Abstract
The contamination of heavy metals (HMs) in the topsoil of agricultural and pastoral areas threatens the yield and quality of agriculture and animal husbandry and also endangers regional ecological security and human health. This study analyzed the HMs (Cd, Pb, As, Cu, Zn, Hg, and Mn) in areas with intensive agricultural and pastoral activities to identify their accumulation, source apportionment, and ecological-health risks using geochemical methods coupled with positive matrix factorization (PMF). It was uncovered that the concentrations of HMs presented varying scales of enrichment and contamination levels in the topsoil. However, except for only one sample, the residual HMs concentrations fell within the associated risk screening values (the RSVs). The combined assessment of geo-accumulation index (Igeo) and enrichment factor (EF) pointed that Hg and Cd were the primary contaminants. The PMF identified four sources of HMs including natural geogenic, industry mining, composite (caused by multi-anthropogenic activities), and agricultural sources accounting for 33.7%, 41.0%, 7.7%, and 17.6% of contribution rates, respectively. The potential ecological risk was largely attributed to the accumulation of Hg, followed by Cd. The non-carcinogenic risk for both groups fell beneath the acceptable risk threshold, and the prospective carcinogenic health threats posed by Cd, As, and Pb for different groups should not be ignored, particularly concerning children. It is of great significance to control the HMs pollution and restore soil cleanliness in the study area.
1. Introduction
As an extremely important material for human survival and development, soil serves as a pivotal link between the atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and constitutes the bedrock for each of earth’s ecosystems []. However, in tandem with industrial and agricultural advancements, coupled with the swift urban sprawl, HMs contamination in soil has escalated drastically, reaching alarming proportions [,,]. Additionally, HMs, owing to their high toxicity, mobility, persistence, and non-degradability, are one of the key factors influencing ecological quality. Even some HMs required by the human body, if overexposed, will cause great harm to the ecosystem and the human body [,]. In this context, soil quality determines the ecological environment, human health, food security, and sustainable development of agriculture and attracts more and more attention in many part of the world [,,].
In general, HMs accumulated in the soil are derived from both geogenic and anthropogenic sources [,]. Geological background conditions such as bedrock and parent material are the natural sources [,,], while human activities such as mining and smelting, industrial manufacturing, agricultural cultivation, urban traffic, etc., are important reasons for causing or aggravating HMs accumulation, especially in the topsoil [,,]. Once introduced into the environmental media, the HMs undergo complex physico-chemical and biological processes that determine their behavior and fates [,]. Importantly, understanding the distributions and source apportionment of HMs is the basis of topsoil contamination prevention and control and is also an important mean of ecological environmental safety protection [,].
Recently, the positive matrix factorization (PMF) model has been frequently adopted for identifying and conducting quantitative evaluations of contaminant sources of receptors, such as atmosphere, dust fall, water body, and sediment [,], especially in the field of topsoil HMs [,,]. In addition, geochemical methods including geo-accumulation index (Igeo) or enrichment factor (EF) and potential ecological-health risks assessment have been widely used in topsoil HMs contamination and ecological risk assessment [,,].
Notably, as an ecological transition zone connecting agricultural and grassland area, the special environment of agricultural and pastoral areas makes the land use type change frequently. It has typical environmental sensitivity and vulnerability and integrates the unique economic form of the common development of agriculture and animal husbandry [,,]. However, with the rapid development of agriculture and animal husbandry economy, large numbers of HMs enter and change the soil function, leading to the decline of soil environmental quality [,,]. This will affect the yield and quality of agriculture and animal husbandry and also endanger regional ecological security and human health.
In this study, Cd, Pb, As, Cu, Zn, Hg, Mn, Al, and Fe in topsoil samples were analyzed to illustrate the accumulation characteristics of HMs in areas characterized by intensive agricultural and pastoral activities. Combining with PMF and Pearson correlation analysis, the source apportionment was investigated. The potential ecological-health risks caused by HMs were evaluated. It is of great significance to prevent and control the contamination of HMs while maintaining ecological environment safety and safeguarding human health in areas undergoing intensive agricultural and pastoral activities.
2. Study Area
The research area is situated in the southeast of Qaidam Basin, Qinghai Province, Northwest China (Figure 1), where agricultural and pastoral activities are predominant. The southern portion is part of the East Kunlun mountain system, which is the southern edge of the Qaidam Basin. The peak elevation is above 4500 m, and the highest peak is 5447 m. The bare bedrock or surface layer is covered with thin layers of aeolian salt-bearing soil layers, presenting a natural desert landscape. Additionally, the soil types in the study area are diverse, and the parent material of soil formation is relatively complex, mainly including meadow saline soil, semi-fixed aeolian sand soil, salinized brown calcium soil, irrigated salinized brown calcium soil, and salinized clay. In the southern mountainous region, the weathering products of granite and diorite rocks predominantly constitute the soil parent material. With the decrease in altitude, the parent material gradually changes to flood alluvial, lake sediment, ice water sediment, and residual slope sediment. In the transition area of mountainous area and basin, the soil parent material becomes complex, mainly dominated by alluvial, diluvium, and loess-like material. A number of agricultural–pastoral areas and towns have been formed in this area, spanning more than 200 km2, which are distributed on the river alluvial plain. Additionally, the area is rich in plentiful ores of various metals such as gold, iron, lead, zinc, and copper ore resources, together with manganese, molybdenum, graphite, fluorite, and rare earth mineral resources.
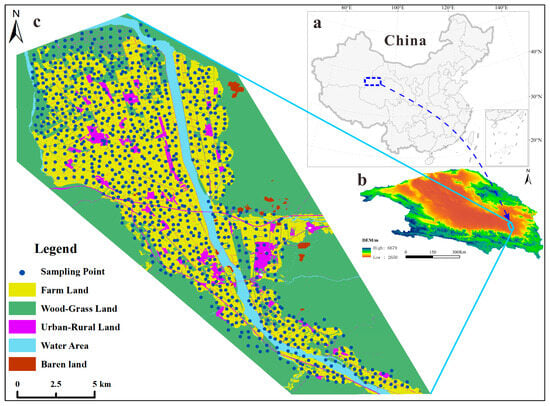
Figure 1.
Land use types and sampling location of HMs in the study area: (a,b) the Qaidam Basin; (c) the study area.
According to the results of remote sensing interpretation in the study area (Figure 1), the land use types mainly include farm and wood–grass lands, urban–rural zones, water area, barren landscapes, etc. Among them, natural grassland is the largest utilization type, and the distribution characteristics of farmland determines that agriculture is mainly oasis. The old oasis agriculture is generally distributed along rivers or lakes in arid desert areas, as well as in groundwater-exposed locations in foothills and alluvial fans. With the development of social productive forces and the improvement of water conservancy conditions, the newly reclaimed agricultural areas are mainly opened up in arid and desert areas where the resources of suitable agricultural land are abundant, and the conditions of development and utilization are superior.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Soil Sampling and Analyses
The topsoil samples were collected employing a strip-grid methodology, and the representative sample at each site was a homogenized mix of five randomly chosen subsamples. In the study area, 1013 samples (from 0 to 20 cm) were systematically gathered via soil drill, including grassplot, irrigable, nature reserve, forest–grass and residential land. And GPS was used to record the coordinates of sampling points. The sampling process avoided obvious contamination sources such as dump, mine slag, cesspit, fertilizer stacking, etc. Prior to sampling, larger stones, grass roots, and other impurities were removed, and each soil sample had an original weight of at least 1 kg. All the collected samples were kept in polythene bags, numbered, and preserved. The collected soil samples underwent an air-drying process at ambient conditions before being passed through a 2.0 mm nylon sieve to remove larger components such as macroscopic organic matter, decomposed plant residue, and miscellaneous debris. The samples were put into polyethene plastic sacks to avoid contamination, numbered, marked separately, and then sent to the laboratory for analyses.
The soil samples were subjected to digestion using a concentrated acid mixture (HNO3-HF-HClO4) in sterile dry Teflon crucibles [,,]. The concentrations of Cu, Pb, Zn, Mn, Al, and Fe were measured via X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF), while Hg and As were measured using atomic fluorescence spectrophotometer (AFS, HGF-V9, Beijing, China). Additionally, the Cd concentrations were quantified using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS, Thermo X series II, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Vacaville, CA, USA), whereas the soil pH was determined through the glass electrode technique after extraction with non-carbon dioxide distilled water. Quality assurance and control measures included the incorporation of both random replicate samples and certified reference materials (CRMs), specifically a national standard soil sample (GBW 07449). The proportion in restoration percentage for all analyzed elements ranged from 90% to 105%, with the RSD (relative standard deviation) of duplicate samples totaling to less than 5%. The method detection limits were 0.8, 2, 2, 0.02, 0.2, 0.0005, 5, 0.05, and 0.05 mg/kg for Cu, Pb, Zn, Cd, As, Hg, Mn, Al, and Fe, respectively.
3.2. Evaluation Method of Pollution Levels
Geochemical assessments, encompassing metrics like the geo-accumulation index (Igeo) and the enrichment factor (EF), are instrumental in evaluating contamination levels and pinpointing anthropogenic influences [,,].
3.2.1. Geo-Accumulation Index (Igeo)
The Igeo is calculated by the following expression:
Igeo = log2 [Ci/(K·Bi)]
In this context, Ci corresponds to the detected concentration of the elements, while Bi stands for their background values (mg/kg). Meanwhile, K denotes a fixed coefficient introduced to accommodate variations in background levels, generally 1.5 [,]. The grading standards of Igeo are shown in Table S1.
3.2.2. Enrichment Factor (EF)
EF is employed to determine the enrichment degree of HMs in soil:
where Ci and Cref represent the concentration of element i and the reference element for normalization, respectively (mg/kg). In general, the most common normalizing element are Al, Fe, Mn, Ti, etc. [,]. In this research, Al was chosen as the reference element due to its significantly higher abundance and greater stability within the Earth’s crust, along with its minimal influence from anthropogenic sources. The classification criteria for EF are also presented in Table S1.
3.3. Positive Matrix Factorization Model (PMF)
In this study, the PMF model, endorsed by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA), was applied for quantitatively elucidating contamination sources using receptor-based data. Additionally, an integrated approach involving both Pearson correlation analysis and PMF model was utilized to effectively allocate the sources of HMs in topsoil. Through successive decompositions of the primary matrix X, the PMF algorithm optimizes matrices G and F, leading to the minimization of the target function Q [,] as follows:
In this formulation, Xij signifies the content of HMs (expressed in mg/kg), whereas Gik illustrates the extent of contribution from the kth source to the ith specimen. Fkj represents the proportion of the jth HM originating from various factors. Eij designates the residual component. Here, n indicates the variety of metallic elements; m identifies the individual samples, and Uij represents the uncertainty associated with HMs, calculated using the method detection limit (MDL) pertinent to each species, combined with the metal concentration and error fraction.
Here, error fraction and C represent the percentage of measurement uncertainty and the element content, respectively.
3.4. Potential Ecological-Health Risks
3.4.1. Potential Ecological Risks Assessment
The potential ecological risk index (RI), initially proposed by Hakanson (1980) [], was formulated to evaluate the potential consequences of contaminations based on both the toxicity of heavy metals and the environmental system’s sensitivity [,]. Its calculation is shown in the following formula:
where is the potential risk index of target element i; and are the measured concentration and the background value of HMs, respectively (mg/kg). Tri refers to the toxic response coefficient of target element, with the relevant values as follows: Zn = Mn = 1, Cu = Pb = 5, As = 10, Cd = 30, and Hg = 40 [,]. The classifying standards of and RI are shown in Table S2.
3.4.2. Human Health Risks Assessment (HRA)
The HRA model proposed by the US EPA [] was utilized to systematically estimate the potential health hazards posed by hazardous substances to the human.
This investigation synthesized multiple evaluation indexes, incorporating insights from the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and the World Health Organization (WHO) on the detrimental impacts of various noxious compounds on human health. Consequently, the model encompassed evaluations of carcinogenic threats attributable to Cd, As, and Pb in addition to non-carcinogenic risk attributable to Cd, Pb, As, Cu, Zn, Hg, and Mn.
Exposure levels incurred through oral intake, dermal absorption, and inhalation can be determined using the subsequent formulas:
where ADIing, ADIdermal, and ADIinh represent the average daily intake from soil ingestion, dermal, and inhalation absorption, respectively (mg/kg·day), The values for the above parameters are listed in Table S3.
- (1)
- Non-carcinogenic risk assessment
The target hazard quotient (HQ) and hazard index (HI) of HMs were calculated using the following equation:
Here, RfDi denotes the reference toxicity threshold dose of target element i [mg/(kg·day)]. The calculated HQ and HI values lower than 1 suggest neglectable non-carcinogen risk, while the values higher than 1 indicate high non-carcinogen risks [,,].
- (2)
- Carcinogenic risk assessment
The CR value represents carcinogenic risk from a single element, and the TCR value indicates combined carcinogenic health risk, both of which were calculated as follows:
where SF is the cancer slope factor, and the values are shown in Table S4. The calculated TCR value lower than 10−6 represents acceptable cancer risk, while the TCR value higher than 10−4 represents unacceptable cancer risk level [,].
CR = ADI × SF
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Description Statistics of HMs
Statistical summaries for the HMs content, including minimum, maximum, and mean values, and upper (Q1, 25%), median, and lower quartiles (Q3, 75%), are presented in Table 1 and Figure 2. Additionally, the geochemical background values (GBVs) of soil in the study area and the soil environmental quality: risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land issued by the Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China (RSVs, GB 15618-2018 []) were employed to contrastively analyze the content characteristics of HMs in the study area. Table 1 illustrates the pH levels observed in the samples that spanned between 7.89 and 9.25, with a mean value of 8.53, reflecting the mildly alkaline characteristics of topsoil. Hence, the risk control threshold of agricultural land soil with pH > 7.5 can be determined (RSVs in Table 1).

Table 1.
Statistical summary of HMs concentrations in soil samples in the study area (mg/kg).
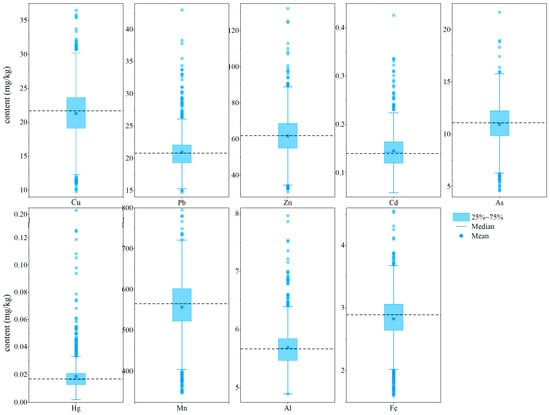
Figure 2.
The concentration box diagrams of HMs in topsoil. The dashed lines represent the background values (BVs) of HMs in the study area.
The CV values of HMs were relatively small, except for Hg with 2.24%, indicating that the dispersion of HMs across different areas was generally uniform, pointing to convoluted sources. The average HMs concentrations (mg/kg) were 21.32 (Cu), 20.96 (Pb), 61.75 (Zn), 0.14 (Cd), 10.96 (As), 0.02 (Hg), 556.61 (Mn), 5.56 (Al), and 2.82 (Fe), respectively. The concentrations (mean) of Cu, Zn, As, Mn, and Fe were slightly below or close to the BVs, while the means of the remaining metals including Pb, Cd, Hg, and Al were slightly higher than the BVs. Additionally, apart from the outlier concentrations of Cd, As, and Hg from only one sample, the HMs contents in the other samples remained beneath their respective risk screening thresholds (the RSVs).
However, according to the quartile (from upper to lower quartile), the contents of each HMs in many topsoil samples were still greater than the BVs (Figure 2). Specifically, in contrast to Pb and Mn, the concentrations of Cd, Cu, As, Zn, and Hg in the majority of samples exceeded the BVs. The exceeding rates of these HMs were higher than 50%, accounting for 50.64% (Cu), 50.05% (Zn), 50.15% (Cd), 50.94% (As), and 50.74% (Hg), respectively. It indicated that the HMs in the topsoil exhibited signs of contamination or enrichment, implying potential ecological hazards and health risks in the study area. Thus, in order to effectively control the harm, identifying the enrichment characteristics, quantifying the source apportionment, and calculating potential eco-health risks of these HMs in topsoil are essential [,].
4.2. Contamination Assessment of HMs
The contamination extent of topsoil HMs was calculated using geochemical indicators Igeo (Figure 3) and EF (Figure 4) to identify the impact of anthropogenic activities in the study area.
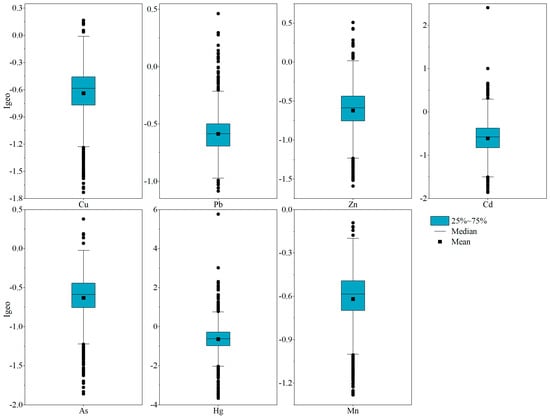
Figure 3.
Igeo box diagrams of HMs in the study area.
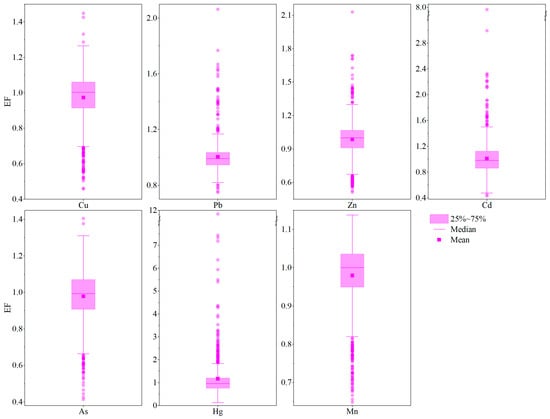
Figure 4.
EF box diagrams of HMs in the study area.
Figure 3 illustrates, except for Hg, the other HMs, ranging from the uncontaminated level (Igeo ≤ 0) to the moderately contaminated level (0 < Igeo ≤ 1) according to the classification of Igeo (Table S1). While the Igeo values of Hg in some samples were at the level of moderately contaminated or higher, the average Igeo values of HMs were less than 0, with Cu (−0.64), Pb (−0.59), Zn (−0.62), Cd (−0.61), As (−0.63), Hg (−0.64), and Mn (−0.62). Overall, the Igeo values of different HMs in the topsoil samples indicated a relatively low pollution extent. However, the proportion of all samples with Igeo above 0 decreased in the order of 12.54% (Hg) > 3.36% (Cd) > 1.38% (Zn) > 1.09% (Cd) > 0.59% (Cu) > 0.49% (As), which also represents the contamination extent of topsoil HMs.
Notably, regarding the contamination of samples with Hg, 10.37%, 1.48%, 0.49%, and 0.2% were uncontaminated to moderately contaminated, moderately contaminated, moderately to heavily contaminated, and heavily contaminated, respectively. Simultaneously, in the case of Cd, the proportion of samples classified as uncontaminated to moderately contaminated and moderately were 3.26% and 0.1%, respectively. While the samples were mostly unaffected by the other HM elements, the outcomes also indicate that Hg and Cd exhibited pollute levels with varying degrees and were the predominant contaminants in the topsoil samples, suggesting that these HMs have been affected by anthropogenic sources [,].
Based on the EF classification in Table S1, the computations disclosed that every EF value for As, Cu, and Mn in the topsoil samples pointed to the minimal enrichment level, and only one Pb and Zn showed moderate enrichment level (Figure 4). Notably, the enrichment of Hg in samples that reached moderate or above levels accounted for 89.55%, including moderate level (76.12%), significant level (11.94%), and extremely high level (1.49%), respectively. Meanwhile, the ratio of samples categorized as moderate and significant enrichment caused by Cd were 14.93% and 1.49%, respectively (Figure 4). Similar to the Igeo, Hg was considered to be the most enriched with EF value indicating that Hg in most topsoil samples were at a serious contamination level, followed by Cd. Relatively, the other types of HMs in samples were primarily situated at or below the level of minimal enrichment. To summarize, combining with the results of Igeo, this implied that the impact of anthropogenic activities on the accumulation of Hg and Cd in the topsoil should not be ignored.
4.3. Source Identification of HMs
Subsequent to executing iterative calculations in the PMF model, an integrated approach involving both Pearson correlation analysis and PMF model was utilized to effectively allocate the sources of HMs in topsoil (Figure 5). According to the Pearson correlation analysis, strong correlations (R2 > 0.6) were observed in the pairwise comparisons of HMs in topsoil (Figure 5c), revealing a potential common source [,,]. Upon assessing their robustness along with the lowest Q values, four factors were derived, accounting for 33.7%, 41.0%, 7.7%, and 17.6% of the contribution, respectively (Figure 5a). All elements were categorized as ‘strong’ due to their high signal-to-noise ratios (S/N). The scaled residuals, falling neatly within the interval of −3 to 3, effectively revealed the influences exerted by each factor. Additionally, the coefficients of determination (R2) between the observed and predicted concentrations in PMF model were all greater than 0.75, which means that the model was appropriate, and the results were reliable [,].
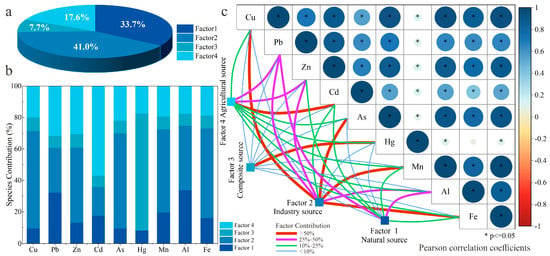
Figure 5.
Source apportionment of HMs in the study area. (a) The contribution percentage of four factors. (b) Factor profiles of HMs according to the PMF result. (c) Determine the interrelationships among HMs by integrating correlation analysis alongside the outcomes of PMF. The degree of correlation between HMs was visualized using a color gradient in their pairwise comparisons. The extent of contribution from each factor identified in PMF was associated specifically with each HM.
Factor 1, responsible for 24.9% of the total contribution (Figure 5a), was chiefly dominated by Al (33.73%) and Pb (32.19%) (Figure 5b). The remaining HMs contributed less than 25% with an order of Mn (19.55%) > Cd (17.52%) > Fe (15.95%) > Zn (13.06%) > Cu (9.48%) > As (9.37%) > Hg (8.11%). In general, the primary determinants shaping the concentration and dispersion of Al and Mn in soils are attributed to the Earth’s crustal materials and pedogenesis. In the metallogenic belt of the study area, some elements such as Mo, Rn, Sr, Al, Na, K, etc. are characterized by high content availability. A considerable number of Al concentration in the samples slightly exceeded the background level (Figure 2), indicating potential additional sources for the observed Al, beyond just parent materials and soil-forming processes. Pb functions as a critical signal for automotive emissions [,,]; the metallogenic geological background, particularly linked to non-ferrous minerals such as lead–zinc ore, offers a plausible source for Pb, Zn, and Cu in topsoil [,,]. Meanwhile, combining with the above Igeo, the EF values of Pb (Figure 3 and Figure 4), the source of Pb could be recognized as natural background influenced by anthropogenic inputs (mainly traffic activity). Consequently, Factor 1 might potentially represent the natural geogenic sources, but only a handful of topsoil samples exhibited signs of anthropogenic impacts.
Factor 2, the biggest contribution that accounted for 41.0% of the total variance, was mainly characterized by Cu (61.83%), As (60.51%), Fe (57.16%), and Mn (52.98%), followed by Zn (47.81%), Al (40.98%), and Pb (28.52%). Relevant studies have established that the emission of metals such as Cu, As, Fe, Mn, Zn, and Pb is associated with intense human activities [,,,,,], and rock weathering [,] could be released through atmospheric deposition. Serving as a principal indicator for automotive emissions, Pb particles originating from vehicle exhaust contribute to soil pollution via the accumulation of dust [,,]. Moreover, for Cu and Zn, predominantly employed in the production of automotive components and traffic signage, their minuscule particles could also be released from tires and braking systems into the topsoil via atmospheric deposition. Additionally, As, Al, and Mn exhibit extensive presence in the Earth’s crustal materials and play crucial roles in pedogenesis [,,,]. Although the Igeo and EF values were not too high, the concentrations of these elements in many samples (even more than 50%) exceeded the background values of the study area. Thus, it was reasonable to assign this factor to industry sources, especially mining operations due to the long mining history within the study area.
Factor 3, accounting for 7.7% source, was the strongest and mainly characterized by Hg (55.73%, Figure 5b), while all contribution rate of other HMs was below 10%. According to the concentration, Igeo and EF values, it revealed Hg to be the predominant contaminant from anthropogenic activities in the topsoil samples. Previous research has reported that the origins of Hg in topsoil were diversified, but mainly anthropogenic through atmospheric deposition and airborne dust adsorption. Notable Hg sources include coal combustion, the extraction and refining of gold and mercury [,], contaminants from copper ore smelting [,], emissions from fossil fuel burning [,,], mercury pesticide, or sludge fertilizer [,]. However, it can be seen that no significant correlation was found between Hg and other HMs at the level of 0.05 (Figure 5c), indicating that the Hg and other HMSs did not exist from the same or similar source. Consequently, it can be deduced that Factor 3 likely represents a conglomerate of sources driven by multiple human activities.
Factor 4, contributing 17.6% to the overall composition, showed a substantial link to Cd (57.03%) and exhibited moderate correlations with Pb (31.72%) and Zn (30.57%). Combined with the results of Igeo and EF, the influence of Cd contaminant may not to be ignored. In particular, as an element in phosphate rocks, Cd mainly exists in phosphate fertilizer [,,], generally regarded as the hallmark of agricultural practice [,,]. Additionally, studies have indicated that Zn is nearly ubiquitous across a range of agricultural inputs, encompassing fertilizers, pesticides, fungicides, and manures [,,]. It indicated that agricultural activities were the main sources of Cd and Zn in topsoil [,,]. Notably, according to the land use types, the proportion of farmland is very high, meaning high intensity of agricultural activities in the study area (Figure 1). Meanwhile, the contents of Cd and Zn showed significant correlation (Figure 5c). Hence, Factor 4 could be attributed to agricultural sources.
In summary, the sources of HMs in topsoil in the study area were diversified. In order to ensure the functional sustainability of the land in the study area, it is urgent to implement some management strategies and governance techniques. The results show that the strict control of anthropogenic emissions including rational use of mercury pesticide or sludge fertilizer and fossil fuels, control of mining activities, and soil remediation such as soil washing, phytoremediation, biochar, in situ chemical oxidation technique, etc., [,,,,,] are of great significance to curb HMs pollution and restore soil cleanliness in the study area.
4.4. Potential Ecological Risks Assessment
The results pertaining to the prospective ecological risk evaluation for topsoil in agricultural and pastoral areas are illustrated in Figure 6. The average Er values of HMs decreased in the order of Hg (47.23) > Cd (31.07) > As (9.87) > Pb (5.04) > Zn (4.98) > Cu (4.91) > Mn (0.99). With the exception of Hg and Cd (Figure 6a), the Er indices for all other metals fell below the threshold for low-risk classification (Table S2), signifying an absence of ecological hazard in the topsoil. Significantly greater ecological hazards were linked to Hg and Cd, with approximately 47.48% of Hg and 9.87% of Cd in samples corresponding to the moderate risk level or higher (Figure 6b). Notably, Hg posed moderate and considerable risk in 41.46% and 4.74% of the sampled sites, respectively. And the Er value of eleven and two samples was at high and extreme risk, respectively.
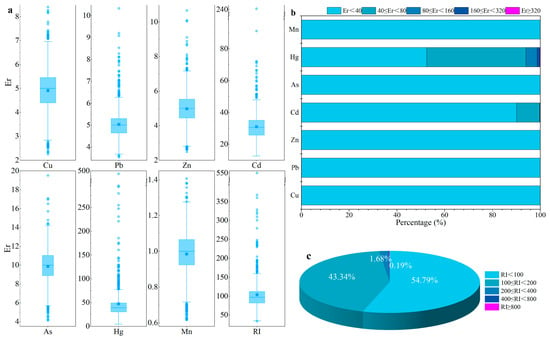
Figure 6.
Statistical examination of Er and RI pertaining to different HMs in topsoil samples. (a) Er box diagrams of HMs in the study area; (b) the cumulative percentage of Er classification level of different heavy metals; (c) the proportion of RI classification level caused by all HMs.
Regarding the total ecological risks, 54.79%, 43.34%, and 1.68% corresponded to slight, moderate, strong, and high risk based on the RI categorization (Figure 6c, Table S2), respectively. Importantly, the calculated RI value of two sample showed quite strong and extremely strong risk levels. In general, the ecological toxicity of HMs is different, and it can lead to higher potential ecological risk due to high enrichment. However, it is crucial to note that even at relatively low levels of contamination, the high toxicity inherent in HMs has the capacity to instigate significant ecological risks [,,]. Overall, the RI values revealed greater potential ecological risk in the study area, and Hg was identified as the primary contributing element, followed by Cd, which should be given more attention.
4.5. Probabilistic Health Risks Assessment
The potential carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risk of hazardous substances to children and adult through different pathways was evaluated, and the findings are presented in Figure 7 and Figure 8. The maximum HI caused by the HMs to both children and adults showed an acceptable risk level (<1), suggesting all topsoil samples posed negligible non-carcinogenic health risks. It is noteworthy that despite both groups presenting non-carcinogenic risks beneath the acceptable threshold, the HI values observed in children surpassed those found in adults. As such, the non-carcinogenic risk for children should also not be ignored.
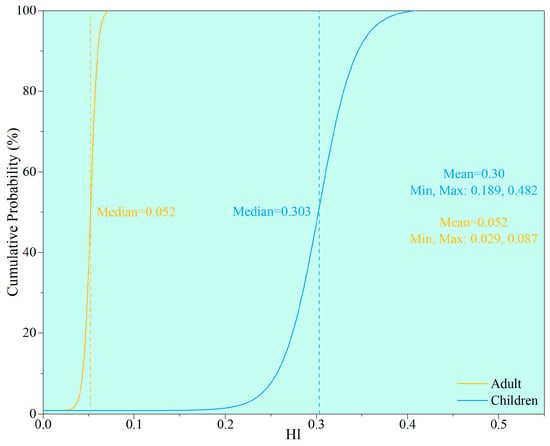
Figure 7.
Cumulative probability of non-carcinogenic HI of all HMs.
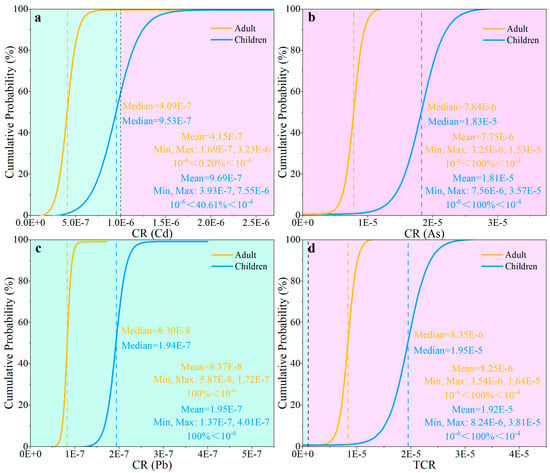
Figure 8.
Box diagram of carcinogenic risk values of HMs (a–d).
Overall, the CR posed to children or adults due to Cd, As, and Pb in topsoil remained under the unacceptable level (10−4) with the order of As > Cd > Pd for both groups (Figure 8). Furthermore, the CR (As), with all values higher than 10−6 signified the most substantial potential for carcinogenic health hazards. Simultaneously, the risk level induced by Cd ranked as the second most significant, whereas that of Pb stood as the least concerning (< 10−6 in all samples). It revealed that As was the main potential carcinogenic element and posed a carcinogenic risk in the topsoil.
Despite the fact that the TCR level presented to children or adults attributable to Cd, As, and Pb was both below the unacceptable level (10−4), the potential carcinogenic hazards were also at high levels with varying degrees (CR > 10−6) (Figure 8d). According to the results of Igeo and EF, the contamination and enrichment degree of Cd, As, and Pb were the relatively low among most samples (Figure 3 and Figure 4), but these HMs still represent heightened cancerous threats to both children and adults, owing to their cancer-inducing toxicity. Notably, the overall TCR level posed by Cr, As, and Cd was considerably more pronounced for children than for adults in the study area, indicating a heightened susceptibility in children. Thus, compared with non-carcinogenic health risks, the potential carcinogenic health risks for different groups should not be ignored, especially for children.
5. Conclusions
This study focused on analyzing primary HMs (Cd, Pb, As, Cu, Zn, Hg, Mn, Al, and Fe) to explore the accumulation, source apportionment, and hazards associated with topsoil HMs in typical intensive agricultural and pastoral areas in the eastern Qaidam Basin, China. On the whole, the contents (mean) of the examined HMs in the topsoil displayed variability, showing different levels of contamination and enrichment. The results further pointed out that Hg and Cd, primarily affected by anthropogenic activities, exhibited accumulations at various levels and served as the leading pollutants. However, the concentrations of HMs fell within the respective risk screening values (RSVs), implying that the potential hazards for agricultural land use could be considered negligible. An integrative analysis, merging the strengths of the PMF model alongside Pearson correlation analysis, significantly enhanced the precision of source determination and successfully quantified the extent of contribution from distinct HMs contamination sources. Natural geogenic, industry mining, composite, and agricultural sources emerged as critical determinants, influencing the accumulation of HMs in the topsoil, whereas mining operations contributed the most significant portion owing to a protracted history of extraction. In summary, the RI values indicated a higher ecological threat, with Hg being distinguished as the main contributor, followed by Cd. Significantly, the non-carcinogenic risk for both groups fell beneath the acceptable risk threshold, and the prospective carcinogenic health threats posed by Cd, As, and Pb for different groups should not be ignored, particularly concerning children.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the following website: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w16243719/s1, Text S1: The assessment criteria for and RI; Table S1: The corresponding relationship between contamination level and value for geo-accumulation index (Igeo) and enrichment factor (EF); Table S2: Criteria of classification levels for (a) and RI (b); Table S3: Parameters of health risk assessment model; Table S4: Reference values of SF and RfD for health risk assessment model. References [,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,] are citied in the Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.Z. and Z.Y.; methodology, Z.Y. and X.X.; software, M.Z. and X.X.; validation, X.X., Y.W. and X.Y.; formal analysis, X.Y.; investigation, M.Z., X.X., Y.W. and X.Y.; resources, Y.W. and X.Y.; data curation, X.X. and M.X.; writing—original draft preparation, M.Z.; writing—review and editing, Z.Y.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lehmann, J.; Bossio, D.A.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Rillig, M.C. The concept and future prospects of soil health. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Árvay, J.; Demková, L.; Hauptvogl, M.; Michalko, M.; Bajčan, D.; Stanovič, R.; Tomáš, J.; Hrstková, M.; Trebichalský, P. Assessment of environmental and health risks in former polymetallic ore mining and smelting area, Slovakia: Spatial distribution and accumulation of mercury in four different ecosystems. Ecotoxicol Environ. Saf. 2017, 144, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, M. Mobilization, Speciation, and Transformation of Organic and Inorganic Contaminants in Soil-Groundwater Ecosystems. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Wang, L.; Liang, T.; Guo, Q.; Guan, Y.; Rinklebe, J. Elucidating the differentiation of soil heavy metals under different land uses with geographically weighted regression and self-organizing map. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.J.; Meng, L.S.; Liu, F.T.; Sheng, Y.Z.; Chen, S.M.; Yang, J.L.; Mao, H.R.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ning, H. Distribution, source investigation, and risk assessment of topsoil heavy metals in areas with intensive anthropogenic activities using the positive matrix factorization (PMF) model coupled with self-organizing map (SOM). Envion. Geochem. Hlth. 2023, 45, 6353–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Deng, M.H.; Wu, S.F.; Japenga, J.; Li, T.Q.; Yang, X.E.; He, Z.L. A modified receptor model for source apportionment of heavy metal pollution in soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 354, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlović, P.; Mitrović, M.; Đorđević, D. Assessment of the contamination of riparian soil and vegetation by trace metals-A Danube River case study. Sci. Total Envion. 2016, 540, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Wu, Y.; Song, B. Spatial distribution and main controlling factor of cadmium accumulation in agricultural soils in Guizhou, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Cheng, Z.; Su, L.M. Pollution characteristics, spatial distributions, and source apportionment of heavy metals in cultivated soil in Lanzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebonye, N.M.; Eze, P.N.; John, K.; Gholizadeh, A.; Dajčl, J.; Drábek, O.; Němeček, K.; Borůvka, L. Self-organizing map artificial neural networks and sequential Gaussian simulation technique for mapping potentially toxic element hotspots in polluted mining soils. J. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 222, 106680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chang, Q.R.; Liu, J.; Clevers, J.G.P.W.; Kooistra, L. Identification of soil heavy metal sources and improvement in spatial mapping based on soil spectral information: A case study in northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Sheng, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, M.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Z.; Li, G.; Baars, O.; Dong, H. Bioavailability of molybdenite to support nitrogen fixation on early Earth by an anoxygenic phototroph. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2024, 647, 119056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Dong, H.; Coffin, E.; Myrold, D.; Kleber, M. The important role of enzyme adsorbing capacity of soil minerals in regulating β-glucosidase activity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL097556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J. Quantitative source apportionment, risk assessment and distribution of heavy metals in agricultural soils from southern Shandong Peninsula of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Z.; Sun, Y.L.; Wang, Z.L. Heavy metal pollution in agricultural soils of a typical volcanic area: Risk assessment and source appointment. Chemosphere 2022, 304, 135340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Liu, Y.; Feng, X.X. Pollution effect assessment of industrial activities on potentially toxic metal distribution in windowsill dust and surface soil in central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 144023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.Z.; Kaley, B.; Bibby, K.; Grettenberger, C.; Macalady, J.L.; Wang, G.C.; Burgos, W.D. Bioreactors for low-pH iron (II) oxidation remove considerable amounts of total iron. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 35962–35972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Sheng, Y.; Shi, J.; Dong, H. Disentangling microbial syntrophic mechanisms for hexavalent chromium reduction in autotrophic biosystems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 6340–6351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Feng, C.T.; Zeng, G.M.; Gao, X.; Zhong, M.Z.; Li, X.D.; Li, X.; He, X.Y.; Fang, Y.L. Spatial distribution and source identification of heavy metals in surface soils in a typical coal mine city, Lianyuan, China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.Y.; Wang, H.F.; Dong, L.R.; Huang, B.; Borggaard, O.K.; Bruun, H.H.; He, Y.; Holm, P.E. Source identification of heavy metals in peri-urban agricultural soils of southeast China: An integrated approach. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, I.; Sajjad, R.U.; Paule-Mercado, M.C.; Memon, S.A.; Lee, B.Y.; Sukhbaatar, C.; Lee, C.H. Comparison of two receptor models PCA-MLR and PMF for source identification and apportionment of pollution carried by runoff from catchment and sub-watershed areas with mixed land cover in South Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 663, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, X.; Lou, Z.; Xiao, R. Contamination assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil through the synthesis of PMF and GeogDetector models. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.L.; Wu, Y.Y.; Sun, J.X.; Li, X.; Geng, X.L.; Zhao, M.L.; Sun, T.; Fan, Z.Q. Health risk assessment of heavy metal(loid)s in park soils of the largest megacity in China by using Monte Carlo simulation coupled with Positive matrix factorization model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltas, H.; Sirin, M.; Gökbayrak, E.; Ozcelik, A.E. A case study on pollution and a human health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soils around Sinop province, Turkey. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Teng, Y.G.; Lu, S.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, J.S. Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, G.C.; Liu, F.; Cui, L.F.; Jiao, Y.J. Supplementary material source apportionment and ecological-health risks assessment of heavy metals in topsoils near a factory, central China. Expo Health 2021, 13, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.Y.; Pu, W.P.; Dong, J.H. Spatiotemporal Changes of Land Use and Its Impact on Ecosystem Service Value in the Agro-pastoral Ecotone of Northern China. Environ. Sci. 2024, 1–19. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Q.; Liu, X.; Liu, C.H. Impacts of grazing pressure on ecosystem health in the agro-pastoral intertwined areas of northern China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 6288–6300. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Chen, H.; Song, L.; Yao, Z.; Meng, F.; Teng, Y. Characterization and source apportionment of heavy metals in the sediments of Lake Tai (China) and its surrounding soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 445–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.J.; Zhu, H.; Bing, H.J.; Tian, X.; Wang, Z.G.; Wang, X.F.; Wu, Y.H. Contamination, sources and health risk of heavy metals in soil and dust from different functional areas in an industrial city of Panzhihua City, Southwest China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Xia, X.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Chen, X.; Zhou, C.H. Levels of arsenic and heavy metals in the rural soils of Beijing and their changes over the last two decades (1985-2008). J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Chen, L.J.; Li, H.H.; Lin, J.B.; Yang, Z.B.; Yang, Y.X.; Xu, X.X.; Xian, J.R.; Shao, J.R.; Zhu, X.M. Characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals exposure via household dust from the urban area in Chengdu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Alharthy, R.D.; Zubair, M.; Ahmed, M.; Hameed, A.; Rafique, S. Toxic and heavy metals contamination assessment in soil and water to evaluate human health risk. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Ahmed, M.K.; Raknuzzaman, M.; Habibullah Al- Mamun, M.; Islam, M.K. Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: A preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Exposure Factors Handbook, Final ed.; U.S. Environment Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- Ning, H.; Jiang, W.J.; Sheng, Y.Z.; Wang, K.L.; Chen, S.M.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, F.T. Comprehensive evaluation of nitrogen contamination in water ecosystems of the Miyun reservoir watershed, northern China: Distribution, source apportionment and risk assessment. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.G.; Lin, Q.; Gao, Y.P. Metals in exposed-lawn soils from 18 urban parks and its human health implications in southern China’s largest city, Guangzhou. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 163, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Chang, Q. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soils and identification of main influencing factors in a typical industrial park in northwest China. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.M.; Wang, Q.S.; Wen, H.H.; Luo, J.; Wang, S. Heavy metals in agricultural soils from a typical township in Guangdong Province, China: Occurrences and spatial distribution. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 168, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.T.; Wang, X.Q.; Liu, B. The characteristics of heavy metal pollution in surface dust in Tangshan, a heavily industrialized city in North China, and an assessment of associated health risks. J. Geochem. Explor. 2020, 210, 106432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CMEE—Ministry of Ecology and Environment of, P.R. Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land (GB15618-2018); China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2018; pp. 1–7. (In Chinese)
- CNEMC—China National Environmental Monitoring Centre. Background Values of Soil Elements in China; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990; pp. 1–500. (In Chinese)
- Jin, Y.L.; O’Connor, D.; Ok, Y.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Liu, A.; Hou, D.Y. Assessment of sources of heavy metals in soil and dust at children’s playgrounds in Beijing using GIS and multivariate statistical analysis. Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrugo-Negrete, J.; Pinedo-Hernandez, J.; Díez, S. Assessment of heavy metal pollution, spatial distribution and origin in agricultural soils along the Sinú River Basin, Colombia. Environ. Res. 2017, 154, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Lei, S.; Bian, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Gan, Y. Geographic distribution of heavy metals and identification of their sources in soils near large, open-pit coal mines using Positive Matrix Factorization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duzgoren-Aydin, N.S.; Li, X.D.; Wong, S.C. Lead contamination and isotope signatures in the urban environment. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadi, M.W. Soil pollution hazardous to environment, a case study on the chemical composition and correlation to automobile traffic of the roadside soil of Jeddah city, Saudi Arabia. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 1280–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; O’Connor, D.; Zhao, B.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, L.; Zheng, N.; Li, X.; Hou, D. Spatial distribution of lead contamination in soil and equipment dust at children’s playgrounds in beijing, china. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 245, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.H.; Lippold, H.; Xiao, T.F.; Li, H.S.; Shen, C.C.; Xie, L.H.; Xie, X.F.; Yang, H.L. Geochemical transfer and preliminary health risk assessment of thallium in a riverine system in the Pearl River Basin, South China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 176, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Ren, S.; Wang, C.; She, J.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Cadmium and lead distribution in pyrite ores: Environmental concerns over geochemically mobile fractions. Elem. Sci. Anth. 2021, 9, 00093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cai, L.M.; Wen, H.H.; Luo, J.; Wang, Q.S.; Liu, X. Spatial distribution and source apportionment of heavy metals in soil from a typical county-level city of Guangdong Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Tai, L.; Qiao, Z.; Zhong, L.; Wang, Z.; Fu, K.; Chen, G. Contamination source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil around municipal solid waste incinerator: A case study in north china. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.L.; Liu, Q.Y.; Ma, J.; Wu, H.W.; Qu, Y.J.; Gong, Y.W.; Yang, S.H.; An, Y.F.; Zhou, Y.Z. Heavy metal(loid)s in the topsoil of urban parks in Beijing, China, concentrations, potential sources, and risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Y.; Dong, H.; Kukkadapu, R.K.; Ni, S.; Zeng, Q.; Hu, J.; Coffin, E.; Zhao, S.; Sommer, A.J.; McCarrick, R.M.; et al. Lignin-enhanced reduction of structural Fe (III) in nontronite: Dual roles of lignin as electron shuttle and donor. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2021, 307, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Baars, O.; Guo, D.; Whitham, J.; Srivastava, S.; Dong, H. Mineral-bound trace metals as cofactors for anaerobic biological nitrogen fixation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 7206–7216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Xu, Y.F.; Hou, H.; Shangguan, Y.X.; Li, F.S. Source identification and health risk assessment of metals in urban soils around the Tanggu chemical industrial district, Tianjin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, J.A.; Nanos, N.; Grau, J.M.; Gil, L.; Lopez-Arias, M. Multiscale analysis of heavy metal contents in Spanish agricultural topsoils. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 1085–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šajn, R.; Halamić, J.; Peh, Z.; Galović, L.; Alijagić, J. Assessment of the natural and anthropogenic sources of chemical elements in alluvial soils from the Drava River using multivariate statistical methods. J. Geochem. Explor. 2011, 110, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiyasu, T.; Kodamatani, H.; Imura, R.; Matsuyama, A.; Miyamoto, J.; Akagi, H.; Kocman, D.; Kotnik, J.ž.; Fajon, V.; Horvat, M. The dynamics of mercury near Idrija mercury mine, Slovenia, horizontal and vertical distributions of total, methyl, and ethyl mercury concentrations in soils. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Wang, S.; Li, R.; Wang, J.J.; Zhang, Z. Soil heavy metal contamination and health risks associated with artisanal gold mining in Tongguan, Shaanxi, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 141, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.B.; Shi, J.B.; Feng, X.B. Mercury pollution in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 3672–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacyna, E.G.; Pacyna, J.M.; Sundseth, K.; Munthe, J.; Kindbom, K.; Wilson, S.; Steenhuisen, F.; Maxson, P. Global emission of mercury to the atmosphere from anthropogenic sources in 2005 and projections to 2020. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2487–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Lin, Z.; Wan, X. Risk assessment for the mercury polluted site near a pesticide plant in Changsha, Hunan, China. Chemosphere 2017, 169, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Wang, T.; Lu, Y.; Giesy, J.P.; Shi, Y.; Zheng, Y. Landscape ecology of the Guanting Reservoir, Beijing, China: Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of metals in soils. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 146, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, Z.R.; Li, J.J.; Zhang, J.M.; Cheng, G.D. Cadmium and zinc interactions and their transfer in soil crop system under actual field conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 285, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, F.A.; Smith, S.R.; Alloway, B.J.; Carlton-Smith, C.; Chambers, B.J. An inventory of heavy metals inputs to agricultural soils in England and Wales. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 311, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abollino, O.; Aceto, M.; Malandrino, M.; Mentasti, E.; Sarzanini, C.; Petrella, F. Heavy metals in agricultural soils from Piedmont, Italy: Distribution, speciation and chemometric data treatment. Chemosphere 2002, 49, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.Y.; Liu, J.S.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.Q.; Yu, H.W. Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and sources of heavy metals in agricultural soil in Dehui, Northeast China. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcbride, M.B.; Spiers, G. Trace element content of selected fertilizers and dairy manures as determined by ICP-MS. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2001, 32, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.T.; Qiu, J.W.; Wang, X.W.; Zhong, Y.; Lan, C.Y.; Shu, W.S. Cadmium contamination in orchard soils and fruit trees and its potential health risk in Guangzhou, China. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 143, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueirol, R.C.; Alleoni, L.R.F.; Nachtigall, G.R.; de Melo, G.W. Sequential extraction and availability of copper in Cu fungicide-amended vineyard soils from Southern Brazil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.X.; Wang, J.H.; Qin, X.Y.; Wang, K.Y.; Han, P.; Zhang, S.Z. Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and origin of heavy metals in the agricultural soils in Shunyi, Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 425, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.C.; Chen, B.N.; Wang, L.A.; Urbanovich, O.; Nagorskaya, L.; Li, X.; Tang, L. A review on phytoremediation of mercury contaminated soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.L.; Yang, W.T.; Zou, Y.Z.; Wu, Y.H.; Mao, W.J.; Zhang, J.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Wang, B.; Wu, P. Quantification of the effect of biochar application on heavy metals in paddy systems: Impact, mechanisms and future prospects. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sizmur, T.; Fresno, T.; Akgül, G.; Frost, H.; Moreno-Jiménez, E. Biochar modification to enhance sorption of inorganics from water. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 246, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.P.; Zhao, Y.C.; Ma, S.M.; Zhu, B.B.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zheng, C.G. Mercury Removal by Magnetic Biochar Derived from Simultaneous Activation and Magnetization of Sawdust. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 12040–12047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.P.; Yao, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, T.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.J.; Xian, J.Q.; Wang, Y.H. Recent advance on application of biochar in remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil: Emphasis on reaction factor, immobilization mechanism and functional modification. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 371, 123212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.P.; Xu, D.; Yue, J.Y.; Ma, Y.C.; Dong, S.J.; Feng, J. Recent advances in soil remediation technology for heavy metal contaminated sites: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astel, A.; Tsakovski, S.; Barbieri, P.; Simeonov, V. Comparison of self-organizing maps classification approach with cluster and principal components analysis for large environmental data sets. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4566–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, B.; Lin, C.; Wu, H.S. Contamination and risk assessment of metals in road-deposited sediments in a medium-sized city of China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 112, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Céréghino, R.; Park, Y.S. Review of the Self-Organizing Map (SOM) approach in water resources: Commentary. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 945–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, D. Spatial characteristics of heavy metal pollution and the potential ecological risk of a typical mining area: A case study in China. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 113, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.; Sisson, S.A.; Sharma, A. Tools for enhancing the application of selforganizing maps in water resources research and engineering. Adv. Water Resour. 2020, 143, 103676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CMEP; Ministry of Environmental Protection of P.R. China. Technical Guidance for Risk Assessment of Contaminated Sites, (HJ 25.3-2014); China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese)
- Fernández, J.; Carballeira, A. Evaluation of contamination, by different elements, in terrestrial mosses. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 40, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferreira-Baptista, L.; Miguel, E. Geochemistry and risk assessment of street dust in Luanda, Angola: A tropical urban environment. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 38, 4501–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, L.Y.; Wang, W.J.; Li, T.Q.; He, Z.L.; Yang, X. Current status of agricultural soil pollution by heavy metals in China: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 3034–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.H.; Cai, L.M.; Wen, H.H.; Hu, G.C.; Chen, L.G.; Luo, J. An integrated approach to quantifying ecological and human health risks from different sources of soil heavy metals. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusin, F.M.; Azani, N.N.M.; Hasan, S.N.M.S.; Sulong, N.A. Distribution of heavy metals and metalloid in surface sediments of heavily-mined area for bauxite ore in Pengerang, Malaysia and associated risk assessment. Catena 2018, 165, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Ma, Z.W.; Kuijp, T.J.; Yuan, Z.W.; Huang, L. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468-469, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Gao, P.; Fu, Y. Risk assessment of toxic metals in street dust from a medium–sized industrial city of China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 106, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Hou, Q.; Duan, J. Pollution and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in surface dust on urban kindergartens. Geogr. Res. 2011, 30, 486–495. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, H.R.; Wang, G.C.; Rao, Z.; Liao, F.; Shi, Z.M.; Huang, X.J.; Chen, X.L.; Yang, Y. Deciphering spatial pattern of groundwater chemistry and nitrogen pollution in Poyang Lake Basin (eastern China) using self-organizing map and multivariate statistics. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 329, 129697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.K.; Ramanathan ALSubramanian, V. Groundwater chemistry and human health risk assessment in the mining region of East Singhbhum, Jharkhand, India. Chemosphere 2018, 204, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.M.; Li, H.R.; Tudi, M.; Yuan, X.; Yang, L.S. Comparison of characteristics, water quality and health risk assessment of trace elements in surface water and groundwater in China. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2021, 219, 112283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA. Supplemental Guidance for Developing Soil Screening Levels for Superfund Sites; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Emergency and Remedial Response: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- USEPA. Region IX, Regional Screening Levels (Formerly PRGs). San Francisco, CA 94105. 2013. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/region9/superfund/prg/ (accessed on 23 November 2014).
- USEPA. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Integrated Risk Information System. 2014. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/iris/ (accessed on 23 November 2014).
- Vesanto, J.; Alhoniemi, E. Clustering of the self-organizing map. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2000, 11, 586–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Meng, B.; Zhang, W.; Bai, J.H.; Ma, Y.X.; Liu, M.D. Multi-Target Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Farmland Soil Based on the Environment-Ecological-Health Effect. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Wang, L.Q.; Huan, Y.Z.; Wang, R.; Liang, T. Concentrations, spatial distribution, sources and environmental health risks of potentially toxic elements in urban road dust across China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yang, F.; Li, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, F.; Ba, Y.; Cui, L.; Sun, L.; Lv, T.; Wang, N. Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of agricultural soil near a smelter in an industrial city in China. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2019, 30, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, L.; Deng, L.; Jin, Z. Characteristics, sources, water quality and health risk assessment of trace elements in river water and well water in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650 Pt 2, 2004–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.F.; Liu, Y.X.; Qiu, H.; Yang, X.S. Quantifying ecological and human health risks of heavy metals from different sources in farmland soils within a typical mining and smelting industrial area. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 45, 5669–5683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Lu, X.W.; Fan, P.; Wang, L.Q.; Yu, B.; Lei, K.; Yang, Y.F.; Chen, Y.R. Concentrations, sources and ecological–health risks of potentially toxic elements in finer road dust from a megacity in north China. J. Clean. Product. 2022, 358, 132036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).