A New Numerical Method to Evaluate the Stability of Dike Slope Considering the Influence of Backward Erosion Piping
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A brief description of Wewer’s BEP model;
- Improvement of Wewer’s BEP model;
- Verification of the improved piping model;
- Simulation and analysis of piping erosion using the improved piping model.
2. Wewer’s BEP Model Based on Porous Media Seepage
3. An Improved Piping Model Considering Unsaturated Seepage in the Dike Body and Seepage–Stress Coupling
3.1. The Governing Equations for Unsaturated Flow in Porous Media
3.2. Seepage–Stress Coupling Equation
3.3. Stability Analysis
4. Numerical Computation Scheme and Validation
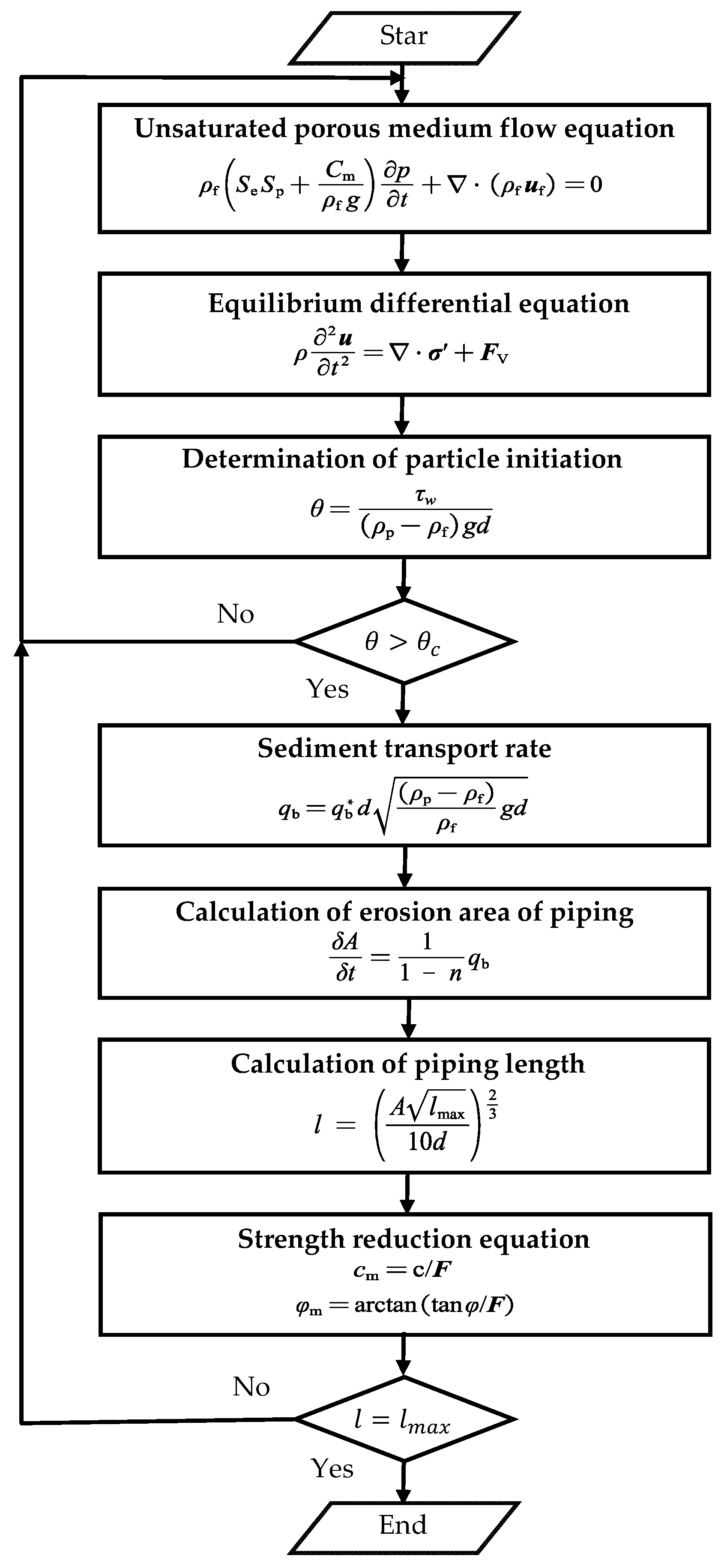
4.1. Numerical Simulation Approach
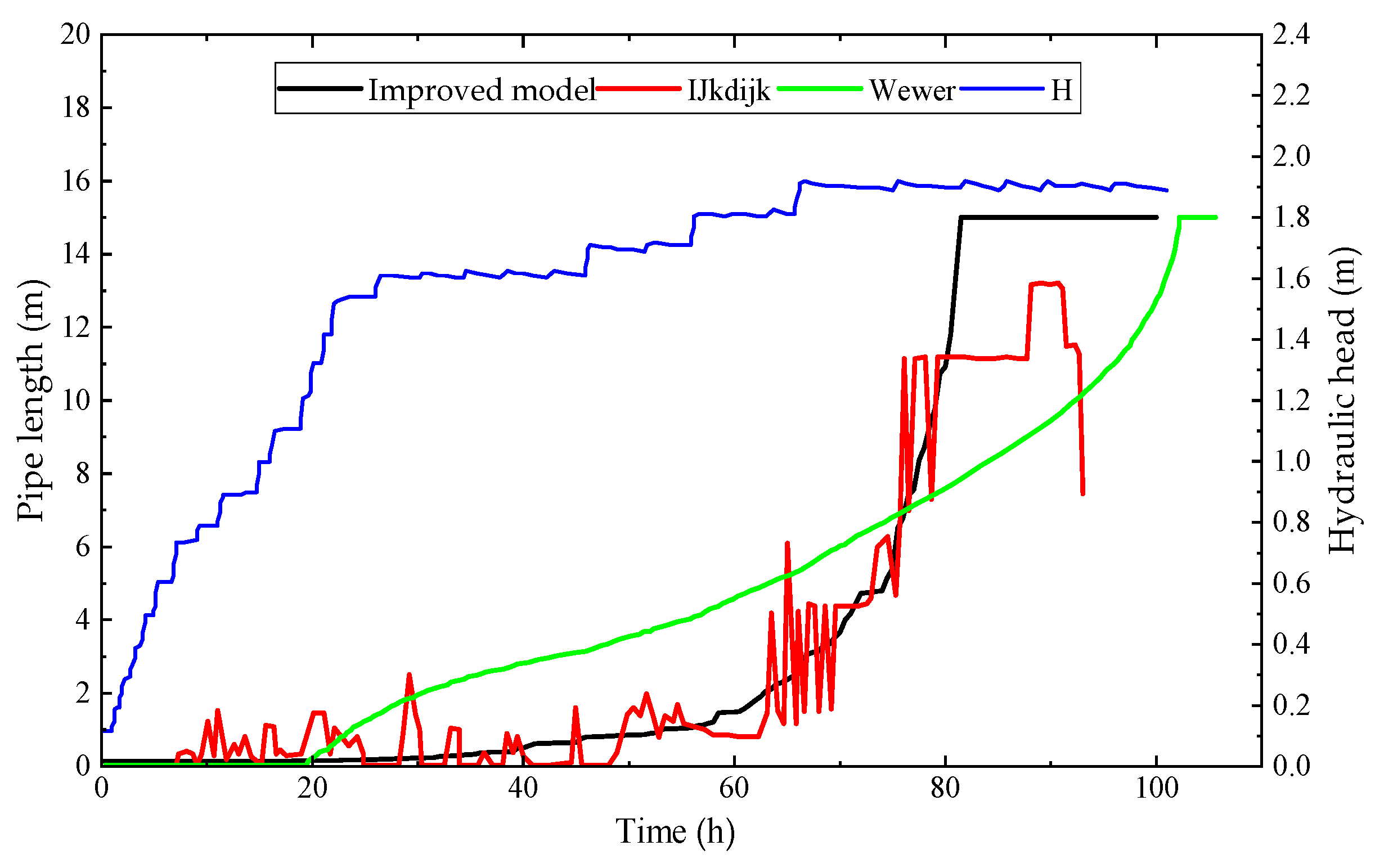
4.2. Validation of the Piping Model
5. Analysis of the Evolution of Piping and Its Impact on the Stability of the Dike Slope
5.1. Calculation Model and Parameter Selection
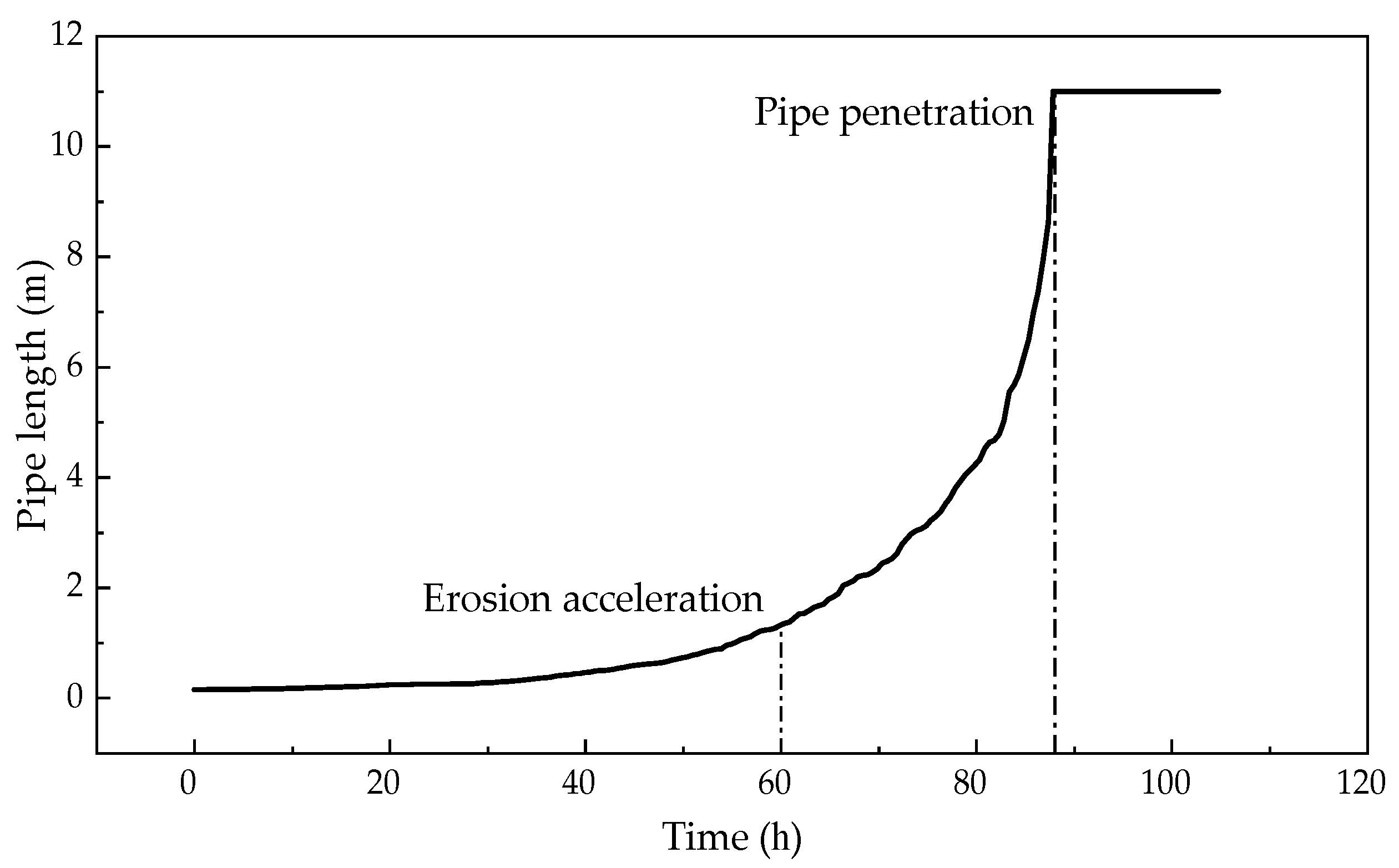
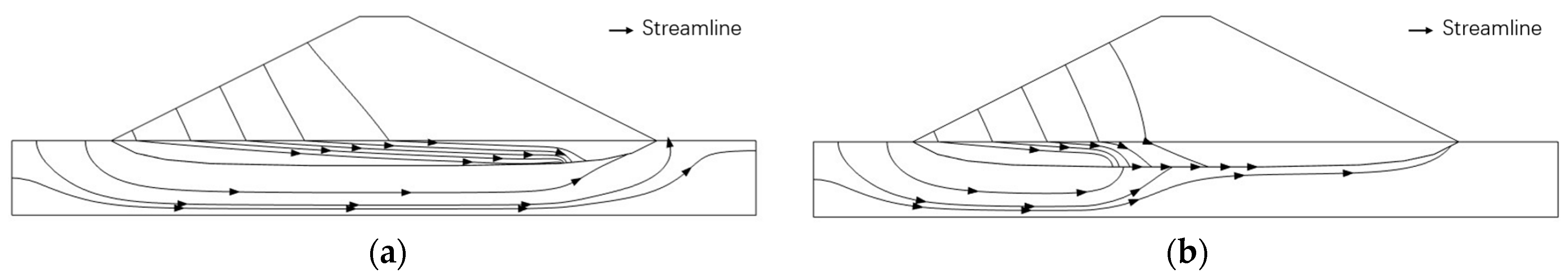
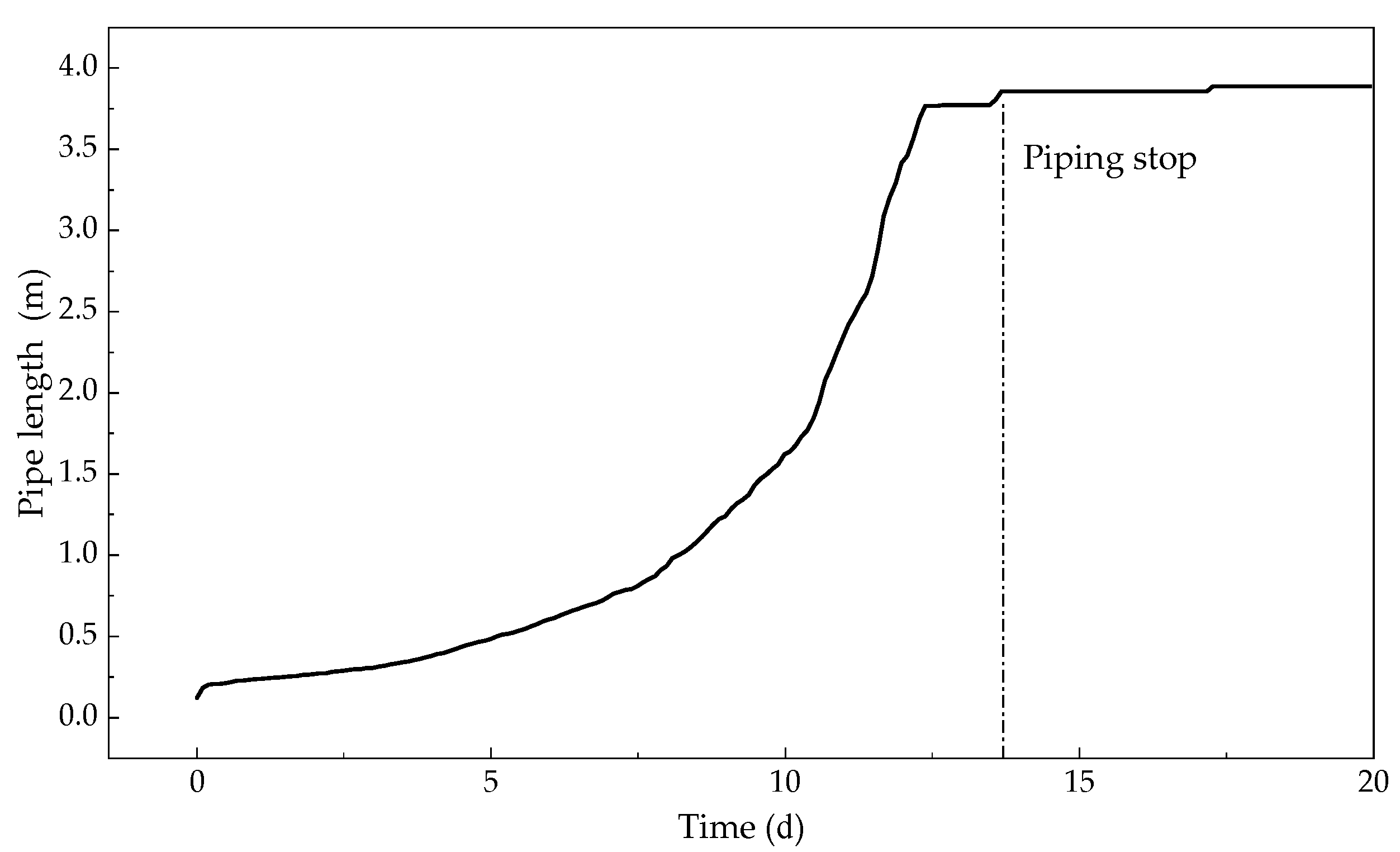
5.2. Development of Piping
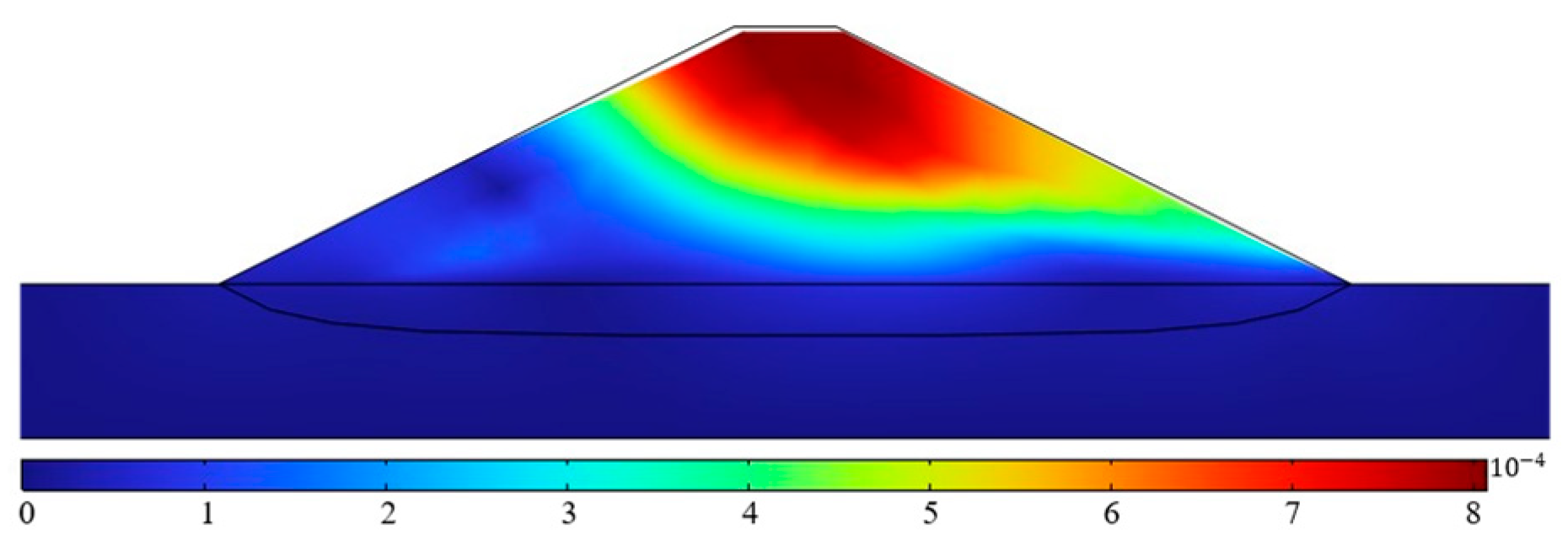
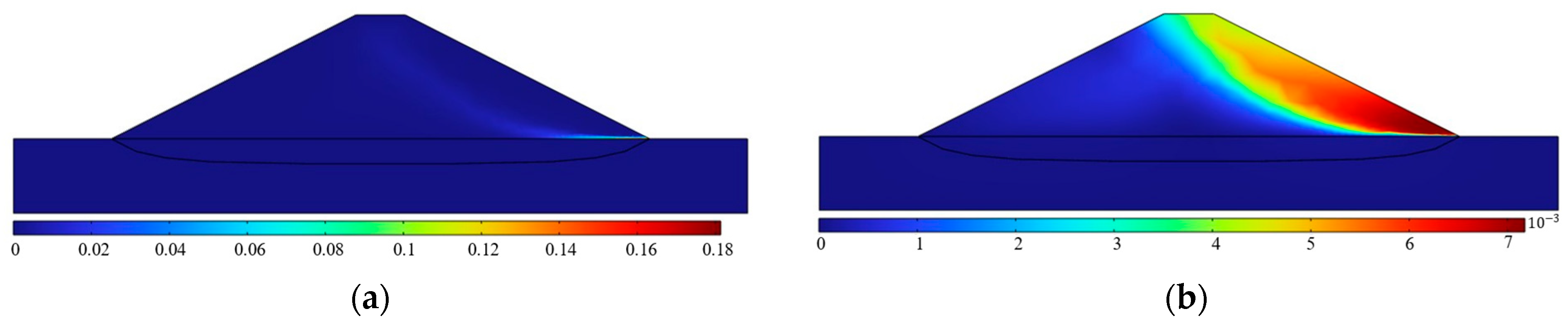
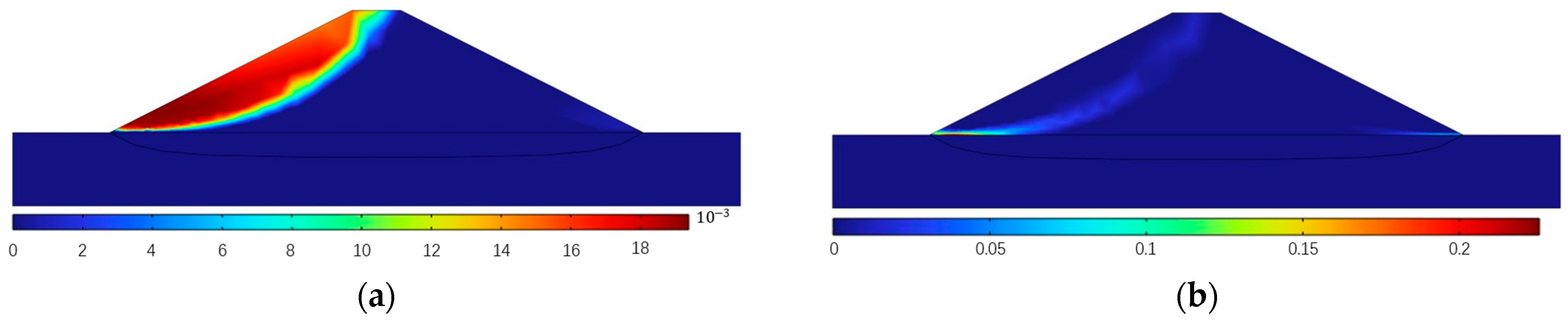
5.3. Analysis of Dike Seepage and Deformation
5.4. Analysis of dike Stability
5.5. Analysis of Piping Development and Dike Stability under Water-Level Changes
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- After adding the seepage field of the dike body, the development trend of the piping channel became more consistent with the experimental result, proving that the seepage field of the dike body indeed affected the development of BEP. By comparing the simulation results, this study concluded that the rapid development of pipe in the final stages of BEP is related to the seepage of the dike body.
- (2)
- BEP will influence the seepage distribution of the dike and promote the convergence of groundwater in the piping channel. After the piping channel was penetrated, the safety factor of the dike significantly decreased, indicating that the penetration of pipe will significantly reduce the stability of the dike.
- (3)
- In situations where the water levels drops suddenly, BEP will stop developing due to factors such as hydraulic conditions. In this situation, due to the influence of the water level difference, the instability will occur on the upstream slope of the dike.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riha, J.; Petrula, L. Experimental research on backward erosion piping progression. Water 2023, 15, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, M.; Tsuyuguchi, Y.; Izumi, N.; Maeda, K. Centrifuge modeling of scale effect on hydraulic gradient of backward erosion piping in uniform aquifer under river levees. Soils Found. 2022, 62, 101214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzaghi, K. Der Grundbruch an Stauwerken und Seine Verhutung. Wasserkraft 1922, 17, 445–449. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, C.X.; Duan, X.B.; Cai, J.B.; Ru, J.H. Experimental study on harmless seepage piping in levee foundation. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2004, 11, 46–53+61. [Google Scholar]
- Ojha, C.S.P.; Singh, V.P.; Adrian, D.D. Influence of Porosity on Piping Models of Levee Failure. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2001, 127, 1071–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovalle-Villamil, W.; Sasanakul, I. Centrifuge Modeling Study of Backward Erosion Piping with Variable Exit Size. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2021, 147, 04021114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Tong, J.B.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.W.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.Q.; Qi, C.Y.; Zhou, H.; Diao, Y. Visualizing the dynamic progression of backward erosion piping in a Hele-Shaw cell. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2022, 23, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Yu, J.T.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, B.; Zhang, H.J.; Gong, S.Y. Experimental study on the effect of skeleton particle composition on piping law of cohesionless soil. J. Hohai Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2024, 52, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Ovalle-Villamil, W.; Sasanakul, I. Influence of Seepage Length on Backward Erosion Piping Behaviors in Centrifuge Model Testing. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2022, 148, 04022102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Oskay, C.; Fascetti, A. Three-dimensional numerical modeling of the temporal evolution of backward erosion piping. Comput. Geotech. 2024, 171, 106381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Fu, X.; Jie, Y.X.; Dong, W.; Hu, D. Simulation of pipe progression in a levee foundation with coupled seepage and pipe flow domains. Soils Found. 2014, 54, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbrand, E.; van Beek, V.; Bezuijen, A. Numerical modelling of the resistance of the coarse sand barrier against backward erosion piping. Géotechnique 2021, 72, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotunno, A.; Callari, C.; Froiio, F. A finite element method for localized erosion in porous media with applications to backward piping in levees. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2018, 43, 293–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froiio, F.; Callari, C.; Rotunno, A.F. A numerical experiment of backward erosion piping: Kinematics and micromechanics. Meccanica 2019, 54, 2099–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenboer, K.; van Beek, V.; Bezuijen, A. 3D finite element method (FEM) simulation of groundwater flow during backward erosion piping. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 2014, 8, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, B.; Griffiths, D. A two-dimensional, adaptive finite element approach for simulation of backward erosion piping. Comput. Geotech. 2020, 129, 103820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ni, X. Hydro-mechanical analysis of piping erosion based on similarity criterion at micro-level by PFC3D. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2013, 17, s187–s204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.P.; Sun, D.Y.; Wang, X.K. Quantitative analysis of the erosion process in horizontal cobble and gravel embankment piping via CFD-DEM coupling method. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2022, 44, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lominé, F.; Scholtès, L.; Sibille, L.; Poullain, P. Modeling of fluid-solid interaction in granular media with coupled lattice Boltzmann/discrete element methods: Application to piping erosion. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2013, 37, 577–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc Kien, T.; Prime, N.; Froiio, F.; Callari, C.; Vincens, E. Numerical modelling of backward front propagation in piping erosion by DEM-LBM coupling. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2016, 21, 960–987. [Google Scholar]
- Sibille, L.; Marot, D.; Poullain, P.; Lominé, F. Phenomenological interpretation of internal erosion in granular soils from a discrete fluid-solid numerical model. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Scour and Erosion, Oxford, UK, 12–15 September 2016; CRC Press: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, C.Y.; Wong, H.; Tong, J.; Dong, J. Modeling dam deformation in the early stage of internal seepage erosion—Application to the teton dam, Idaho, before the 1976 Incident. J. Hydrol. 2021, 605, 127378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.J.; Jie, Y.X.; Li, G.X. Numerical simulation of piping based on coupling seepage and pipe flow. Rock Soil Mech. 2009, 30, 3154–3158. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.J.; Jie, Y.X.; Li, G.X. Numerical simulation of piping in levee. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2011, 30, 100–106. [Google Scholar]
- van Beek, V.; Robbins, B.; Rosenbrand, E.; Esch, J. 3D modelling of backward erosion piping experiments. Geomech. Energy Environ. 2022, 31, 100375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, B.; van Beek, V.; Pol, J.; Griffiths, D. Errors in finite element analysis of backward erosion piping. Geomech. Energy Environ. 2022, 31, 100331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Beek, V.; Robbins, B.; Hoffmans, G.; Bezuijen, A.; Rijn, L. Use of incipient motion data for backward erosion piping models. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2019, 34, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wewer, M.; Aguilar López, J.P.; Kok, M.; Bogaard, T. A transient backward erosion piping model based on laminar flow transport equations. Comput. Geotech. 2021, 132, 103992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Wang, S.; Jasim, O.H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, P. Variability effect of strength and geometric parameters on the stability factor of failure surfaces of rock slope by numerical analysis. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, S.K. Stability analysis of embankments and slopes. Geotechnique 1973, 23, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Li, D. Effect of spatial variability of shear strength parameters on critical slip surfaces of slopes. Eng. Geol. 2018, 239, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, R.W.; Woodward, R.J. Analysis of embankment stresses and deformations. J. Soil Mech. Found. Div. 1967, 93, 529–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.D.; Xiao, T.; Cao, Z.J.; Tang, X.S.; Fang, G.G. Auxiliary slope reliability analysis using limit equilibrium method and finite element method. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2016, 38, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, Z.; Yousuf, S.; Wang, S.; Rehman, S.U.; Gul, M.; Hanif, M.S. An Artificial Neural Network Method for Forecasting the Stability of Soil Slopes. Proc. Pak. Acad. Sci. A Phys. Comput. Sci. 2024, 61, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, L.; Takahashi, A. Strength reduction of cohesionless soil due to internal erosion induced by one-dimensional upward seepage flow. Soils Found. 2012, 52, 698–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Q.; Li, J.C. Effects of water seepage on the stability of soil-slopes. Procedia IUTAM 2015, 17, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. Influences of internal erosion on infiltration and slope stability. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 1815–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.; Shafieezadeh, A. Coupled backward erosion piping and slope instability performance model for levees. Transp. Geotech. 2020, 24, 100394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Esch, J.M.; Sellmeijer, J.B.; Stolle, D. Modeling transient groundwater flow and piping under dikes and dams. In Third International Symposium on Computational Geomechanics (ComGeo III); Taylor I& Francis: Krakow, Poland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Koelewijn, A.R.; Pals, N.; Sas, M.J.; Zomer, W.S. Ljkdijk Piping Experiment: Validatie van Sensor-en Meettechnologie Voor Detectie van Optreden van Piping in Waterkeringen. Stowa Rapport. 2011. Available online: https://repository.tudelft.nl/islandora/object/uuid:2d43fe32-0e1a-4543-8536-5156ab007261 (accessed on 1 June 2022.).
- Van Genuchten, M. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalin, M.S.; Karahan, E. Inception of Sediment Transport. J. Hydraul. Div. 1979, 105, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Porosity (dike body) | 0.5 | |
| Porosity (clay) | 0.25 | |
| Porosity (soil) | 0.37 | |
| Kinematic viscosity | ||
| Particle density | ||
| Fluid density | ||
| Particle compressibility coefficient | ||
| Fluid compressibility coefficient | ||
| Cohesive strength (dike body) | ) | |
| Internal friction angle (dike body) | 24 (°) | |
| Cohesive strength (soil) | ) | |
| Internal friction angle (soil) | 40 (°) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Z.; Wang, X.; Shang, N.; Zhang, Q. A New Numerical Method to Evaluate the Stability of Dike Slope Considering the Influence of Backward Erosion Piping. Water 2024, 16, 1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16121706
Ma Z, Wang X, Shang N, Zhang Q. A New Numerical Method to Evaluate the Stability of Dike Slope Considering the Influence of Backward Erosion Piping. Water. 2024; 16(12):1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16121706
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Zhen, Xiaobing Wang, Ning Shang, and Qing Zhang. 2024. "A New Numerical Method to Evaluate the Stability of Dike Slope Considering the Influence of Backward Erosion Piping" Water 16, no. 12: 1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16121706
APA StyleMa, Z., Wang, X., Shang, N., & Zhang, Q. (2024). A New Numerical Method to Evaluate the Stability of Dike Slope Considering the Influence of Backward Erosion Piping. Water, 16(12), 1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16121706