Refinement and Validation of the SPEcies at Risk Index for Metals (SPEARmetal Index) for Assessing Ecological Impacts of Metal Contamination in the Nakdong River, South Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Labortory Acute Toxicity Test
2.1.1. Test Chemical and Test Organisms
2.1.2. Toxicity Test Method
2.2. Field Monitoring Data
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Calculation of Hazard Quotients (HQs) and Probable Effect Level Quotients (PELqs)
2.3.2. Community Indices
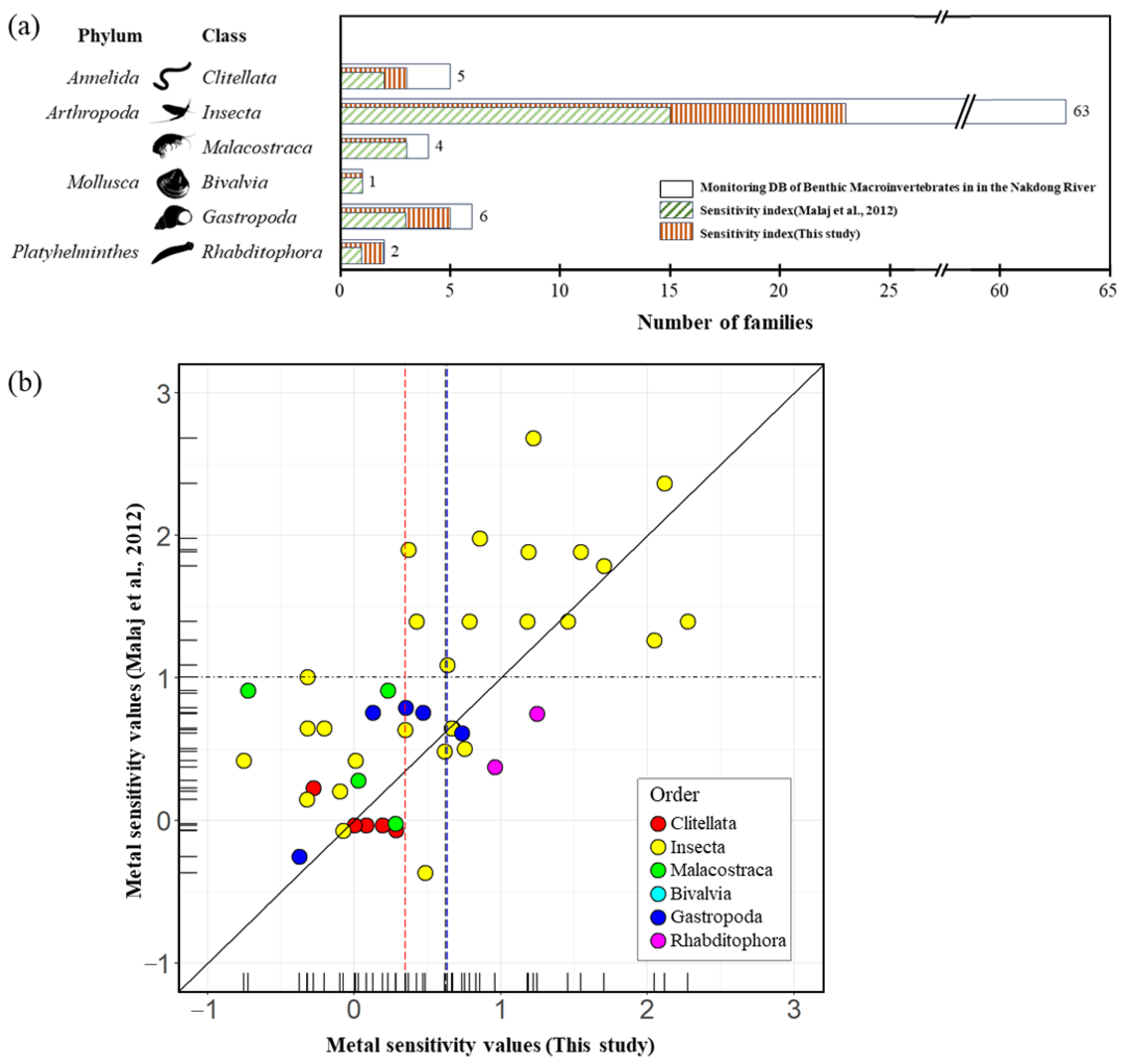
2.3.3. Calculation of Metal Sensitivity Value
2.3.4. Calculation of the SPEAR Index for Metals
2.3.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Updated Metal Sensitivity and SPEAR Index Calculation
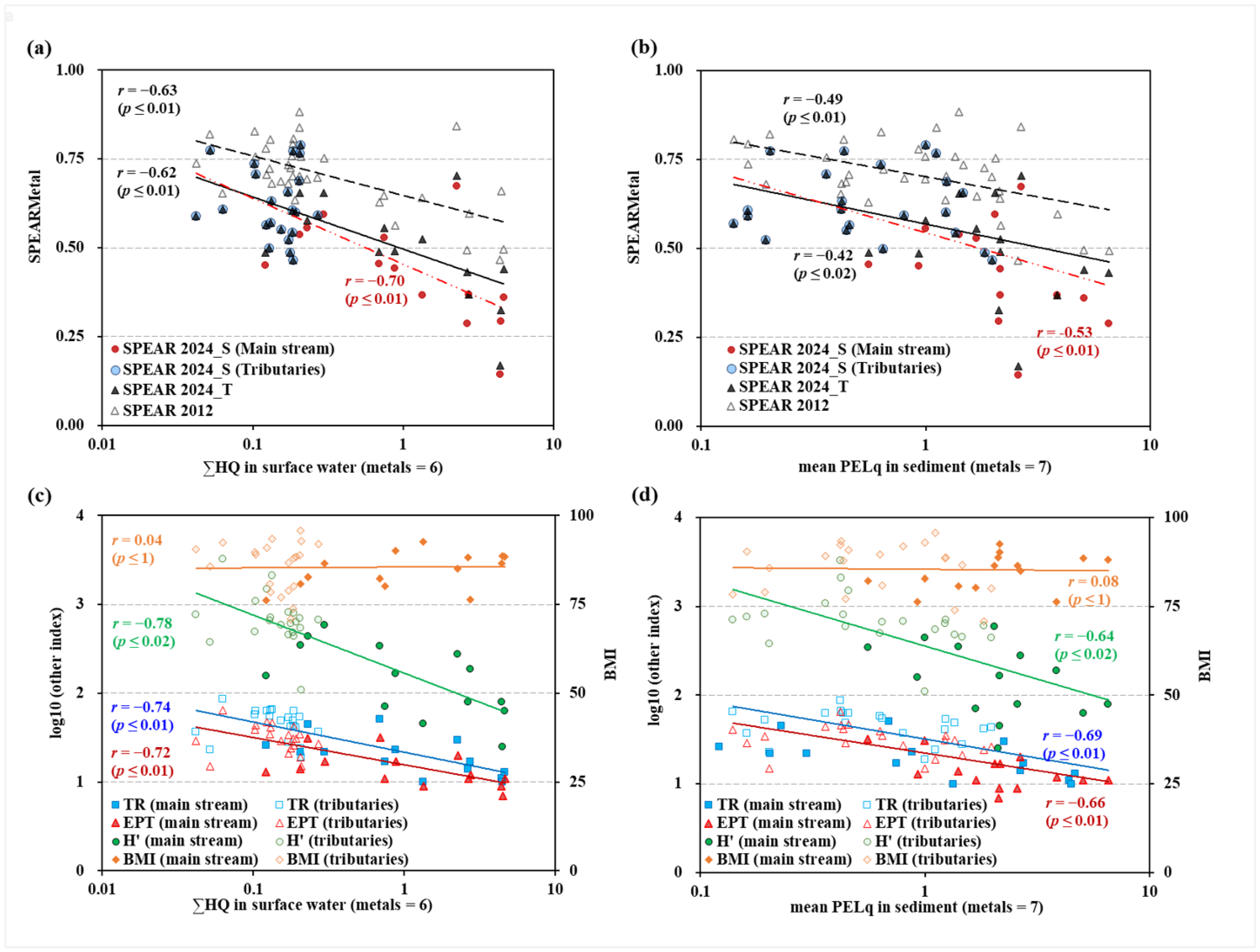
3.2. Association Between Metal Concentrations and SPEAR Index
3.3. Association Between Metal Contamination and Generic Ecological Indices
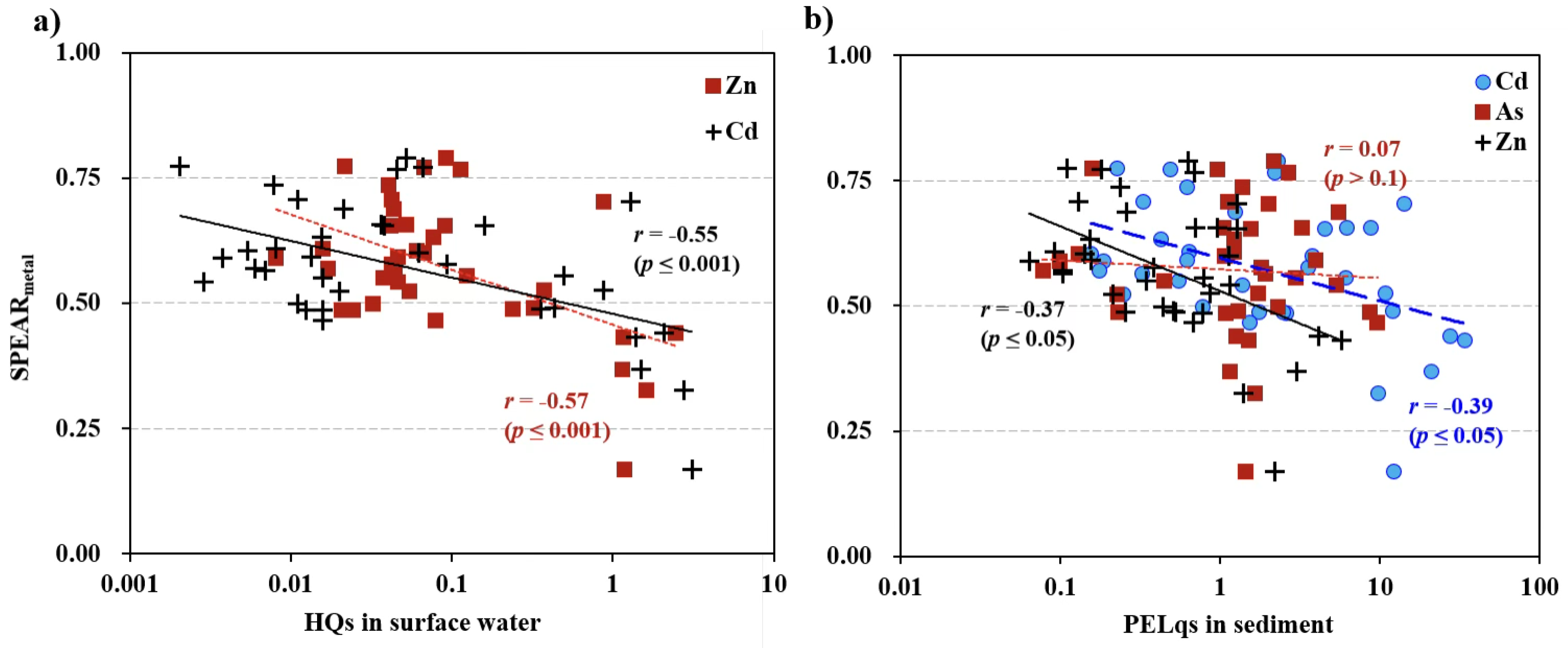
3.4. Relationship Between Individual Metal Concentrations and SPEAR Index
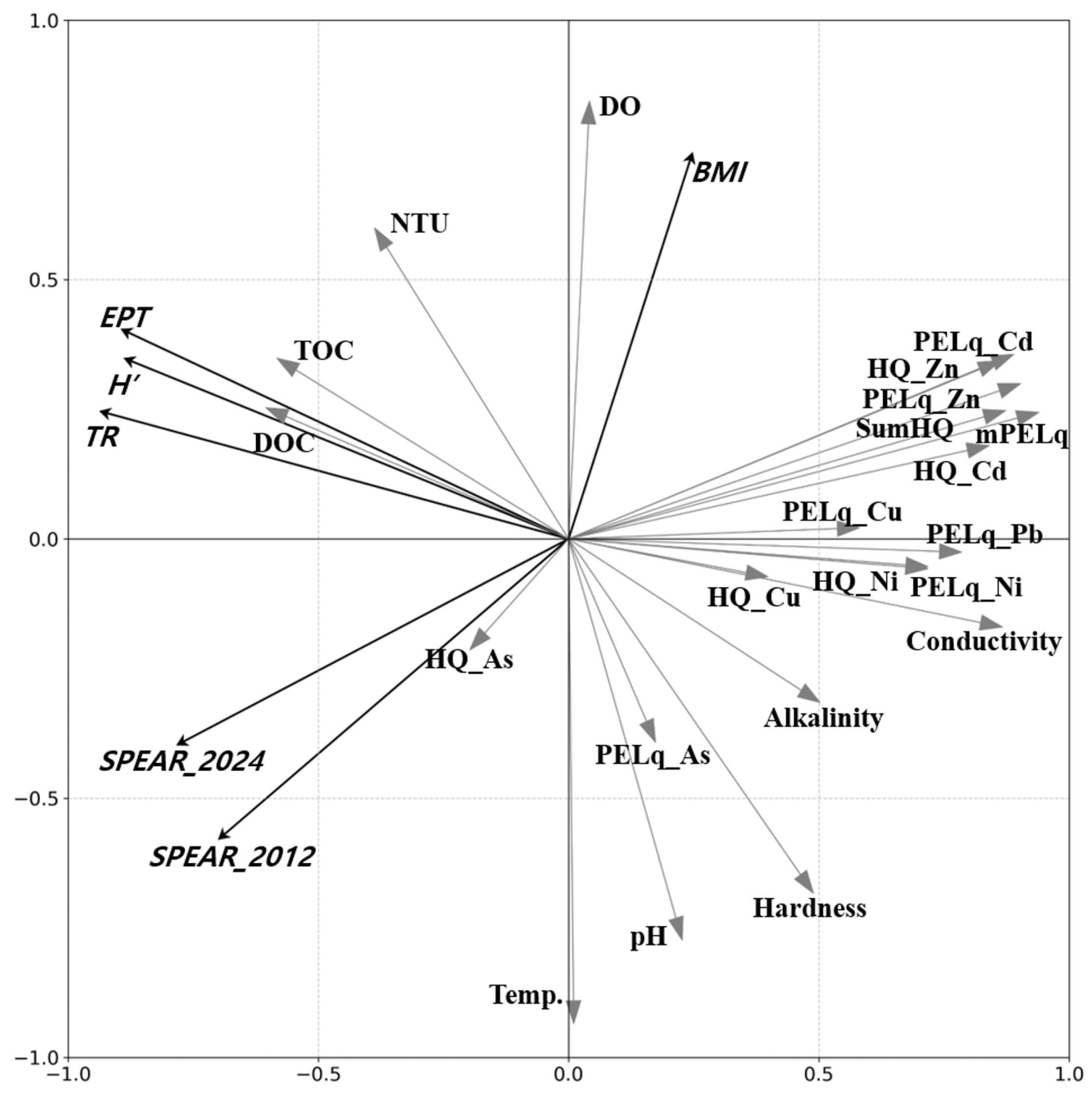
3.5. Multivariate Statistical Analysis to Analyze the Association Between Environmental Factors and Community Indices
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Detailed Results of Data Analysis for Individual Metals
Appendix A.1. Gradient of Metal Concentration and SPEAR Index for Metals in the Main Stream and Tributaries
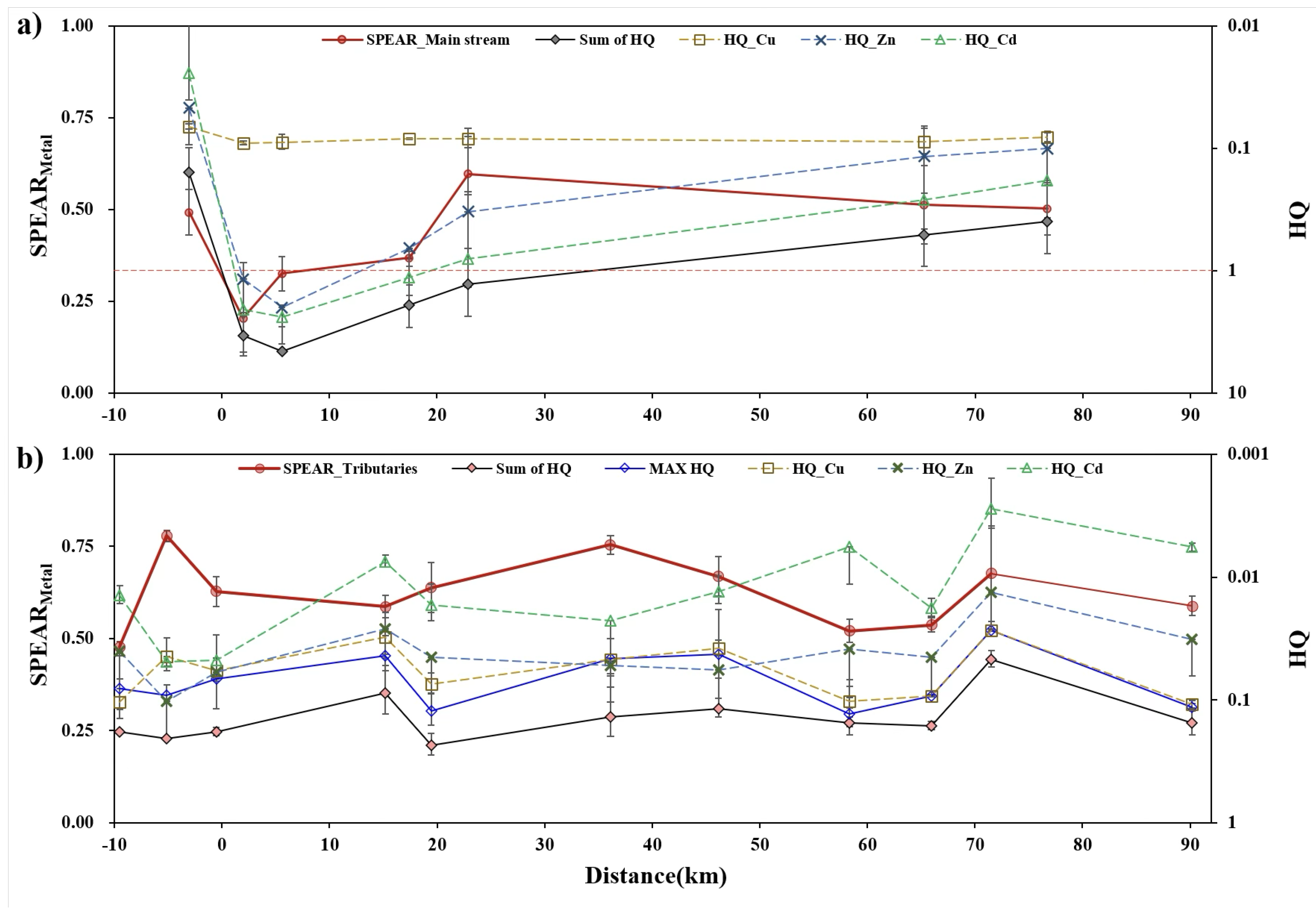
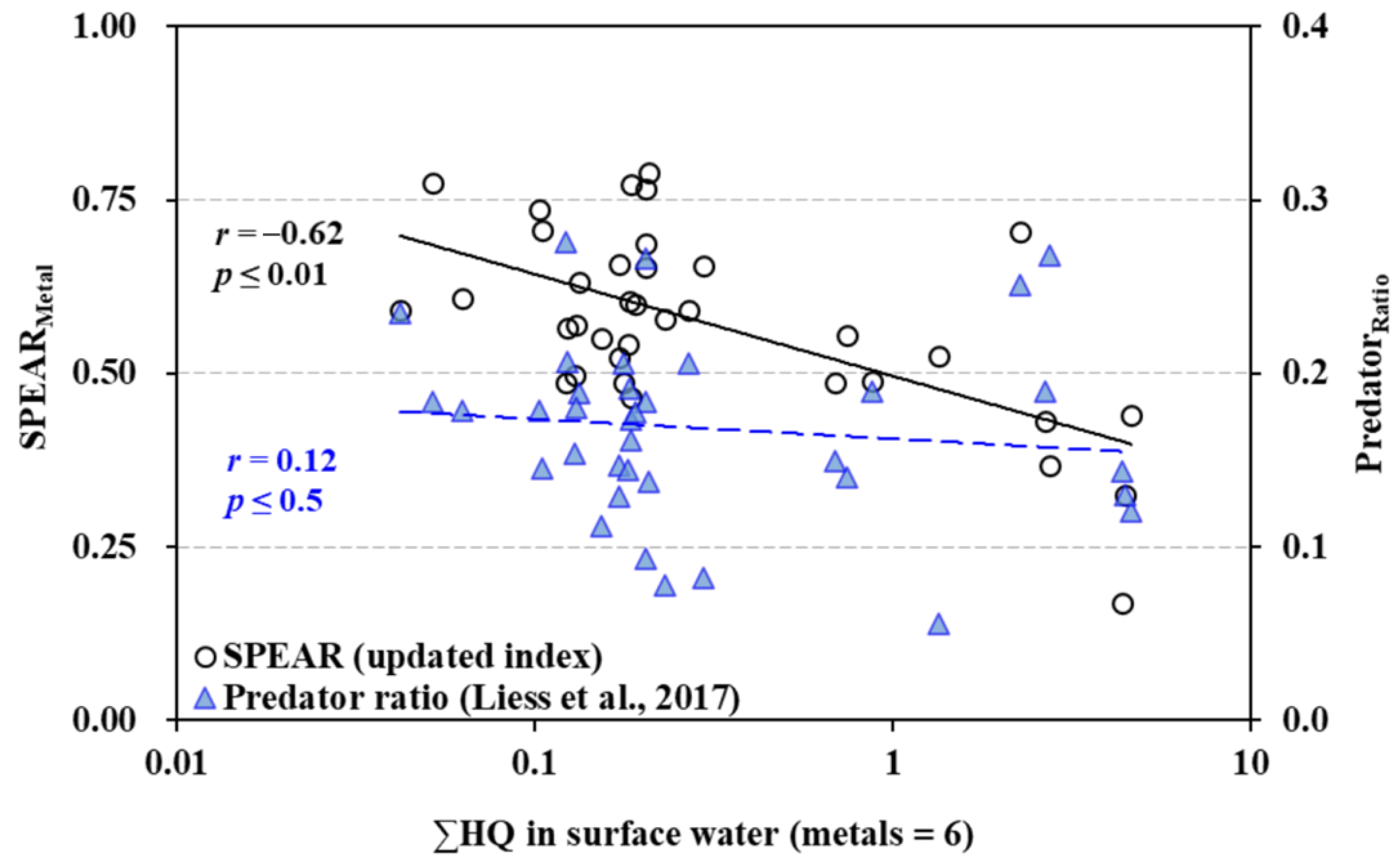
Appendix A.2. Relationship of the Sum of Toxic Units and SPEAR Index for Metals and Predator Ratio
References
- Suter, G.W., II; Norton, S.B.; Cormier, S.M. A methodology for inferring the causes of observed impairments in aquatic ecosystems. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2000, 19, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, G.A., Jr.; Chapman, P.M.; Smith, E.P. Weight-of-evidence approaches for assessing ecosystem impairment. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2002, 8, 1657–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormier, S.M.; Suter, G.W. A framework for fully integrating environmental assessment. Environ. Manag. 2008, 42, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posthuma, L.; Dyer, S.D.; de Zwart, D.; Kapo, K.; Holmes, C.M.; Burton, G.A., Jr. Eco-epidemiology of aquatic ecosystems: Separating chemicals from multiple stressors. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 1303–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, G.W.; Cormier, S.M. Why and how to combine evidence in environmental assessments: Weighing evidence and building cases. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1406–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magurran, A.E. Measuring Biological Diversity; John Wiley & Sons: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mouillot, D.; Graham, N.A.J.; Villéger, S.; Mason, N.W.H.; Bellwood, D.R. A functional approach reveals community responses to disturbances. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liess, M.; Von Der Ohe, P.C. Analyzing effects of pesticides on invertebrate communities in streams. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 954–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beketov, M.A.; Liess, M. An indicator for effects of organic toxicants on lotic invertebrate communities: Independence of confounding environmental factors over an extensive river continuum. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beketov, M.; Foit, K.; Schäfer, R.; Schriever, C.; Sacchi, A.; Capri, E.; Biggs, J.; Wells, C.; Liess, M. SPEAR indicates pesticide effects in streams—Comparative use of species-and family-level biomonitoring data. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.D.; Maxted, J.R. A User Guide for the Macroinvertebrate Community Index; Prepared for the Ministry for the Environment; Cawthron Report 1166; Cawthron Institute: Nelson, New Zealand, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, Y.C.; Won, D.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kong, D.S.; Hwang, S.J. A multimetric benthic macroinvertebrate index for the assessment of stream biotic integrity in Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 3599–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Son, S.H.; Hwang, S.J.; Won, D.H.; Kim, M.C.; Park, J.H.; Jeon, T.S.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; et al. Development of benthic macroinvertebrates index (BMI) for biological assessment on stream environment. J. Korean Soc. Water Environ. 2018, 34, 183–201. [Google Scholar]
- Culp, J.M.; Armanini, D.G.; Dunbar, M.J.; Orlofske, J.M.; Poff, N.L.; Pollard, A.I.; Yates, A.G.; Hose, G.C. Incorporating traits in aquatic biomonitoring to enhance causal diagnosis and prediction. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2011, 7, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaj, E.; Grote, M.; Schäfer, R.B.; Brack, W.; von der Ohe, P.C. Physiological sensitivity of freshwater macroinvertebrates to heavy metals. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1754–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liess, M.; Gerner, N.V.; Kefford, B.J. Metal toxicity affects predatory stream invertebrates less than other functional feeding groups. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, L.K.; Park, J.; Son, D.H.; Kim, W.; Islam, M.S.; Choi, S.; Lee, H.; Han, T. Assessment of metal contamination in water and sediments from major rivers in South Korea from 2008 to 2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.J.; Bong, K.M.; Kang, T.W.; Hwang, S.H.; Na, E.H. Assessing heavy metals in surface sediments of the Seomjin River Basin, South Korea, by statistical and geochemical analysis. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, E.; Noh, H.; Seo, Y.; Lim, H.; Shin, H.; Lee, I.; Jung, H.; Na, T.; et al. Probabilistic ecological risk assessment of heavy metals using the sensitivity of resident organisms in four Korean rivers. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 183, 109483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagihara, M.; Hiki, K.; Iwasaki, Y. Which distribution to choose for deriving a species sensitivity distribution? Implications from analysis of acute and chronic ecotoxicity data. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 278, 116379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 203: Fish, acute toxicity test. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development: Paris, France, 1992; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Test No. 202: Daphnia sp., acute immobilisation test. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development: Paris, France, 1975; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Greve, G.D.; Van der Geest, H.G.; Stuijfzand, S.C.; Engels, S.; Kraak, M.H. Development of ecotoxicity tests using laboratory reared larvae of the riverine caddisflies Hydropsyche angustipennis and Cyrnus trimaculatus. In Proceedings of the Section Experimental and Applied Entomology of the Netherlands Entomological Society (N. E. V.), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; Volume 9, pp. 205–210. [Google Scholar]
- Greve, G.D.; Van der Geest, H.G.; Stuijfzand, S.C.; Kureck, A.; Kraak, M.H. Development and validation of an ecotoxicity test using field collected eggs of the riverine mayfly Ephoron virgo. Proc. Sect. Exp. Appl. Entomol. Neth. Entomol. Soc. (Nev) 1999, 10, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Edition, F. Methods for Measuring the Acute Toxicity of Effluents and Receiving Waters to Freshwater and Marine Organisms; US Environmental Protection Agenc y US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM E 2122-01; Standard Guide for Conducting In-situ Field Bioassays With Marine, Estuarine, and Freshwater Bivalves. American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM): West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2001.
- Test Guidelines OPPTS 850.1035; Mysid Acute Toxicity Test. Office of Prevention, Pesticides and Toxic Substances. United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 1996.
- Test Guidelines OCSPP 850.1020; Gammarid Amphipod Acute Toxicity Test. Office of Chemical Safety and Pollution Prevention, United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- Chung, J.; Kim, S.H.; Hwang, D.S.; Sung, C.G.; Moon, S.D.; Kim, C.; Choi, M.; Lee, J.H. Integrated Chemical and Ecotoxicological Assessment of Metal Contamination in the Andong Watershed: Identifying Key Toxicants and Ecological Risks. Water 2024, 16, 3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Survey and Evaluation Method for River and Stream Ecosystem Health Assessment; Technical Report; National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER): Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2024.
- Stephan, C.E.; Mount, D.I.; Hansen, D.J.; Gentile, J.; Chapman, G.A.; Brungs, W.A. Guidelines for Deriving Numerical National Water Quality Criteria for the Protection of Aquatic Organisms and Their Uses; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- DeForest, D.K.; Van Genderen, E.J. Application of US EPA guidelines in a bioavailability-based assessment of ambient water quality criteria for zinc in freshwater. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1264–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mebane, C.A.; Dillon, F.S.; Hennessy, D.P. Acute toxicity of cadmium, lead, zinc, and their mixtures to stream-resident fish and invertebrates. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1334–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, D.R.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, C.K.; Moon, S.D.; Huh, I.A.; Kim, S.; Park, M.S.; Lee, J.H. Development and validation of freshwater sediment quality assessment guidelines for trace elements in Korea. Environ. Eng. Res. 2022, 27, 200643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepš, J.; Šmilauer, P. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data Using CANOCO; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, J.L.; Resh, V.H.; Hannaford, M.J. Macroinvertebrates as biotic indicators of environmental quality. In Methods in Stream Ecology; Academic Press: London, UK, 1996; Volume 99, pp. 2230–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.A. Stopping rules in principal components analysis: A comparison of heuristical and statistical approaches. Ecology 1993, 74, 2204–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, R.B.; von der Ohe, P.C.; Rasmussen, J.; Kefford, B.J.; Beketov, M.A.; Schulz, R.; Liess, M. Thresholds for the effects of pesticides on invertebrate communities and leaf breakdown in stream ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 5134–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.M. Integrating toxicology and ecology: Putting the “eco” into ecotoxicology. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 44, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, G.W.I. Ecological Risk Assessment and Ecological Epidemiology for Contaminated Sites. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2006, 12, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, I. Toxicological Benchmarks for Screening of Potential Contaminants of Concern for Effects on Aquatic Biota on the Oak Ridge Reservation, Oak Ridge, Tennessee; Technical Report; Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL): Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Malaj, E.; Guénard, G.; Schäfer, R.B.; von der Ohe, P.C. Evolutionary patterns and physicochemical properties explain macroinvertebrate sensitivity to heavy metals. Ecol. Appl. 2016, 26, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Brink, P.J.; Ter Braak, C.J.F. Principal response curves: Analysis of time-dependent multivariate responses of biological community to stress. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 22, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, W.H. Integrating effects of contaminants across levels of biological organization: An overview. J. Aquat. Ecosyst. Stress Recovery 2000, 7, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, W.H.; Carlisle, D.M.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Johnson, P.C. Heavy metals structure benthic communities in Colorado mountain streams. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, W.H.; Cadmus, P.; Brinkman, S.F. Responses of aquatic insects to Cu and Zn in stream microcosms: Understanding differences between single species tests and field responses. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 5176–5182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM E1440-91; Standard Guide for Acute Toxicity Test with the Rotifer Brachionus. American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM): West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012.
- ASTM E729-96; Standard Guide for Conducting Acute Toxicity Tests on Test Materials with Fishes, Macroinvertebrates, and Amphibians. American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM): West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- Brinkman, S.F.; Vieira, N.K.M. Water Pollution Studies; Job Progress Report; Federal Aid Project F-243-R14; Colorado Division of Wildlife: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Greve, G.D.; van der Geest, H.G.; Stuijfz, S.C.; Engels, A.; Kraak, M.H.S. Development of ecotoxicity tests using laboratory reared larvae of the riverine caddisflies Hydropsyche angustipennis and Cyrnus trimaculatus (Trichoptera). Proc. Sect. Exp. Appl. Entomol. Neth. Entomol. Soc. (NEV) 1998, 9, 205–210. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Test No. 235: Chironomus sp., Acute Immobilisation Test. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development: Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- US EPA-821-R-02-012. Methods for Measuring the Acute Toxicity of Effluents and Receiving Waters to Freshwater and Marine Organisms Fifth Edition. 2002. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-08/documents/acute-freshwater-and-marine-wet-manual_2002.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2024).

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, D.-s.; Kim, J.; Chung, J.; Lee, J. Refinement and Validation of the SPEcies at Risk Index for Metals (SPEARmetal Index) for Assessing Ecological Impacts of Metal Contamination in the Nakdong River, South Korea. Water 2024, 16, 3308. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223308
Hwang D-s, Kim J, Chung J, Lee J. Refinement and Validation of the SPEcies at Risk Index for Metals (SPEARmetal Index) for Assessing Ecological Impacts of Metal Contamination in the Nakdong River, South Korea. Water. 2024; 16(22):3308. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223308
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Dae-sik, Jongwoo Kim, Jiwoong Chung, and Jonghyeon Lee. 2024. "Refinement and Validation of the SPEcies at Risk Index for Metals (SPEARmetal Index) for Assessing Ecological Impacts of Metal Contamination in the Nakdong River, South Korea" Water 16, no. 22: 3308. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223308
APA StyleHwang, D.-s., Kim, J., Chung, J., & Lee, J. (2024). Refinement and Validation of the SPEcies at Risk Index for Metals (SPEARmetal Index) for Assessing Ecological Impacts of Metal Contamination in the Nakdong River, South Korea. Water, 16(22), 3308. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223308





