Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Center Pivot Irrigation Systems in the Brazilian Tropical Savanna (1985–2020)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
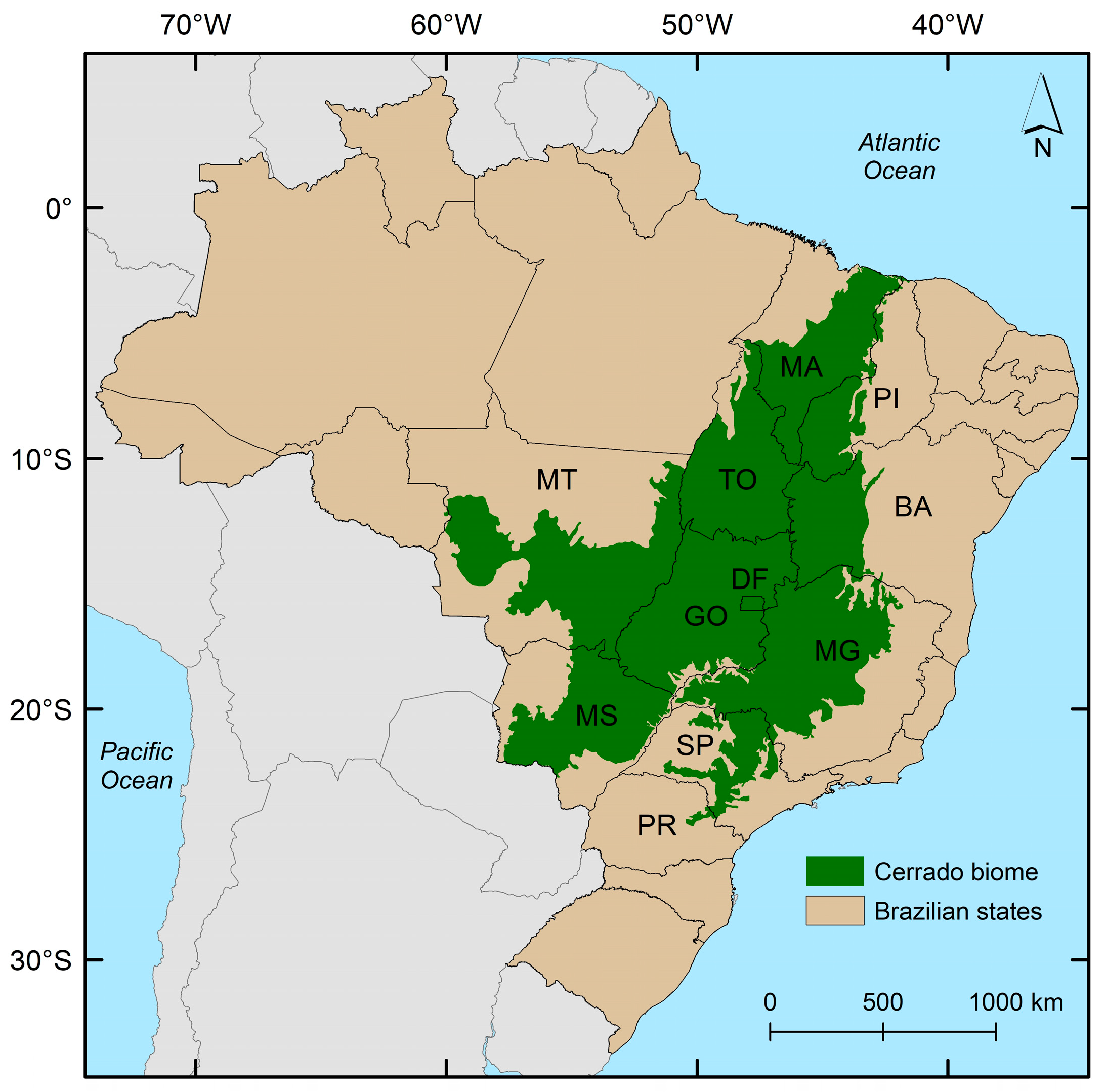
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
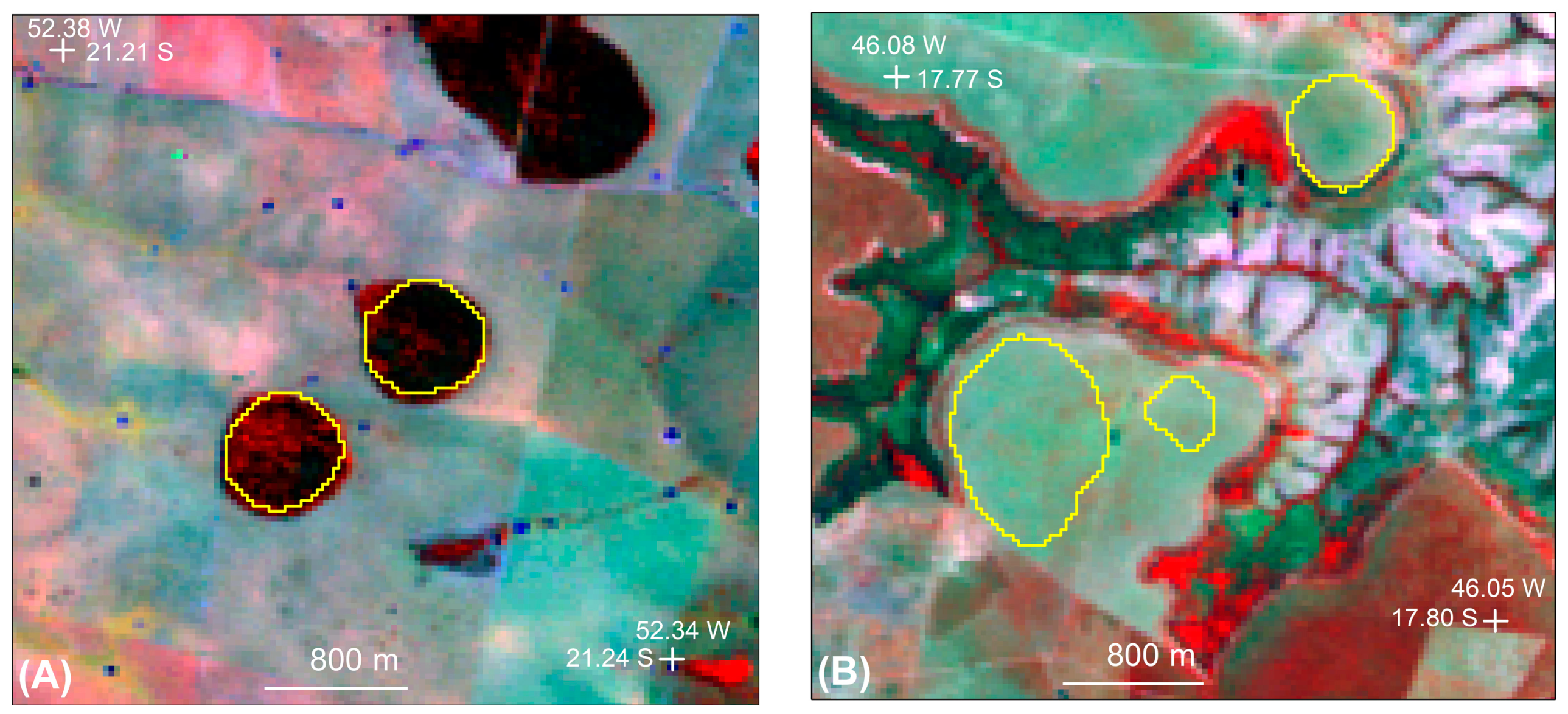
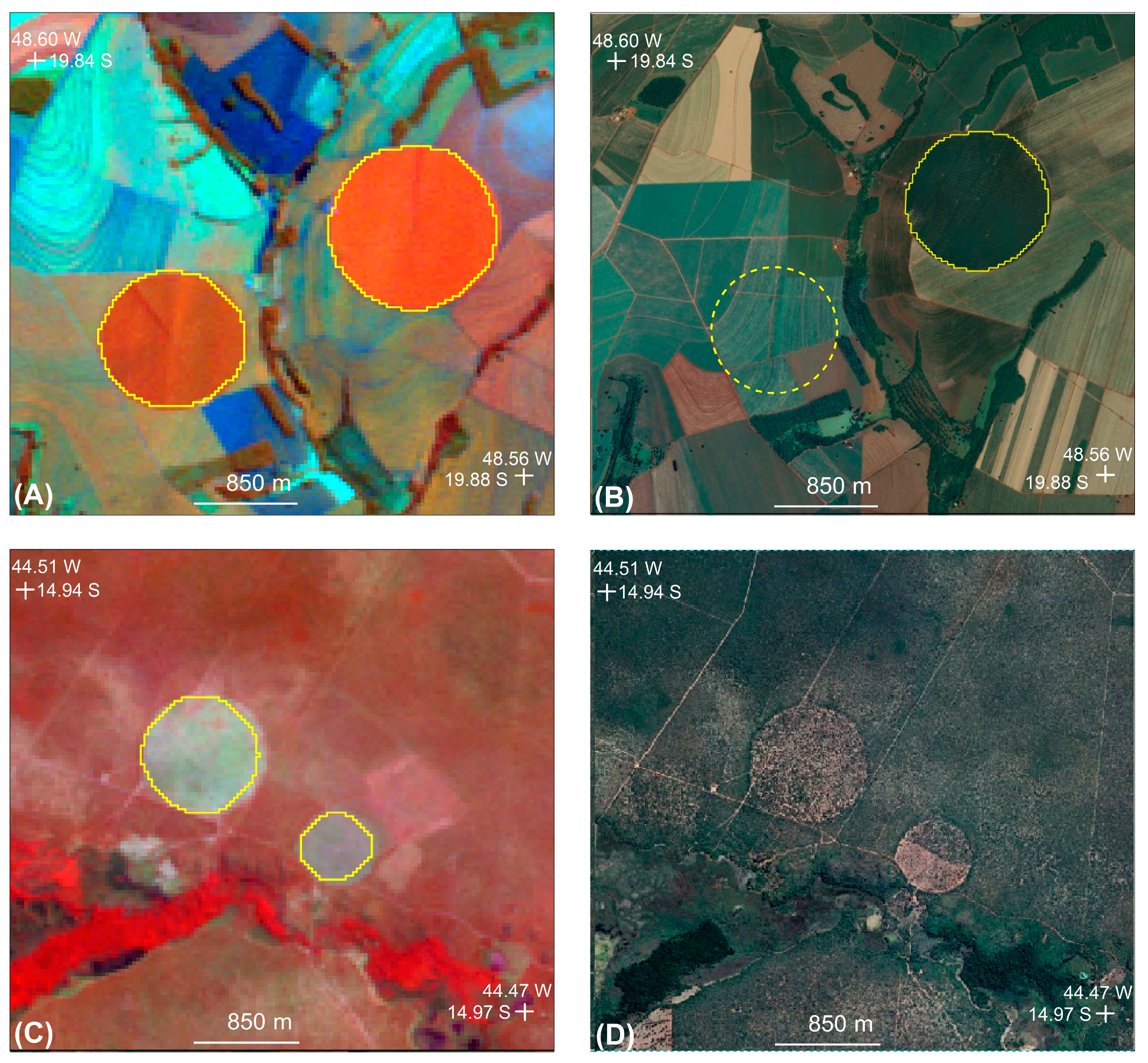
2.3. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Expansion of Center Pivots
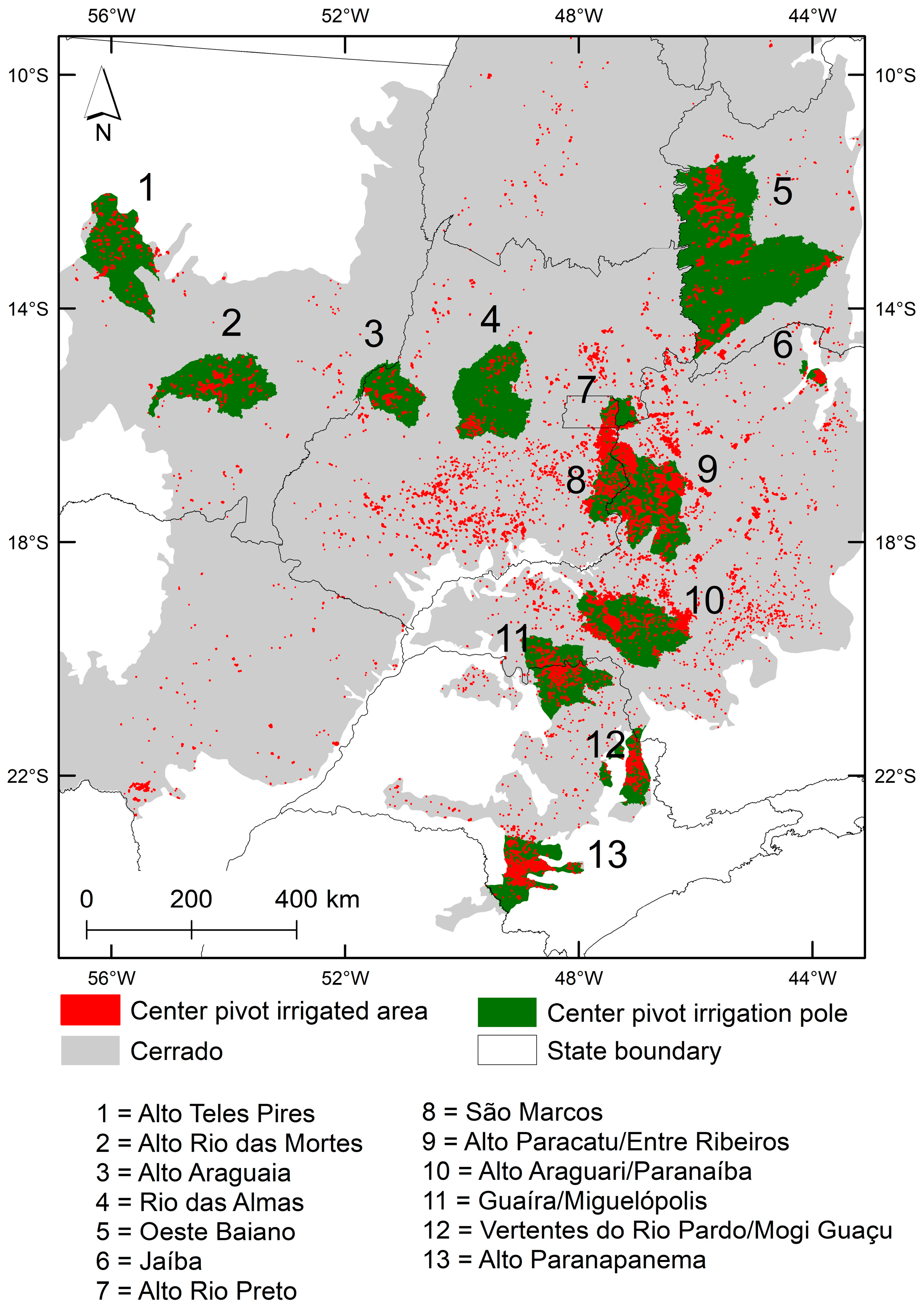
3.2. Cerrado´s Irrigation Poles
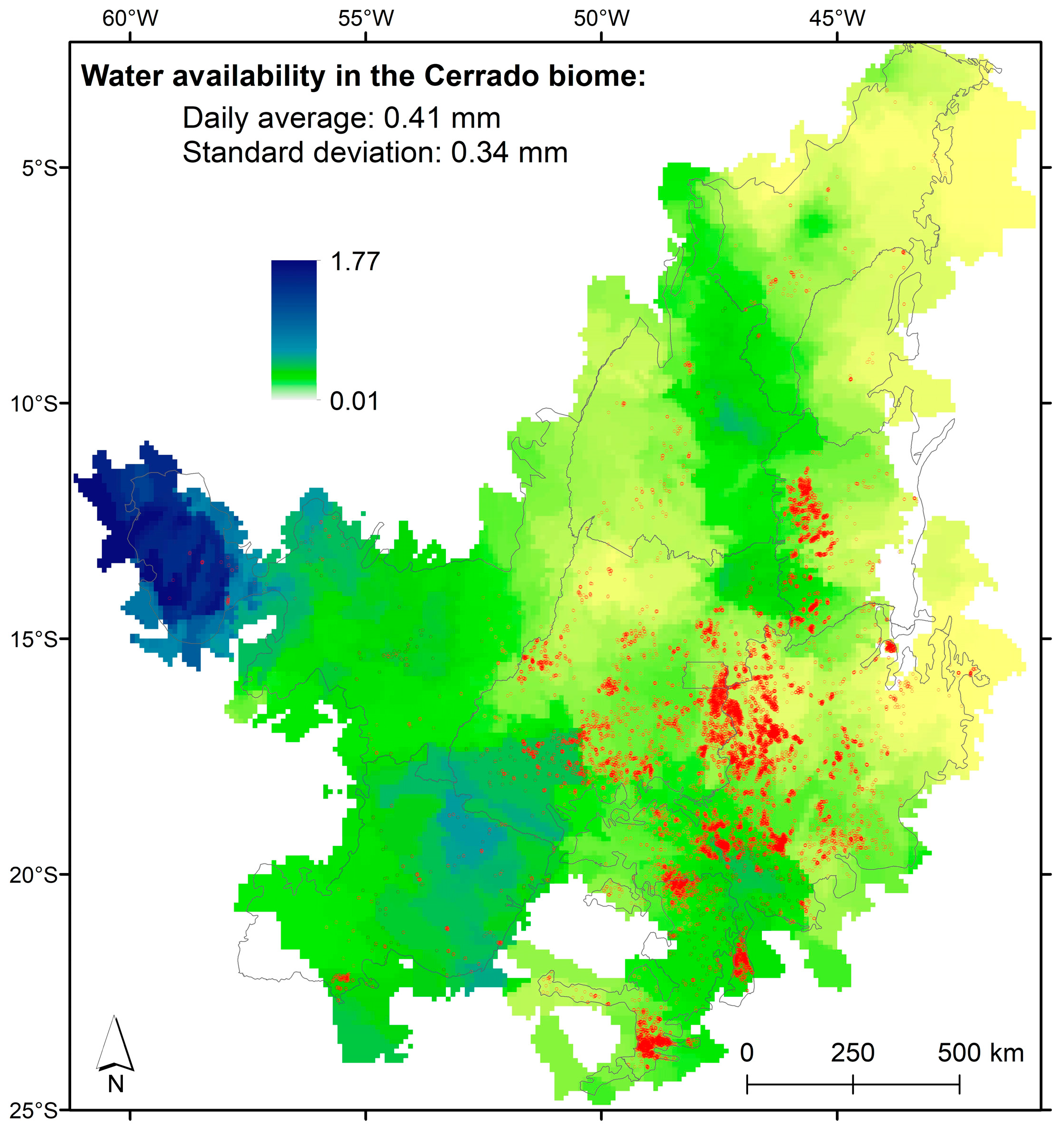
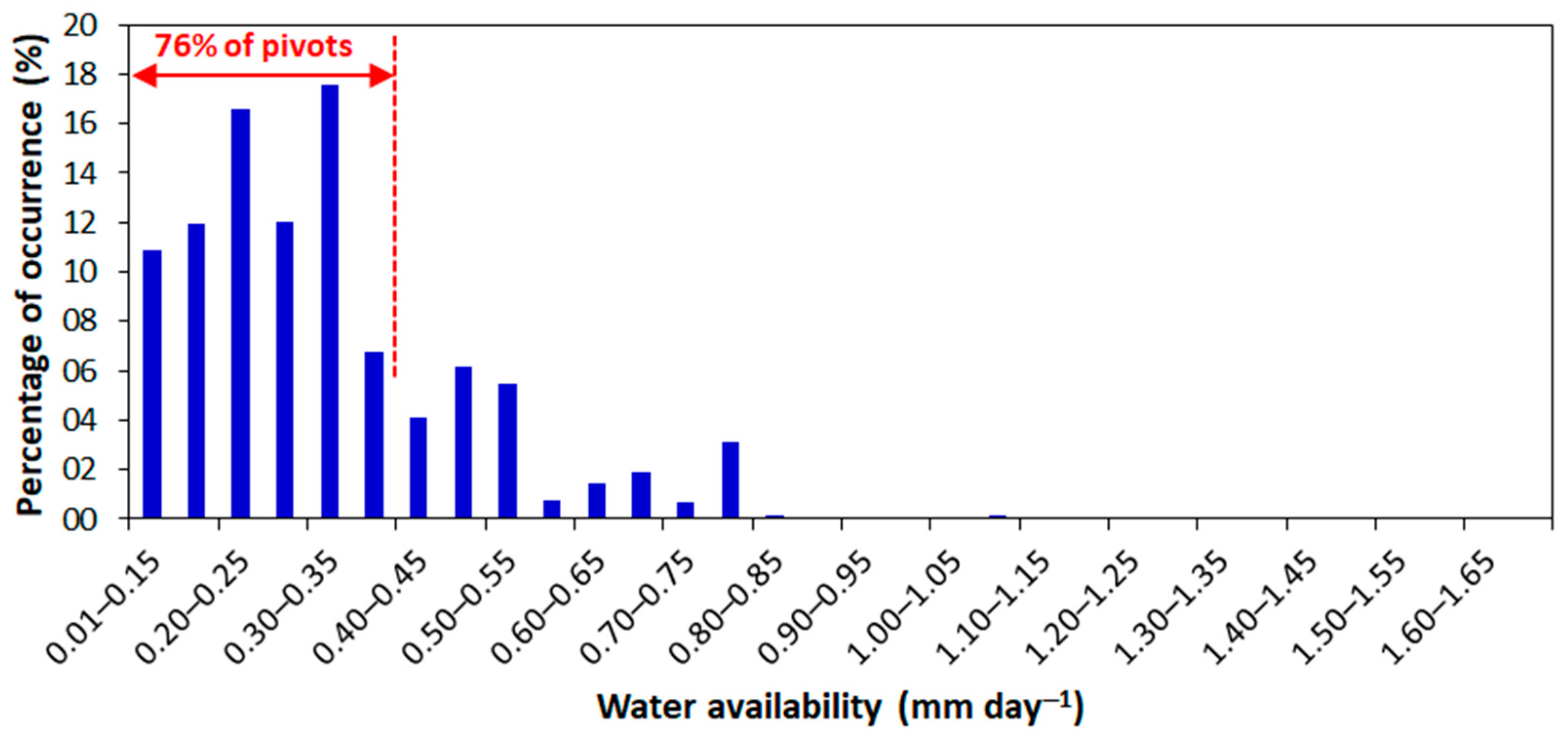
3.3. Water Availability
3.4. Retraction of Center Pivots
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The magnitude of expansion of the center pivots in the Cerrado during the period 1985–2020 was about 17 times in terms of number of pivots and even higher (26 times) in terms of total irrigated area.
- (2)
- Among the 13 irrigation poles located in the Cerrado biome, the Oeste Baiano, Bahia State, and the São Marcos, Goiás State, presented the largest areas of center pivots: approximately 173,000 ha and 102,000 ha, respectively.
- (3)
- Most of the center pivots are concentrated in regions with low water availability.
- (4)
- The retraction of center pivots in the Cerrado biome was, to some extent, significant over a 15-year period. More than 10% of active pivots in 2005 were inactive in 2020, mostly encompassed by a much larger rain-fed cropland or even abandoned.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zalles, V.; Hansen, M.C.; Potapov, P.V.; Stehman, S.V.; Tyukavina, A.; Pickens, A.; Song, X.P.; Adusei, B.; Okpa, C.; Aguilar, R.; et al. Near doubling of Brazil´s intensive row crop area since 2000. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, E.E.; Rodrigues, A.A.; Martins, E.S.; Bettiol, G.M.; Bustamante, M.M.C.; Bezerra, A.S.; Couto, A.F., Jr.; Vasconcelos, V.; Schuler, J.; Bolfe, E.L. Cerrado ecoregions: A spatial framework to assess and prioritize Brazilian savanna environmental diversity for conservation. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrosatélite. Análise Geoespacial da Expansão da Soja no Bioma Cerrado: 2001 a 2021; Agrosatélite: Florianópolis, SC, Brazil, 2021; p. 25. [Google Scholar]
- Alvares, C.A.; Stape, J.L.; Sentelhas, P.C.; Gonçalves, J.L.M.; Sparovek, G. Köppen’s climate classification map for Brazil. Meteorol. Z. 2013, 22, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spangler, K.R.; Lynch, A.H.; Spera, S.A. Precipitation drivers of cropping frequency in the Brazilian Cerrado: Evidence and implications for decision-making. Weather Clim. Soc. 2017, 9, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.A.M.; Assad, E.D.; Evangelista, B.A. Caracterização climática do bioma Cerrado. In Cerrado: Ecologia e Flora; Sano, S.M., Almeida, S.P., Ribeiro, J.F., Eds.; Embrapa Informação Tecnológica: Brasília, DF, Brazil, 2008; pp. 69–106. [Google Scholar]
- Grafton, R.Q.; Williams, J.; Perry, C.J.; Molle, F.; Ringler, C.; Stedutor, P.; Udall, B.; Wheeler, S.A.; Wang, Y.; Allen, R.G. The paradox of irrigation efficiency: Higher efficiency rarely reduces water consumption. Science 2018, 361, 748–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, I.S.; Mantovani, E.C.; Venancio, L.P.; Cunha, F.F.; Aleman, C.C. Controlled water stress in agricultural crops in Brazilian Cerrado. Biosci. J. 2020, 36, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANA. Atlas Irrigação: Uso da Água na Agricultura Irrigada, 2nd ed.; ANA: Brasília, DF, Brazil, 2021; p. 130. [Google Scholar]
- Althoff, D.; Rodrigues, L.N. The expansion of center-pivot irrigation in the Cerrado biome. Irriga 2019, 1, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, R.C.; Johnson, K.A. Estimating irrigated land acreage from Landsat imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1979, 45, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar]
- Ozdogan, M.; Gutman, G. A new methodology to map irrigated areas using multi-temporal MODIS and ancillary data: An application example in the continental US. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3520–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, D.; Luo, L.; Pokhrel, Y.; Deb, K.; Huang, J.; Ran, Y. Detecting irrigation extent, frequency, and timing in a heterogeneous arid agricultural region using MODIS time series, Landsat imagery, and ancillary data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANA. Levantamento da Agricultura Irrigada por Pivôs Centrais no Brasil (1985–2017), 2nd ed.; ANA: Brasília, DF, Brazil, 2019; p. 46. [Google Scholar]
- Rundquist, D.C.; Hoffman, R.O.; Carlson, M.P.; Cook, A.E. The Nebraska Center-Pivot Inventory: An example of operational satellite remote sensing on a long-term basis. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1989, 55, 587–590. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, W.; Coelho, R.D.; Jacomazzi, M.A.; Antunes, M.A. Spatial distribution of center pivots in Brazil: I—Southeast region. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agríc. Ambient. 2004, 8, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, E.E.; Lima, J.E.; Silva, E.M.; Oliveira, E.C. Estimative variation in the water demand for irrigation by center pivot in Distrito Federal-Brazil, between 1992 and 2002. Eng. Agríc. 2005, 25, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MapBiomas. Irrigation–Appendix, Collection 8. Available online: https://brasil.mapbiomas.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2023/08/Irrigation-Appendix-C8.docx.pdf (accessed on 22 March 2024).
- MapBiomas. MapBiomas v. 8.0. Available online: https://plataforma.brasil.mapbiomas.org/irrigacao (accessed on 22 March 2024).
- Saraiva, M.; Protas, E.; Salgado, M.; Souza, C., Jr. Automatic mapping of center pivot irrigation systems from satellite images using deep learning. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, A.O.; Carvalho Júnior, O.A.; Carvalho, O.L.F.; Bem, P.P.; Ferreira, P.H.G.; Moura, R.S.; Silva, C.R.; Gomes, R.A.T.; Guimarães, R.F. Deep semantic segmentation of center pivot irrigation systems from remote sensed data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBGE. Mapa de Biomas e de Vegetação; IBGE: Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil, 2004. Available online: https://agenciadenoticias.ibge.gov.br/agencia-sala-de-imprensa/2013-agencia-de-noticias/releases/12789-asi-ibge-lanca-o-mapa-de-biomas-do-brasil-e-o-mapa-de-vegetacao-do-brasil-em-comemoracao-ao-dia-mundial-da-biodiversidade (accessed on 22 March 2024).
- Sano, E.E.; Rosa, R.; Brito, J.L.S.; Ferreira, L.G. Land cover mapping of the tropical savanna region in Brazil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 166, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BFG. Brazilian Flora 2020: Leveraging the Power of a Collaborative Scientific Network; Taxon; BFG: Araquari, SC, Brazil, 2021; Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/tax.12640 (accessed on 26 March 2024).
- Françoso, R.D.; Brandão, R.; Nogueira, C.C.; Salmona, Y.B.; Machado, R.B.; Colli, G.R. Habitat loss and the effectiveness of protected areas in the Cerrado biodiversity hotspot. Nat. Conserv. 2015, 13, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.A.; Macedo, M.N.; Silvério, D.V.; Maracahipes, L.; Coe, M.T.; Brando, P.M.; Shimbo, J.Z.; Rajão, R.; Soares-Filho, B.; Bustamante, M.M.C. Cerrado deforestation threatens regional climate and water availability for agriculture and ecosystems. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 6807–6822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althoff, D.; Rodrigues, L.N. Recursos hídricos superficiais no Cerrado. In Agricultura Irrigada no Cerrado: Subsídios para o Desenvolvimento Sustentável; Rodrigues, L.N., Ed.; Embrapa: Brasília, DF, Brazil, 2023; Chapter 4; pp. 92–113. [Google Scholar]
- IBGE; Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics. Manual Técnico de Geomorfologia; IBGE: Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil, 2009; p. 182. [Google Scholar]
- Althoff, D.; Rodrigues, L.N.; Silva, D.D. Assessment of water availability in the Cerrado. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpalatha, R.; Perrin, C.; Le Moine, N.; Mathevet, T.; Andréassian, V. A downward structural sensitivity analysis of hydrological models to improve low-flow simulation. J. Hydrol. 2011, 411, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hufman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Braithwaite, D.; Hsu, K.; Joyce, R.; Kidd, C.; Nelkin, E.J.; Sorooshian, S.; Tan, J.; Xie, P. Integrated Multi-Satellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG); Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document, National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; p. 38. [Google Scholar]
- NICFI. Norway´s International Climate and Forest Initiative. Standing with the World’s Tropical Forests. 2021. Available online: https://www.nicfi.no/ (accessed on 22 March 2024).
- Farias, D.B.S.; Rodrigues, L.N. Agricultura Irrigada no Cerrado. In Agricutura Irrigada no Cerrado: Subsídios para o Desenvolvimento Sustentável; Rodrigues, L.N., Ed.; Embrapa: Cerrados, Planaltina, DF, Brazil, 2023; Chapter 7; pp. 176–200. [Google Scholar]
- IBGE; Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics. Censo Agro 2017. Available online: https://censoagro2017.ibge.gov.br/ (accessed on 22 March 2024).
- Nogueira, S.M.C.; Macedo, C.R. Mapeamento de lavouras de café irrigado por pivô central no extremo oeste baiano por meio de imagens do satélite ResourceSat-1. In Proceedings of the XVI Simpósio Brasileiro de Sensoriamento Remoto, Foz do Iguaçu, PR, Brazil, 13–18 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- ANA. Agência Nacional de Águas. Polos nacionais de agricultura irrigada. In Mapeamento de Áreas Irrigadas com Imagens de Satélite; ANA: Brasília, DF, Brazil, 2020; p. 46. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, R.D.; Stollberg, R.; Weiss, H.; Chang, H.K. Using GRACE to quantify the depletion of terrestrial water storage in Northeastern Brazil: The Urucuia aquifer system. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosono, A.; Hamaguchi, N.; Bojanic, A. The spatial economics of agricultural development and the formation of agro-industrial value chains: The Brazilian Cerrado. In Innovation with Spatial Impact: Sustainable Development of the Brazilian Cerrado; Hosono, A., Hamaguchi, N., Bojanic, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; Chapter 1; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, L.N. Quantidade de água utilizada na agricultura irrigada: Certezas e incertezas nas estimativas. Item 2017, 114, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, B.D.S.; Colombo, A.; Souza, J.G.N.; Baptista, V.B.; Araújo, A.C.S. Energy efficiency of a center pivot irrigation system. Eng. Agrícola 2018, 38, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaloppi, E.J.; Allen, R.G. Hydraulics of center pivot laterals. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1993, 119, 554–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assad, E.D.; Sano, E.E.; Masutomo, R.; Castro, L.H.R.; Silva, F.A.M. Veranicos na região dos Cerrados brasileiros: Frequência e probabilidade de ocorrência. Pesq. Agrop. Bras. 1993, 28, 993–1003. [Google Scholar]
- ANA. Agência Nacional de Águas e Saneamento Básico. In Conjuntura dos Recursos Hídricos no Brasil 2023; Informe anual.: Brasília, DF, Brazil, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, J.E.F.W.; Sano, E.E.; Silva, E.M.; Lopes, T.S.S. Levantamento da área irrigada por pivõ-central no Cerrado por meio da análise de imagens de satélite: Uma contribuição para a gestão dos recursos hídricos. In XVII Simpósio Brasileiro de Recursos Hídricos; ABRH: São Paulo, SP, Brazil, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, F.L.V.; Rodrigues, L.N.; Althoff, D.; Amorim, R.S.S. Spatial-temporal variability of climatic water balance in the Brazilian savannah region river basins. Water 2023, 15, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latrubesse, E.M.; Arima, E.; Ferreira, M.E.; Nogueira, S.H.; Wittmann, F.; Dias, M.S.; Dagosta, F.C.P.; Bayer, M. Fostering water resource governance and conservation in the Brazilian Cerrado biome. Conserv. Sci. Pract. 2019, 1, e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christofidis, D. Oportunidades de irrigação no Cerrado: Recursos hídricos dos Cerrados e seu potencial de utilização na irrigação. Item 2006, 69/70, 87–97. [Google Scholar]
- ANA. Agência Nacional de Águas e Saneamento Básico. In Subsídios para a DISCUSSÃO da compatibilização da Geração de Energia Hidrelétrica com Expansão da Agricultura Irrigada na Bacia do Rio São Marcos; ANA: Brasília, DF, Brazil, 2014; p. 64. [Google Scholar]



| Year | Number of Pivots | Total Area (ha) |
|---|---|---|
| 1985 | 1085 | 47,550 |
| 1990 | 2506 | 155,139 |
| 1995 | 4444 | 288,484 |
| 2000 | 5889 | 388,631 |
| 2005 | 9104 | 584,012 |
| 2010 | 10,539 | 678,088 |
| 2015 | 14,117 | 925,191 |
| 2020 | 17,764 | 1,191,887 |
| Year | Biomes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amazonia | Caatinga | Cerrado | Mata Atlântica | Pampa | Pantanal | Total | |
| 1985 | 858 | 7549 | 37,962 | 16,186 | 4187 | 0 | 66,742 |
| 1990 | 887 | 22,883 | 120,549 | 44,286 | 4032 | 31 | 192,668 |
| 1995 | 889 | 32,416 | 246,870 | 56,857 | 5193 | 68 | 342,293 |
| 2000 | 2174 | 36,080 | 348,431 | 68,056 | 8537 | 23 | 463,301 |
| 2005 | 8202 | 46,516 | 537,421 | 94,197 | 23,757 | 0 | 710,093 |
| 2010 | 9161 | 67,832 | 625,877 | 101,983 | 35,518 | 0 | 840,371 |
| 2015 | 21,943 | 89,430 | 863,539 | 117,474 | 48,888 | 0 | 1,141,274 |
| 2020 | 42,065 | 93,716 | 1,117,446 | 150,501 | 76,114 | 19 | 1,479,861 |
| Year | Federative Unit | Cerrado | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BA | DF | GO | MA | MG | MS | MT | PI | SP | TO | ||
| 1990 | 79 | 63 | 62 | 47 | 63 | 71 | 64 | 58 | 54 | 42 | 62 |
| 1995 | 87 | 62 | 66 | 68 | 62 | 76 | 63 | 47 | 52 | 69 | 65 |
| 2000 | 86 | 64 | 70 | 60 | 62 | 84 | 77 | 47 | 52 | 55 | 66 |
| 2005 | 86 | 61 | 68 | 58 | 60 | 77 | 90 | 44 | 48 | 57 | 64 |
| 2010 | 90 | 60 | 68 | 68 | 60 | 76 | 92 | 58 | 48 | 56 | 65 |
| 2015 | 96 | 56 | 67 | 70 | 59 | 84 | 108 | 55 | 47 | 67 | 66 |
| 2020 | 100 | 56 | 65 | 64 | 56 | 84 | 108 | 66 | 49 | 74 | 65 |
| Average | 89 | 60 | 67 | 62 | 60 | 79 | 86 | 54 | 50 | 60 | 65 |
| Gemorphological Unit | Average Size (ha) | Standar Deviation (ha) |
|---|---|---|
| Plateau | 81.3 | 47.8 |
| Tableland | 71.9 | 33.6 |
| Highland | 65.8 | 41.0 |
| Mountain range | 61.9 | 43.4 |
| Depression | 61.3 | 40.2 |
| Lowland | 48.0 | 40.6 |
| Platform | 46.9 | 31.4 |
| Irrigation Pole | State | Number of Pivots | Total Area (ha) | Average Size (ha) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alto Teles Pires | Mato Grosso | 266 | 34,001 | 127 |
| Oeste Baiano | Bahia | 1402 | 173,048 | 123 |
| Alto Araguaia | Goiás | 183 | 21,958 | 119 |
| Jaíba | Minas Gerais | 103 | 11,565 | 112 |
| São Marcos | Goiás | 1060 | 101,725 | 95 |
| Alto Rio Preto | Federal District and Goiás | 233 | 19,144 | 82 |
| Alto Paracatu/Entre Ribeiros | Minas Gerais | 1259 | 97,379 | 77 |
| Alto Paranapanema | São Paulo | 877 | 65,832 | 75 |
| Guaíra/Miguelópolis | Minas Gerais and São Paulo | 590 | 42,742 | 72 |
| Alto Rio das Mortes | Mato Grosso | 979 | 69,583 | 71 |
| Alto Araguari/Paranaíba | Minas Gerais | 979 | 69,583 | 71 |
| Rio das Almas | Goiás | 262 | 14,323 | 54 |
| Vertentes do Rio Pardo/Mogi Guaçu | São Paulo | 483 | 24,253 | 50 |
| Land Conversion | Number of Center Pivots | Total Area (ha) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 2020 | 2005 | 2020 | |
| Center pivot | 8382 | 7262 | 581,280 | 510,232 |
| Abandoned pivot | – | 395 | – | 27,050 |
| Rainfed cropland | – | 709 | – | 43,384 |
| Others (reforestation, urban area, rural community, water reservoir) | – | 16 | – | 614 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sano, E.E.; Magalhães, I.A.L.; Rodrigues, L.N.; Bolfe, É.L. Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Center Pivot Irrigation Systems in the Brazilian Tropical Savanna (1985–2020). Water 2024, 16, 1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131897
Sano EE, Magalhães IAL, Rodrigues LN, Bolfe ÉL. Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Center Pivot Irrigation Systems in the Brazilian Tropical Savanna (1985–2020). Water. 2024; 16(13):1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131897
Chicago/Turabian StyleSano, Edson Eyji, Ivo Augusto Lopes Magalhães, Lineu Neiva Rodrigues, and Édson Luis Bolfe. 2024. "Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Center Pivot Irrigation Systems in the Brazilian Tropical Savanna (1985–2020)" Water 16, no. 13: 1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131897
APA StyleSano, E. E., Magalhães, I. A. L., Rodrigues, L. N., & Bolfe, É. L. (2024). Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Center Pivot Irrigation Systems in the Brazilian Tropical Savanna (1985–2020). Water, 16(13), 1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131897










