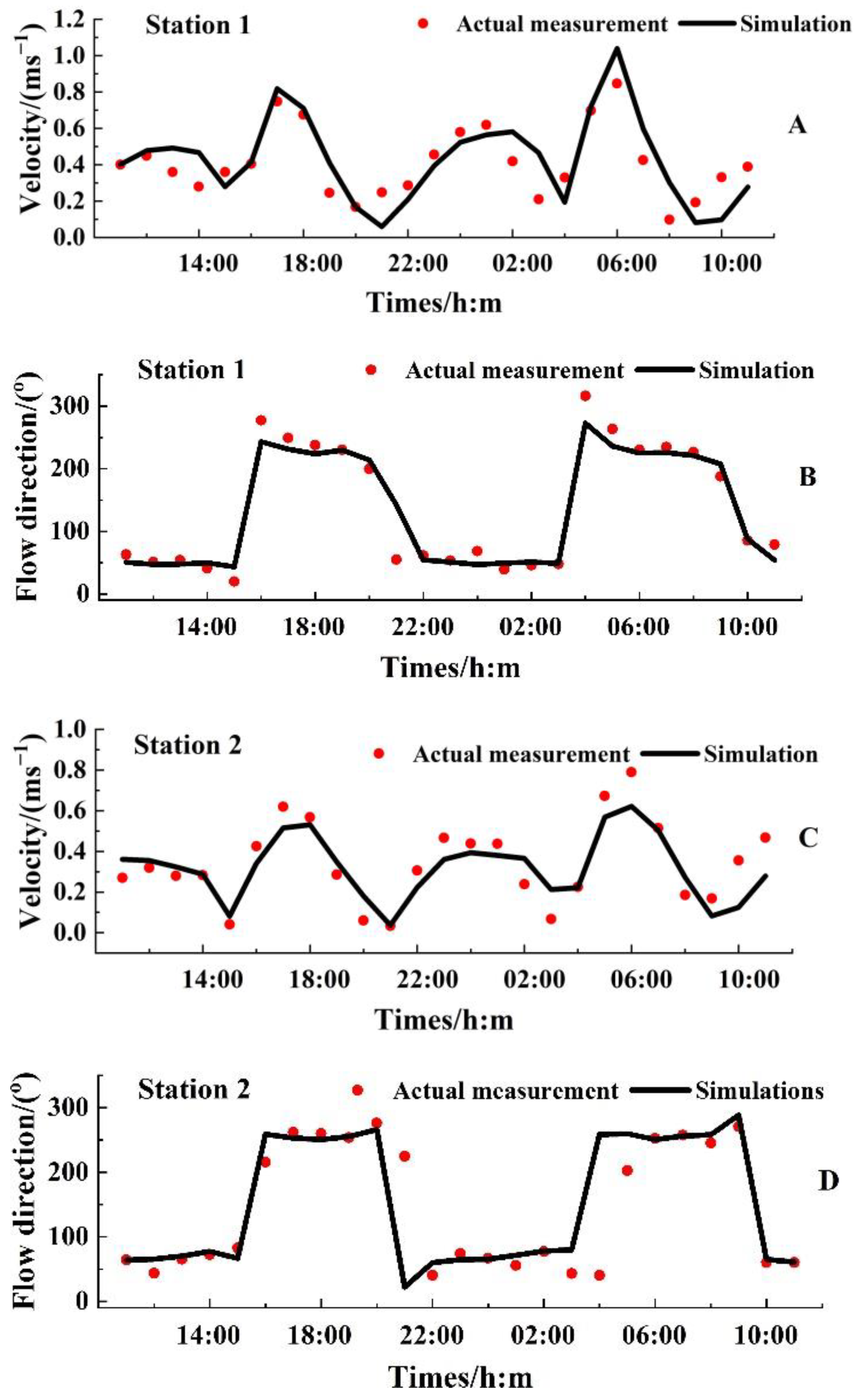
3.2. Trend Validation
4. Tritium Migration and Diffusion under Different Operating Conditions
4.1. Tidal Effects on Radionuclide Transport Diffusion
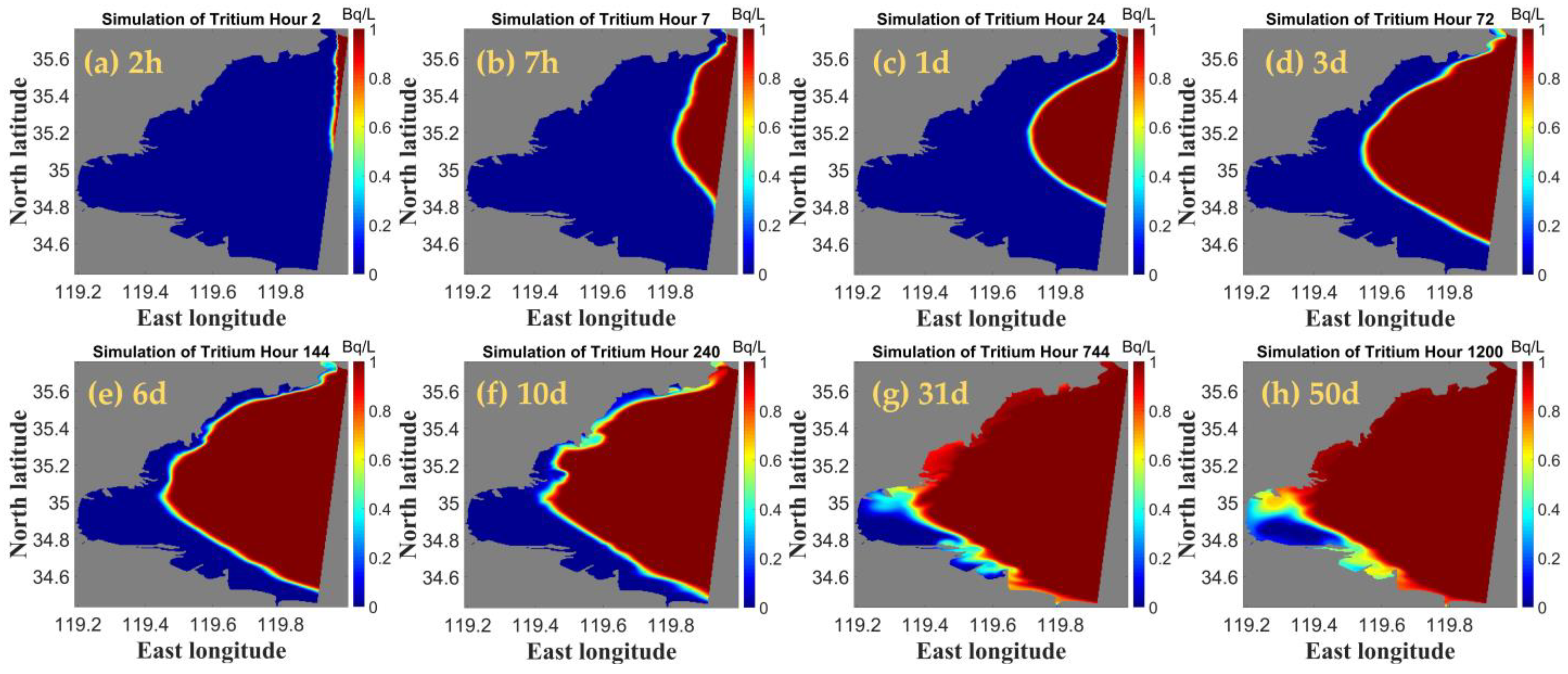
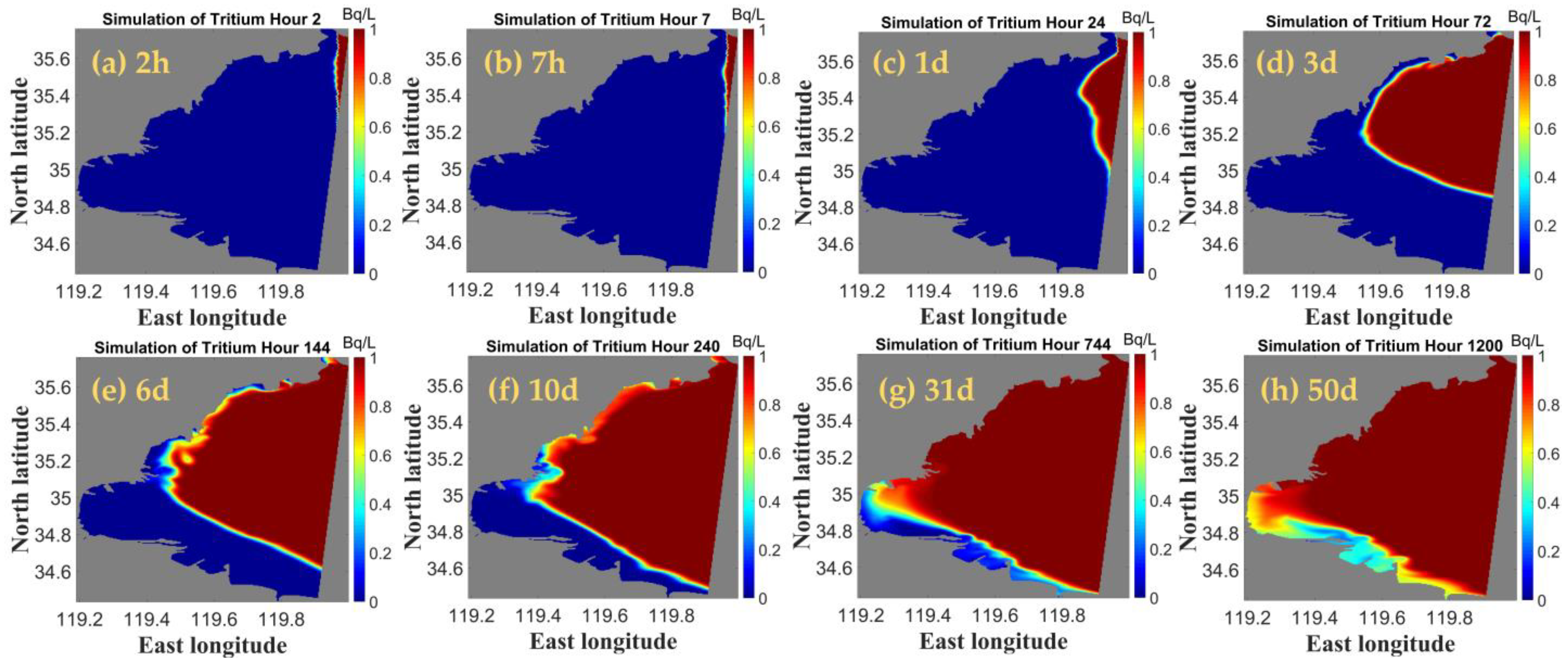
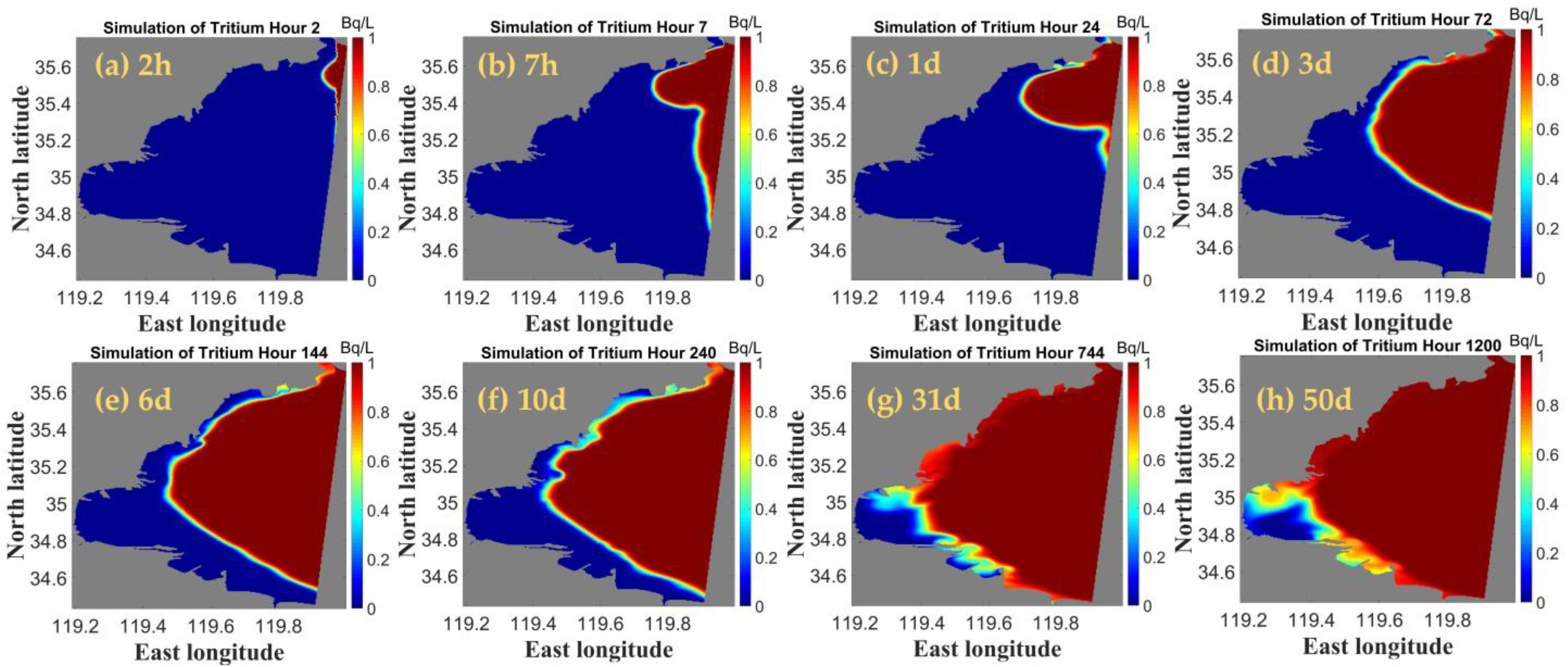
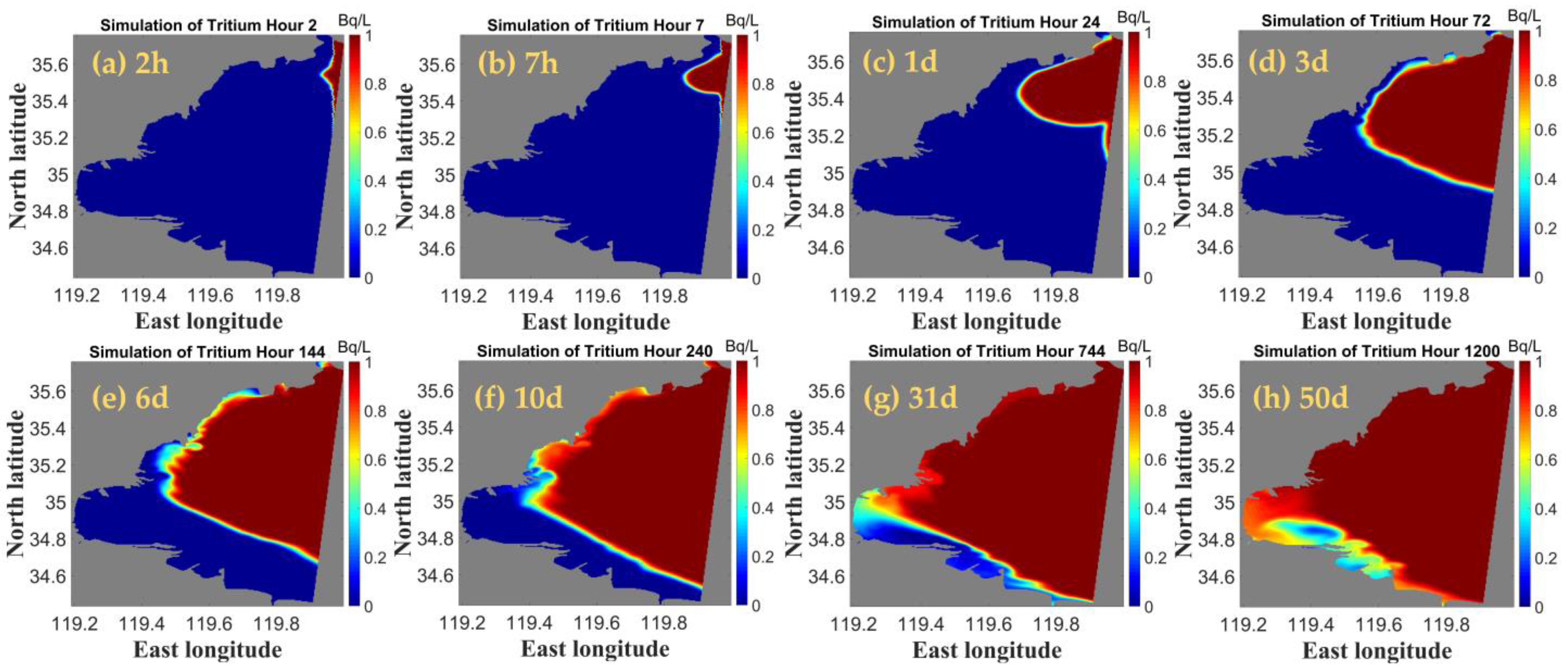
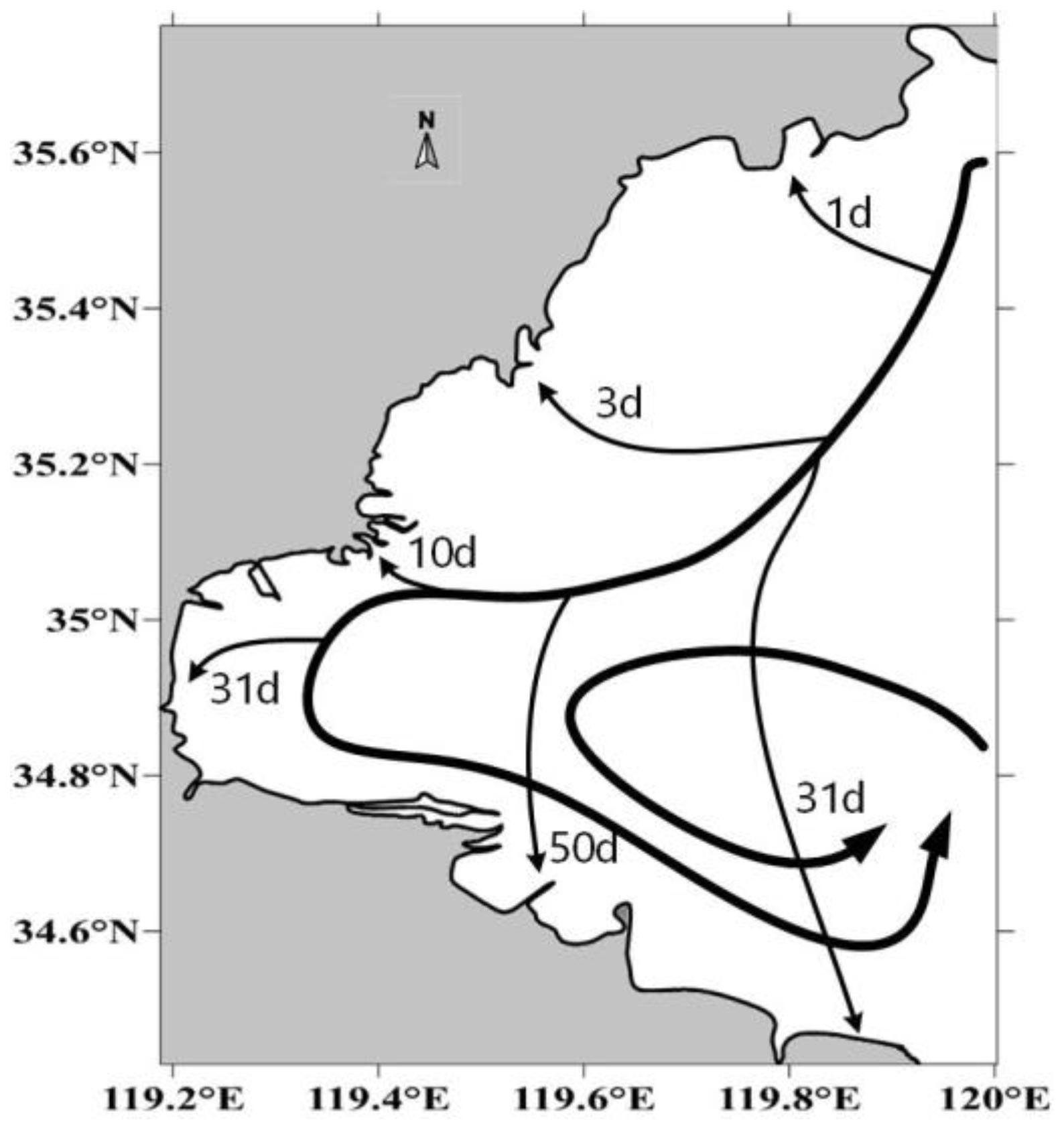
4.1.1. Radionuclide Tritium Diffusion Path Analysis
4.1.2. Analysis of the Transmission Range of Radionuclide Tritium
4.1.3. Characterization of the Distribution of Highly Concentrated Nuclides and Analysis of Diffusion Rates
4.2. Monsoon Effects on Radionuclide Transport and Dispersion
5. Conclusions
- Under the influence of tides and monsoon winds, the radionuclides continue to diffuse into the harbour over time. The hydrodynamic effect in Haizhou Bay is weak, the water exchange rate is slow, and the diffusion of radionuclides in the bay is slow, while that outside the harbour is fast. The water body at the mouth of the bay is more active, and the flow rate inside the bay is weak, which is not conducive to the dilution of pollutants.
- The concentration distribution of the radionuclide tritium is affected by the flow field, which is mainly influenced by the tides. Due to the tides, radionuclide contamination is more severe in winter than it is in summer.
- The simulation of the transport diffusion of nuclides shows that, in general, monsoons have a weak effect on the diffusion of radionuclides in Haizhou Bay. Monsoons promote the diffusion of radionuclides outside the harbour and inhibit their diffusion inside the harbour.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ken, O.B.; Steven, R.J.; Nicholas, S.F.; Irina, I.R.; Hannes, B.; Zofia, B.; Crystaline, F.B.; Elizabeth, M.D.; Jennifer, G.; Alison, M.M.; et al. Fukushima-derived radionuclides in the ocean and biota off Japan. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5984–5988. [Google Scholar]
- Bing, L.; Chen, Y.; Yu, S.; Chen, X.; Yang, D. Post-accident leakage and discharge of radioactive waste liquid at Fukushima da-ichi NPP and its environmental impacts. Radiat. Prot. 2012, 32, 33–347. [Google Scholar]
- Bezhenar, R.; Takata, H.; de With, G.; Maderich, V. Planned release of contaminated water from the Fukushima storage tanks into the ocean: Simulation scenarios of radiological impact for aquatic biota and human from seafood consumption. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 173, 112969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, M.; Hamajima, Y.; Hult, M.; Uematsu, M.; Oka, E.; Tsumune, D.; Kumamoto, Y. 134Cs and 137Cs in the North Pacific Ocean derived from the March 2011 TEPCO Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, Japan. Part one: Surface pathway and vertical distributions. J. Oceanogr. 2016, 72, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, M.; Hult, M.; Hamajima, Y.; Lutter, G.; Marissens, G.; Stroh, H.; Tzika, F. Tracing radioactivity from Fukushima in the Northern Pacific Ocean. Appl. Radiat. Isot. Incl. Data Instrum. Methods Use Agric. Ind. Med. 2016, 109, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhauser, G. Fukushima’s forgotten radionuclides: A review of the understudied radioactive emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4649–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanial, V.; Buesseler, K.O.; Charette, M.A.; Nagao, S. Unexpected source of Fukushima-derived radiocesium to the coastal ocean of Japan. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11092–11096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.; Periáñez, R.; Kim, I.; Suh, K. Marine dispersion assessment of 137Cs released from the Fukushima nuclear accident. Mar. Pollut Bull 2013, 72, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, Y.; Masumoto, Y.; Varlamov, S.M.; Miyama, T.; Takigawa, M.; Honda, M.; Saino, T. Inverse estimation of source parameters of oceanic radioactivity dispersion models associated with the Fukushima accident. Biogeosci. Discuss 2012, 9, 13783–13816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.W.; Zhang, K.; Chen, H.Y.; Mao, Y.X.; Zhang, A.L.; Tan, C.J. Study on Radionuclide Migration in Near-shore WatersAround a Coastal Nuclear Power Plant. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2016, 34, 272–279. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.N.; Brown, R.M.; Williams, W.J.; Robert, M.; Nelson, R.; Moran, S.B. Arrival of the Fukushima radioactivity plume in North American continental waters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier-Laplace, J.; Beaugeln-Seiller, K.; Hinton, T.G. Fukushima wildlife dose reconstruction signals ecological consequences. Env. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5077–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaizer, J.; Kumamoto, Y.; Molnár, M.; Palcsu, L.; Povinec, P.P. Temporal changes in tritium and radiocarbon concentrations in the western North Pacific Ocean (1993–2012). J. Environ. Radioact. 2020, 218, 106238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, Q.; Xu, Y. Input function and simulated distributions of tritium in the North Pacific. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, G.; Zhang, M.; Wang, G.; de With, G.; Bezhenar, R.; Qiao, F. Transport and dispersion of tritium from the radioactive water of the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 169, 112515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhlke, T.R.; Sültenfuß, J.; Trachte, K.; Huneau, F.; Garel, E.; Santoni, S.; van Geldern, R. Tritium as a hydrological tracer in Mediterranean precipitation events. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 3555–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Li, Y.X.; Hu, G.H.; Pan, M. Research on distribution of H-3 concentration filed by the liquid waste discharging from the Dayawan nuclear power station. J. Jinan Univ. 2001, 22, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Su, K. The Research on the Law of Tide Induced Dispersion of the Liquid Radioactive Wastes of Daya Bay Nuclear Power Station and on the Law of Radionuclide Transfer in the Marine Ecosystems; Jinan University: Guangzhou, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Su, K. The numerical simulation for the transfer of the radionuclide from the liquid releases of the nuclear power station to the ocean systems in the ecosystems. Mar. Sci. 2007, 31, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L.F. Research on Radioecology at Daya Bay-A Study on the Transfer of Radionuclide in the Marine Ecosystem and Entrainment Effect of Marine Organism; Jinan University: Guangzhou, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.Y.; Yang, H.W. Diffusion model of radioactive pollutants in nearshore zone. J. Radiat. Res. Radiat. Process 2019, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.F. The Research of Offshore Liquid Radioactive Material Diffusion Model; Chengdu University of Technology: Chengdu, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Khangaonkar, T.; Nugraha, A.; Hinton, S.; Michalsen, D.; Brown, S. Sediment transport into the Swinomish Navigation Channel, Puget Sound—Habitat restoration versus navigation maintenance needs. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2017, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayache, M.; Dutay, J.C.; Jean-Baptiste, P.; Beranger, K.; Arsouze, T.; Beuvier, J.; Roether, W. Modelling of the anthropogenic tritium transient and its decay product helium-3 in the Mediterranean Sea using a high-resolution regional model. Ocean Sci. 2015, 11, 323–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, B.K.; Trudel, M.; Wilson, B.M.; Carr, J.; Daniels, J.; Haigh, S.; Page, F. Modelling the effects of currents and migratory behaviours on the dispersal of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) post-smolts in a coastal embayment. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2022, 79, 2087–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connan, O.; Du Bois, P.B.; Solier, L.; Hebert, D.; Voiseux, C. Flux of tritium from the sea to the atmosphere around a nuclear reprocessing plant: Experimental measurements and modelling for the Western English channel. J. Environ. Radioact. 2023, 257, 107068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Hong, G.; Li, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Ma, Y. Seasonal dynamics of coastal pollution migration in open waters with intensive marine ranching. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 190, 106101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Cong, S.; Zang, Z.; Bi, N.; Bian, C.; Wu, X. Rapid oscillation of sediment transport between the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea induced by Typhoon Lekima (2019). Mar. Geol. 2023, 465, 107160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.L.; Pan, M. Effect of the tide on the diffusion of 3H the liquid effluent discharged from daya bay nuclear power station. Radiat. Prot. 2006, 26, 215–219. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.S.; Liu, H.D.; Beardsley, R.C. An unstructured grid, finite-volume, three-dimensional, primitive equations ocean model: Application to coastal ocean and estuaries. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 159–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.S.; Huang, H.S.; Beardsley, R.C.; Liu, H.D.; Qi, C. A finite volume numerical approach for coastal ocean circulation studies: Comparisons with finite difference models. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2007, 112, C03018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Z.; Zhang, R.J.; Qiao, M.A.; Jiang, Y.B.; Sun, J.W. Numerical simulation of tidal waves in Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea based on FVCOM. J. Dalian Fish. Univ. 2017, 32, 618–624. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.X. Latest Advances of Global Ocean Tide Models and Their Accuracy Comparisons in Coastal Areas of China. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2019, 39, 477–481. [Google Scholar]
- Periáñez, R. Three-dimensional modelling of the tidal dispersion of non-conservative radionuclides in the marine environment. Application to 239,240Pu dispersion in the eastern Irish Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 1999, 22, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumune, D.; Aoyama, M.; Hirose, K. Numerical simulation of 137Cs and 239;240Pu concentrations by an ocean general circulation model. Env. Radioact. 2003, 69, 61–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, R.J.; Huang, J.M.; Sheng, Z.J.; Wang, S. FVCOM Model-based study on tidal prism and water exchange capacity of Haizhou Bay. Water Resour. Hydropower Eng. 2021, 52, 143–151. [Google Scholar]
| Case | Time | Considerations | Continuous Pollutant Release (Activity Concentration, Bq/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | summer | tides | 1 |
| 2 | winter | tides | 1 |
| 3 | summer | tides | 1 |
| summer monsoon | 1 | ||
| 4 | winter | tides | 1 |
| winter monsoon | 1 |
| Hydrological/Radiological Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| AH | 1 m2s−1 |
| Km | 2.825 m2s−1 |
| Kh | 1.5 × 10−4 m2s−1 |
| w | 0 ms−1 |
| 1.8 × 10−9 s−1 |
| Tide Level | Maximum Error (m) | Minimum Error (m) | Average Error (m) | RMS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lanshangang Station | 0.35 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.02 |
| Lianyungang Station | 0.41 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.02 |
| Currents | Maximum Error | Minimum Error | Average Error | RMS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Station 1 | 0.38 m/s | 0.03 m/s | 0.04 m/s | 0.02 m/s |
| Station 1 | 30° | 0.05° | 3.4° | 2.68° |
| Station 2 | 0.31 m/s | 0.13 m/s | 0.02 m/s | 0.02 m/s |
| Station 2 | 13° | 0.07° | 8.8° | 8.88° |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, T.; Feng, X.; Xie, T.; Liu, H. The Impact of Tides and Monsoons on Tritium Migration and Diffusion in Coastal Harbours: A Simulation Study in Lianyungang Haizhou Bay, China. Water 2024, 16, 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040615
Zhang Y, Zhang J, Liu T, Feng X, Xie T, Liu H. The Impact of Tides and Monsoons on Tritium Migration and Diffusion in Coastal Harbours: A Simulation Study in Lianyungang Haizhou Bay, China. Water. 2024; 16(4):615. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040615
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yangxin, Jiangmei Zhang, Tuantuan Liu, Xinghua Feng, Tengxiang Xie, and Haolin Liu. 2024. "The Impact of Tides and Monsoons on Tritium Migration and Diffusion in Coastal Harbours: A Simulation Study in Lianyungang Haizhou Bay, China" Water 16, no. 4: 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040615
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhang, J., Liu, T., Feng, X., Xie, T., & Liu, H. (2024). The Impact of Tides and Monsoons on Tritium Migration and Diffusion in Coastal Harbours: A Simulation Study in Lianyungang Haizhou Bay, China. Water, 16(4), 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040615






