Abstract
Anaerobic wastewater treatment technology has been intensively and extensively investigated in the industry and scientific research. Inspired by the advantages of multi-stage and multi-phase anaerobic reactor technology (SMPA) in recent years, a three-stage anaerobic reactor (3S-AR) was designed and applied to treat poplar chemical–mechanical pulp wastewater, and various operation parameters, including the volume loading rate (VLR), hydraulic retention time (HRT), ascending velocity, reflux ratio, pH and temperature of the 3S-AR, were optimized to evaluate the reactor’s removal efficiency for poplar wastewater. The properties of anaerobic granular sludge and the composition of wastewater were also characterized to assess microorganism growth and pollutant migration. Results show that the COD removal rate was over 75% with a volume loading rate range of 15–25 gCOD/(L·d) in the 3S-AR; the hydraulic retention time was also found to be an important factor affecting the performance of the 3S-AR reactor. The volume loading rate and degradation efficiency of the 3S-AR reactor are higher than those of the up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor. Microorganism separation can be achieved in the 3S-AR, which is conducive to the growth and methanogenesis activity of bacteria, thereby leading to enhanced removal and buffering efficiency. After treatment in the 3S-AR, the main pollutants of poplar wastewater were benzene aromatic acids and long-chain esters, which do no biodegrade easily; in contrast, most of the fatty acid substances with small molecules were completely degraded.
1. Introduction
The papermaking industry is a significant contributor to global economic development, providing essential materials for various applications ranging from packaging to printing [1,2,3]. However, large quantities of wastewater were produced during the pulping process, and the wastewater typically contains a variety of organic and inorganic substances, including lignin, cellulose, hemicellulose, resins, solvents, dyes, bleaching agents, and suspended solids [4,5,6]. Without proper treatment, the discharge of untreated or inadequately treated papermaking wastewater can have severe environmental and public health implications [7,8,9].
Effective treatment of papermaking wastewater is essential to mitigate these environmental and health risks [10,11,12,13]. Anaerobic biological treatment has emerged as a promising approach for the remediation of papermaking wastewater, offering numerous advantages over conventional treatment methods [14,15]. This method harnesses the metabolic activity of anaerobic microorganisms to degrade organic pollutants present in wastewater, converting them into methane and carbon dioxide gases [16,17,18]. The utilization of anaerobic processes in papermaking wastewater treatment has gained traction due to its potential for energy recovery, reduced sludge production and low cost [19,20].
In recent years, significant advancements have been made in the application of anaerobic bioreactors for papermaking wastewater treatment [21,22,23,24]. Various reactor configurations, such as anaerobic baffled reactors (ABRs), upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactors, and anaerobic sequencing batch reactors (ASBRs), have been investigated for their efficacy in treating papermaking effluents [25,26]. These reactors offer different operational advantages and performance characteristics, allowing for flexibility in system design and optimization. Parameters such as temperature, pH, organic loading rate, hydraulic retention time, nutrient availability, and mixing significantly influence the performance and efficiency of anaerobic reactors. However, their implementation faces several hurdles that hinder efficient treatment. These challenges span various aspects, including the intricate composition of the wastewater, substrate inhibition, slow reactor start-up, volatile fatty acid accumulation, foaming and scum formation, and nutrient limitations [27,28,29,30,31]. Overcoming these obstacles demands a holistic understanding of the interplay between wastewater properties, microbial communities, and reactor dynamics.
The design of anaerobic reactors tailored to the specific characteristics of water quality is essential for achieving efficient and effective treatment of wastewater [30,32]. Anaerobic reactors operate based on complex microbial processes that are influenced by the composition of the wastewater feedstock [33,34]. Ghosh [35] proposed the concept of two-phase separation in anaerobic bioreactors, which involves two independently operated reactors connected in series. Each reactor is controlled according to the optimal growth conditions for either acid-producing fermentation bacteria or methanogens, allowing each type of microbial community to maximize its metabolic function. Practically, two-phase separation has been shown to significantly reduce acidification issues caused by acid accumulation in traditional processes, which provides suitable environmental and operational conditions for each phase, thereby enhancing operational stability, pH resilience, tolerance to toxins, organic load rate, methane content in biogas, and overall treatment efficiency. However, the two-phase separation process only separates acidifying bacteria and methanogens. Even in methanogens, there are significant physiological differences between species. Housing microorganisms with such diverse characteristics in the same phase still compromises some of their functions. Therefore, further separation of biological phases could improve wastewater treatment efficiency and stability.
Herein, a three-stage anaerobic reactor (3S-AR) was designed and applied to treat poplar P-RC APMP wastewater. The operation parameters of the reactor and sludge property were studied. The pollutant migration and degradation of the wastewater were detected, and the compositions of the APMP wastewater before and after the treatment were also analyzed by GC-MS spectra. This result shows that the 3S-AR system has excellent performance in the treatment of industrial wastewater.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characteristics of Poplar P-RC APMP Wastewater
The wastewater utilized in this investigation was obtained from the pulping process of an integrated coated paper mill. Table 1 presents the primary pollution characteristics of the wastewater.

Table 1.
Characteristics of poplar P-RC APMP effluent.
2.2. 3S-AR and UASB Reactor
The anaerobic degradation process of organic particulate matter is roughly divided into hydrolysis, acidogenesis, and methanogenesis stages. To achieve phase separation and higher pollutant efficiency for the poplar APMP wastewater with a high concentration, the 3S-AR reactor was tailored according to muti-phase anaerobic theory. The 3S-AR (Figure 1a) was composed of three cylindrical reaction units connected to each other in sequence. The first and second reactors were made of quartz glass, each with an effective volume of 360 mL, diameter of 44.6 mm and height of 230 mm. The diameter and height of third reactor were 44.6 mm and 460 mm, respectively, with an effective volume of 720 mL. The total effective volume of the 3S-AR was 1440 mL. Additionally, the UASB reactor (Figure 1b) consisted of a common single-stage cylindrical column with a diameter of 44.6 mm and a height of 230 mm, possessing an effective volume of 360 mL. Both reactors were equipped with water jackets to regulate temperature.

Figure 1.
Experimental apparatus of 3S-AR (a) and UASB reactor (b) in laboratory.
2.3. Startup of 3S-AR and UASB Reactors
The inoculated sludge with a black color was taken from the remaining granular sludge of the internal circulation (IC) reactor of a brewery in Nanjing, which was then poured into the reactor for inoculation. The diameter size of the sludge ranged from 0.5 mm to 2 mm, with a specific gravity of 1.065 kg/L. The total suspended solid (TSS) and volatile suspended solid (VSS) of the sludge were 97.34 g/L and 55.51 g/L, with a VSS-to-TSS ratio of 0.570.
In the 3S-AR system, seed sludges of 110 mL, 130 mL and 280 mL were successively subjected to the first, second, and third unit reactors in sequence. Conversely, 130 mL of seed sludge was added to the UASB reactor. The volume loading rate of the setup reactor was regulated by modulating the influent COD concentration, maintaining a COD:N:P ratio of 400:5:1, respectively. The initial COD of influent was maintained at approximately 1500 mg/L, with a volume loading rate of ca. 1 gCOD/(L·d). As the COD removal rate was higher than 40% with a VFA value lower than 10 mmol/l, the volume loading rate increased by 20–30% with increased COD concentration during each adjustment phase. The changes in volume loading rate, pH, VFA and their impact during the start-up of the reactor were monitored until the completion of sludge acclimation. When VFA in the 3S-AR reactor was higher than 15 mmol/L, the reactor volume loading rate was reduced until the sludge acclimation was completed. For the UASB reactor, the sludge acclimation was considered to be completed when the reactor volume loading rate reached 5 gCOD/(L·d) with a stable COD removal rate. The volume loading rate (VLR) was determined using the following formula:
where Q represents the volume of wastewater entering the reactor per unit time (m3/d), S0 represents the influent COD concentration (mg/L or kg/m3), and V represents the total volume of the reactor (L).
2.4. Experimental Parameters
After complete acclimation of the sludge, the experiments of 3S-AR and UASB for the poplar APMP wastewater were performed. The efficiencies of the 3S-AR reactor and UASB reactor were evaluated under different process conditions, which are shown in Table 2. The tests ran for 6 days with the volume loading rate adjustment. When the process parameter was changed, the tests were first ran for 3 days, and the formal test was carried out after the operating data were stable.

Table 2.
Conditions of lab tests in treatment of poplar effluent by 3S-AR.
2.5. Characterization
Chemical oxygen demand (COD) is typically measured using the dichromate method. BOD is determined by measuring the oxygen consumption of microorganisms during the biological degradation of organic matter in the wastewater sample over a specific incubation period. Suspended solids (SS) and total suspended solids (TSS) are typically measured using gravimetric methods, where the suspended solids are separated from the wastewater sample by filtration and then dried and weighed. Volatile fatty acids (VFAs) and alkalinity are typically measured by titration with a standardized acid and alkaline solution. The granular sludges were taken from the middle of each unit, and the size of the sludges was measured using a laser particle size analyzer (Mastersizer 2000, Malvern, UK) with a measurement range of 0.02–2000 μm. Anaerobic granular sludge was collected from the reactor and treated with dehydration stepwise. The morphology of the sludge was detected using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The specific methanogenic activity (SMA) of granular sludge was measured according to the previous study [36].
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. The Influence of Operation Parameters of the 3S-AR on the Pollutant Removal
After the completion of reactor startup, the influences of the volume loading rate, influent COD, hydraulic retention time (HRT) and reflux ratio on the degradation efficiency of 3S-AR were assessed; the results are shown in Figure 2 and Table 3. Figure 2a,b illustrate the impact of volume loading rates on COD removal with an influent COD of 7724 mg/L. In the first unit, the COD removal declined quickly with the increasing volume loading rate [37]. In the second unit, the COD removal initially increased slightly and then decreased when the volume loading rate increased to above 22 gCOD/(L·d). Inspiringly, the COD removal in the third unit was stable and even continued to increase given the increased volume loading rate and decreased COD removal in the first unit, indicating a good compensatory effect, and the COD removal rate started to decrease when the volume loading rate was above 25 gCOD/(L·d). The 3S-AR can automatically redistribute the volume loading rate within the system to a certain extent, thereby improving the operational stability of the system. The total COD removal rate of the 3S-AR remained consistently above 75% with volume loading rates between 15 and 28 gCOD/(L·d), only slightly decreasing at 28 gCOD/(L·d) with an HRT of 6.62 h. For subsequent experiments, a volume loading rate of 22 gCOD/(L·d) was selected. Figure 2c,d show the effects of the influent COD concentration on the COD removal efficiency. When the influent COD increased from 5620 mg/L to 9530 mg/L, the COD removal rate decreased slightly. The COD removal efficiency was still as high as 76.68% with the influent COD of 9530 mg/L.
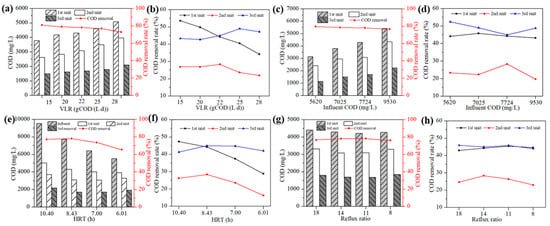
Figure 2.
Effects of volume loading rate (a,b) with influent COD of 7724 mg/L, influent COD (c,d) at HRT of 8.34 h, hydraulic retention time (e,f) and reflux ratio with a volume loading rate of 22 gCOD/(L·d) (g,h) on the COD and COD removal rate of the 3S-AR.

Table 3.
Result of poplar P-RC APMP effluent treatment under different conditions.
As the hydraulic retention time (HRT) decreased, the COD removal rate of the reactor (Figure 2d,e) initially increased and then decreased. A significant drop in COD removal efficiency was observed when the HRT fell below 8.43 h. Therefore, an optimal influent COD concentration and hydraulic retention time is crucial for a specific volume loading rate. For instance, when the volume loading rate is 22 gCOD/(L·d), the ideal influent COD concentration and HRT to maximize efficiency were found to be 7724~9530 mg/L and 8.43~10.4 h, respectively. Under the same volume loading rate, a higher inlet COD concentration resulted in better effluent COD removal efficiency, underscoring the importance of sufficient contact time between pollutants and microorganisms [38,39]. Experimental analysis indicates that the 3S-AR can maintain high COD removal efficiency with increased volume loading rate at a suitable hydraulic retention time. Each unit in the 3S-AR plays a distinct role, rather than merely being physically connected, in the pollutant degradation process. Over time, microbial colonies adapted to specific substrates develop in each unit, enabling biological phase separation and supporting the reactor’s efficient and stable operation.
As illustrated in Figure 2g,h, the ascending velocity and reflux ratio significantly influenced the different units of the 3S-AR. A higher reflux ratio and rising flow rate notably affected the first unit, which was due to the higher COD concentration of the influent and larger gas production in the first unit [40]. In contrast, the influence of reflux ratio on the second unit was different from that of the first unit, and the COD removal of second unit increased initially and then decreased even the continuous decreased COD removal of the first unit, indicating that the reflux ratio has a certain impact on the transition phase to the second unit. Interestingly, the effect of the reflux ratio on the third unit can be neglected, and the COD removal fluctuates within a small range with the increase in rising flow rate and reflux ratio.
Figure 3a demonstrates the 3S-AR system’s excellent performance in treating P-RC APMP wastewater, achieving high removal rates for COD (77.86%), BOD (82.09%), SS (54.86%), and TS (53.85%). Accumulation of organic acids, which can lower pH and hinder anaerobic reactions, is common in anaerobic processes. Figure 3b shows a gradual decrease in volatile fatty acids (VFAs) across the three units of the 3S-AR during continuous operation at a volume loading rate of 25 gCOD/(L·d). The VFA levels in the first, second, and third unit were 7.34 mmol/L, 3.62 mmol/L, and 1.78 mmol/L, respectively, indicating a robust and effective system [41]. Concurrently, alkalinity increased across the units, with the lowest levels in the first unit due to higher acid generation, and continuous increases in the second and third units due to VFA consumption and alkaline substance production. The changes in VFAs and alkalinity demonstrates that microorganisms of the wastewater in three units were synergized well with each other, providing a good buffering capacity, stability, and high efficiency of the 3S-AR.
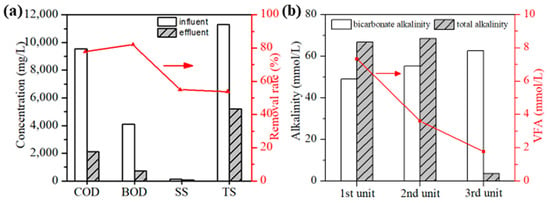
Figure 3.
Degradation effect of poplar APMP effluent through the 3S-AR (a), variation in the VFA and alkalinity (b) in each unit.
A control experiment comparing the 3S-AR to a UASB reactor revealed superior performance of the 3S-AR in treating poplar wastewater. It can be seen from Figure 4a,b that the COD removal rate of the poplar wastewater for 3S-AR was higher than that of UASB under the same volume loading rate. The 3S-AR maintained a high COD removal rate as the volume loading rate increased from 5 gCOD/(L·d) to 25 gCOD/(L·d), only significantly dropping when the volume loading rate reached 28 gCOD/(L·d) due to a low HRT of 6.62 h. In contrast, the COD removal of the UASB reactor remained at over 70% at a volume loading rate lower than 15 gCOD/(L·d) but declined sharply at 20 gCOD/(L·d). When the volume loading rate increased to 28 gCOD/(L·d), the pH and VFA of the effluent through the UASB reactor were 6.2 and over 10.3 mmol/L, respectively, implying that the UASB system was damaged markedly.
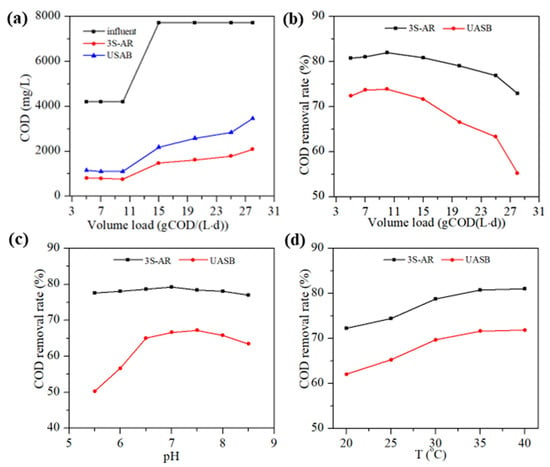
Figure 4.
The effect of volume loading rate (a,b), pH (c) and temperature (d) on the COD removal efficiency through UASB and 3S-AR.
Figure 4c illustrates the pH influence of the poplar PRC-APMP wastewater on the degradation efficiency at a volume loading rate of 20 COD/(L·d) at 37 °C with the ascending velocity of 2.01 m/h. As the influent pH ranged from 5.5 to 8.5, the pH variations in the first, second and third unit (Figure S1) were 5.33–7.46, 6.76–7.85 and 7.59–8.28, respectively. When the influent pH varied from 5.5 to 6.0, the pH of the first unit was affected, but no operating abnormalities occurred. This was mainly due to acid-producing bacteria being the dominant bacteria in the first unit, which could still grow normally in this environment [42]. The pH of the effluent from the second unit reactor rose to above 6.5, thereby avoiding the proliferation of acid-producing species in the subsequent reaction, and the produced alkaline substances could neutralize the acids. When the influent pH was 8.5, the pH of the effluent in the first unit was 7.46 due to hydrolysis and acidification, thus preventing damage from the biochemical process in the second unit. During the pH change process, the COD removal efficiency of the 3S-AR was high, with minimal fluctuation in effluent COD, reflecting its good adaptability to pH changes. The excellent strong buffering capacity of the 3S-AR for pH is mainly due to the biological phase separation achieved by each stage of the three-stage reactor. However, the UASB does not have strong buffering capacity for pH. The COD removal efficiency of UASB decreased significantly when the influent pH was higher than 8.0 and lower than 6.5, dropping to 56.68% when the pH was 6.0. This is mainly owing to various functional microorganisms coexisting in the same reactor and methanogens being very sensitive to environmental pH, with the optimal growth pH being 6.5–7.8. Lower pH inhibits the methanogenesis process, thereby eventually causing decreased pH and rancidity.
The impact of the temperature on the reactor was assessed with a volume loading rate of 15 gCOD/(L·d) and influent COD of 7724 mg/L at an ascending velocity of 2.07 m/h. As shown in Figure 4d, the COD removal rates of the 3S-AR and UASB have a similar trend as the reaction temperature varied from 20 °C to 40 °C, with the COD removal rate of both reactors decreasing synchronously as the temperature dropped. Temperature is a crucial factor in anaerobic reactions [43]. The anaerobic system has been operated at a medium temperature (35 ± 1 °C) for a long time, forming a relatively stable microbial system at this temperature, and a sudden temperature change inevitably affects the degradation efficiency of the system [44]. Notably, the COD removal rate decreased significantly when the system temperature dropped below 30 °C. For the 3S-AR, temporary temperature fluctuations between 35 and 40 °C did not have a major impact on the operation, but the reactor will try to keep the system temperature stable. Considering actual application process fluctuations, the suitable temperature for the 3S-AR is between 35 °C and 38 °C.
3.2. Properties of Granular Sludge
The morphology and performance of the sludge in each unit of 3S-AR were evaluated and are presented in Figure 5. Fresh granular sludge inoculated (Figure 5a) in the three reactor units initially displayed a regular oval or spherical shape with clear boundaries and irregular surfaces featuring gaps and pores, facilitating substrate and metabolite transport into the particles and methane gas escape [45,46]. Over time, the biological phases and microorganisms underwent significant changes. The biological phase of the first unit (Figure 5b) predominantly consisted of rod-shaped bacteria, with a minor number of filamentous bacteria and cocci, which is attributed to the higher organic load and nutrient availability. On the other hand, the sludge in the second-stage (Figure 5c) unit was mainly composed of rod-shaped bacilli and cocci, and the number of filamentous bacteria was higher than that in the first stage unit. As shown in Figure 5d, the filamentous bacteria of the sludge in the third stage unit increased, and the dominant bacteria were rod-shaped bacteria and filamentous bacteria. The filamentous bacteria increased from the first unit to the third unit, owing to the reduction in organic load in wastewater. Herein, it can be considered that rod-shaped and filamentous bacteria play crucial roles in forming granular sludge, creating a network structure that supports the adhesion of other bacteria and inert substrates, promoting granular sludge formation [47,48]. This network structure is similar to the structure of activated carbon, which is conducive to the adsorption of pollutants to the surface of the granular sludge and sequential degradation.
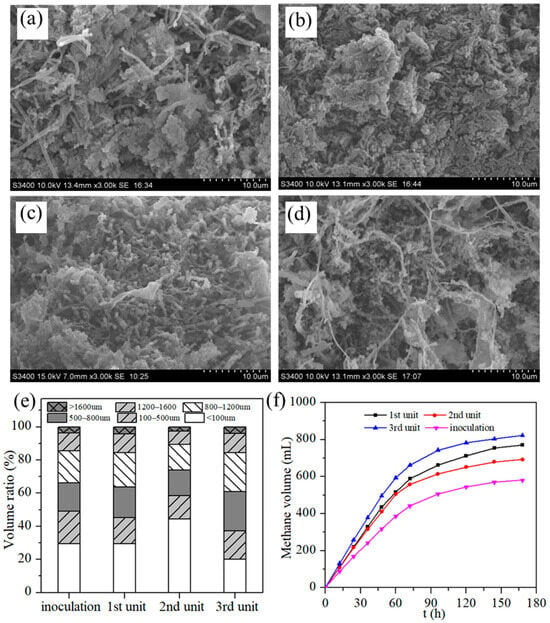
Figure 5.
SEM images of sludge in the inoculation (a), first (b), second (c) and third (d) unit; size distribution (e) and methanogenic performance (f) of the sludge in each unit of 3S-AR.
Granular sludge particle sizes changed notably after various operational processes, including start-up, low-load, high-load, impact-load, and stable operations. The average particle sizes of the sludge (Table S1) in the inoculation, first unit, second unit and third unit were 581 μm, 611 μm, 462 μm and 676 μm, respectively. Compared with inoculated sludge, the average size of sludge more than 500 μm in the first unit increased by 4%, and the sludge with a particle size of more than 1200 μm also increased slightly. The increased size of sludge in the first unit was due to a high-volume loading rate and gas production. Meanwhile, the proportion of sludge with a size less than 100 μm in the secondary sludge significantly increased, which was due to the low COD removal rate gas production. Compared with the sludge of inoculation and second unit, the granular sludge with a particle size less than 100 μm in the third unit decreased by ca. 9% and 24%, and the granular sludge with a particle size greater than 500 μm increased by ca. 10% and 20%, respectively.
The quality of the anaerobic granular sludge can also be evaluated by the specific methanogenic activity (SMA), and the results are shown in Figure 5f and Table 4. The methanogenic activity of the sludge (SMA) can be calculated using the following formula [49,50]:
where R is the methane production rate, V is the reactor liquid volume, and VSS is the sludge concentration; CF is a methane conversion coefficient of 418 mL/g CODCH4. It can be clearly seen that the sludge in the third unit has the highest specific methane production activity, reaching 1.07 gCODCH4/gVSS·d, followed by the first-stage sludge, reaching 0.96 gCODCH4/gVSS·d, indicating that the anaerobic microorganisms in the granular sludge have higher activity.
SMA = (gCODCH4/gVSS·d)

Table 4.
Specific methanogenic activity of sludge.
3.3. Migration of the Pollutant in the Treatment of 3S-AR
The GC-MS spectra of the fresh and treated wastewater are presented in Figure 6a, and the retention time and peak area ratio of main products in the wastewater are also given in Tables S2–S5. The poplar P-RC APMP wastewater contains various fatty acids, aromatic compounds, and other organics. Specially, straight-chain fatty acids with fewer than six carbon atoms, such as acetic, propionic, and butyric acids, comprise approximately 46% of the total organic matter, while benzene-ring-containing fatty acids, such as benzoic and phenylacetic acids, account for ca. 42%. The relative content of straight-chain fatty acids with a C number higher than 8 was 5%, and the relative content of total fatty acids accounted for ca. 94%. The species of the wastewater in the first unit increased due to hydrolysis and acidification. The species and content of the organics in the second and third unit were significantly reduced, and the composition of the effluent through the 3S-AR was mainly composed of the refractory aromatic acid and aromatic phenol. The contents of long-chain fatty acid, benzene-containing aromatic acid, aromatic esters and aromatic phenols were ca. 10%, 28%, 16% and 30%, respectively.
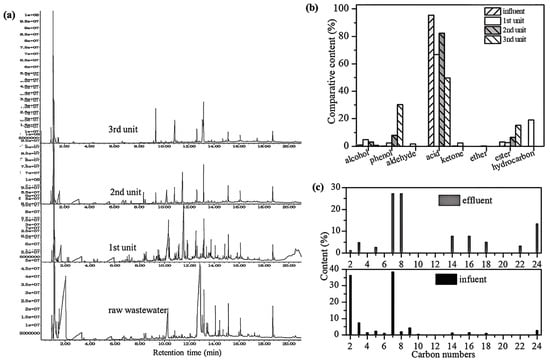
Figure 6.
GC-MS spectra (a), functional groups (b) and carbon numbers (c) variation in raw and treated wastewater.
GC-MS analysis (Figure 6b) revealed carbon atom distribution variations between influent and effluent. The main carbon atoms were C2, C3, C7, and C9, comprising 87% of the total organics, with C2 and C7 each exceeding 35%. Moreover, other carbon atoms, such as C4–C10, C14, C16, and C18, were also presented in the wastewater. The maximum number of carbon atoms was C24, and the organic compounds including C11–C13, C15 and C19–C23 were not detected. The primary carbon atom distributions of organic pollutants (Figure 6b) in the third unit were C7, C8, C14, C16, and C24, contributing to 80% of the total organics. The relative content of C7 and C8 was more than 25%, and the content of C24 was greater than 10%. The composition of residual organic pollutants after anaerobic treatment included methyl phenol (C7), acid (C8) and 1,2-ethylhexyl phthalate (C24), respectively, which all belong to the benzene compounds. The carbon atoms of organics in Poplar P-RC APMP wastewater were mainly less than nine carbons, such as acetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid, and benzoic acid, etc., possessing a better biodegradability of wastewater. Pollutant degradation occurs principally in the third unit, and large numbers of organisms are consumed by microorganisms, producing refractory organics, such as benzene, long-chain fatty acids and esters in the wastewater.
Figure 6c shows the functional group variations in organic compounds in the wastewater. The original poplar P-RC APMP wastewater predominantly contained carboxylic acids, including acetic, propionic, butyric, and benzoic acids. In the first unit, the presence of fatty acids and hydrocarbons indicated macromolecular chain breakage or benzene ring opening through acidification and hydrolysis, forming hydrocarbons. The first unit had the highest diversity of organic functional groups, confirming hydrolysis and the generation of transitional products like hydrocarbons, aldehydes, ketones, and other organic substances. In the second unit, the effluent primarily contained fatty acids, aromatic acids, esters, and phenolics. In the third unit, functional groups were more concentrated, mainly aromatic acids, esters, and phenolics. Combined with the above characterization and analysis, aromatic acids or long-chain esters do not degrade easily, while most of the small-molecular-weight fatty acids can be easily decomposed.
4. Conclusions
A three-stage anaerobic reactor (3S-AR) was designed based on the wastewater properties, microbial communities, and reactor dynamics. The parameters, including the volume loading rate, hydraulic retention time, reflux ratio, ascending velocity, pH, and temperature, must be considered for tailoring the reactor to achieve optimal treatment efficiency. The 3S-AR shows excellent performance in the pollutant removal and impact resistance for the poplar APMP wastewater, mainly due to the separation of microbial phases. Each unit of the 3S-AR served distinct roles: the first unit focused on hydrolysis and acidification, the second on the conversion of organic matter, and the third on methanogenesis. The COD removal rate of 3S-AR is higher than that of UASB. The sludge exhibited a gradual increase in filamentous bacteria across the three stages, and methanogenesis activity increased by 10–28% compared to the inoculated sludge. The macromolecular pollutants were degraded through molecular chain scission, benzene ring opening, and aliphatic ring opening, forming small molecular acid substances that can be directly utilized by methanogens. The primary pollutants of the wastewater through the 3S-AR were benzene-containing organic compounds and long-chain ester substances. The research provides a theoretical basis for designing anaerobic reactors and efficient pollutant degradation.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w16152173/s1: Figure S1: The effect of influent pH on the variations in pH in each unit of 3S-AR; Figure S2: Relationship between fluctuating concentration of influent COD and effluent COD removal ratio in impact load experiment; Table S1: Variation at size distribution of granule sludge; Table S2: Identified products and content by GC-MS of poplar P-RC APMP wastewater; Table S3: Identified products and content by GC-MS of poplar P-RC APMP wastewater in the first unit; Table S4: Identified products and content by GC-MS of poplar P-RC APMP wastewater in the second unit; Table S5: Identified products and content by GC-MS of poplar P-RC APMP wastewater in the third unit.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.D. and Q.T.; methodology, L.D.; software, R.Y. and S.Z.; validation, R.Y. and J.Z.; formal analysis, R.Y. and Q.G.; investigation, L.D.; resources, F.L. and Q.G.; data curation, L.D.; writing—original draft preparation, L.D.; writing—review and editing, Q.T.; visualization, Q.G.; supervision, G.F. and Q.T.; project administration, G.F.; funding acquisition, G.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Biomass Energy and Material (JSBEM-S-202207).
Data Availability Statement
No data were used for the research described in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Qingwen Tian, Fuping Liu, Sophia Zhang and Guigan Fang are employed by the companies. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Dai, M.; Sun, M.; Chen, B.; Shi, L.; Jin, M.; Man, Y.; Liang, Z.; de Almeida, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, P.; et al. Country-specific net-zero strategies of the pulp and paper industry. Nature 2024, 626, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.; Sun, M.; Chen, B.; Xie, H.; Zhang, D.; Han, Z.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y. Advancing sustainability in China’s pulp and paper industry requires coordinated raw material supply and waste paper management. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 198, 107162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, S.; Moharana, S.; Kim, K.H. Cellulose nano-papers: A comprehensive review of their synthesis methods, applications, and influence on the circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 451, 142045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeeli, A.; Sarrafzadeh, M.; Zeighami, S.; Kalantar, M.; Bariki, S.G.; Fallahi, A.; Asgharnejad, H.; Ghaffari, S.-B. A comprehensive review on pulp and paper industries wastewater treatment advances. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 8119–8145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AJagaba; Birniwa, A.; Usman, A.; Mu’azu, N.; Yaro, N.; Soja, U.; Abioye, K.; Almahbashi, N.; Al-dhawi, B.; Noor, A. Trend and current practices of coagulation-based hybrid systems for pulp and paper mill effluent treatment: Mechanisms, optimization techniques and performance evaluation. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 429, 139543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zang, H.; Li, C. Biodegradation characteristics of lignin in pulping wastewater by the thermophilic Serratia sp. AXJ-M: Performance, genetic background, metabolic pathway and toxicity assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 322, 121230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Verma, P. A critical review on environmental risk and toxic hazards of refractory pollutants discharged in chlorolignin waste of pulp and paper mills and their remediation approaches for environmental safety. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, F.; Han, D.; Wan, J.; Wang, G.; Zhu, B.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S. New insights into toxicity reduction and pollutants removal during typical treatment of papermaking wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 915, 169937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Zhao, H.; Wei, G.; Zhu, Y.; Li, T.; Xu, M.; Guo, X.; Shi, H.; Lian, Y.; Liu, H. Sustainable Papermaking in China: Assessing Provincial Economic and Environmental Performance of Pulping Technologies. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 4517–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Srivastava, N.K.; Gera, P. Removal of color from pulp and paper mill wastewater-methods and techniques—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 298, 113527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Kong, M.; Xie, X.; Sun, J.; Wei, D.; Li, A. Feasibility and safety of papermaking wastewater in using as ecological water supplement after advanced treatment by fluidized-bed Fenton coupled with large-scale constructed wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaur, V.; Sharma, P.; Sirohi, R.; Awasthi, M.; Dussap, C.; Pandey, A. Assessing the impact of industrial waste on environment and mitigation strategies: A comprehensive review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 123019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, A.; Bilal, M.; Prasad, S.; Rameshwari, K.; Chandra, R. Paper and pulp mill wastewater: Characterization, microbial-mediated degradation, and challenges. In Nanotechnology in Paper and Wood Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 371–387. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, T.; Edwards, E. Anaerobic digestion of pulp and paper mill wastewater and sludge. Water Res. 2014, 65, 321–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Thakur, I.; Shah, M. Bioremediation approaches for treatment of pulp and paper industry wastewater: Recent advances and challenges. In Microbial Bioremediation & Biodegradation; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, T.; Yu, H. Iron-assisted biological wastewater treatment: Synergistic effect between iron and microbes. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 44, 107610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Su, Z.; Lai, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Insights into the fate and removal of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes using biological wastewater treatment technology. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xu, X.; Wang, H.; Yan, J.; Zhou, X.; Ren, N.; Lee, D.; Chen, C. Biological treatment of refractory pollutants in industrial wastewaters under aerobic or anaerobic condition: Batch tests and associated microbial community analysis. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 17, 100927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Lei, Z.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, Z.; Lee, D. Energy and resource recovery from a future aerobic granular sludge wastewater treatment plant and benefit analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 487, 150558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohra, V.; Ahamad, K.; Kela, A.; Vaghela, G.; Sharma, A.; Deka, B. Energy and resources recovery from wastewater treatment systems. In Clean Energy and Resource Recovery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 17–36. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, C.; Vo, T.; Chen, T. A novel of biohythane gaseous fuel production from pineapple peel waste juice in two-stage of continuously stirred anaerobic bioreactors. Fuel 2020, 279, 118526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Kashif, A.; Rout, P.; Aslam, M.; Fuwad, A.; Choi, Y.; Park, J.; Kumar, G. A brief review of anaerobic membrane bioreactors emphasizing recent advancements, fouling issues and future perspectives. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, S.; Giri, B.; Nitayavardhana, S.; Gadhamshetty, V. Anaerobic bioreactors/digesters: Design and development. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 261–279. [Google Scholar]
- Show, K.; Yan, Y.; Yao, H.; Guo, H.; Li, T.; Show, D.; Chang, J.; Lee, D. Anaerobic granulation: A review of granulation hypotheses, bioreactor designs and emerging green applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 300, 122751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, A.; Bakr, M.; Nasr, M.; Haider, J.; Lim, H.; Qyyum, M.; Lam, S. Economic and environmental sustainability for anaerobic biological treatment of wastewater from paper and cardboard manufacturing industry. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakraoui, M.; El Gnaoui, Y.; Lahboubi, N.; Karouach, F.; El Bari, H. Kinetic study and experimental productions of methane production from UASB reactor treating wastewater from recycled pulp and paper for the continuous test. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 139, 105604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Castillo, A.; Garibay, M.; Senés-Guerrero, C.; Orozco-Nunnelly, D.; de Anda, J.; Gradilla-Hernández, M. A review of the sustainability of anaerobic reactors combined with constructed wetlands for decentralized wastewater treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 371, 133428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wan, N.; Han, H. Effects of methanol, sodium citrate, and chlorella powder on enhanced anaerobic treatment of coal pyrolysis wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 311, 119932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.; Singh, A.; Cheng, L.; Hussain, A.; Maiti, A. Occurrence of antibiotics in wastewater: Potential ecological risk and removal through anaerobic–aerobic systems. Environ. Res. 2023, 226, 115678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozak, M.; Cirik, K.; Başak, S. Treatment of textile wastewater using combined anaerobic moving bed biofilm reactor and powdered activated carbon-aerobic membrane reactor. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliopoulou, A.; Arvaniti, O.; Deligiannis, M.; Gatidou, G.; Vyrides, I.; Fountoulakis, M.A. Stasinakis, Combined use of strictly anaerobic MBBR and aerobic MBR for municipal wastewater treatment and removal of pharmaceuticals. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 343, 118211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, J.; Lohani, S. Design, installation, operation and experimentation of septic tank–UASB wastewater treatment system. Renew. Energy 2019, 143, 1406–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Singh, V.; Ormeci, B.; Hussain, A.; Cheng, L.; Venkiteshwaran, K. Anaerobic–aerobic treatment of wastewater and leachate: A review of process integration, system design, performance and associated energy revenue. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 327, 116898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C.; Tilmans, S.; Chen, F.; Criddle, C. Anaerobic membrane bioreactor model for design and prediction of domestic wastewater treatment process performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 131912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S. Two-phase anaerobic digestion of high-metal-content municipal-industrial sludge. Biomass 1986, 10, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, A.; Yu, N.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y. Enhancing methane production and organic loading capacity from high solid-content wastewater in modified granular activated carbon (GAC)-amended up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB). Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, W.; Li, G.; Song, Q.; Ismail, M.; Wang, Y.; Ren, L.; Cheng, C. Anaerobic biodegradation of soybean-process wastewater: Operation strategy and sludge bed characteristics of a high-performance Spiral Symmetric Stream Anaerobic Bioreactor. Water Res. 2021, 197, 117095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.; Ji, J.; Li, Y.; Kubota, K. Microbial characteristics in anaerobic membrane bioreactor treating domestic sewage: Effects of HRT and process performance. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 111, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Song, X.; Ding, X.; Xia, R.; Lin, X.; Li, G.; Nghiem, L.D.; Luo, W. Antibiotic removal from swine farming wastewater by anaerobic membrane bioreactor: Role of hydraulic retention time. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 677, 121629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Li, J.; Meng, J.; Li, J.; Jha, A.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Wang, X. Effects of reflux ratio on the anaerobic sludge and microbial social behaviors in an expanded granular sludge bed reactor: From the perspective of acyl-homoserine lactones-mediated quorum sensing. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 337, 125360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.; Zhao, X.; Wang, N.; Suo, Y.; Yuan, J.; Peng, Y. Redirecting carbon to recover VFA to facilitate biological short-cut nitrogen removal in wastewater treatment: A critical review. Water Res. 2023, 238, 120015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, F.; Sepúlveda-Muñoz, C.; Prádanos, P.; Hernández, A.; Palacio, L.; Muñoz, R. Influence of pH on the performance of anaerobic piggery wastewater treatment coupled with membrane-based NH3 extraction. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 55, 104226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Z.; Dai, X. Perspective on enhancing the anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Lu, B.; Chen, R. Kinetic and thermodynamic effects of temperature on methanogenic degradation of acetate, propionate, butyrate and valerate. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 396, 125366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Feng, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M.; Bao, X. Continuous medium chain carboxylic acids production from excess sludge by granular chain-elongation process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, Y. Evolution of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in aerobic sludge granulation: Composition, adherence and viscoelastic properties. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Yan, P.; Chen, Y.; Fang, F.; Guo, J. Effect of different feeding strategies on performance of aerobic granular sludge: From perspective of extracellular polymeric substances and microorganisms. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 111688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Guo, H.; Ma, F.; Zhang, J.; Ma, X.; You, S. New insights into mycelial pellets for aerobic sludge granulation in membrane bioreactor: Bio-functional interactions among metazoans, microbial communities and protein expression. Water Res. 2023, 228, 119361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadaleti, W.; Gomes, J.; de Souza, E.; Santos, M.; Belli, P.; Borges, A.; Mohedano, R.; Libardi, N.; da Silva, F.M.R.; Correa, E. Biomethane and biohydrogen production from an anaerobic sludge used in the treatment of rice parboiling effluent: Specific methanogenic and hydrogenic activity. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2024, 60, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Pan, Q.; Yang, J.; Gong, S.; Liu, X.; Fu, Y. Effects of Mixtures of Engineered Nanoparticles and Cocontaminants on Anaerobic Digestion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 2598–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).