Synthesis of Fe-Loaded Biochar Obtained from Rape Straw for Enhanced Degradation of Emerging Contaminant Antibiotic Metronidazole
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
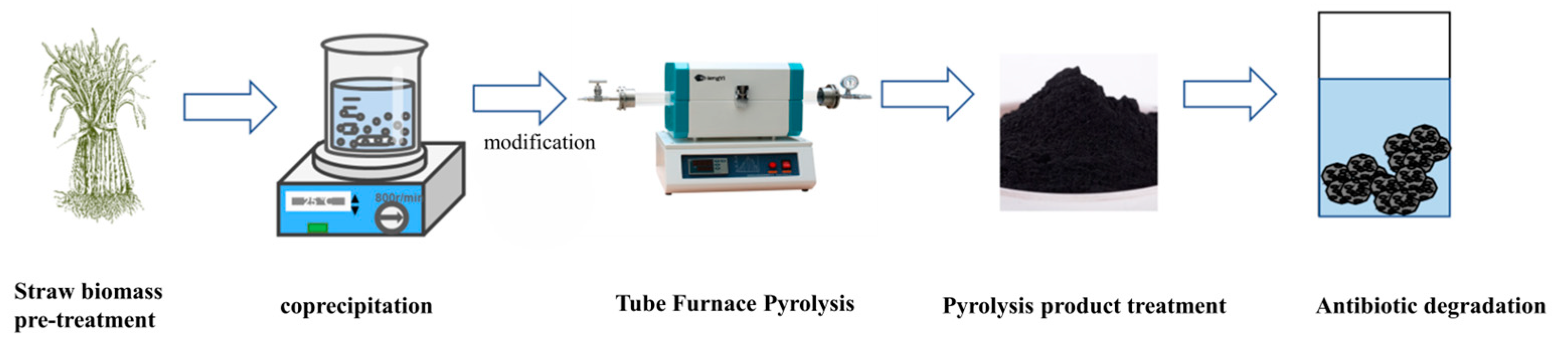
2.2. Preparation of Rape Straw Biomass
2.3. Preparation of Sodium Ferrate Modified Biochar
2.4. Catalyst Characterization
2.5. Degradation Experiment
2.6. Influencing Factors Experiment
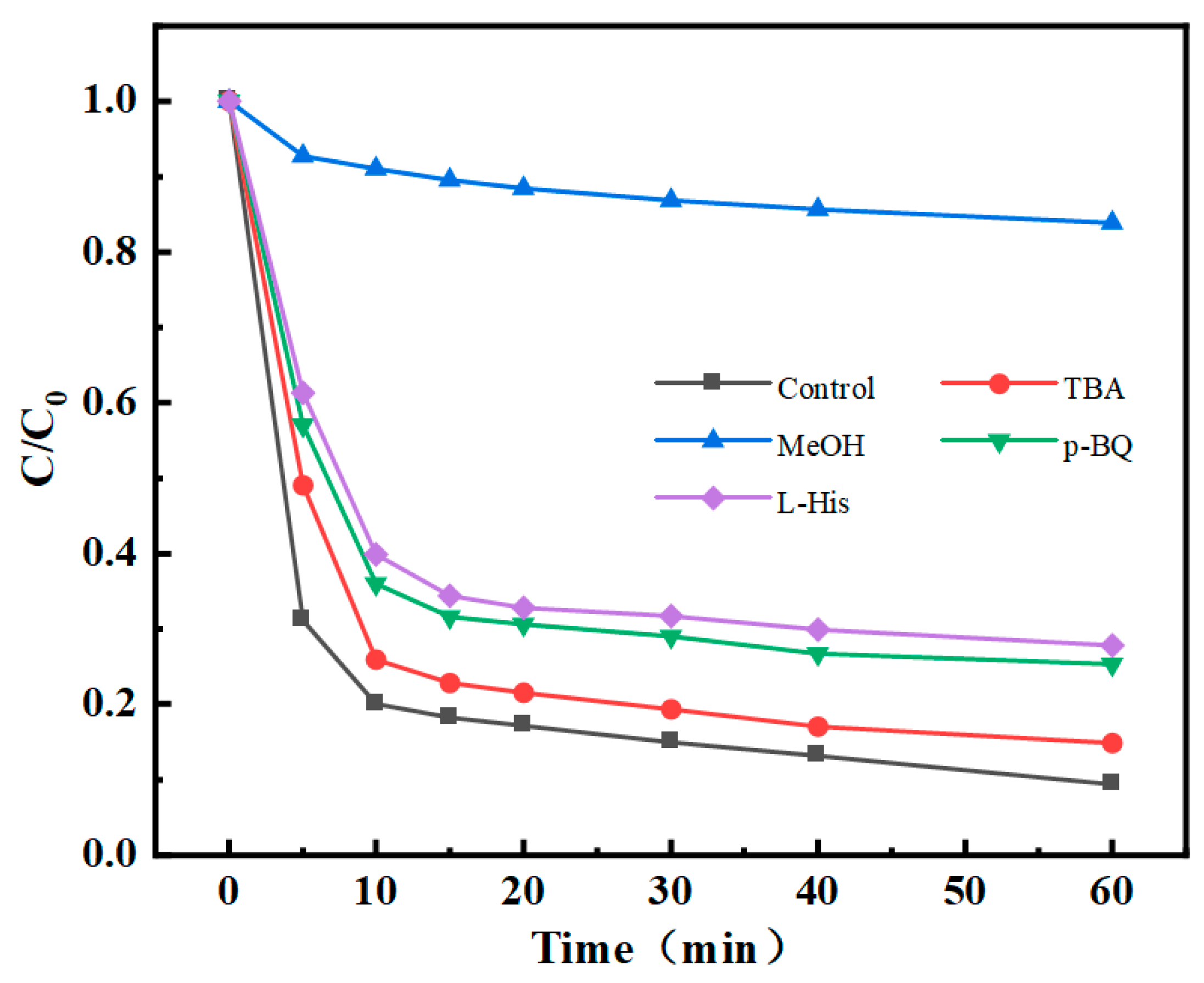
2.7. Free-Radical Scavenging Experiment
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Morphology and Structure Analysis
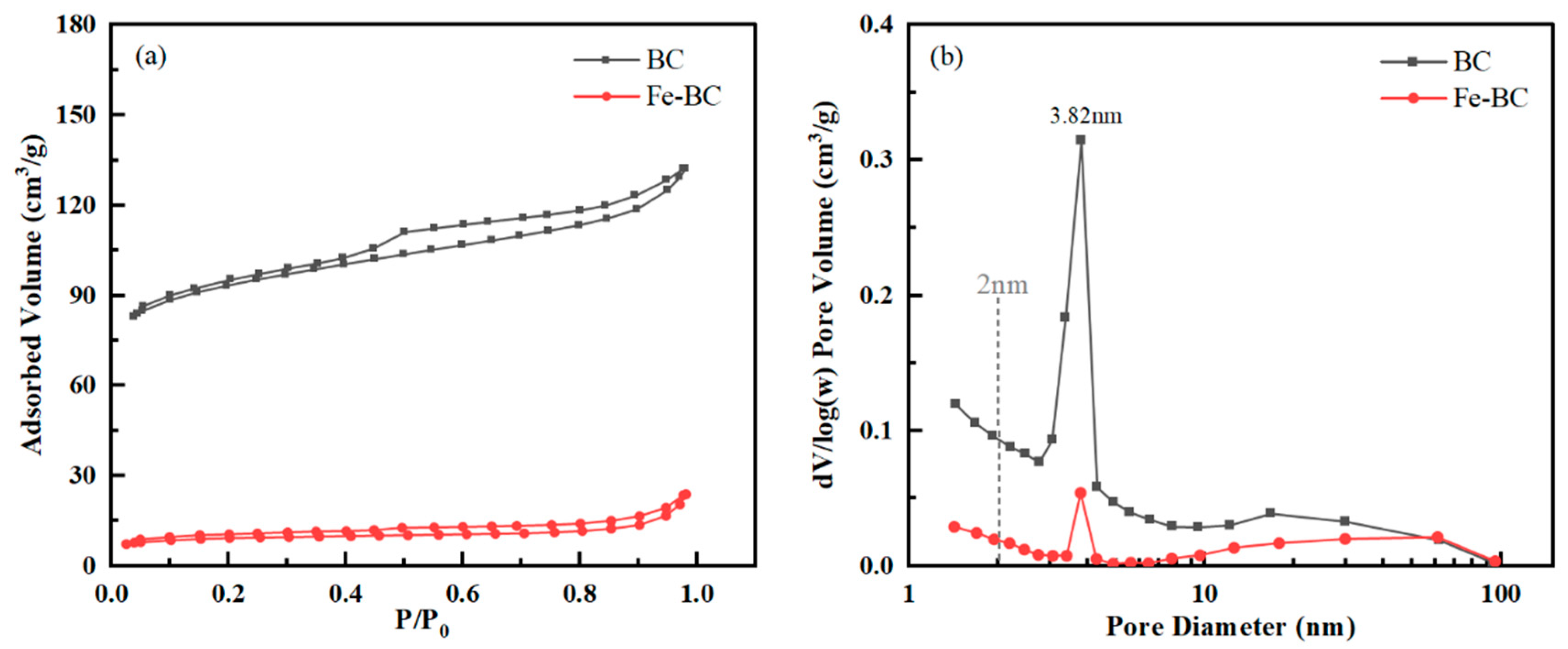
3.2. Surface Structure Analysis
3.3. Materials Analysis
3.4. Functional Group Analysis
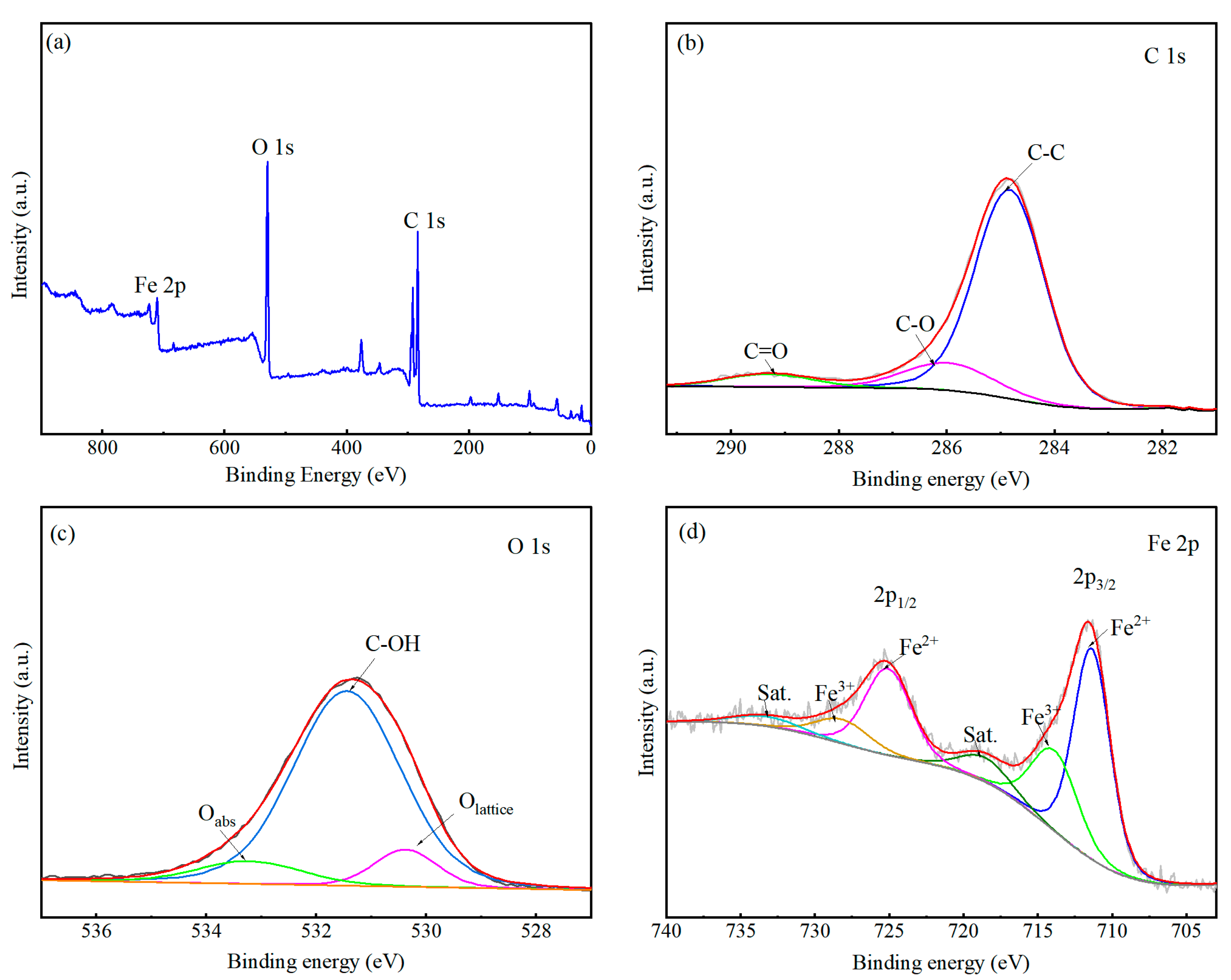
3.5. Bonding State and Elements Analysis
4. Catalytic Assessment
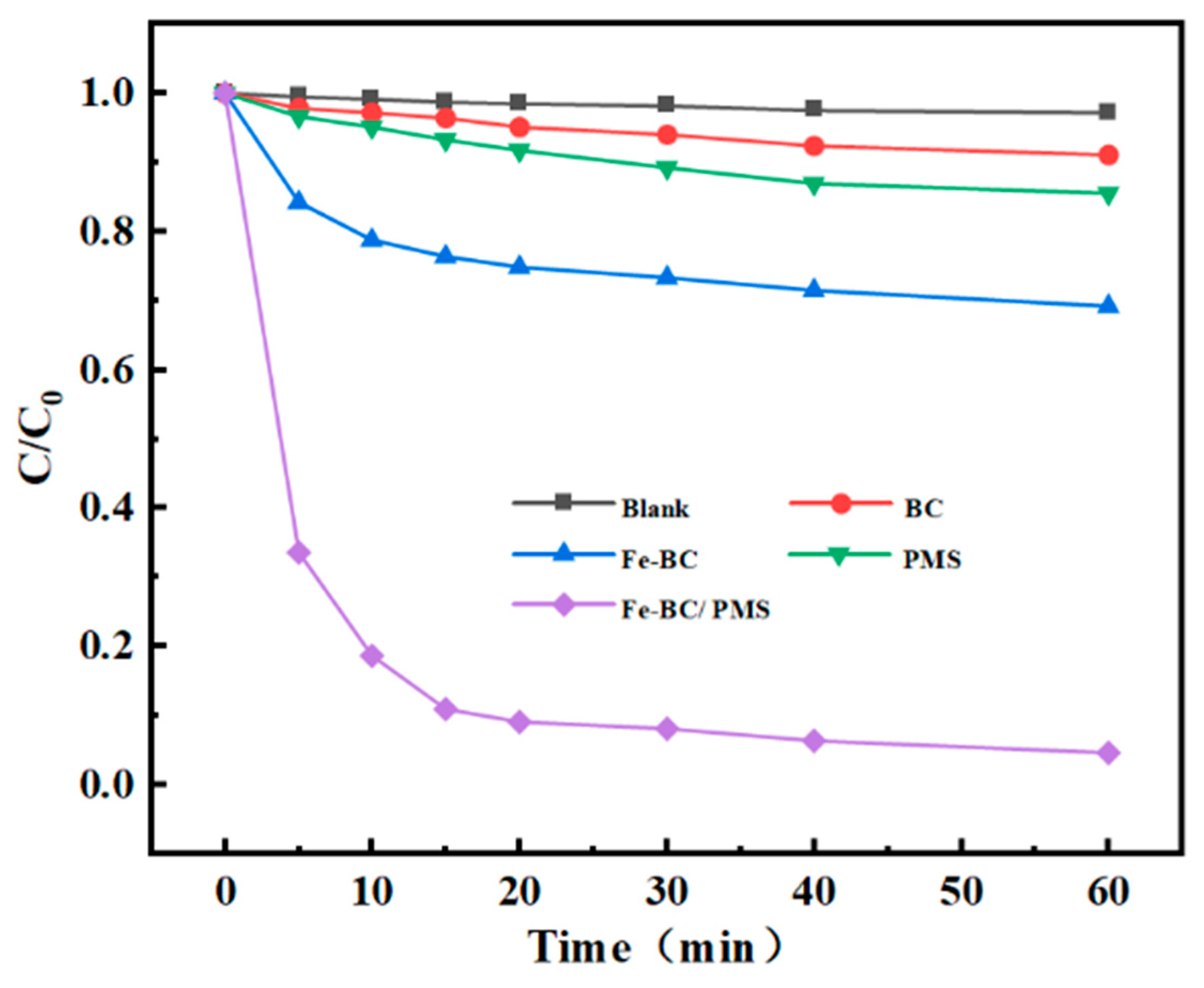
4.1. MNZ Degradation in Different Catalytic Systems
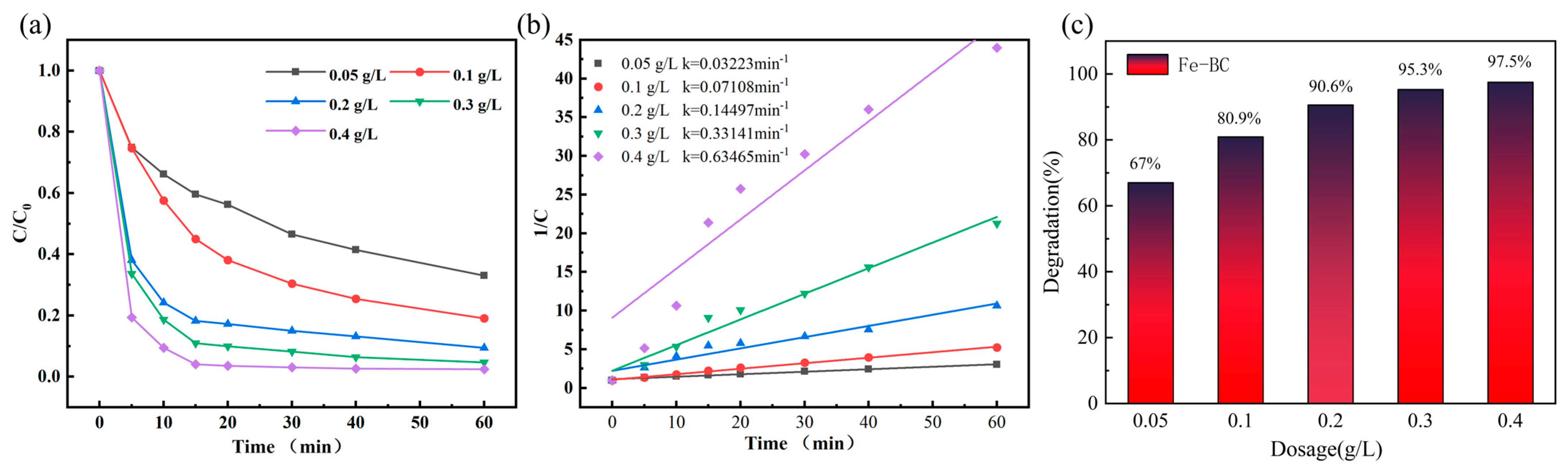
4.2. Catalyst Dosage’s Impact on MNZ Degradation
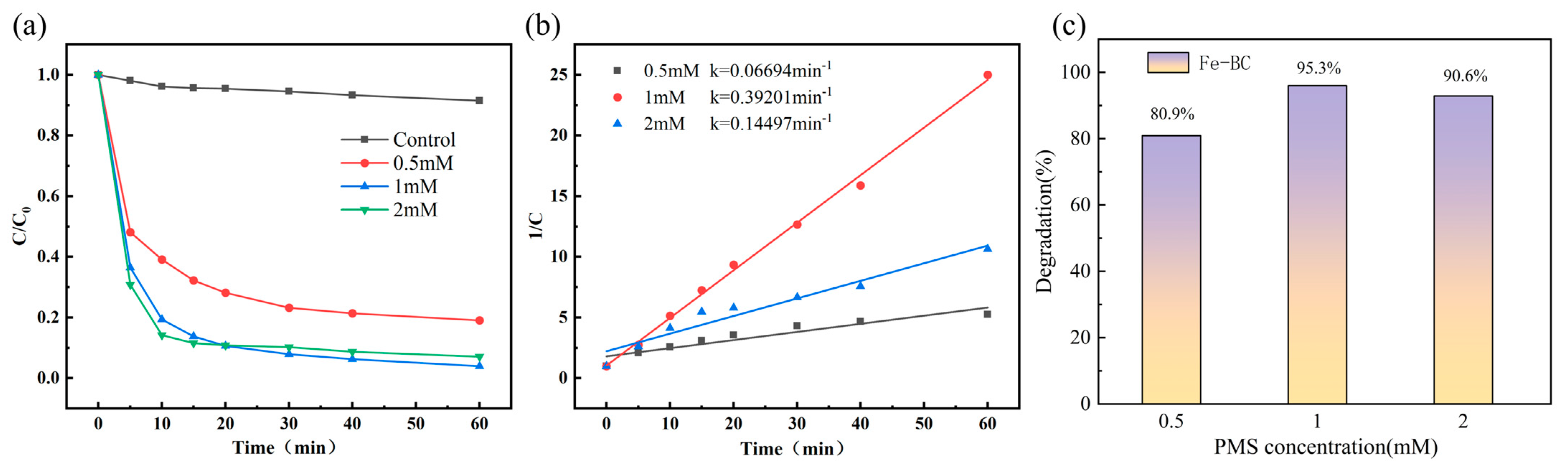
4.3. Effect of PMS Concentration on MNZ Degradation
4.4. Effect of pH on MNZ Degradation
4.5. Effects of Inorganic Anions on MNZ Degradation
4.6. Reaction Mechanism
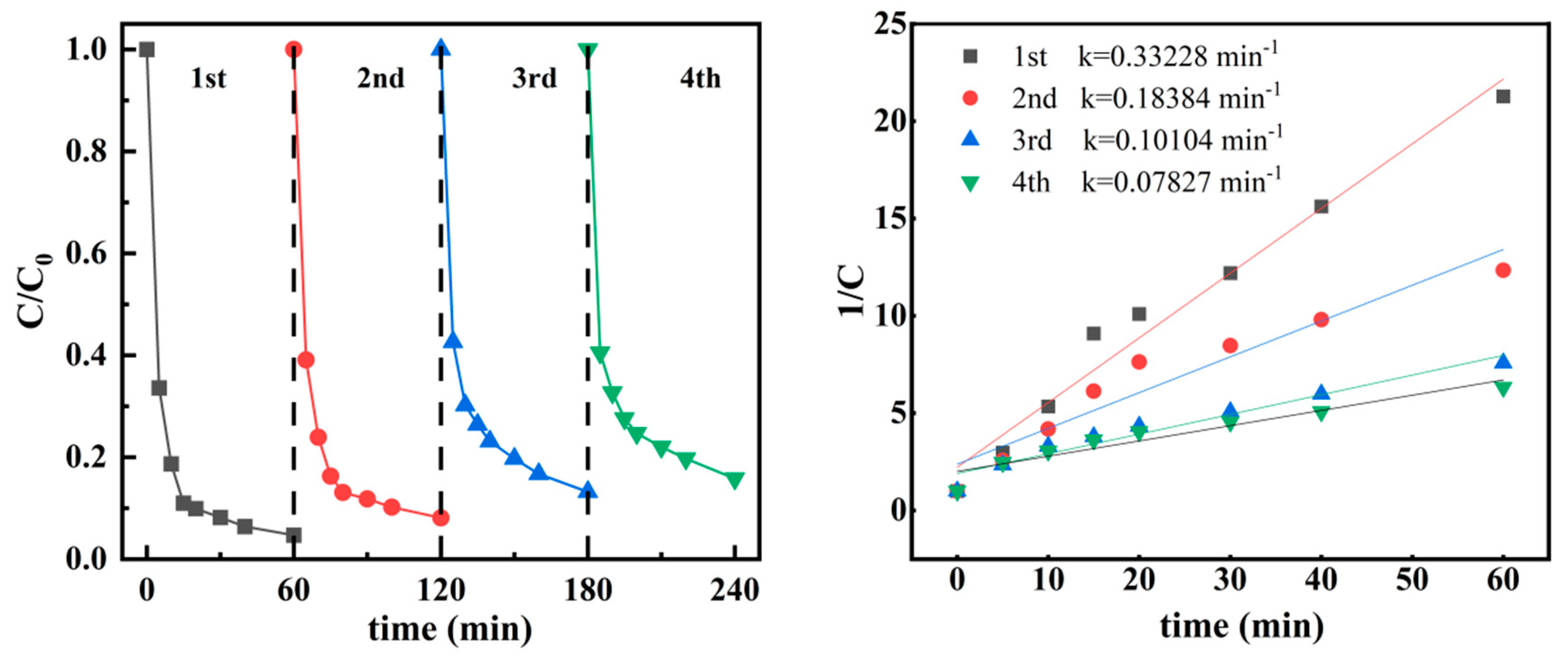
4.7. Cyclic Experiments
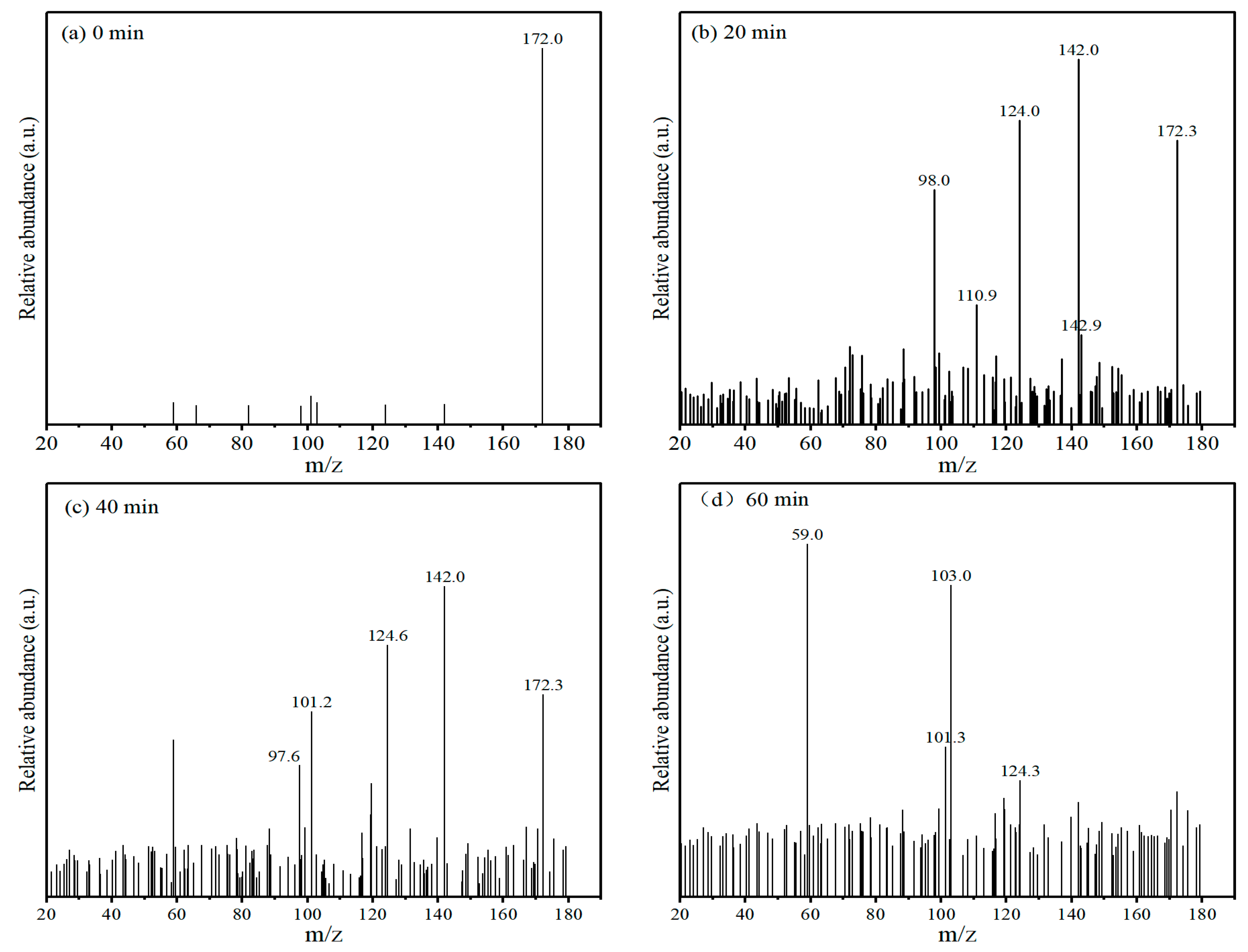
4.8. Degradation Pathways of MNZ
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ji, Y.; Shi, Y.; Dong, W.; Wen, X.; Jiang, M.; Lu, J. Thermo-activated persulfate oxidation system for tetracycline antibiotics degradation in aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 298, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, C.; Lyu, J.; Hu, Z.; Ge, M. Tetracycline degradation by persulfate activated with magnetic Cu/CuFe2O4 composite: Efficiency, stability, mechanism and degradation pathway. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Pal, D. Antibiotic resistance and wastewater: Correlation, impact and critical human health challenges. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Ying, G.-G.; Singer, A.C.; Zhu, Y.-G. Review of antibiotic resistance in China and its environment. Environ. Int. 2018, 110, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Chamorro, S.; Marti, E.; Huerta, B.; Gros, M.; Sànchez-Melsió, A.; Borrego, C.M.; Barceló, D.; Balcázar, J.L. Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in hospital and urban wastewaters and their impact on the receiving river. Water Res. 2015, 69, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Han, N.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Jiang, M.; Bokhari, A.; Zhang, W.; Race, M.; Shen, Z.; Chen, R.; et al. Perovskite oxide for emerging photo(electro)catalysis in energy and environment. Environ. Res. 2022, 205, 112544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingerslev, F.; Halling-Sorensen, B. Biodegradability of metronidazole, olaquindox, and tylosin and formation of tylosin degradation products in aerobic soil–manure slurries. Ecotoxicol. Env. Saf. 2001, 48, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro-Catala, N.; Kuzmanovic, M.; Roig, N.; Sierra, J.; Ginebreda, A.; Barcelo, D.; Perez, S.; Petrovic, M.; Pico, Y.; Schuhmacher, M.; et al. Ecotoxicity of sediments in rivers: Invertebrate community, toxicity bioassays and the toxic unit approach as complementary assessment tools. Sci. Total Env. 2016, 540, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Huang, F.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, K.; He, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Determination and toxicity evaluation of the generated byproducts from sulfamethazine degradation during catalytic oxidation process. Chemosphere 2019, 226, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Cho, D.-W.; Graham, N.J.D.; Hou, D.; Yip, A.C.K.; Khan, E.; Song, H.; Li, Y.; Tsang, D.C.W. Degradation of antibiotics by modified vacuum-UV based processes: Mechanistic consequences of H2O2 and K2S2O8 in the presence of halide ions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Deng, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, C.; Shi, Z. Development of oxygen vacancies enriched CoAl hydroxide@hydroxysulfide hollow flowers for peroxymonosulfate activation: A highly efficient singlet oxygen-dominated oxidation process for sulfamethoxazole degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Wu, X.-L.; Yang, L.; Chen, C.; Lin, H.; Chen, J. Efficient degradation and mineralization of antibiotics via heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate by using graphene supported single-atom Cu catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 394, 124904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coha, M.; Farinelli, G.; Tiraferri, A.; Minella, M.; Vione, D. Advanced oxidation processes in the removal of organic substances from produced water: Potential, configurations, and research needs. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 414, 128668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, M.; Wang, D.; Yan, M.; Liu, Z. Different activation methods in sulfate radical-based oxidation for organic pollutants degradation: Catalytic mechanism and toxicity assessment of degradation intermediates. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Dong, H.; Li, L.; Tang, L.; Tian, R.; Li, R.; Chen, J.; Xie, Q.; Jin, Z.; Xiao, J.; et al. Recent advances in waste water treatment through transition metal sulfides-based advanced oxidation processes. Water Res. 2021, 192, 116850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, D.; Zhang, C.; Tang, S.; Sun, M.; Zhang, Y.; Rao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ke, J. Fe3+-sulfite complexation enhanced persulfate Fenton-like process for antibiotic degradation based on response surface optimization. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delavaran Shiraz, A.; Takdastan, A.; Borghei, S.M. Photo-Fenton like degradation of catechol using persulfate activated by UV and ferrous ions: Influencing operational parameters and feasibility studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 249, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Sun, J.; Li, G.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xia, D.; Jiang, F. Integration of •SO4−-based AOP mediated by reusable iron particles and a sulfidogenic process to degrade and detoxify Orange II. Water Res. 2020, 174, 115622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, X.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y. N, S-Doped porous carbons for persulfate activation to remove tetracycline: Nonradical mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 391, 122055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Liu, P.; Shao, S.; Wang, M.; Zhan, X.; Gao, S. An efficient graphene supported copper salen catalyst for the activation of persulfate to remove chlorophenols in aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wu, D.; Mao, S. Activation of persulfate with metal–organic framework-derived nitrogen-doped porous Co@C nanoboxes for highly efficient p-Chloroaniline removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Dai, L.; Shi, P.; Fan, J.; Min, Y.; Xu, Q. Rational design of efficient metal-free catalysts for peroxymonosulfate activation: Selective degradation of organic contaminants via a dual nonradical reaction pathway. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, N.; Su, Y.; Liu, Z.; Gao, R.; Du, C. Insight to unprecedented catalytic activity of double-nitrogen defective metal-free catalyst: Key role of coal gangue. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2020, 263, 118316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Korshin, G.V.; Yang, B. Insights into the mechanism of nonradical reactions of persulfate activated by carbon nanotubes: Activation performance and structure-function relationship. Water Res. 2019, 157, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.J.; Zeng, G.M.; Tan, X.F.; Wu, H.P.; Liang, J.; Song, B.; Tang, N.; Zhang, P.; Yang, Y.Y.; Chen, Q.; et al. Nitrogen-doped biochar fiber with graphitization from Boehmeria nivea for promoted peroxymonosulfate activation and non-radical degradation pathways with enhancing electron transfer. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2020, 269, 118850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.F.; Ge, B.X.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Jiang, B.; Wang, C.Z.; Akram, M.; Xu, X. Three-dimensional porous graphene-like biochar derived from Enteromorpha as a persulfate activator for sulfamethoxazole degradation: Role of graphitic N and radicals transformation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 399, 123039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Du, M.M.; Du, X.D.; Huang, S.B. Insights into the mechanism of non-radical activation of persulfate via activated carbon for the degradation of pchloroaniline. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Liu, H.; Feng, M.B.; Guo, L.; Zhai, Z.C.; Fang, Y.S.; Zhang, X.S.; Sharma, V.K. Nitrogen-sulfur co-doped industrial graphene as an efficient peroxymonosulfate activator: Singlet oxygen-dominated catalytic degradation of organic contaminants. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2019, 251, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.R.; Tong, W.H.; Li, Y.L.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Y.D.; Wen, Z.Q.; Feng, S.F.; Wang, X.Q.; Li, P.Y.; Wang, Y.B.; et al. Hydrothermal route-enabled synthesis of sludge-derived carbon with oxygen functional groups for bisphenol A degradation through activation of peroxymonosulfate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Huang, Z.; Lu, B.; Xian, J.; Tsang, E.P.; Cheng, W.; Fang, J.; Fang, Z. Magnetic biochar for environmental remediation: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 298, 122468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Chen, G. Preparation and application of magnetic biochar in water treatment: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Q.; Hou, H.; Liang, S.; Qiu, J.; Tao, S.; Yang, L.; Yu, W.; Xiao, K.; Liu, B.; Hu, J.; et al. Sludge-derived biochar with multivalent iron as an efficient Fenton catalyst for degradation of 4-Chlorophenol. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Yang, X.; Liang, G.; Xie, X. Insight into enhanced carbamazepine photodegradation over biochar-based magnetic photocatalyst Fe3O4/BiOBr/BC under visible LED light irradiation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 600–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhu, X.; Chen, B. Magnetic biochar supported α-MnO2 nanorod for adsorption enhanced degradation of 4-chlorophenol via activation of peroxydisulfate. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Dai, Y.; Guo, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, D.; Zhai, Y. Solvothermal synthesis of biochar@ZnFe2O4/BiOBr Z-scheme heterojunction for efficient photocatalytic ciprofloxacin degradation under visible light. Appl. Surf. Sci 2019, 493, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Han, B. Preparation of amino-functionalized magnetic biochar with excellent adsorption performance for Cr(VI) by a mild one-step hydrothermal method from peanut hull. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 563, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewu, D.D.; Tran, H.N.; Ohemeng-Boahen, G.; Woo, S.H. Facile magnetic biochar production route with new goethite nanoparticle precursor. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Z.; Feng, W.; Huang, H.; Wang, B.; Chen, L.; Miao, Y.; Su, S. Green synthesis of a novel Mn–Zn ferrite/biochar composite from waste batteries and pine sawdust for Pb2+ removal. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, L.; Ding, D.; Cai, T. From rice straw to magnetically recoverable nitrogen doped biochar: Efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate for the degradation of metolachlor. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2019, 254, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azalok, K.A.; Oladipo, A.A.; Gazi, M. UV-light-induced photocatalytic performance of reusable MnFe-LDO–biochar for tetracycline removal in water. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2021, 405, 112976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Bo, S.; Qin, Y.; An, Q.; Xiao, Z.; Zhai, S. Transforming goat manure into surface-loaded cobalt/biochar as PMS activator for highly efficient ciprofloxacin degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 395, 125063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, V.; Ahmad, M.; Siddiqui, K.A. Fe-doped Zinc-MOF composites and its test-strip employed for colorimetric detection of glucose in model and real urine samples. Mater. Today Chem. 2024, 38, 102138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakici, M.; Kakarla, R.R.; Alonso-Marroquin, F. Advanced electrochemical energy storage supercapacitors based on the flexible carbon fiber fabric-coated with uniform coral-like MnO2 structured electrodes. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 309, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Guo, T.; Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G. Efficient activation of persulfate by a magnetic recyclable rape straw biochar catalyst for the degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride in water. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Peng, H.; Wen, Y.; Li, N. Re-examination of characteristic FTIR spectrum of secondary layer in bilayer oleic acid-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci 2010, 256, 3093–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, P.; Wei, K.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X. Enhanced H2O2 activation and sulfamethoxazole degradation by Fe-impregnated biochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; She, Y.; Yu, Y.; Hong, J. High-efficiency degradation of bisphenol A by heterogeneous Mn–Fe layered double oxides through peroxymonosulfate activation: Performance and synergetic mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 270, 118770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Yadav, A.; Fernandes, R.; Popat, Y.; Orlandi, M.; Dashora, A.; Kothari, D.C.; Miotello, A.; Ahuja, B.L.; Patel, N. Tungsten-doped TiO2 /reduced Graphene Oxide nano-composite photocatalyst for degradation of phenol: A system to reduce surface and bulk electron-hole recombination. J. Env. 2017, 203, 364–374. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.-H.; Wen, X.-J.; Fei, Z.-H.; Liu, Z.-T.; Mu, Q.-M. Visible-light-driven activation of peroxymonosulfate for accelerating ciprofloxacin degradation using CeO2/Co3O4 p-n heterojunction photocatalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 391, 123612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; He, X.; Nadagouda, M.N.; O’Shea, K.E.; Dionysiou, D.D. The effect of basic pH and carbonate ion on the mechanism of photocatalytic destruction of cylindrospermopsin. Water Res. 2015, 73, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Reactive species in advanced oxidation processes: Formation, identification and reaction mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 401, 126158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, V.; Siddiqui, K.A. Dosage Dependent Photocatalytic Degradation of NFT and Other Antibiotics and Energy Storage Application of Unprecedented Gd-doped Zinc-MOF Composite. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, G.; Huang, W.; Wei, Z.; Fang, H.; Shen, F. Visible light driven S-scheme heterojunction Zn3In2S6/Bi2MoO6 for efficient degradation of metronidazole. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 917, 165507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Yi, Y.; Ying, G.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Activation of persulfate for highly efficient degradation of metronidazole using Fe(II)-rich potassium doped magnetic biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 152089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Lu, X.; Wu, D.; Xiao, P. Sustainable activation of sulfite by oxygen vacancies-enriched spherical Li3PO4-Co3O4 composite catalyst for efficient degradation of metronidazole. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Pollutants | Initial Pollutant Concentration | Biochar Dosage | PMS Concentration | Reaction Time | Removal Rate % | Bibliography |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tetracycline | 20 mg/L | 0.1 g/L | 1 mM | 2.5 h | 96.5% | [25] |
| Sulfamethoxazole | 5 mg/L | 0.05 g/L | 4 mM | 1.5 h | 100% | [26] |
| p-Chloroaniline | 5 mg/L | 3 g/L | 2.5 mM | 1 h | 92% | [27] |
| Methyl para-hydroxybenzoate | 15 mg/L | 0.02 g/L | 307 mg/L | 30 min | 100% | [28] |
| Bisphenol A | 20 mg/L | 0.4 g/L | 0.4 g/L | 20 min | 100% | [29] |
| Samples | Specific Surface Area (m2g−1) | Average Pore Size (nm) | Micropore Volume (cm3g−1) | Mesopore Volume (cm3g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC | 355.009 | 2.3042 | 0.1484 | 0.0820 |
| Fe-BC | 34.477 | 4.2783 | 0.0126 | 0.0243 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, D.; Shi, L.; Dawolo, E.H.; Chen, B.; Ding, N.; Liu, H. Synthesis of Fe-Loaded Biochar Obtained from Rape Straw for Enhanced Degradation of Emerging Contaminant Antibiotic Metronidazole. Water 2024, 16, 1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131822
Zhang D, Shi L, Dawolo EH, Chen B, Ding N, Liu H. Synthesis of Fe-Loaded Biochar Obtained from Rape Straw for Enhanced Degradation of Emerging Contaminant Antibiotic Metronidazole. Water. 2024; 16(13):1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131822
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Dongyuan, Lin Shi, Edwin Hena Dawolo, Bingfa Chen, Ning Ding, and Hong Liu. 2024. "Synthesis of Fe-Loaded Biochar Obtained from Rape Straw for Enhanced Degradation of Emerging Contaminant Antibiotic Metronidazole" Water 16, no. 13: 1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131822
APA StyleZhang, D., Shi, L., Dawolo, E. H., Chen, B., Ding, N., & Liu, H. (2024). Synthesis of Fe-Loaded Biochar Obtained from Rape Straw for Enhanced Degradation of Emerging Contaminant Antibiotic Metronidazole. Water, 16(13), 1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131822







