Tolerance of the Marine Anammox Candidatus Scalindua to High Nitrate Concentrations: Implications for Recirculating Aquaculture Systems
Abstract
Highlights
- The anammox process has significant potential to treat nitrogen-rich marine RAS WW.
- The marine anammox species Ca. Scalindua demonstrated effective treatment of synthetic WW with high NO3− levels typically encountered in RAS, at a laboratory scale.
- Despite a relative decline in the population over time, Ca. Scalindua remained a key species within the anammox granules and sustained a high nitrogen removal rate over a period of 262 days of exposure to elevated NO3− levels.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
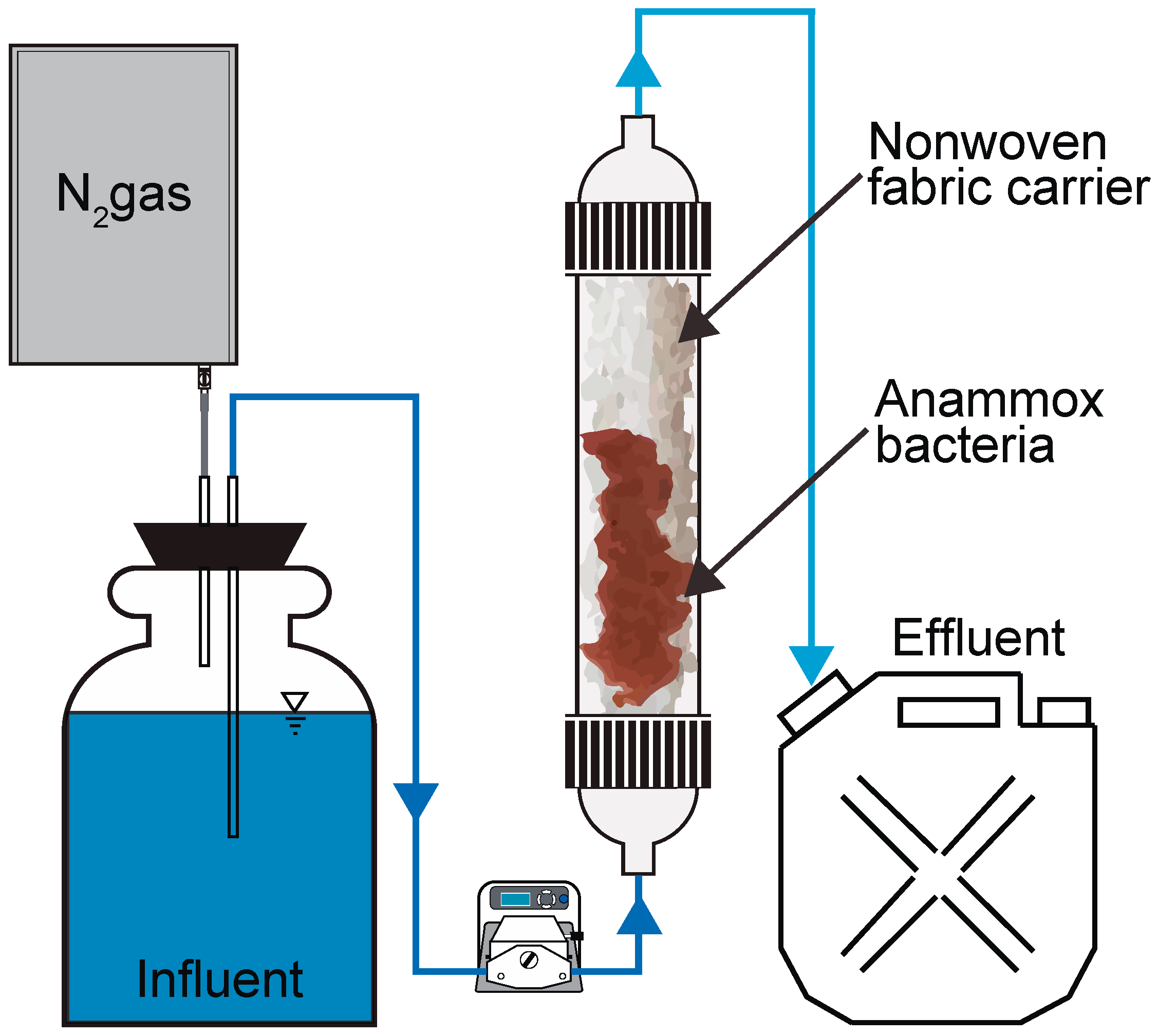
2.1. Reactor Operation
2.2. Experimental Protocol
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Microbial Community Analysis
2.5. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH)
3. Results
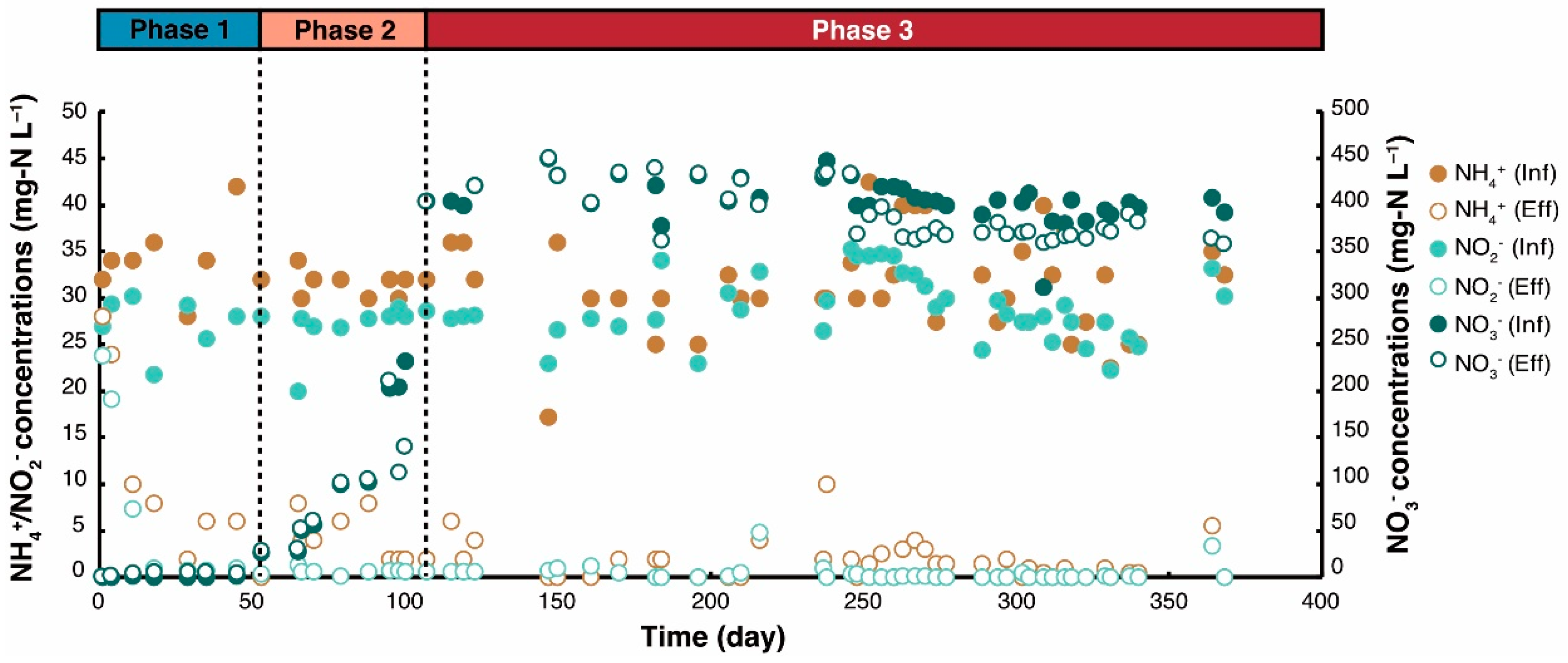
3.1. Reactor Performance
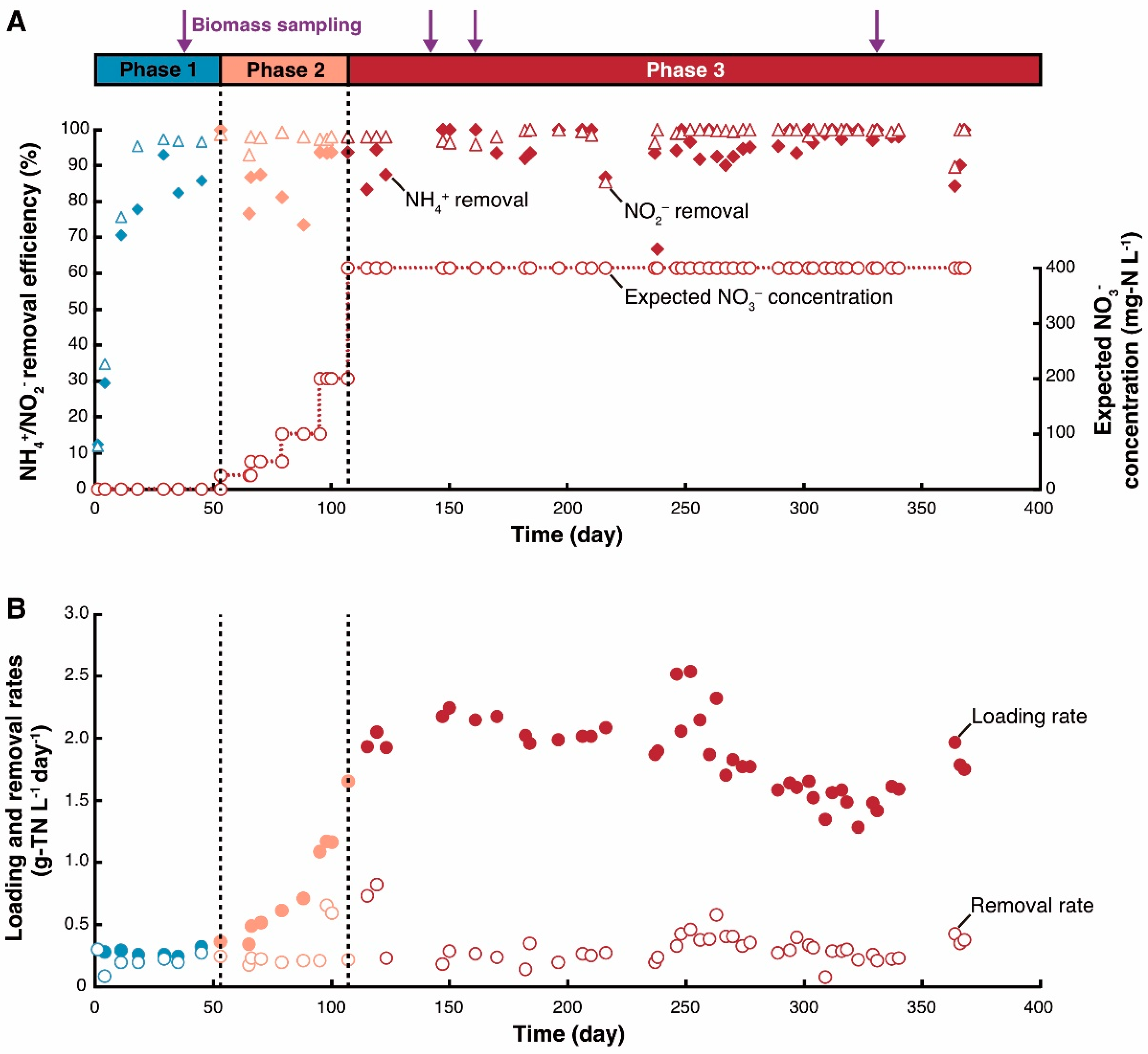
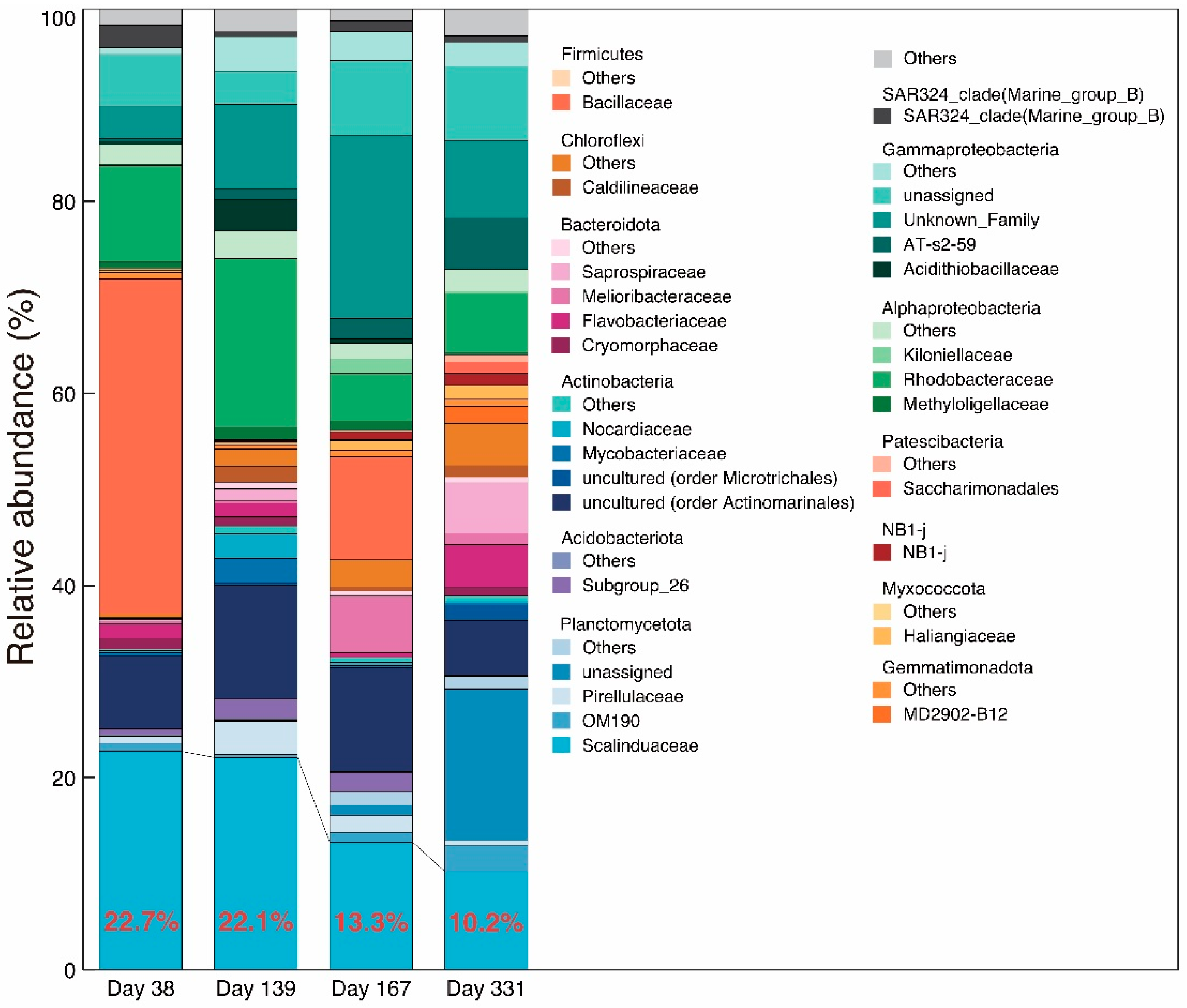
3.2. Microbial Community Analysis and FISH

4. Discussion
4.1. Reactor Performance
4.2. Microbial Community
4.3. Future Directions: Scaling Up Ca. Scalindua Applications in RAS
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA), Population Division. World Population Prospects 2019. 2019. Available online: https://www.un.org/es/desa/world-population-prospects-2019-highlights (accessed on 7 October 2024).
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture (SOFIA) 2022; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Béné, C.; Barange, M.; Subasinghe, R.; Pinstrup-Andersen, P.; Merino, G.; Hemre, G.-I.; Williams, M. Feeding 9 billion by 2050–Putting fish back on the menu. Food Secur. 2015, 7, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahri, S.D.R.; Mohamed, A.F.; Samat, A. LCA for open systems: A review of the influence of natural and anthropogenic factors on aquaculture systems. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2015, 20, 1324–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.; Eding, E.H.; Verdegem, M.C.; Heinsbroek, L.T.; Schneider, O.; Blancheton, J.-P.; d’Orbcastel, E.R.; Verreth, J. New developments in recirculating aquaculture systems in Europe: A perspective on environmental sustainability. Aquac. Eng. 2010, 43, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolarevic, J.; Baeverfjord, G.; Takle, H.; Ytteborg, E.; Reiten, B.K.M.; Nergård, S.; Terjesen, B.F. Performance and welfare of Atlantic salmon smolt reared in recirculating or flow through aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 2014, 432, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padervand, M.; Gholami, M.R. Removal of toxic heavy metal ions from waste water by functionalized magnetic core–zeolitic shell nanocomposites as adsorbents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 3900–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelfatah, A.G.; Ali, M.A.; Abdelbary, K.M. Mechanical filtration pretreatment effect on ammonia biofiltration performance indicators in fish aquaculture wastewater. Misr J. Agric. Eng. 2022, 39, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øvrebø, T.K.; Balseiro, P.; Imsland, A.K.D.; Stefansson, S.O.; Tveterås, R.; Sveier, H.; Handeland, S. Investigation of growth performance of post-smolt Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) in semi closed containment system: A big-scale benchmark study. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 4178–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijn, J. Waste treatment in recirculating aquaculture systems. Aquac. Eng. 2013, 53, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Turchini, G.M. Recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS): Environmental solution and climate change adaptation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Hasan, H.A.; Othman, A.R.; Ismail, N.I. Aquaculture industry: Supply and demand, best practices, effluent and its current issues and treatment technology. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 287, 112271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, J.A.; Alonso, A.; Salamanca, A. Nitrate toxicity to aquatic animals: A review with new data for freshwater invertebrates. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 1255–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, J.; Good, C.; Williams, C.; Summerfelt, S.T. Evaluating the chronic effects of nitrate on the health and performance of post-smolt Atlantic salmon Salmo salar in freshwater recirculation aquaculture systems. Aquac. Eng. 2017, 79, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, J.; Good, C.; Welsh, C.; Summerfelt, S.T. Comparing the effects of high vs. low nitrate on the health, performance, and welfare of juvenile rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss within water recirculating aquaculture systems. Aquac. Eng. 2014, 59, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, F.B.; Williams, E. Nitrite and freshwater fish. Chem. Ecol. 1987, 3, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schram, E.; Roques, J.A.C.; Abbink, W.; Yokohama, Y.; Spanings, T.; de Vries, P.; Bierman, S.; van de Vis, H.; Flik, G. The impact of elevated water nitrate concentration on physiology, growth and feed intake of African catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell 1822). Aquac. Res. 2014, 45, 1499–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schram, E.; Roques, J.A.C.; van Kuijk, T.; Abbink, W.; van De Heul, J.; de Vries, P.; Bierman, S.; van de Vis, H.; Flik, G. The impact of elevated water ammonia and nitrate concentrations on physiology, growth and feed intake of pikeperch (Sander lucioperca). Aquaculture 2014, 420, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preena, P.G.; Rejish Kumar, V.J.; Singh, I.S.B. Nitrification and denitrification in recirculating aquaculture systems: The processes and players. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 2053–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. Recirculating Systems Effluents and Treatments; Aquaculture and the Environment in the United States; World Aquaculture Society: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2002; pp. 119–140. [Google Scholar]
- Stavrakidis-Zachou, O.; Ernst, A.; Steinbach, C.; Wagner, K.; Waller, U. Development of denitrification in semi-automated moving bed biofilm reactors operated in a marine recirculating aquaculture system. Aquac. Int. 2019, 27, 1485–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Lee, J.W.; Chandran, K.; Kim, S.; Khanal, S.K. Nitrous oxide (N2O) emission from aquaculture: A review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6470–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Asher, R.; Gendel, Y.; Lahav, O. Electrochemical applications in RAS: A review. Rev. Aquac. 2024, 16, 86–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.; Hall, S.G. Biochar and zeolite as alternative biofilter media for denitrification of aquaculture effluents. Water 2021, 13, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roques, J.A.C.; Micolucci, F.; Hosokawa, S.; Sundell, K.; Kindaichi, T. Effects of recirculating aquaculture system wastewater on anammox performance and community structure. Processes 2021, 9, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micolucci, F.; Roques, J.A.C.; Ziccardi, G.S.; Fujii, N.; Sundell, K.; Kindaichi, T. Candidatus Scalindua, a Biological Solution to Treat Saline Recirculating Aquaculture System Wastewater. Processes 2023, 11, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, B.; van Niftrik, L.; Keltjens, J.T.; den Camp, H.J.O.; Jetten, M.S. Anammox—Growth physiology, cell biology, and metabolism. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2012, 60, 211–262. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Biddle, J.F.; Jørgensen, S.L. Introducing Candidatus Bathyanammoxibiaceae, a family of bacteria with the anammox potential present in both marine and terrestrial environments. ISME Commun. 2022, 2, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dapena-Mora, A.; Campos, J.; Mosquera-Corral, A.; Jetten, M.; Méndez, R. Stability of the ANAMMOX process in a gas-lift reactor and a SBR. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 110, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strous, M.; Kuenen, J.G.; Jetten, M.S. Key physiology of anaerobic ammonium oxidation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 3248–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strous, M.; Heijnen, J.; Kuenen, J.G.; Jetten, M. The sequencing batch reactor as a powerful tool for the study of slowly growing anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing microorganisms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 50, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, B.; Van Niftrik, L.; Rattray, J.; Van De Vossenberg, J.L.; Schmid, M.C.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.; Jetten, M.S.; Strous, M. Candidatu s ‘Brocadia fulgida’: An autofluorescent anaerobic ammonium oxidizing bacterium. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 63, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okabe, S.; Oshiki, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Satoh, H. N2O emission from a partial nitrification–anammox process and identification of a key biological process of N2O emission from anammox granules. Water Res. 2011, 45, 6461–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenen, J.G. Anammox bacteria: From discovery to application. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dongen, U.; Jetten, M.S.; van Loosdrecht, M. The SHARON®-Anammox® process for treatment of ammonium rich wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 44, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tal, Y.; Schreier, H.J.; Yechezkel, E.; Van Rijn, J. Characterization and abundance of anaerobic ammonia oxidizing (anammox) bacteria in biofilters of recirculating aquaculture systems. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Recirculating Aquaculture, Roanoke, VA, USA, 22–25 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- van Kessel, M.A.; Harhangi, H.R.; Flik, G.; Jetten, M.S.; Klaren, P.H.; Op den Camp, H.J. Anammox bacteria in different compartments of recirculating aquaculture systems. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011, 39, 1817–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tal, Y.; Watts, J.E.; Schreier, H.J. Anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing (anammox) bacteria and associated activity in fixed-film biofilters of a marine recirculating aquaculture system. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2896–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoman, E.S.; Ingall, E.D.; Davis, D.A.; Arnold, C.R. A nitrogen budget for a closed, recirculating mariculture system. Aquac. Eng. 2001, 24, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, J.; Liao, X.; Li, S.; Chen, S.; Huang, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, B.; Sun, S. Nitrogen removal performance and sludge characteristics of wastewater from industrial recirculating aquaculture systems via anammox coupled with denitrification. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Vilcherrez, D.; Carvajal-Arroyo, J.M.; Sierra-Alvarez, R.; Field, J.A. Exogenous nitrate attenuates nitrite toxicity to anaerobic ammonium oxidizing (anammox) bacteria. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 2360–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salter, S.; Gardner, C. Online or face-to-face microbiology laboratory sessions? First year higher education student perspectives and preferences. Creat. Educ. 2016, 7, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhuang, J.-L.; Zhou, Y.-Y.; Meng, F.-G.; Kang, D.; Zheng, P.; Shapleigh, J.P. Metagenomics reveals microbial community differences lead to differential nitrate production in anammox reactors with differing nitrogen loading rates. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qiao, S.; Bi, Z.; Zhou, J. Nitrate removal by anammox biomass with intracellular carbon source as electron donors via DNRA pathway. Environ. Res. 2021, 200, 111390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Graaf, A.A.; de Bruijn, P.; Robertson, L.A.; Jetten, M.S.; Kuenen, J.G. Autotrophic growth of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing micro-organisms in a fluidized bed reactor. Microbiology 1996, 142, 2187–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindaichi, T.; Awata, T.; Tanabe, K.; Ozaki, N.; Ohashi, A. Enrichment of marine anammox bacteria in Hiroshima Bay sediments. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 964–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kindaichi, T.; Awata, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Tanabe, K.; Hatamoto, M.; Ozaki, N.; Ohashi, A. Enrichment using an up-flow column reactor and community structure of marine anammox bacteria from coastal sediment. Microbes Environ. 2011, 26, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojiri, A.; Ohashi, A.; Ozaki, N.; Aoi, Y.; Kindaichi, T. Integrated anammox-biochar in synthetic wastewater treatment: Performance and optimization by artificial neural network. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 243, 118638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoiful, A.; Kambara, H.; Cao, L.T.T.; Matsushita, S.; Kindaichi, T.; Aoi, Y.; Ozaki, N.; Ohashi, A. Mn (II) oxidation and manganese-oxide reduction on the decolorization of an azo dye. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2020, 146, 104820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awata, T.; Goto, Y.; Kuratsuka, H.; Aoi, Y.; Ozaki, N.; Ohashi, A.; Kindaichi, T. Reactor performance and microbial community structure of single-stage partial nitritation anammox membrane bioreactors inoculated with Brocadia and Scalindua enrichment cultures. Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 170, 107991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F. QIIME 2: Reproducible, interactive, scalable, and extensible microbiome data science. PeerJ Prepr. 2018, 6, e27295v1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awata, T.; Oshiki, M.; Kindaichi, T.; Ozaki, N.; Ohashi, A.; Okabe, S. Physiological characterization of an anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing bacterium belonging to the “Candidatus Scalindua” group. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 4145–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daims, H.; Brühl, A.; Amann, R.; Schleifer, K.-H.; Wagner, M. The domain-specific probe EUB338 is insufficient for the detection of all Bacteria: Development and evaluation of a more comprehensive probe set. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 22, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.C.; Maas, B.; Dapena, A.; van de Pas-Schoonen, K.; van de Vossenberg, J.; Kartal, B.; van Niftrik, L.; Schmidt, I.; Cirpus, I.; Kuenen, J.G. Biomarkers for in situ detection of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing (anammox) bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1677–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torno, J.; Einwächter, V.; Schroeder, J.P.; Schulz, C. Nitrate has a low impact on performance parameters and health status of on-growing European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) reared in RAS. Aquaculture 2018, 489, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.-C.; Yang, G.-F.; Yu, J.-J.; Zheng, P. The inhibition of the Anammox process: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 197, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joicy, A.; Song, Y.-C.; Yu, H.; Chae, K.-J. Nitrite and nitrate as electron acceptors for bioelectrochemical ammonium oxidation under electrostatic field. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 250, 109517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocour Kroupová, H.; Valentová, O.; Svobodová, Z.; Šauer, P.; Máchová, J. Toxic effects of nitrite on freshwater organisms: A review. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindholm-Lehto, P. Water quality monitoring in recirculating aquaculture systems. Aquacult. Fish Fish. 2023, 3, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, C.E.; Wu, S.; Bhattacharjee, A.S.; Hamilton, J.J.; McMahon, K.D.; Goel, R.; Noguera, D.R. Metabolic network analysis reveals microbial community interactions in anammox granules. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce-Jahen, S.J.; Cercado, B.; Estrada-Arriaga, E.B.; Rangel-Mendez, J.R.; Cervantes, F.J. Anammox with alternative electron acceptors: Perspectives for nitrogen removal from wastewaters. Biodegradation 2024, 35, 47–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Soda, S.; He, X.; Hao, S.; You, Y.; Peng, Y. Effect of fulvic acid on bioreactor performance and on microbial populations within the anammox process. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 318, 124094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasalari, H.; Gholami, M.; Rezaee, A.; Esrafili, A.; Farzadkia, M. Perspectives on microbial community in anaerobic digestion with emphasis on environmental parameters: A systematic review. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 128618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Deng, T.; Yan, L.; Zhou, J.; He, Z.; Deng, Y.; Xu, M. Elevated nitrate simplifies microbial community compositions and interactions in sulfide-rich river sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-Y.; Li, Z.-L.; Chen, F.; Wang, S.-P.; Nan, J.; Huang, C.; Chen, X.-Q.; Cao, D.; Bai, C.-H.; Wang, H.-C. Influence of nitrate concentration on trichloroethylene reductive dechlorination in weak electric stimulation system. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrighton, K.C.; Virdis, B.; Clauwaert, P.; Read, S.T.; Daly, R.A.; Boon, N.; Piceno, Y.; Andersen, G.L.; Coates, J.D.; Rabaey, K. Bacterial community structure corresponds to performance during cathodic nitrate reduction. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1443–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Sun, F. Nitrogen metabolism potential in biofilm microbial communities: Potential applications in the mariculture wastewater treatment. Aquac. Eng. 2024, 104, 102387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Qi, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q. The study of natural biofilm formation and microbial community structure for recirculating aquaculture system. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; He, S.; Han, M.; Wang, B.; Niu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H. Nitrogen removal performance and microbial community structure in the start-up and substrate inhibition stages of an anammox reactor. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2018, 126, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speth, D.R.; in’t Zandt, M.H.; Guerrero-Cruz, S.; Dutilh, B.E.; Jetten, M.S. Genome-based microbial ecology of anammox granules in a full-scale wastewater treatment system. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraiem, K.; Wahab, M.A.; Kallali, H.; Fra-Vazquez, A.; Pedrouso, A.; Mosquera-Corral, A.; Jedidi, N. Effects of short-and long-term exposures of humic acid on the Anammox activity and microbial community. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 19012–19024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strous, M.; Fuerst, J.A.; Kramer, E.H.; Logemann, S.; Muyzer, G.; Van De Pas-Schoonen, K.T.; Webb, R.; Kuenen, J.G.; Jetten, M.S. Missing lithotroph identified as new planctomycete. Nature 1999, 400, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosokawa, S.; Kuroda, K.; Narihiro, T.; Aoi, Y.; Ozaki, N.; Ohashi, A.; Kindaichi, T. Cometabolism of the superphylum Patescibacteria with anammox bacteria in a long-term freshwater anammox column reactor. Water 2021, 13, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetten, M.S.; Wagner, M.; Fuerst, J.; Van Loosdrecht, M.; Kuenen, G.; Strous, M. Microbiology and application of the anaerobic ammonium oxidation (‘anammox’) process. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2001, 12, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jetten, M.S.; Horn, S.J.; van Loosdrecht, M.C. Towards a more sustainable municipal wastewater treatment system. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 35, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Phase | Period (d) | [NO3−-N] (mg·L−1) | HRT (h) | pH Influent | pH Effluent | Nitrogen Loading Rate (g-TN·L−1·day−1) | Nitrogen Removal Rate (g-TN·L−1·day−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0–52 | 0 | 5.4 ± 0.4 | 7.16 ± 0.18 | 7.51 ± 0.21 | 0.28 ± 0.03 | 0.21 ± 0.07 |
| 2 | 53–105 | 25 → 400 | 5.8 ± 0.4 | 7.24 ± 0.31 | 7.54 ± 0.34 | 0.81 ± 0.44 | 0.21 ± 0.02 |
| 3 | 106–368 | 400 | 6.2 ± 0.8 | 7.45 ± 0.27 | 7.64 ± 0.54 | 1.85 ± 0.30 | 0.29 ± 0.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roques, J.A.C.; Unegbu, E.; Fujii, N.; Marqué, A.; Micolucci, F.; Sundell, K.S.; Kindaichi, T. Tolerance of the Marine Anammox Candidatus Scalindua to High Nitrate Concentrations: Implications for Recirculating Aquaculture Systems. Water 2024, 16, 3705. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16243705
Roques JAC, Unegbu E, Fujii N, Marqué A, Micolucci F, Sundell KS, Kindaichi T. Tolerance of the Marine Anammox Candidatus Scalindua to High Nitrate Concentrations: Implications for Recirculating Aquaculture Systems. Water. 2024; 16(24):3705. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16243705
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoques, Jonathan Armand Charles, Ebuka Unegbu, Naoki Fujii, Amélie Marqué, Federico Micolucci, Kristina Snuttan Sundell, and Tomonori Kindaichi. 2024. "Tolerance of the Marine Anammox Candidatus Scalindua to High Nitrate Concentrations: Implications for Recirculating Aquaculture Systems" Water 16, no. 24: 3705. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16243705
APA StyleRoques, J. A. C., Unegbu, E., Fujii, N., Marqué, A., Micolucci, F., Sundell, K. S., & Kindaichi, T. (2024). Tolerance of the Marine Anammox Candidatus Scalindua to High Nitrate Concentrations: Implications for Recirculating Aquaculture Systems. Water, 16(24), 3705. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16243705







