A National-Scale Study of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Surface Water: Levels, Sources, and Carcinogenic Risk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
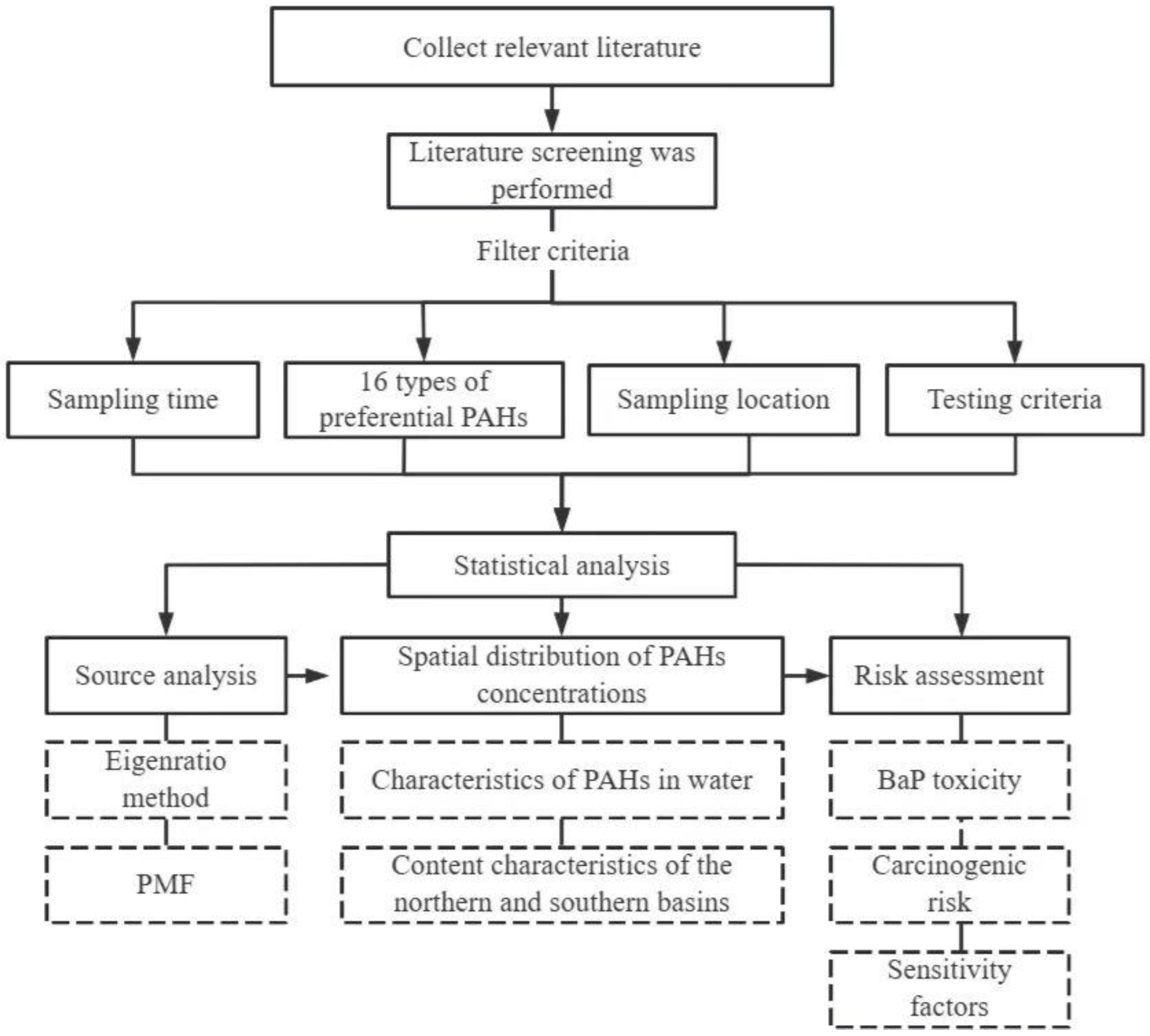
2.1. Data Collection and Processing
2.2. Positive Matrix Factorization
2.3. Incremental Lifetime Cancer Risk
2.4. Uncertainty Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
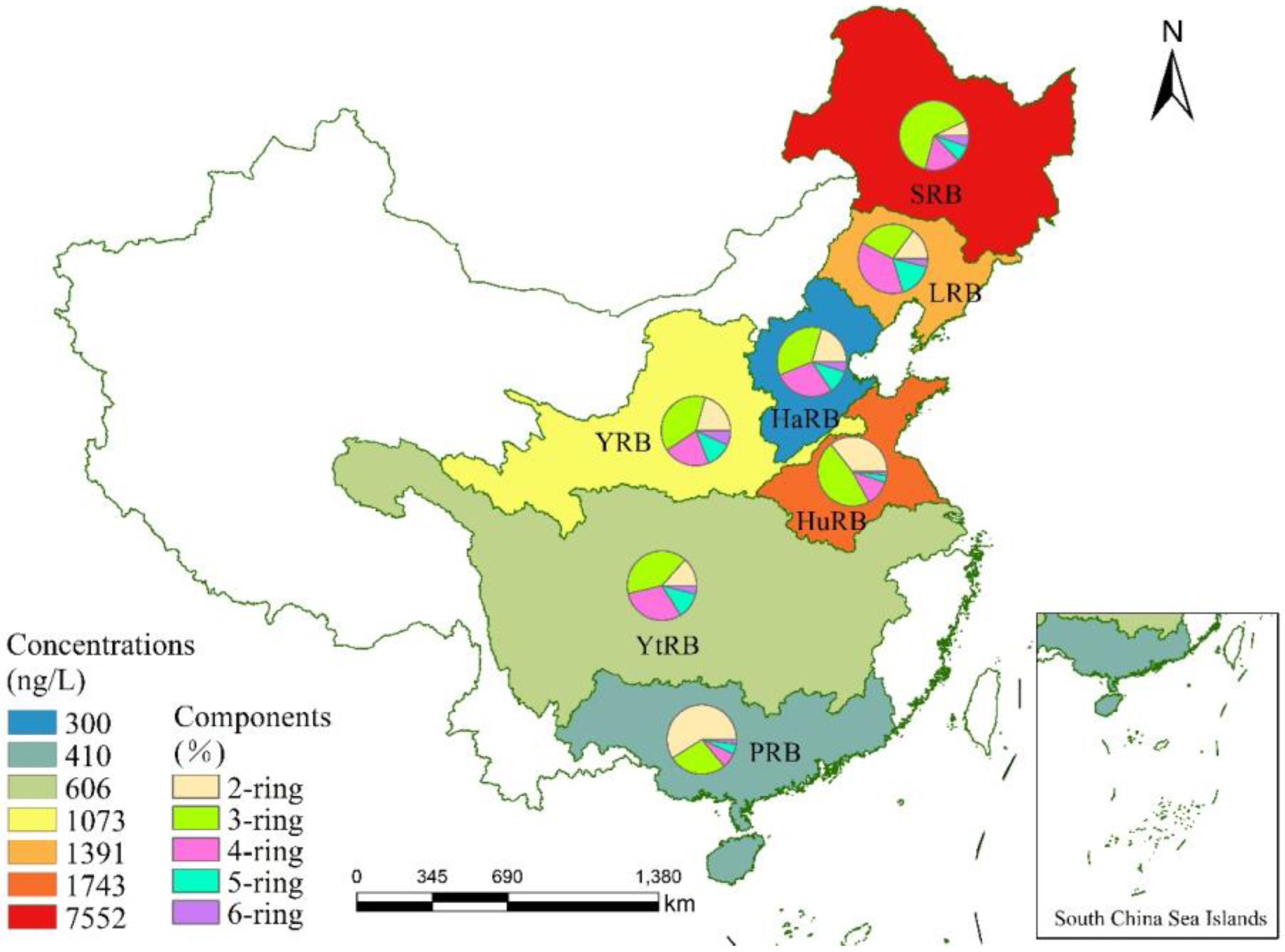
3.1. Geographical Distributions of PAH Concentrations
3.2. Geographical Distributions of PAH Compositions
3.3. Pollution Levels of PAHs
4. Discussion
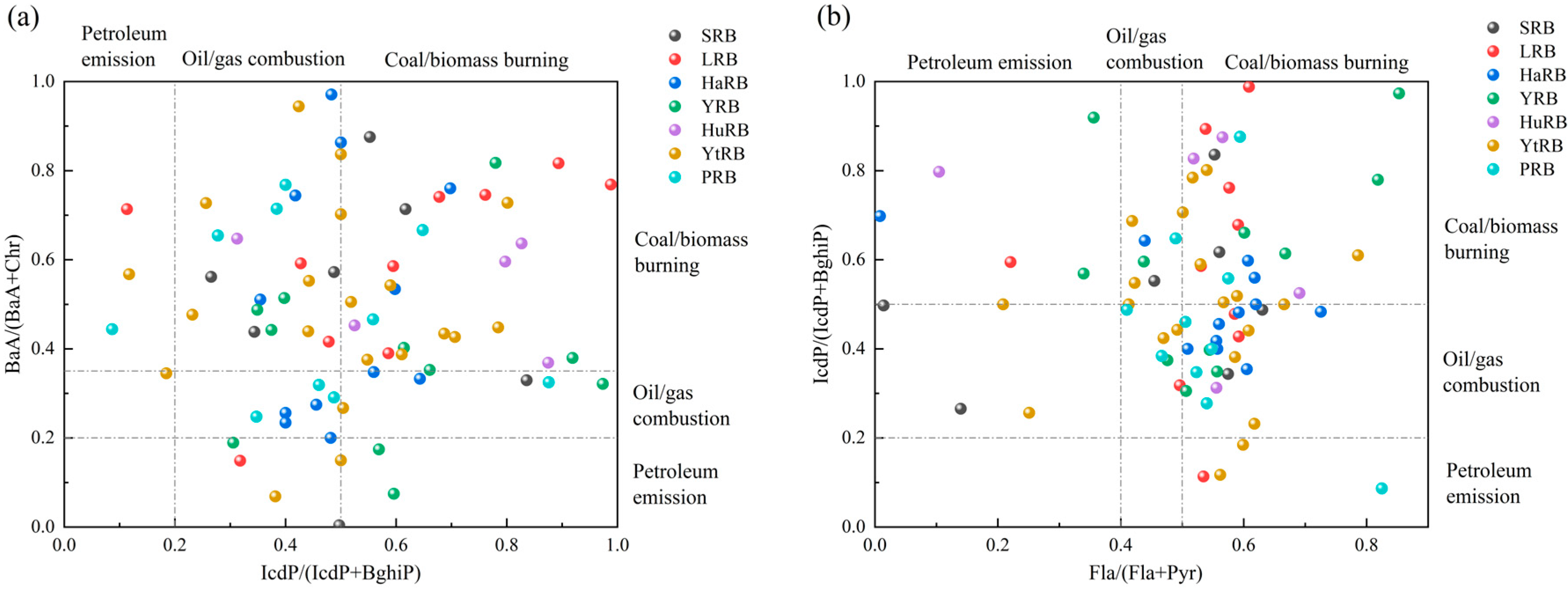
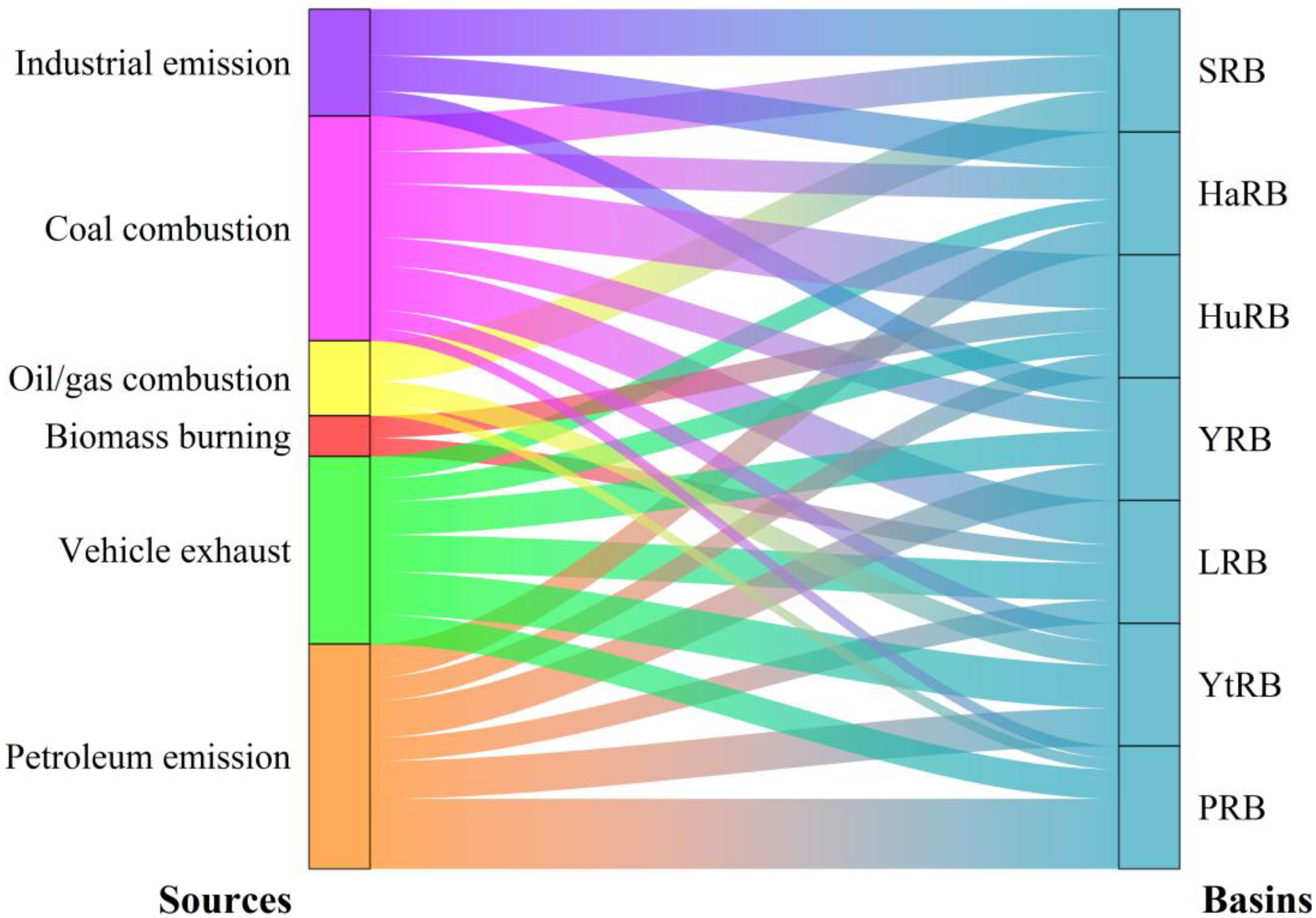
4.1. Spatial Heterogeneity of PAH Sources
4.1.1. Characteristic Ratio
4.1.2. Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF)
4.2. Assessment of Carcinogenic Risks of PAHs
4.2.1. Distribution and Toxicity Characterization of BaP Concentrations
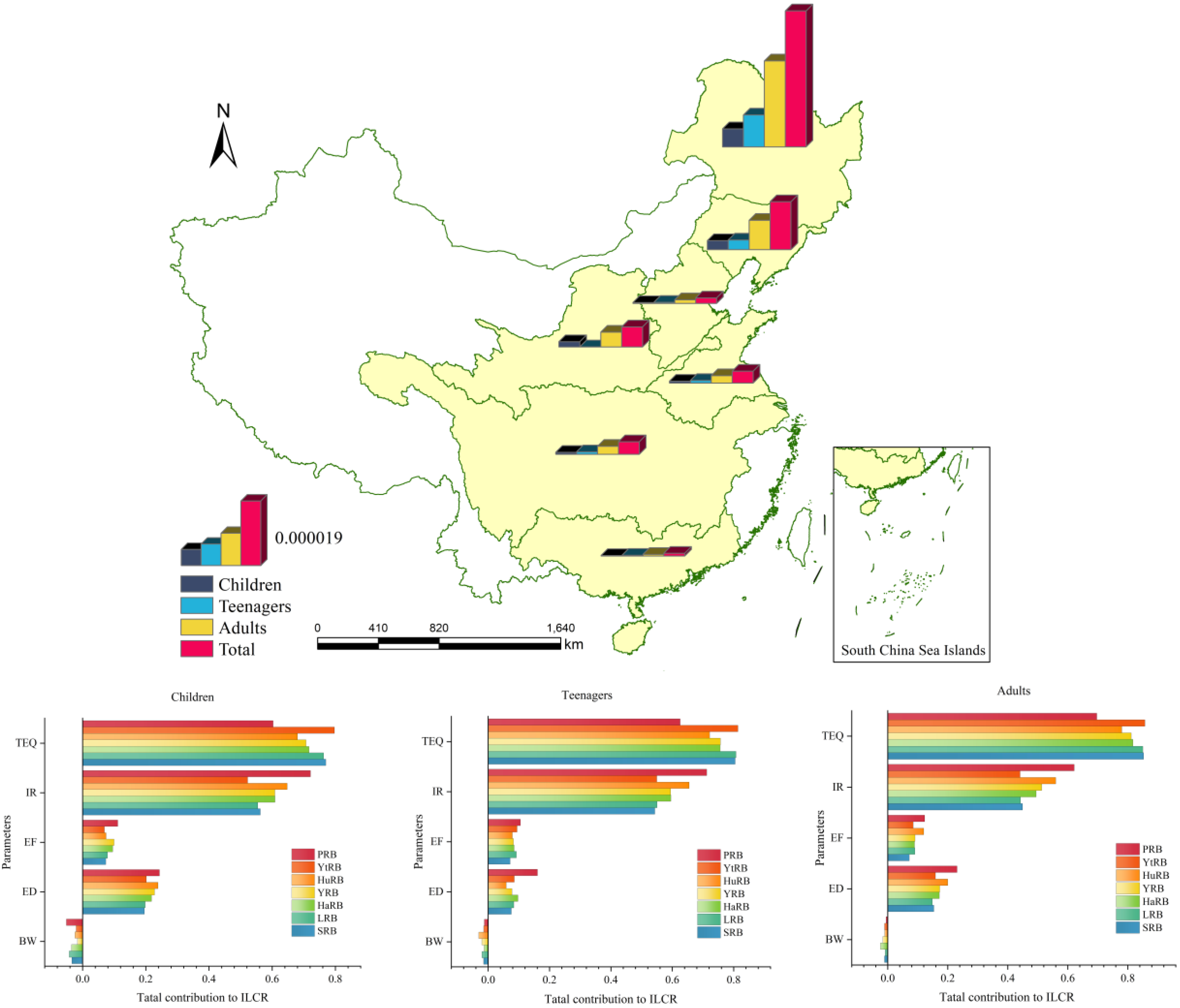
4.2.2. Assessment of Life-Long Carcinogenic Risks (ILCRs) in Different Basins
4.2.3. Sensitivity and Uncertainty
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xie, Z.; Lan, J.; Li, T.; Yuan, D.; Xing, B. Characteristics and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil seepage water in karst terrains, southwest China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.J.; Zhang, Z.F.; Liu, L.Y.; Yao, H.; Jia, H.L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.F. Influence on the levels of PAHs and methylated PAHs in surface soil from pollution control in China: Evidence in 2019 data compared with 2005 and 2012 data. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drwal, E.; Rak, A.; Gregoraszczuk, E.L. Review: Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)- Action on placental function and health risks in future life of newborns. Toxicology 2019, 411, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzyszczak, A.; Czech, B. Occurrence and toxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons derivatives in environmental matrices. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.C.; Jones, K.C. Bioremediation of soil contaminated with polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): A review. Environ. Pollut. 1993, 81, 229–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivella, M.A.; Ribalta, T.G.; De Febrer, A.R.; Mollet, J.M.; De Las Heras, F.X.C. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in riverine waters after Mediterranean forest fires. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 355, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Živančev, J.; Antić, I.; Buljovčić, M.; Đurišić-Mladenović, N. A case study on the occurrence of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in indoor dust of Serbian households: Distribution, source apportionment and health risk assessment. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, R.; Furumai, H.; Nakajima, F.; Yoshimura, C. Carcinogenic profile, toxicity and source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons accumulated from urban road dust in Tokyo, Japan. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 165, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yu, X.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y. Occurrence, characteristics and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in arable soils of Beijing, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 159, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zarfl, C.; Basu, N.B.; Cirpka, O.A. Turnover and legacy of sediment-associated PAH in a baseflow-dominated river. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Gao, H.; Ji, Z.; Jin, S.; Ge, L.; Zong, H.; Na, G. Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the water column of Kongsfjorden, Arctic. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 97, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Liu, X.H.; Lu, S.Y.; Zhang, T.T.; Jin, B.C.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Z.R.; Liu, Y.; Guo, X.C.; Zhou, J.L.; et al. A review on occurrence and risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in lakes of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2497–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostami, R.; Zarei, A.; Saranjam, B.; Ghaffari, H.R.; Hazrati, S.; Poureshg, Y.; Fazlzadeh, M. Exposure and risk assessment of PAHs in indoor air of waterpipe cafés in Ardebil, Iran. Build. Environ. 2019, 155, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munyeza, C.F.; Rohwer, E.R.; Forbes, P.B.C. A review of monitoring of airborne polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: An African perspective. Trends. Environ. Anal. 2019, 24, e00070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.F.; Ju, Y.R.; Su, Y.C.; Lim, Y.C.; Kao, C.M.; Chen, C.W.; Dong, C.D. Distribution, sources, and behavior of PAHs in estuarine water systems exemplified by Salt River, Taiwan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 154, 111029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areguamen, O.I.; Calvin, N.N.; Gimba, C.E.; Okunola, O.J.; Elebo, A. Seasonal assessment of the distribution, source apportionment, and risk of water-contaminated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 5415–5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Y.; Xing, F.; Qin, L. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAHs) geographical distribution in China and their source, risk assessment analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 251, 312–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Wu, S.; Zhou, S.; Tong, G.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, B. Characteristics, sources and health risk assessment of airborne particulate PAHs in Chinese cities: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Ma, Z.R.; Cai, Y.Y.; Li, H.R.; Ying, G.G. Agricultural plastic pollution in China: Generation of plastic debris and emission of phthalic acid esters from agricultural films. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 12459–12470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Meng, W.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, C.; Lv, J.; Wan, J. Occurrence, distribution, environmental risk assessment and source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in water and sediments of the Liaohe River Basin, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 93, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Gao, L.; Liang, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Zhu, A.; Wang, Z. Characteristics, sources, and risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in topsoil and surface water from the Liuxi River Basin, South China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 78, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yao, S.; Xue, B. North-south geographic heterogeneity and control strategies for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Chinese lake sediments illustrated by forward and backward source apportionments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 431, 128545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paatero, P.; Tapper, U. Analysis of different modes of factor analysis as least squares fit problems. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. 1993, 18, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sun, P.; Zhang, X.; Wei, X.Y.; Huang, Y.P.; Du, W.N.; Huang, Y. Source apportionment of PAHs in roadside agricultural soils of a megacity using positive matrix factorization receptor model and compound-specific carbon isotope analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, G. Epa Positive Matrix Factorization (pmf) 3.0 Fundamentals & User Guide, US. Environmental Protection Agency. 2008. Available online: https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyNET.exe/P100GDUM.TXT?ZyActionD=ZyDocument&Client=EPA&Index=2006+Thru+2010&Docs=&Query=&Time=&EndTime=&SearchMethod=1&TocRestrict=n&Toc=&TocEntry=&QField=&QFieldYear=&QFieldMonth=&QFieldDay=&IntQFieldOp=0&ExtQFieldOp=0&XmlQuery=&File=D%3A%5Czyfiles%5CIndex%20Data%5C06thru10%5CTxt%5C00000033%5CP100GDUM.txt&User=ANONYMOUS&Password=anonymous&SortMethod=h%7C-&MaximumDocuments=1&FuzzyDegree=0&ImageQuality=r75g8/r75g8/x150y150g16/i425&Display=hpfr&DefSeekPage=x&SearchBack=ZyActionL&Back=ZyActionS&BackDesc=Results%20page&MaximumPages=1&ZyEntry=1&SeekPage=x&ZyPURL (accessed on 21 March 2023).
- He, Y.; Yang, C.; He, W.; Xu, F. Nationwide health risk assessment of juvenile exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the water body of Chinese lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, I.C.; Lagoy, P.K. Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Regul. Toxicol. Pharm. 1992, 16, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA 1997; Exposure Factors Handbook. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, National Center for Environmental Assessment Office of Research and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- Fang, B.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, H.; Liu, J.J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H.W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, M.M. PM2.5-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Sources and health risk during non-heating and heating periods (Tangshan, China). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, K.M.; Burmaster, D.E.; Crouch, E.A. Monte Carlo techniques for quantitative uncertainty analysis in public health risk assessments. Risk Anal. 1992, 12, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Liu, G. Health risk assessment of potentially harmful elements in subsidence water bodies using a Monte Carlo approach: An example from the Huainan coal mining area, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 171, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Duan, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, X.; Qin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wei, F. Health benefit from decreasing exposure to heavy metals and metalloid after strict pollution control measures near a typical river basin area in China. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Zhao, X.; Gu, X.; Li, X.; Luan, M.; Yu, M. Presence, sources, and risk assessment of heavy metals in the upland soils of northern China using Monte Carlo simulation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 230, 113–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wang, Q.M.; He, W.; Xu, F.L. The occurrence, composition and partitioning of phthalate esters (PAEs) in the water-suspended particulate matter (SPM) system of Lake Chaohu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 661, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Wu, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Geng, X.; Zhao, M.; Sun, T.; Fan, Z. Health risk assessment of heavy metal(loid)s in park soils of the largest megacity in China by using Monte Carlo simulation coupled with positive matrix factorization model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125629–125909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Han, C.; Fang, H.; Weng, J.; Shu, X.; Ma, L. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface waters from the seven main river basins of China: Spatial distribution, source apportionment, and potential risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.; Lin, X.; Du, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, L. Risk assessment of organic contamination in shallow groundwater around a leaching landfill site in Kaifeng, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 2749–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, Y. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contamination in surface soil of China: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.N.; Dang, L.H.; Ding, R.M.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, P.G.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.F. Distribution, sources and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in wetland surface water in Yinchuan. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 3068–3077, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tong, B.F.; Liu, L.H.; Liu, X.R.; Gao, J.J.; Lu, J.; Zhou, H.D.; Zhu, D.W. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aqueous phase, suspended solids and sediments of Yuyuantan, Beijing. China Environ. Sci. 2007, 27, 450–455, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, M.; Takada, H.; Toyoda, K.; Yoshida, A.; Shibata, A.; Nomura, H.; Ohwada, K. Study on the fate of petroleum-derived polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and the effect of chemical dispersant using an enclosed ecosystem, mesocosm. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 47, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Wade, T.L.; Sweet, S.T. Atmospheric deposition of PAHs, PCBs, and organochlorine pesticides to Corpus Christi Bay, Texas. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 1707–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Yu, L.J.; Zou, Y.M.; Ji, L.; Li, Y.W. Sources and historical sedimentary re-cord: Temporal variability of n-alkane and PAHs from the Yellow River Estuary, China. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 114, 104475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Qu, X.; Lin, D.; Yang, K. Octanol-water partition coefficient (logKow) dependent movement and time lagging of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from emission sources to lake sediments: A case study of Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Qadeer, A.; Liu, M.; Zhu, J.M.; Huang, Y.P.; Du, W.N.; Wei, X.Y. Occurrence, source, and partition of PAHs, PCBs, and OCPs in the multiphase system of an urban lake, Shanghai. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 106, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.L.; Liu, L.Y.; Qi, H.; Zhang, Z.F.; Song, W.W.; Shen, J.M.; Li, Y.F. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water, sediment and soil of the Songhua River Basin, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 8399–8409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, K.; Zaccone, C.; Tao, Y.; Wang, J.; Shen, J.; Zhang, Y. Source apportionment of priority PAHs in 11 lake sediment cores from Songnen Plain, Northeast China. Water Res. 2020, 168, 115158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA 2002; National Recommended Water Quality Criteria. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- GB 3838-2002; Surface Water Environmental Quality Standards. China Environmental Protection Administration: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Baumard, P.; Budzinski, H.; Michon, Q.; Garrigues, P.; Burgeot, T.; Bellocq, J. Origin and bioavailability of PAHs in the Mediterranean Sea from mussel and sediment records. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1998, 47, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.B.; Sicre, M.A.; Boireau, A.; Tronczynski, J. Polyaromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) distributions in the Seine River and its estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1997, 34, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, M.; Tibbetts, I.R.; Müller, J.F. Monitoring PAHs in the Brisbane River and Moreton Bay, Australia, using semipermeable membrane devices and EROD activity in yellowfin bream, Acanthopagrus australis. Chemosphere 2004, 56, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.M.; Melymuk, L.; Bharat, G.K.; Přibylová, P.; Sáňka, O.; Klánová, J.; Nizzetto, L. Spatial gradients of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in air, atmospheric deposition, and surface water of the Ganges River basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrolecco, L.; Ademollo, N.; Capri, S.; Pagnotta, R.; Polesello, S. Occurrence of priority hazardous PAHs in water, suspended particulate matter, sediment and common eels (Anguilla anguilla) in the urban stretch of the River Tiber (Italy). Chemosphere 2010, 81, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Wu, J.L.; Zhan, S.E. Distribution, sources and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Amu River Basin of Uzbekistan. Lake Sci. 2022, 34, 855–867, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, F.; Syed, J.H.; Malik, R.N.; Katsoyiannis, A.; Mahmood, A.; Li, J.; Jones, K.C. Occurrence of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Soan River, Pakistan: Insights into distribution, composition, sources and ecological risk assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 109, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, A.S.; Simon, G.; Szabó, J.; Vass, I. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface water and bed sediments of the Hungarian upper section of the Danube River. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 4619–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eremina, N.; Paschke, A.; Mazlova, E.A.; Schüürmann, G. Distribution of polychlorinated biphenyls, phthalic acid esters, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organochlorine substances in the Moscow River, Russia. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 210, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Darisaw, S.; Ehie, O.; Wang, G. Simultaneous quantification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), and pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in Mississippi river water, in New Orleans, Louisiana, USA. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.T.; Proulx, S.; Brochu, C.; Moore, S. Composition of PCBs and PAHs in the Montreal urban community wastewater and in the surface water of the St. Lawrence River (Canada). Water Air Soil Pollut. 1999, 111, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, M.I.; Embaby, M.A. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in drinking water in Egypt. Desalination 2010, 251, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarria-Villa, R.; Ocampo-Duque, W.; Páez, M.; Schuhmacher, M. Presence of PAHs in water and sediments of the Colombian Cauca River during heavy rain episodes, and implications for risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 540, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, E.R.; Bzdusek, P.A. PAHs in sediments of the Black River and the Ashtabula River, Ohio: Source apportionment by factor analysis. Water Res. 2005, 39, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Yang, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; He, E.K.; Liu, M. Spatial modeling and source identification of PAHs in soils and roadside dusts from Hangzhou, a new first-tier megcity of China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 460, 132366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunker, M.B.; Macdonald, R.W.; Vingarzan, R.; Mitchell, R.H.; Goyette, D.; Sylvestre, S. PAHs in the Fraser River basin: A critical appraisal of PAH ratios as indicators of PAH source and composition. Org. Geochem. 2002, 33, 489–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.T.; Lee, B.K. Characteristics, toxicity, and source apportionment of polycylic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in road dust of Ulsan, Korea. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Xu, J.; Qu, X.; Lin, D.; Yang, K. Current and future trends of low and high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface water and sediments of China: Insights from their long-term relationships between concentrations and emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 3397–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Tang, Z.; Yin, H.; Meng, T. Concentrations, distribution and risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments from seven major river basins in China over the past 20 years. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NBSC (National Bureau of Statistics of China). China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Umeh, A.C.; Duan, L.; Naidu, R.; Esposito, M.; Semple, K.T. In vitro gastrointestinal mobilization and oral bioaccessibility of PAHs in contrasting soils and associated cancer risk: Focus on PAH nonextractable residues. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Z.; Liao, C.M. Health risk assessment on human exposed to environmental polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons pollution sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 366, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.J. Study on the Residue Law of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Multi-Medium Environment of Zhalong Wetland. Master’s Thesis, Harbin University of Engineering, Harbin, China, 2012. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.Z. Analytical Study on Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Sources in Jilin Reach of Songhua River. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2011. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.S.; Zhou, M.H. Preliminary study on pollution status of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the lower reaches of Songhua River. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 31, 132–135, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, N.W.; Zhao, C.Y.; Wang, X.X. Distribution of PAHs and ecological risk in water body of Daqing area. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 38, 78–83, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.L. Environmental Characteristics of Persistent Pollutants in Water Environment in Songhua River Basin (Part of Jilin Province); Jilin University: Changchun, China, 2013; (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Liu, C.; Guo, Q.; Yang, J.; Okoli, C.P.; Lang, Y.; Song, G. Characteristics, source, and potential ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Songhua River Basin, Northeast China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2017, 24, 17090–17102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ding, J.; You, H. Spatial distribution and temporal trends of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in water and sediment from Songhua River, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 36, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Meng, F.S.; Wang, Y.Y. Source analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Songhua River based on principal component analysis and multiple linear regression. Environ. Monit. China 2016, 4, 49–53, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.F.; Feng, Y.J.; Gao, P.; Zhang, Z.H.; Ren, N.Q. Environmental risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Songhua River. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2010, 42, 568–572, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Gong, X.H.; Wei, H.Y.; Gui, Z.F.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Z.H. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in rivers in the southwest foothills of Daxing’an Mountains. Environ. Chem. 2023, 43, 3054–3069, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.L.; Liu, L.Y.; Qi, H.; Bai, Y.; Shen, J.M.; Chen, Z.G.; Li, Y.F. Study on pollution characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in frozen water of Songhua River Basin. Environ. Sci. 2012, 33, 4220–4225, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Deng, Q.; Chen, S.; Hua, X.Y.; Liang, D.P.; Guo, Z.Y.; Dong, D.M. Study on the source of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the river water of Jilin section of Songhua River. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2015, 15, 22–230, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J. Study on Spatio-Temporal Distribution of PCBs, OCPs and PAHs in the Mainstream of Songhua River. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2008. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.Y. Study on Spatio-Temporal Distribution, Risk Assessment and Fate of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Yinma River Basin. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, China, 2017. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, D.M.; Sun, L.; Liu, Z.Y.; Luo, Q. Distribution, sources and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Xihe River, Shenyang. J. Ecol. 2010, 29, 2010–2015, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, X.X. Migration, Sources and Ecological Health Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Groundwater and Soil Profiles in Shenfu New Area. Master’s Thesis, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.L. Study on Pollution Characteristics of Typical Persistent Toxic Substances in Sipingtiaozi River. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2014. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.F.; Chang, S.; Fu, Q.; Fan, Y.T.; Wang, E.R.; Sun, X.B.; Wang, S.J. Pollution characteristics and risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in underground-surface drinking water sources in northeast Mongiolia. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 3005–3015, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Hu, J.; Liu, B.J.; Li, S.L.; Guan, J. Distribution and Source Analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Liaohe River Basin. Earth Environ. 2012, 40, 188–194, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.F.; Ren, X.J.; Li, M.R.; Li, J. Residual characteristics and health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Guanting Reservoir. J. Beijing Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2015, 51, 60–63, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, L.; Sun, T.; Li, H.; Luo, Q. Spatial distribution and seasonal variation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) contaminations in surface water from the Hun River, Northeast China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; He, M.; Yang, Z.; Lin, C.; Quan, X.; Wang, H. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water, suspended particulate matter and sediment from Daliao River watershed, China. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Sun, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Q.; Chen, S.; Wu, H. The Levels and Risks of Heavy Metals, Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, and Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Hun River in Northeastern China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 25, 2167–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Lu, Y.; Jia, Y.X. Identification of the source of organic pollution in Liaohe River. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2011, 36, 19–21, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Han, F.; Ma, X.P.; Liu, Y.Y. Pollution level and Source Analysis of PAHs in Liaohe River. J. Meteorol. Environ. 2009, 25, 68–71, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; He, M.; Yang, Z.; Lin, C.; Quan, X. Aliphatic and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Xihe River, an urban river in China’s Shenyang City: Distribution and risk assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.J.; Li, L.F.; Guo, Z.Y.; Wen, Y.M.; Hua, X.Y.; Dong, D.M.; Liang, D.P. Pollution characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the surface water of Tiaozi River, a tributary of Liaohe River. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2015, 15, 212–217, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, X.S.; Kong, F.Q.; Xu, M.X. Seasonal pollution characteristics and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organochlorine pesticides in baiyangdian lake. Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 964–978, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.H. Screening and Potential Risk Study of Organic Pollutants in Surface Water of Yongding River Basin. Master’s Thesis, South Central University for nationalities, Beijing, China, 2019. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xing, S.P.; Li, L.F.; Fu, G.X.; Feng, H.Y.; Hao, Z.P.; Zhang, S.; Chen, B.D. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of PAHs in surface water from a coking plant in Tangshan. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2021, 41, 3586–3597, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.G.; Liu, J.L.; Wang, X.M.; Xu, J. Pollution characteristics, risk assessment and source discrimination of dissolved polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface water of Zhangweinan Canal. Acta Sci. Cricumstantiae 2010, 30, 254–260, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Zhang, S.L.; Kong, F.Q.; Yuan, Y. Seasonal distribution, composition and source analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organochlorine pesticides in the main stream of Luanhe River. Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 4194–4211, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Wu, W.J.; Wang, J.J.; Qin, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, Q.S.; Xu, F.L. Distribution, sources and ecological risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the water-sediment system of Xiaobaiyangdian Lake. J. Lake Sci. 2009, 21, 637–646, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.W.; Li, B.H.; Zhang, D.S.; Wang, J.; Jiang, C. Distribution and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in river and groundwater in the North Canal Basin of Beijing. S. N. Water Transf. Water Conserv. Sci. Technol. (Chin. Engl.) 2021, 19, 179–190, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.F.; Zhao, Y.X.; Hou, H.; Wang, L.Q.; Li, F.S. Pollution characteristics and source discrimination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in suburban water of Xi’an. Agric. Res. Arid. Areas 2015, 33, 201–206, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Tao, S.; Pan, B.; Fan, W.; He, X.C.; Zuo, Q.; Wong, P.K. Contamination of rivers in Tianjin, China by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 134, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Lin, C.; Zhou, X.S.; Zhang, Y.; Han, C.G. Occurrence, composition and ecological restoration of organic pollutants in water environment of South Canal, China. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 82, 012033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.B.; Meng, X.Z.; Zhang, S.L.; Wang, Y.Z.; Xu, W.; Xu, M.X. Pollution characteristics and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface water sources of Haihe River Basin. Environ. Monit. Manag. Technol. 2020, 32, 61–64, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.L.; Li, X.Y.; Liu., Q.; Liu, S.H.; Sun, J.H. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface water of Xinxiang City. Environ. Chem. 2015, 34, 725–732, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Tan, L.; Lu, Y.B.; Teng, E.J.; Teng, M. Distribution and source analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface water of Chongqing section of the Yangtze River. Environ. Chem. 2015, 34, 18–22, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Du, S.L.; Ding, T.T.; Dong, H.J.; Liu, X.X.; Zhang, Y.H.; He, H.H.; He, L.S. Pollution and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water environment of Shaying River Basin. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 301–611, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Dang, J.H.; Wang, F. Study on spatial variation and ecological risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in river system and surface sediments of Fenhe River Basin. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2017, 12, 579–596, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Xu, J.; Guo, W.F.; Dai, S.G. Preliminary study on pollution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water environment of Lanzhou section of the Yellow River. China Environ. Monit. China 2007, 23, 48–51, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lang, Y.H.; Jia, Y.G.; Liu, Z.F.; Gao, Z.H.; Wang, X.P. Seasonal Distribution characteristics and Source Analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Yellow River Estuary. Period. Ocean. Univ. China 2008, 38, 640–646, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Pei, G.X.; Li, H.Q.; Gao, L.H.; Wang, Q. Distribution characteristics and Source Analysis of PAHs in Baotou Section of the Yellow River during freezing and thawing. Res. Environ. Sci. 2016, 29, 211–217, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.C.; Xia, X.H.; Wang, R.; He, M.C.; Xiang, X.Q. Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River. Environ. Sci. 2006, 27, 1738–1743, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Wu, X.J.; Zhao, J. Occurrence characteristics, sources and toxicity risk analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in typical rivers of Kuangqu mining area in northern Shaanxi. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 2040–2051, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.H.; Wang, G.L.; Chai, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Feng, J. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Henan reach of the Yellow River, Middle China. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 1614–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, Z.; Niu, J.; Wang, J. Characterization, ecological risk assessment and source diagnostics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water column of the Yellow River Delta, one of the most plenty biodiversity zones in the world. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jia, R.; Yang, S. Distribution and source of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in water dissolved phase, suspended particulate matter and sediment from Weihe river in Northwest China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 14148–14163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.J.R.; Sun, X.L.; Wang, X.L.; Zhou, X.J.; Cen, P.P.; Ding, R.M.; Tian, D.N. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Ningxia section of the Yellow River. Mod. Prev. Med. 2023, 50, 3833–3888, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, A.S.; Sun, Y.Q.; Ye, F.; Jiang, J.; Yang, S.Y.; Li, Q.; Qu, P.F. Study on distribution characteristics and potential ecological risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in trunk and tributaries of Weihe River in Shaanxi Province. Water Conserv. Hydropower Technol. (Chin. Engl.) 2023, 55, 133–137, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Han, B.P.; Jiang, H.; Liu, K. Distribution and source of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Weishan lake aquaculture lake. Sichuan Environ. 2010, 29, 21–24, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.L. Distribution Characteristics and Ecological Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Upper Reaches of Huaihe River. Master’s Thesis, Henan Normal University, Xinxiang, China, 2016. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.C.; Zhang, X.L.; Ye, Y. Preliminary study on Distribution characteristics and risk Assessment of PAHs in Water Environment of the Middle reaches of Huaihe River. J. AnhuiUniv. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2010, 34, 85–93, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Feng, J.; Hu, P.; Tan, L.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J. Spatial-temporal distributions, sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface water and suspended particular matter from the upper reach of Huaihe River, China. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Chen, J.W.; Pan, L.; Zhang, Y.W.; Da, C.N.; Zhang, L.J. Distribution characteristics, sources and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Huaihe River (Anhui section). J. Xinyu Univ. 2023, 28, 25–32, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q. Distribution of PAHs and Screening of Degrading Bacteria in the Middle and Lower Reaches of Huaihe River. Master’s Thesis, Anhui University, Hefei, China, 2012. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.P.; Ding, Y.; Li, Y.C. Study on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the main stream of heavy chemical industry accumulation area in the middle reaches of Huaihe River. Sci. Technol. Bull. 2009, 27, 83–88, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.J.; Feng, S.B.; Luo, X.S. Content characteristics and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in B River of Anhui Province. Geol. Anhui 2022, 32, 59–63, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Xu, F.; Xu, Z.A. Source analysis and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface water of Taihu Lake Basin. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 41, 198–204, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cai, W.L.; Luo, G.Y.; Xu, X.Y.; Du, X. Pollution characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface water of Chongqing section of Jialing River. Environ. Sci. 2012, 33, 2341–2346, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Qin, N.; He, W.; Wang, Y.; He, Q.S.; Kong, X.Z.; Ouyang, H.L.; Xu, F.L. Content and health risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water and aquatic products of Chaohu Lake. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2013, 33, 230–239, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.P.; Nan, B.G.; Hu, P.L.; Qiao, Y.Z. Distribution and risk analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the surface waters of the Daliao Estuary and its adjacent areas. Annu. Meet. Chin. Soc. Environ. Sci. 2015, 1, 50–56, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Mu, X.P.; Cui, W.; Bai, Y.B.; Li, G. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Caohai water. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2015, 34, 2176–2182, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.J.; Zheng, J.X.; Li, S.X.; Liang, Y.G.; Chi, S.Y.; Zhou, L.F.; Xiong, W. Distribution characteristics and health risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water and fish in the lower reaches of Hanjiang River. J. Hydroecology 2016, 37, 51–58, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.B.; Sun, Y.C.; Liang, Z.B.; Jiang, Z.L.; Liao, Y.; Xie, Z.L.; Zhang, M. Pollution and migration characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Qingmuguan underground river basin, Chongqing. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2016, 36, 812–819, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jia, T.Q.; Lei, R.G.; Wu, X.L.; Ni, T.T.; Sun, S.R.; Guo, W.; Liu, W.B. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in tributaries of lower yangtze river. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 2221–2228, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Hu, T.P.; Xing, X.L.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhan, C.L.; Qi, S.H. Distribution, sources and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments-water of Daye Lake. Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 170–179, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.L.; Zou, X.Q.; Zhao, Y.F.; Li, B.J. Source analysis and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Yangtze River Basin based on PMF model. Environ. Sci. 2016, 37, 3789–3797, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Bi, C.J.; Chen, Z.L.; Wang, X.P. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of PAHs in sediment and soil of Dishui Lake and its water exchange area. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 2664–2671, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Chang, Y.; Ye, X.Y.; Ji, Y.F.; Gao, S.Y.; Qu, M.X. Environmental evolution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in baihua lake, guizhou. Guizhou Sci. 2010, 28, 85–89, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gong, X.Y.; He, Y.Z.; Sun, Y.L. Distribution characteristics and source analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in groundwater in the upper area of Sihu Basin in Jianghan Plain. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2015, 35, 789–796, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.X. Pollution Status and Source Analysis of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Water and Sediment of Hongfeng Lake. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou Normal University, Guiyang, China, 2005. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Bai, H.Y.; Yang, P.H.; Han, B.; Yang, Y. Pollution level and source analysis of PAHs in coastal waters of Zhapu Bay, Hangzhou. Environ. Chem. 2015, 34, 2281–2286, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Feng, C.L.; Xia, X.H.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, L.J. Distribution and source analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Wuhan section of the Yangtze River. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2007, 27, 1900–1908, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.S.; Han, J.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, B.H.; Xu, Z.B.; Zuo, Y.; Yao, J.B.; Wang, Y.; Jin, T.S. Distribution and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of Anqing section of the Yangtze River and adjacent lakes. Environ. Chem. 2016, 35, 739–748, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.G. Pollution Characteristics, Source Analysis and Ecological Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Hangbu-Fengle River Environment. Master’s Thesis, Anhui University, Hefei, China, 2017. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Peng, B.; Huang, H.; Kuang, Y.; Qian, Z.; Zhu, W.; Qi, S. Distribution and potential sources of OCPs and PAHs in waters from the Danshui River Basin in Yichang, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 19, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.Y.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Wang, J.H.; Zhu, H.; Dou, J.F.; Narres, H.D.; Klumpp, E. Distribution and characterizing sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons of surface water from Jialing River. J. Cent. South Univ. 2012, 19, 850–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.L. Study on Time Variation and Output of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Datong Station of the Yangtze River. Master’s Thesis, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai, China, 2023. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W.P.; Zhu, X.P.; Shan, Q.; Ma, L.S. Content and health risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water and fish in tilapia culture area of Guangdong. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2014, 33, 2450–2456, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X.S.; Qi, S.H.; Oramah, I.T.; Zhang, Y. Pollution characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in underground river water of Tiankeng Group, Dashiwei, Guangxi. Environ. Sci. 2011, 32, 1081–1087, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Xie, Q.L.; Liu, X.Y.; Tang, J.J. Pollution characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Liuxi River and its ecological risk to freshwater organisms. J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2014, 33, 367–374, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.Q.; Zhang, R.J.; Yu, K.F.; Wang, Y.H.; Pan, C.G.; Zeng, W.B. Occurrence, Distribution and Source Analysis of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Surface Waters of the Lianzhou Bay and Sanniang Bay, Guangxi. Trop. Geogr. 2019, 39, 337–346, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.Y.; Chang, S.; Qing, F.; Wang, S.J.; Yang, G.; Zhao, X.; Geng, M.J. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Qingyuan section of Beijiang River during flood season. Res. Environ. Sci. 2018, 31, 61–69, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.R.; Yin, P.H.; Zhao, L.; Li, S.T.; Yang, Y.F. Distribution and composition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the subsurface and subsurface layers of Guangzhou section of Pearl River. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2010, 30, 868–873, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.; Huang, W.; Song, J. Distribution and loadings of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Xijiang River in Guangdong, South China. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Wang, Z.; Pei, J. Sources and contamination characteristics of PAHs in environmental media in a karst underground river system (southern China). Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 2315–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Study Area | Range (ng·L−1) | Mean (ng·L−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nile River, Egypt | 1112.7–4364.3 | 1877.5 | 61 |
| Seine River and Estuary, France | 4–36 | 20 | 51 |
| Brisbane River, Australia | 6.67–11.54 | 9.45 | 52 |
| Cauca River, Colombian | 52.1–12888.2 | 2344.5 | 62 |
| Ganges River, India | 0.05–65.9 | 32.5 | 53 |
| Soan River, Pakistan | 61–207 | 134.4 | 56 |
| Danube River, Hungary | 25–1208 | 122.6 | 57 |
| Amu River Basin, Uzbekistan | 3.19–779 | 98.4 | 55 |
| Moscow River, Russia | 50.6–120.1 | — | 58 |
| Mississippi River, USA | 62.9–144.7 | 114.9 | 59 |
| Tiber River, Italy | 23.9–72 | 43.4 | 54 |
| St. Lawrence River, Canada | — | 326 | 60 |
| Seven River Basin, China | 300–7552 | 1868 | — |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Yao, X.; Zang, S.; Wan, L.; Sun, L. A National-Scale Study of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Surface Water: Levels, Sources, and Carcinogenic Risk. Water 2024, 16, 3027. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213027
Liu S, Yao X, Zang S, Wan L, Sun L. A National-Scale Study of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Surface Water: Levels, Sources, and Carcinogenic Risk. Water. 2024; 16(21):3027. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213027
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shuang, Xin Yao, Shuying Zang, Luhe Wan, and Li Sun. 2024. "A National-Scale Study of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Surface Water: Levels, Sources, and Carcinogenic Risk" Water 16, no. 21: 3027. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213027
APA StyleLiu, S., Yao, X., Zang, S., Wan, L., & Sun, L. (2024). A National-Scale Study of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Surface Water: Levels, Sources, and Carcinogenic Risk. Water, 16(21), 3027. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213027






