Cobalt-Based MOF Material Activates Persulfate to Degrade Residual Ciprofloxacin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instruments, and Experimental Reagents
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. ZIF-67(Co) Material Preparation
2.2.2. Material Characterization
2.2.3. ZIF-67(Co) Activated Persulfate for Removal of Ciprofloxacin
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of ZIF-67(Co) Material
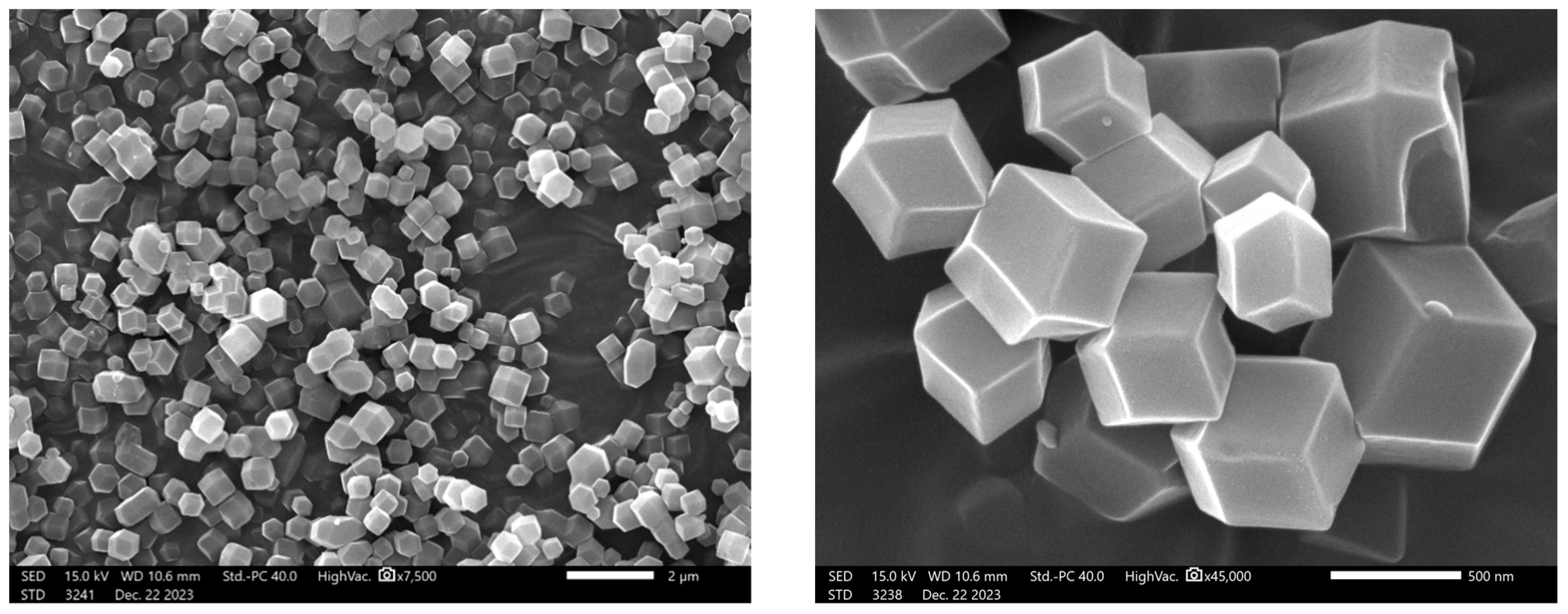
3.1.1. SEM Characterization
3.1.2. XRD Characterization
3.1.3. FT-IR Characterization
3.1.4. XPS Characterization
3.2. ZIF-67(Co)/PMS System for CIP Removal
3.2.1. Adsorption Efficiency of ZIF-67(Co) on CIP
3.2.2. PMS Degradation Capability on CIP
3.2.3. Degradation of Ciprofloxacin by ZIF-67(Co)/PMS System
3.3. Impact of ZIF-67(Co) Dosage on Experimental Results
3.4. Impact of PMS Dosage on Experimental Results
3.5. Impact of pH Conditions on CIP Degradation
3.6. Impact of Anions on Experimental Outcomes
3.7. Impact of Different Environment Water
3.8. Degradation Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zou, M.; Tian, W.; Zhao, J.; Chu, M.; Song, T. Quinolone antibiotics in sewage treatment plants with activated sludge treatment processes: A review on source, concentration and removal. Process. Saf. Environ. 2022, 160, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Ying, G.G.; Pan, C.G.; Liu, Y.S.; Zhao, J.L. Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China: Source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6772–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Zhao, H.X.; Wang, Y.; Xie, H.J.; Zhu, M.H.; Chen, J.W. Presence and environmental risk assessment of selected antibiotics in coastal water adjacent to mariculture areas in the Bohai Sea. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2019, 177, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Du, Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.Q.; Li, E.H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.L. Occurrence and ecological hazard assessment of selected antibiotics in the surface waters in and around Lake Honghu, China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 609, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Zheng, H.L.; Li, H.; Sun, Y.J.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, C. Magnetic nickel cobalt sulfide/sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate with excellent ciprofloxacin adsorption capacity and wide pH adaptability. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 127208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, N.; Nadeem, R.; Ai Musaimi, O. Photocatalytic Degradation of Antibiotics via Exploitation of a Magnetic Nanocomposite: A Green Nanotechnology Approach toward Drug-Contaminated Wastewater Reclamation. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 7986–8004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golmohammadi, M.; Hanafi-Bojd, H.; Shiva, M. Photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin antibiotic in water by biosynthesized silica supported silver nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 7717–7726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, S.A.; Shnain, Z.Y.; Ibrahim, S.S.; Majdi, H.S. Photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin by UV light using n-doped TiO2 in suspension and coated forms. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Sun, S.; Geng, J.; Ma, L.; Jiang, J.; Li, B.; Yabo, S.D.; Lu, L.; Fu, D.; Shen, J. Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment of quinolone antibiotics in municipal sewage sludges throughout China. J. Hazard Mater. 2023, 453, 131322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, N.; Pereira, R.; Abrantes, N.; Pereira, J.; Gonçalves, F.; Marques, C.R. Ecotoxicological effects of ciprofloxacin on freshwater species: Data integration and derivation of toxicity thresholds for risk assessment. Ecotoxicology 2012, 21, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Feng, C.; Bi, Z.; Islam, A.; Cai, Y. Toxicity effects of ciprofloxacin on biochemical parameters, histological characteristics, and behaviors of Corbicula fluminea in different substrates. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 23700–23711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayri-Senel, T.; Kahraman, E.; Sezer, S.; Erdol-Aydin, N.; Nasun-Saygili, G. Photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin from water with waste polystyrene and TiO2 composites. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadmoazzam, M.; Takdastan, A.; Neisi, A.; Ahmadi, M.; Babaei, A.; Jorfi, S. Photocatalytic removal of ciprofloxacin antibiotic from aqueous medium by applying AgI/Ag2O nanocomposite: Activity test, reaction kinetics, and catalyst reusability. Environ. Health Eng. Manag. J. 2022, 9, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoon, B.L.; Ong, C.C.; Mohamed Saheed, M.S.; Show, P.L.; Chang, J.S.; Ling, T.C.; Lam, S.S.; Juan, J.C. Conventional and emerging technologies for removal of antibiotics from wastewater. J. Hazard Mater. 2020, 400, 122961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.H.; Wang, F.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.T. The adsorption performance of tetracyclines on magnetic graphene oxide: A novel antibiotics absorbent. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 475, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Chen, Z.L.; Shen, J.M.; Kang, J.; Zhang, X.L.; Li, J.; Zhao, X. Effect of carbon source on pollutant removal and microbial community dynamics in treatment of swine wastewater containing antibiotics by aerobic granular sludge. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaffney, V.D.; Cardoso, V.V.; Benoliel, M.J.; Almeida, C.M.M. Chlorination and oxidation of sulfonamides by free chlorine: Identification and behaviour of reaction products by UPLC-MS/MS. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, Q.; Addo-Bankas, O.; Ji, B.; Yuan, Y.; Wei, T.; Esteve-Núñez, A. A review on antibiotics removal: Leveraging the combination of grey and green techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltran, F.J.; Aguinaco, A.; García-Araya, J.F.; Oropesa, A.J.W.R. Ozone and photocatalytic processes to remove the antibiotic sulfamethoxazole from water. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3799–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, R.; Chai, L.; Tang, C.; Li, B.; Yang, Z. Comparison of the degradation of molecular and ionic ibuprofen in a UV/H2O2 system. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 2174–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.U.; Gul, N.S.; Sabahat, S.; Sun, J.Y.; Tahir, K.; Shah, N.S.; Muhammad, N.; Rahim, A.; Imran, M.; Iqbal, J.; et al. Removal of organic pollutants through hydroxyl radical-based advanced oxidation processes. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2023, 267, 115564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Dai, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Y.; Ouyang, D. Metronidazole degradation by UV and UV/H2O2 advanced oxidation processes: Kinetics, mechanisms, and effects of natural water matrices. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.B.; Ren, X.; Duan, X.Y.; Sarmah, A.K.; Zhao, X.S. Remediation of environmentally persistent organic pollutants (POPs) by persulfates oxidation system (PS): A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 160818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.P.; Yang, Y.Y.; Duan, X.G.; Wang, S.B. Oxidative polymerization versus degradation of organic pollutants in heterogeneous catalytic persulfate chemistry. Water Res. 2024, 255, 121485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Mishra, I.M.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Kumar, V. Oxidative removal of Bisphenol A by UV-C/peroxymonosulfate (PMS): Kinetics, influence of co-existing chemicals and degradation pathway. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 276, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Wang, L.; Peng, L.B.; Deng, Y.R.; Deng, D.Y. A combo system consisting of simultaneous persulfate recirculation and alternating current electrical resistance heating for the implementation of heat activated persulfate ISCO. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Huo, Y.; Lu, W.; Shen, X.; Xu, L. A comparative study of sulfite activation using different transition metal ions for the degradation of bisphenol A. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouzesh, M.; Ebadi, A.; Abedini, F. Thermocatalytic persulfate activation for metronidazole removal in the continuous operation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 258, 118055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Xie, C.; Alhassan, S.I.; Huang, S.; Chen, R.; Xiang, S.; Wang, Z.; Huang, L. Oxygen reduction reaction in the field of water environment for application of nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Zhang, H.; Chen, F.; Wang, Z.; Huang, L. Applications of single atom catalysts for environmental management. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, M.; Gao, M.; Wang, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Wang, Z.; Shen, B. Metal-catechol group modified Zr-based MOFs for efficient SO2 trapping: GCMC and DFT study. Fuel 2024, 370, 131853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Shan, F.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Liu, M. Efficient decontamination of tetracycline via fenton-like process mediated by chitosan-based Fe-MOFs under wide pH range. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 344, 127212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Feng, M.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Yang, S. CdS QDs interspersed onto MOF-808 as adsorptive photocatalyst for efficient visible-light driven degradation of ciprofloxacin. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 988, 174247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghir, S.; Zhang, S.J.; Wang, Y.Q.; Fu, E.F.; Xiao, Z.G.; Zahid, A.H.; Pu, C.K. Review, recent advancements in zeolitic imidazole frameworks-67 (ZIF-67) and its derivatives for the adsorption of antibiotics. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Guo, X.; Li, J. From nano- to macroarchitectures: Designing and constructing MOF-derived porous materials for persulfate-based advanced oxidation processes. Chem. Commun. 2024, 60, 4395–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Hu, R.; Zhang, J.; Hou, T.; Li, F. Two-dimensional metal-organic framework nanozyme-mediated portable paper-based analytical device for dichlorophen assay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 255, 116271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, M.; He, R.; Zhou, J.; Fei, H.; Yang, K. Thermal conductivity enhancement and shape stability of composite phase change materials using MIL-101(Cr)-NH2/expanded graphite/multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Energy Storage 2024, 86, 111244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihsan, U.; Muhammad, T.; Mamriz, M.; Jehangeer, K.; Abdur, R.; Zuhairi, A.A. UV photocatalytic remediation of Methyl Red in aqueous medium by sulfate (SO4•−) and hydroxyl (•OH) radicals in the presence of Fe2+and Co@TiO2 NPs photocatalysts. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 679, 132614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W. Research on Efficient Enzyme Fixation Method and Analytical Application Based on Metal Organic Skeleton and Its Derivative Materials. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijng, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Ma, H.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Chen, C.; Shi, S.; Qu, M.; Feng, N.; Xu, J. Efficient oxidation of ethylbenzene catalyzed by cobalt zeolitic imidazolate framework ZIF-67 and NHPI. J. Energy Chem. 2014, 23, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.F.; Sherman, E.; Vajo, J.J. Aqueous room temperature synthesis of cobalt and zinc sodalite zeolitic imidizolate frameworks. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 5458–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, H.; Xie, T.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Q.; Yang, J.; Cao, L.; Yang, J. Highly efficient Hg2+ removal via a competitive strategy using a Co-based metal organic framework ZIF-67. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 119, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Chen, W.; Ivey, D.G. Rock Salt−Spinel Structural Transformation in Anodically Electrodeposited Mn−Co−O Nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 1941–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreca, D.; Massignan, C.; Daolio, S.; Fabrizio, M.; Piccirillo, C.; Armelao, L.; Tondello, E. Composition and Microstructure of Cobalt Oxide Thin Films Obtained from a Novel Cobalt(II) Precursor by Chemical Vapor Deposition. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castner, D.G.; Watson, P.R.; Chan, I.Y. X-ray absorption spectroscopy, x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and analytical electron microscopy studies of cobalt catalysts. 1. Characterization of calcined catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. 1989, 93, 3188–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, J.; Xing, L.; Li, J.; Xu, M.; Pan, G.; Li, J. Superoxide radical mediated persulfate activation by nitrogen doped bimetallic MOF (FeCo/N-MOF) for efficient tetracycline degradation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 282, 120124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Lin, Q.; Zheng, J.; Fu, H.; Xu, K.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; He, J. Peroxydisulfate activation by nano zero-valent iron graphitized carbon materials for ciprofloxacin removal: Effects and mechanism. J. Hazard Mater. 2022, 437, 129392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Peng, T.; Zhang, X. Effect of graphitic carbon nitride microstructures on the activity and selectivity of photocatalytic CO2 reduction under visible light. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H. Degradation of clofibric acid in aqueous solution by an EC/Fe3+/PMS process. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 244, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Li, Z.; Cheng, F.; Dai, X.; Wang, H.; Luo, Y.; Huang, L. Advances in the Degradation of Emerging Contaminants by Persulfate Oxidation Technology. Water Air Soil Poll. 2023, 234, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Su, R.; Yao, H.; Zhang, A.; Xiang, S.; Huang, L. Degradation of trimethoprim by sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation processes: Kinetics, mechanisms, and effects of natural water matrices. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 62572–62582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Pignatello, J.J.; Ma, J.; Mitch, W.A. Comparison of halide impacts on the efficiency of contaminant degradation by sulfate and hydroxyl radical-based advanced oxidation processes (AOPs). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2344–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Wan, J.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Z.; Ma, Y.J.C.E.J. Activation of persulfate by molecularly imprinted Fe-MOF-74@ SiO2 for the targeted degradation of dimethyl phthalate: Effects of operating parameters and chlorine. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 422, 130406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Name | Model | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| Digital magnetic stirrer | ZGCJ-3A | Shanghai Zigui Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| Ultra-pure water purifier | UPT-11-40 | Chengdu Youpu Instrument Equipment Co., Ltd., Chengdu, China |
| Vacuum drying oven | DZ-2BCIV | Tianjin Test Instrument Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China |
| Desktop high-speed centrifuge | TG16-WS | Hunan Xiangyi Centrifuge Instrument Co., Ltd., Changsha, China |
| Electronic balance | DHG-9023A | Shanghai Precision Experimental Equipment Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| Digital acidity meter | PHS-3E | Shanghai Yidian Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| Fourier transform infrared spectrometer | NICOLET iS20 | Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA |
| XRD | MiniFlex600 | Rigaku, Tokyo, Japan |
| SEM | JSM-7610FPlus | Jeol, Tokyo, Japan |
| UV visible spectrophotometer | UV-2700i | Shimadzu Instrument Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan |
| Pipette | 100–1000 μL | Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA |
| Name | Chemical Formula or Abbreviation | Specifications | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cobalt Nitrate Hexahydrate | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | 99% | Shanghai McLean Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| 2-Methylimidazole | 2-MI | 98% | |
| Potassium Monopersulfate | PMS | AR | |
| Cobalt Nitrate Hexahydrate | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | ≥88.5% | |
| Methanol | MeOH | Analytical Reagent (AR) | China National Pharmaceutical Group Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| Hydrochloric Acid | HCl | AR | |
| Sodium Hydroxide | NaOH | AR | |
| Potassium Nitrate | KNO3 | AR | |
| Potassium Sulphate | K2SO4 | AR | |
| Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride | C17H18FN3O3·HCl | AR | Beijing Solaibao Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China |
| Potassium Chloride | KCl | AR | Tianjin Hengxing Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Y.; Su, R. Cobalt-Based MOF Material Activates Persulfate to Degrade Residual Ciprofloxacin. Water 2024, 16, 2299. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162299
Luo Y, Su R. Cobalt-Based MOF Material Activates Persulfate to Degrade Residual Ciprofloxacin. Water. 2024; 16(16):2299. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162299
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Yiting, and Rongkui Su. 2024. "Cobalt-Based MOF Material Activates Persulfate to Degrade Residual Ciprofloxacin" Water 16, no. 16: 2299. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162299
APA StyleLuo, Y., & Su, R. (2024). Cobalt-Based MOF Material Activates Persulfate to Degrade Residual Ciprofloxacin. Water, 16(16), 2299. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162299







