Do Submerged Macrophytes Influence the Response of Zooplankton and Benthic Ostracoda to NaCl Salinity Gradients in Shallow Tropical Lakes?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experimental Material and Design
- Treatment 1: Plant treatment
- Treatment 2: Salinity treatment
2.2. Sampling and Analyses
2.2.1. Water Quality
2.2.2. Plankton Community
2.2.3. Plant Volume Inhabited
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
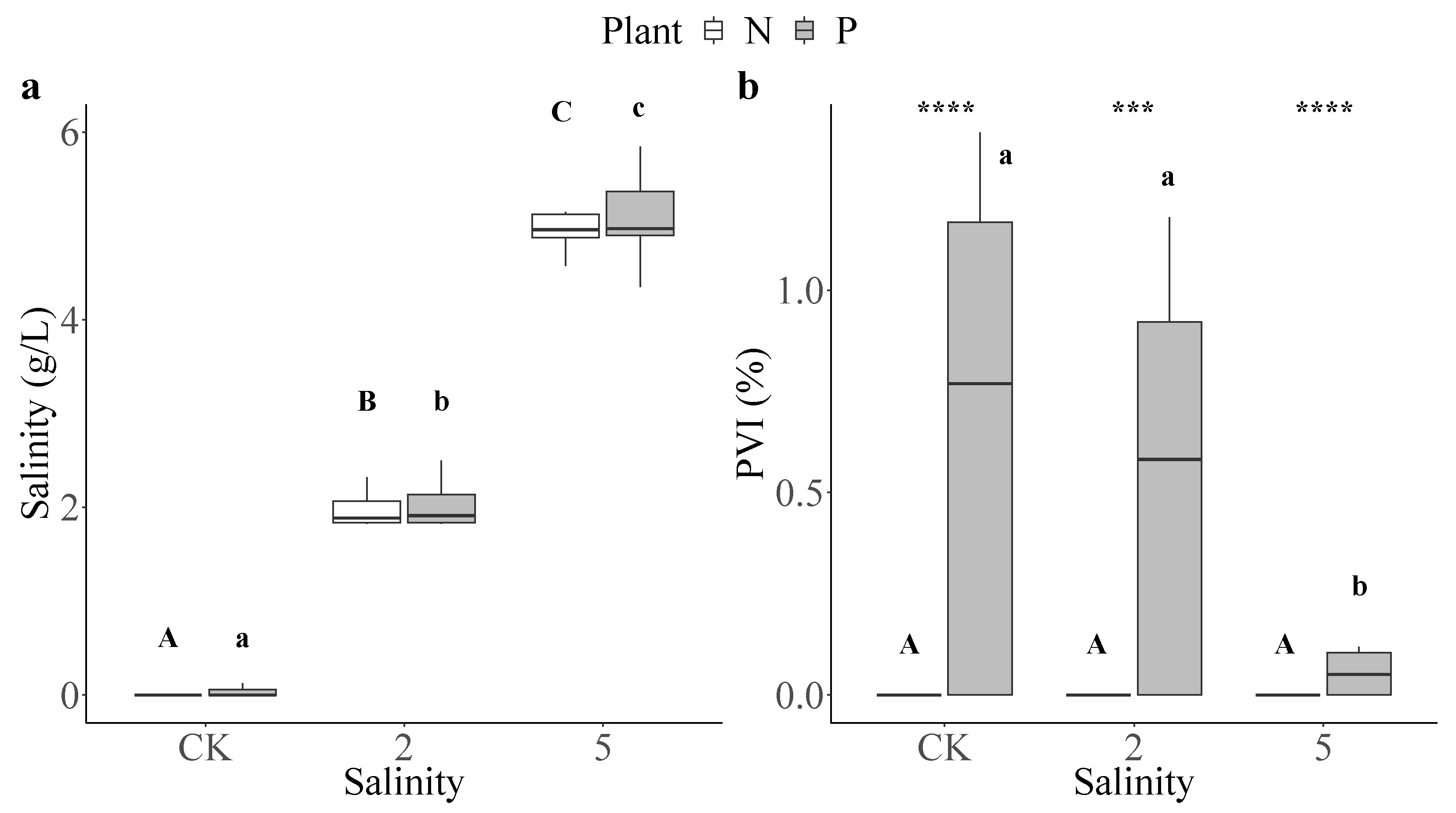
3.1. Water Quality and PVI
3.2. Phytoplankton and Periphyton
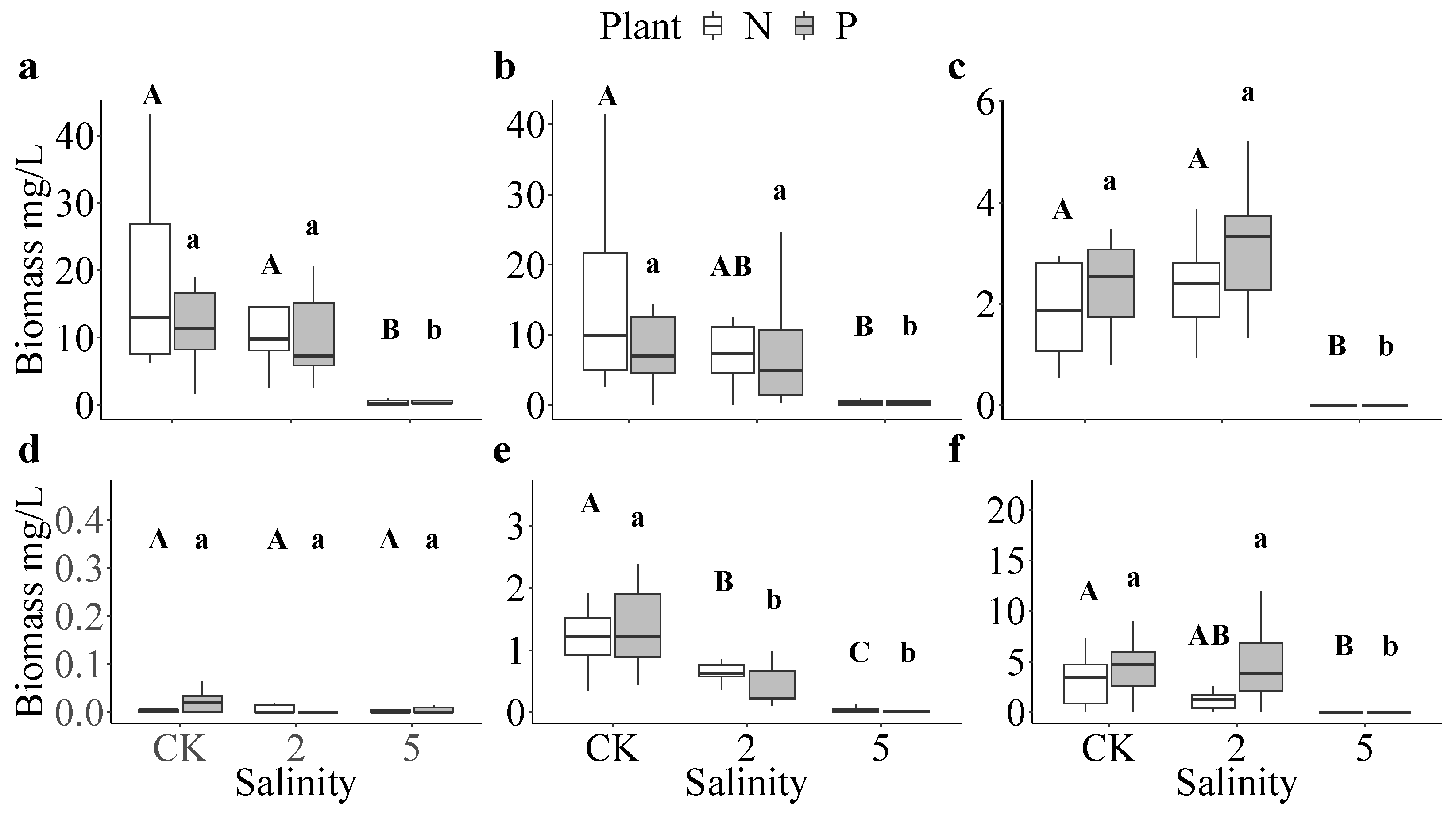
3.3. Zooplankton and Ostracoda
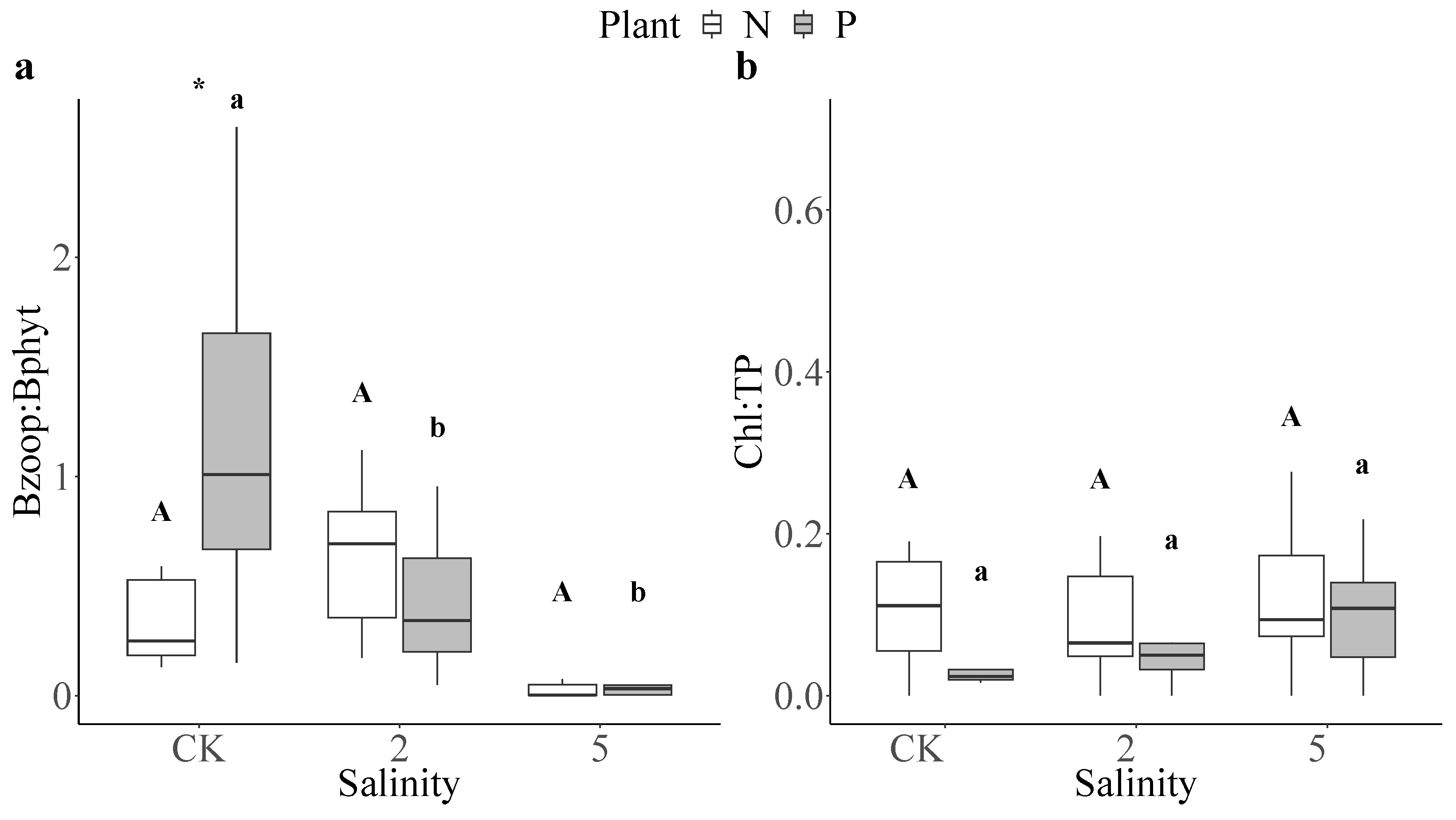
3.4. Top-Down Effects
4. Discussion
4.1. Hypothesis 1: Increased Salinity Would Lead to a Decrease in the Biomass of Zooplankton and Benthic Ostracoda
4.2. Hypothesis 2: The Presence of Submerged Macrophytes Would Have a Positive Impact on the Biomass of Zooplankton and Benthic Ostracoda
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Field, C.B.; Barros, V.R. Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability; Part A: Global and sectoral aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC); Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Babcock, R.C.; Bustamante, R.H.; Fulton, E.A.; Fulton, D.J.; Haywood, M.D.E.; Hobday, A.J.; Kenyon, R.; Matear, R.J.; Plagányi, E.E.; Richardson, A.J.; et al. Severe Continental-Scale Impacts of Climate Change Are Happening Now: Extreme Climate Events Impact Marine Habitat Forming Communities Along 45% of Australia’s Coast. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorrain-Soligon, L.; Robin, F.; Barbraud, C.; Brischoux, F. Some like it salty: Spatio-temporal dynamics of salinity differentially affect anurans and caudates in coastal wetlands. Freshw. Biol. 2023, 68, 279–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, K.R.; Cant, B.; Ryan, T. Responses of freshwater biota to rising salinity levels and implications for saline water management: A review. Aust. J. Bot. 2003, 51, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiyar, Y.; Arafat, M.Y.; Andrabi, S.; Tak, H.I. Zooplankton: The Significant Ecosystem Service Provider in Aquatic Environment. In Bioremediation and Biotechnology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 3, pp. 227–244. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, W.; Huang, X.; Chen, Y.; Fu, R.; Du, X.; Chen, X.; Zhan, A. Zooplankton biodiversity monitoring in polluted freshwater ecosystems: A technical review. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2020, 1, 100008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, B.A.; Dutkiewicz, S.; Jahn, O.; Follows, M.J. A size-structured food-web model for the global ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 1877–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesh, I.V. Plankton of the Baltic estuarine ecosystems with emphasis on Neva Estuary: A review of present knowledge and research perspectives. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 49, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Meter, R.J.; Swan, C.M.; Leips, J.; Snodgrass, J.W. Road salt stress induces novel food web structure and interactions. Wetlands 2011, 31, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.L.; Shurin, J.B. Regional zooplankton biodiversity provides limited buffering of pond ecosystems against climate change. J. Anim. Ecol. 2012, 81, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meter, R.J.; Swan, C.M. Road Salts as Environmental Constraints in Urban Pond Food Webs. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintz, W.D.; Relyea, R.A. A review of the species, community, and ecosystem impacts of road salt salinisation in fresh waters. Freshw. Biol. 2019, 64, 1081–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, E.; Brucet, S.; Meerhoff, M.; Nathansen, L.; Jeppesen, E. Community Structure and Diel Migration of Zooplankton in Shallow Brackish Lakes: Role of Salinity and Predators. Hydrobiologia 2010, 646, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.-J.; Tao, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.-H.; Zhou, L.; Wang, P.-Z.; Li, Y.-Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, H.-J.; et al. Interactive effects of nutrients and salinity on zooplankton in subtropical plateau lakes with contrasting water depth. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1110746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attayde, J.L.; Bozelli, R.L. Assessing the Indicator Properties of Zooplankton Assemblages to Disturbance Gradients By Canonical Correspondence Analysis. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1998, 55, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Xu, L.; Hou, J.; Liu, Z.; Jeppesen, E.; Han, B.P. Responses of trophic structure and zooplankton community to salinity and temperature in Tibetan lakes: Implication for the effect of climate warming. Water Res. 2017, 124, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Kluijver, A.; Ning, J.; Liu, Z.; Jeppesen, E.; Gulati, R.D.; Middelburg, J.J. Macrophytes and periphyton carbon subsidies to bacterioplankton and zooplankton in a shallow eutrophic lake in tropical China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2015, 60, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Christoffersen, K. (Eds.) The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Manatunge, J.; Asaeda, T.; Priyadarshana, T. The Influence of Structural Complexity on Fish–zooplankton Interactions: A Study Using Artificial Submerged Macrophytes. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2004, 58, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerhoff, M.; Iglesias, C.; Teixeira-de Mello, F.; Clemente, J.; Jensen, E.; Lauridsen, T.; Jeppesen, E. Effects of habitat complexity on community structure and predator avoidance behaviour of littoral zooplankton in temperate versus subtropical shallow lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadouani, A.; Pinel-Alloul, B.; Prepas, E.E. Effects of experimentally induced cyanobacterial blooms on crustacean zooplankton communities. Freshw. Biol. 2003, 48, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Bergonzoni, I.; Meerhoff, M.; Davidson, T.A.; Teixeira-de Mello, F.; Baattrup-Pedersen, A.; Jeppesen, E. Meta-analysis Shows a Consistent and Strong Latitudinal Pattern in Fish Omnivory Across Ecosystems. Ecosystems 2012, 15, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Sondergaard, M.; Pedersen, A.R.; Jurgens, K.; Strzelczak, A.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Johansson, L.S. Salinity Induced Regime Shift in Shallow Brackish Lagoons. Ecosystems 2007, 10, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Jiang, H.S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Yin, L.; Cao, Y. Responses of five submerged macrophytes to NaCl salinity in a tropical mesocosm study. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2020, 193, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, L.; Jiang, H.S.; Li, W.; Gontero, B.; Maberly, S.C. Biochemical and biophysical CO2 concentrating mechanisms in two species of freshwater macrophyte within the genus Ottelia (Hydrocharitaceae). Photosynth. Res. 2014, 121, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.F.; Chen, W.M.; Cai, Q.M. Survey, Observation and Analysis of Lake Ecology—Standard Methods for Observation and Analysis in Chinese Ecosystem Research Network; Series, V., Ed.; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- McEnnulty, F.R.; Davies, C.H.; Armstrong, A.O.; Atkins, N.; Coman, F.; Clementson, L.; Edgar, S.; Eriksen, R.S.; Everett, J.D.; Anthony Koslow, J.; et al. A database of zooplankton biomass in Australian marine waters. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Li, S.; Ke, J.; Liao, C.; Hansen, A.G.; Jeppesen, E.; Zhang, T.; Li, W.; Liu, J. The feeding habits of small-bodied fishes mediate the strength of top-down effects on plankton and water quality in shallow subtropical lakes. Water Res. 2023, 233, 119705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Jensen, J.P.; Jensen, C.; Faafeng, B.; Hessen, D.O.; Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.; Brettum, P.; Christoffersen, K. The impact of nutrient state and lake depth on top-down control in the pelagic zone of lakes: A study of 466 lakes from the temperate zone to the arctic. Ecosystems 2003, 6, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Jin, H.; Jeppesen, E.; Li, K.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Fish-mediated plankton responses to increased temperature in subtropical aquatic mesocosm ecosystems: Implications for lake management. Water Res. 2018, 144, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, S.; Chan, F.; Li, W.; Zhao, S.; Søndergaard, M.; Jeppesen, E. Strong impact of nitrogen loading on submerged macrophytes and algae: A long-term mesocosm experiment in a shallow Chinese lake. Freshw. Biol. 2015, 60, 1525–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.r-project.org (accessed on 23 July 2020).
- Frenzel, P.; Henkel, D.; Siccha, M.; Tschendel, L. Do ostracod associations reflect macrophyte communities? A case study from the brackish water of the southern Baltic Sea coast. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 67, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.; Castro, B.; Pardal, M.; Gonçalves, F. Salinity effects on survival and life history of two freshwater cladocerans (Daphnia magna and Daphnia longispina). Ann. Limnol.—Int. Lim. 2007, 43, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, J.M.; Bozelli, R.L.; Rocha, A.d.M.; Esteves, F.d.A. Effects of slight salinity increases on Moina micrura (Cladocera) populations: Field and laboratory observations. Mar. Freshwater Res. 2008, 59, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do-Hong, L.C.; Slooten, K.B.-V.; Tarradellas, J. Tropical ecotoxicity testing with Ceriodaphnia cornuta. Environ. Toxicol. 2004, 19, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lance, J. The salinity tolerance of some estuarine planktonic Copepods. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1963, 8, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finney, C.M. Salinity stress in harpacticoid copepods. Estuaries 1979, 2, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.L. Life-History Strategies, Trophic Patterns and Community Structure in the Fishes of Lake Biandantang. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Hydrobiology, The Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Liu, Z.; He, H.; Zhen, W.; Guan, B.; Chen, F.; Li, K.; Zhong, P.; Mello, F.T.; Jeppesen, E. Submerged macrophytes facilitate dominance of omnivorous fish in a subtropical shallow lake: Implications for lake restoration. Hydrobiologia 2016, 775, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Kanstrup, E.; Petersen, B.; Eriksen, R.B.; Hammershøj, M.; Mortensen, E.; Jensen, J.P.; Have, A. Does the impact of nutrients on the biological structure and function of brackish and freshwater lakes differ? Hydrobiologia 1994, 275, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, F.; Abad, M.; Bodergat, A.M.; Carbonel, P.; Rodríguez-Lázaro, J.; González-Regalado, M.L.; Toscano, A.; García, E.X.; Prenda, J. Freshwater Ostracods as Environmental Tracers. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 10, 1115–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timms, R.M.; Moss, B. Prevention of growth of potentially dense phytoplankton populations by zooplankton grazing, in the presence of zooplanktivorous fish, in a shallow wetland ecosystem. Limnolsm. Oceanogr. 1984, 29, 472–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Donk, E.; van De Bund, W.J. Impact of submerged macrophytes including charophytes on phyto- and zooplankton communities: Allelopathy versus other mechanisms. Aquat. Bot. 2002, 72, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | F Value and Significance | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Salinity | Plant | Salinity × Plant | |
| pH | 5.292 * | 56.219 *** | 7.838 ** |
| Alk | 98.056 *** | 38.989 *** | 9.615 ** |
| EC | 2820.963 *** | 0.093 | 1.177 |
| TP | 0.260 | 1.430 | 2.952 |
| TN | 2.599 | 0.314 | 1.358 |
| WT | 0.861 | 0.511 | 0.520 |
| Variables | F Value and Significance | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Salinity | Plant | Salinity × Plant | |
| Total zooplankton | 6.390 ** | 0.496 | 0.585 |
| Copepods | 53.622 *** | 2.643 | 1.393 |
| Cladocerans | 3.706 * | 0.716 | 0.607 |
| Nauplii | 34.579 *** | 0.007 | 0.951 |
| Rotifer | 1.394 | 0.873 | 1.875 |
| Ostracoda | 17.779 *** | 13.956 ** | 7.000 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, T.; Yin, L.; Li, W.; Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Y. Do Submerged Macrophytes Influence the Response of Zooplankton and Benthic Ostracoda to NaCl Salinity Gradients in Shallow Tropical Lakes? Water 2024, 16, 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16111542
Chen T, Yin L, Li W, Huang J, Zhang X, Cao Y. Do Submerged Macrophytes Influence the Response of Zooplankton and Benthic Ostracoda to NaCl Salinity Gradients in Shallow Tropical Lakes? Water. 2024; 16(11):1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16111542
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Tao, Liyan Yin, Wei Li, Jiaquan Huang, Xiaohang Zhang, and Yu Cao. 2024. "Do Submerged Macrophytes Influence the Response of Zooplankton and Benthic Ostracoda to NaCl Salinity Gradients in Shallow Tropical Lakes?" Water 16, no. 11: 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16111542
APA StyleChen, T., Yin, L., Li, W., Huang, J., Zhang, X., & Cao, Y. (2024). Do Submerged Macrophytes Influence the Response of Zooplankton and Benthic Ostracoda to NaCl Salinity Gradients in Shallow Tropical Lakes? Water, 16(11), 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16111542







