The Microbial Community Composition and Nitrogen Cycling Metabolic Potential of an Underground Reservoir in Rizhao, Shandong Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
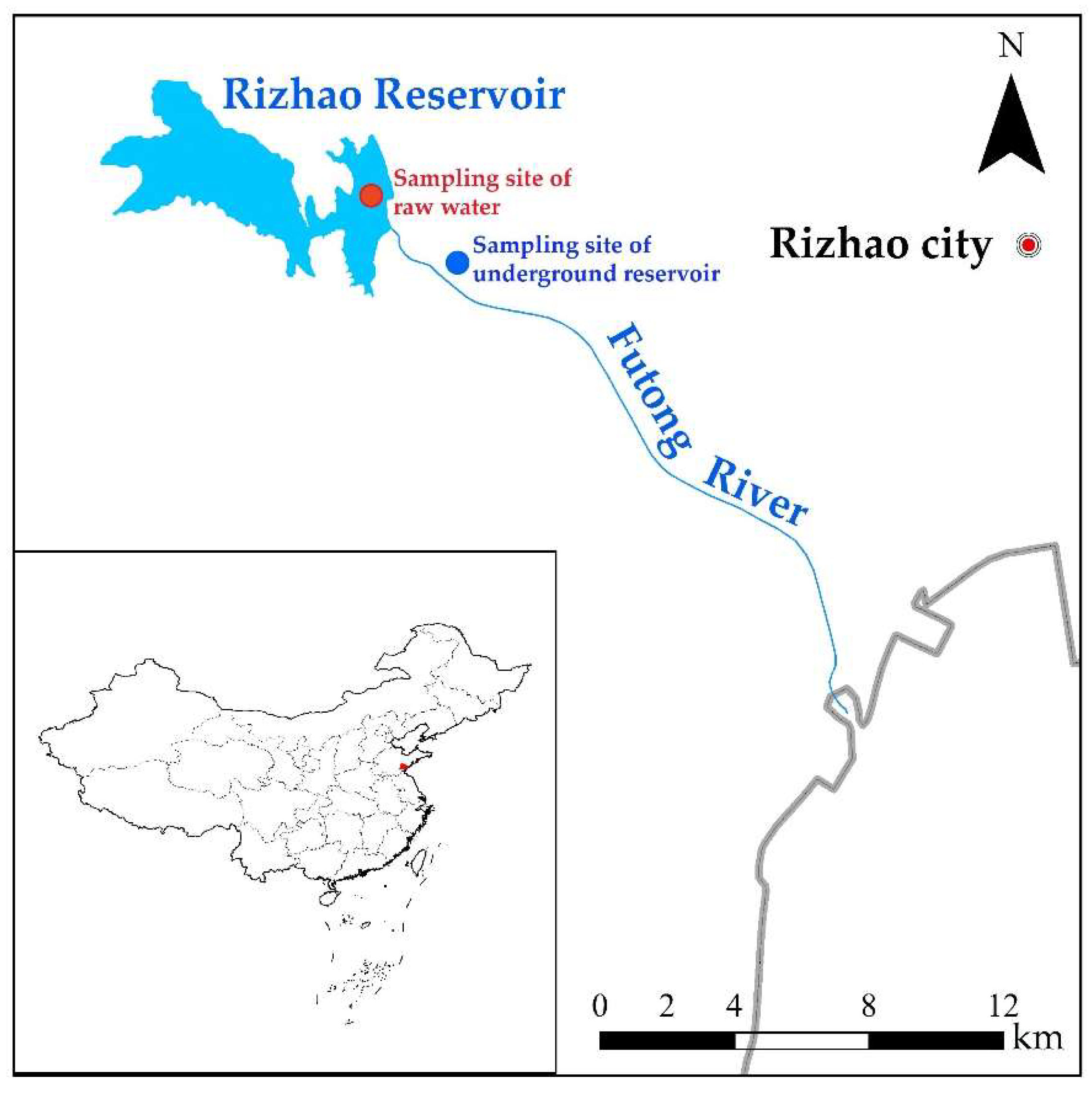
2.1. Information about the Studied Underground Reservoir
2.2. Sample Collection and Physicochemical Analyses
2.3. DNA Extraction, Amplification, and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.4. GeoChip Analysis and Data Preprocessing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
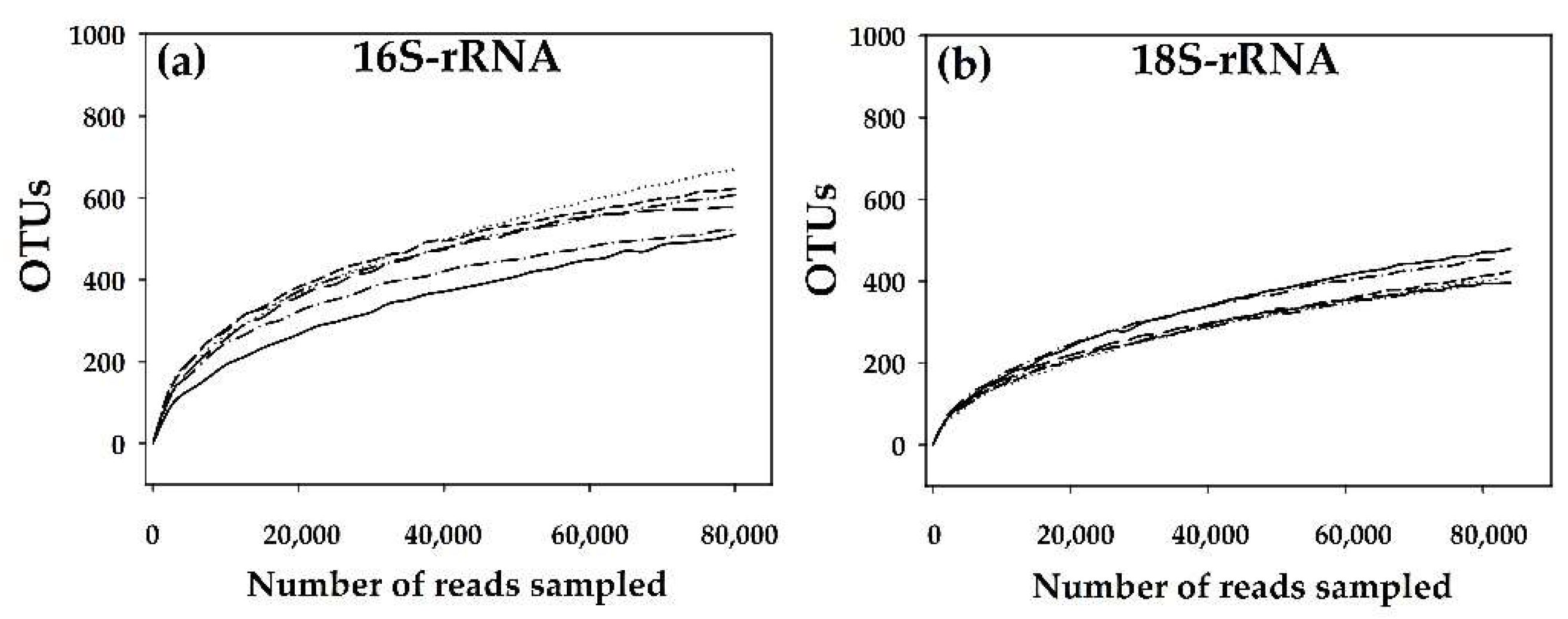
3.1. Description of the Obtained Sequences and Physicochemical Index of Water Samples
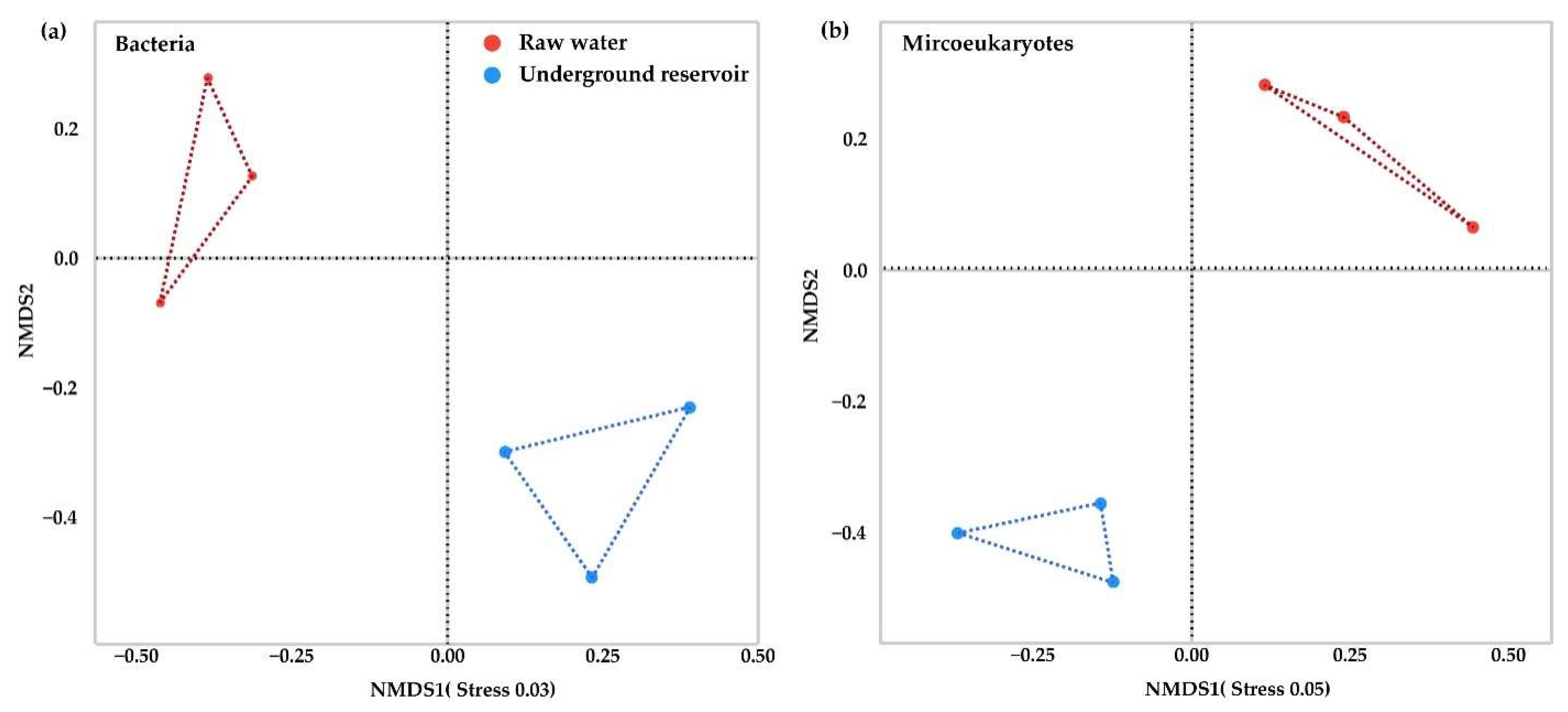
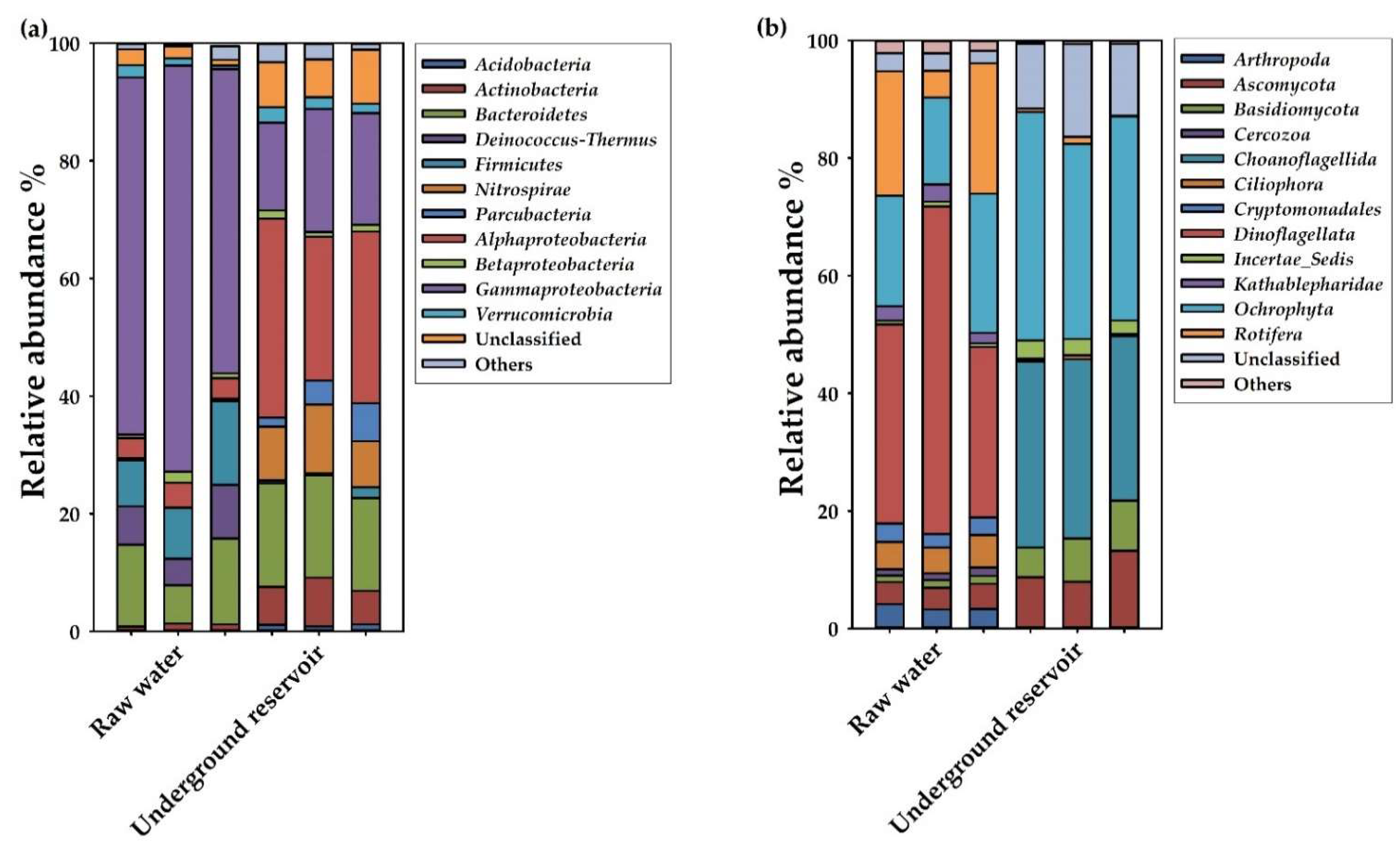
3.2. Succession of Microbial Community Structure in the Underground Reservoir
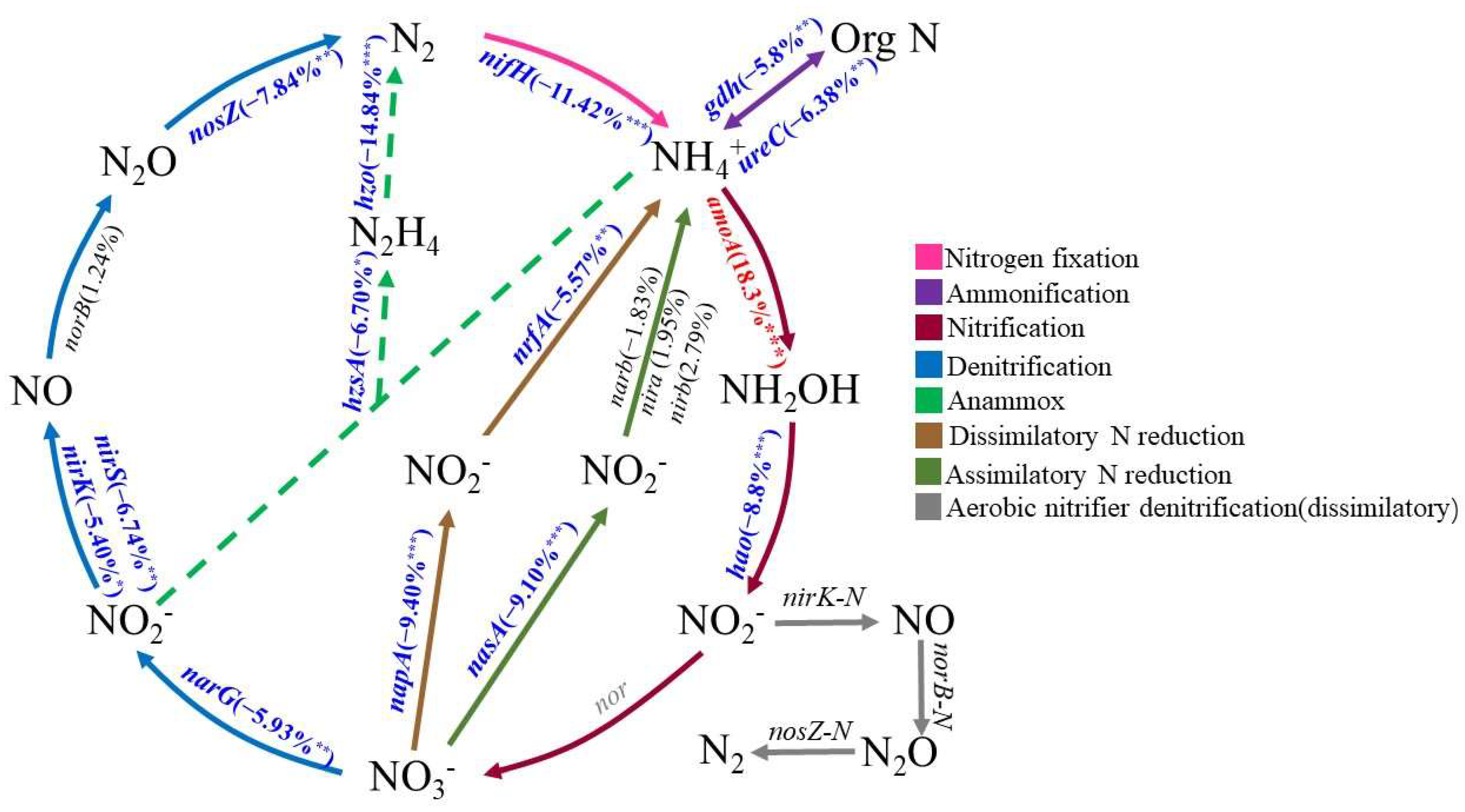
3.3. Nitrogen Cycling Metabolic Potential of the Microbial Community in the Underground Reservior
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, J.; Chen, K.Q.; Liang, P. Problems and application prospect of ASR technology in the underground reservoir construction of China. South-North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 12, 192–195. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.R.; You, A.J.; Shu, L.C. Current Situation and Prospect on Groundwater Reservoir Research. Zhejiang Hydrotech. 2018, 219, 68–71. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, H.; Guo, Q.; Lin, P.; Bai, L.; Yang, S.; Sitharam, T.G.; Liu, J. Feasibility Study of Coastal Reservoirs in the Zhoushan Islands, China. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 35, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, K.; Gao, J.; Yang, Y.; Bai, L.; Yan, J. Research on Temporal Patterns of Water–Rock Interaction in the Coal Mine Underground Reservoir Based on the Dynamic Simulation Test. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 13819–13832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Sun, C.; Yan, P.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Luo, S.; Mao, Y. Dynamic changes of nitrogen and dissolved organic matter during the transport of mine water in a coal mine underground reservoir: Column experiments. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2019, 223, 103473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pingping, K.; Shiguo, X.; Shouquan, Y. Analysis of influence of underground reservoir on nitrogen distribution through tracing of isotope source. Water Resour. Prot. 2016, 32, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Hou, W.; Jiang, H.; Huang, L.; Dong, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Lin, B.; Deng, Y. Microbial diversity accumulates in a downstream direction in the Three Gorges Reservoir. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 101, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Wang, H.; Dsouza, M.; Lou, J.; He, Y.; Dai, Z.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J.; Gilbert, J.A. Geographic patterns of co-occurrence network topological features for soil microbiota at continental scale in eastern China. ISME J. 2015, 10, 1891–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Han, H.; Zhuang, H.; Hou, B. The pollutants removal and bacterial community dynamics relationship within a full-scale British Gas/Lurgi coal gasification wastewater treatment using a novel system. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 200, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, T.; Williams, R.L.; Bogatyrev, S.R.; Doyle, J.C.; Henry, C.S.; Ismagilov, R.F. Metabolic multistability and hysteresis in a model aerobe-anaerobe microbiome community. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba0353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, R.J.; Jones, S.E.; Eiler, A.; McMahon, K.D.; Bertilsson, S. A Guide to the Natural History of Freshwater Lake Bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 14–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gad, M.; Hou, L.; Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Rashid, A.; Chen, N.; Hu, A. Distinct mechanisms underlying the assembly of microeukaryotic generalists and specialists in an anthropogenically impacted river. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 748, 141434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zeng, J.; Ren, L.; Wang, J.; Xing, P.; Wu, Q.L. Contrasting patterns of diversity of abundant and rare bacterioplankton in freshwater lakes along an elevation gradient. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, 1570–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.L.; Zwart, G.; Wu, J.; Agterveld, K.V.; Liu, S.; Hahn, M.W. Submersed Macrophytes Play a Key Role in Structuring Bacterioplankton Community Composition in the Large, Shallow, Subtropical Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Microb. 2010, 9, 2765–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Dong, H.; Zhang, G.; Yu, B.; Chapman, L.R.; Fields, M.W. Microbial Diversity in Water and Sediment of Lake Chaka, an Athalassohaline Lake in Northwestern China. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 3832–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-García, P.; Kazmierczak, J.; Benzerara, K.; Kempe, S.; Guyot, F.; Moreira, D. Bacterial diversity and carbonate precipitation in the giant microbialites from the highly alkaline Lake Van, Turkey. Extremophiles 2005, 9, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xue, Y.; Ventosa, A.; Grant, W.D. Bacterial diversity of the Inner Mongolian Baer Soda Lake as revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequence analyses. Extremophiles 2004, 8, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yannarell, A.C.; Kent, A.D.; Lauster, G.H.; Kratz, T.K.; Triplett, E.W. Temporal Patterns in Bacterial Communities in Three Temperate Lakes of Different Trophic Status. Microb. Ecol. 2003, 46, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Xie, G.; Shao, K.; Tian, W.; Gao, G.; Qin, B. Aquatic Bacterial Diversity, Community Composition and Assembly in the Semi-Arid Inner Mongolia Plateau: Combined Effects of Salinity and Nutrient Levels. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Kong, X.; Xie, S.; Xu, J. The combination of multiple environmental stressors strongly alters microbial community assembly in aquatic ecosystems. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 350, 119594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keys, T.A.; Caudill, M.F.; Scott, D.T. Storm effects on nitrogen flux and longitudinal variability in a river–reservoir system. River Res. Appl. 2019, 35, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, S.; Chen, J. Hysteretic response of Microbial Eukaryotic Communities to Gradually Decreased Nutrient Concentrations in Eutrophic Water. Microb. Ecol. 2020, 79, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Qin, W.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Gao, H.; Gu, J.; Xia, X. Linkages between anammox and denitrifying bacterial communities and nitrogen loss rates in high-elevation rivers. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Niu, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L. Nitrogen cycling processes and the role of multi-trophic microbiota in dam-induced river-reservoir systems. Water Res. 2021, 206, 117730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santillan, E.; Phua, W.X.; Constancias, F.; Wuertz, S. Sustained organic loading disturbance favors nitrite accumulation in bioreactors with variable resistance, recovery and resilience of nitrification and nitrifiers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Zheng, M.; Liu, S.; Chen, Q.; Ni, J. Comammox Nitrospira within the Yangtze River continuum: Community, biogeography, and ecological drivers. ISME J. 2020, 14, 2488–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, E.W.; Bridgewater, L.; Association, A.P.H. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Aminot, A.; Rey, F. Standard Procedure for the Determination of Chlorophyll A by Spectroscopic Methods; ICES Techniques in Marine Environmental Sciences: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2000; Volume 28. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.L.; Zwart, G.; Schauer, M.; Agterveld, M.P.K.-V.; Hahn, M.W. Bacterioplankton Community Composition along a Salinity Gradient of Sixteen High-Mountain Lakes Located on the Tibetan Plateau, China. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5478–5485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Chen, C.; Liang, B.; Huang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, X.; Tan, W.; Zhou, X.; Gao, S.; Sun, D.; et al. Fine-tuning key parameters of an integrated reactor system for the simultaneous removal of COD, sulfate and ammonium and elemental sulfur reclamation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 269, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Deng, Y.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Tu, Q.; Xu, M.; Hemme, C.L.; Li, X.; Wu, L.; Gentry, T.J.; Yin, Y.; et al. GeoChip 3.0 as a high-throughput tool for analyzing microbial community composition, structure and functional activity. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, J.; Liu, X.; Lu, H.; Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Deng, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y. Analyses of the influencing factors of soil microbial functional gene diversity in tropical rainforest based on GeoChip 5.0. Genom. Data 2015, 5, 397–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhou, J. Empirical Evaluation of a New Method for Calculating Signal-to-Noise Ratio for Microarray Data Analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2957–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Deng, Y.; He, Z.; Wu, L.; Van Nostrand, J.D. Applying GeoChip Analysis to Disparate Microbial Communities. Microbe Mag. 2010, 5, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faith, D.P. Conservation evaluation and phylogenetic diversity. Biol. Conserv. 1992, 61, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, H.H.; Broz, L. The influence of a deep-storage and an underground reservoir on the physicochemical limnology of a permanent central Texas river. Hydrobiologia 1976, 51, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-H.; Cai, L.-Y.; Lin, T.-F.; Chung, C.-L.; Van der Linden, L.; Burch, M. Assessment of the Impacts of Climate Change on the Water Quality of a Small Deep Reservoir in a Humid-Subtropical Climatic Region. Water 2015, 7, 1687–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, J. Reducing eutrophication risk of a reservoir by water replacement: A case study of the Qingcaosha reservoir in the Changjiang Estuary. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comte, J.; Fauteux, L.; del Giorgio, P.A. Links between metabolic plasticity and functional redundancy in freshwater bacterioplankton communities. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; He, D.; Chen, Z.; Jeppesen, E.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Søndergaard, M.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Q.L. Warming and nutrient enrichment in combination increase stochasticity and beta diversity of bacterioplankton assemblages across freshwater mesocosms. ISME J. 2016, 11, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velghe, K.; Vermaire, J.C.; Gregory-Eaves, I. Declines in littoral species richness across both spatial and temporal nutrient gradients: A palaeolimnological study of two taxonomic groups. Freshw. Biol. 2012, 57, 2378–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvy, M.; Bettarel, Y.; Bouvier, C.; Domaizon, I.; Jacquet, S.; Le Floch, E.; Montanié, H.; Mostajir, B.; Sime-Ngando, T.; Torréton, J.-P. Trophic interactions between viruses, bacteria and nanoflagellates under various nutrient conditions and simulated climate change. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1842–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, S.-I.; Ishii, N.; Manage, P.M.; Kawabata, Z. Trophic roles of heterotrophic nanoflagellates and ciliates among planktonic organisms in a hypereutrophic pond. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1998, 16, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, B.; Mckee, D.; Atkinson, D.; Collings, S.E.; Eaton, J.W.; Gill, A.B.; Harvey, I.; Hatton, K.; Heyes, T.; Wilson, D. How important is climate? Effects of warming, nutrient addition and fish on phytoplankton in shallow lake microcosms. J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 40, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haukka, K.; Kolmonen, E.; Hyder, R.; Hietala, J.; Vakkilainen, K.; Kairesalo, T.; Haario, H.; Sivonen, K. Effect of Nutrient Loading on Bacterioplankton Community Composition in Lake Mesocosms. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 51, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, J.H.; Kevin, R.T.; Donald, G.U.; Deric, R.L. Microbial community structure and microbial networks correspond to nutrient gradients within coastal wetlands of the Laurentian Great Lakes. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz033. [Google Scholar]
- Waite, D.W.; Vanwonterghem, I.; Rinke, C.; Parks, D.H.; Hugenholtz, P. Comparative Genomic Analysis of the Class Epsilonproteobacteria and Proposed Reclassification to Epsilonbacteraeota (phyl. nov.). Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, P.; Guo, L.; Tian, W.; Wu, Q.L. Novel Clostridium populations involved in the anaerobic degradation of Microcystis blooms. ISME J. 2010, 5, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.W.; Bock, E.; Valois, F.W.; Waterbury, J.B.; Schlosser, U. Nitrospira marina gen. nov. sp. nov.: A chemolithotrophic nitrite-oxidizing bacterium. Arch. Microbiol. 1986, 144, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.W.; Waterbury, J.B. Characteristics of two marine nitrite oxidizing bacteria, Nitrospina gracilis nov. gen. nov. sp. and Nitrococcus mobilis nov. gen. nov. sp. Arch. Microbiol. 1971, 77, 203–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, S.A.; Tamsyn, G.; Mona, H.; Neilan, B.A.; Nicolas, S. Genetic Diversity, Morphological Uniformity and Polyketide Production in Dinoflagellates (Amphidinium, Dinoflagellata). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macêdo, R.L.; Franco, A.C.S.; Russo, P.; Collart, T.; Mammola, S.; Jeppesen, E.; Branco, C.W.C.; dos Santos, L.N.; Rocha, O. Climate and landscape changes enhance the global spread of a bloom-forming dinoflagellate related to fish kills and water quality deterioration. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagan, G.; Zeitoun, D. Seawater-freshwater interface in a stratified aquifer of random permeability distribution. J. Contam. Hydrol. 1998, 29, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachiadaki, M.G.; Sintes, E.; Bergauer, K.; Brown, J.M.; Record, N.R.; Swan, B.K.; Mathyer, M.E.; Hallam, S.J.; Lopez-Garcia, P.; Takaki, Y.; et al. Major role of nitrite-oxidizing bacteria in dark ocean carbon fixation. Science 2017, 358, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollingsworth, A.L.; Jones, D.O.B.; Young, C.R. Spatial Variability of Abyssal Nitrifying Microbes in the North-Eastern Clarion-Clipperton Zone. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 663420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, F.; Brissac, T.; Le Bris, N.; Felbeck, H.; Gros, O. First description of giant Archaea (Thaumarchaeota) associated with putative bacterial ectosymbionts in a sulfidic marine habitat. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 2371–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jean-Christophe, A.; Casamayor, E.O. Partitioning of Thaumarchaeota populations along environmental gradients in high mountain lakes. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 84, 154–164. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, J.-C.; Sun, S.; Rehman, M.M.U.; He, S.; Zhou, W. Dissimilatory nitrate reduction processes and corresponding nitrogen loss in tidal flow constructed wetlands. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Z. The cycle of nitrogen in river systems: Sources, transformation, and flux. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2018, 20, 863–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, C.A.; Roberts, K.J.; Beman, J.M.; Santoro, A.E.; Oakley, B.B. Ubiquity and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in water columns and sediments of the ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14683–14688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Song, C.; Cao, X.; Zhou, Y. Shifts between ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea inrelation to nitrification potential across trophic gradients intwo large Chinese lakes (Lake Taihu and Lake Chaohu). Water Res. 2013, 47, 2285–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Raw Water | Underground Reservoir | p-Value (ANOVA) |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.92 ± 0.19 | 7.69 ± 0.07 | 0.183 |
| DO (mg/L) | 8.67 ± 0.37 | 3.46 ± 0.15 | <0.001 |
| TN (mg/L) | 2.05 ± 0.2 | 4.28 ± 0.09 | <0.001 |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.022 ± 0.006 | 0.067 ± 0.005 | <0.01 |
| NH4+-N (mg/L) | 0.311 ± 0.018 | 0.062 ± 0.004 | <0.001 |
| NO3−-N (mg/L) | 1.69 ± 0.08 | 3.99 ± 0.04 | <0.001 |
| NO2−-N (mg/L) | 0.001 ± 0.001 | 0.006 ± 0.001 | <0.01 |
| Chl a (μg/L) | 0.0093 ± 0.0005 | 0.7758 ± 0.0085 | <0.001 |
| Values | Bacterial Communities | Microeukaryotic Communities | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Water | Underground Reservoir | p-Value (ANOVA) | Raw Water | Underground Reservoir | p-Value (ANOVA) | |
| OTU richness | 662 ± 31 | 562 ± 18 | 0.018 | 459 ± 11 | 411 ± 23 | 0.004 |
| Shannon index | 4.37 ± 0.37 | 4.32 ± 0.15 | >0.05 | 5.30 ± 0.23 | 4.87 ± 0.14 | >0.05 |
| Simpson index | 0.290 ± 0.02 | 0.190 ± 0.04 | 0.046 | 0.106 ± 0.016 | 0.040 ± 0.013 | 0.010 |
| Mantel Test | Bacterial Communities | Microeukaryotic Communities | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | p-Value | R | p-Value | |
| pH | −0.112 | NS | 0.037 | NS |
| DO (mg/L) | 0.437 | 0.018 | 0.238 | NS |
| TN (mg/L) | 0.747 | <0.001 | 0.623 | <0.001 |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.707 | <0.001 | 0.597 | <0.001 |
| NH4+-N (mg/L) | 0.594 | 0.009 | 0.375 | 0.041 |
| NO3−-N (mg/L) | 0.237 | NS | 0.078 | NS |
| NO2−-N (mg/L) | −0.220 | NS | −0.150 | NS |
| Chl a (μg/L) | 0.672 | <0.001 | 0.528 | 0.005 |
| All factors | 0.786 | <0.001 | 0.724 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhang, J.; Mu, Z.; Ma, S.; Liu, B.; Cheng, Y.; Ren, J.; Ikram, R.M.A. The Microbial Community Composition and Nitrogen Cycling Metabolic Potential of an Underground Reservoir in Rizhao, Shandong Province, China. Water 2024, 16, 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040573
Chen Y, Cao X, Zhang J, Mu Z, Ma S, Liu B, Cheng Y, Ren J, Ikram RMA. The Microbial Community Composition and Nitrogen Cycling Metabolic Potential of an Underground Reservoir in Rizhao, Shandong Province, China. Water. 2024; 16(4):573. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040573
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yue, Xinyi Cao, Juan Zhang, Ziyao Mu, Shenjia Ma, Bojun Liu, Yufeng Cheng, Jingxuan Ren, and Rana Muhammad Adnan Ikram. 2024. "The Microbial Community Composition and Nitrogen Cycling Metabolic Potential of an Underground Reservoir in Rizhao, Shandong Province, China" Water 16, no. 4: 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040573
APA StyleChen, Y., Cao, X., Zhang, J., Mu, Z., Ma, S., Liu, B., Cheng, Y., Ren, J., & Ikram, R. M. A. (2024). The Microbial Community Composition and Nitrogen Cycling Metabolic Potential of an Underground Reservoir in Rizhao, Shandong Province, China. Water, 16(4), 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040573







