Effects of Brookite TiO2/CeO2 Nanocomposite on Artemia salina: Induction of Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Brookite TiO2/CeO2 Nanocomposites, CeO2 NPs and Brookite TiO2 NPs
2.2. Aquatic Organisms
2.3. Preparation of Nanoparticles Solutions
2.4. Acute Toxicity Assessment
2.5. Optical Microscopy
2.6. Reactive Oxygen Species Generation (ROS)
2.7. Acridine Orange Staining
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Toxicity towards Artemia sp.
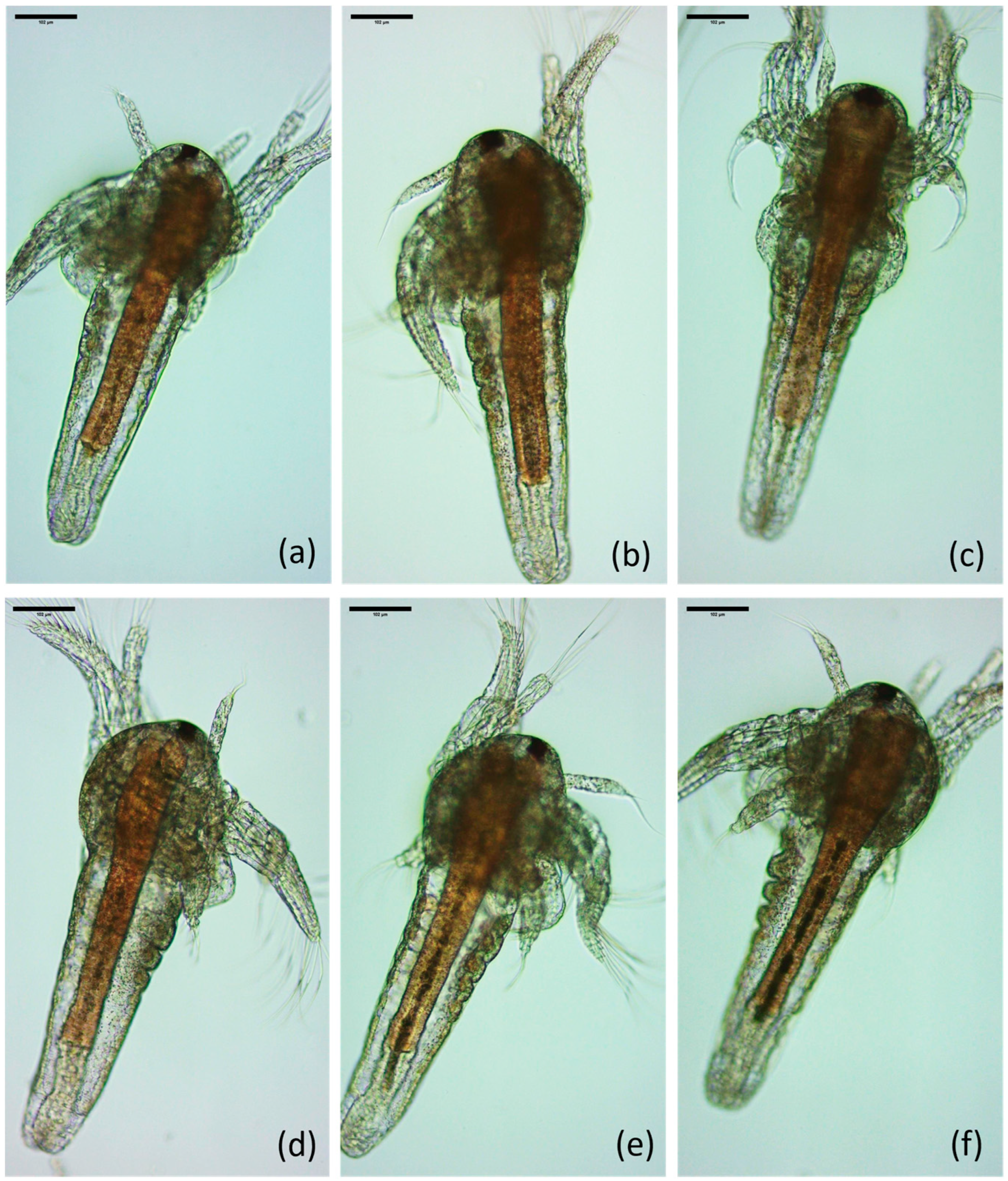
3.2. Optical Microscopy
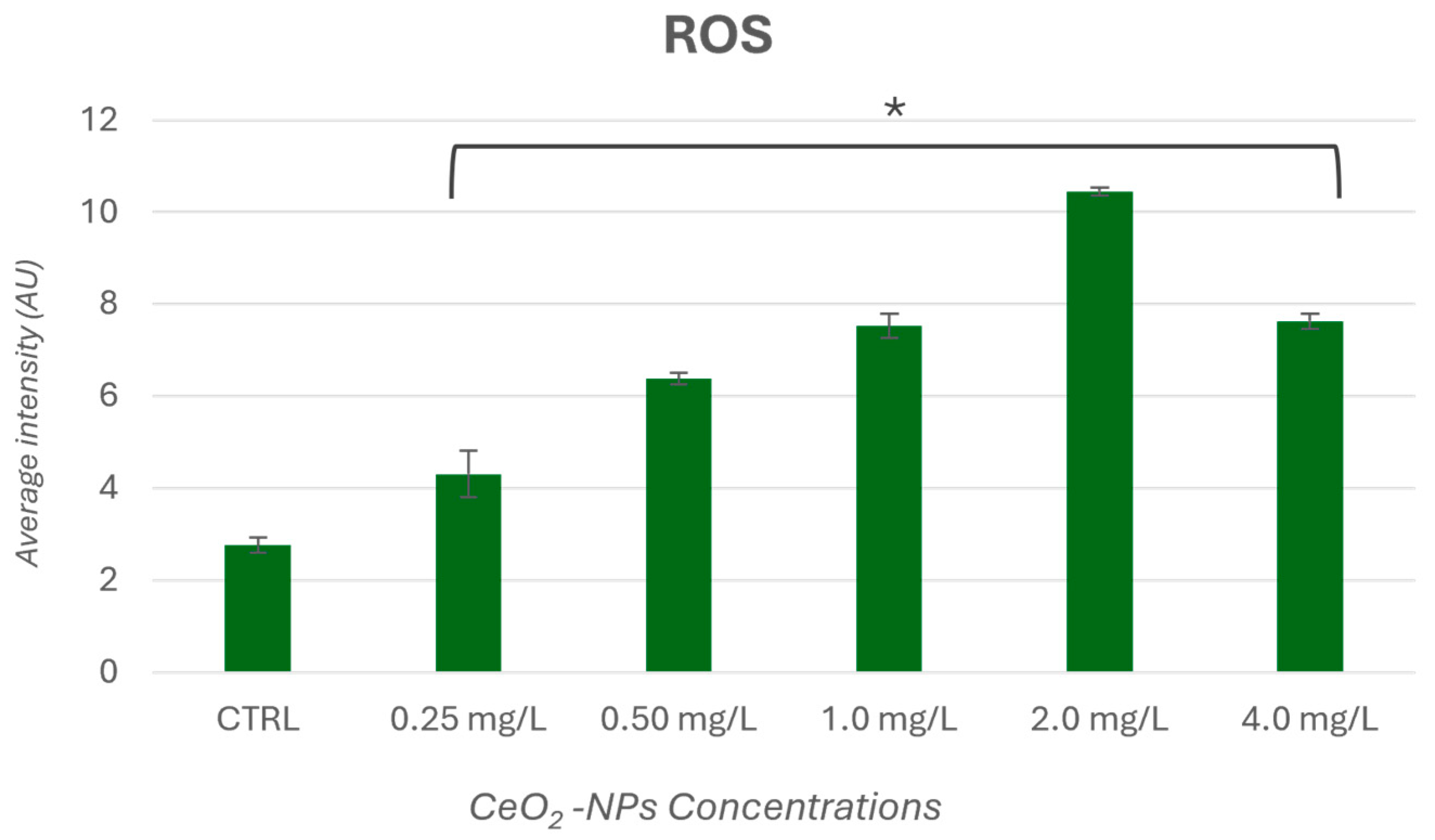
3.3. Reactive Oxygen Species Generation (ROS)
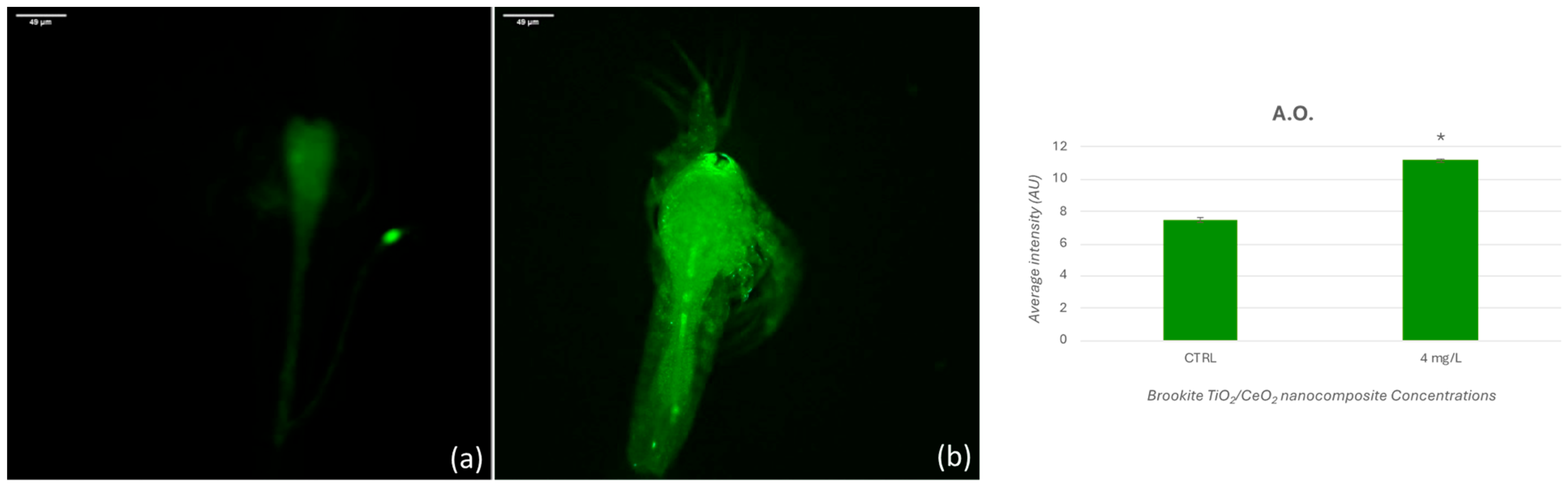
3.4. Acridine Orange Staining
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martis, E.; Badve, R.; Degwekar, M. Nanotechnology based devices and applications in medicine: An overview. Chron. Young Sci. 2012, 3, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikalje, A.P. Nanotechnology and its Applications in Medicine. Med. Chem. 2015, 5, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, A.; Azoia, N.G.; Gomes, A.C.; Cavaco, A.P. Albumin-Based Nanodevices as Drug Carriers. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 1371–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, J.W.; Martinez, E.; Louka, P.; Wingett, D.G. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Selective Destruction of Tumor Cells and Potential for Drug Delivery Applications. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loutfy, S.A.; Al-Ansary, N.A.; Abdel-Ghani, N.T.; Hamed, A.R.; Mohamed, M.B.; Craik, J.D.; Eldin, T.A.S.; Abdellah, A.M.; Hussein, Y.; Hasanin, M.; et al. Anti-proliferative Activities of Metallic Nanoparticles in an In Vitro Breast Cancer Model. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 6039–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourmand, A.; Abdollahi, M. Current opinion on nanotoxicology. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 20, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santonastaso, M.; Mottola, F.; Colacurci, N.; Iovine, C.; Pacifico, S.; Cammarota, M.; Cesaroni, F.; Rocco, L. In vitro genotoxic effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles (nTiO2) in human sperm cells. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2019, 86, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, P.; Ong, C.; Bay, B.H.; Baeg, G.H. Nanotoxicity: An Interplay of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Cell Death. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 1163–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassal, M.; Rebelo, S.; Pereira, M.D.L. Metal Oxide Nanoparticles: Evidence of Adverse Effects on the Male Reproductive System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnam, M.A.; Emami, F.; Sobhani, Z.; Dehghanian, A.R. The application of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles in the photo-thermal therapy of melanoma cancer model. Iran J. Basic Med. Sci. 2018, 21, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagopati, N.; Evangelou, K.; Falaras, P.; Tsilibary, E.C.; Vasileiou, P.V.S.; Havaki, S.; Angelopoulou, A.; Pavlatou, E.A.; Gorgoulis, V.G. Nanomedicine: Photo-activated nanostructured titanium dioxide, as a promising anticancer agent. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 222, 107795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K.; Irie, H.; Fujishima, A. TiO2 photocatalysis: A historical overview and future prospects. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 44, 8269–8285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binas, V.; Venieri, D.; Kotzias, D.; Kiriakidis, G. Modified TiO2 based photocatalysts for improved air and health quality. J. Materiomics 2017, 3, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Stathatos, E.; Dionysiou, D.D. Sol–gel preparation of mesoporous photocatalytic TiO2 films and TiO2/Al2O3 composite membranes for environmental applications. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2006, 63, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, A. Titanium dioxide photocleans polluted air. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, A229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R. Application photocatalysis for treatment of industrial waste water—A short review. OALib J. 2014, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhd Julkapli, N.; Bagheri, S.; Bee Abd Hamid, S. Recent advances in heterogeneous photocatalytic decolorization of synthetic dyes. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 692307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratovčić, A. Photocatalytic degradation of organic compounds in wastewaters. Technol. Acta 2019, 11, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Wan, Y.; Long, Y.; Cai, Z. Recent advances and applications of semiconductor photocatalytic technology. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Sanderson, B.J.; Wang, H. Cyto-and genotoxicity of ultrafine TiO2 particles in cultured human lymphoblastoid cells. Mutat. Res. 2007, 628, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onuma, K.; Sato, Y.; Ogawara, S.; Shirasawa, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Yoshitake, J.; Yoshimura, T.; Iigo, M.; Fujii, J.; Okada, F. Nano-scaled particles of titanium dioxide convert benign mouse fibrosarcoma cells into aggressive tumor cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 2171–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Virgilio, A.L.; Reigosa, M.; de Mele, M.F. Response of UMR 106 cells exposed to titanium oxide and aluminum oxide nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 92, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carriere, M.; Arnal, M.E.; Douki, T. TiO2 genotoxicity: An update of the results published over the last six years. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2020, 854–855, 503198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, M.M.; Forte Tavčer, P.; Tomšič, B. Influence of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on Human Health and the Environment. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalisi, E.M.; Pecoraro, R.; Salvaggio, A.; Capparucci, F.; Fortuna, C.G.; Zimbone, M.; Impellizzeri, G.; Brundo, M.V. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: Effects on Development and Male Reproductive System. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsvik, C.; Patil, S.; Seal, S.; Self, W.T. Superoxide dismutase mimetic properties exhibited by vacancy engineered ceria nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2007, 14, 1056–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, S.; Patil, S.; Kuchibhatla, S.V.; Seal, S. Size dependency variation in lattice parameter and valency states in nanocrystalline cerium oxide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 133113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Patil, S.; Bhargava, N.; Kang, J.F.; Riedel, L.M.; Seal, S.; Hickman, J.J. Auto-catalytic ceria nanoparticles offer neuroprotection to adult rat spinal cord neurons. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1918–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Patil, S.; Seal, S.; McGinnis, J.F. Rare earth nanoparticles prevent retinal degeneration induced by intracellular peroxides. In Nano-Enabled Medical Applications, 1st ed.; Balogh, L.P., Ed.; Jenny Stanford Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 2, pp. 525–546. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, K.A.; Hassan, M.S.; Awad, E.-S.T.; Hashem, K.S. The protective effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles against hepatic oxidative damage induced by monocrotaline. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Azfer, A.; Rogers, L.M.; Wang, X.; Kolattukudy, P.E. Cardioprotective effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles in a transgenic murine model of cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 73, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnurangam, S.; O’Connell, G.D.; Chernyshova, I.V.; Wood, K.; Hung, C.T.; Somasundaran, P. Beneficial effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles in development of chondrocyte-seeded hydrogel constructs and cellular response to interleukin insults. Tissue Eng. Part A 2014, 20, 2908–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horie, M.; Nishio, K.; Kato, H.; Fujita, K.; Endoh, S.; Nakamura, A.; Miyauchi, A.; Kinugasa, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Niki, E.; et al. Cellular responses induced by cerium oxide nanoparticles: Induction of intracellular calcium level and oxidative stress on culture cells. J. Biochem. 2011, 150, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfra, L.; Tornambè, A.; Savorelli, F.; Rotini, A.; Canepa, S.; Mannozzi, M.; Cicero, A.M. Ecotoxicity of diethylene glycol and risk assessment for marine environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 284, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viarengo, A.; Lowe, D.; Bolognesi, C.; Fabbri, E.; Koehler, A. The use of biomarkers in biomonitoring: A 2-tier approach assessing the level of pollutant-induced stress syndrome in sentinel organisms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 146, 281–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellardita, M.; Fiorenza, R.; D’Urso, L.; Spitaleri, L.; Gulino, A.; Compagnini, G.; Scirè, S.; Palmisano, L. Exploring the photothermo-catalytic performance of Brookite TiO2-CeO2 composites. Catalysts 2020, 10, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorenza, R.; Bellardita, M.; Balsamo, S.A.; Spitaleri, L.; Gulino, A.; Condorelli, M.; D’Urso, L.; Scirè, S.; Palmisano, L. A solar photothermocatalytic approach for the CO2 conversion: Investigation of different synergisms on CoO-CuO/brookite TiO2-CeO2 catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorenza, R.; Bellardita, M.; Balsamo, S.A.; Gulino, A.; Condorelli, M.; Compagnini, G.; Scirè, S.; Palmisano, L. A solar photothermo-catalytic combined process for the VOCs combustion and the subsequent CO2 valorization using noble metal-free catalysts. Catal. Today 2023, 413, 113949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorenza, R.; Spitaleri, L.; Gulino, A.; Sciré, S. High-Performing Au-Ag Bimetallic Catalysts Supported on Macro-Mesoporous CeO2 for Preferential Oxidation of CO in H2-Rich Gases. Catalysts 2020, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecoraro, R.; Scalisi, E.M.; Messina, G.; Fragalà, G.; Ignoto, S.; Salvaggio, A.; Zimbone, M.; Impellizzeri, G.; Brundo, M.V. Artemia salina: A microcrustacean to assess engineered nanoparticles toxicity. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2021, 84, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzini, P.; Azzoni, R.; Sansoni, G.; Spaggiari, R.; Baldaccini, G.N.; Fochetti, R.; Mancini, L. Saggio di tossicità acuta con Artemia sp. In Biologia Ambientale; Centro Italiano Studi di Biologia Ambientale (C.I.S.B.A.) Bollettino, Ed.; Bollettino CISBA: Milano, Italy, 1997; Volume 1, pp. 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Thiagarajana, V.; Seenivasana, R.; Jenkinsb, D.; Chandrasekarana, N.; Mukherjee, A. Combined effects of nano-TiO2 and hexavalent chromium towards marine crustacean Artemia salina. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 225, 105541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignoto, S.; Pecoraro, R.; Scalisi, E.M.; Buttigé, S.E.; Contino, M.; Ferruggia, G.; Salvaggio, A.; Brundo, M.V. Acute Toxicity of a Marine Emerging Pollutant (Promethazine Hydrochloride) on Artemia sp. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 39619–39623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulm, L.; Krivohlavek, A.; Jurašin, D.; Ljubojević, M.; Šinko, G.; Crnković, T.; Žuntar, I.; Šikić, S.; Vrček, I.V. Response of biochemical biomarkers in the aquatic crustacean Daphnia magna exposed to silver nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 19990–19999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arulvasu, C.; Jennifer, S.M.; Prabhu, D.; Chandhirasekar, D. Toxicity Effect of Silver Nanoparticles in Brine Shrimp Artemia. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 256919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkheil, M.; Johari, S.A.; An, H.J.; Asghari, S.; Park, H.S.; Sohn, E.K.; Yu, I.J. Acute toxicity, uptake, and elimination of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) using saltwater microcrustacean, Artemia franciscana. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 57, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ates, M.; Daniels, J.; Arslan, Z.; Farah, I.O.; Rivera, H.F. Comparative evaluation of impact of Zn and ZnO nanoparticles on brine shrimp (Artemia salina) larvae: Effects of particle size and solubility on toxicity. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugantharaj David, E.M.D.; Madurantakam Royam, M.; Rajamani Sekar, S.K.; Manivannan, B.; Jalaja Soman, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Natarajan, C. Toxicity, uptake, and accumulation of nano and bulk cerium oxide particles in Artemia salina. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 24187–24200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambardella, C.; Mesarič, T.; Milivojević, T.; Sepčić, K.; Gallus, L.; Carbone, S.; Ferrando, S.; Faimali, M. Effects of selected metal oxide nanoparticles on Artemia salina larvae: Evaluation of mortality and behavioural and biochemical responses. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 4249–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaraby, M.; Hernández, A.; Annangi, B.; Demir, E.; Bach, J.; Rubio, L.; Creus, A.; Marcos, R. Antioxidant and antigenotoxic properties of CeO2 NPs and cerium sulphate: Studies with Drosophila melanogaster as a promising in vivo model. Nanotoxicology 2015, 9, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bour, A.; Mouchet, F.; Verneuil, L.; Evariste, L.; Silvestre, J.; Pinelli, E.; Gauthier, L. Toxicity of CeO2 nanoparticles at different trophic levels–effects on diatoms, chironomids and amphibians. Chemosphere 2015, 120, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekulapally, R.; Murthy Chavali, L.N.; Idris, M.M.; Singh, S. Toxicity of TiO2, SiO2, ZnO, CuO, Au and Ag engineered nanoparticles on hatching and early nauplii of Artemia sp. PeerJ 2019, 6, e6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, Y.; Altinok, I.; Ilhan, H.; Sokmen, M. Determination of TiO2 and AgTiO2 nanoparticles in Artemia salina: Toxicity, morphological changes, uptake and depuration. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 96, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecoraro, R.; Scalisi, E.M.; Indelicato, S.; Contino, M.; Coco, G.; Stancanelli, I.; Capparucci, F.; Fiorenza, R.; Brundo, M.V. Toxicity of Titanium Dioxide–Cerium Oxide Nanocomposites to Zebrafish Embryos: A Preliminary Evaluation. Toxics 2023, 11, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuvaneshwari, M.; Thiagarajan, V.; Nemade, P.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Mukherjee, A. Toxicity and trophic transfer of P25 TiO2 NPs from Dunaliella salina to Artemia salina: Effect of dietary and waterborne exposure. Environ. Res. 2018, 160, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, M.S.; Jung, M.; Teoh, W.Y.; Gunawan, C.; Vassie, J.A.; Amal, R.; Whitelock, J.M. Cellular uptake and reactive oxygen species modulation of cerium oxide nanoparticles in human monocyte cell line U937. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7915–7924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenkranz, P.; Fernández-Cruz, M.L.; Conde, E.; Ramírez-Fernández, M.B.; Flores, J.C.; Fernández, M.; Navas, J.M. Effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles to fish and mammalian cell lines: An assessment of cytotoxicity and methodology. Toxicol. Vitr. 2012, 26, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, S.; Pandey, A.K. Cerium oxide nanoparticles induced toxicity in human lung cells: Role of ROS mediated DNA damage and apoptosis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2891934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, A.L.; Popova, N.R.; Selezneva, I.I.; Akkizov, A.Y.; Ivanov, V.K. Cerium oxide nanoparticles stimulate proliferation of primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts in vitro. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 68, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.; Mozafari, M. Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles: Recent Advances in Tissue Engineering. Materials 2020, 13, 3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shcherbakov, A.B.; Zholobak, N.M.; Ivanov, V.K. Biological, biomedical and pharmaceutical applications of cerium oxide. In Cerium Oxide (CeO2): Synthesis, Properties and Applications; Scirè, S., Palmisano, L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 279–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Treatments | % Vitality to 24 h (Means ± SD) | % Vitality to 48 h (Means ± SD) |
|---|---|---|
| CTRL | 98% ± 0.030 | 98% ± 0.064 |
| 0.25 mg/L | 98.96% ± 0.025 | 87.72% ± 0.078 |
| 0.50 mg/L | 97% ± 0.072 | 88.85% ± 0.129 |
| 1.0 mg/L | 99% ± 0.025 | 91.72% ± 0.071 |
| 2.0 mg/L | 99% ± 0.027 | 92.59% ± 0.098 |
| 4.0 mg/L | 100% ± 0.000 | 98% ± 0.051 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Indelicato, S.; Pecoraro, R.; Scalisi, E.M.; Coco, G.; Cartelli, S.; Lo Faro, R.; Scalisi, A.; Salvaggio, A.; Fiorenza, R.; Brundo, M.V. Effects of Brookite TiO2/CeO2 Nanocomposite on Artemia salina: Induction of Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis Assessment. Water 2024, 16, 1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16141946
Indelicato S, Pecoraro R, Scalisi EM, Coco G, Cartelli S, Lo Faro R, Scalisi A, Salvaggio A, Fiorenza R, Brundo MV. Effects of Brookite TiO2/CeO2 Nanocomposite on Artemia salina: Induction of Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis Assessment. Water. 2024; 16(14):1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16141946
Chicago/Turabian StyleIndelicato, Stefania, Roberta Pecoraro, Elena Maria Scalisi, Giuliana Coco, Simone Cartelli, Riccardo Lo Faro, Agata Scalisi, Antonio Salvaggio, Roberto Fiorenza, and Maria Violetta Brundo. 2024. "Effects of Brookite TiO2/CeO2 Nanocomposite on Artemia salina: Induction of Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis Assessment" Water 16, no. 14: 1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16141946
APA StyleIndelicato, S., Pecoraro, R., Scalisi, E. M., Coco, G., Cartelli, S., Lo Faro, R., Scalisi, A., Salvaggio, A., Fiorenza, R., & Brundo, M. V. (2024). Effects of Brookite TiO2/CeO2 Nanocomposite on Artemia salina: Induction of Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis Assessment. Water, 16(14), 1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16141946










