Dynamic Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Mechanisms of Vegetation in the Lower Reaches of the Tarim River, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Processing
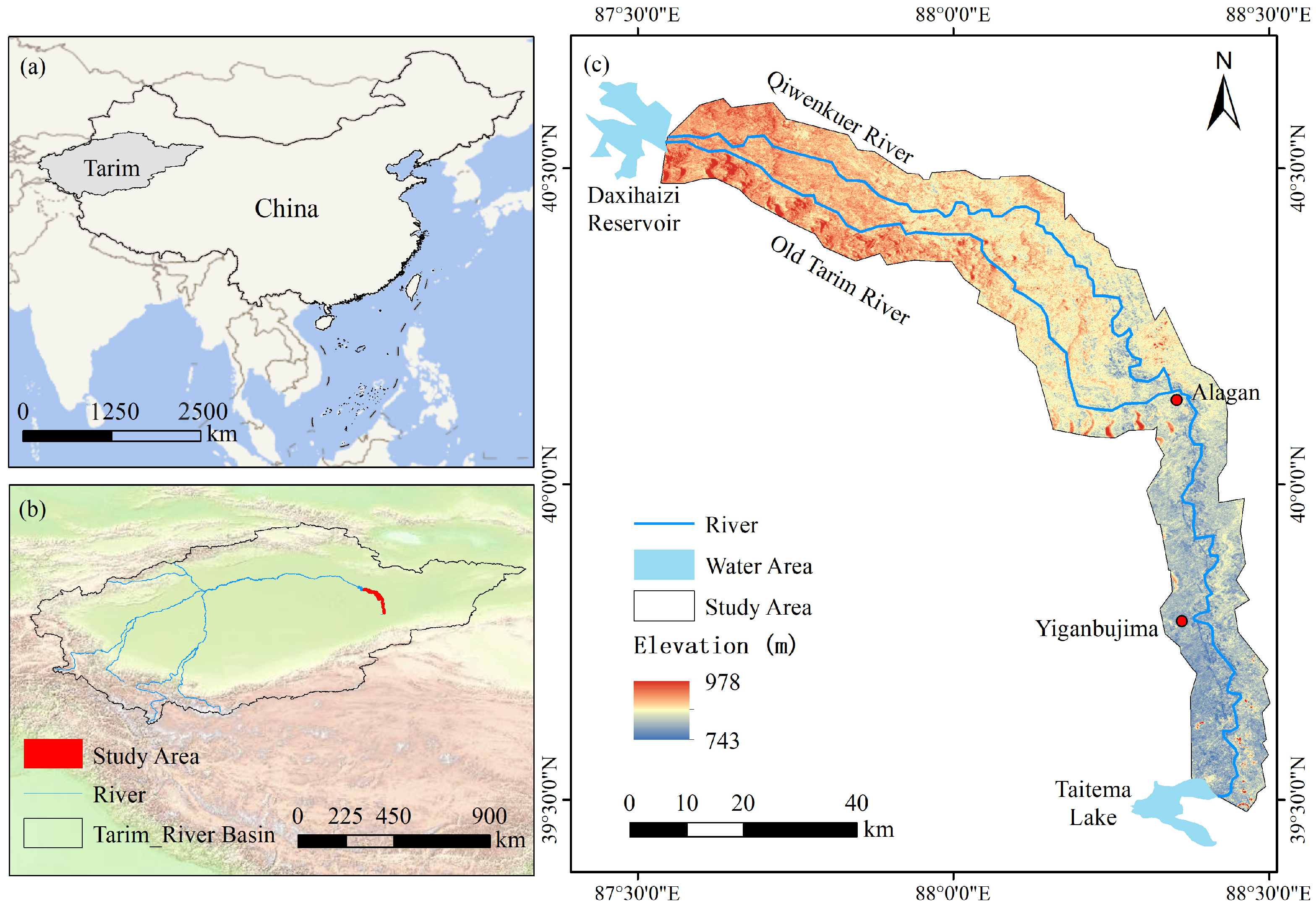
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source and Preprocessing
3. Method
3.1. Theil-Sen Estimator
3.2. Mann-Kendall (M-K) Significance Test
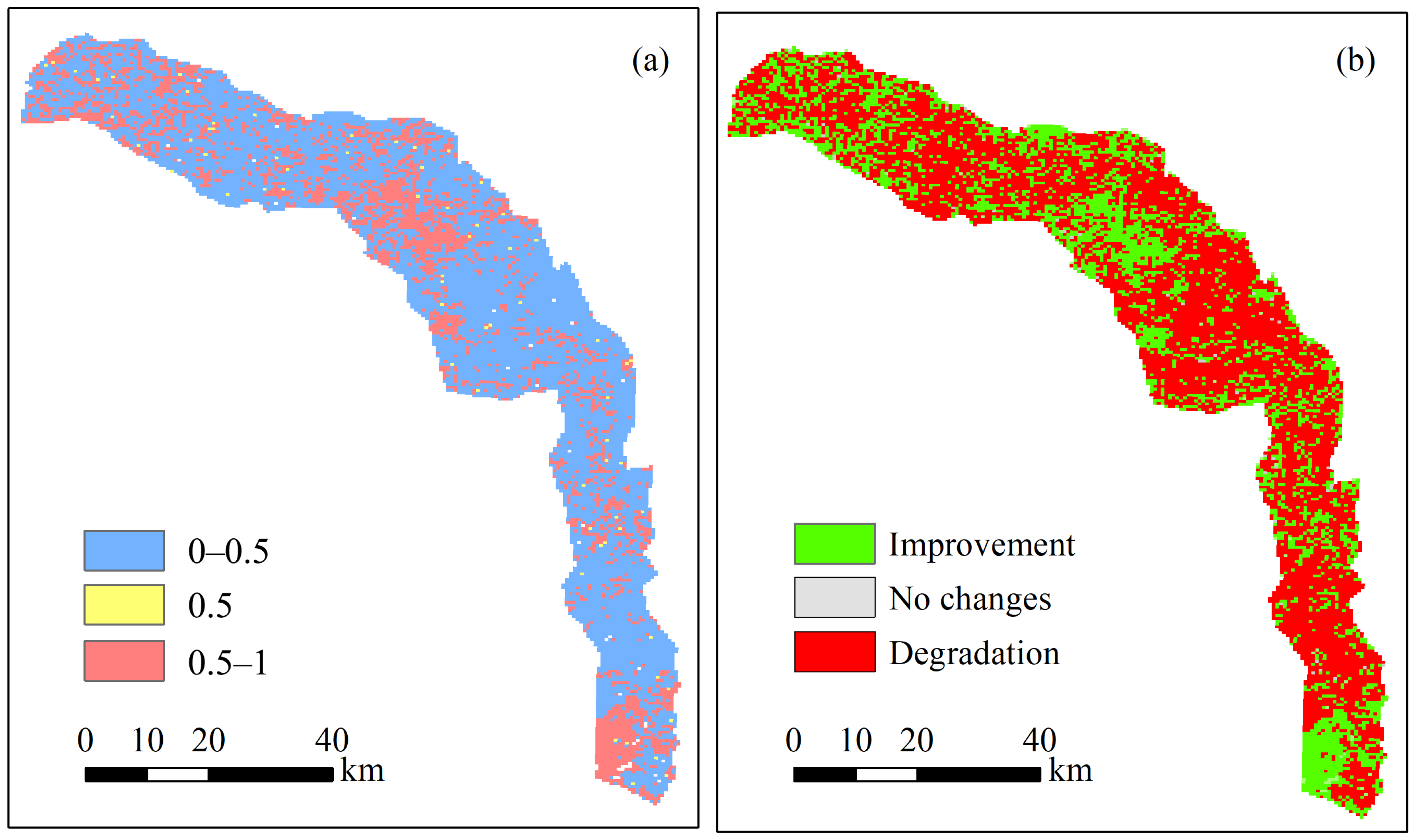
3.3. Hurst Exponent Method
3.4. Multivariate Residual Analysis
3.5. Geodetector Method
4. Results
4.1. Temporal Variation Characteristics of the NDVI
4.2. Spatial Variation Characteristics of the NDVI
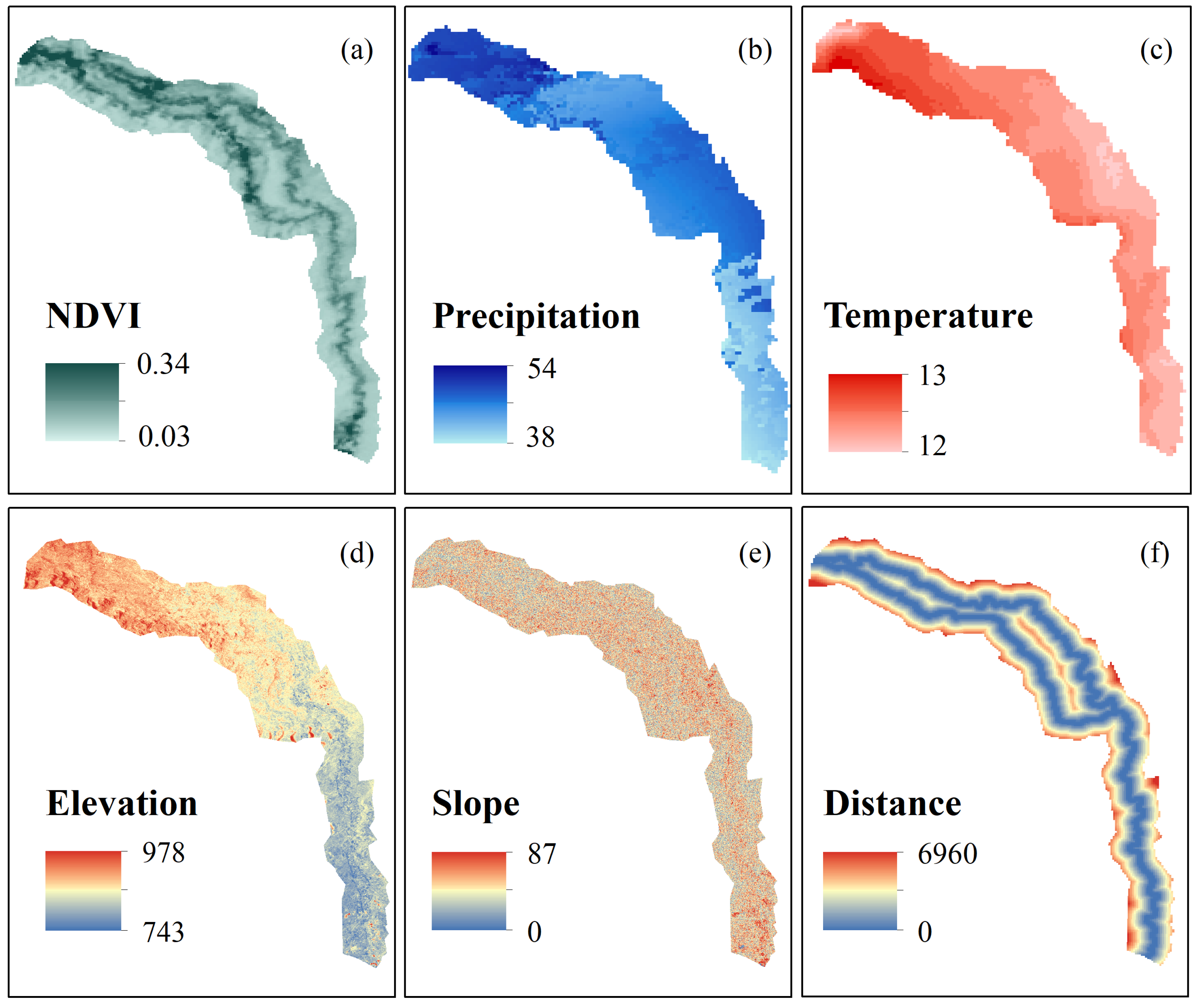
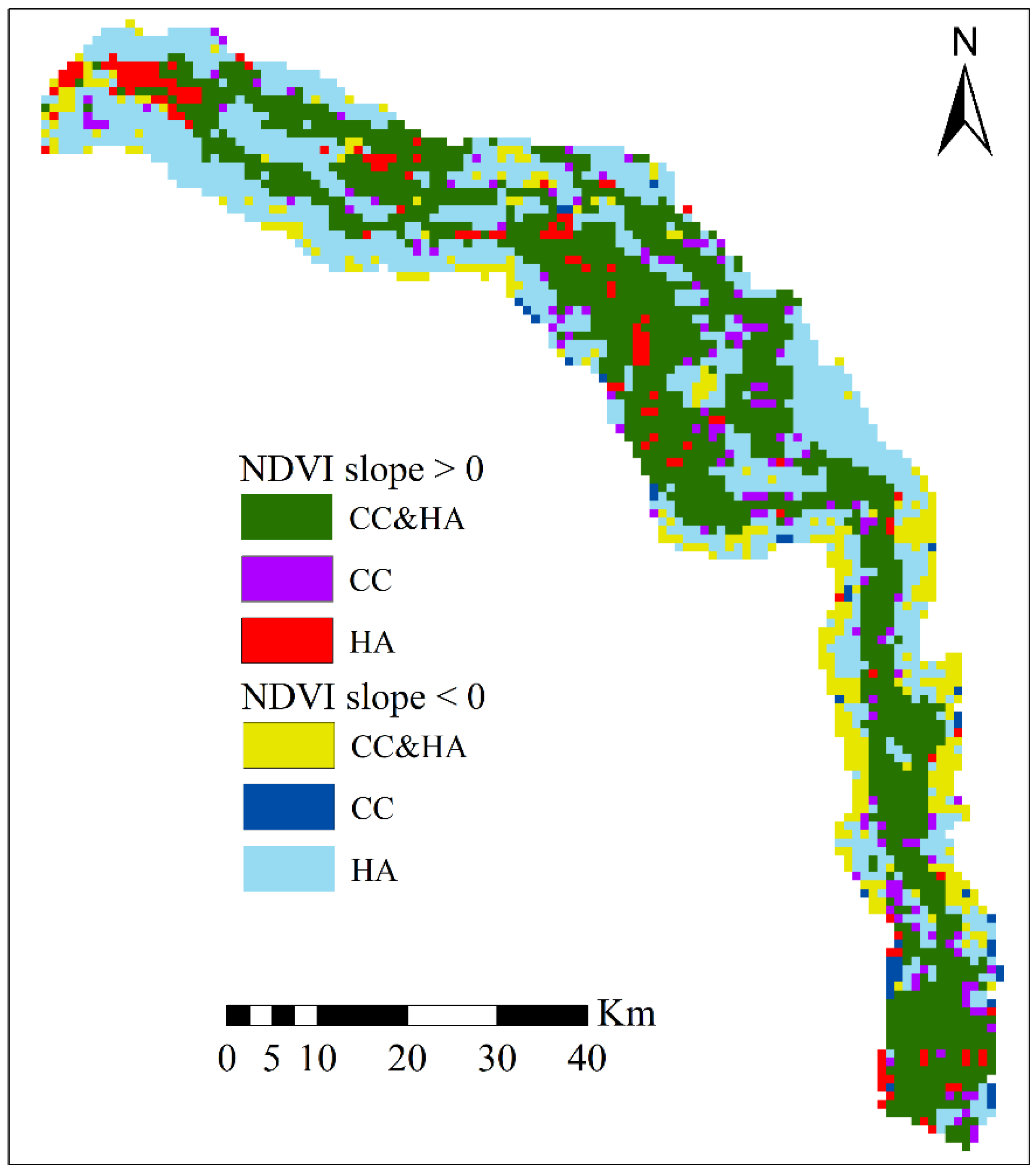
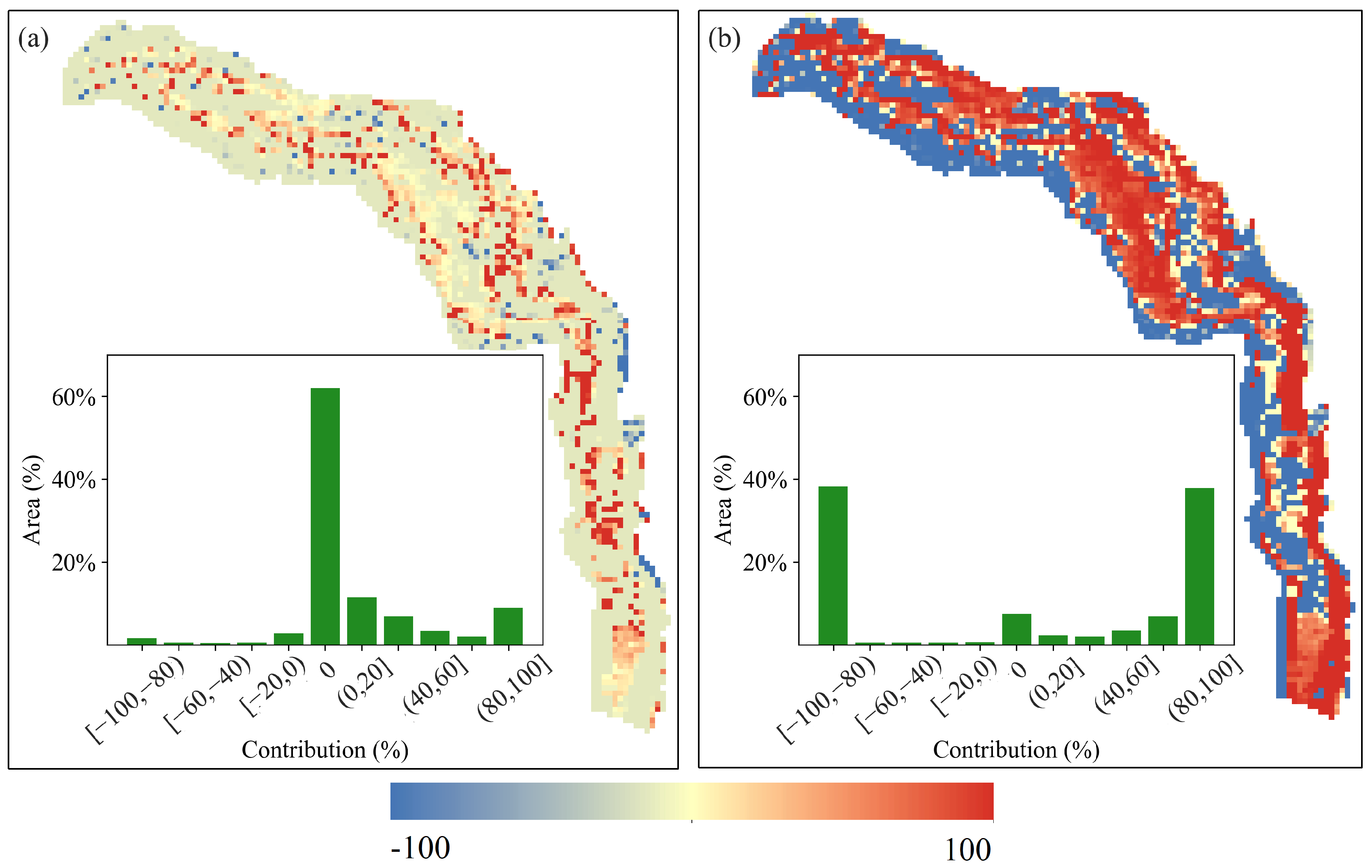
4.3. Contribution of Climate Change and Human Activity to Vegetation Dynamics
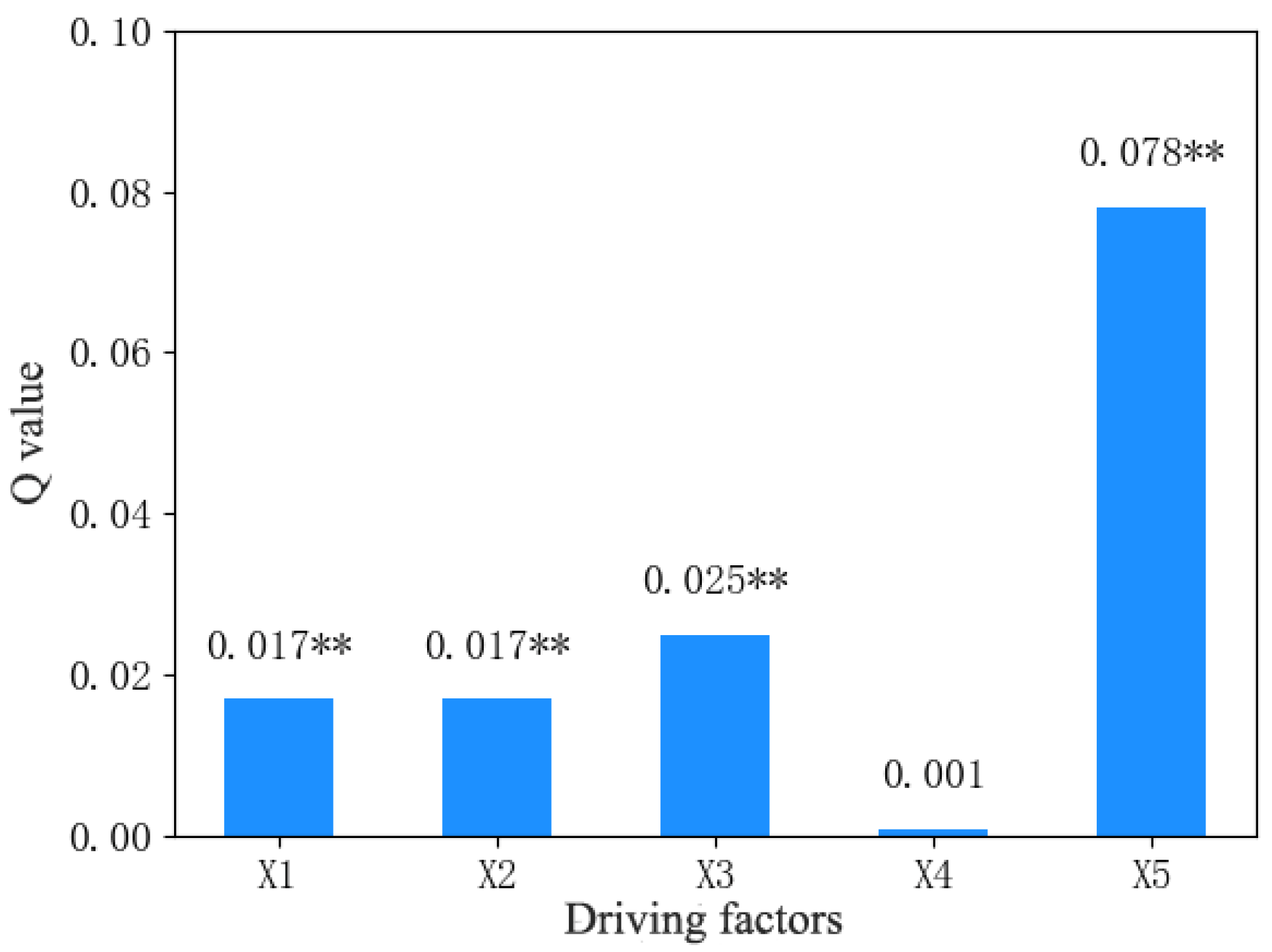
4.4. Detection of Factors Influencing Vegetation Distribution
5. Discussion
5.1. Vegetation Variation Characteristics in the LRTR
5.2. Effect of Driving Factors on LRTR Vegetation Change
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karnieli, A.; Qin, Z.; Wu, B.; Panov, N.; Yan, F. Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Land-Use and Land-Cover in the Mu Us Sandy Land, China, Using the Change Vector Analysis Technique. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9316–9339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Xue, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, M.; Chu, X.; Liu, S. Developing a multi-objective simulation-optimization model for ecological water conveyance in arid inland river basins. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 50, 101551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Dai, Q.-Y.; Lu, Y.-G.; Zhao, C.; Huang, W.-T.; Xu, M.; Feng, Y.-X. Identification of ecologically sensitive zones affected by climate change and anthropogenic activities in Southwest China through a NDVI-based spatial-temporal model. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Guan, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Du, Q.; Yuan, T. Investigating the underlying drivers of vegetation dynamics in cold-arid mountainous. Catena 2024, 237, 107831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, D.; Fan, J.; Yang, J. Trends and contribution of different grassland types in restoring the Three River Headwater Region, China, 1988–2012. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanaum, M.M.; Qi, T.; Boutin, K.D.; Otte, M.L.; Lin, Z.; Chu, X. Assessing the Impacts of Wetlands on Discharge and Nutrient Loading: Insights from Restoring Past Wetlands with GIS-Based Analysis and Modeling. Wetlands 2023, 43, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, M.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Wei, C.; Wang, L. Analysis of Vegetation Cover Change in the Geomorphic Zoning of the Han River Basin Based on Sustainable Development. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Ren, X.; Fan, L.; He, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Zeng, N.; Chen, X. Assessing the Vegetation Dynamics and Its Influencing Factors in Central Asia from 2001 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhao, W.; Daryanto, S.; Wang, L.; Fan, H.; Feng, Q.; Wang, Y. The spatial distribution and temporal variation of desert riparian forests and their influencing factors in the downstream Heihe River basin, China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 2405–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shijie, P.; Lei, W.; Yongkun, L.; Ruowen, W.; Tianming, G.; Zongjun, G. A study on ecohydrological mutual feedback relationship of the Shangdong River basin based on hydrological connectivity. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 171957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, C. Impacts of climate change and human activities on vegetation cover in hilly southern China. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, K.; Anees, S.A.; Rehman, A.; Pan, S.; Tariq, A.; Zubair, M.; Liu, Q.; Rabbi, F.; Khan, K.A.; Luo, M. Exploring spatiotemporal dynamics of NDVI and climate-driven responses in ecosystems: Insights for sustainable management and climate resilience. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 80, 102532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faheem, Z.; Kazmi, J.H.; Shaikh, S.; Arshad, S.; Mohammed, S. Random forest-based analysis of land cover/land use LCLU dynamics associated with meteorological droughts in the desert ecosystem of Pakistan. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamian, A.; Rashki, A.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Gholami, A.; Opp, C.; Middleton, N. Assessing vegetation restoration potential under different land uses and climatic classes in northeast Iran. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-L.; Shan, M.; Pei, X.-R.; Zhang, X.-K.; Yang, Y.-L. Assessment of the impacts of climate change and human activities on vegetation cover change in the Haihe River basin, China. Phys. Chem. Earth 2020, 115, 102834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Zhao, X.; Chen, F.; Wei, J.; Feng, Z.; Hou, T.; Chen, Y.; Yue, W.; Shang, H.; et al. Changes in Vegetation NDVI and Its Response to Climate Change and Human Activities in the Ferghana Basin from 1982 to 2015. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Wang, H.; Jiang, C.; Jin, S.; Ai, J.; Sun, O.J. Satellite view of vegetation dynamics and drivers over southwestern China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, T.; Dong, X.; Liu, Y. Vegetation dynamics influenced by climate change and human activities in the Hanjiang River Basin, central China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Du, X.; Du, Z.; Sun, M. Alpine grassland greening on the Northern Tibetan Plateau driven by climate change and human activities considering extreme temperature and soil moisture. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 916, 169995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.; Guo, E.; Wang, Y.; Bao, Y.; Bao, Y.; Mandula, N. Monitoring Vegetation Change and Its Potential Drivers in Inner Mongolia from 2000 to 2019. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Bi, R.-T.; Xu, L.-S.; Wang, J.-S.; Cao, C.-B. Using geographical detection to analyze responses of vegetation growth to climate change in the Loess Pla-teau, China. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao = J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 33, 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Meng, J.; Zhu, L. Applying Geodetector to disentangle the contributions of natural and anthropogenic factors to NDVI variations in the middle reaches of the Heihe River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whetton, R.; Zhao, Y.; Shaddad, S.; Mouazen, A.M. Nonlinear parametric modelling to study how soil properties affect crop yields and NDVI. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 138, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Xue, L.; Qi, T.; Liu, Y.; Yang, M.; Chu, X.; Liu, S. Assessing the Impacts of Future Climate and Land-Use Changes on Streamflow under Multiple Scenarios: A Case Study of the Upper Reaches of the Tarim River in Northwest China. Water 2024, 16, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Xue, L.; Dong, Z.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, K.; Wei, Q.; Fu, F.; Wei, G. Cumulative ecohydrological response to hydrological processes in arid basins. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 111, 106005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Wei, G.; Zhu, B. Spatiotemporal analysis of ecological vulnerability and management in the Tarim River Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Pang, Z. Changes in groundwater induced by water diversion in the Lower Tarim River, Xinjiang Uygur, NW China: Evidence from environmental isotopes and water chemistry. J. Hydrol. 2010, 387, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, C.; Ye, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhu, C.; Ma, X. Effects of ecological water conveyance on groundwater dynamics and riparian vegetation in the lower reaches of Tarim River, China. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Li, W.; Huang, X.; Zhu, C.; Ma, J. Assessment of the groundwater threshold of desert riparian forest vegetation along the middle and lower reaches of the Tarim River, China. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, X.; Li, J. Multiscale Detection and Assessment of Vegetation Eco-Environmental Restoration following Ecological Water Compensation in the Lower Reaches of the Tarim River, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, K.; Zuo, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, W. Land use/land cover change responses to ecological water conveyance in the lower reaches of Tarim River, China. J. Arid. Land 2021, 13, 1274–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Ma, X.; Liu, Y.; Qian, K.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. Ecological Assessment of Terminal Lake Basins in Central Asia under Changing Landscape Patterns. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, K. Whether the ecological benefits will continue to increase as usual and improve under the background of continuous ecological water delivery?—Taking the Lower Tarim River in China as an example. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yang, K.; Tang, W.; Lu, H.; Qin, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, X. The first high-resolution meteorological forcing dataset for land process studies over China. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; He, J.; Tang, W.; Qin, J.; Cheng, C.C.K. On downward shortwave and longwave radiations over high altitude regions: Observation and modeling in the Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 150, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Tian, Z.; Wei, H.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Y. Spatiotemporal evolution and driving mechanisms of vegetation in the Yellow River Basin, China during 2000–2020. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the Regression Coefficient Based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods. Br. J. Psychol. 1990, 25, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Non-parametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, H.E. Long-Term Storage Capacity of Reservoirs. Trans. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1951, 116, 770–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B.B.; Wallis, J.R. Robustness of the rescaled range R/S in the measurement of noncyclic long run statistical dependence. Water Resour. Res. 1969, 5, 967–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y. Analysis of vegetation dynamics in the Qinling-Daba Mountains region from MODIS time series data. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 108029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Duan, X.; Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Pan, X. Spatiotemporal variation in vegetation coverage and its response to climatic factors in the Red River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xu, G.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Jia, L.; Zhang, J. Vegetation dynamics and their relationships with climatic factors in the Qinling Mountains of China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 108, 105719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Wang, Y.; Chang, J.; Istanbulluoglu, E.; Guo, A.; Meng, X.; Li, Z.; He, B.; Zhao, Y. Coupling water cycle processes with water demand routes of vegetation using a cascade causal modeling approach in arid inland basins. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 840, 156492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Yu, J.; Wang, T.; Shi, S. Detection of the nonlinear response of vegetation to terrestrial water storage changes in central Asian endorheic basins. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Betz, F.; Aishan, T.; Halik, U.; Abliz, A. Impact of water supply on the restoration of the severely damaged riparian plants along the Tarim River in Xinjiang, Northwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Dai, H.; Gui, D.; Hu, B.X.; Ye, M.; Wei, G.; Qin, J.; Zhang, J. Evaluation and optimization of the water diversion system of ecohydrological restoration megaproject of Tarim River, China, through wavelet analysis and a neural network. J. Hydrol. 2022, 608, 127586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Ochoa, C.G.; Chen, X.; Zhang, D. Modeling oasis dynamics driven by ecological water diversion and implications for oasis restoration in arid endorheic basins. J. Hydrol. 2021, 593, 125774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, D.; Li, S. Elevation-dependent decline in vegetation greening rate driven by increasing dryness based on three satellite NDVI datasets on the Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 107, 105569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, K.; Dickhoefer, U.; Schlecht, E.; Buerkert, A. Quantification of Aboveground Rangeland Productivity and Anthropogenic Degradation on the Arabian Peninsula Using Landsat Imagery and Field Inventory Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Yu, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, P.; Jin, K. Quantitative contributions of climate change and human activities to vegetation changes over multiple time scales on the loess plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755 Pt 2, 142419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Jiapaer, G.; Bao, A.; Guo, H.; Ndayisaba, F. Vegetation dynamics and responses to climate change and human activities in Central Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599, 967–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

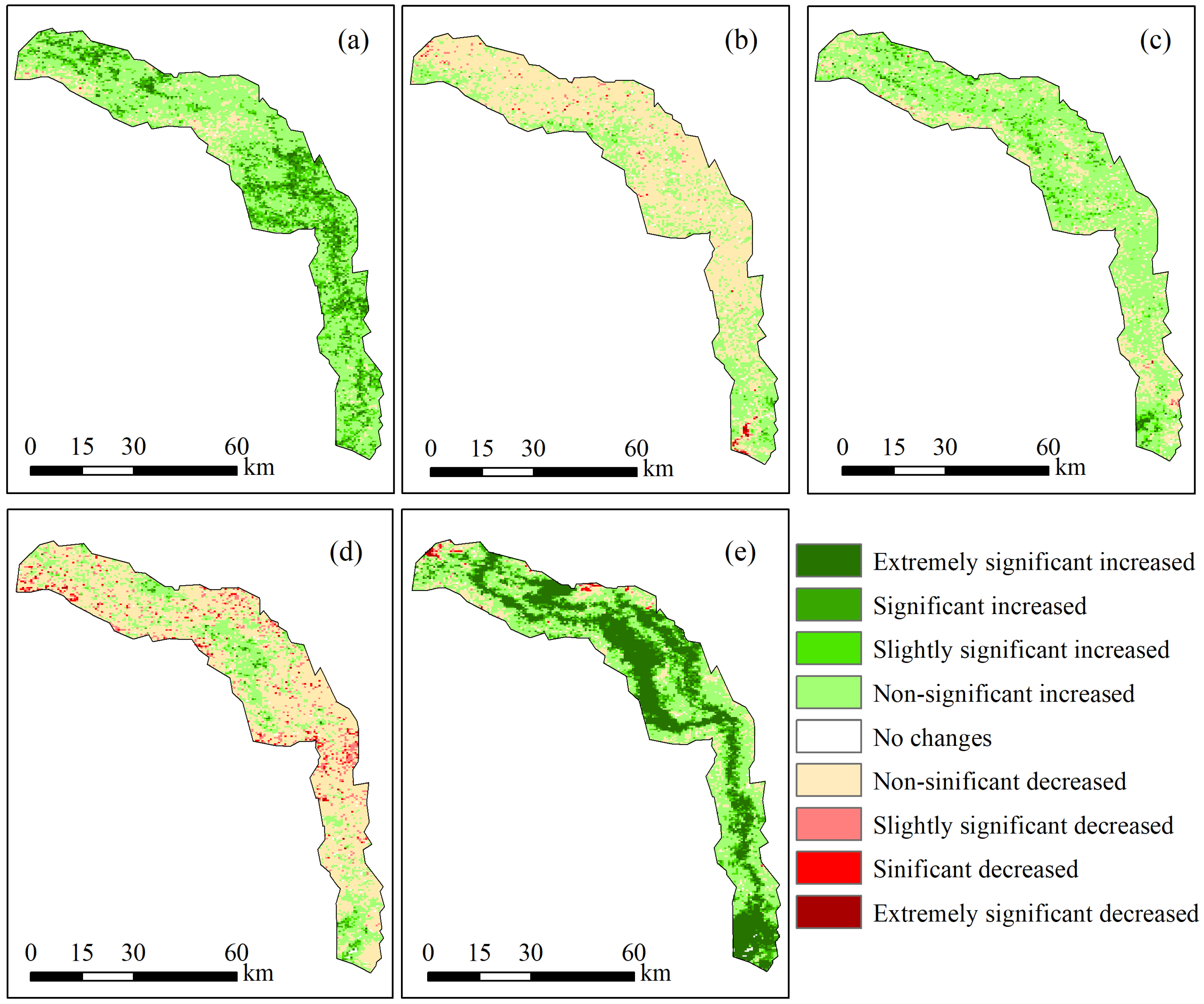


| Sen’s Slope | Z Value | Trend Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Extremely significant increased | ||
| significant increased | ||
| slightly significant increased | ||
| Non-significant increased | ||
| 0 | No changes | |
| Non-significant decreased | ||
| slightly significant decreased | ||
| significant decreased | ||
| Extremely significant decreased |
| Hurst | Sen’s Slope | Future Trends |
|---|---|---|
| Improvement | ||
| Degradation | ||
| - | Uncertain | |
| Degradation | ||
| Improvement |
| Slope (NDVIobs) | Driving Factors | Division Criteria | Contribution Rate/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope (NDVICC) | Slope (NDVIHA) | Climate Change (CC) | Human Activity (HA) | ||
| >0 | CC&HA | >0 | >0 | ||
| CC | >0 | <0 | 100 | 0 | |
| HA | <0 | >0 | 0 | 100 | |
| <0 | CC&HA | <0 | <0 | ||
| CC | <0 | >0 | 100 | 0 | |
| HA | >0 | <0 | 0 | 100 | |
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| annual precipitation | annual average temperature | elevation | slope | distance to the river channel |
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | \ | ||||
| X2 | N | \ | |||
| X3 | N | N | \ | ||
| X4 | N | N | N | \ | |
| X5 | Y | Y | Y | Y | \ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Q.; Xue, L.; Qi, T.; Liu, Y.; Yang, M.; Chu, X.; Liu, S. Dynamic Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Mechanisms of Vegetation in the Lower Reaches of the Tarim River, China. Water 2024, 16, 2157. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152157
Han Q, Xue L, Qi T, Liu Y, Yang M, Chu X, Liu S. Dynamic Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Mechanisms of Vegetation in the Lower Reaches of the Tarim River, China. Water. 2024; 16(15):2157. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152157
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Qiang, Lianqing Xue, Tiansong Qi, Yuanhong Liu, Mingjie Yang, Xinyi Chu, and Saihua Liu. 2024. "Dynamic Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Mechanisms of Vegetation in the Lower Reaches of the Tarim River, China" Water 16, no. 15: 2157. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152157
APA StyleHan, Q., Xue, L., Qi, T., Liu, Y., Yang, M., Chu, X., & Liu, S. (2024). Dynamic Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Mechanisms of Vegetation in the Lower Reaches of the Tarim River, China. Water, 16(15), 2157. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152157







