Abstract
The frequency and intensity of urban flooding continuously increase due to the dual influences of climate change and urbanization. Conducting individual importance classification of urban stormwater channel networks (USCNs) is of significant importance for alleviating urban flooding and facilitating targeted stormwater management implementation. However, a quantitative classification method is lacking for trellis networks, which are a common type of USCN. This study proposed a novel importance classification methodology for channel segments in most types of USCNs, especially suitable for trellis networks, based on permutation and algebraic graph theory. The concept of permutation was integrated into the methodology to measure the importance of each channel segment to the USCN. Algebraic graph theory was employed to quantify the topological structure and hydraulic characteristics of the USCN. To verify the applicability and rationality of the proposed methodology, a real-world city with trellis USCNs in China (i.e., Huai’an) was selected as the study area. Seventy channel segments in the USCN were efficiently classified into three categories based on individual importance. This study provided a decision-support methodology from the perspective of individual importance classification in the USCN and offered valuable reference for urban flooding managers.
1. Introduction
Extreme precipitation has become increasingly prominent under the background of climate change [1], marked by more concentrated frequency and greater intensity [2]. The frequency of extreme precipitation was indicated to increase globally by 4.5% per decade between 1960 and 2010 [3], which posed significant challenges to urban stormwater channel networks (USCNs) [4]. USCNs, serving as drainage systems of urban infrastructure, drain stormwater out of urban areas to prevent inundation and minimize risks of urban flooding. However, USCNs are continuously degrading owing to land encroachment from rapid urbanization [5], which reduces the drainage capacity to retain and drain urban floodwaters [6]. Under the dual pressures of climate change and urbanization, the deteriorating USCNs struggle to meet the continuously rising drainage demands. The issue of urban flooding has become increasingly severe [7], resulting in economic losses of up to $651 billion in cities over the past decade [8]. Without intervention, the damage from urban flooding is predicted to increase 20-fold by the late 21st century [9]. To enhance the drainage capacity of USCNs, it is essential to classify the importance of each channel segment to the USCN, which is a prerequisite for implementing targeted stormwater management strategies.
In previous studies, two categories of methods were applied to classify the individual importance of each channel segment to USCNs. One category of methods, from a geographical and geomorphological perspective (e.g., the Horton method [10], the Strahler method [11], and the Shreve method [12], etc.), focuses on the topological structure of the USCN. The non-branching channel segments in the USCN were classified at the lowest importance level. Channel segments of higher importance were formed by the confluence of segments from lower levels [13,14]. These methods classified the channel segments qualitatively and are suitable for the USCNs with well-defined hierarchical relationships. Another category of methods concentrated on the impact of each channel segment, considering factors such as the catchment area, drainage flow, and social value and establishing various criteria for classifying individual importance [15,16,17]. This category applies to the USCNs with clearly defined segment boundaries. The aforementioned two categories of methods are effectively applied to dendritic or pinnate USCNs [18,19], but they face notable challenges in trellis USCNs. During the application of the previous category methods, the identification of non-branching and confluence channel segments becomes complicated due to the non-hierarchical structure of channels [20]. Meanwhile, the fuzzy individual boundaries of intertwined channels hinder the effective use of the latter category of methods.
Although the complicated structure of trellis USCNs makes the classification difficult, scholars have made great efforts to develop modified methods. Jung et al. performed a statistical analysis of tributary junction angles between channel segments. A support vector machine was utilized to classify tributary junction angles based on the beta distribution [21]. Li et al. employed the Cauchy distribution to fit the distribution characteristics of channel segment sinuosity, which were used further for classification [22]. The probability distribution of single critical parameters (e.g., tributary junction angles and channel segment sinuosity) were selected as indicators for classifying the channel segments. Then, multiple parameter methods were proposed to obtain better classification results. Li et al. developed a classification tree to evaluate the importance of each channel segment based on drainage density, stream frequency, and distribution uniformity [23]. Previous studies focused on the topological structure of channel networks, with little attention on the hydraulic parameters that directly impact drainage efficiency. Integrating the hydraulic characteristics of channel segments into the classification method is conducive to achieving a comprehensive result for stormwater drainage [24,25]. Algebraic graph theory, which determines the robustness of edges in the communication, traffic, and electric network effectively, may be a potential approach [26,27,28,29]. Thus, the topological structure of the channel network and the hydraulic characteristic of the channel segment can be considered concurrently.
This study proposed a novel importance classification methodology for channel segments in USCNs based on permutation and algebraic graph theory, which is particularly suitable for trellis networks. Based on the concept of permutation, the importance of each channel segment to the USCN is classified by simulating the blockage of channel segments sequentially. Algebraic graph theory is employed to quantify the topological structure and hydraulic characteristics of the USCN. The topological structure of the channel network is expressed in the form of a graph model, and the hydraulic characteristics of each channel segment are integrated into the graph model as edge weights. A trellis USCN in Huai’an, located in the alluvial plain of the Yangtze River in China, was selected as the study area to demonstrate the applicability and rationality of the proposed methodology. This study provides a decision-support methodology and valuable reference for urban flooding managers.
2. Methodology
2.1. Individual Importance Classification Based on Permutation Algebraic Graph Algorithm (PAGA)
Natural river channels are the final component of urban stormwater networks, accommodating inflow from stormwater pipe networks and surface runoff and playing a crucial role in draining floodwater [30,31]. Enhancing the drainage capacity of urban stormwater channel networks (USCNs) is a direct approach to controlling urban floods. It is economical and efficient to identify key channel segments and implement targeted engineering measures [32]. A novel importance classification methodology was proposed and realized through the permutation algebraic graph algorithm (PAGA). Permutation, a widely used method in regression analysis, is often employed to identify significant variables [33]. The importance of each channel segment to the USCN is classified by sequentially simulating blockages, drawing on the concept of permutation. Algebraic graph theory is a branch of mathematics that applies algebraic methods to graph-related problems. The USCN naturally exhibits graph-like characteristics, allowing its topological structure and hydraulic characteristics to be represented within a weighted adjacency matrix. In this representation, the channel network’s topological structure forms a graph model, with hydraulic characteristics of the channel segments embedded as edge weights. The largest eigenvalue of this weighted adjacency matrix reflects the connectivity of USCNs. By simulating blockages and assessing the resulting perturbations of the largest eigenvalue, which represents the decrease of connectivity, the individual importance of channel segments can be classified effectively. This methodology is suitable for most types of USCNs, especially for trellis networks, where previous methods encountered limitations. Table 1 presents a comparative analysis of different method types, highlighting their respective applicable networks, factors under consideration, and limitations. The flowchart of the methodology is shown in Figure 1.

Table 1.
The comparison of various types of methods.
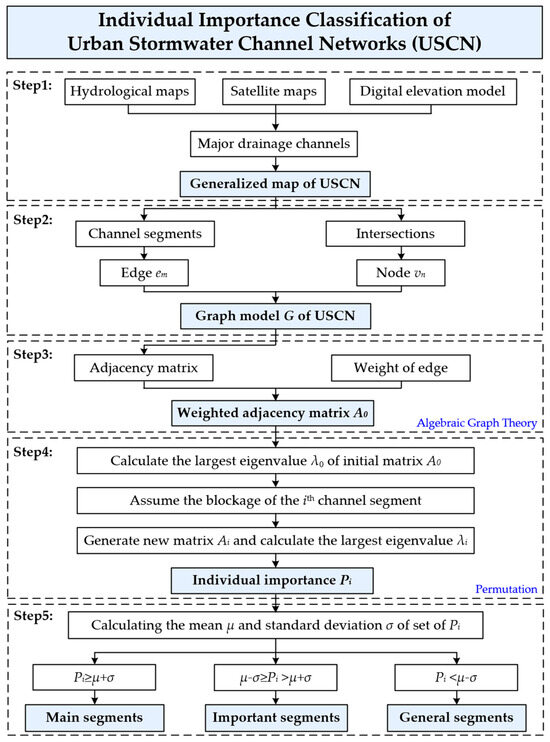
Figure 1.
The methodology of the individual importance classification to urban stormwater channel networks is based on a permutation algebraic graph algorithm.
2.2. Specific Steps
The details of the above methodology are as follows:
Step 1. Generalization of the urban stormwater channel network;
Identifying the existing drainage channels in the USCN is fundamental to the following steps. For small regions with few rivers, the drainage channels are delineated based on satellite maps, supplemented by hydrological maps. For large regions with many rivers, a rough water system network is generated through a digital elevation model in GIS software (QGIS 3.28.15) and then refined with satellite and hydrological maps. If necessary, field surveys can be conducted. During this process, the major drainage channels are selected, while short and minor channels, which function as floodwater storage [34], are disregarded. After identifying the drainage channels, simplify the network to create a generalized map while maintaining the topological structure of the USCN.
Step 2. Construction of the graph model;
The stormwater channel network is a natural graph [35]. Based on the generalized map, a graph model of the USCN is constructed. The intersections between drainage channels are treated as the nodes of the graph, and the channel segments as the edges. The graph model is denoted as G = (V, E),
where G is the graph model of the USCN, V = {v1, v2, …, vₙ} represents the set of nodes, vₙ is the intersection between drainage channels (i.e., node of the graph model), n is the number of intersections, E = {e1, e2, …, eₘ} represents the set of edges, eₘ is the channel segment (i.e., edge of the graph model), m is the number of channel segments.
Step 3. Establishment of weighted adjacency matrix;
For subsequent quantitative calculations, a weighted adjacency matrix is established to represent the topology and hydraulic characteristics of USCN [36,37]. The hydraulic characteristics of each channel segment are used as the weights Wij of the edge elements em in the weighted adjacency matrix A0. Based on the graph model, a weighted adjacency matrix is established as follows:
where A0 is the weighted adjacency matrix of the graph model, aij is the element in the ith row and jth column of the matrix, n is both the dimension of the matrix and the number of nodes, and Wij is the weight of the edge element between node i and node j (i.e., em). Various hydraulic characteristics (e.g., maximum volume, maximum flow, and the rate of water level reduction, etc.), which represent the drainage capacity of a channel segment [38], can be selected as the value of Wij, either individually or in combination. The maximum volume directly represents the maximum capacity of a channel segment to hold flooding water and can be conveniently obtained through geometric measurements. The maximum flow directly reflects the rate at which flooding water can be drained, which requires regular monitoring over time. The rate of water level reduction indirectly represents the likelihood of channel segment inundation, necessitating monitoring under specific timing or conditions. For illustration, the maximum volume is used as an example, as it is easy to obtain without the need for particular timing or conditions. The maximum volume can be calculated as the following equation:
where Voln is the maximum volume of nth channel segment, in cubic meters (m3); ln is the length of nth channel segment, in meters (m); bn is the average width of the riverbed in nth channel segment, in meters (m); mn is the side slope coefficient of nth channel segment, unitless; Hn is the average ground elevation of nth channel segment, in meters (m); and hn is the average riverbed elevation of nth channel segment, in meters (m).
Step 4. Quantification of individual channel segment importance
The permutation method, which is used in statistics to compare differences among multiple groups of samples, is applied in this step [39]. By simulating the impact of blockages in each channel segment on the USCN, the importance of each segment can be quantified. The largest eigenvalue of the weighted adjacency matrix is chosen as the observed statistic, which reflects the connectivity of the graph and the significance of edge weights in the graph’s structure [40]. Based on the weighted adjacency matrix A0 obtained, the largest eigenvalue λ0 of this matrix is calculated. Then, assuming the blockage of the ith channel segment, the ith channel segment is removed to obtain its corresponding weighted adjacency matrix Ai, and the largest eigenvalue λi of matrix Ai is calculated. By calculating the change ratio of the largest eigenvalue of the weighted adjacency matrix during the river section blockage, the importance of the channel segment to USCN, denoted as Pi, can be calculated as the following equation:
where Pi is the change ratio of the largest eigenvalue of the weighted adjacency matrix during the river section blockage, unitless; λ0 is the largest eigenvalue of the initial weighted adjacency matrix, unitless; and λi is the largest eigenvalue of the weighted adjacency matrix after removing the ith channel segment, unitless. The illustration of the permutation process and the calculation process is detailed in Figure 2.
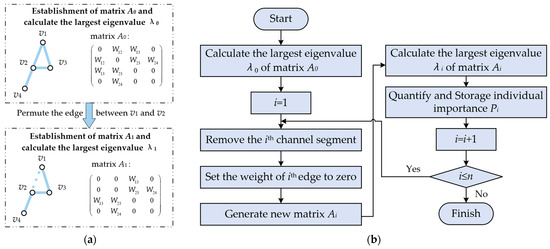
Figure 2.
(a) Illustration of the permutation process in the methodology; (b) flowchart of the quantification process for individual channel segment importance.
Step 5. Importance classification of channel segments
Based on the quantification of individual channel segment importance, arrange each channel segment in descending order to classify their importance levels, which can be specifically categorized into three levels (i.e., main segments, important segments, and general segments). The distribution of the largest eigenvalues of the weighted adjacency matrix is close to a Gaussian distribution, and the standard deviation method is used for classification [41]. This involves calculating the mean μ and standard deviation σ of the sample set and dividing them into three levels: Pi ≥ μ + σ, μ − σ ≥ Pi > μ + σ, and Pi < μ − σ, respectively.
3. Application
3.1. Study Area
Huai’an, an important economic city in the alluvial plain of the Yangtze River in China, was selected as the study area. It is located at 118°12′~119°46′ E longitude and 32°40′~34°45′ N latitude, with a total area of 277.2 km2. This area experiences abundant rainfall and exhibits a significant monsoon climate, with an annual average precipitation of 975.4 mm. Over 50% of the yearly rainfall occurs during the rainy season from July to September, heightening the risk of urban flooding. Furthermore, the area’s trellis USCN poses challenges for applying existing methods to classify the importance of channel segments, making it an ideal focus for this study. The specific location and the regional drainage channels are shown in Figure 3.
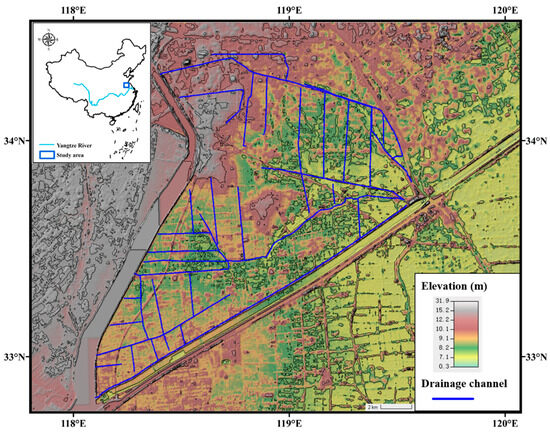
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of study area location and regional drainage channels.
3.2. Data Collection and Software
To conduct the importance classification, channel geometry, hydrological maps, satellite maps, and a digital elevation model (DEM) were collected. Hydrological maps and specific dimensions of each drainage channel were provided by the Jiangsu Provincial Water Resources Department (jswater.jiangsu.gov.cn). High-resolution satellite maps (1 × 1 m) were obtained from Google Maps, while a digital elevation model with a 30 × 30 m spatial resolution was sourced from www.gscloud.cn. For areas where the data were unclear, on-site surveys were conducted to supplement and correct the information. In this study, QGIS (ver. 3.28.15) was used to generalize the urban stormwater channel network, and MATLAB (ver. R2022b) was employed to quantify the importance of individual channel segments. All software packages are supported by student licenses and open-source privileges.
3.3. Graph Model of the Urban Stormwater Channel Network in the Study Area
Using the collected digital elevation model, a rough urban stormwater channel network (USCN) was extracted with QGIS software. However, due to the flat terrain of the study area, the accuracy of the initial extraction was limited. To improve accuracy, the rough USCN was compared with hydrological and satellite maps. As a result, 35 main urban channels with flood drainage functions were selected. These channels were abstracted while retaining their topological relationships, producing a generalized map of the USCN, as shown in Figure 4.
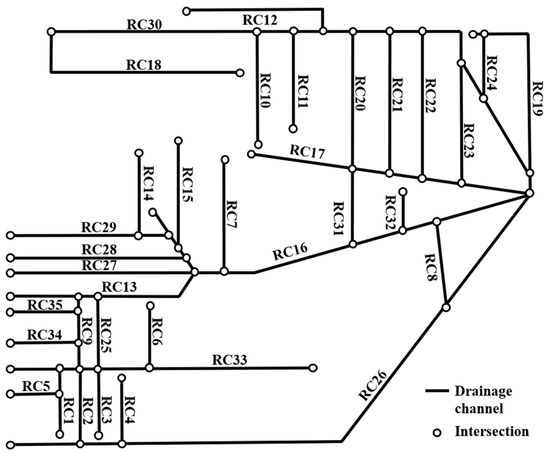
Figure 4.
Generalized map of the urban stormwater channel network (USCN) in the study area.
Based on the generalized map of the study area, the USCN was divided into 70 channel segments and 62 intersections. The intersections vₙ between the drainage channels were treated as nodes, and the channel segments em as edges in the graph model. A graph model G of the USCN was constructed, as shown in Figure 5. A correspondence table of channel segment names and edges is provided in Table A1.
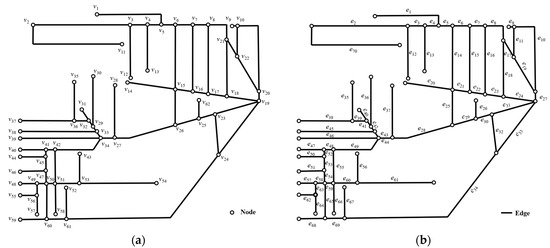
Figure 5.
Graph model of the urban stormwater channel network in the study area: (a) distribution of nodes in the graph model; (b) distribution of edges in the graph model.
3.4. Weighted Adjacency Matrix of the Graph Model
The adjacency matrix of the graph model was constructed using Formula 2. Due to the lack of hydrological data for the study area, the maximum drainage volume of each channel segment was selected as the sole weighting indicator. Based on the collected geometric data, the edge weights for the graph model were calculated using Formula 3, and the values for each channel segment are provided in Table A1. These edge weights were then incorporated into the adjacency matrix to produce the weighted adjacency matrix of the graph model. The weighted adjacency matrix is a real symmetric matrix, with the lower triangular portion shown in Figure 6.

Figure 6.
The lower triangular portion of the weighted adjacency matrix.
As shown in Figure 6, the maximum drainage volume of each channel segment is unevenly distributed between 1.0 × 104 and 85.0 × 104 m3. Channel segments with a drainage volume below 10.0 × 104 m3 are highly concentrated and densely distributed between nodes 40 and 60, indicating that the scale of channel segments in this area is relatively small. In contrast, channel segments with drainage volumes exceeding 10.0 × 104 m3 are more evenly distributed. Several segments with larger volumes are concentrated around node 20. From a structural perspective, most nodes are connected with two nodes, while a few nodes are connected to more. For example, node 19 is connected to nodes 18, 20, 23, and 24. Additionally, the northeastern corner of the region has the most complex structure, exhibiting a dense trellis network.
4. Results and Discussion
Based on the initial weighted adjacency matrix of USCN, the maximum eigenvalue of the matrix was calculated to be 1,041,893.93. By simulating blockages in each drainage channel, new weighted adjacency matrices were generated, and the corresponding maximum eigenvalues were computed sequentially. The importance of each channel segment was quantified by Formula 4, with the results provided in Table A1. Additionally, the mean of date was 5033.89 × 10−7, and the standard deviation was 18,182.11 × 10−7. The channel segments were classified into three levels, including 4 main segments, 2 important segments, and 64 general segments after rounding, as shown in Table 2. The uneven distribution of segments within the same level aligns with the standard deviation results.

Table 2.
The results of individual importance classification in the study area.
The classification results were integrated into the generalized map, as illustrated in Figure 7. The main segments are positioned downstream of RC30, where a major drainage channel exists, with a range of Pi between 45,573.6 × 10−7 to 92,124.4 × 10−7. These segments exhibit significant accommodation capacity while taking in floodwater from upstream channels. Important segments are located midstream of RC30 and downstream of RC19, with Pi values of 8291.3 × 10−7 and 9178.5 × 10−7, respectively. They function as transitional channels in the USCN, effectively channeling floodwaters from general segments into important segments. General segments are situated in the southwestern of the region, where they manage drainage from urban sewer systems and surface runoff from adjacent areas.
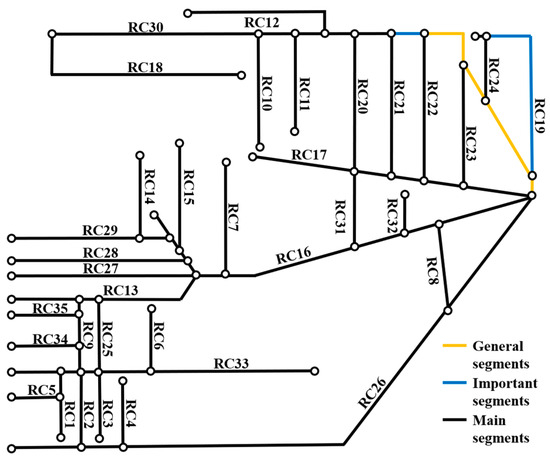
Figure 7.
The schematic diagram of individual importance classification in the study area.
The classification results indicate that the proposed methodology effectively captures both the drainage capacity of individual segments and their influence on the structure of the USCN. For example, RC30-9 with maximum volume of 327,524 × 104 m3, which is smaller than RC30-10’s 724,933 × 104 m3. However, RC30-9 is crucial for connecting segments RC30-10 and RC30-8 within the overall structure, which results in its higher importance ranking compared to RC30-10. Furthermore, to examine the potential sensitivity of the classification results, the input Voln was increased and decreased by 10%, yet the classification results remained unchanged. These results are consistent with the region’s long-standing flood management practices, which enhances the credibility of the findings and demonstrates the feasibility of the methodology.
For urban flooding managers, the classification results provide valuable insights for developing targeted management strategies. Main segments, identified as the most critical drainage sections, could benefit from enhancements to their maximum volume to better accommodate floodwater. For segments prone to external water level backflow, constructing drainage pumping stations at their termini may help mitigate issues. Important segments, which serve as key watercourses, require regular desilting to maintain efficient flood discharge. If necessary, widening their cross-sectional area or lining the channel walls can further improve discharge capacity. General segments, acting as collectors of floodwater, should undergo routine inspections of urban pipeline outlets to prevent blockages. Additionally, planting vegetation with effective interception capabilities around these segments can help prolong runoff time and reduce peak flood levels.
5. Conclusions
This study proposed a novel importance classification methodology for channel segments in USCNs based on permutation and algebraic graph theory, which simultaneously considers the topological structure and hydraulic characteristics. As an example, the methodology was applied to the trellis USCN in Huai’an, Jiangsu Province, located in the alluvial plain of the Yangtze River in China. The importance of 70 channel segments in the study area was quantified and classified based on the permutation algebraic graph algorithm (PAGA). All segments were categorized into three levels of importance. The results show that the classification effectively distinguishes different importance of channel segments.
This study provides a quantitative methodology for evaluating the importance of channel segments in trellis USCNs, offering a valuable reference for urban stormwater management in similar regions. Beyond complex trellis networks, this methodology is applicable to other network types with varied geographical structures, as they can be represented as graph models with lower complexity. The classification results provide practical guidance, enabling regions to develop tailored, long-term flood management strategies based on their financial capabilities and future urban development plans. By prioritizing key segments according to their importance, this approach allows for more effective allocation of resources, ensuring that critical areas receive necessary enhancements while also planning for gradual improvements in less urgent segments.
In the future, to meet diverse management needs, indicators related to ecology and the environment could be incorporated into the methodology. Ecological indicators, such as biomass, riparian vegetation coverage, and indicator species, could be combined with environmental indicators, including pH, dissolved oxygen (DO), chemical oxygen demand (COD), and biological oxygen demand (BOD), along with hydraulic indicators. Based on regional requirements, varying weights can be assigned to each indicator, creating a comprehensive graph model edge weight for more comprehensive classification.
Author Contributions
Methodology, Z.Z.; data curation, J.W.; writing—original draft preparation, H.B.; software, Z.G.; investigation, T.L.; resources, F.W.; visualization, Q.S.; data curation, X.Q.; writing—review and editing, L.W.; funding acquisition, J.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Research on Soil and Water Conservation and Water Ecological Environment Protection Countermeasures and Measures for the Recent Construction Project of the Flood Detention and Storage Area around Hongze Lake funded by the National Key Projects (A3200000001004892001).
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request due to privacy: The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our respect and gratitude to the anonymous reviewers and editors for their professional comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
Author F.W. was employed by Huai’an Water Conservancy Survey and Design Institute Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Results of maximum volume and quantified importance for each channel segment.
Table A1.
Results of maximum volume and quantified importance for each channel segment.
| Name of Drainage Channels | Index of Channel Segments | Index of Edges | Voln (104 m3) | Pi (10−7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RC1 | 1 | e63 | 15,255 | 0 |
| 2 | e64 | 6538 | 0 | |
| RC2 | 1 | e65 | 21,445 | 0.0111 |
| RC3 | 1 | e66 | 15,206 | 0 |
| RC4 | 1 | e67 | 12,678 | 0.7877 |
| RC5 | 1 | e62 | 55,840 | 0 |
| RC6 | 1 | e56 | 95,665 | 0 |
| RC7 | 1 | e37 | 157,292 | 0.0055 |
| RC8 | 1 | e32 | 54,266 | 361.8366 |
| RC9 | 1 | e47 | 7004 | 0 |
| 2 | e52 | 39,561 | 0 | |
| 3 | e53 | 50,026 | 0 | |
| 4 | e54 | 50,933 | 0 | |
| RC10 | 1 | e12 | 15,980 | 0.0023 |
| RC11 | 1 | e13 | 125,215 | 0.1785 |
| RC12 | 1 | e1 | 501,158 | 29.6839 |
| RC13 | 1 | e48 | 142,616 | 0 |
| 2 | e49 | 267,283 | 0.0002 | |
| RC14 | 1 | e35 | 50,447 | 0 |
| RC15 | 1 | e36 | 139,622 | 0 |
| RC16 | 1 | e40 | 290,918 | 0 |
| 2 | e41 | 138,688 | 0 | |
| 3 | e42 | 69,344 | 0 | |
| 4 | e43 | 118,083 | 0 | |
| 5 | e44 | 111,397 | 0.003 | |
| 6 | e28 | 400,042 | 0.2016 | |
| 7 | e29 | 140,015 | 1.1982 | |
| 8 | e30 | 126,680 | 50.9895 | |
| 9 | e31 | 152,976 | 2888.5039 | |
| RC17 | 1 | e20 | 81,772 | 0.015 |
| 2 | e21 | 58,434 | 1.2945 | |
| 3 | e22 | 59,190 | 40.8047 | |
| 4 | e23 | 98,620 | 384.8343 | |
| 5 | e24 | 177,103 | 4828.3902 | |
| RC18 | 1 | e70 | 352,968 | 0.5969 |
| RC19 | 1 | e9 | 252,072 | 767.518 |
| 2 | e10 | 172,883 | 8291.3245 | |
| RC20 | 1 | e14 | 16,784 | 1.0304 |
| RC21 | 1 | e15 | 110,086 | 174.4012 |
| RC22 | 1 | e16 | 161,774 | 1887.1536 |
| RC23 | 1 | e18 | 40,617 | 1713.5119 |
| RC24 | 1 | e11 | 75,596 | 4666.7021 |
| RC25 | 1 | e55 | 49,054 | 0 |
| RC26 | 1 | e68 | 104,255 | 0.2585 |
| 2 | e69 | 72,177 | 25.6048 | |
| 3 | e34 | 630,359 | 3246.2007 | |
| 4 | e33 | 217,401 | 7961.9953 | |
| RC27 | 1 | e46 | 73,565 | 0 |
| RC28 | 1 | e45 | 86,838 | 0 |
| RC29 | 1 | e38 | 24,037 | 0 |
| 2 | e39 | 10,302 | 0 | |
| RC30 | 1 | e2 | 846,717 | 1.5645 |
| 2 | e3 | 235,171 | 1.9807 | |
| 3 | e4 | 220,182 | 9.0993 | |
| 4 | e5 | 238,894 | 113.2594 | |
| 5 | e6 | 348,692 | 1331.6747 | |
| 6 | e7 | 397,317 | 9178.494 | |
| 7 | e8 | 413,463 | 45,573.66 | |
| 8 | e17 | 796,632 | 92,124.436 | |
| 9 | e19 | 327,524 | 91,494.407 | |
| 10 | e27 | 724,933 | 61,049.612 | |
| RC31 | 1 | e25 | 53,130 | 0.0994 |
| RC32 | 1 | e26 | 46,220 | 0.1043 |
| RC33 | 1 | e57 | 25,965 | 0 |
| 2 | e58 | 21,836 | 0 | |
| 3 | e59 | 26,285 | 0 | |
| 4 | e60 | 53,452 | 0 | |
| 5 | e61 | 121,012 | 0 | |
| RC34 | 1 | e51 | 32,500 | 0 |
| RC35 | 1 | e50 | 28,976 | 0 |
References
- Emmerling, J.; Andreoni, P.; Charalampidis, I.; Dasgupta, S.; Dennig, F.; Feindt, S.; Fragkiadakis, D.; Fragkos, P.; Fujimori, S.; Gilli, M.; et al. A Multi-Model Assessment of Inequality and Climate Change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2024, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, T.; Rind, D. Increasing Contribution of the Atmospheric Vertical Motion to Precipitation in a Warming Climate. Commun Earth Environ 2024, 5, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Donat, M.G.; Zong, S.; Alexander, L.V.; Manzanas, R.; Kruger, A.; Choi, G.; Salinger, J.; He, H.S.; Li, M.-H.; et al. Extreme Precipitation on Consecutive Days Occurs More Often in a Warming Climate. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2022, 103, E1130–E1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wu, Z. Study on the Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Traditional Villages and Their Response to the Water Network System in the Lower Yangtze River Basin. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dissanayake, L. Stream Corridor Encroachment and Its Consequences: The Case of Pinga Oya Tributary in the Upper Mahaweli River in Sri Lanka. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 7, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Wu, J.; Tang, R.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y. A Review of Flood Risk in China During 1950–2019: Urbanization, Socioeconomic Impact Trends and Flood Risk Management. Water 2022, 14, 3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Villarini, G.; Vecchi, G.A.; Smith, J.A. Urbanization Exacerbated the Rainfall and Flooding Caused by Hurricane Harvey in Houston. Nature 2018, 563, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutori, M.; Debarati, G.-S. Human Cost of Disasters: An Overview of the Last 20 Years (2000–2019); Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters (CRED): Brussels, Belgium; United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR): Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Winsemius, H.C.; Aerts, J.C.J.H.; Van Beek, L.P.H.; Bierkens, M.F.P.; Bouwman, A.; Jongman, B.; Kwadijk, J.C.J.; Ligtvoet, W.; Lucas, P.L.; van Vuuren, D.P.; et al. Global Drivers of Future River Flood Risk. Nature Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.E. Erosional Development of Streams and Their Drainage Basins; Hydrophysical Approach to Quantitative Morphology. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull 1945, 56, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strahler, A.N. Quantitative Analysis of Watershed Geomorphology. Eos Trans. AGU 1957, 38, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shreve, R.L. Statistical Law of Stream Numbers. J. Geol. 1966, 74, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamboj, V.; Kamboj, N.; Sharma, A.K. A Review on General Characteristics, Classification and Degradation of River Systems. Environ. Degrad. Causes Remediat. Strateg. 2020, 1, 47–62. [Google Scholar]
- Sah, R.K.; Das, A.K. Minimizing Ambiguities in Stream Classification of Complex Drainage Structures. J. Hydrol. 2017, 553, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallaire, C.O.; Lehner, B.; Sayre, R.; Thieme, M. A Multidisciplinary Framework to Derive Global River Reach Classifications at High Spatial Resolution. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 024003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadaki, M.; Brierley, G.; Cullum, C. River Classification: Theory, Practice, Politics. WIREs Water 2014, 1, 349–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meynell, P.-J.; Metzger, M.; Stuart, N. Identifying Ecosystem Services for a Framework of Ecological Importance for Rivers in South East Asia. Water 2021, 13, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Lee, M.; An, H.; Um, M.-J.; Park, D. Characterization and Classification of River Networks in South Korea. Environ. Model. Softw. 2022, 156, 105495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, S.; Comte, L.; Filipa Filipe, A.; Fortin, M.; Jacquet, C.; Ryser, R.; Tedesco, P.A.; Brose, U.; Erős, T.; Giam, X.; et al. The Geography of Metapopulation Synchrony in Dendritic River Networks. Ecol. Lett. 2021, 24, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía, A.I.; Niemann, J.D. Identification and Characterization of Dendritic, Parallel, Pinnate, Rectangular, and Trellis Networks Based on Deviations from Planform Self-similarity. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, 2007JF000781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Shin, J.-Y.; Park, D. A New Approach for River Network Classification Based on the Beta Distribution of Tributary Junction Angles. J. Hydrol. 2019, 572, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawen, L.; Qingyang, L.; Yong, Z. Characterization and Classification of River Network Types. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 37, 6219–6236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wu, B.; Chen, Y.; Li, D. Quantification of River Network Types Based on Hierarchical Structures. Catena 2022, 211, 105986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Shen, D.; Huang, N.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y. Urban Flood Risk Assessment Using Storm Characteristic Parameters Sensitive to Catchment-Specific Drainage System. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valizadeh, N.; Shamseldin, A.Y.; Wotherspoon, L. Quantification of the Hydraulic Dimension of Stormwater Management System Resilience to Flooding. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 4417–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardene, I.; Herath, P.; Venayagamoorthy, G.K. A Graph Theory-Based Clustering Method for Power System Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 Clemson University Power Systems Conference (PSC), Clemson, SC, USA, 10–13 March 2020; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Said, B.; Lathamaheswari, M.; Singh, P.K.; Ouallane, A.A.; Bakhouyi, A.; Bakali, A.; Talea, M.; Dhital, A.; Deivanayagampillai, N. An Intelligent Traffic Control System Using Neutrosophic Sets, Rough Sets, Graph Theory, Fuzzy Sets and Its Extended Approach: A Literature Review. Neutrosophic Sets Syst. 2022, 50, 10–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kaveh, A. Introduction to Graph Theory and Algebraic Graph Theory. In Topological Transformations for Efficient Structural Analysis; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 5–21. ISBN 978-3-031-12299-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ebel, H.; Eberhard, P. A Comparative Look at Two Formation Control Approaches Based on Optimization and Algebraic Graph Theory. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2021, 136, 103686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Yu, J. Impact of Rainstorm Patterns on the Urban Flood Process Superimposed by Flash Floods and Urban Waterlogging Based on a Coupled Hydrologic–Hydraulic Model: A Case Study in a Coastal Mountainous River Basin within Southeastern China. Nat. Hazards 2022, 112, 301–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthusamy, M.; Casado, M.R.; Butler, D.; Leinster, P. Understanding the Effects of Digital Elevation Model Resolution in Urban Fluvial Flood Modelling. J. Hydrol. 2021, 596, 126088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heritage, G.; Entwistle, N. Impacts of River Engineering on River Channel Behaviour: Implications for Managing Downstream Flood Risk. Water 2020, 12, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frossard, J.; Renaud, O. Permutation Tests for Regression, ANOVA, and Comparison of Signals: The Permuco Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2021, 99, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithila Devi, N.; Sridharan, B.; Bindhu, V.M.; Narasimhan, B.; Bhallamudi, S.M.; Bhatt, C.M.; Usha, T.; Vasan, D.T.; Kuiry, S.N. Investigation of Role of Retention Storage in Tanks (Small Water Bodies) on Future Urban Flooding: A Case Study of Chennai City, India. Water 2020, 12, 2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, S. Investigating Topologic and Geometric Properties of Synthetic and Natural River Networks under Changing Climate. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Central Florida, Orlando, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Royle, G.F.; Godsil, C. Algebraic Graph Theory; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 207. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, C.; Mukherjee, G. Role of Adjacency Matrix in Graph Theory. IOSR J. Comput. Eng. 2014, 16, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shit, P.K.; Bera, B.; Islam, A.; Ghosh, S.; Bhunia, G.S. Introduction to Drainage Basin Dynamics: Morphology, Landscape and Modelling. In Drainage Basin Dynamics; Shit, P.K., Bera, B., Islam, A., Ghosh, S., Bhunia, G.S., Eds.; Geography of the Physical Environment; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1–9. ISBN 978-3-030-79633-4. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnini, S.; Assegie, G.M.; Trzcinska, K. Review about the Permutation Approach in Hypothesis Testing. Mathematics 2024, 12, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, F.R. Spectral Graph Theory; American Mathematical Soc.: Providence, RI, USA, 1997; Volume 92. [Google Scholar]
- Hastie, T.; Friedman, J.; Tibshirani, R. The Elements of Statistical Learning; Springer Series in Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001; ISBN 978-1-4899-0519-2. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).