Variations in Greenhouse Gas Fluxes at the Water–Gas Interface in the Three Gorges Reservoir Caused by Hydrologic Management: Implications for Carbon Cycling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Field Measurements
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
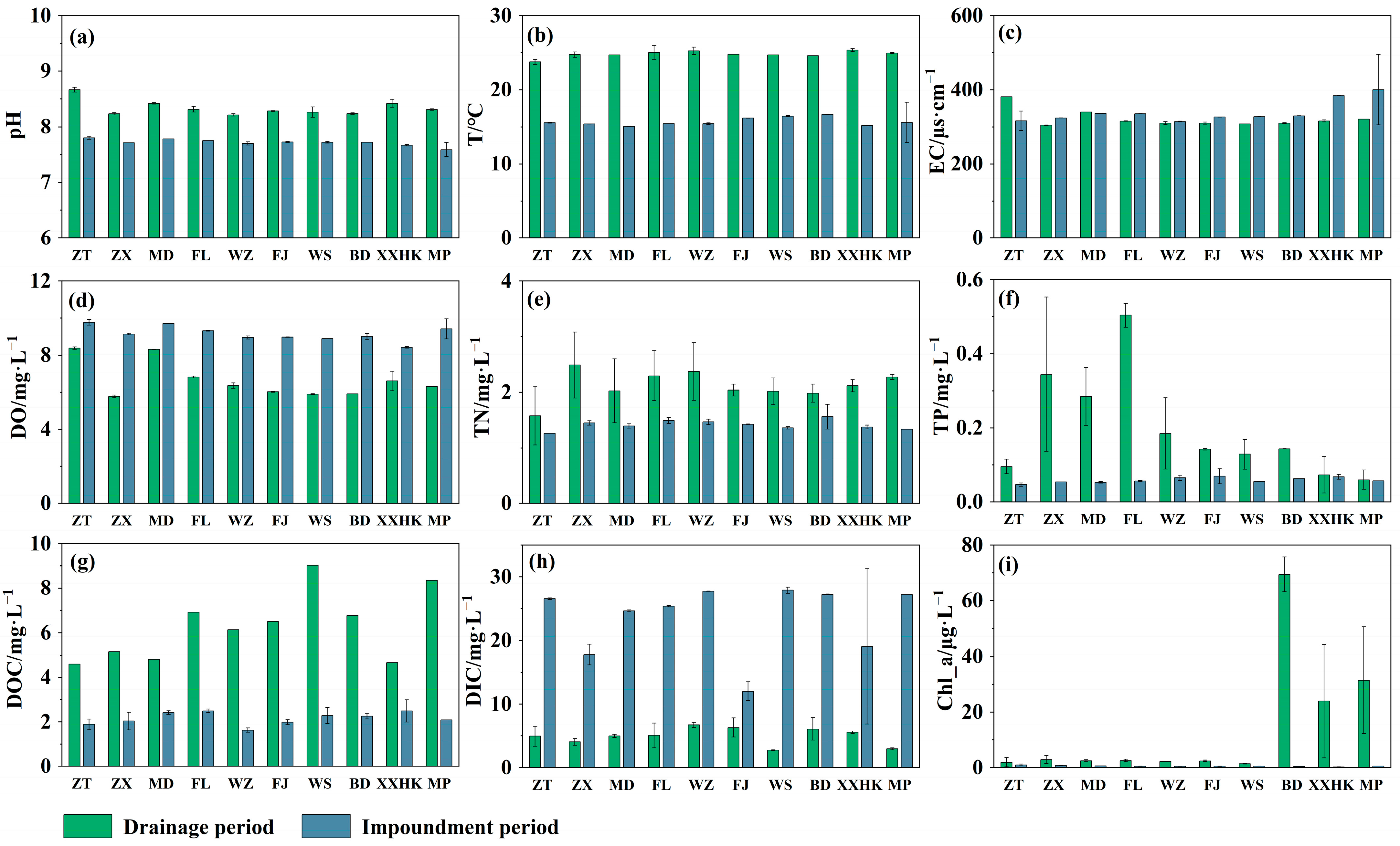
3.1. Physiochemical Variations in the Surface Waters of the TGR
3.2. Carbon Isotope Characteristics
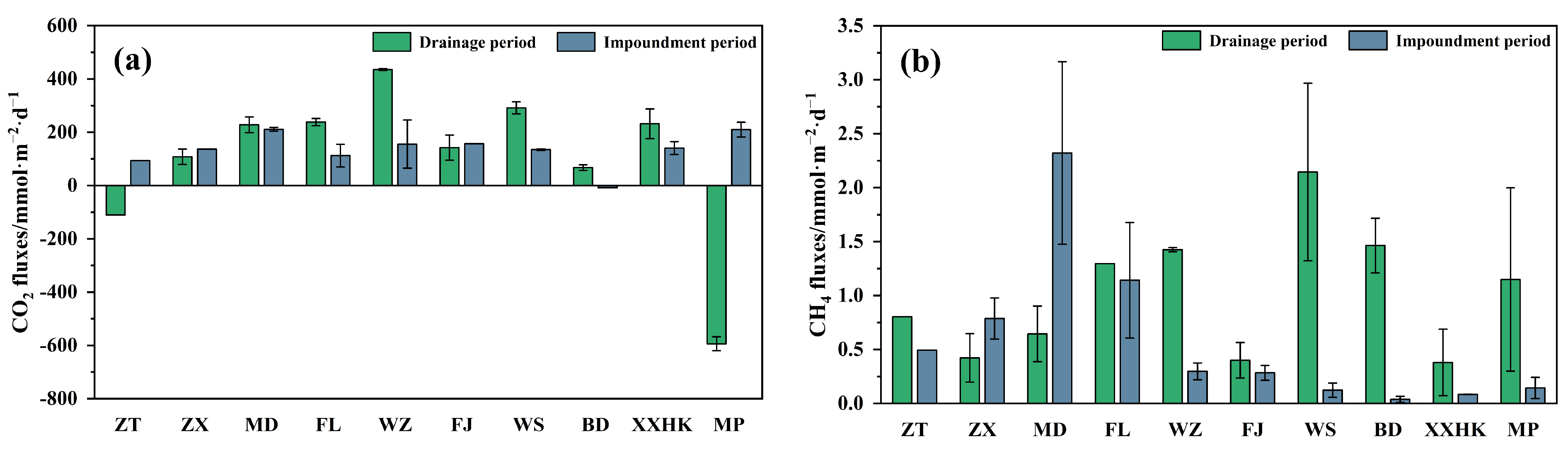
3.3. Spatiotemporal Variation of Greenhouse Gas Fluxes
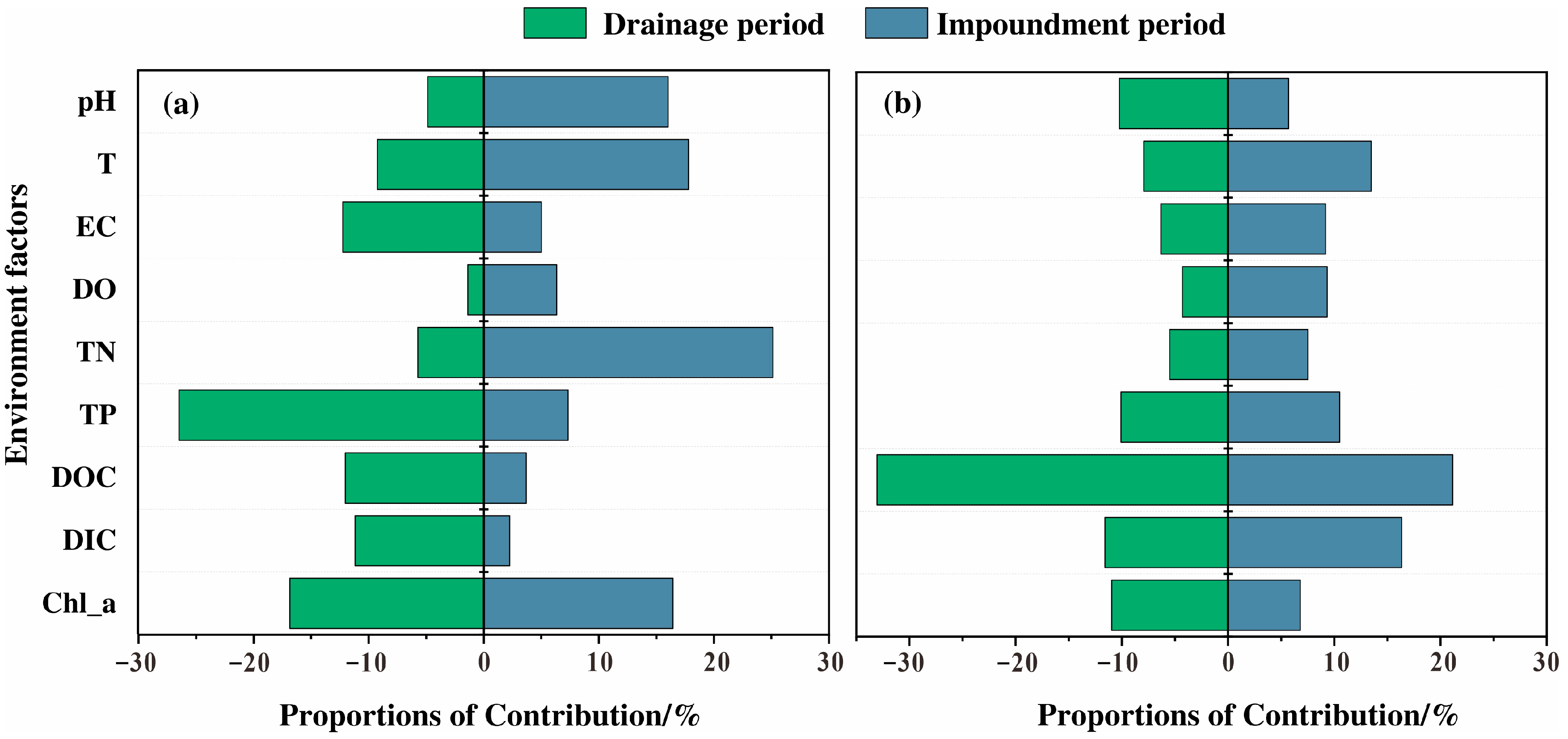
3.4. Correlation of Environmental Factors
3.4.1. Hydrochemical Factors
3.4.2. Nutrient Factors
3.4.3. Carbon Source Factors
3.4.4. Chlorophyll-a
4. Discussion
4.1. Sources of Carbon in the Waters of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area
| Organic Carbon End-Member | δ13C (V-PDB, ‰) | Reference | Inorganic Carbon End-Member | δ13C (V-PDB, ‰) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | −26~−23 | [47] | Soil CO2 | −21.8~−10.8 | [43,44] |
| River Plankton | −42~−24 | [48,49,50] | Carbonate rock | −3.33~2.4 | [45,46] |
| Sewage | −28.5~−23 | [51,52,53] | Atmosphere | −8~−6 | [40] |
| Vascular Plant | −30~−16 | [47,54] | |||
| C3 Plants | −38~−23 | [46] | |||
| C4 Plants | −17~−9 | [55] |
4.2. The Assessment of Feature Importance for Environmental Factors
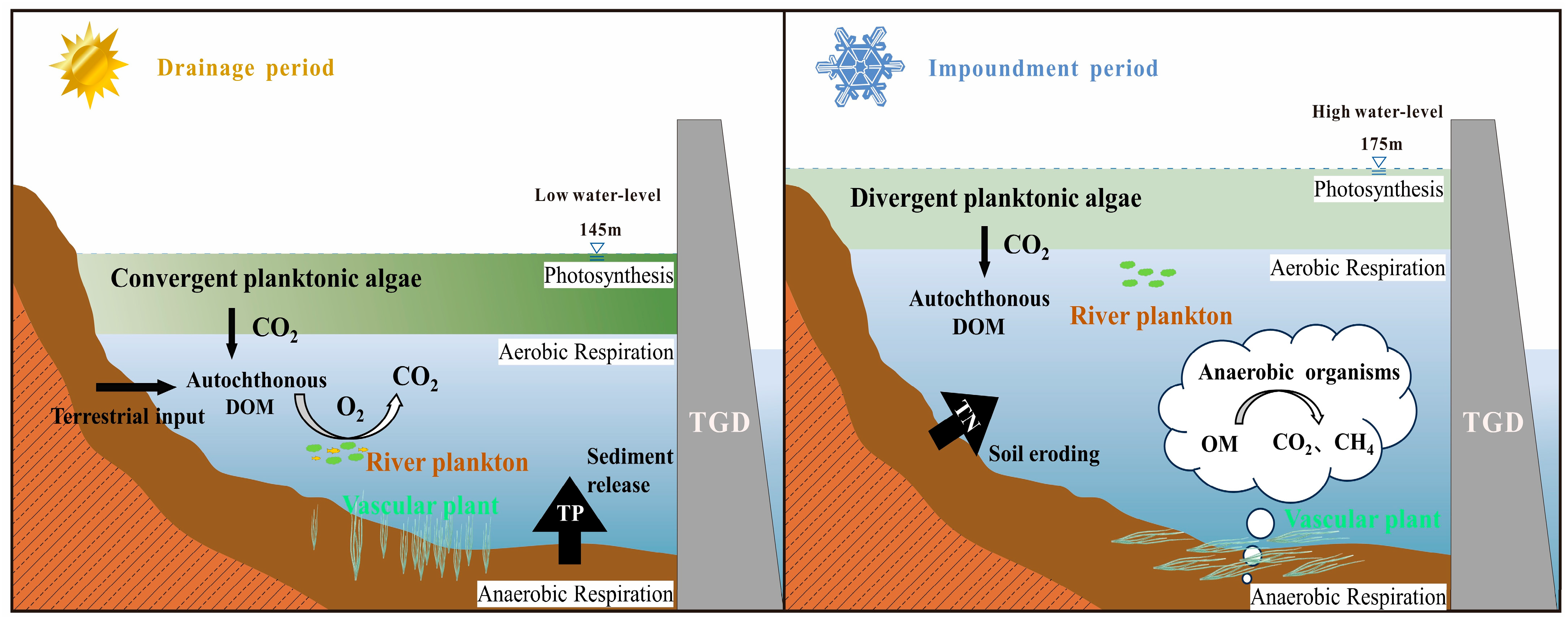
4.3. Exploration of the Mechanisms of Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Reservoirs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S. Carbon Dioxide Exchange Flux in the Water- Air Interface and Its Mechanism in the Changjiang River Basin. Ph.D. Thesis, Shanghai University, Shanghai, China, 2018. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Levitus, S.; Antonov, J.I.; Wang, J.; Delworth, T.L.; Dixon, K.W.; Broccoli, A.J. Anthropogenic Warming of Earth’s Climate System. Science 2001, 292, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Guo, Q.; Du, C.; Deng, Y. Advances in water environmental carbon cycle in the Yangtze River Basin. Chin. J. Ecol. 2022, 42, 736–747, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Stanley, E.H.; Casson, N.J.; Christel, S.T.; Crawford, J.T.; Loken, L.C.; Oliver, S.K. The ecology of methane in streams and rivers: Patterns, controls, and global significance. Ecol. Monogr. 2015, 86, 146–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, P.A.; Hartmann, J.; Lauerwald, R.; Sobek, S.; McDonald, C.; Hoover, M.; Butman, D.; Striegl, R.; Mayorga, E.; Humborg, C.; et al. Global carbon dioxide emissions from inland waters. Nature 2013, 503, 335–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holgerson, A.M.; Raymond, A.P. Large contribution to inland water CO2 and CH4 emissions from very small ponds. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallard, R.F. Terrestrial sedimentation and the carbon cycle: Coupling weathering and erosion to carbon burial. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1998, 12, 231–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, N.; Cole, J.J.; Tranvik, L.J.; Prairie, Y.T.; Bastviken, D.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Giorgio, P.d.; Roland, F. Carbon emission from hydroelectric reservoirs linked to reservoir age and latitude. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regnier, P.; Friedlingstein, P.; Ciais, P.; Mackenzie, F.T.; Gruber, N.; Janssens, I.A.; Laruelle, G.G.; Lauerwald, R.; Luyssaert, S.; Andersson, A.J.; et al. Anthropogenic perturbation of the carbon fluxes from land to ocean. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maavara, T.; Lauerwald, R.; Regnier, P.; van Cappellen, P. Global perturbation of organic carbon cycling by river damming. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill, G.; Lehner, B.; Lumsdon, A.E.; MacDonald, G.K.; Zarfl, C.; Liermann, C.R. An index-based framework for assessing patterns and trends in river fragmentation and flow regulation by global dams at multiple scales. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borzì, I. Evaluating Sustainability Improvement of Pressure Regime in Water Distribution Systems Due to Network Partitioning. Water 2022, 14, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearnside, P.M. Hydroelectric Dams in the Brazilian Amazon as Sources of ‘Greenhouse’ Gases. Environ. Conserv. 1995, 22, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Guo, J.; Gao, X.; Fang, F.; Jiang, T. Preliminary study of CO2 and CH4 fluxes at soil-air interface in drawdown area of the Pengxi River of the Three Gorges Reservoir. J. Lake Sci. 2013, 25, 674–680, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Guo, J.; Li, Z.; Fang, F.; Bai, L.; Liu, J. Air-water surface greenhouse gas flux in pengxi river at different operational stages of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Environ. Sci. 2012, 33, 1463–1470, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, B.; Zeng, Y. Spatial and temporal patterns of greenhouse gas emissions from Three Gorges Reservoir of China. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Wu, B.; Lü, Y.; Xu, Z.; Cao, J.; Niu, D.; Yang, G.-S.; Zhou, Y.M. Three Gorges Project: Efforts and challenges for the environment. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2010, 34, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, J.; Rasul, G.; Liu, S.; Xie, F.; Cao, M.; Liu, E. Household livelihood strategies and dependence on agriculture in the mountainous settlements in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Sustainability 2015, 7, 4850–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Gao, P.; He, X. The water-level fluctuation zone of Three Gorges Reservoir—A unique geomorphological unit. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 150, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Dong, R.; Jiang, C.; Ni, M. Influences of land use metrics at multi-spatial scales on seasonal water quality: A case study of river systems in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 206, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Milliman, J.D.; Xu, K.; Deng, B.; Zhang, X.; Luo, X. Downstream sedimentary and geomorphic impacts of the Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze River. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 138, 469–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, R.; Chen, H.; Li, S. Phosphorus availability as a primary control of dissolved organic carbon biodegradation in the tributaries of the Yangtze River in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 1472–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Niggemann, J.; Huang, D.; Dittmar, T.; Kao, S.J. Different Responses of Dissolved Black Carbon and Dissolved Lignin to Seasonal Hydrological Changes and an Extreme Rain Event. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2019, 124, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høj, L.; Olsen, R.A.; Torsvik, V.L. Effects of temperature on the diversity and community structure of known methanogenic groups and other archaea in high Arctic peat. ISME J. 2008, 2, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, C.; Ji, J.; Luo, Y.; Yuan, X.; Yang, Z.; Song, Y.; Chen, J. Seasonal variation in the flux and isotopic composition of particulate organic carbon along the mainstream of the Changjiang River. Earth Sci. Front. 2011, 18, 161–168, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Crill, P.M.; Bartlett, K.B.; Wilson, J.O.; Sebacher, D.I.; Harriss, R.C.; Melack, J.M.; MacIntyre, S.; Lesack, L.; Smith-Morrill, L. Tropospheric methane from an Amazonian floodplain lake. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1988, 93, 1564–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolking, S.; Crill, P. Climate controls on temporal variability of methane flux from a poor fen in southeastern New Hampshire: Measurement and modeling. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1994, 8, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Wang, K.; Pang, Y.; He, C.; Li, P.; Li, Y.; Xiao, S.; Shi, Q.; Sun, Y. Hydrological management constraints on the chemistry of dissolved organic matter in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Water Res. 2020, 187, 116413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Siciliano, S.; Helgason, B.; Bedard-Haughn, A. Responses of a mountain peatland to increasing temperature: A microcosm study of greenhouse gas emissions and microbial community dynamics. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 110, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, J.T.; Stanley, E.H.; Spawn, S.A.; Finlay, J.C.; Loken, L.C.; Striegl, R.G. Ebullitive methane emissions from oxygenated wetland streams. Glob. Change Biol. 2014, 20, 3408–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastviken, D.; Tranvik, L.J.; Downing, J.A.; Crill, P.M.; Enrich-Prast, A. Freshwater Methane Emissions Offset the Continental Carbon Sink. Science 2011, 331, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkum, A.; Mccomb, A.; Shepherd, S. Biology of Seagrasses; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, J.L.; Patel, B.K.C.; Ollivier, B. Taxonomic, Phylogenetic, and Ecological Diversity of Methanogenic Archaea. Anaerobe 2000, 6, 205–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.J.; Cole, J.J.; Caraco, N.F.; Caraco, N.F. Carbon in catchments: Connecting terrestrial carbon losses with aquatic metabolism. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2001, 52, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohman, K.; Jones, J.R.; Baysinger-Daniel, C. Experimental evidence for nitrogen limitation in a northern Ozark stream. J. North Am. Benthol. Soc. 1991, 10, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, W.; Yang, J.; Wu, G.; Jiang, H. The synergy of environmental and microbial variations caused by hydrologic management affects the carbon emission in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.I.; Eckert, W.; Conrad, R. Response of the methanogenic microbial community of a profundal lake sediment (Lake Kinneret, Israel) to algal deposition. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tank, S.E.; Lesack, L.F.W.; Gareis, J.A.L.; Osburn, C.L.; Hesslein, R.H. Multiple tracers demonstrate distinct sources of dissolved organic matter to lakes of the Mackenzie Delta, western Canadian Arctic. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Bao, L. Identification of dissolved sulfate sources and the role of sulfuric acid in carbonate weathering using dual-isotopic data from the Jialing River, Southwest China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 42, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerling, T.E.; Solomon, D.K.; Quade, J.; Bowman, J.R. On the isotopic composition of carbon in soil carbon dioxide. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 1991, 55, 3403–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, Q.; Hong, G.; Cooper, L. Sources and distribution of carbon within the Yangtze River system. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 71, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiotte-Suchet, P.; Aubert, D.; Probst, J.-L.; Gauthier-Lafaye, F.; Probst, A.; Andreux, F.; Viville, D. δ13C pattern of dissolved inorganic carbon in a small granitic catchment: The Strengbach case study (Vosges mountains, France). Chem. Geol. 1999, 159, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telmer, K.; Veizer, J. Carbon fluxes, pCO2 and substrate weathering in a large northern river basin, Canada: Carbon isotope perspectives. Chem. Geol. 1999, 159, 61–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aucour, A.-M.; Sheppard, S.M.; Guyomar, O.; Wattelet, J. Use of 13C to trace origin and cycling of inorganic carbon in the Rhône river system. Chem. Geol. 1999, 159, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galy, A.; France-Lanord, C. Weathering processes in the Ganges–Brahmaputra basin and the riverine alkalinity budget. Chem. Geol. 1999, 159, 31–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Gan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Du, Y. The Principle and Application of Environmental Isotopes; China Science Publishing & Media Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2019; (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lu, F.; Liu, Z.; Ji, H. Carbon and nitrogen isotopes analysis and sources of organic matter in the upper reaches of the Chaobai River near Beijing, China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfield, A.C. The influence of organisms on the composition of seawater. Sea 1963, 2, 26–77. [Google Scholar]
- Thorp, J.H.; Delong, M.D.; Greenwood, K.S.; Casper, A.F. Isotopic analysis of three food web theories in constricted and floodplain regions of a large river. Oecologia 1998, 117, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vander Zanden, M.J.; Rasmussen, J.B. Primary Consumer δ13C and δ15N and the Trophic Position of Aquatic Consumers. Ecology 1999, 80, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, S.; McManus, J. Application of organic carbon and nitrogen stable isotope and C/N ratios as source indicators of organic matter provenance in estuarine systems: Evidence from the Tay Estuary, Scotland. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1994, 38, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Kao, S.; Wen, L.; Chen, K. Carbon and nitrogen isotopic compositions of particulate organic matter and biogeochemical processes in the eutrophic Danshuei Estuary in northern Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 382, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.E.; Greenaway, A.M.; Dennis, P.F. Combined Carbon Isotope and C/N Ratios as Indicators of Source and Fate of Organic Matter in a Poorly Flushed, Tropical Estuary: Hunts Bay, Kingston Harbour, Jamaica. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1998, 46, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogrinc, N.; Markovics, R.; Kanduč, T.; Walter, L.M.; Hamilton, S.K. Sources and transport of carbon and nitrogen in the River Sava watershed, a major tributary of the River Danube. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 3685–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutton, T. Stable carbon isotopes ratios of natural materials. In Carbon Isotopes Techniques; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991; p. 200. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Ouyang, C.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Fang, P. Comparison between tributary and main stream and preliminary influence mechanism of CO2 flux across water-air interface in Wanzhou in the Three Gorges reservoir area. Enviroment Sci. 2022, 43, 377–386, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hua, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhao, C.; Wu, C. The effects of the environmental conditions on phosphorus release in lake sediments. Environ. Chem. 1996, 15, 15–19, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.; Mao, C.; Wang, S.; Jia, Z.; Rao, W. Seasonal variation and provenance of organic matter in the surface sediments of the three gorges reservoir: Stable isotope analysis and implications for agricultural management. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 870, 161886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Ding, L.; Zhang, L.; Gu, Z.; Ren, H. Performance, Sludge Characteristics, and the Microbial Community Dynamics of Bulking Sludge Under Different Nitrogen and Phosphorus Imbalances. Enviroment Sci. 2018, 39, 1782–1793, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Ren, N.; Chen, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y. Control of sludge bulking during treatment of phosphorized wastewater with low organic loading. J. Harbin Univ. Civ. Eng. Archit. 2001, 34, 58–60, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, P. Environmental Microbiology; Zhejiang University Press: Hangzhou, China, 2012; (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Weimer, P.J.; Zeikus, J.G. Acetate assimilation pathway of Methanosarcina barkeri. J. Bacteriol. 1979, 137, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
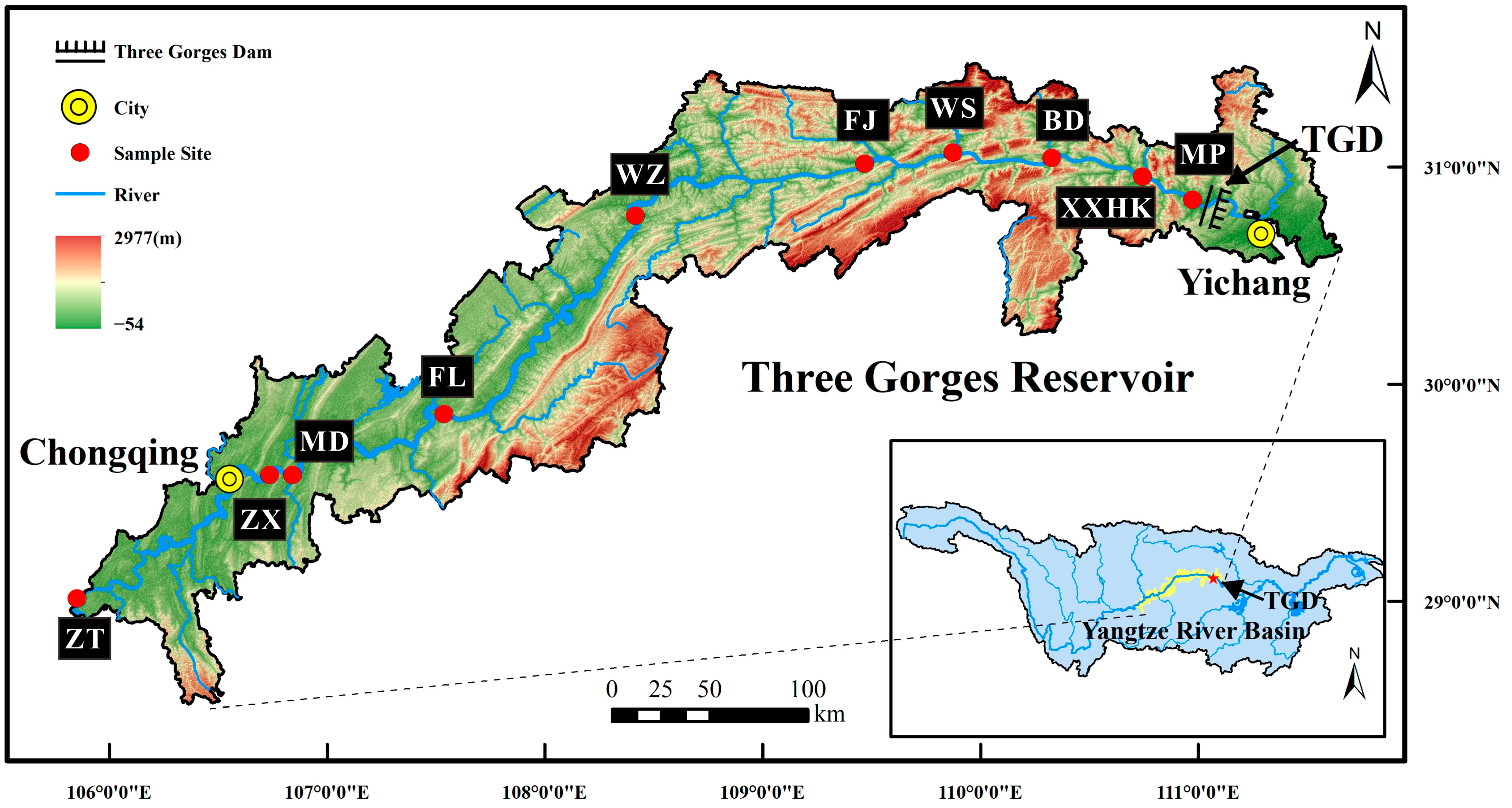
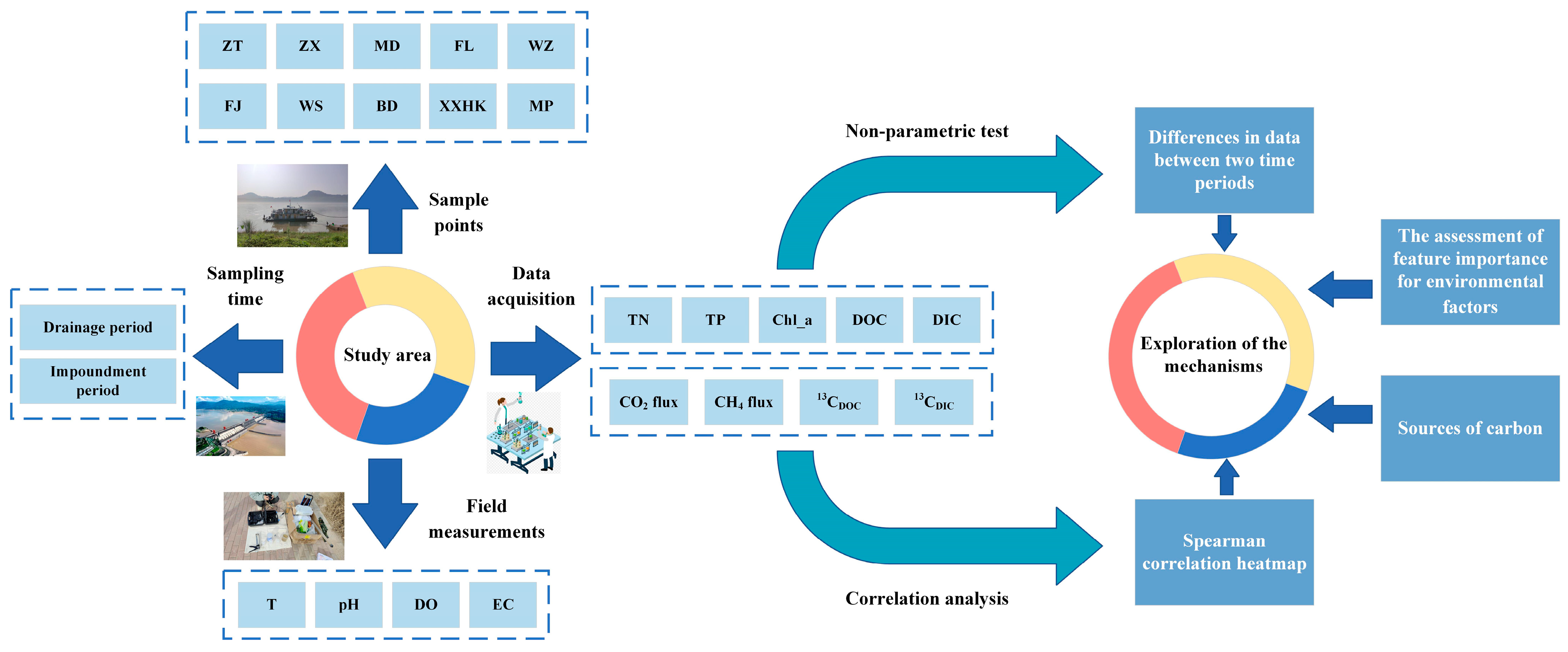

| Sampling Points | Altitude (m) | Distance from the Previous Sampling Site (Km) | Maximum Annual Runoff | Minimum Annual Runoff | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZT | 205 | 0 | 3179 | 1934 | 2591 |
| ZX | 163 | 166 | 4221 | 2479 | 3375 |
| MD | 171 | 13.7 | - | - | - |
| FL | 171 | 115.4 | - | - | - |
| WZ | 166 | 165.1 | - | - | - |
| FJ | 124 | 120.3 | - | - | - |
| WS | 134 | 43.1 | - | - | - |
| BD | 141 | 47.5 | - | - | - |
| XXHK | 113 | 44.6 | - | - | - |
| MP | 129 | 25.8 | 5442 | 2848 | 4173 |
| Parameter | Drainage Period | Impoundment Period | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Mean | Range | Mean | |
| pH | 8.21~8.67 | 8.34 ± 0.14 | 7.59~7.8 | 7.71 ± 0.05 |
| T/°C | 23.75~25.35 | 24.79 ± 0.44 | 15.08~16.69 | 15.7 ± 0.55 |
| TN/mg·L−1 | 1.58~2.49 | 2.12 ± 0.26 | 1.26~1.56 | 1.41 ± 0.09 |
| TP/mg·L−1 | 0.06~0.504 | 0.20 ± 0.14 | 0.05~0.07 | 0.06 ± 0.007 |
| DO/mg·L−1 | 5.78~8.38 | 6.64 ± 0.95 | 8.42~9.78 | 9.17 ± 0.41 |
| DOC/mg·L−1 | 4.59~9.02 | 6.29 ± 1.54 | 1.63~2.94 | 2.16 ± 0.28 |
| DIC/mg·L−1 | 2.77~6.76 | 4.96 ± 1.35 | 12.04~27.88 | 23.54 ± 5.39 |
| Chl_a/μg·L−1 | 1.53~69.41 | 14.13 ± 22.17 | 0.25~1.07 | 0.60 ± 0.24 |
| EC/μs·cm−1 | 304.5~381 | 321.6 ± 23.13 | 314.25~400.4 | 339.53 ± 29.03 |
| Sampling Points | δ13CDOC/‰ | δ13CDIC/‰ |
|---|---|---|
| ZT | −31.80 | −4.89 |
| ZX | −30.86 | −6.01 |
| MD | −30.34 | −5.55 |
| FL | −32.57 | −7.25 |
| WZ | −32.61 | −7.96 |
| FJ | −30.84 | −7.56 |
| WS | −31.31 | −7.81 |
| BD | −31.02 | −7.44 |
| XXHK | −30.11 | −6.71 |
| MP | −32.06 | −6.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, X.; Liu, M.; Pan, H.; Yao, H.; Ren, Y. Variations in Greenhouse Gas Fluxes at the Water–Gas Interface in the Three Gorges Reservoir Caused by Hydrologic Management: Implications for Carbon Cycling. Water 2024, 16, 1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16121642
Wei X, Liu M, Pan H, Yao H, Ren Y. Variations in Greenhouse Gas Fluxes at the Water–Gas Interface in the Three Gorges Reservoir Caused by Hydrologic Management: Implications for Carbon Cycling. Water. 2024; 16(12):1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16121642
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Xing, Mingliang Liu, Hongzhong Pan, Huaming Yao, and Yufeng Ren. 2024. "Variations in Greenhouse Gas Fluxes at the Water–Gas Interface in the Three Gorges Reservoir Caused by Hydrologic Management: Implications for Carbon Cycling" Water 16, no. 12: 1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16121642
APA StyleWei, X., Liu, M., Pan, H., Yao, H., & Ren, Y. (2024). Variations in Greenhouse Gas Fluxes at the Water–Gas Interface in the Three Gorges Reservoir Caused by Hydrologic Management: Implications for Carbon Cycling. Water, 16(12), 1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16121642





