Case of Vibrio vulnificus Infection in Orechromis niloticus during Suspension of Recirculating Aquaculture System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
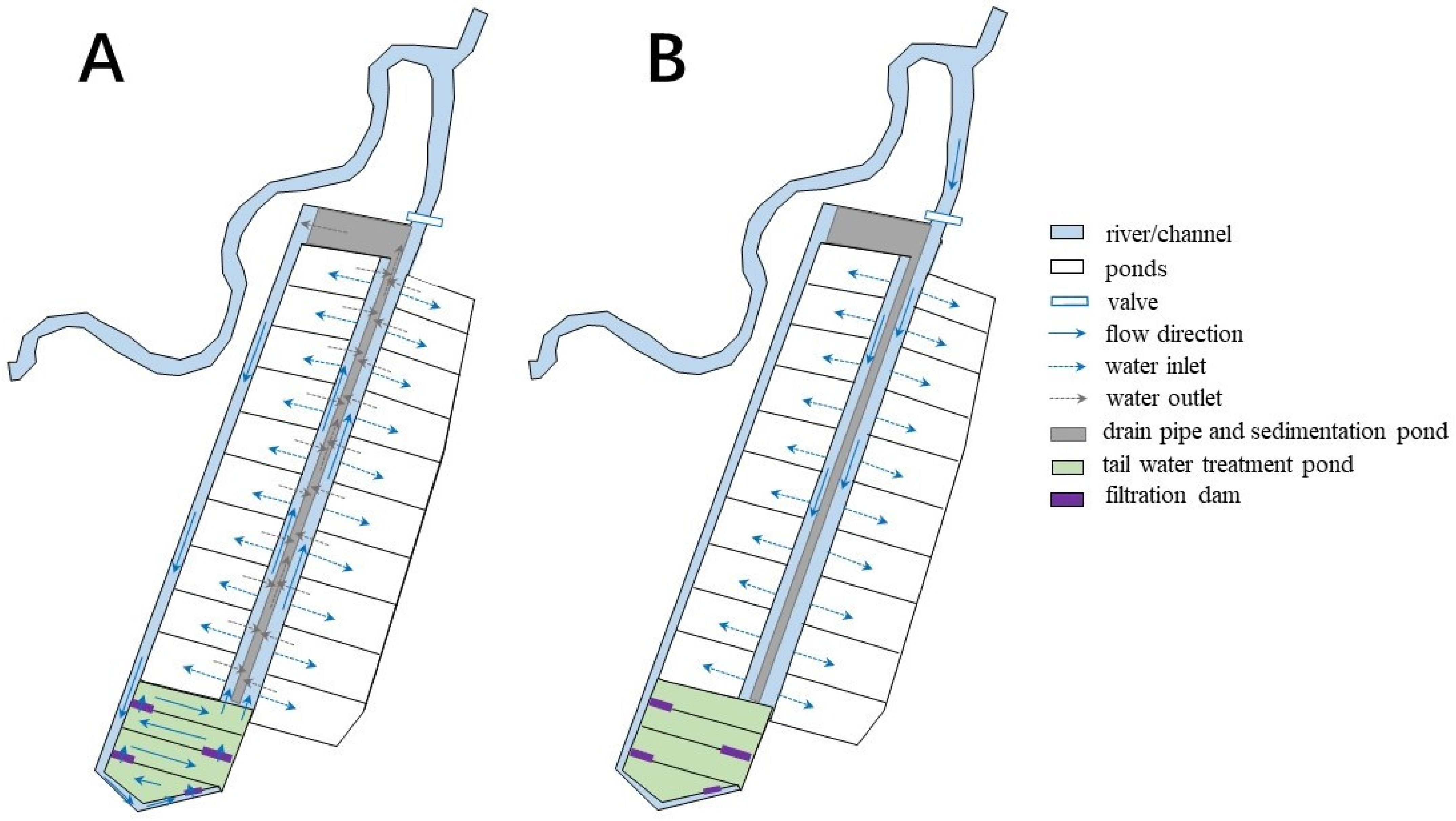
2.1. History of the Case
2.2. Fish
2.3. Water Quality Evaluation
2.4. Pathologic Diagnosis
2.4.1. External and Anatomical Observation
2.4.2. Histopathology
2.5. Bacterial Isolation and Identification
2.5.1. Bacterial Isolation
2.5.2. Virulence Test
2.5.3. Bacterial Identification
- 1.
- Physiological and biochemical tests
- 2.
- Molecular identification
2.5.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test
2.5.5. Challenge Experiments and LD50
2.6. Analysis and Influence of Risk Factors
3. Results
3.1. Water Quality Evaluation
3.2. Pathologic Diagnosis
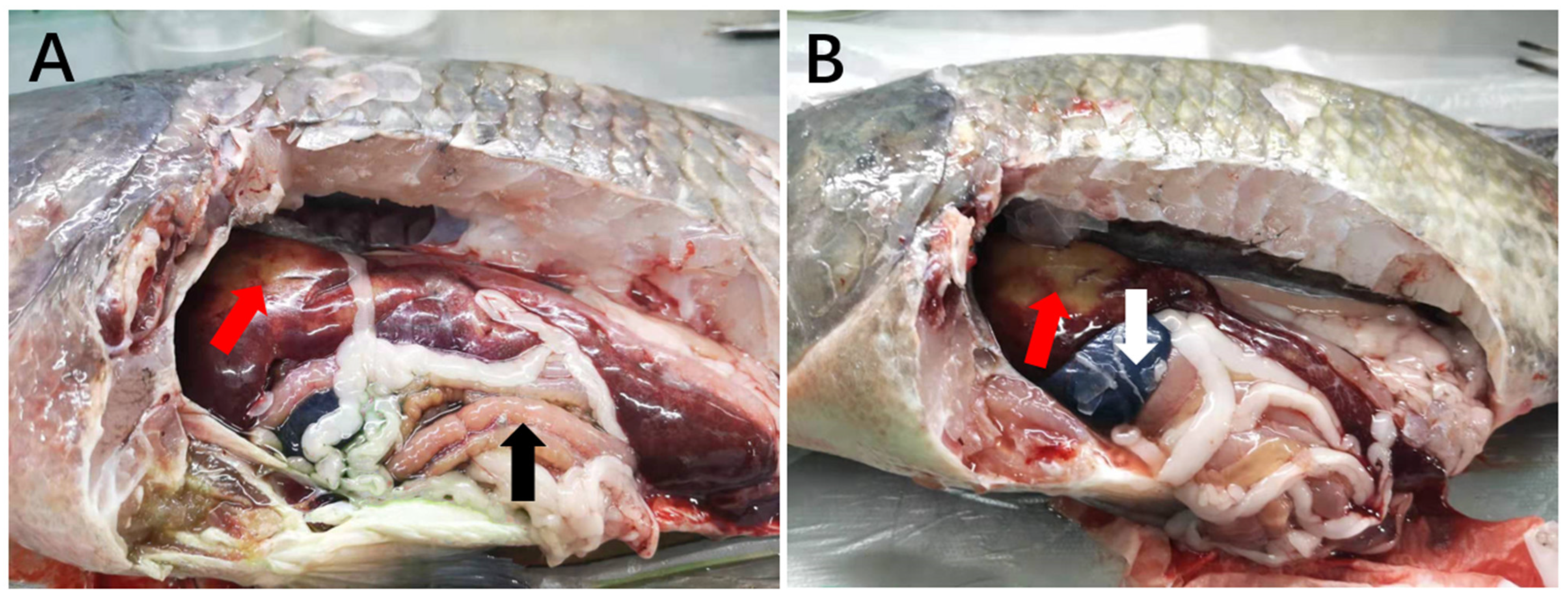
3.2.1. Gross Observations
3.2.2. Histopathology
3.3. Bacterial Isolation and Identification
3.3.1. Virulence Test
3.3.2. Physiological and Biochemical Tests
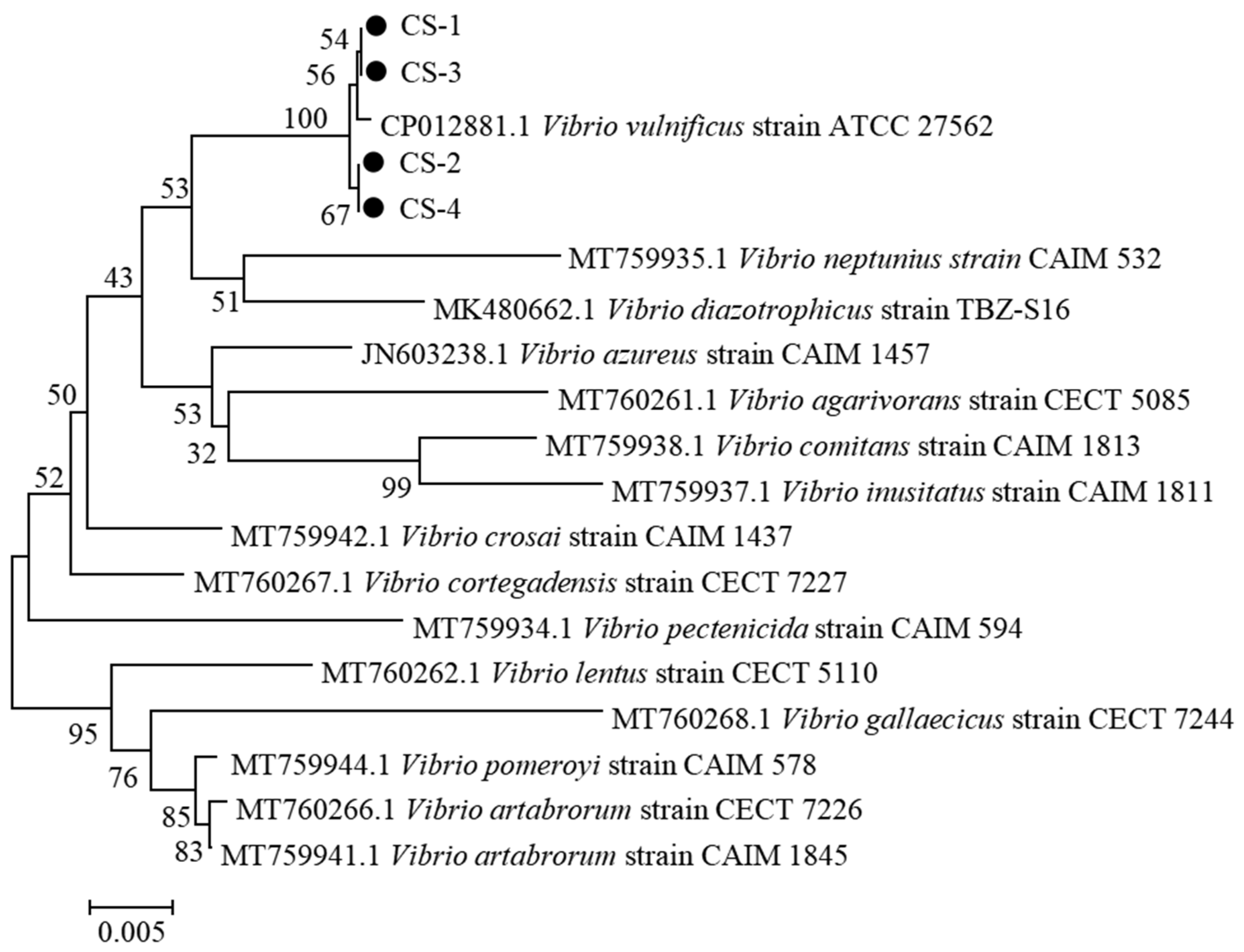
3.3.3. Sequence Analysis of 16S rRNA Gene
3.3.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Results
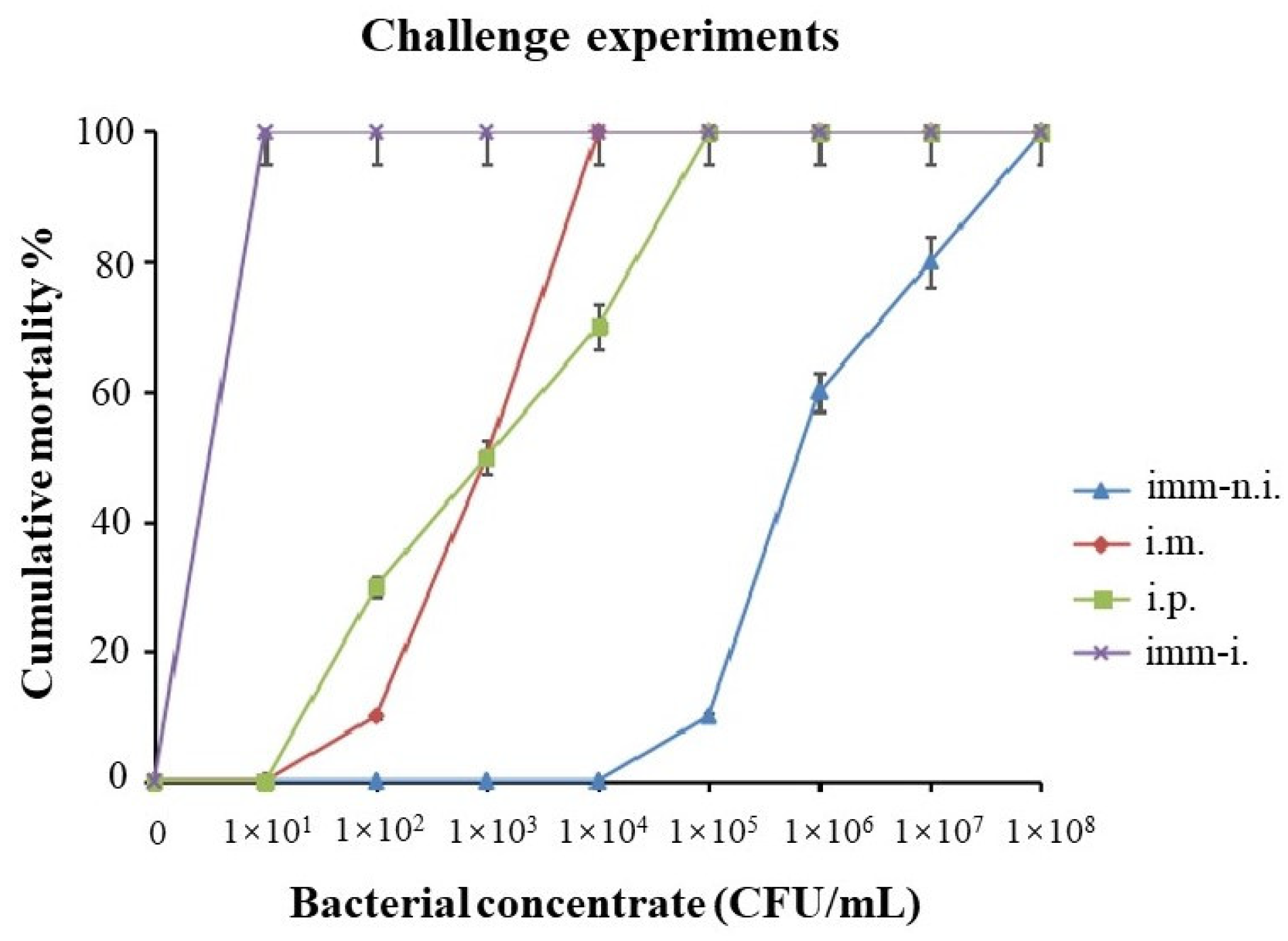
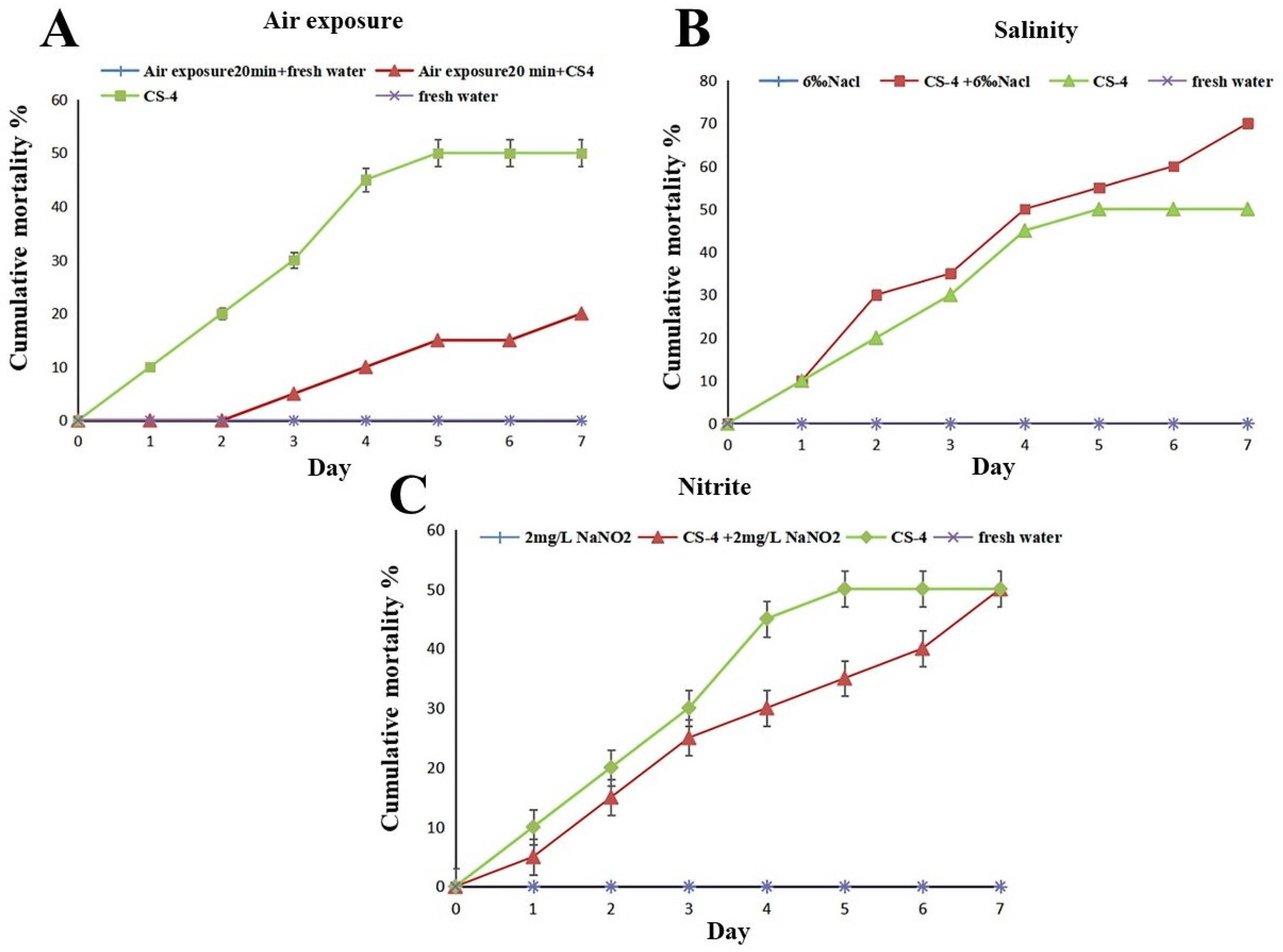
3.3.5. Challenge Experiments and LD50 Values
3.4. Analysis and Influence of Risk Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Biochemical Test | CS-4 | Vibrio vulnificus ATCC27562 |
|---|---|---|
| Gram staining | − | − |
| TCBS growth | G | G |
| Not NaCl tryptone broth | − | − |
| 1% NaCl tryptone broth | + | + |
| 3% NaCl tryptone broth | + | + |
| 6% NaCl tryptone broth | + | + |
| 8% NaCl tryptone broth | − | − |
| 10% NaCl tryptone broth | − | − |
| ONPG reaction | + | N |
| Catalase | + | + |
| Oxidase | + | N |
| VP reaction | − | N |
| Malonate | − | − |
| Arginine hydrolase | − | − |
| Iysine decarboxylase | + | + |
| Esculin hydrolysis | + | N |
| Mannitol | + | N |
| Rhamnose | + | − |
| Mannose | + | + |
| Lactose | − | N |
| Sorbitol | − | − |
| Glucose | + | + |
| Citrate | + | N |
| Cellobiose | + | + |
| Indole production | + | N |
| Salican | − | + |
| Antibiotics | Content (μg/Tablet) | Diameters of Inhibition Zone (mm) | Critical Range | Susceptibility | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R (mm) | I (mm) | S (mm) | ||||
| Penicillin | 10 U | 18.59 ± 0.50 | ≤19 | 20–27 | ≥28 | R |
| Mezlocillin | 75 | 19.58 ± 0.53 | ≤17 | 18–20 | ≥21 | S |
| Cefradine | 30 | 15.18 ± 2.61 | ≤14 | 15–17 | ≥18 | I |
| Cefotaxime | 30 | 20.42 ± 2.05 | ≤14 | 15–22 | ≥23 | I |
| Gentamicin | 10 | 20.33 ± 0.85 | ≤12 | 13–14 | ≥15 | S |
| Kanamycin | 30 | 18.89 ± 0.56 | ≤13 | 14–17 | ≥18 | S |
| Streptomycin | 10 | 18.71 ± 0.94 | ≤11 | 12–14 | ≥15 | S |
| Tobramycin | 10 | 17.44 ± 1.10 | ≤12 | 13–14 | ≥15 | S |
| Neomycin | 30 | 15.59 ± 0.80 | ≤12 | 13–16 | ≥17 | S |
| Tetracycline | 30 | 22.84 ± 1.74 | ≤14 | 15–18 | ≥19 | S |
| Nalidixic acid | 30 | 26.48 ± 1.56 | ≤13 | 14–18 | ≥19 | S |
| Aboren | 30 | 19.32 ± 0.68 | ≤13 | 14–17 | ≥18 | S |
| Lincomycin | 2 | 0.00 | ≤14 | 15–20 | ≥21 | R |
| Vancomycin | 30 | 13.22 ± 0.62 | ≤9 | 10–11 | ≥12 | S |
| Polymyxin B | 300 | 0.00 | ≤8 | 8–11 | ≥12 | R |
| Cotrimoxazole | 25 | 28.11 ± 1.55 | ≤10 | 11–15 | ≥16 | S |
| Amoxicillin | 20 | 18.3 ± 0.37 | ≤13 | 14–17 | ≥18 | S |
| Rifampicin | 5 | 24.31 ± 0.83 | ≤16 | 17–19 | ≥20 | S |
| Trimethoprim | 5 | 20.70 ± 1.27 | ≤10 | 11–15 | ≥16 | S |
| Enrofloxacin | 10 | 23.34 ± 0.64 | ≤15 | 16–20 | ≥21 | S |
| Bacitracin | 10 U | 10.66 ± 0.71 | ≤8 | 9–12 | ≥13 | I |
| Florfenicol | 30 | 24.18 ± 1.22 | ≤12 | 13–17 | ≥18 | S |
| Cefamandole | 30 | 18.50 ± 0.35 | ≤14 | 15–17 | ≥18 | S |
| Doxycycline | 30 | 20.47 ± 1.33 | ≤12 | 13–15 | ≥16 | S |
| Norfloxacin | 10 | 27.91 ± 1.49 | ≤12 | 13–16 | ≥17 | S |
References
- Naylor, R.L.; Hardy, R.W.; Buschmann, A.H.; Bush, S.R.; Cao, L.; Klinger, D.H.; Little, D.C.; Lubchenco, J.; Shumway, S.E.; Troell, M. A 20-year retrospective review of global aquaculture. Nature 2021, 591, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Abdullah, S.R.S.A.; Hasan, H.A.; Othman, A.R.; Ismail, N.I. Aquaculture industry: Supply and demand, best practices, effluent and its current issues and treatment technology. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 287, 112271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.; Turchini, G.M. Recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS): Environmental solution and climate change adaptation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cui, Z.G.; Cui, H.W.; Bai, Y.; Yin, Z.D.; Qu, K.M. Hazardous substances and their removal in recirculating aquaculture systems: A review. Aquaculture 2023, 569, 739399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badiola, M.; Basurko, O.C.; Piedrahita, R.; Hundley, P.; Mendiola, D. Energy use in recirculating aquaculture systems(RAS): A review. Aquac. Eng. 2018, 81, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Engle, C.R. Technological Advances that Led to Growth of Shrimp, Salmon, and Tilapia Farming. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2016, 24, 136–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Thompson, K.D.; Wangkahart, E.; Yamkasem, J.; Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; Tattiyapong, P.; Jian, J.; Surachetpong, W. Strategies to enhance tilapia immunity to improve their health in aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, K. The many challenges of disease management in aquaculture. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2022, 53, 1080–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes-Trujillo, A.; Mendoza-Carranza, M. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the relationship between farm management, water quality and pathogen outbreaks in tilapia culture. J. Fish Dis. 2022, 45, 1529–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anil, M.K.; Krishna, M.V.R.; Gomathi, P.; Surya, S.; Gop, A.P.P.; Santhosh, B.; Siju, R.; Anand, V.; Krishnapriya, P.M.; Shalini, O.; et al. Recent advances in marine ornamental breeding and seed production at Vizhinjam Regional Centre of CMFRI India. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 907568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglade, I.; Krogli, T.M.; Reitan, K.I. Sludge from sea-based Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) production: Quantification, composition, and potential application in integrated multi-trophic aquaculture. Aquac. Int. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, E.; Cai, Y.; Wang, S.; Ren, Z.; Li, Q.; Guo, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y. Isolation, identification and pathogenicity characterization of Vibrio ponticus from the golden pompano Trachinotus ovatus. Aquaculture 2018, 496, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Yan, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, S.; Li, A.; Xiong, Y.; Tang, J.; Sun, Y.; Guo, W.; Zhou, Y. First case of Aeromonas schubertii infection in brackish water wild Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, in China. Aquaculture 2019, 501, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). Test No. 425: Acute Oral Toxicity: Up-and-Down Procedure. In OECD Guideline for Testing of Chemicals, Section 4: Health Effects; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, J.P. Genus I. Vibrio. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology; Brenner, D.J., Krieg, N.R., Staley, J.T., Eds.; Springer: East Lansing, MI, USA, 2005; Volume 2, Part B, pp. 494–546. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, T.; Liang, L.; Kai, C.; Xi, B.; Xu, P. Isolation, identification and phenotypic and molecular characterization of pathogenic Vibrio vulnificus isolated from Litopenaeus vannamei. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 0186135. [Google Scholar]
- Baker-Austin, C.; Oliver, J.D.; Alam, M.; Ali, A.; Waldor, M.K.; Qadri, F.; Martinez-Urtaza, J. Vibrio spp. Infections. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haenen, O.L.M.; Dong, H.T.; Hoai, T.D.; Crumlish, M.; Karunasagar, I.; Barkham, T.; Chen, S.L.; Zadoks, R.; Kiermeier, A.; Wang, B.; et al. Bacterial diseases of tilapia, their zoonotic potential and risk of antimicrobial resistance. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 154–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiel, B.; Cohen, D.I.; Harding, R.M.; Daniel, F.; Crook, D.W.; Tim, P. Hybrid Vibrio vulnificus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, H.; Liu, S.; Guo, Z.; Cheng, C.; Ma, H.; Feng, J. Prevalence, virulence genes, and antimicrobial resistance of Vibrio species isolated from diseased marine fish in South China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sony, M.; Sumithra, T.G.; Anusree, V.N.; Amala, P.V.; Reshma, K.J.; Alex, S.; Sanil, N.K. Antimicrobial resistance and virulence characteristics of Vibrio vulnificus, Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio harveyi from natural disease outbreaks of marine/estuarine fishes. Aquaculture 2021, 539, 736608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.; Al-Dulaimi, K.; Sahilah, A. Article Multiple Antibiotic Resistance (MAR), Plasmid Profiles, and DNA Polymorphisms among Vibrio vulnificus isolates. Antibiotics 2019, 68, 2–13. [Google Scholar]
- Cabello, F.C.; Godfrey, H.P.; Tomova, A.; Ivanova, L.; Dölz, H.; Millanao, A.; Buschmann, A.H. Antimicrobial use in aquaculture re-examined: Its relevance to antimicrobial resistance and to animal and human health. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1917–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, S.H.; Garcia, F.; Gozi, K.S.; Romera, D.M.; Francisco, J.G.; Moura-Andrade, G.C.; Tornisielo, V.L. Relationship between antibiotic residues and occurrence of resistant bacteria in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) cultured in cage-farm. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B Pestic. Food Contam. Agric. Wastes 2016, 51, 17–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, E.; Zayas, M.; Tobar, J.; Illanes, O.; Yount, S.; Francis, S.; Dennis, M.M. Laboratory- controlled challenges of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) with Streptococcus agalactiae: Comparisons between immersion, oral, intracoelomic and intramuscular routes of infection. J. Comp. Pathol. 2016, 155, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welker, A.F.; Moreira, D.C.; Campos, E.G.; Hermes-Lima, M. Role of redox metabolism for adaptation of aquatic animals to drastic changes in oxygen availability. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2013, 165, 384–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lushchak, V.I.; Bagnyukova, T.V.; Husak, V.V.; Luzhna, L.I.; Lushchak, O.V.; Storey, K.B. Hyperoxia results in transient oxidative stress and an adaptive response by antioxidant enzymes in goldfish tissues. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2005, 37, 1670–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paital, B. Modulation of redox regulatory molecules and electron transport chain activity in muscle of air breathing fish Heteropneustes fossilis under air exposure stress. J. Comp. Physiol. B Biochem. Syst. Environ. Physiol. 2014, 184, 65. [Google Scholar]
- Arleta, K.S.; Elisabetta, M.; Marco, B.; Fatemeh, N.; Jesús, M. Impact of Air Exposure on Vasotocinergic and Isotocinergic Systems in Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata): New Insights on Fish Stress Response. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 96. [Google Scholar]
- Eskandari, G.; Saghavi, H.; Zabayeh Najafabadi, M.; Dehghan Madiseh, S.; Koochaknejad, E. Effect of salinity on reproductive performance of Acanthopagrus latus (Houttuyn) in spawning tanks. Aquac. Res. 2013, 44, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Yin, S. Effects of salinity change on two superoxide dismutases (SODs) in juvenile marbled eel Anguilla marmorata. PeerJ 2016, 4, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Tan, P.; Yang, L.; Zhu, W.; Xu, D. Effects of salinity on the growth, plasmaion concentrations, osmoregulation, non-specific immunity, and intestinal microbiota of the yellow drum (Nibea albiflora). Aquaculture 2020, 528, 735470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atli, G.; Canli, M. Response of antioxidant system of freshwater fish Oreochromis niloticus to acute and chronic metal (Cd, Cu, Cr, Zn, Fe) exposures. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 1884–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Mai, K.; Hongming, M.A.; Qinghui, A.I.; Zhang, W.; Wei, X.U. Rearing in intermediate salinity enhances immunity and disease-resistance of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2011, 30, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Cope, W.G.; Harms, C.A.; Law, J.M. Rapid decreases in salinity, but not increases, lead to immune dysregulation in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.). Fish Dis. 2012, 36, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, R.; Chen, L.; Xin, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, X.; Huang, J.; Liao, Z.; Li, W. Effects of salinity stress on immune-related parameters of the Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Fish. China 2020, 44, 978–986. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, C.M.; Nawata, C.M. A nose-to-nose comparison of the physiological and molecular responses of rainbow trout to high environmental ammonia in seawater versus freshwater. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 3557–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saoud, P.; Naamani, S.; Ghanawi, J.; Nasser, N. Effects of acute and chronic nitrite exposure on rabbitfish Siganus rivulatus growth, hematological parameters, and gill histology. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2014, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Han, C.; Lei, J.L.; Liu, B.L.; Huang, B.; Huo, H.H.; Yin, S.T. Effects of nitrite exposure on haematological parameters, oxidative stress and apoptosis in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 169, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hvas, M.; Damsgaard, C.; Jensen, F.B.; Bayley, M. The effect of environmental hypercapnia and size on nitrite toxicity in the striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus). Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 176, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciji, A.; Sahu, N.P.; Pal, A.K.; Dasgupta, S.; Akhtar, M.S. Alterations in serum electrolytes, antioxidative enzymes and haematological parameters of Labeo rohita on short-term exposure to sublethal dose of nitrite. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 1355–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Miao, L.H.; Pan, W.J.; Huang, X.; Deng, J.M.; Zhang, W.X.; Ge, X.P.; Liu, B.; Ren, M.C.; Zhou, Q.L.; et al. Effect of nitrite exposure on the antioxidant enzymes and glutathione system in the liver of bighead carp, Aristichthys nobilis. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 76, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | Expected Size/bp | Annealing Tm (°C) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16S rRNA | 27F: AGAGTTTGATCATGGCTCAG | 1504 | 55 | [13] |
| 1492R: GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT |
| Group | Sub-Experiment A | Sub-Experiment S | Sub-Experiment N |
|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment #1 | Crowding stress (20 min) + air exposure (20 min) + freshwater | NaCl (6 g/L) | NaNO2 (2 mg/L) |
| Treatment #2 | Crowding stress (20 min) + air exposure (20 min) + CS-4 (20 min) + freshwater | CS-4 (20 min) + NaCl (6 g/L) | CS-4 (20 min) + NaNO2 (2 mg/L) |
| Control | CS-4 (20 min) + freshwater | ||
| Blank | freshwater | ||
| Salinity (g/L) | Ammonia Nitrogen (mg/L) | Nitrate Nitrogen (mg/L) | Nitrite Nitrogen (mg/L) | Total Nitrogen (mg/L) | Total Phosphorus (mg/L) | Orthophosphate (μmol/L) | Chemical Oxygen Demand (mg/L) | Suspended Solids (mg/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before RAS suspension | ≤1 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.013 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 2.89 | 19.9 | 9 |
| After water refill | 6 | 0.04 | 0.20 | 0.115 | 2.2 | 1.1 | 3.06 | 28.6 | 26 |
| During disease outbreak | 6 | 0.06 | 0.15 | 0.95 | 1.8 | 1.3 | 2.32 | 24.7 | 25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S. Case of Vibrio vulnificus Infection in Orechromis niloticus during Suspension of Recirculating Aquaculture System. Water 2024, 16, 1878. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131878
Cai Y, Jiang L, Wang S, Zhao Z, Zhou Y, Wang S. Case of Vibrio vulnificus Infection in Orechromis niloticus during Suspension of Recirculating Aquaculture System. Water. 2024; 16(13):1878. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131878
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Yan, Liu Jiang, Shaoqun Wang, Zhangding Zhao, Yongcan Zhou, and Shifeng Wang. 2024. "Case of Vibrio vulnificus Infection in Orechromis niloticus during Suspension of Recirculating Aquaculture System" Water 16, no. 13: 1878. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131878
APA StyleCai, Y., Jiang, L., Wang, S., Zhao, Z., Zhou, Y., & Wang, S. (2024). Case of Vibrio vulnificus Infection in Orechromis niloticus during Suspension of Recirculating Aquaculture System. Water, 16(13), 1878. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131878








