Abstract
Climate changes linked to extreme events pose a threat to freshwater biodiversity, impacting organs, behaviour, and reproduction. Moreover, these changes can be amplified by pollution. Copper sulphate (CuSO4) is used in agriculture and aquaculture, so the copper can reach streams, rivers, and lakes impacting fish. This study evaluated the combined effects of temperature and copper on gills and liver histology biomarkers and in the behaviour of Mozambique tilapia over 28 days. Tilapias were exposed to different water temperatures (25 °C and 32 °C) and CuSO4 concentrations (1.1 and 3.6 mg/L). Fish from the control group were exposed to water without copper sulphate and at 25 °C (within their optimum range). Histopathological analysis revealed significant tissue lesions, namely aneurysms and bending of gill lamellae, and hyalinization and vacuolization in the liver at the higher temperature and CuSO4 level. Moreover, behavioural observations revealed increased stress changes under the same conditions. These findings highlight the effects of fast climate change, and rising temperatures on copper toxicity, underlining the necessity for strict monitoring and regulation of copper use due to future climate change scenarios to protect aquatic ecosystems, ichthyofauna population and trophic web dynamics. This data also alerts for similar problems with other toxic metals or chemicals, at short term, in streams and rivers, under rapid climate changes and more frequent extreme events.
1. Introduction
Aquatic ecosystems are delicate but essential habitats for a wide range of organisms, including fish populations [1]. However, at present, these environments face numerous threats, including exotic species, over-fishing, anthropogenic pollution and climate change adverse effects [2]. The increase in air temperature caused Global Warming (GW) disturbing the climate that affects freshwater ecosystems, including ichthyofauna. In recent years, there has been a growing concern about the interaction between chemical contamination and environmental factors [1], such as changes in the water temperature, alterations in hydrologic variables (i.e., rainfall patterns), pH and dissolved oxygen due to the present climate change impacts [3]. Thus, understanding these interactions is crucial to predict and mitigate the ecological consequences of the chemical contamination of aquatic ecosystems under climate change predictions. It was been show that GW will continue to rise, impacting the dynamics of fish assemblages (directly and indirectly), river flow, pH, water temperature and dissolved oxygen decline [4].
Copper sulphate (CuSO4) is recurrently used in agriculture practices due to its pesticide properties, namely fungicide activity [5], and in aquaculture to control algae, parasites, and pathogens [6]. Its low cost, high availability, and broad-spectrum activity make CuSO4 a popular choice. Therefore, it is considered a pollutant of concern since there is a global extensive use, and when applied excessively or inappropriately, CuSO4 can contaminate rivers, and thereafter impact aquatic organisms, like fish, and their ecosystems [7,8]. One of the main routes for CuSO4 to enter aquatic compartments is through runoff from agricultural fields and aquaculture facilities [9,10]. CuSO4 residues from treated crops or aquaculture ponds can be washed into nearby water bodies, where they can accumulate and persist [6]. Additionally, its direct water application to control parasites or algae can result in focal contamination.
After entering rivers, CuSO4 can undergo several chemical transformations and environmental interactions [11]. Factors such as pH, temperature and the presence of organic matter can influence the bioavailability of copper ions in aquatic environments [12]. In particular, temperature plays a crucial role in regulating the physicochemical behaviour of Cu and its toxicity to aquatic organisms [6,13]. At higher temperatures, the solubility of CuSO4 increases, leading to high concentrations of copper ions dissolved in water [12]. This increased solubility can exacerbate the toxic effects of CuSO4 on organisms. Furthermore, higher temperatures can increase the bioavailability of copper ions, making them more accessible for absorption by organisms through physiological mechanisms, such as gills uptake or fish feeding [14].
In addition to the direct effects that temperature can have on CuSO4 bioavailability, this variable can also influence the physiological responses of ichthyofauna. For example, several fish physiology mechanisms, such as the respiration rate, are temperature dependent [15]. High temperatures can induce physiological stress in fish exposed to CuSO4, leading to adverse health effects, and reduced physical fitness [6]. Additionally, temperature-induced changes in water quality parameters, such as dissolved oxygen levels and pH, can further exacerbate the effects of CuSO4 on fish, consequently leading to population declines and ecosystem disruption [16,17]. Furthermore, the effect of the metallic compound of CuSO4 on fish is well known, and sublethal exposure to realistic environmental concentrations of Cu has produced neurotoxicity, oxidative stress and altered metabolism in several fish species [7,8,18].
Tilapias are a group of freshwater fish species commonly found in tropical habitats. This cichlid is used as a biological model in aquatic toxicology [19]. They are economically and ecologically important, playing essential roles in food chains. Furthermore, tilapia has emerged as a food source for human populations—Asia dominated the contribution of tilapia production at 68.8% followed by Africa at 21.8%, and tilapia ranked fourth biggest species group in 2018 with 6 million tonnes of production, accounting for more than 40% increase from 1990 [20].
Additionally, tilapia populations are affected by aquatic contamination and are therefore widely used as biological indicators of the quality of aquatic ecosystems [21]. Several deleterious effects of CuSO4 on the test organism Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) have been documented in the literature [13,22,23]. High concentrations of copper ions dissolved in water can directly affect the health and behaviour of O. niloticus, leading to a reduction in feeding activity, changes in behaviour and increased mortality [24]. Furthermore, chronic exposure to sublethal concentrations of CuSO4 revealed deleterious effects on O. niloticus, such as impaired reproduction and compromised immune function. Mutlu, et al. [25] showed that prolonged exposure led to decreased levels of several blood biochemical parameters in O. niloticus, while Ezeonyejiaku, et al. [26] observed behavioural changes and increased mortality in both Nile tilapia and catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Nouh and Selim [9] reported histopathological changes in the gills, liver, and kidneys of O. niloticus due to CuSO4 exposure. Regarding the effects of temperature on O. niloticus, the results of the literature vary. Pandit and Nakamura [27] found that high temperatures (35–37 °C) significantly reduced survival, growth, and feed conversion rates. In contrast, El-Sherif and El-Feky [15] observed significant reductions in growth performance and survival rate at lower temperatures (15–20 °C), with 25–30 °C being the most suitable range for O. niloticus fingerlings. However, to the best of our knowledge, no studies have been found to evaluate the effects of CuSO4 in conjunction with increased temperature in O. niloticus.
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), 4.5 and 8.5 Representative Concentration Pathway (RCP) global climate scenarios represent different greenhouse gas emission trajectories and their respective impacts on global warming and impacts on climate fast changes [28]. RCP 4.5 global climate scenarios assume a stabilization of emissions from the middle of the 21st century, resulting in a moderate increase in the global average temperature between 1.7 °C and 3.2 °C by 2100 compared to pre-industrial levels. In contrast, the RCP 8.5 global climate scenario projects a continued increase in emissions, leading to severe warming, with global average temperature increases of between 3.2 °C and 5.4 °C by the end of the century [29]. Both scenarios imply significant changes in climate patterns, including increased air and water temperatures, greater frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, and adverse impacts on aquatic ecosystems [30]. Lakes respond very quickly to precipitation changes, and a range of atmospheric inputs, making them sentinels of contemporary climate change signals [28]. Water scarcity and rising freshwater demand have socioeconomic, hydro-political, and geopolitical ramifications. For a pessimistic scenario in 2100 (RCP8.5) a significant reduction in the reservoir water level in Brazil by around 35% compared to current conditions and the surface water temperature is expected to increase (0.6 °C) [29] and in Tanganika lake in Africa the water surface temperatures have increased by about 1.3 °C [31]. An increase in river water temperature worldwide that can rise from 3.1 to 7.8 °C is expected in Indian rivers for 2071–2100 using NASA Earth Exchange Global Daily Downscaled Projections of air temperature with RCP8.5 scenario.
The consequences of these climate changes for freshwater aquatic species are of special concern. Under the RCP4.5 scenario, it is predicted that the moderate warming of the surface waters and the occurrence of extreme weather events will cause thermal stress and negatively impact the growth rate and survival of these species [32]. In an 8.5 scenario, water temperatures may frequently exceed the tolerance limits of O. mossambicus, resulting in chronic heat stress, decreased reproduction, and increased mortality [33]. Furthermore, extreme events such as alterations in rainfall patterns (floods and droughts) can drastically alter freshwater habitats, further compromising the viability of tilapia populations and other aquatic species [34]. Moreover, a global change scenario, which will cause water acidification and warming, may enhance toxic effects caused by environmental realistic concentrations of chemical stressors on aquatic biota [35,36].
The purpose of this work was to assess the effects of CuSO4 in the freshwater fish species O. mossambicus during long-term exposure (28 days), and whether a warming scenario may enhance the potential effects of this contaminant. Since the existent research related to this subject has focused mostly on heavy metals (mercury, lead, arsenic, and cadmium), the hereby study focused on CuSO4, given the wide application of this compound as a large-scale pesticide in agriculture and aquaculture activities carried out in many tropical and subtropical regions. The main goal was to evaluate the interference of rising temperatures in copper toxicity to fish—an expected scenario in the upcoming years due to fast climate change.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Organisms
In this work, Mozambique tilapia was selected as a model organism due to its wide use in aquaculture, ease of maintenance in laboratory conditions, resilience and adaptability to various environmental conditions and also for its easy obtainability.
O. mossambicus used in the assay were healthy adult male fish (n = 60; total length 17.8 ± 1.2 cm; and total weight 40.5 ± 10.1 g) provided by the Instituto Universitário de Ciências Psicológicas, Sociais e da Vida (ISPA), in Lisbon. Animals were randomly distributed in tanks of 500 L of freshwater with saturated water oxygenation using air pumps (approximately 8.26 mg/L), and controlled temperature (25 ± 0.5 °C) and photoperiod (14 h of light: 10 h of darkness), for 2 weeks for acclimatization before the assay. During this period, individuals were fed daily with a specific diet for tilapia produced at the University of Trás-os-Montes and Alto Douro (UTAD), containing about 28% crude protein, 8% fat and micronutrients in concentrations appropriate to this species.
2.2. Exposure Conditions
After acclimatization, fish were randomly distributed in six aquaria (n = 10), each with approximately 175 L of freshwater. Supplemental aeration was provided to maintain the dissolved oxygen near saturation. No mechanical or biological filtration was used to prevent losses of CuSO4 and one-third water was changed every three days after feeding the animals.
The aquarium systems were grouped for two different temperatures, at 25 °C (3 aquaria) and 32 °C (3 aquaria). The water temperature was kept stable between 25 ± 0.5 °C and 32 ± 0.5 °C through the presence of a 200 W precision heater inside each aquarium (Eheim Jager Thermocontrol 200, Ehiem, Deizisau, Germany) using an internal thermometer to calibrate the heater. The control temperature (25 °C) was chosen considering the optimum range for O. mossambicus (22–30 °C). As a thermal stress factor, the temperature of 32 °C was selected considering the higher limit of optimum ranges, adding 2 °C to mimic the estimated consequences of climate change in water temperature considering the worst scenario RCP8.5 [37].
For each temperature, there was a negative control aquarium (non-exposed individuals) and two aquaria with two different measured concentrations of CuSO4 (1.1 and 3.6 mg/L). The concentrations of CuSO4 were chosen based on studies already carried out with the compound under study [38,39,40]. At the beginning of the assay, CuSO4 was weighed and added to each aquarium at the corresponding concentration. Subsequently, when renewing water, the corresponding amount of CuSO4 was added to maintain the same concentration of copper.
At 14 and 28 days of exposure, five fish from each aquarium were randomly removed, placed in cold water with ice, and then sacrificed with a percussive blow to the head. All experimental procedures were conducted by experienced and certified animal welfare researchers following the ethical guidelines of Portuguese Decree-Law (113/2013) and the European Directive (2010/63/EU) for the use of laboratory animals.
The following water quality parameters were measured at the end of the experiment: pH 7.1–7.6, alkalinity 85.4 as HCO3, conductivity 185 µS/cm and ammonia 0.12 mg/L. The real concentration of copper in water aquariums was measured before every water change by flame atomic emission spectrometry and the results for the end of exposure are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Copper concentrations measured in water during the assay.
2.3. Histological Slide Preparation
Per individual, the second and third-gill arches (less subject to pressures and alterations due to sampling) and liver parenchyma samples were randomly collected and placed in buffered 10% formaldehyde (Panreac, Darmstadt, Germany) for 24 h for chemical fixation. The samples were then dehydrated in graded ethanol series, diaphanized, and embedded in paraffin wax. Sagittal sections (3 μm thick) were obtained using a Leica RM2245 manual rotary microtome (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany) and mounted on glass slides. Posteriorly, each section was deparaffinized in xylene, hydrated in decreased ethanol grades and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E).
2.4. Gills’ Lesions Scoring
The histopathological changes in lamellae and filaments of two branchial arches randomly selected were blindly assessed and photographed using a NIKON E-600 microscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) and a NIS—Elements D program. Posteriorly, the lesions observed were assessed using a simplified classification system, based on several methodologies: Bernet, et al. [41], Velmurugan, et al. [42], Monteiro, et al. [43] and Flores-Lopes and Thomaz [44]. Thus, the histological changes were classified from 1 to 4 according to their severity: when there were no injuries, grade 1 was assigned and for more severe injuries, grade 4 (maximum value) was defined. The lesions were also assessed according to their extension along the branchial arch from 0 to 100%.
The number of filaments with lesions and the total number of filaments (with and without lesions) were counted to obtain the value corresponding to the average degree (gm) for each lesion and animal, calculated using the following formula:
2.5. Liver Histopathology Scoring
For the present study, the grading scale was based on the grading of Carrola [45], with some modifications, allowing for a semi-qualitative assessment of the changes and lesions in tilapias liver.
The grading was done on 10 random fields of view in each glass slide (one per fish). For each field, alterations/lesions were scored using 6 levels grading system (0 to 5), considering their extension and frequency. In this grading scale: grade 0 represents the absence of alterations/lesions; grade 1—very slight alterations/lesions; grade 2—slight alterations/lesions; grade 3—moderate alterations/lesions; grade 4—intense alterations/lesions; and grade 5—very intense alterations/lesions.
Main liver lesions were posteriorly photographed using an Olympus IX51 microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) with an attached digital camera, Color View III (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan).
2.6. Condition Factor and Hepatosomatic Index
These morphometric parameters are used as indicators of fish health status. The condition factor (CF) allows us to check if the fish have gained or lost weight, which can indicate effects on fish fitness and health [46], since it reflects exposure to factors such as nutritional status, pathogen effects and toxic chemical exposure, and it is considered an integrated general well-being index of fish reflecting many levels of organization [47]. The CF of the fish was calculated based on Froese’s [48] formula:
where CF corresponds to the condition factor, BW to the body weight in grams, and TL to the total length in centimetres.
An increase or decrease in the hepatosomatic index (HSI) allows us to infer about the relative liver weight (ratio of the organ to body weight) that the organ was under target chemical stress, particularly due to exposure to a single or mixture of contaminants (increased liver detoxification metabolism) or also a reduction in feed ingestion linked to nutritional and energy status (caused by behaviour changes) [49]. The HSI is one of the most used indexes due to the central role of the liver in detoxification. The HSI was calculated using the formula employed by Pinto [50]:
where HSI is the hepatosomatic index, LW corresponds to the liver weight, and BW to the body weight of the fish, both in grams.
2.7. Behavioural Analysis
Visual observations were performed by the same researcher for 20 min (with an acclimatization period of 5 min), in the morning and the afternoon in the beginning (P0: 0 days), middle (P1: 14 days) and end of the experiment (P2: 28 days). The video recording at the beginning of the experiment (P0) was used as a baseline for normal behaviour. The behaviours registered at the subsequent periods (P1 and P2) were compared against this standard to identify deviations caused by exposure to copper and water temperature.
Different types of behaviour were documented: normal, stationary in the bottom (SB) when the fish remained at the bottom motionless, feeding inhibition (FI) observing the lack of feeding habits of the fish, hoovering in the water column (HC), and gasping at the surface (GS) when fish stood at the top of the water column pursuing oxygen. For that, the number of times that the fish presented each behaviour was registered in an ethogram for posterior conversion into quantitative data.
Also, a frontal video recording of each aquarium was made at P0, P1 and P2, with the placement of a recording camera in front of each aquarium using a tripod. These 15-min video recordings were posteriorly analysed by placing a horizontal line in the middle of the video and counting how many times the fish went from the bottom to the top of the aquarium. The times for observation were chosen according to Barton and Iwama [51].
2.8. Statistical Analysis
The gill and liver histology data were analysed with the GraphPad Prism® software (version 8.00, GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). To detect and exclude outliers, a Grubbs test for outliers (GraphPad, USA) was used. The data are presented as means ± S.D. Data analysis was performed for homogeneity of variance by using the Bartlett’s test. The three-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to determine the significant effect of CuSO4, temperature and exposure time. Additionally, the Tukey test with 95% confidence limit was applied to compare the means values whenever the data was significant.
3. Results
3.1. Gill Histopathology
The histological assessment of control O. mossambicus gills revealed a normal structure arrangement of the gill’s filaments and lamellae (Figure 1A). The filaments presented normal histology with a central axis surrounded by connective tissue and venous sinus. The filaments were covered by a stratified squamous epithelium, intersected by lamellae containing erythrocytes and pillar cells. The gills of Mozambique tilapia exposed to different Cu concentrations and temperatures for 14 and 28 days exhibit several histopathological changes, namely aneurysms, vasodilatation, lamellar epithelium lifting, filament epithelium proliferation, lamellar fusion, oedema and bending of gill lamellae (Figure 1B–F).
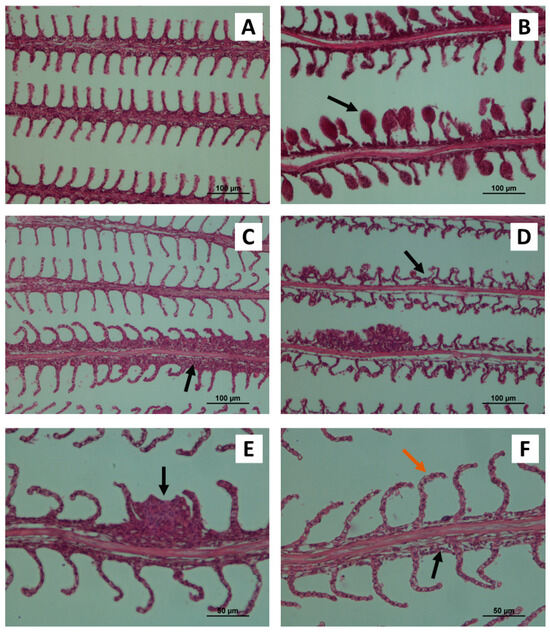
Figure 1.
Histological images of Mozambique tilapia (O. mossambicus) gills. (A)—gills from control tilapia showing a normal structure of filament epithelium and lamellae (magnified 200×). (B–F)—gills from exposed fish to CuSO4 showing different histopathological changes. (B)—aneurysms in the terminal part of the lamellae (black arrow, magnified 200×); (C)—filament epithelium proliferation (black arrow, magnified 200×); (D)—detachment of the lamellar epithelium (black arrow, magnified 200×); (E)—lamellar fusion (black arrow, magnified 400×); (F)—filamentary oedema (black arrow, magnified 400×) and bending of gill lamellae (orange arrow, magnified 400×). Coloration H&E.
In general, the lesions observed at 14 days of exposure were similar to those found at 28 days, however, the severity rates and extension were higher at the end of the assay, showing elevated gm. This high severity at 28 days was mainly observed in organisms present in water temperature at 32 °C and exposed to 3.6 mg/L of CuSO4 (Table 2).

Table 2.
Effects of different concentrations of Cu interaction with water temperature, on gills histology of O. mossambicus at 14 and 28 days. Statistical analysis was performed using three-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s pairwise comparison tests. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatments (p-value ≤ 0.05).
Histological analysis demonstrated that the gills of animals exposed to a copper concentration of 1.1 mg/L and 25 °C at 14 days presented lamellar epithelium lifting associated with a high level of filament epithelium proliferation. However, these lesions after the 28 days of exposure were more evident in gills exposed to a copper concentration of 3.6 mg/L and 32 °C. At 28 days of exposure, it was possible to detect that the gills where filament epithelium proliferation was observed also showed lamellar fusion, which did not happen at 14 days. Additionally, the presence of aneurysms in gills was observed at 14 and 28 days, and the severity of the lesions was statistically higher at 3.6 mg/L and temperature of 25 °C. Similarly, bending of gill lamellae and oedema in the tilapia gills were also observed at both time points. However, the oedema appeared in a few gills analysed and with a low gm index. In opposition, the bending of gill lamellae at 14 days was statistically more severe at a concentration of 1.1 mg/L and 25 °C, however at 28 days the highest gm index was recorded at the lowest Cu concentration and high temperature of water. Vascular disorders, such as vasodilation were also evident in the deep region of the filament, being more apparent after 28 days of exposure to a concentration of 3.6 mg/L and 32 °C.
In general, it can be said that aneurysms and bending of gill lamellae were the most recurrent lesions found in the tilapia gills analysed and with greater severity, that is higher gm index.
3.2. Hepatosomatic Index and Condition Factor
For hepatosomatic index (HSI), when compared to the control values, temperature alone seemed to have affected HSI values for the first 14 days, when analysing fish that were not exposed to Cu. HSI decreased in the first 14 days, but at 28 days, the highest temperature showed an increase in this index (Figure 2A).
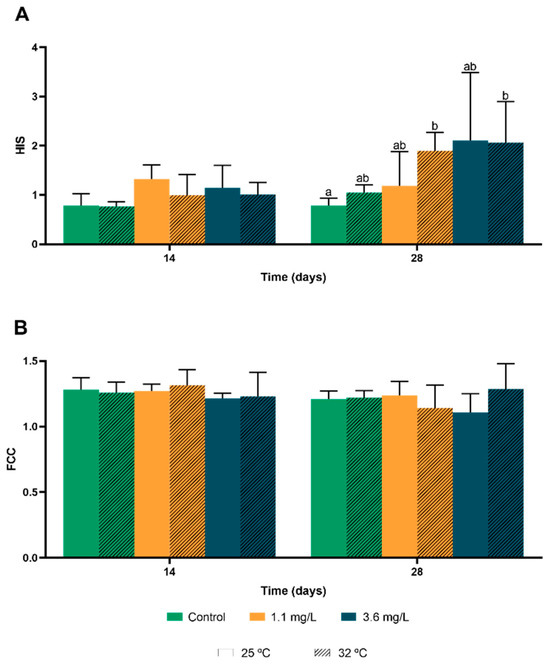
Figure 2.
Effects of different concentrations of Cu in interaction with water temperature, on the hepatosomatic index (HSI, A) and condition factor (CF, B) of O. mossambicus at 14 and 28 days. Different letters indicate statistically significant differences. Statistical analysis was performed using three-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s pairwise comparison tests. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatments at 28 days of HIS (p-value ≤ 0.05).
Regarding fish exposed to the contaminant, it was registered a higher increase of HSI at the lowest temperature at 14 days. However, at 28 days there was a significant increase of HSI in fish exposed at the highest Cu concentration, on both temperatures.
For the condition factor (FCC), exposed fish did not show a specific pattern accompanying the duration of the study, nor did the increase in Cu concentration or the increased temperature (Figure 2B).
3.3. Liver Histopathology
Several liver lesions were observed in fish exposed to Cu, and the most frequently detected are macrophage aggregates (Figure 3A,B), vacuolization, hyalinization (Figure 3E,F), granulomas, and focal necrosis (Figure 3C).
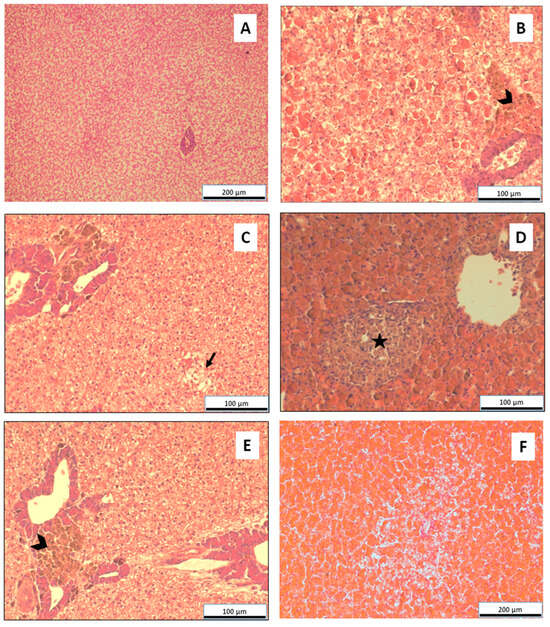
Figure 3.
Histological images of Mozambique tilapia (O. mossambicus) livers. (A)—liver parenchyma of an individual from the control group (magnified 100×); (B)—macrophage aggregate (open arrow) in the hepatic parenchyma (magnified 200×) (C)—Focal necrosis (arrow) of the hepatic parenchyma (magnified 200×); (D)—nonspecific granuloma (star) in the hepatic parenchyma (magnified 200×); (E)—macrophage aggregate (open arrow), associated with the hepatopancreas in the hepatic parenchyma (magnified 200×); (F)—parenchyma of a liver showing very intense hyalinization (magnified 100×).
After 14 days of exposure to only different temperatures with no Cu exposure, only hyalinization was completely absent, but the other lesions appeared very slightly in this group of tilapia. During this time frame, lesions were mostly assessed as very slight. At the highest temperature and highest contaminant concentration, there was moderate hyalinization, with a significant increase compared to the fish group not exposed to Cu.
On fish studied at 28 days, most of the lesions found were classified as very slight. There were slight differences in the severity level between the sampling at 14 days and 28, from very slight to slight. Hyalinization, though, showed the highest levels of severity, especially at the highest temperature, classified as intense at the lower concentration of Cu, and very intense at the higher concentration. When compared to the values registered on the 14th day, there was a significant increase in the severity of this lesion.
Vacuolization showed a significant increase at 14 days, at 1.1 mg/L of CuSO4 and 25 °C, when compared to fish not exposed to Cu at the same temperature. It is also significantly higher than vacuolization found in fish exposed to the highest concentration and temperature for 28 days. Although these differences are significant, regarding severity this translates to a difference between slight and very slight.
The systematic appearance of some degree of lesions (macrophage aggregates, vacuolization, and necrosis) may indicate that the fish were subjected to some level of stress, but hyalinization showed a strong correlation with time, temperature, and contaminant concentration (Table 3).

Table 3.
Effects of different concentrations of Cu in interaction with water temperature, on liver histology of O. mossambicus at 14 and 28 days. Statistical analysis was performed using three-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s pairwise comparison tests. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatments (p-value ≤ 0.05).
3.4. Behavioural Observations
The behaviour results for O. mossambicus are presented in Table 4. During the 28 days of the assay, the behaviour of tilapia was normal in a water temperature of 25 °C and without the addition of Cu. At the control concentration of Cu at 32 °C, the normal behaviour of O. mossambicus was observed until the middle of the assay where feeding inhibition started to be observed. For the concentration of 1.1 mg/L, normal behaviour of the organisms was observed at the beginning of the test for the two temperatures tested. In the following two periods of observation, O. mossambicus showed feeding inhibition at 14 days for both temperatures and at the end of the test at a temperature of 25 °C it was observed that 60% of tilapia were stationary at the bottom of the aquarium (p-value = 0.010) and at the temperature of 32 °C, 60% of the fish were gasping at the surface (p-value = 0.046). Finally, for the highest concentration of Cu (3.6 mg/L), different behaviours were observed depending on the water temperature. The O. mossambicus present in water with a temperature of 25 °C showed hoovering behaviour in the water column at the beginning of the test, feeding inhibition in P1 and stationary at the bottom of the aquarium in P2. At a temperature of 32 °C, O. mossambicus showed normal behaviour at P0, gasping at the surface at P1 and P2.

Table 4.
Main behaviours observed in tilapia exposed to different treatments, at different periods of observation. P0 = Beginning of exposure; P1 = 14 days of exposure; P2 = 28 days of exposure; Normal = No alterations in behaviour; FI = Feeding inhibition; HC = Hoovering in the water column; GS = Gasping at the surface; SB = Stationary in the bottom.
4. Discussion
The increased use of CuSO4 on a large scale for both agriculture and aquaculture purposes [5] and the presence of this compound in aquatic ecosystems [52,53] make the toxicological assessment of aquatic organisms essential. Some studies have already evaluated the effects of copper on different aquatic organisms, demonstrating its toxic potential on several fish species and endpoints [22,23,54]. However, the toxic effects on fish depend not only on the concentration of the compound in the water and time of exposure but also on water chemical content, since there may be an interaction between compounds and environmental factors. For example, it has been demonstrated that in the presence of high temperatures, above the optimum for the species under study, the tolerance limits of organisms to toxic compounds are lower [55]. This occurs because the increase in water temperature accelerates the fish’s metabolism and modifies the bioavailability and up-take of pollutants, increasing their toxicity [14]. Carvalho and Fernandes [56] found a strong interaction between temperature and copper in the water on blood parameters of the neotropical fish Prochilodus scrofa, which also led to osmoregulatory and respiratory disturbances with increased energy consumption to restore homeostasis. Therefore, in this work, the interaction of Cu with water temperature on the gill and liver histology and behaviour of Mozambique tilapia were evaluated, under a fast climate change reality. To the best of our knowledge, the hereby work is the first attempt to investigate the influence of temperature on Cu toxicity at different endpoints of O. mossambicus, namely gill and liver histology and behaviour changes.
Histopathological alterations in fish organs and behavioural responses of fish have been commonly applied as useful biomarkers to evaluate the effects of environmental factors present in aquatic ecosystems [33,40], as they reflect the organism’s health and the ecological status of ecosystems [57]. Likewise, gills present sensitive epithelium and are directly exposed to water pollutants so gill lesions are useful biomarkers. The gill’s histological changes reflect direct water quality and can additionally affect fish oxygen supply which can cause several adverse effects, including fish mortality [41]. The present study revealed that O. mossambicus control gills, even when exposed to a temperature of 32 °C, presented a normal structural organization of filaments and lamellae. However, in tilapia gills exposed to Cu and different temperatures, the aneurysms and bending of gill lamellae were the most prominent histological lesions observed. In general, these histopathological alterations were observed at 14 and 28 days. The results show that the appearance of lamellar aneurysms may be related to short-term exposure since this lesion appears at 14 days of exposure and the gm index remained constant over time. Also, these differences were observed at the same Cu concentration (3.6 mg/L) and water temperature (25 °C). Similarly, Monteiro et al. [43] found that aneurysms were only found in fish treated with copper and that the severity was almost constant over time, with no differences observed at different exposure times. In comparison with aneurysms, the gm index of bending of gill lamellae was higher after 28 days of exposure, with the temperature of 32 °C inducing more significant effects at both sampling times.
In addition, other gill lesions were also observed, namely vasodilatation, lifting of the lamellar epithelium, filament epithelium proliferation, lamellar fusion, and oedema, despite their presence on the gills being less constant and with lower gm index. Vascular disorders of the gills, such as vasodilation, have also been one of the lesions reported in studies evaluating the effect of copper on different fish [40,58]. This lesion can be associated with changes in the normal structure of pillar cells and, consequently, the loss of support function, which can lead to the development of aneurysms in the organisms [59]. However, in our study, vasodilation of the lamellar axis and the appearance of aneurysms do not seem to be related, since the highest gm index in vasodilation was not recorded in organisms exposed to the same concentration and water temperature as the organisms where lamellar aneurysms were found. At 14 days, the lamellar epithelium lifting appears to be associated with the proliferation of the filament epithelium in organisms exposed to low concentrations of Cu and temperature, although these lesions appear in a few fish gills analysed. Similarly, after a long period of exposure (28 days), the appearance of the two lesions seems to be associated, however, for this period of exposure, the highest gm index was observed at the higher Cu concentration and temperature. These lesions are considered as a defense mechanism of the fish against the toxic compounds, since with the appearance of the lamellar epithelium lifting and the filament epithelium proliferation in the gills, the distance between the compound present in the water and the bloodstream increases [60], thus reducing the gill surface area. However, these changes will reduce the oxygen uptake by red blood cells causing breathing problems and survival of the fish, a main concern in summer with higher water temperatures, higher metabolism and low levels of oxygen (hypoxia) inducing mass fish kill in some cases related with infections [61]. As observed in other studies, these lesions develop after long periods of exposure [43,62]. Remarkably, in our study, a progressive increase in gm levels was observed until 28 days of exposure. Moreover, oedema and lamellar fusion are considered defensive responses against adverse external conditions, such as contaminants and temperature [63,64], increasing the diffusion barrier of compounds. The lamellar fusion observed at 28 days (where there was a higher gm index and presence) may be associated with cell proliferation with filament epithelium proliferation. Identical results were previously reported in fish exposed to different levels of copper [40,65].
At 14 days, it appears that the 25 °C temperature led to greater copper toxicity with higher gm levels, except lamellar fusion and bending of gill lamellae. In contrast, at 28 days, the increase in water temperature by 7 °C led to greater copper toxicity, with lesions showing higher gm indices, except for aneurysms. Data analysis also showed that all lesions, except aneurysms, appear to be related to chronic exposure since the presence of lesions on the gills was greater at 28 days. The gill cell damage observed may affect gas exchange and ionic regulation processes and, consequently, compromise fish respiration. These effects can be problematic for fish species, since with an increase in water temperature above the optimum for the species, there is an increase in metabolism which can reduce fish survival.
The condition factor can be informative about fish health and fitness [48,66]. Camara [67] refers to this index as an indicator of tissue energy reserves, based on the premise the fish in relatively better body condition will show higher growth rates, alongside greater reproductive potential and survival, when compared to other fish in worse conditions in comparable environmental situations. However, it was not possible to establish a pattern or correlation in the present study.
On the other hand, the hepatosomatic index showed some significant results. This index establishes a link between the weight of the specimen’s liver and its total body weight. On one hand, a decrease in this index may indicate stress and loss of energy reserves. On the other hand, its increase is associated with contaminant exposure, due to the need for increased metabolization capacity [49]. In fish not exposed to Cu, there was a decrease in HSI at 14 days, which is aligned with signs of stress, but not pollutant contamination. However, prolonged exposure showed an increased his as it was expected due to more detoxification time. This does not align with the definition of Murray [49], but it does align with the findings of Figueiredo-Fernandes [40], as well as of Pinto [50] and Carrola [66]. Figueiredo-Fernandes [40] registered an increase in HSI with Cu exposure. Pinto [50] and Carrola [66] found increased HSI in fish that inhabited very polluted rivers in Portugal.
The liver is one of the main storage organs, capable of concentrating more toxic compounds than other organs combined, being also the main organ responsible for xenobiotics biotransformation [68]. Usually, the appearance of hepatic lesions is related to exposure to aquatic pollutants [23]. Several studies have found hepatic lesions associated with polluted environments with heavy metals, such as copper [50,66,69].
Several liver lesions were found in the present study, such as macrophage aggregates, vacuolization, hyalinization, granulomas, and necrosis. Macrophage aggregates were systematic in the observed fish, however, generally with a very slight severity. Generally, this lesion increases in number and size when fish are exposed to environmental stress or chemical pollution [50,70]. Hoseini [54] and Al-Bairuty [71] exposed fish to Cu, and the first recorded a severe increase in lesion frequency and size. The latest found an increase in the number of macrophage aggregates. In situ studies in polluted environments have also shown a higher frequency of this lesion [50,69,70].
Vacuolization was another lesion that was generally found at a very mild severity degree. This lesion is characterized by the presence of a light-coloured vacuole in the cytoplasm of the hepatocytes, and it may indicate degenerative alterations or energy storage in the form of lipids or glycogen [72]. It is a lesion typically found in fish in captivity [73], which can explain its presence in the hepatic parenchyma of fish sampled on day 0 (control) of the present study. Vacuolization is also associated with the initial stages of necrosis and is frequently found in studies involving copper [38,40,71]. In the present study, there was a significant increase in the severity level, from very slight to slight in individuals sampled at 14 days, at 25 °C and exposed to 1.1 mg/L of Cu.
As for necrosis, it is a consequence of damage to cell membranes, protein synthesis, and carbohydrate metabolism [23]. Several studies have found hepatic necrosis associated with Cu exposure [38,40,54]. Necrosis has been found in Oreochromis niloticus [40], Channa punctatus [38], and Cyprinid carpio [54]. All three studies exposed fish to lower Cu concentrations than those used in the present study, which may indicate that O. mossambicus may have a higher resistance to Cu exposure, which may also be related to the results found, that did not align with those expected, considering several previous studies. We know that tilapia is less sensitive than other fish and can support low levels of dissolved oxygen as well as low water quality, it can explain the difference with other fish species mainly freshwater fish from cold waters.
Granulomas were the least frequent lesion, with few sample groups presenting them overall. These appear as a defence reaction of the liver, and similar to macrophage aggregates, they are frequently observed in field studies [45,50]. In the present study, it was not possible to establish a correlation between this lesion and the variables studied.
Hyalinization was the lesion that showed the most significant results. This lesion is associated with disturbances in protein synthesis, it’s characterized by dense eosinophilic inclusions within hepatocytes and can result in structural changes in the liver [74]. Van Dyk [74] associated increased hyalinization with the exposure time of heavy metals (cadmium and zinc), observing a higher progression of the lesion in shorter periods (6 to 96 h). Exposure for 28 days showed no presence of hyalinization. Two similar studies done on different species [56,75] showed that younger fish were more susceptible to copper toxicity when combined with a higher temperature. The present study corroborates these findings, as the most intense hyalinization was found at the highest concentration and temperature, on a higher severity degree than at a lower temperature. Perschbacher [76] noted greater copper toxicity at a lower temperature, associating this with a decrease in the functioning of defence mechanisms against this metal. These findings may indicate that higher temperatures may promote greater toxicity. However, the presence of hyalinization in fish not exposed to copper, even at lower severity degrees, may indicate that hyalinization is not necessarily associated with Cu exposure.
The findings of the present may indicate that O. mossambicus may be more resistant to Cu exposure than other species, as it did not show the typical lesions and severities of this type of study, but registered a lesion at a severity level that may indicate a correlation between higher temperatures and higher liver toxicity.
Copper exposure in fish has been extensively studied and has been found to induce a range of behavioural changes. Some authors observed erratic swimming, loss of balance, and other disruptive behaviours in fish exposed to copper [77,78]. These effects were dose-dependent, with higher concentrations of copper leading to more severe outcomes. Furthermore, one study has shown that the physiological responses to copper exposure can be influenced by social hierarchy, with subordinate fish exhibiting a higher accumulation of copper in their tissues [79].
In addition to copper contamination, temperature fluctuations can also significantly impact tilapia’s behaviour. King and Sardella [80] found that tilapia exhibit specific behaviours, such as ventilation cessation and aquatic surface respiration, in response to thermal challenges. Pandit and Nakamura [27] demonstrated that high water temperatures can reduce the survival, growth, and feed conversion ratio of Nile tilapia.
The interaction between copper contamination and temperature caused more behavioural responses in tilapia. Gasping at the surface and stationary at the bottom, may also be related to changes observed in the gills (e.g., aneurysms and bending of the gill lamellae). These gill pathologies can severely impair the fish’s ability to efficiently exchange gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide), leading to respiratory distress and forcing the fish to spend more energy on gas changes. Thus, the observable behaviours are indications of underlying physiological stress caused by this structural damage to the gill but also by thermal stresses.
Elevated water temperatures can exacerbate the toxic effects of copper, leading to increased stress and behavioural disturbances. Tilapia exposed to both copper and high temperatures may exhibit heightened avoidance behaviour, reduced foraging activity, and altered social dynamics compared to those experiencing either stressor alone [26]. Furthermore, the combined effects of copper and temperature stress may compromise the ability of O. mossambicus to cope with other environmental challenges, such as predation pressure, habitat degradation, or hypoxia effects.
While several studies have investigated the individual and interactive effects of copper and temperature on tilapia behaviour, there are still many gaps in our understanding. Factors such as the duration and magnitude of exposure, the age and physiological condition of the fish, and the presence of other environmental stressors can modulate the behavioural responses of tilapia to copper and temperature stress. The long-term consequences of these stressors on tilapia populations and ecosystem dynamics require further investigation.
Furthermore, the role of sediments in the accumulation and redistribution of copper is a factor that affects the bioavailability of copper in aquatic environments, as these can act both as a sink and as a source of the contaminant [81]. This implies that not all copper will remain immediately bioavailable, which could influence the extent of the potential toxic effects observed. This delayed release can pose long-term risks to fish, especially in aquaculture environments where sediment disturbance can be affected by climate change like rain patterns and extreme events. Understanding the dynamics of copper in sediments is crucial for aquaculture managers as it can affect the severity of copper exposure in fish populations. Furthermore, our results underline the need for comprehensive management strategies for aquaculture managers since copper sulphate is used in aquaculture to control algae and fish parasites [6] which can lead to increased concentration in the water and sediments, as well as in fish. Therefore, the concentration of copper sulphate that is added to the water as well as the temperature at which organisms are present must be considered so that the fish produced by aquaculture are not under stress.
5. Conclusions
The current study assessed the effects of two CuSO4 concentrations (1.1 and 3.6 mg/L) in combination with two different water temperatures (25 and 32 °C) on gills and liver histology, and behaviour of O. mossambicus, considering the actual fast climate change impacts in freshwater ichthyofauna. According to our findings, exposure to CuSO4 especially at the higher temperature tested, induced several behavioural alterations (mainly feeding inhibition and hoovering in the water column) in addition to significant lesions in the liver (hyalinization and vacuolization) and gills histology (aneurysms and bending of gill lamellae). Thus, these results emphasize the interaction between water temperature and copper contamination, which amplified the observed harmful consequences in fish.
This highlights the necessity of considering climate change and environmental contamination when managing and conserving aquatic ecosystems. Polluted freshwater ecossystems will be more affected under fast climate changes (rainfall reduction and hypoxia events) and can cause huge adverse impacts on fish populations mainly for more sensitive species, with mass killing fish during extreme climate events. Given the persistence of increasing drought events and heatwaves in the actual warming climate scenario, this work advances some knowledge of the complementary impacts of thermal stress, oxygen depletion and copper toxicity on fish health and survival. It also emphasises the significance of assessing a variety of environmental stressors to study fish and namely alerts for the importance of planning the conservation and management of fish populations with collaborative and coordinated conservation actions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, O.R., M.Q.P., D.T. and J.S.C.; methodology, O.R., M.Q.P., D.T. and J.S.C.; validation, J.V.F.-C., A.T.C. and J.S.C.; formal analysis, O.R.; investigation, O.R., M.Q.P. and D.T.; resources, J.V.F.-C. and J.S.C.; data curation, O.R., M.Q.P., D.T. and J.S.C.; writing—original draft preparation, O.R., M.Q.P. and D.T.; writing—review and editing, J.V.F.-C., A.T.C. and J.S.C.; supervision, J.S.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financed by National Funds from FCT—Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology, through the FCT/MCTES (PIDDAC), under the project UIDB/04033/2020 (CITAB/Inov4Agro, https://doi.org/10.54499/UIDB/04033/2020).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was performed by experienced and certified fish welfare researchers (FELASA and DGAV accredited courses) and conducted according to the national and institutional guidelines for the protection of animal welfare of EU Directive, 2010/63/EU and National Decreto-Lei 113/2013 legislation.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Priya, A.K.; Muruganandam, M.; Sivarethinamohan, R.; Sivarethinamohan, S.; Gaddam, M.K.R.; Velusamy, P.; Gomathi, R.; Ravindiran, G.; Gurugubelli, T.R.; Muniasamy, S.K. Impact of climate change and anthropogenic activities on aquatic ecosystem—A review. Environ. Res. 2023, 238, 117233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S. Impact of Climate change on Aquatic Ecosystem and its Biodiversity: An overview. Int. J. Biol. Innov. 2021, 3, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alava, J.J.; Cheung, W.W.; Ross, P.S.; Sumaila, U.R. Climate change–contaminant interactions in marine food webs: Toward a conceptual framework. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 3984–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backhaus, T.; Brack, W.; Van den Brink, P.J.; Deutschmann, B.; Hollert, H.; Posthuma, L.; Segner, H.; Seiler, T.-B.; Teodorovic, I.; Focks, A. Assessing the ecological impact of chemical pollution on aquatic ecosystems requires the systematic exploration and evaluation of four lines of evidence. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2019, 31, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamm, L.; Thuerig, B.; Apostolov, S.; Blogg, H.; Borgo, E.; Corneo, P.E.; Fittje, S.; de Palma, M.; Donko, A.; Experton, C. Use of copper-based fungicides in organic agriculture in twelve European countries. Agronomy 2022, 12, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares-Dias, M. Toxic, physiological, histomorphological, growth performance and antiparasitic effects of copper sulphate in fish aquaculture. Aquaculture 2021, 535, 736350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, B.; Caldeira, C.; Pereira, J.L.; Gonçalves, F.; Correia, A.T. Perturbations in ROS-related processes of the fish Gambusia holbrooki after acute and chronic exposures to the metals copper and cadmium. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 3756–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, B.; Capela, R.C.; Sérgio, T.; Caldeira, C.; Gonçalves, F.; Correia, A.T. Effects of chronic exposure to lead, copper, zinc, and cadmium on biomarkers of the European eel, Anguilla anguilla. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 5689–5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouh, W.G.; Selim, A.G. Toxopathological studies on the effect of formalin and copper sulphate in tilapia as a commonly used disinfectant in aquaculture. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. Sci. 2013, 3, 7–20. [Google Scholar]
- Senior, W.; de La Cruz, R.; Troccoli, L. Copper: Essential and noxious to aquatic organisms. In Coastal and Deep Ocean Pollution; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 107–152. [Google Scholar]
- Rader, K.J.; Carbonaro, R.F.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Baken, S.; Delbeke, K. The fate of copper added to surface water: Field, laboratory, and modeling studies. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2019, 38, 1386–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akilan, C.; Hefter, G.; Rohman, N.; Buchner, R. Ion association and hydration in aqueous solutions of copper (II) sulfate from 5 to 65 C by dielectric spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 14961–14970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, R.T.; Copatti, C.E.; Albinati, A.C.; Campeche, D.F.B.; Bonfá, H.; Melo, J. Waterborne copper sulfate toxicity in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) juveniles affect survival, growth, and physiology. J. Appl. Aquac. 2024, 36, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiaune, L.; Singhasemanon, N. Pesticidal copper (I) oxide: Environmental fate and aquatic toxicity. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology Volume 213; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sherif, M.S.; El-Feky, A.M.I. Performance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fingerlings. II. Influence of different water temperatures. Int. J. Agric. Biol 2009, 11, 1814–9596. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.-W.; Oh, Y.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, D.; Joung, D. Assessment of water quality in a coastal region of sea dike construction in Korea and the impact of low dissolved oxygen concentrations on pH changes. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debels, P.; Figueroa, R.; Urrutia, R.; Barra, R.; Niell, X. Evaluation of water quality in the Chillán River (Central Chile) using physicochemical parameters and a modified water quality index. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2005, 110, 301–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, B.; Brandão, F.; Sérgio, T.; Rodrigues, S.; Gonçalves, F.; Correia, A.T. Effects of environmentally relevant concentrations of metallic compounds on the flatfish Scophthalmus maximus: Biomarkers of neurotoxicity, oxidative stress and metabolism. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 7501–7511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnadurai, K.; Prema, P.; Veeramanikandan, V.; Kumar, K.R.; Nguyen, V.-H.; Marraiki, N.; Zaghloul, N.S.S.; Balaji, P. Toxicity evaluation and oxidative stress response of fumaronitrile, a persistent organic pollutant (POP) of industrial wastewater on tilapia fish (Oreochromis mossambicus). Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Cordero, F.J.; Delgadillo, T.; Sanchez-Zazueta, E.; Cai, J. Tilapia Aquaculture in Mexico-Assessment with a Focus on Social and Economic Performance; Food & Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rashed, M. Cadmium and lead levels in fish (Tilapia nilotica) tissues as biological indicator for lake water pollution. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2001, 68, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.M.; dos Santos, N.M.; Calejo, M.; Fontainhas-Fernandes, A.; Sousa, M. Copper toxicity in gills of the teleost fish, Oreochromis niloticus: Effects in apoptosis induction and cell proliferation. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 94, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Khalek, A.A.; Badran, S.R.; Marie, M.A. Toxicity evaluation of copper oxide bulk and nanoparticles in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, using hematological, bioaccumulation and histological biomarkers. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 42, 1225–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Al-Ogaily, S.; Al-Asgah, N.; Gropp, J. Effect of sublethal concentrations of copper on the growth performance of Oreochromis niloticus. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2003, 19, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, E.; Aydın, S.; Kutlu, B. Alterations of growth performance and blood chemistry in nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) affected by copper sulfate in long-term exposure. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 15, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeonyejiaku, C.D.; Obiakor, M.O.; Ezenwelu, C.O. Toxicity of copper sulphate and behavioral locomotor response of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and catfish (Clarias gariepinus) species. Online J. Anim. Feed Res. (OJAFR) 2011, 1, 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- Pandit, N.; Nakamura, M. Effect of high temperature on survival, growth and feed conversion ratio of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Our Nat. 2010, 8, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Annex VI: Climatic Impact-driver and Extreme Indices. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 2205–2214. [Google Scholar]
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Zhang, X.; Adnan, M.; Badi, W.; Dereczynski, C.; Di Luca, A.; Ghosh, S.; Iskandar, I.; Kossin, J.; Lewis, S.; et al. Weather and Climate Extreme Events in a Changing Climate. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1513–1766. [Google Scholar]
- Verburga, P.; Hecky, R.E. The physics of the warming of Lake Tanganyika by climate change. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2418–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hack, M.E.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Nader, M.M.; Salem, H.M.; El-Tahan, A.M.; Soliman, S.M.; Khafaga, A.F. Effect of environmental factors on growth performance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Int. J. Biometeorol. 2022, 66, 2183–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan-kishiya, A.S.; Solomon, J.R.; Alhaji, U.A. Influence of temperature on the respiratory rate of Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (Pisces: Cichlidae) in the laboratory. Res. J. Costa Rican Distance Educ. Univ. 2016, 8, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.-I.; Knowler, D.J.; Lévêque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.-H.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L. Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol. Rev. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, D.; Nunes, B.; Pinto, E.; Ferreira, I.M.; Correia, A.T. Assessment of paracetamol toxic effects under varying seawater pH conditions on the marine polychaete Hediste diversicolor using biochemical endpoints. Biology 2022, 11, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionisio, R.; Daniel, D.; Arenas, F.; Campos, J.C.; Costa, P.C.; Nunes, B.; Correia, A.T. Effects of pH on salicylic acid toxicity in terms of biomarkers determined in the marine gastropod Gibbula umbilicalis. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 158, 104995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, C.C.; Calijuri, M.d.C.; dos Santos, A.C.A.; Ladwig, R.; de Oliveira, L.F.A.; Buarque, A.C.S. Future projections of water level and thermal regime changes of a multipurpose subtropical reservoir (Sao Paulo, Brazil). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 144741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Nath, K.; Sharma, Y.; Trivedi, S. Hepatotoxic effect of Cu (II) in freshwater fish, Channa punctatus: A histopathological study. Res. Environ. Life Sci. 2008, 1, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Arellano, J.M.; Storch, V.; Sarasquete, C. Histological changes and copper accumulation in liver and gills of the Senegales sole, Solea senegalensis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1999, 44, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo-Fernandes, A.; Ferreira-Cardoso, J.V.; Garcia-Santos, S.; Monteiro, S.M.; Carrola, J.; Matos, P.; Fontaínhas-Fernandes, A. Histopathological changes in liver and gill epithelium of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, exposed to waterborne copper. Pesqui. Veterinária Bras. 2007, 27, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernet, D.; Schmidt, H.; Meier, W.; Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Wahli, T. Histopathology in fish: Proposal for a protocol to assess aquatic pollution. J. Fish Dis. 1999, 22, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, B.; Selvanayagam, M.; Cengiz, E.I.; Unlu, E. Histopathology of lambda-cyhalothrin on tissues (gill, kidney, liver and intestine) of Cirrhinus mrigala. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 24, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.M.; Rocha, E.; Fontaínhas-Fernandes, A.; Sousa, M. Quantitative histopathology of Oreochromis niloticus gills after copper exposure. J. Fish Biol. 2008, 73, 1376–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Lopes, F.; Thomaz, A. Histopathologic alterations observed in fish gills as a tool in environmental monitoring. Braz. J. Biol. 2011, 71, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrola, J.S. Histopatologia Hepática como Biomarcador da Poluição em Sistemas Aquáticos—Bacias Hidrográficas dos Rios Douro e Ave. Master’s Thesis, Universidade de Trás-os-Montes e Alto Douro, Vila Real, Portugal, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lima-Junior, S.E.; Cardone, I.B.; Goitein, R. Determination of a method for calculation of Allometric Condition Factor of fish. Acta Sci. Biol. Health Sci. 2002, 24, 397–400. [Google Scholar]
- Morado, C.N.; Araújo, F.G.; Gomes, I.D. The use of biomarkers for assessing effects of pollutant stress on fish species from a tropical river in Southeastern Brazil. Acta Scientiarum. Biol. Sci. 2017, 39, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, R. Cube law, condition factor and weight–length relationships: History, meta-analysis and recommendations. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2006, 22, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, L.; Rennie, M.D.; Enders, E.C.; Pleskach, K.; Martin, J.D. Effect of nanosilver on cortisol release and morphometrics in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 1606–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.L.; Varandas, S.; Coimbra, A.M.; Carrola, J.; Fontaínhas-Fernandes, A. Mullet and gudgeon liver histopathology and macroinvertebrate indexes and metrics upstream and downstream from a wastewater treatment plant (Febros River—Portugal). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 169, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, B.A.; Iwama, G.K. Physiological changes in fish from stress in aquaculture with emphasis on the response and effects of corticosteroids. Annu. Rev. Fish Dis. 1991, 1, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hullebusch, E.; Chatenet, P.; Deluchat, V.; Chazal, P.M.; Froissard, D.; Botineau, M.; Ghestem, A.; Baudu, M. Copper accumulation in a reservoir ecosystem following copper sulfate treatment (St. Germain Les Belles, France). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2003, 150, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smriti, A.A.; Lodhi, S.; Shukla, S. Copper toxicity in aquatic ecosystem: A Review. Int. J. Fish Aquat. Stud. 2023, 11, 134–138. [Google Scholar]
- Hoseini, S.M.; Hedayati, A.; Mirghaed, A.T.; Ghelichpour, M. Toxic effects of copper sulfate and copper nanoparticles on minerals, enzymes, thyroid hormones and protein fractions of plasma and histopathology in common carp Cyprinus carpio. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2016, 68, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitriadis, V.K.; Gougoula, C.; Anestis, A.; Pörtner, H.O.; Michaelidis, B. Monitoring the biochemical and cellular responses of marine bivalves during thermal stress by using biomarkers. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 73, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, C.S.; Fernandes, M.N. Effect of temperature on copper toxicity and hematological responses in the neotropical fish Prochilodus scrofa at low and high pH. Aquaculture 2006, 251, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Q.-Q.; Yan, H.; Luo, X.-W.; Kang, Y.-H.; Hu, J.-M.; Chen, L.-Q. Integration of transcriptomics and metabolomics reveals damage and recovery mechanisms of fish gills in response to nanosilver exposure. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 237, 105895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Cui, A.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, W. Effects of copper exposure and recovery in juvenile yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi): Histological, physiological and molecular responses. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 31, 101669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Santos, S.; Fontaínhas-Fernandes, A.; Wilson, J.M. Cadmium tolerance in the Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) following acute exposure: Assessment of some ionoregulatory parameters. Environ. Toxicol. Int. J. 2006, 21, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, C.M.; Eom, J. The osmorespiratory compromise in the fish gill. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2021, 254, 110895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, J.; Houben, N.; Pauly, D. On being the wrong size, or the role of body mass in fish kills and hypoxia exposure. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2023, 106, 1651–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashkina, N.A.; Moiseenko, T.I.; Shuman, L.A.; Koroleva, I.M. Biological responses of whitefish (Coregonus lavaretus L.) to reduced toxic impact: Metal accumulation, haematological, immunological, and histopathological alterations. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 239, 113659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.N.; Mazon, A.F. Environmental pollution and fish gill morphology. In Fish Adaptations; Science Publishers: Enfield, CT, USA, 2003; pp. 203–231. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, M.; Paulino, M.; Sakuragui, M.; Ramos, C.; Pereira, C.D.S.; Sadauskas-Henrique, H. Organochlorines and metals induce changes in the mitochondria-rich cells of fish gills: An integrative field study involving chemical, biochemical and morphological analyses. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 126, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paruruckumani, P.; Maharajan, A.; Ganapiriya, V.; Narayanaswamy, Y.; Jeyasekar, R.R. Surface ultrastructural changes in the gill and liver tissue of asian sea bass Lates calcarifer (Bloch) exposed to copper. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2015, 168, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrola, J.; Fontaínhas-Fernandes, A.; Matos, P.; Rocha, E. Liver Histopathology in Brown Trout (Salmo trutta f. fario) from the Tinhela River, Subjected to Mine Drainage from the Abandoned Jales Mine (Portugal). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 83, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camara, E.M.; Caramaschi, E.P.; Petry, A.C. Fator de condição: Bases conceituais, aplicações e perspectivas de uso em pesquisas ecológicas com peixes. Oecol. Aust. 2011, 15, 249–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaínhas-Fernandes, A. The use of biomarkers in aquatic toxicology studies. Rev. Port. Zootec. 2005, 12, 67–86. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Moneim, A.M.; Al-Kahtani, M.A.; Elmenshawy, O.M. Histopathological biomarkers in gills and liver of Oreochromis niloticus from polluted wetland environments, Saudi Arabia. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, M.M.P.; Martinez, C.B.R. Histopathology of gills, kidney and liver of a Neotropical fish caged in an urban stream. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2007, 5, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bairuty, G.A.; Shaw, B.J.; Handy, R.D.; Henry, T.B. Histopathological effects of waterborne copper nanoparticles and copper sulphate on the organs of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 126, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, J.C.; Wheeler, J.R. A critical review of histopathological findings associated with endocrine and non-endocrine hepatic toxicity in fish models. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 197, 60–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.C.; Wolfe, M.J. A Brief Overview of Nonneoplastic Hepatic Toxicity in Fish. Toxicol. Pathol. 2005, 33, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dyk, J.C.; Pieterse, G.M.; van Vuren, J.H.J. Histological changes in the liver of Oreochromis mossambicus (Cichlidae) after exposure to cadmium and zinc. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2007, 66, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussey, G.; Van Vuren, J.H.J.; Du Preez, H.H. Acute toxicity tests of copper on juvenile Mozambique tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus (Cichlidae), at different temperatures. S. Afr. J. Wildl. Res.—24-Mon. Delayed Open Access 1996, 26, 47–55. [Google Scholar]
- Perschbacher, P.W. Temperature effects on acute copper toxicity to juvenile channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus. Aquaculture 2005, 243, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tamimi, A.H.; Al-Azzawi, A.J. The acute and chronic toxicity of copper on the behavioral responses and hematological parameters of freshwater fish, common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Iraqi J. Sci. 2015, 56, 2835–2845. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, A.A.; Noori Arifa, N.A. Toxicity of heavy metal copper and its effect on the behaviour of freshwater Indian catfish, Clarias batrachus (Linn.). Curr. Biot. 2011, 4, 405–411. [Google Scholar]
- Sloman, K.A.; Baker, D.W.; Wood, C.M.; McDonald, G. Social interactions affect physiological consequences of sublethal copper exposure in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 2002, 21, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.; Sardella, B. The effects of acclimation temperature, salinity, and behavior on the thermal tolerance of Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). J. Exp. Zool. Part A Ecol. Integr. Physiol. 2017, 327, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-W.; Chai, Z.Y.; Yen, P.-L.; How, C.M.; Yu, C.-W.; Chang, C.-H.; Liao, V.H.-C. The bioavailability and potential ecological risk of copper and zinc in river sediment are affected by seasonal variation and spatial distribution. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 227, 105604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).