Effective Removal of Cu(II) Ions from Aqueous Solution by Cross-Linked Chitosan-Based Hydrogels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. pH Value of Zero-Point Charge (pHzpc)
2.3. Adsorption Investigations
2.4. Adsorption Kinetic Studies
- Pseudo-first-order model
- Pseudo-second-order model
- Elovich model
- Intraparticle diffusion model
2.5. Investigation of Adsorption Isotherms
- The Langmuir isotherm model is expressed by Equations (12)–(14):
- The Freundlich isotherm model is expressed by Equations (15) and (16):
- Temkin isotherm model
- Dubinin–Radushkevich (D-R) isotherm model
2.6. Desorption Investigation
3. Results and Discussion
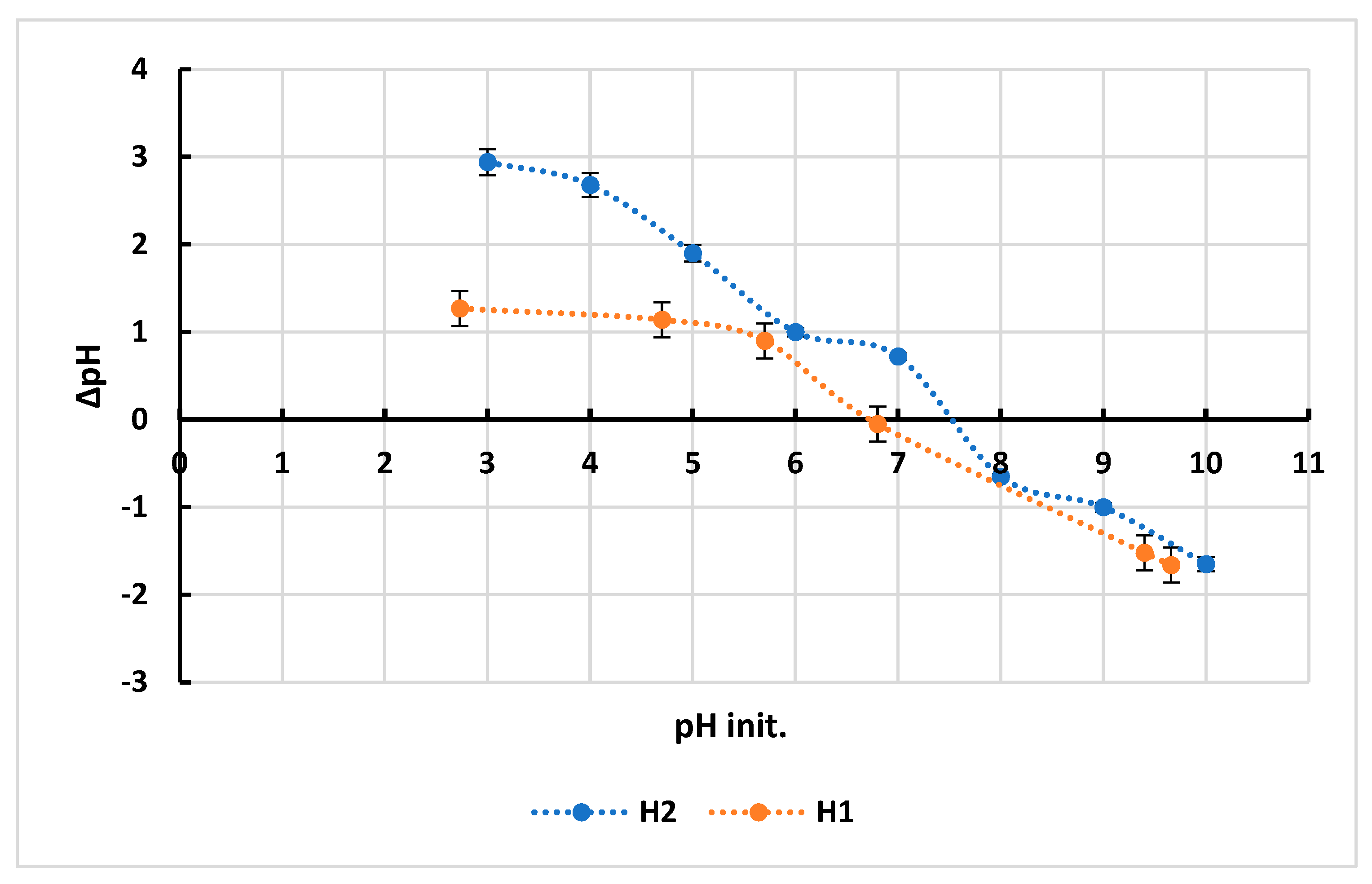
3.1. pH of Zero-Point Charge (pHzpc)
3.2. Optimizing Adsorption
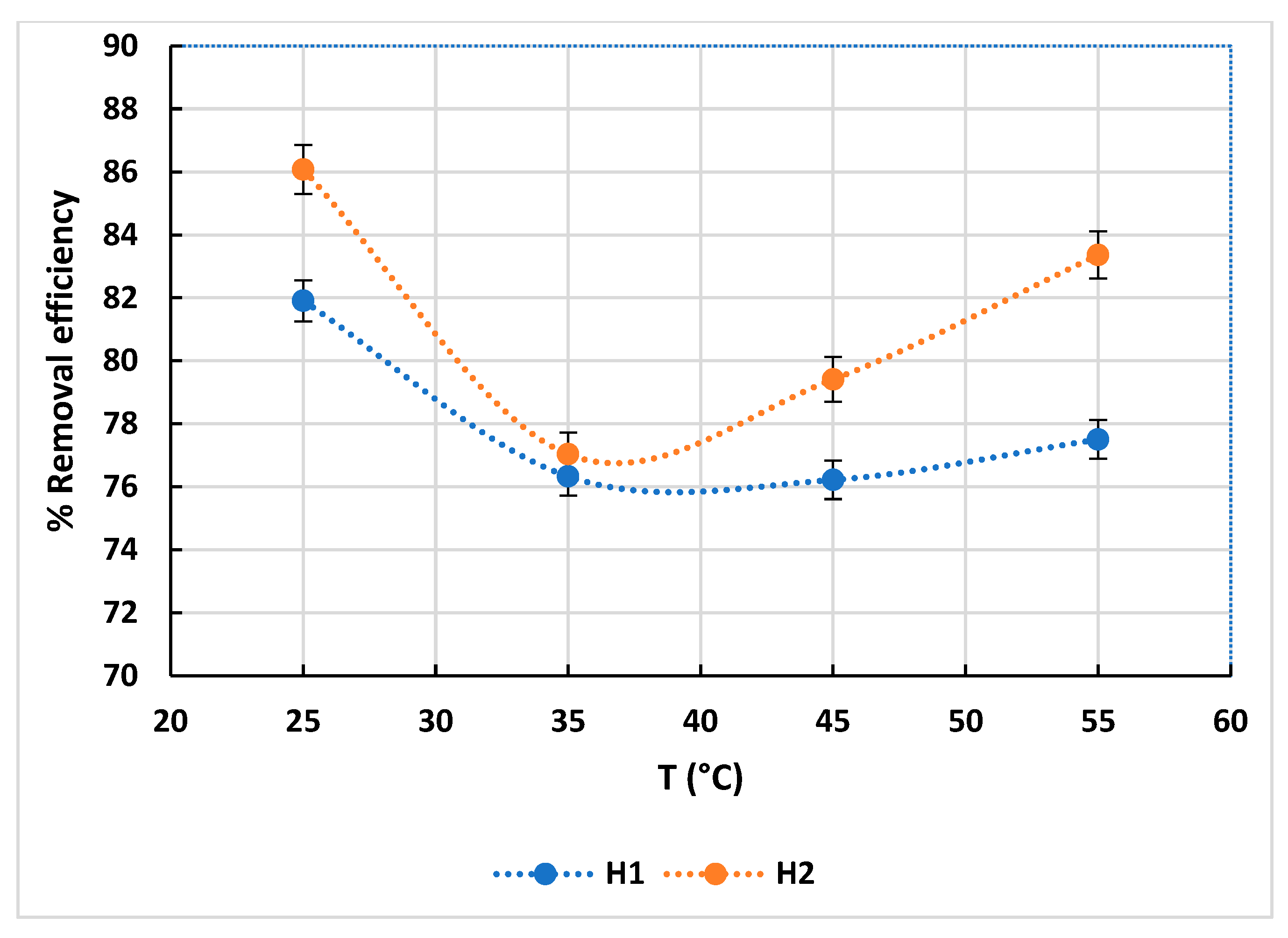
3.2.1. Effect of Temperature
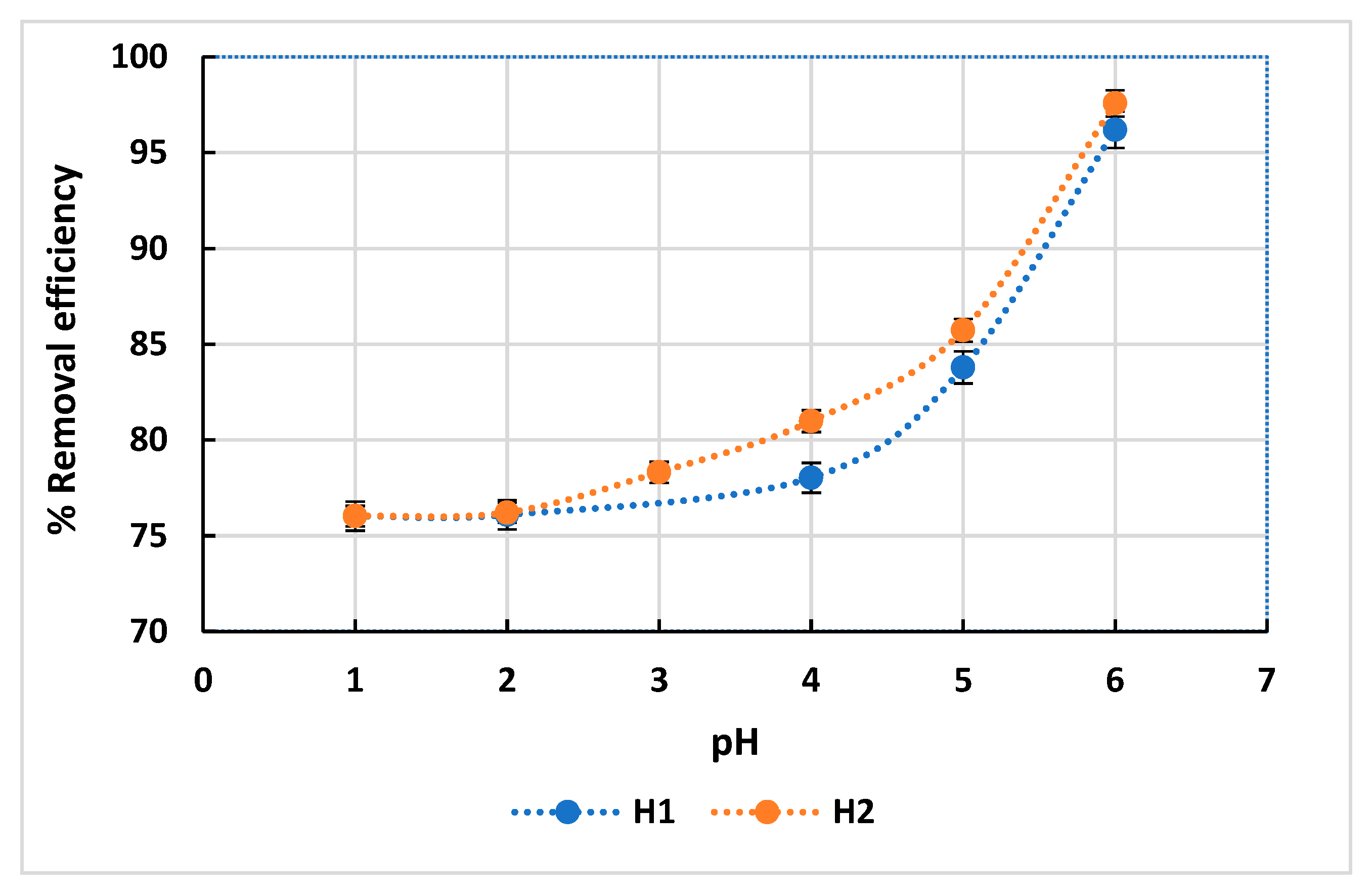
3.2.2. Effect of the pH
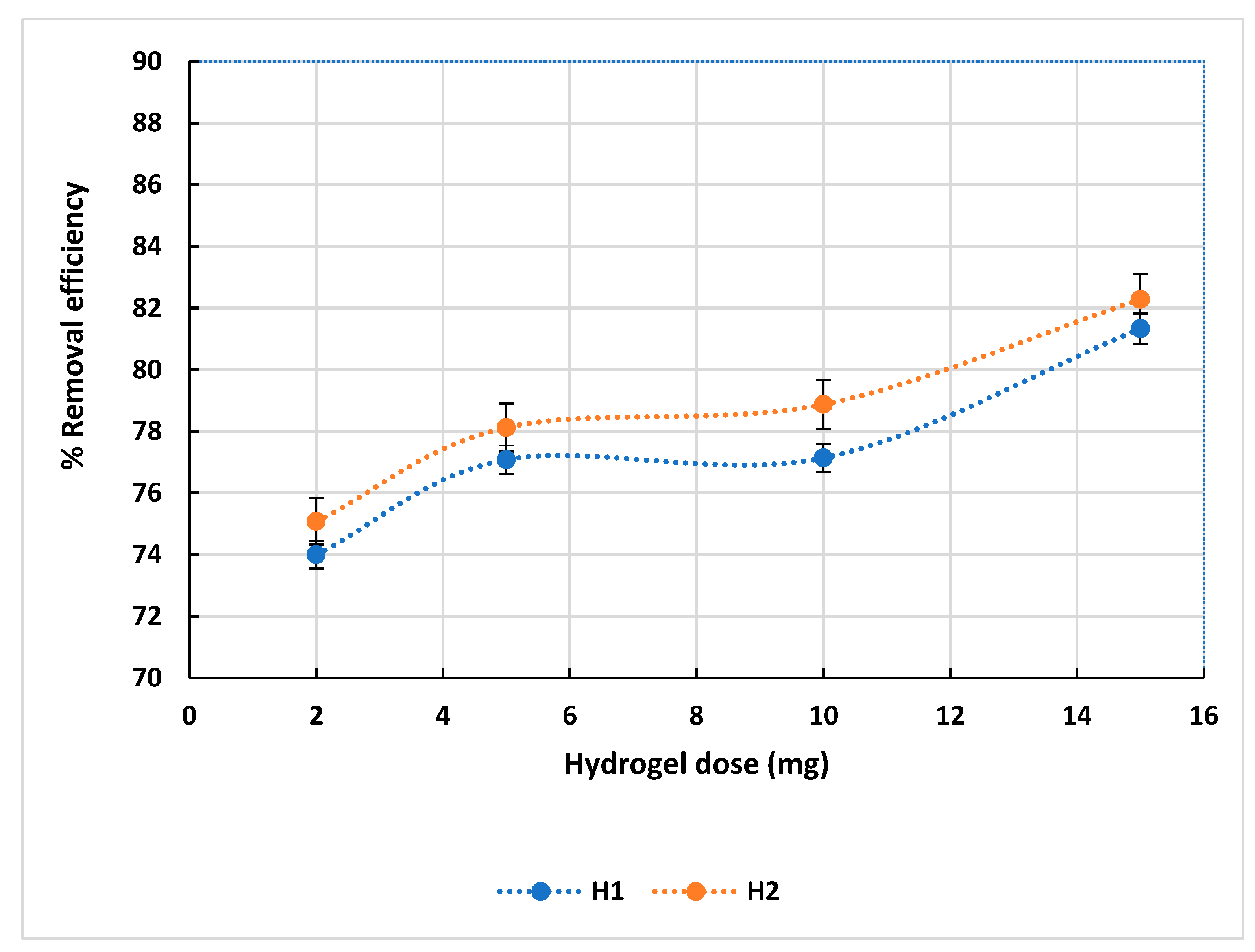
3.2.3. Hydrogel Dosage Effect
3.2.4. Cross-Linking Content Effect
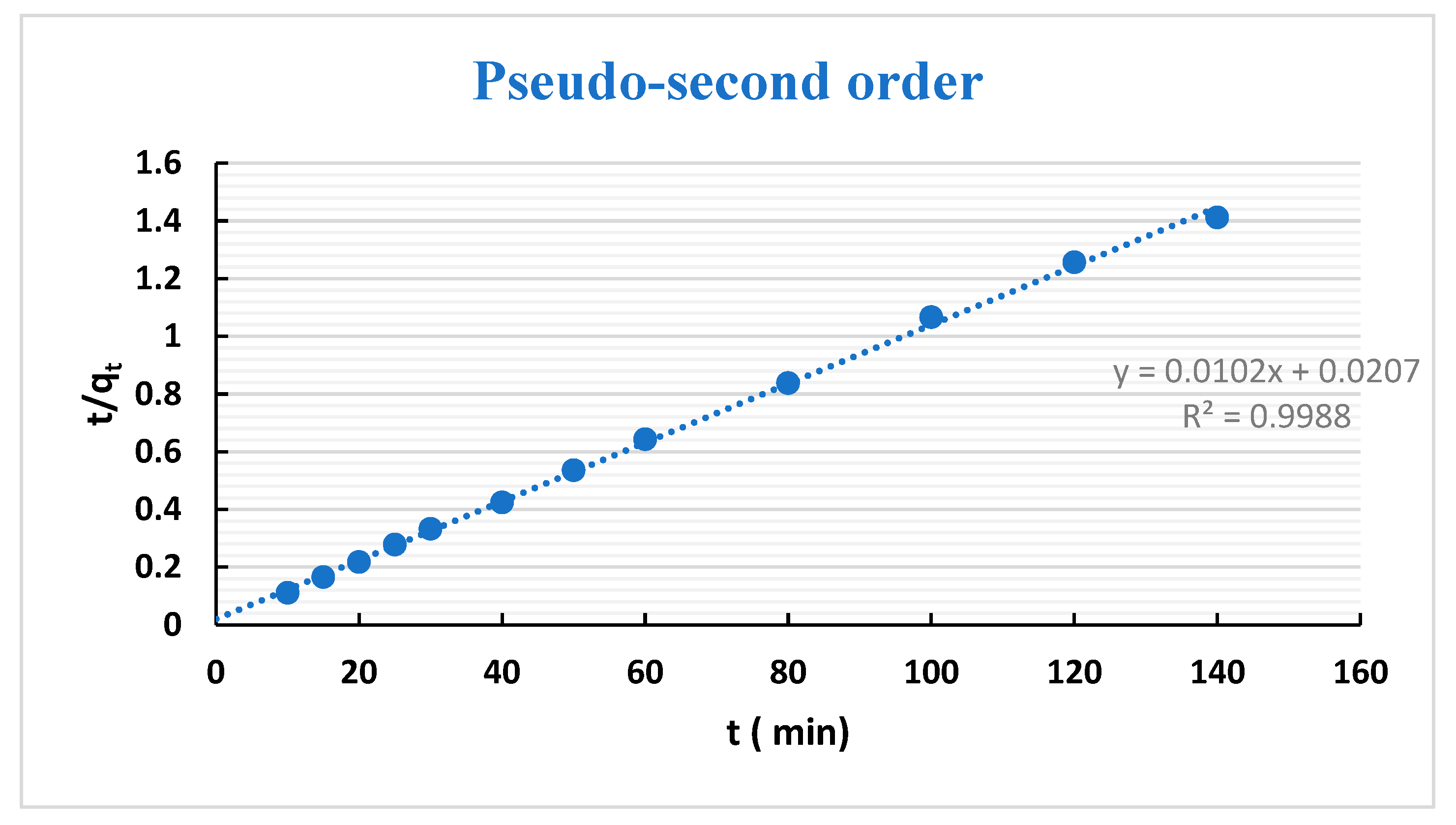
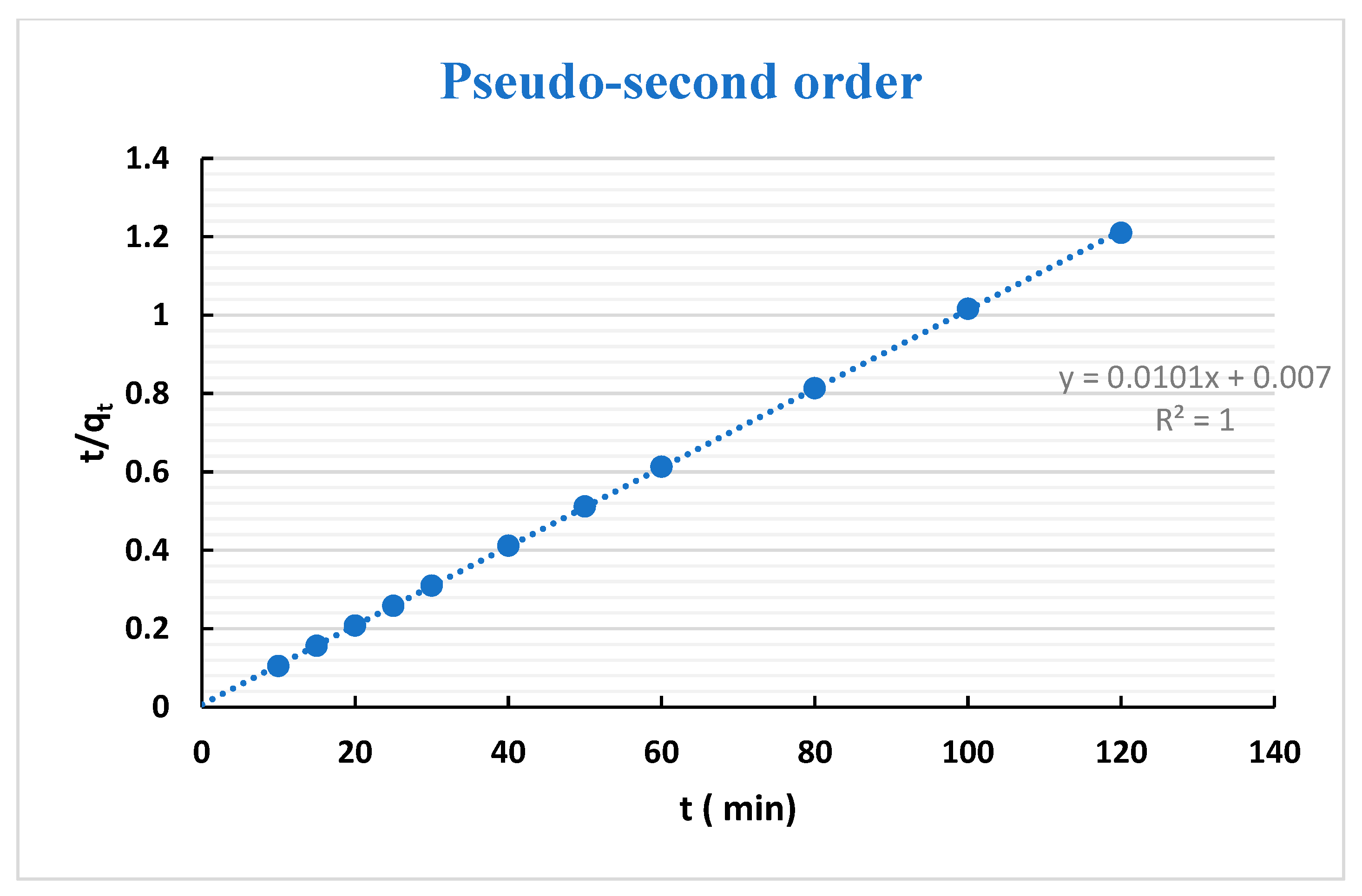
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics
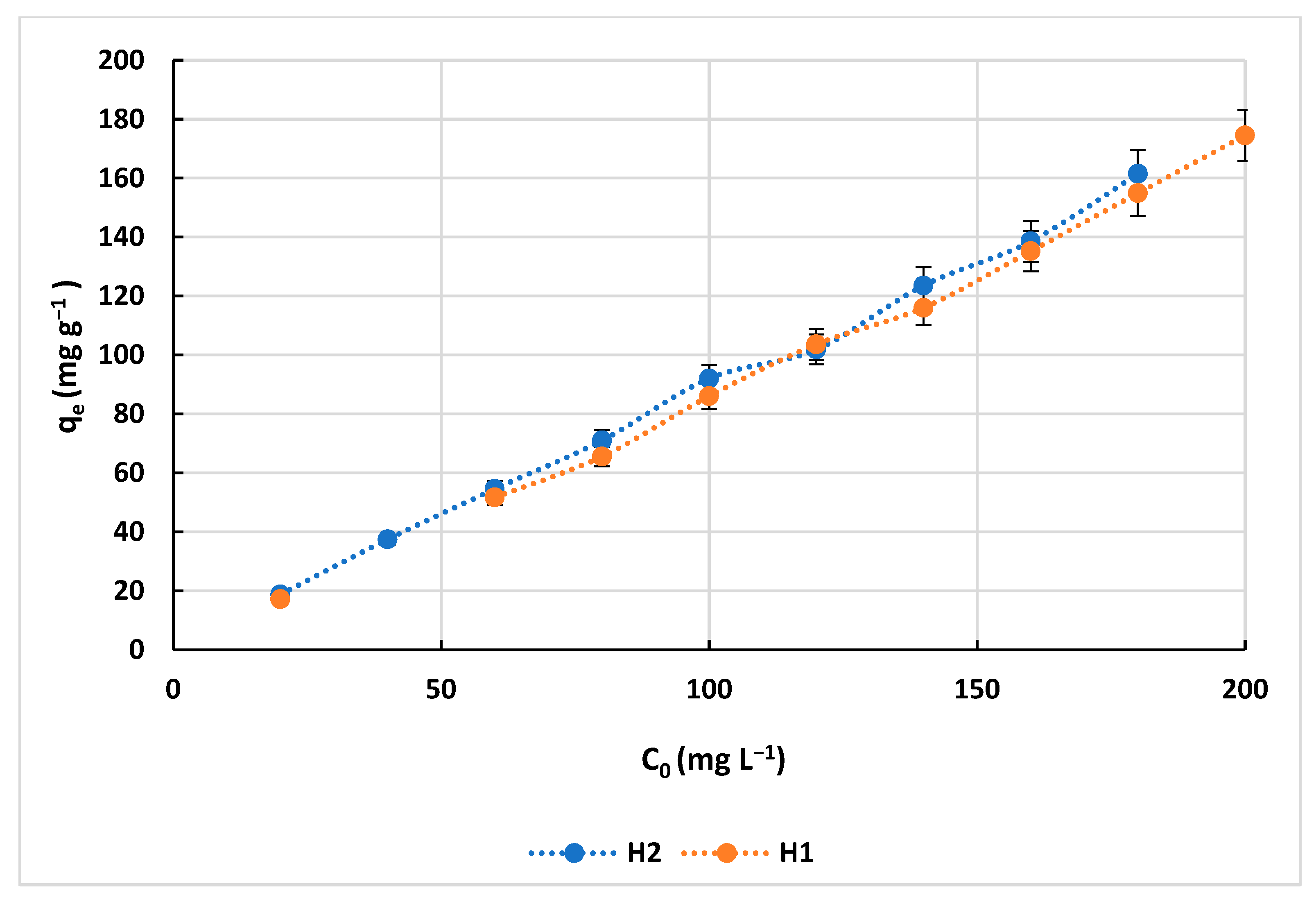
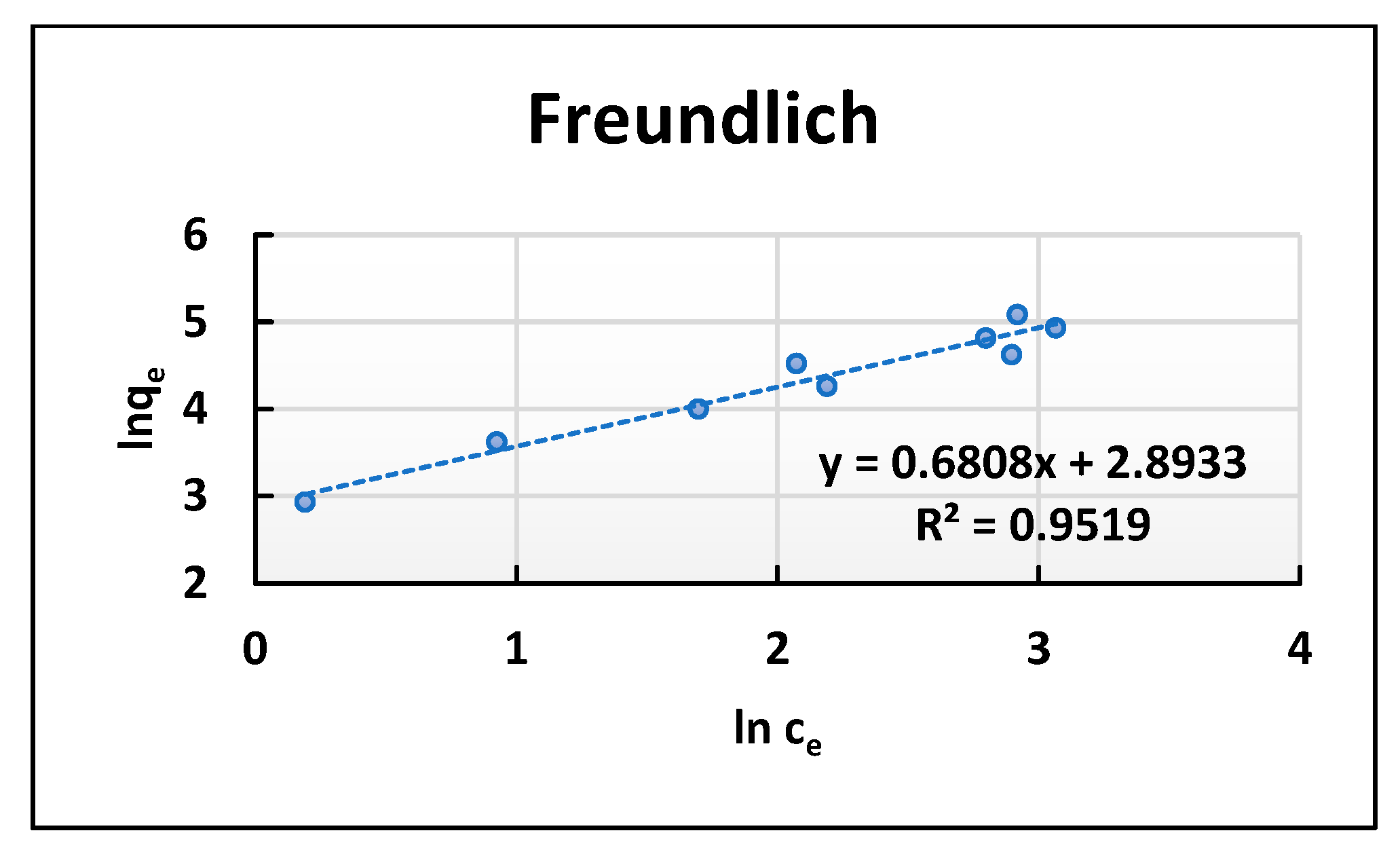
3.4. Isotherms of Adsorption
3.5. Desorption Evaluation
3.6. Comparison of Adsorption Capacity of Different Adsorbents for Cu(II) Ions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martins, R.J.; Rosana, P.; Boaventura, R.A. Cadmium (II) and zinc (II) adsorption by the aquatic moss Fontinalis antipyretica: Effect of temperature, pH and water hardness. Water Res. 2004, 38, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renu, M.A.; Kailash, S. Methodologies for removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: An overview. Interdiscip. Environ. Rev. 2017, 18, 124–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, C.S. Metal Recovery from Industrial Waste; Lewis Publishers Ins.: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1991; Volume 27. [Google Scholar]
- Tiravanti, G.; Petruzzelli, D.; Passino, R. Pretreatment of tannery wastewaters by an ion exchange process for Cr(III) removal and recovery. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 36, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Lei, L.; Li, Y.; Ni, Y. Chromium adsorption on high performance activated. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2003, 31, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, N.A.; Abd El-Ghany, N.A. Evaluation of in vitro antimicrobial, antioxidant and anticancer activity of a new carboxymethylchitosan-based cyanoguanidine copolymer. Cell. Chem. Technol. 2024, 58, 481–493. [Google Scholar]
- Vimala, R.; Nilanjana, D. Biosorbtion of cadmium (II) and lead (II) from aqueous solutions using mushrooms: A comparative study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmehbad, N.Y.; Mohamed, N.A. Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of novel N-acetyl,N’-chitosanacetohydrazide and its metal complexes. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2022, 71, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbaş, Ö.; Karadağ, A.; Alkan, M.; Doğan, M. Removal of copper ions from aqueous Solutions by hazelnuts. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.W.; Cho, H.J.; Yim, J.H.; Kim, J.M.; Jeon, J.K.; Sohn, J.M.; Yoo, K.S.; Kim, S.S.; Park, Y.K. Removal of Cu(II)-ion over amine-functionalized mesoporous silica materials. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2011, 17, 504–509. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.H.; Teng, T.T.; Ismail, N. Extraction of Cu (II) from aqueous solutions by vegetable oil-based organic solvents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, N.A.; Abd El-Ghany, N.A.; Fahmy, M.M.; Khalaf-Alla, P.A. Novel polymaleimide containing dibenzoyl hydrazine pendant group as chelating agent for antimicrobial activity. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2018, 67, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manahan, S.E. Environmental Chemistry, 5th ed.; Lewis Publishers: Chelsea, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Atalay, E.; Gode, F.; Sharma, Y.C. Removal of selected toxic metals by a modified adsorbent. Pract. Period. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste Manag. 2010, 14, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guijuan, J.I.; Weiwei, B.A.O.; Guimei, G.A.O.; Baichao, A.N.; Shucai, G.A.N. Removal of Cu (II) from aqueous solution using a novel crosslinked alumina-chitosan hybrid adsorbent. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 20, 641–648. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, N.A. Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of in vitro potential antimicrobial efficiency of new chitosan hydrogels and their CuO nanocomposites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 276, 133810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reza, B.L.; Hamid, R.Z.; Mohammad, E.B. Removal of Cu(II) Ions from aqueous solutions by low-cost natural hydroxyapatite/chitosan composite: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 1642–1648. [Google Scholar]
- Uchenna, O.; Mamookho, M.; Lukhanyo, M.; Nkemdinma, U.O.; Tendani, S.; Vuyo, M. Toxic metal implications on agricultural soils, plants, animals, aquatic life and human health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization and United Nations Environment Programme. Health Risks from Marine Pollution in the Mediterranean. Part VII. Evaluation of Health Risks from Chemically-Contaminated Seafood; World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Motaal, M.; Aldakhili, D.A.; Elmaaty, A.A.; Sharaky, M.; Mourad, M.A.E.; Alzahrani, A.Y.A.; Mohamed, N.A.; Al-Karmalawy, A.A. Design and synthesis of novel tetrabromophthalimide derivatives as potential tubulin inhibitors endowed with apoptotic induction for cancer treatment. Drug Dev. Res. 2024, 85, e22197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Council of the European Communities. Directive 82/176/EEC—On Pollution Caused by Certain Dangerous Substances Discharged into the Aquatic Environment of the Community; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Sahariah, P.; Másson, M. Antimicrobial chitosan and chitosan derivatives. A review of the structure-activity relationship. Biomacromology 2017, 13, 3846–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, N.A.; Abd El-Ghany, N.A.; Fahmy, M.M. Novel antimicrobial superporous cross-linked chitosan/pyromellitimide benzoyl thiourea hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngah, W.S.; Wan, F.S. Adsorption characterization of Pb (II) and Cu (II) ions onto chitosan-tripolyphosphate beads: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmehbad, N.Y.; Mohamed, N.A. Terephthalohydrazido cross-linked chitosan hydrogels: Synthesis, characterization and applications. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2022, 71, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harby, N.F.; Albahly, E.F.; Mohamed, N.A. Synthesis and characterization of novel uracil-modified chitosan as a promising adsorbent for efficient removal of Congo red dye. Polymers 2022, 14, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, N.A.; Al-Harby, N.F.; Almarshed, M.S. Enhancement of adsorption of Congo red dye onto novel antimicrobial trimellitic anhydride isothiocyanate-cross-linked chitosan hydrogels. Polym. Bull. 2022, 77, 6135–6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annu, S.; Ahmed, S.; Ikram, S. Chitin and chitosan: History, composition and properties. In Chitosan Shakeel Ahmed and Saiqa Ikram; Scrivener & Wiley: Austin, TX, USA, 2017; pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, L.; Chen, X.; Chen, C.; Yang, R.; Gong, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Q. Ice-templated porous polymer/UiO-66 monolith for Congo red adsorptive removal. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 5669–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferfera-Harrar, H.; Benhalima, T.; Lerari, D. Sustainable hydrogel nanocomposites based on grafted chitosan and clay for effective adsorption of cationic dye. Int. J. Mater. Metall. Eng. 2020, 14, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Alfuraydi, R.T.; Alminderej, F.M.; Mohamed, N.A. Evaluation of antimicrobial and anti-biofilm formation activities of novel poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels reinforced with crosslinked chitosan and silver nano-particles. Polymers 2022, 14, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmehbad, N.Y.; Mohamed, N.A.; Abd El-Ghany, N.A.; Abdel-Aziz, M.M. Evaluation of the in vitro anti-inflammatory and anti-Helicobacter pylori activities of chitosan-based biomaterials modified with copper oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, R.A.; Alminderej, F.M.; Al-harby, N.F.; Elmehbad, N.Y.; Mohamed, N.A. Design, synthesis, and characterization of novel bis-uracil chitosan hydrogels modified with zinc oxide nanoparticles for boosting their antimicrobial activity. Polymers 2023, 15, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, N.A.; Abd El-Ghany, N.A. Novel amino hydrazide cross-linked chitosan filled with multi-walled carbon nanotubes as antimicrobial agents. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, N.A.; Abd El-Ghany, N.A. Synthesis. Characterization and antimicrobial activity of novel aminosalicylhydrazide cross linked chitosan modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Cellulose 2019, 26, 1141–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugapriya, A.; Ramya, R.; Ramasubramaniam, S.; Sudha, P.N. Studies on removal of Cr(VI) and Cu(II) ions using chitosan grafted-polyacrylonitrile. Arch. Appl. Sci. Res. 2011, 3, 424–435. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.; Liang, H.; Chen, W.; Wang, Z. Synthesis and adsorption behavior of chitosan-coated MnFe2O4 nanoparticles for trace heavy metal ions removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 285, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonetti, C.; Ferrero, F.; Periolatto, M.; Vineis, C.; Varesano, A.; Mazzuchetti, G. Chitosan coated cotton textiles for copper and chromium ions adsorption. In Proceedings of the XIIIth International Izmir Textile and Apparel Symposium, Izmir, Turkey, 2–5 April 2014; pp. 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, L.; Chen, N.; Feng, C.; Zhanga, J.; Li, M. Heavy metal ions removal from aqueous solution by xanthate-modified cross-linked magnetic chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) particle. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 27992–28000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutirman, Z.A.; Sanagi, M.M.; Abd Karim, K.J.; Wan, I.W.A.; Hadi, J.B. Equilibrium, kinetic and mechanism studies of Cu(II) and Cd(II) ions adsorption by modified chitosan beads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trikkaliotis, D.G.; Christoforidis, A.K.; Mitropoulos, A.C.; Kyzas, G.Z. Adsorption of copper ions onto chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) beads functionalized with poly(ethylene glycol). Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 234, 115890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zare, H.; Taleghanib, H.G.; Khanjani, J. Efficient removal of copper ion from aqueous solution using crosslinked chitosan grafted with polyaniline. Int. J. Eng. 2021, 34, 305–312. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, N.A.; Al-Harby, N.F.; Almarshed, M.S. Synthesis and characterization of novel trimellitic anhydride isothiocyanate-cross linked chitosan hydrogels modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes for enhancement of antimicrobial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 132, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, K.; Verma, A.; Verma, L.; Rawat, S.; Singh, J. A novel approach to utilize used disposable paper cups for the development of adsorbent and its application for the malachite green and rhodamine-B dyes removal from aqueous solutions. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2020, 19, 57–70. [Google Scholar]
- Antony, V.S.; Shobana, N.; Durga, S.; Chamarthy, S. Utilization of chitosan coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for chromium removal. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 192. [Google Scholar]
- Soon, C.Y.; Rahman, N.A.; Tee, Y.B.; Talib, R.A.; Tan, C.H.; Abdan, K.; Chan, E.W.C. Electrospun biocomposite: Nanocellulose and chitosan entrapped within a poly (hydroxyalkanoate) matrix for Congo red removal. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 5091–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, R.A.; Alminderej, F.M.; Al-Harby, N.F.; Elmehbad, N.Y.; Mohamed, N.A. Preparation and characterization of a new bis-uracil chitosan-based hydrogel as efficient adsorbent for removal of anionic Congo red dye. Polymers 2023, 15, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harby, N.F.; Almutairi, R.S.; Elmehbad, N.Y.; Mohamed, N.A. A novel O-carboxymethyl chitosan-based hydrogel of an outstanding adsorption performance for removal of cationic Basic Red 12 dye from its aqueous solution. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2023, 63, 2336–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, A.A.; Ahmed, A.M.; Abdel-Rahman, H.H.; Abouzeid, F.M.; Abdel Maksoud, M.O. Removal of nickel ions by adsorption on nano bentonite: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamics. J. Dispersion Sci. Technol. 2017, 38, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najim, T.S.; Elais, N.J.; Dawood, A.A. Adsorption of copper and iron using low cost material as adsorbent. J. Chem. 2009, 6, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barka, N.; Abdennouri, M.; Makhfouk, M.E.; Qourzal, S. Biosorption characteristics of cadmium and lead onto eco-Friendly dried cactus (opuntia ficus indica) cladodes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, B.H.; Ahmad, A.A. Batch adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution by garlic peel, an agricultural waste biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahat, A.; Awual, M.R.; Naushad, M. Functional ligand anchored nanomaterial based facial adsorbent for cobalt(II) detection and removal from water samples. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 271, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awual, M.R. Assessing of lead(III) capturing from contaminated wastewater using ligand doped conjugate adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 289, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, R.; Liu, B.; Chen, X.; Wang, N.; Yang, J. Adsorption of Cu (II) and Co (II) from aqueous solution using lignosulfonate/chitosan adsorbent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, A.; Pagnanelli, F.; Lodi, A.; Solisio, C.; Vegliò, F. Biosorption of heavy metals by sphaerotilus natans: An equilibrium study at different pH and biomass concentrations. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 60, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babel, S.; Kurniawan, T.A. Cr (VI) removal from synthetic wastewater using coconut shell charcoal and commercial activated carbon modified with oxidizing agents and/or chitosan. Chemosphere 2004, 54, 951–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, N.A.; Al-Harby, N.F.; Almarshed, M.S. Effective removal of Basic red 12 dye by novel antimicrobial trimellitic anhydride isothiocyanate-cross linked chitosan hydrogels. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2021, 29, S274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ola, A. Kinetic and isotherm studies of copper (II) removal from wastewater using various adsorbents. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2007, 33, 125–143. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Teo, T.T.; Balasubramanian, R.; Joshi, U.M. Application of sargassum biomass to remove heavy metal ions from synthetic multimetal solutions and urban storm water runoff. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.J.; Yu, X.Y.; Luo, T.; Jia, Y.; Liu, J.H.; Huang, X.J. Γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles encapsulated millimeter-sized magnetic chitosan beads for removal of Cr (VI) from water: Thermodynamics, kinetics, regeneration, and uptake mechanisms. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 2013, 58, 3142–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Ying, D.; Liang, X.; Zhu, M.; Lin, X.; Xu, Q.; Cai, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L. A novel cationic polyelectrolyte microsphere for ultrafast and ultra-efficient removal of heavy metal ions and dyes. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 410, 128404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngueagni, P.T.; Woumfo, E.D.; Kumar, P.S.; Siéwé, M.; Vieillard, J.; Brun, N.; Nkuigue, P.F. Adsorption of Cu(II) ions by modified horn core: Effect of temperature on adsorbent preparation and extended application in river water. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 298, 112023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.W.; Qi, P.Y.; Feng, Q.C.; Hua, X.G.; Jie, H.J.; Liang, Z.C.; Lai, B. Enhanced adsorption/photocatalytic removal of Cu(II) from wastewater by a novel magnetic chitosan and bismuth tungstate coated by silver (MCTS-Ag/Bi2WO6) composite. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.H.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.L. Competitive adsorption of Pb(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II) onto xanthate-modified magnetic chitosan. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 221–222, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannamba, B.; Reddy, K.L.; AppaRao, B.V. Removal of Cu(II) from aqueous solutions using chemically modified chitosan. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, F.; Mohammadzai, I.U.; Khan, A.; Shah, Z.; Hassan, W.; Ali, N. Removal of toxic metals with activated carbon prepared from Salvadora persica. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 2205–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguayo-Villarreal, I.; Muñiz-Valencia, B.P.A.A.R. Preparation of activated carbons from pecan nutshell and their application in the antagonistic adsorption of heavy metal ions. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 230, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Samples | Trimellitic Anhydride Chloride (mmol) | Ammonium Thiocyanate (mmol) | Chitosan (mmol) | Elemental Analysis (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | N | O | S | ||||
| Chitosan | - | - | - | 45.10 | 6.77 | 8.43 | 39.70 | - |
| H1 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 40 | 46.61 | 5.48 | 7.86 | 36.81 | 3.24 |
| H2 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 40 | 47.54 | 4.68 | 7.51 | 35.03 | 5.24 |
| Kinetic Models | Parameters | H1 | H2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| qe.exp (mg g−1) | 96.2 | 97.59 | |
| Pseudo- first-order | R2 | 0.645 | 0.944 |
| qe.cal (mg g−1) | 3.043 | 1.98 | |
| k1 (min−1) | 0.0151 | 0.0166 | |
| Δq | 47.14 | 52.23 | |
| Pseudo- second-order | R2 | 0.999 | 1 |
| qe.cal (mg g−1) | 98.04 | 99.01 | |
| k2 (10−5) | 0.005 | 0.0146 | |
| (g mg−1 min−1) | |||
| Δq | 3.2 | 2.93 | |
| Elovich | R2 | 0.722 | 0.979 |
| β (g mg−1) | 0.361 | 0.698 | |
| α (1013) | 2.714 | 1.105 × 1015 | |
| (mg g−1 min−1) | |||
| Δq | 85.44 | 42.64 | |
| Intraparticle diffusion | R2 | 0.778 | 0.967 |
| k (mg g−1 min−1/2) | 0.853 | 0.446 | |
| Δq | 89.79 | 93.47 | |
| Models | Parameter | H1 | H2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | qmax (mg g−1) | 2500 | 227.27 |
| RL | 0.333–0.833 | 0.357–0.833 | |
| KL (L mg−1) | 0.002 | 0.068 | |
| R2 | 0.014 | 0.744 | |
| Freundlich | 1/n | 0.969 | 0.681 |
| Kf (mg g−1) | 6.33 | 18.05 | |
| R2 | 0.965 | 0.952 | |
| Temkin | B (kJ mol−1) | 62.7 | 44.02 |
| KT (L g−1) | 2.921 | 1.066 | |
| R2 | 0.802 | 0.843 | |
| D-R | qm (mg g−1) | 113.52 | 101.19 |
| E kJ mol−1 | 0.408 | 0.845 | |
| B × 10−6 | 3 | 0.7 | |
| R2 | 0.785 | 0.765 |
| Adsorbent | Adsorption Capacity (mg g−1) | Temperature (°C) | Metal Conc. (mg L−1) | Adsorbent Dose (g) | pH | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-linked chitosan grafted with polyaniline | 131.58 | 20–40 | 100 | 0.05 | 6 | [42] |
| Quaternized chitosan@chitosan cationic polyelectrolyte microsphere | 687.6 | 25 | 0–2000 | 0.075 | 5 | [62] |
| Horn Core calcined at 400 °C (P400) | 99.98 | 25 | 100–500 | 0.02 | 5 | [63] |
| Magnetic chitosan@bismuth tungstate coated by silver (MCTS-Ag/ Bi2WO6) | 181.8 | 20–40 | 20 -120 | 0.02 | 6 | [64] |
| Xanthate-modified magnetic chitosan | 34.5 | 25 | 100 | - | 5 | [65] |
| Epichlorohydrin cross-linked xanthate chitosan | 43.47 | 50 | 100 | - | 5 | [66] |
| Medicinal plant (Salvadora persica) | 74.30 | 25 | 100 | - | 4 | [67] |
| Pecan nutshell (Carya illinoinensis) | 23.37 | 30 | - | - | 5 | [68] |
| H1 | 96.20 | 25 | 100 | 0.01 | 6 | Present study |
| H2 | 97.59 | 25 | 100 | 0.01 | 6 | Present study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Harby, N.F.; Alrasheedi, M.; Mohammed, A.e.M.E.; Soliman, S.M.A.; Mohamed, N.A. Effective Removal of Cu(II) Ions from Aqueous Solution by Cross-Linked Chitosan-Based Hydrogels. Water 2024, 16, 2324. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162324
Al-Harby NF, Alrasheedi M, Mohammed AeME, Soliman SMA, Mohamed NA. Effective Removal of Cu(II) Ions from Aqueous Solution by Cross-Linked Chitosan-Based Hydrogels. Water. 2024; 16(16):2324. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162324
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Harby, Nouf F., Muneera Alrasheedi, Ard elshifa M. E. Mohammed, Soliman M. A. Soliman, and Nadia A. Mohamed. 2024. "Effective Removal of Cu(II) Ions from Aqueous Solution by Cross-Linked Chitosan-Based Hydrogels" Water 16, no. 16: 2324. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162324
APA StyleAl-Harby, N. F., Alrasheedi, M., Mohammed, A. e. M. E., Soliman, S. M. A., & Mohamed, N. A. (2024). Effective Removal of Cu(II) Ions from Aqueous Solution by Cross-Linked Chitosan-Based Hydrogels. Water, 16(16), 2324. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162324






