Impact of Climate Change on the Water Balance of the Akaki Catchment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
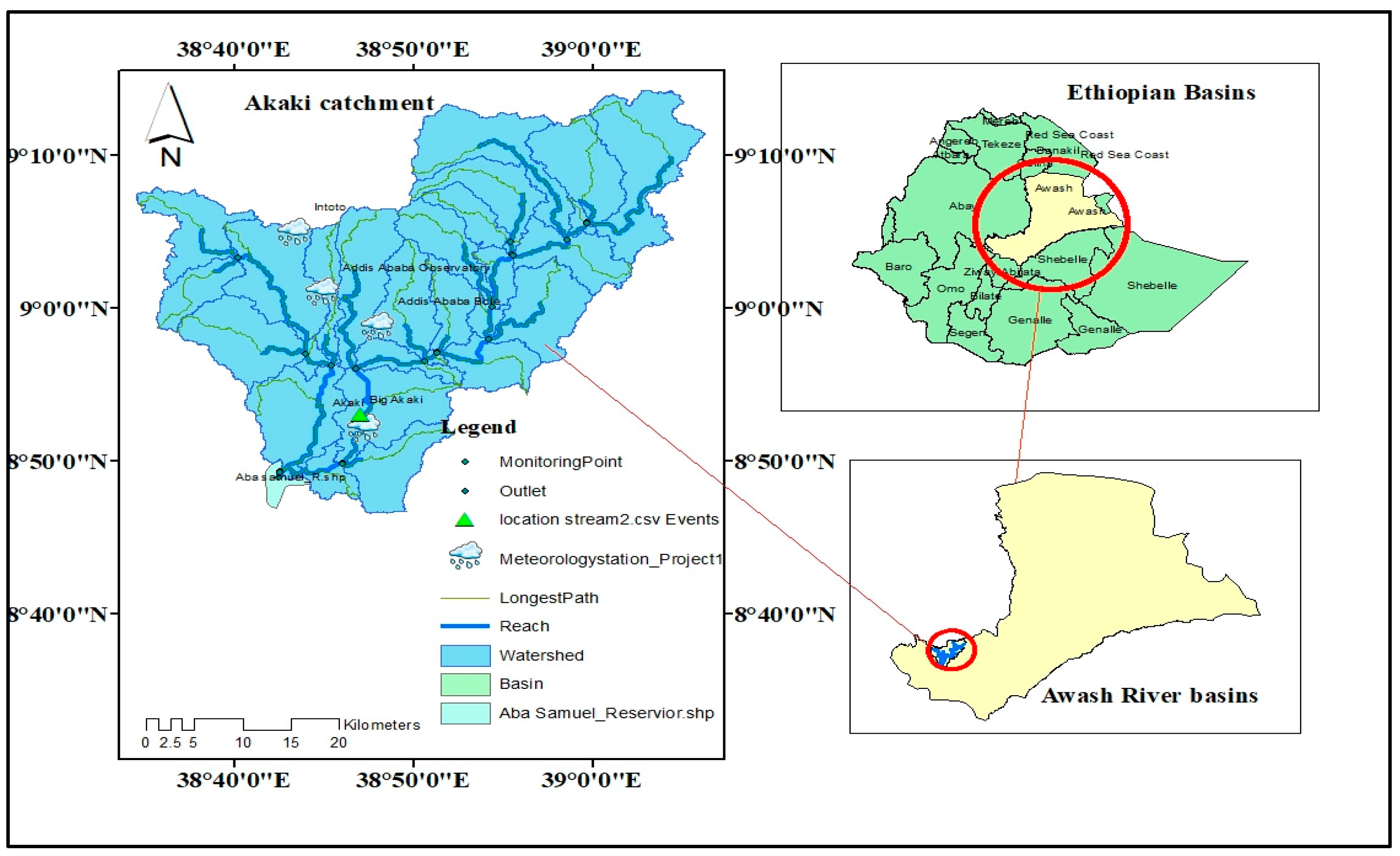
2.1. Description of the Study Area
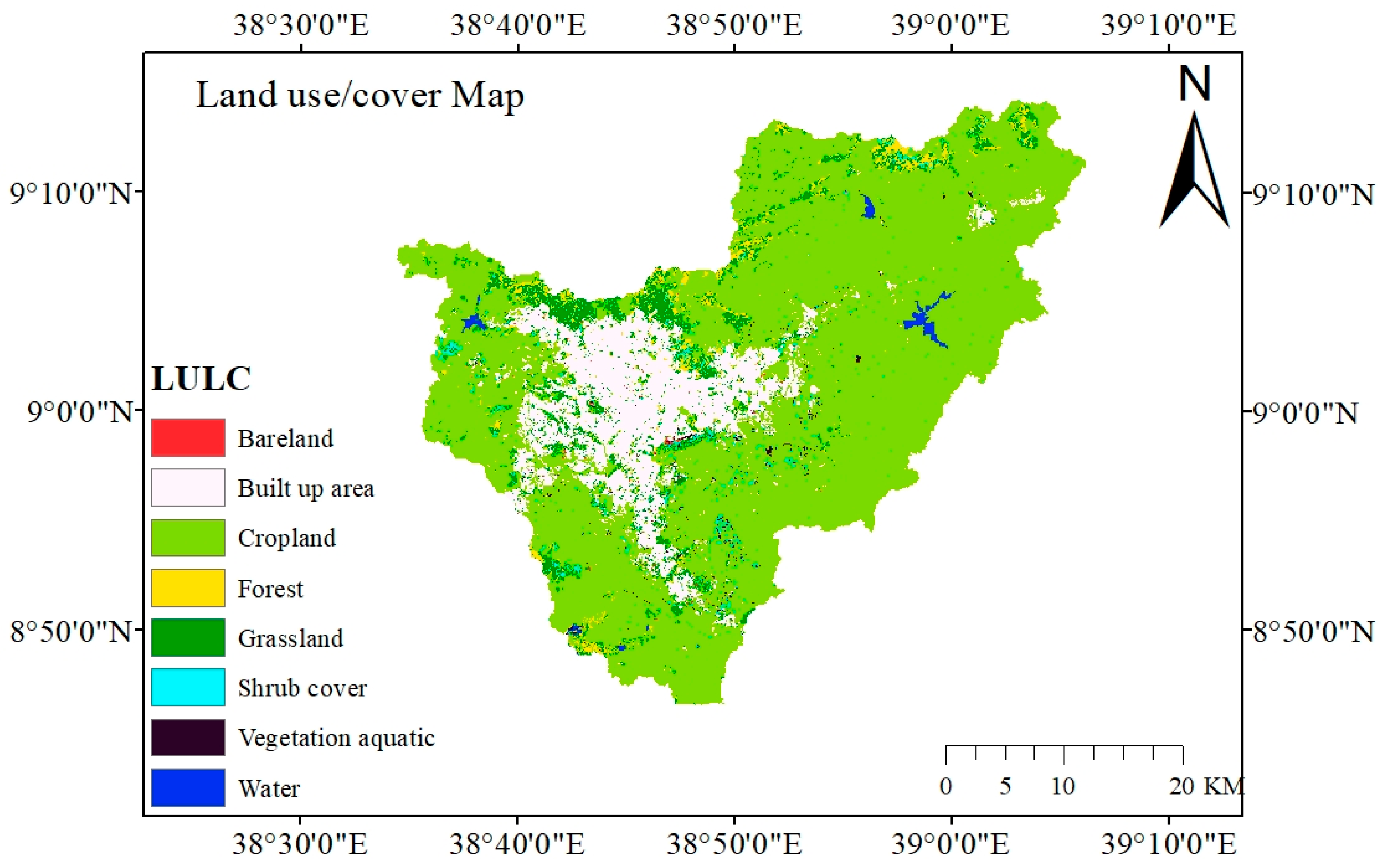
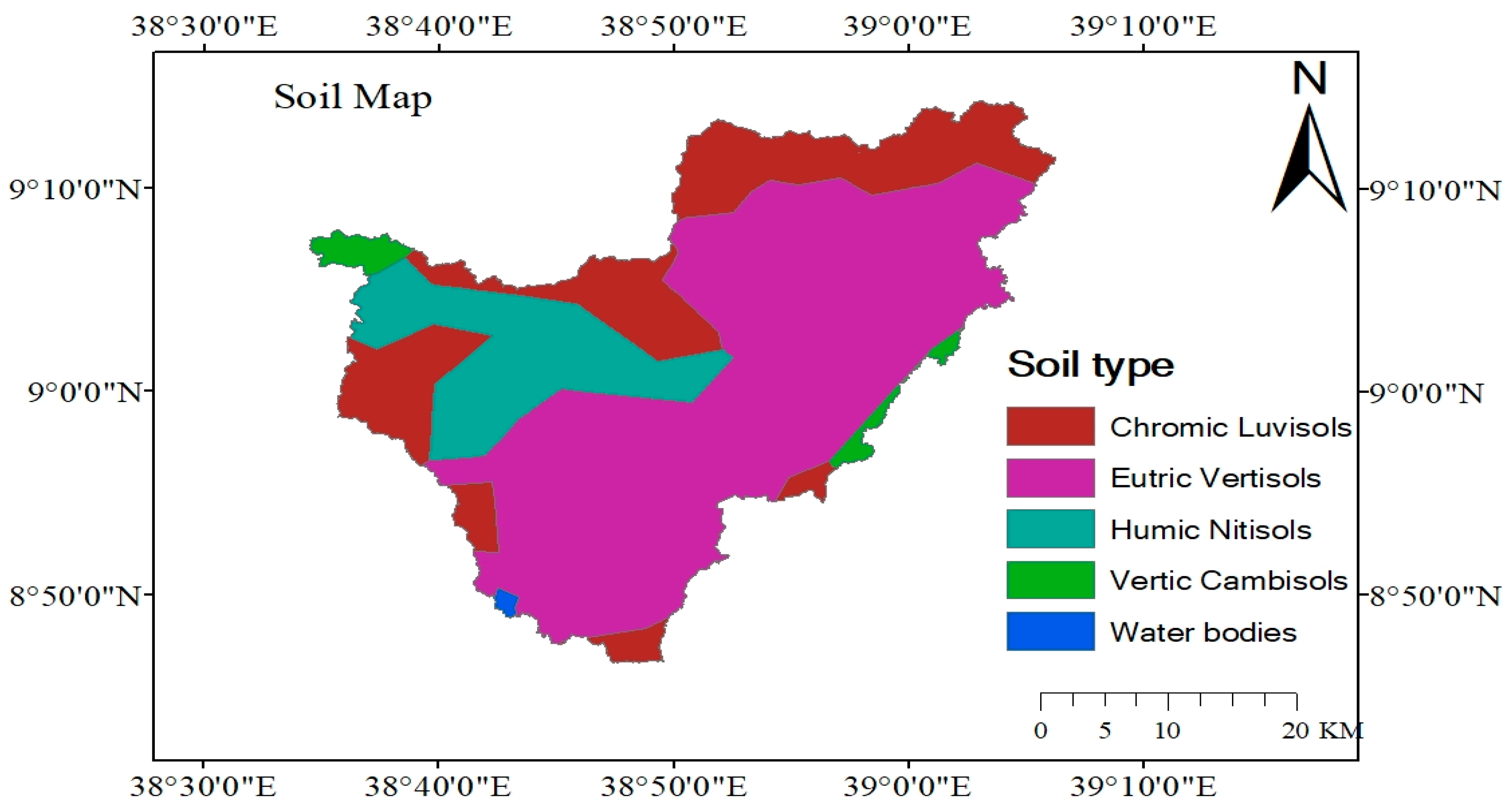
2.2. Data Used
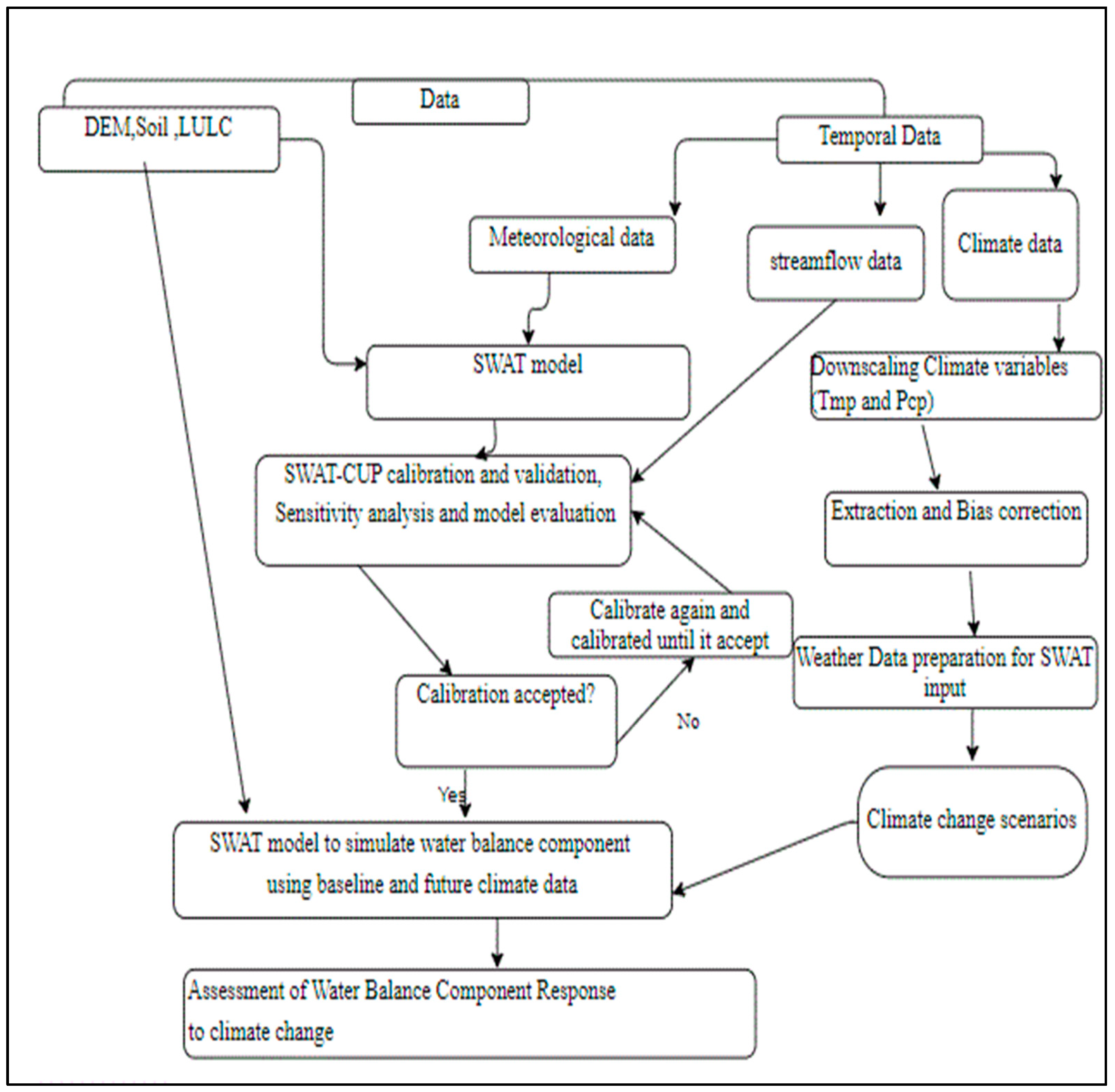
3. Performed Methodology
3.1. The Hydrologic Model
3.2. Model Calibration and Validation
3.3. Hydrologic Model Performance Evaluation
3.4. The Bias Correction Method
4. Result and Discussion
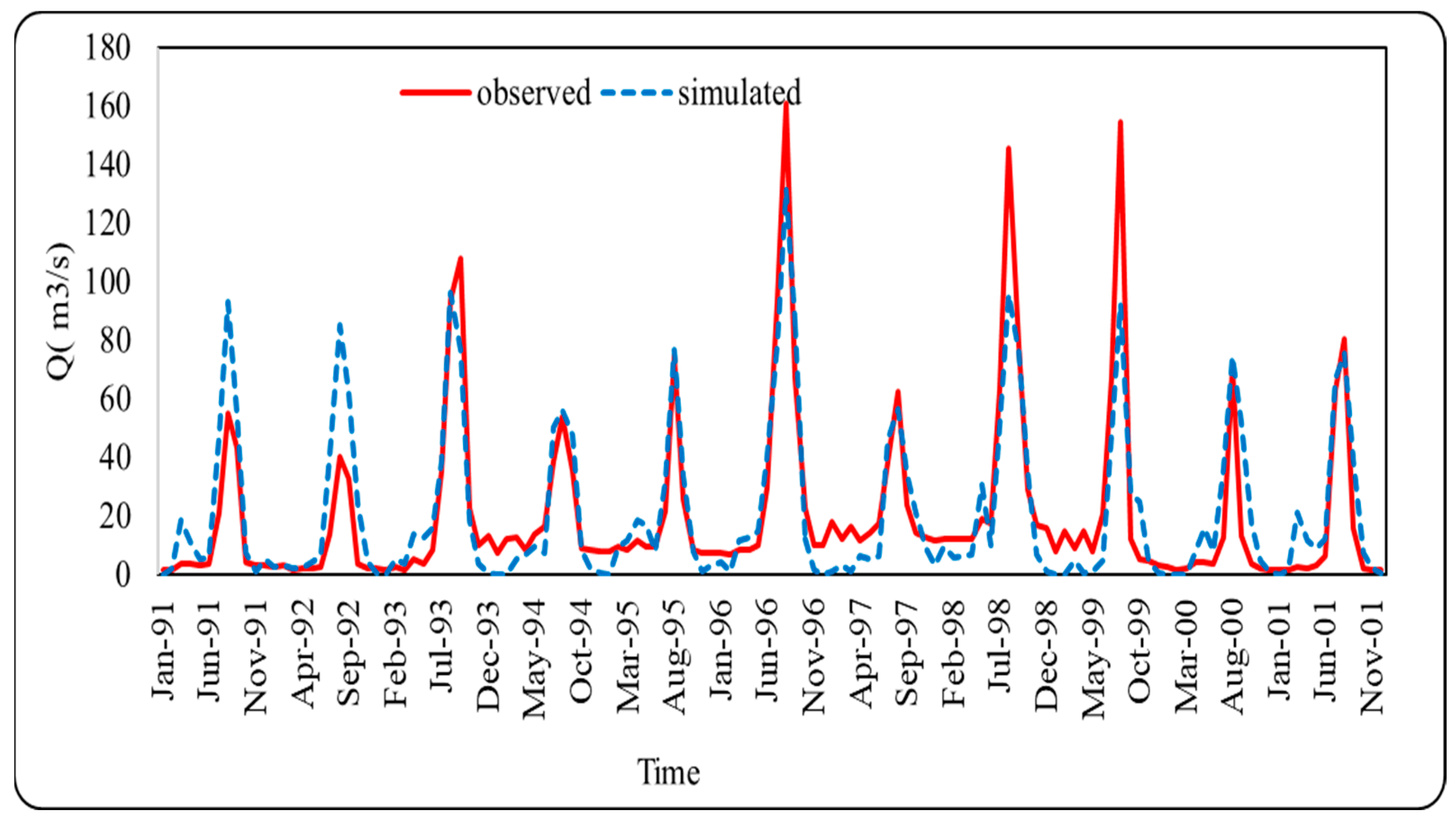
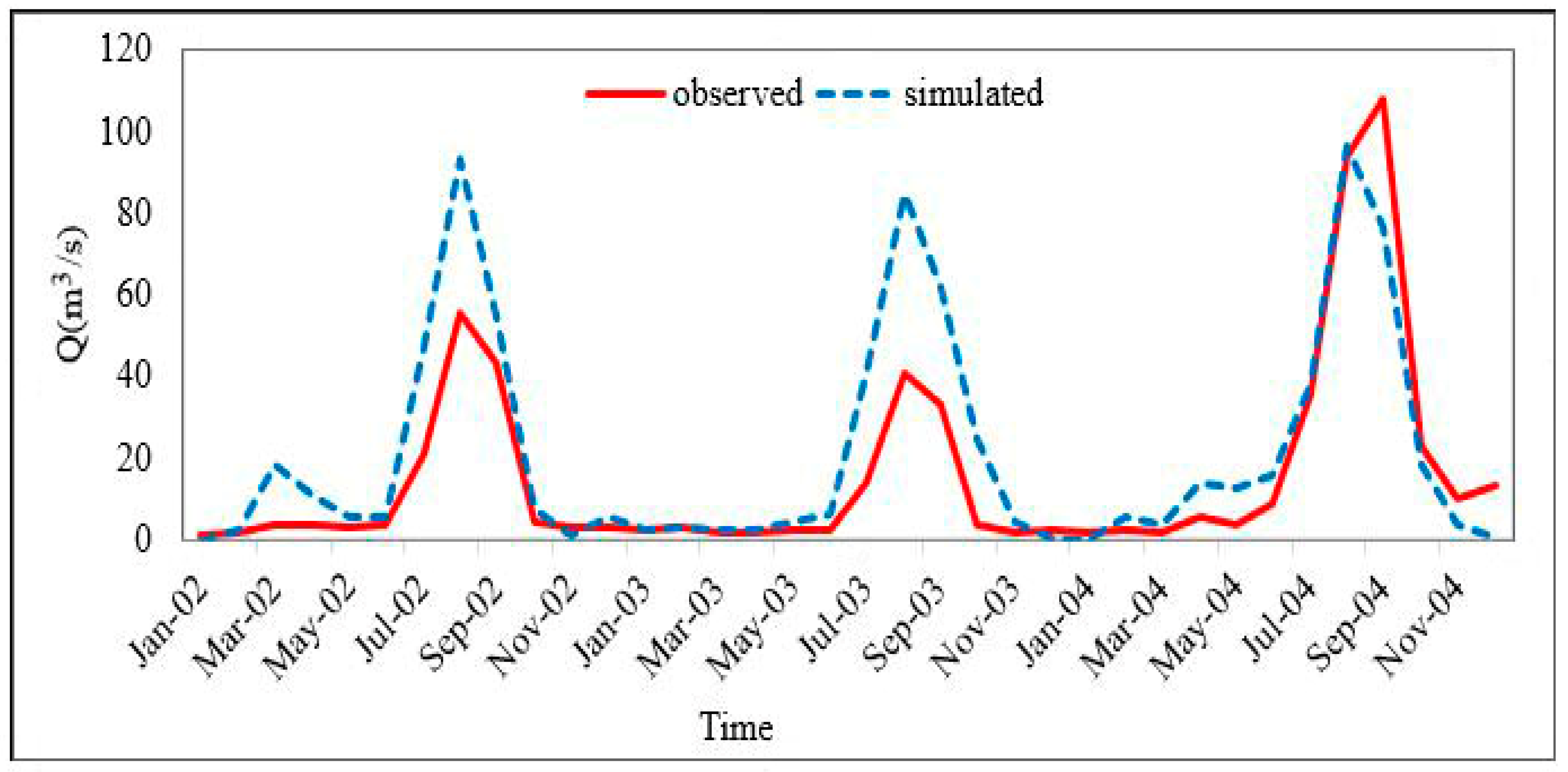
4.1. SWAT Mode Calibrated and Validated Result
4.2. Change in Future Climate
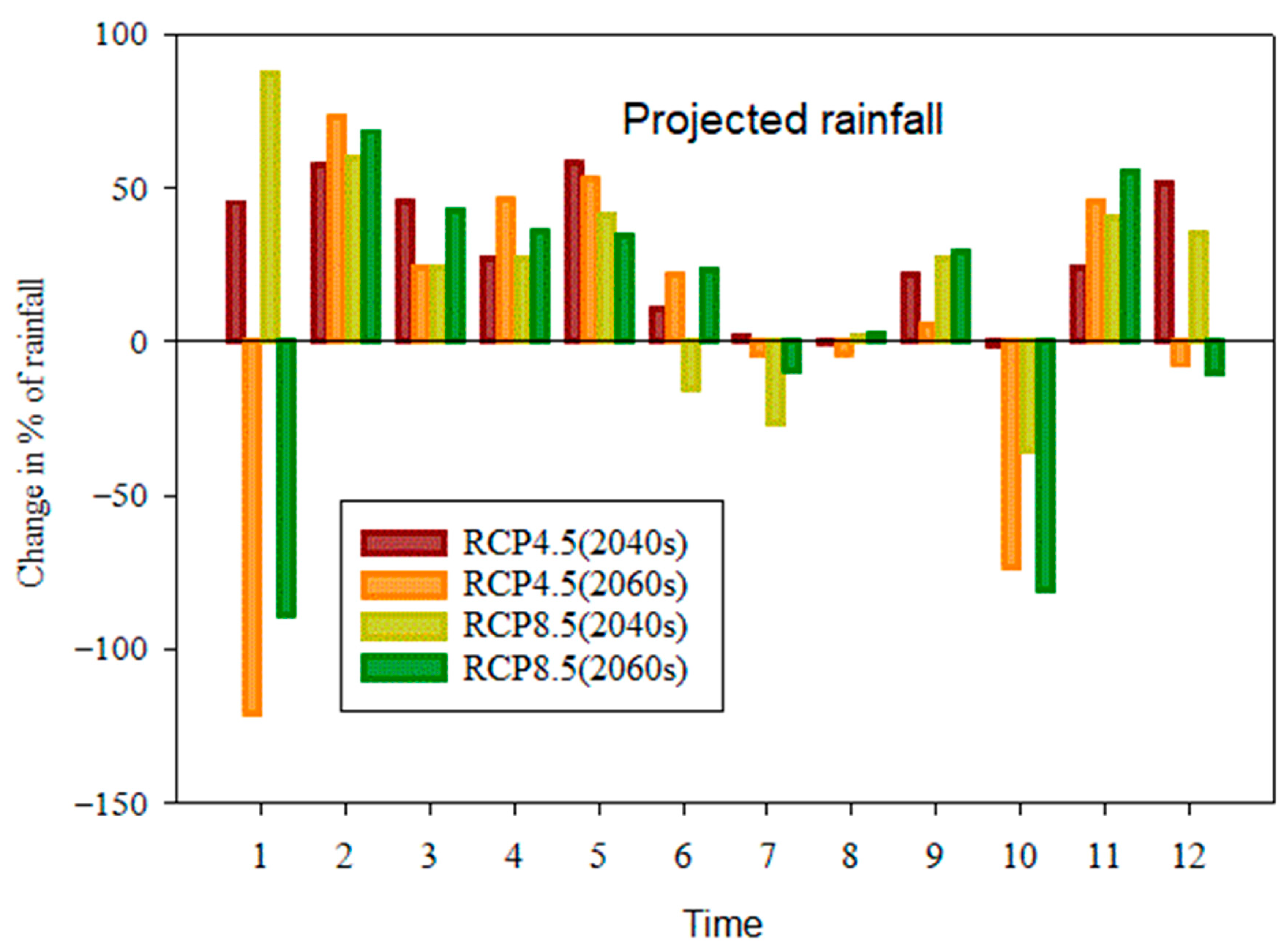
4.2.1. Rainfall Projection under RCPs
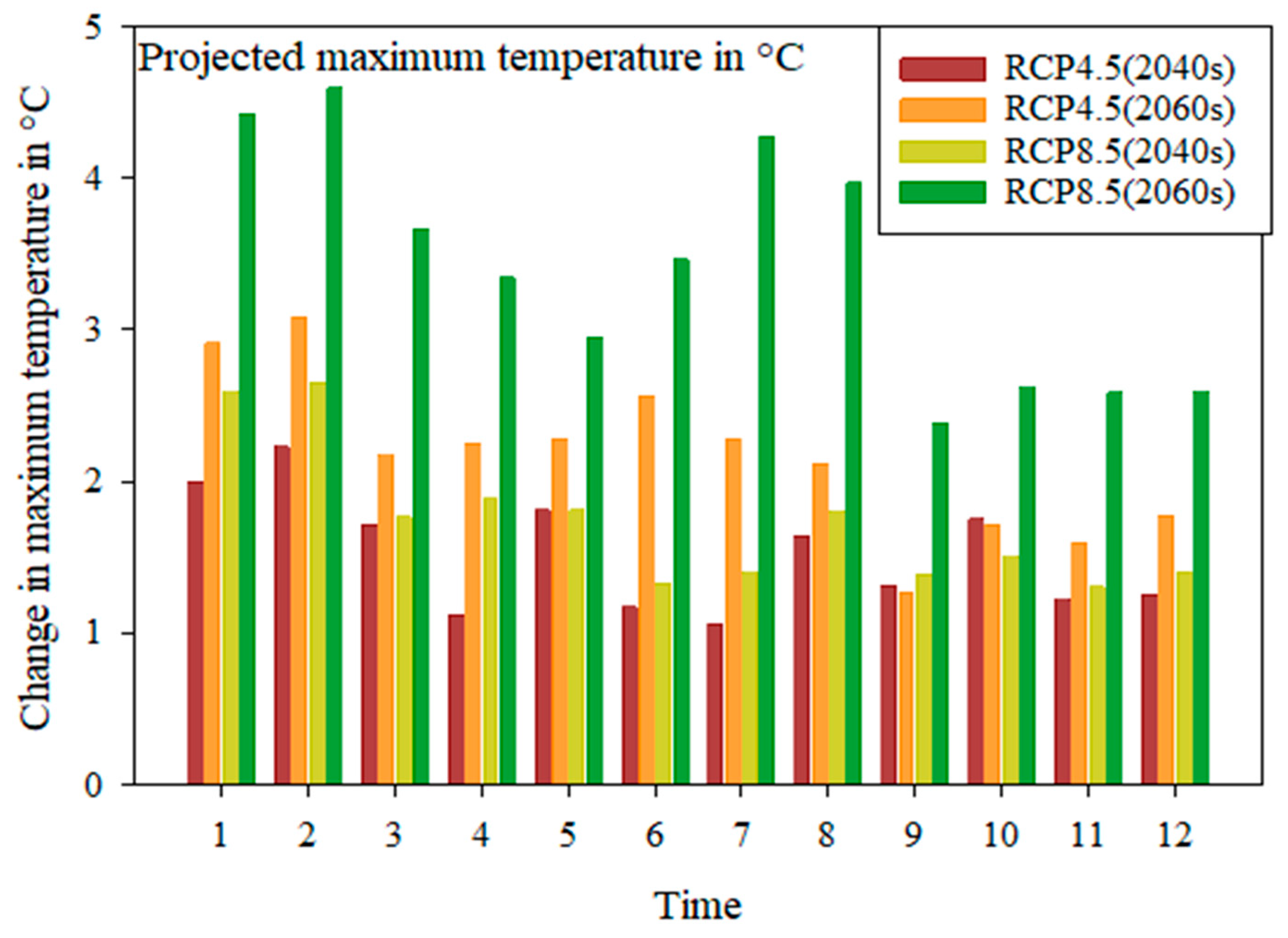
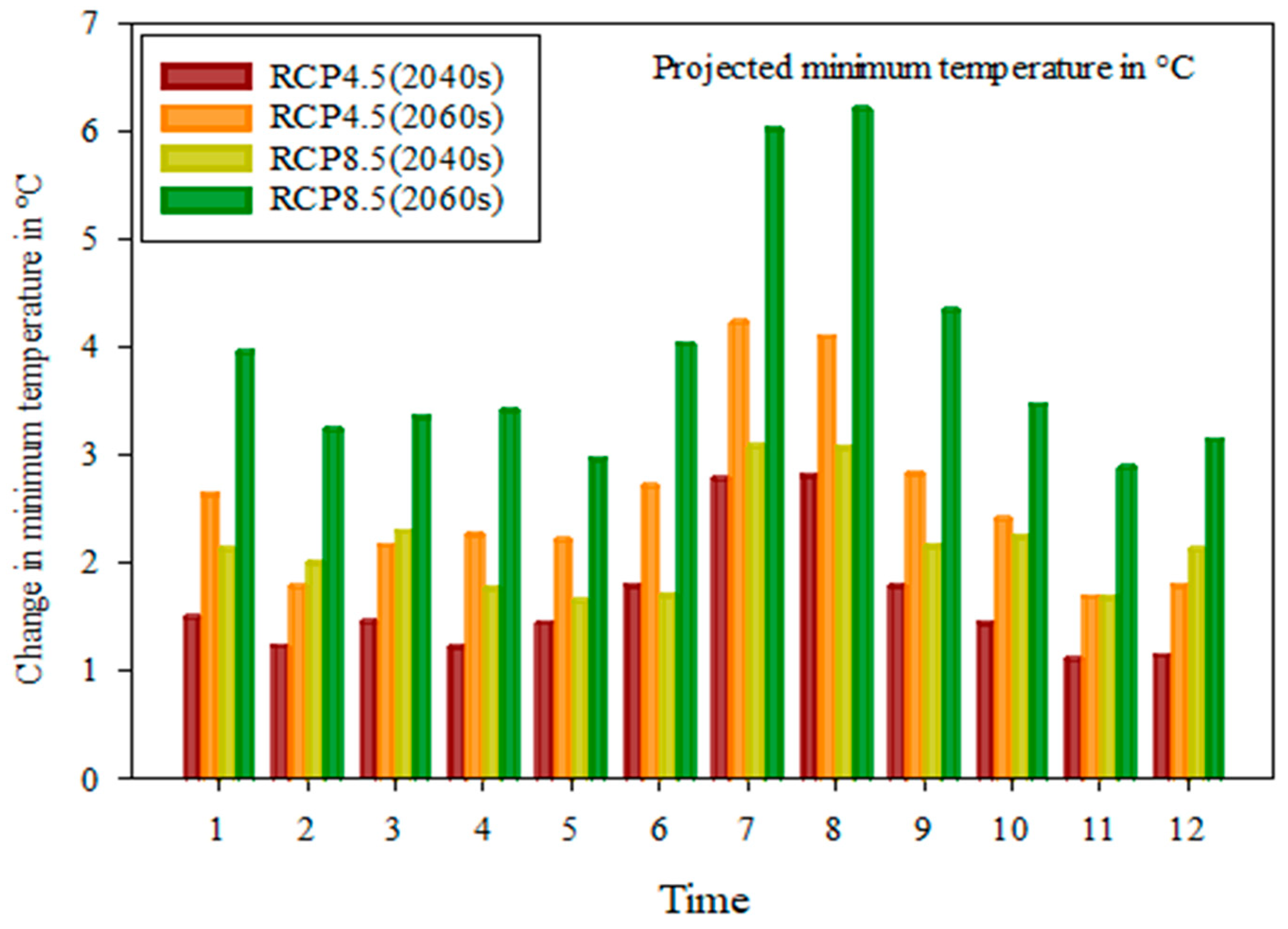
4.2.2. Change in Temperature under RCPs
4.2.3. Projected Water Balance Response to Climate Change
4.3. Water Balance Change at the Sub-Basin Level
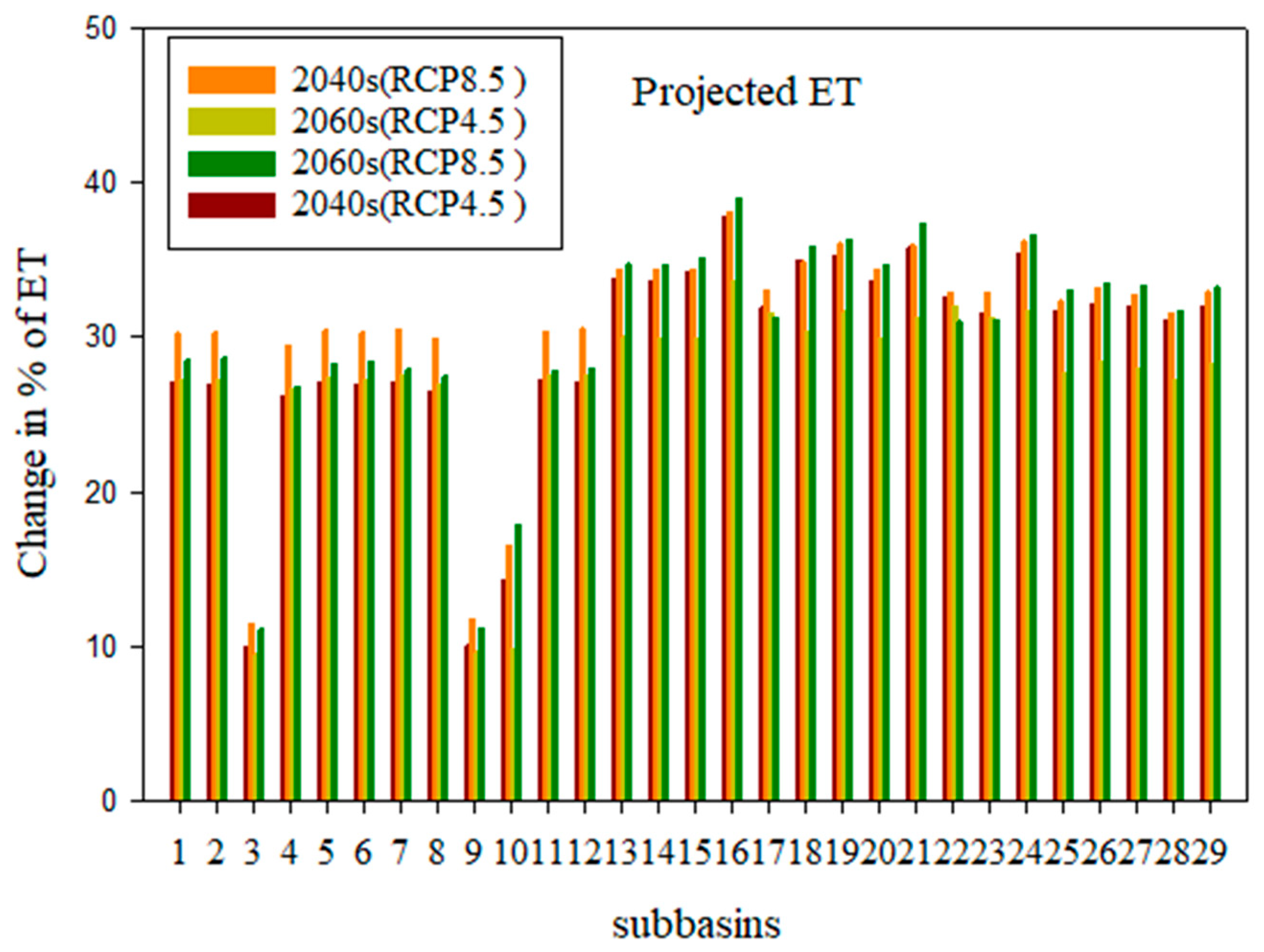
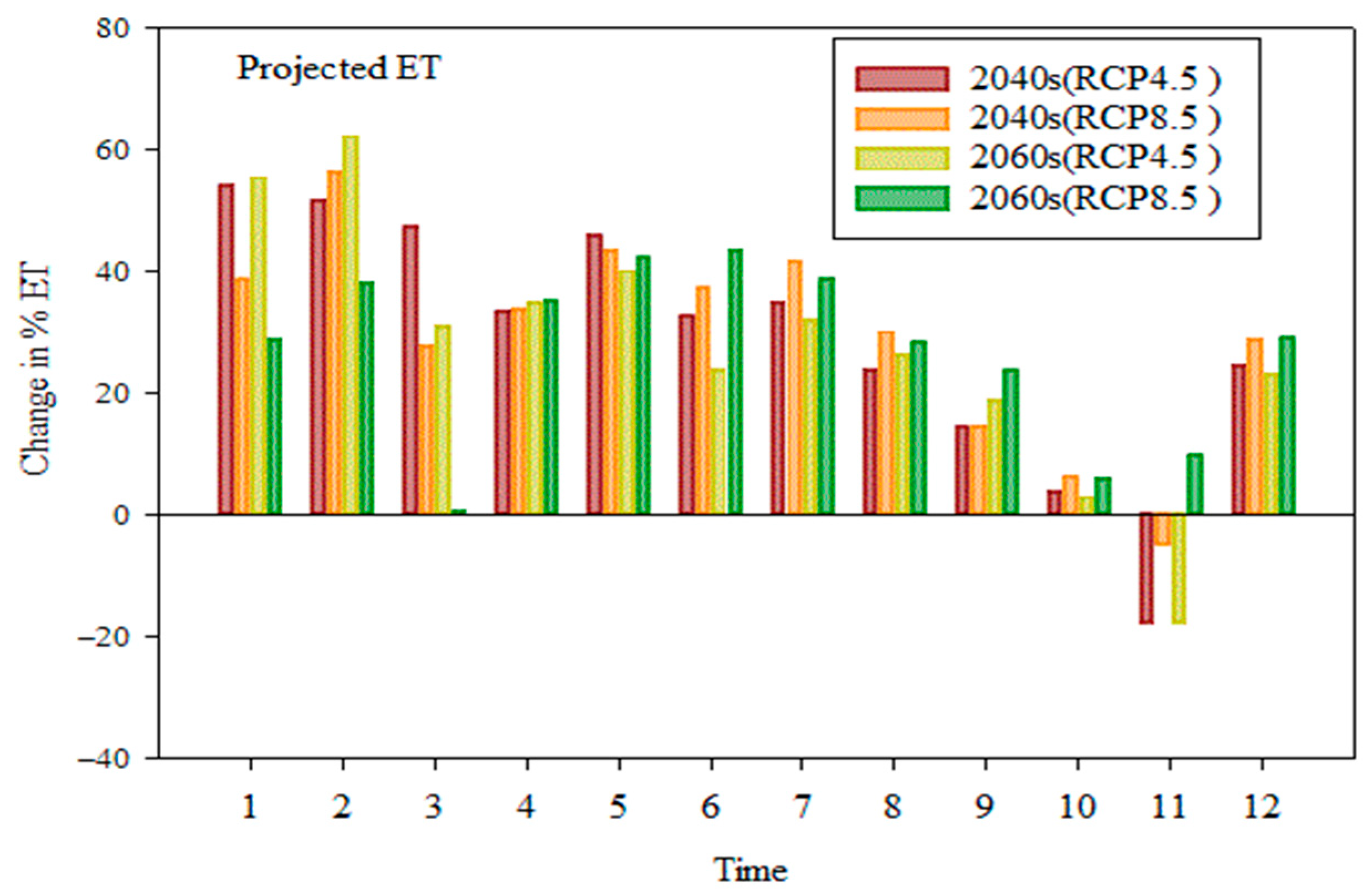
4.3.1. Change in Evapotranspiration at the Sub-Basin
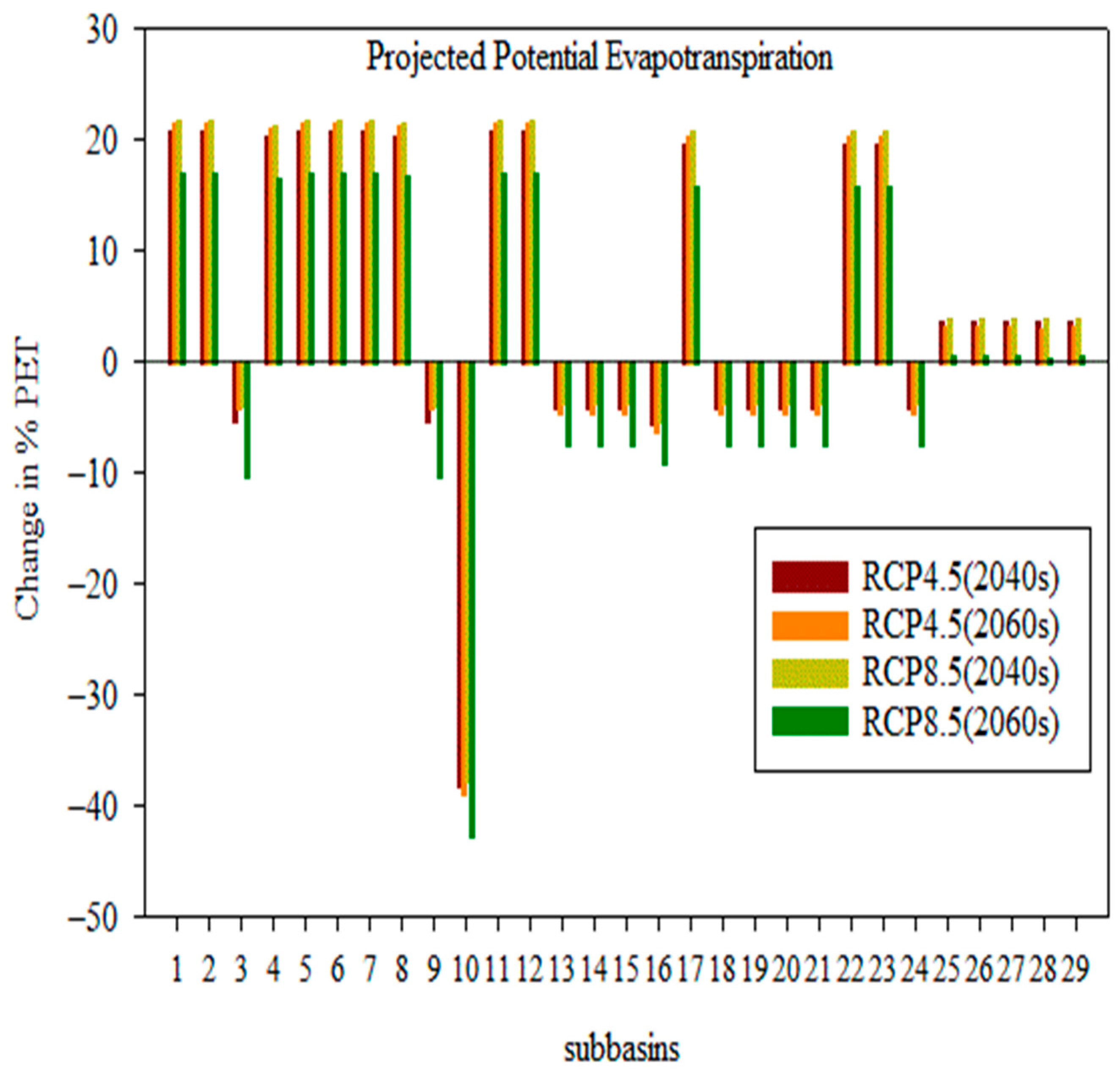
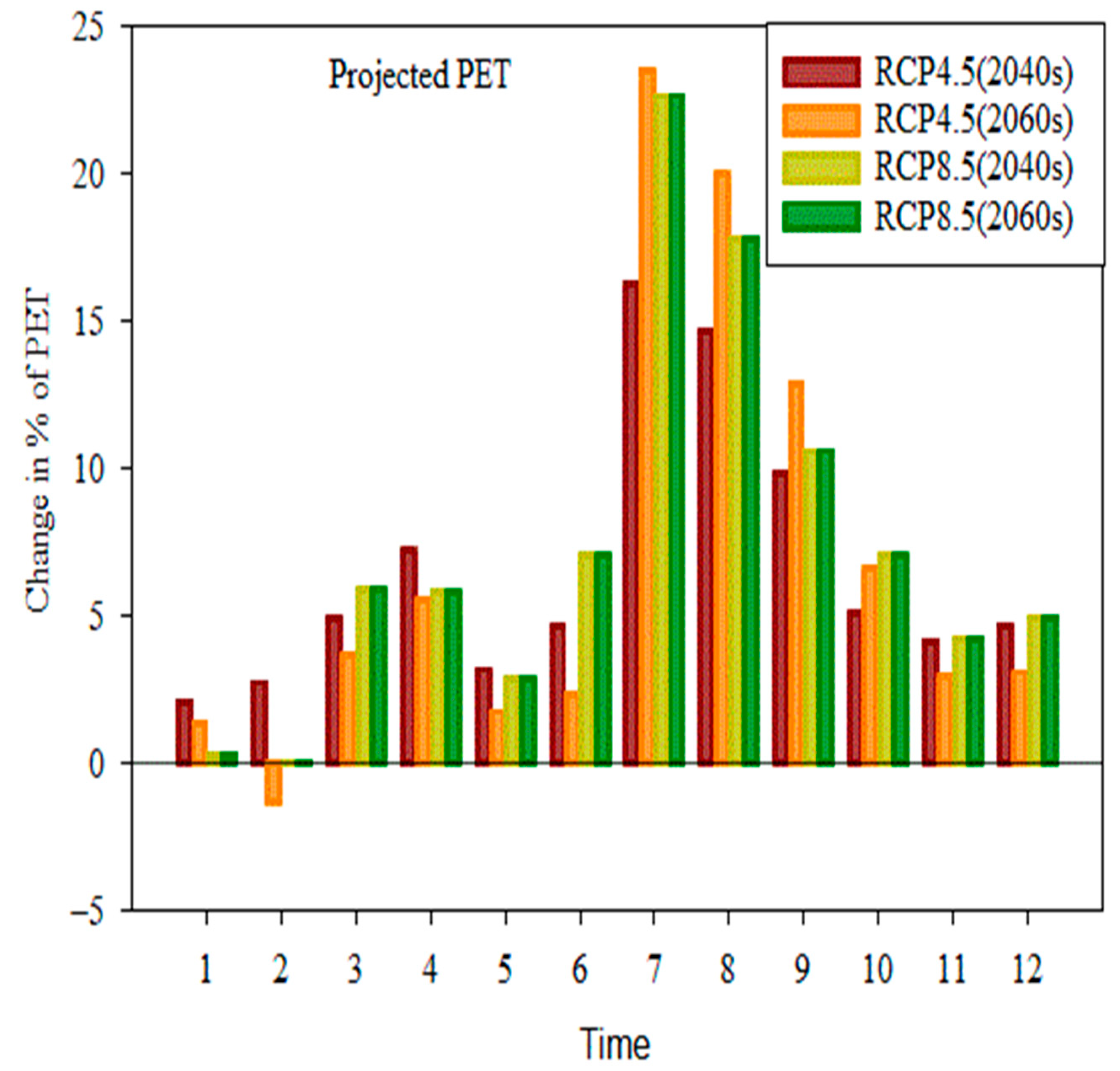
4.3.2. Change in Potential Evapotranspiration in the Sub-Basin
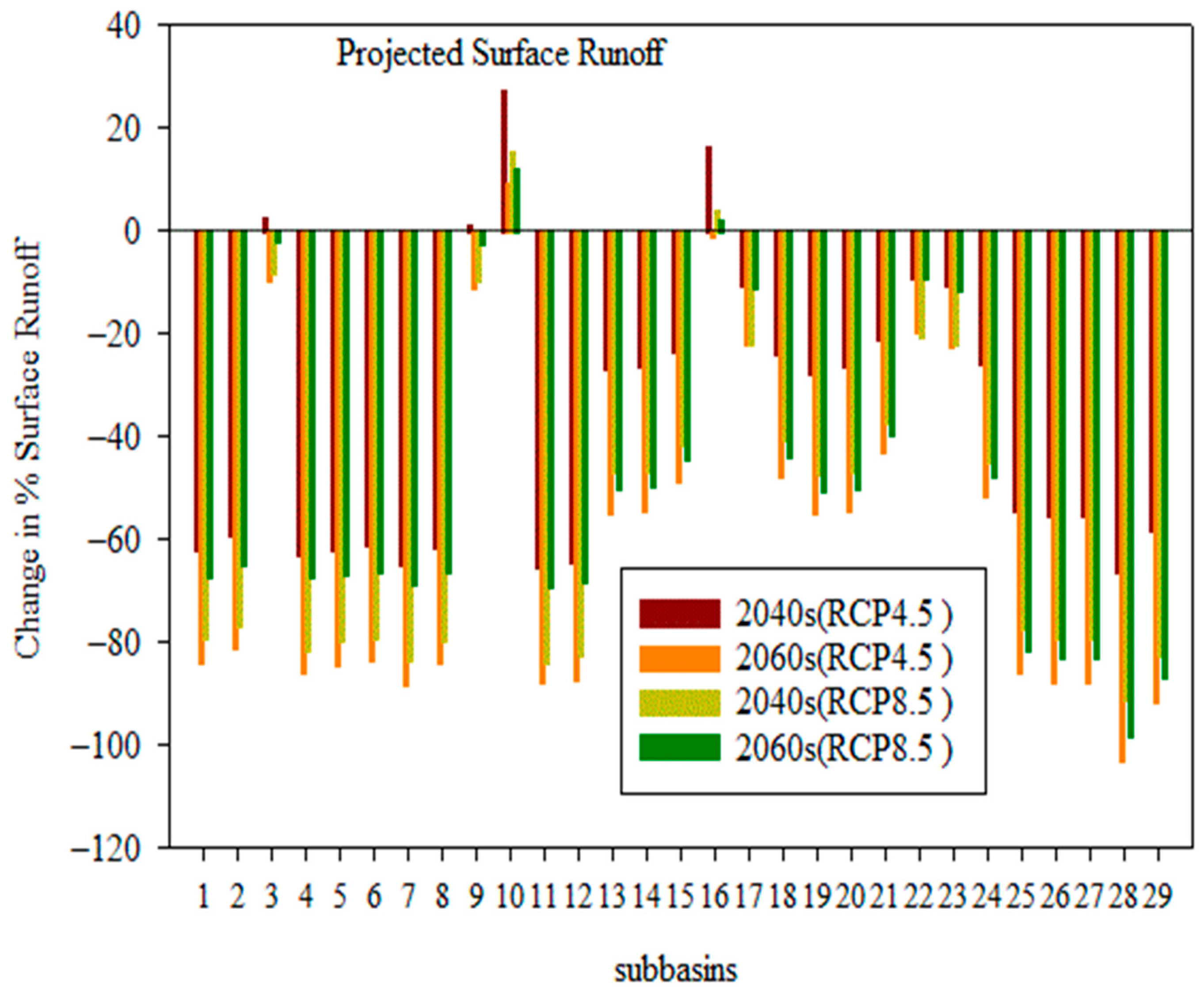
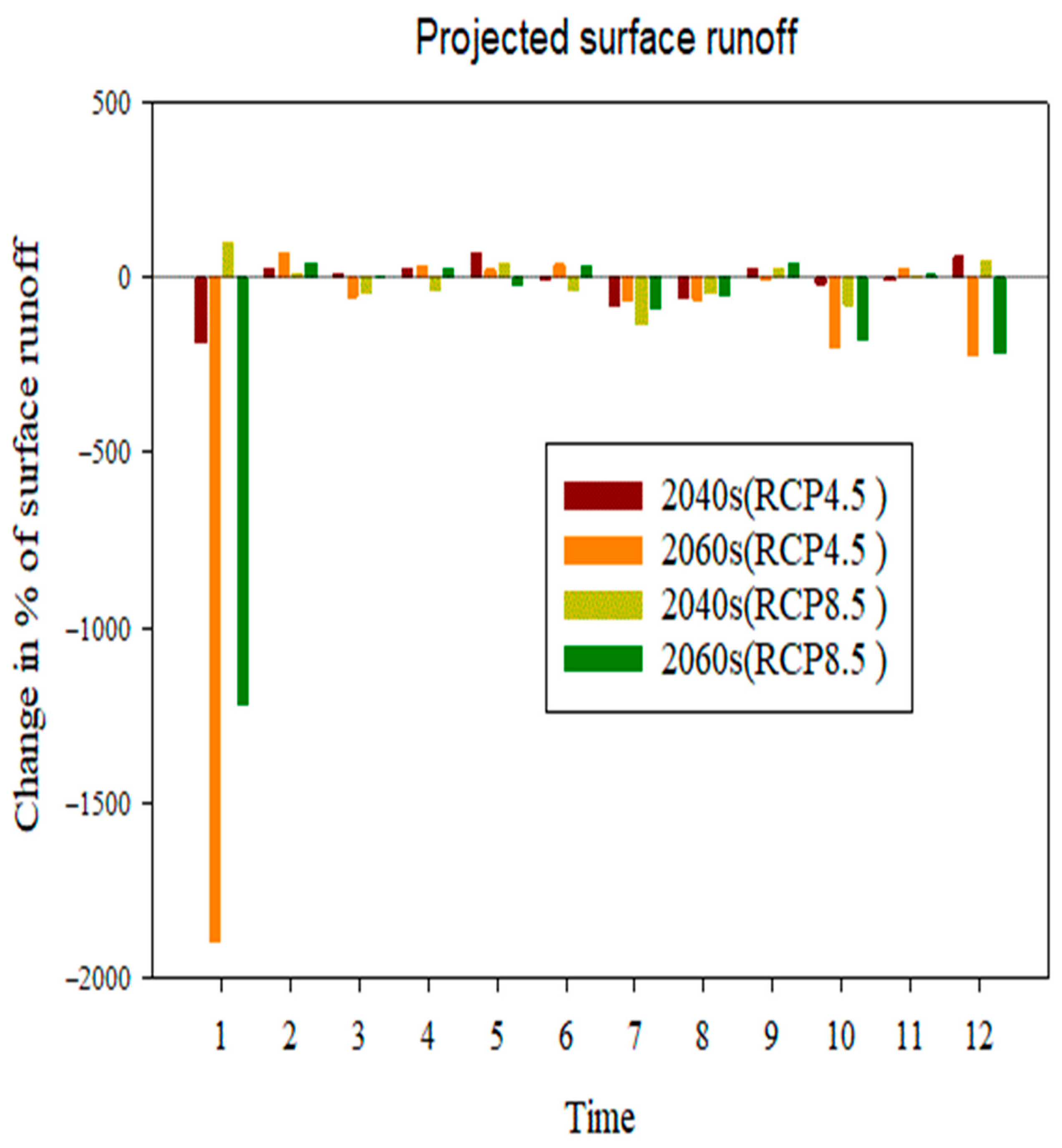
4.3.3. Change in Surface Runoff in the Sub-Basin
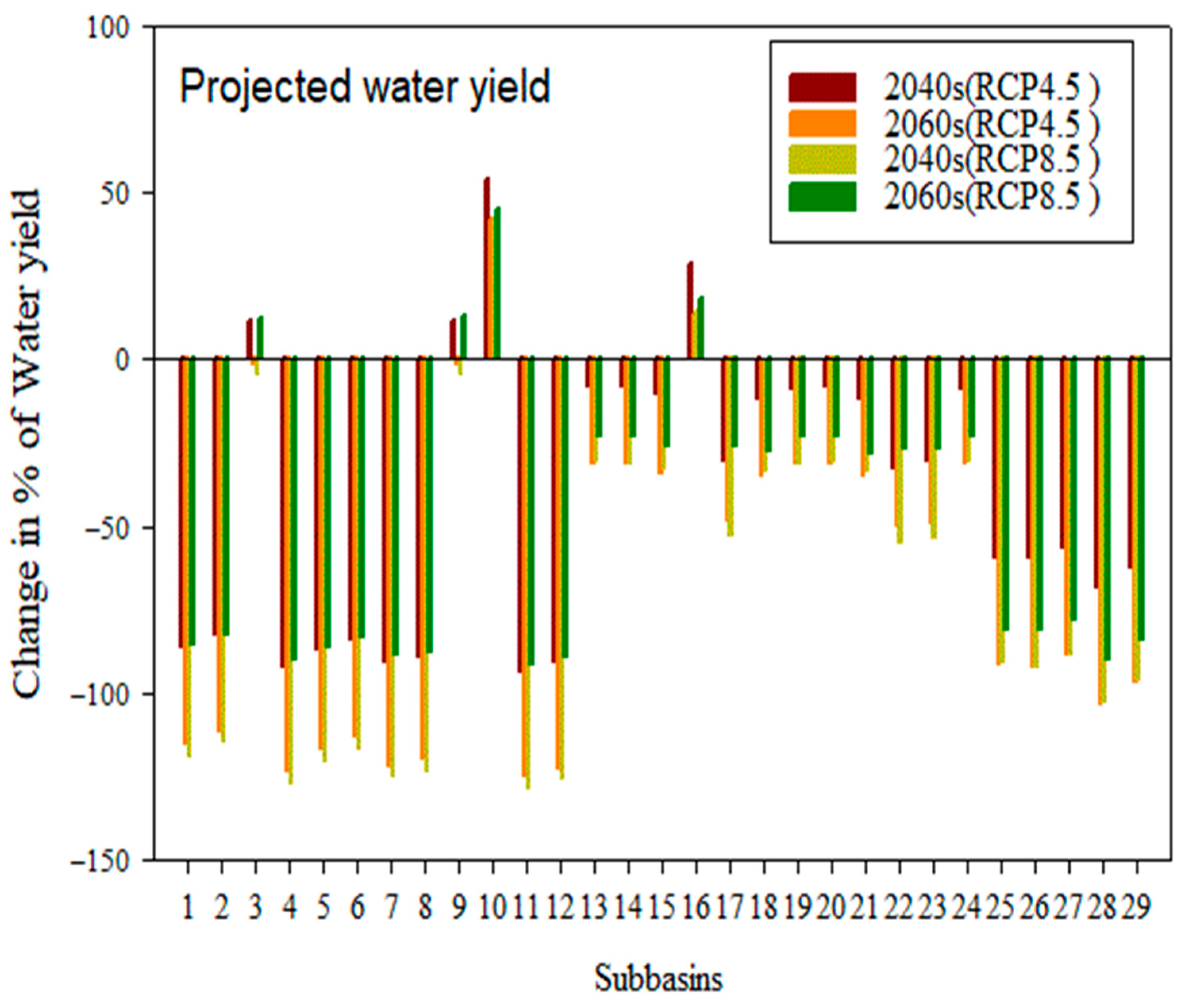
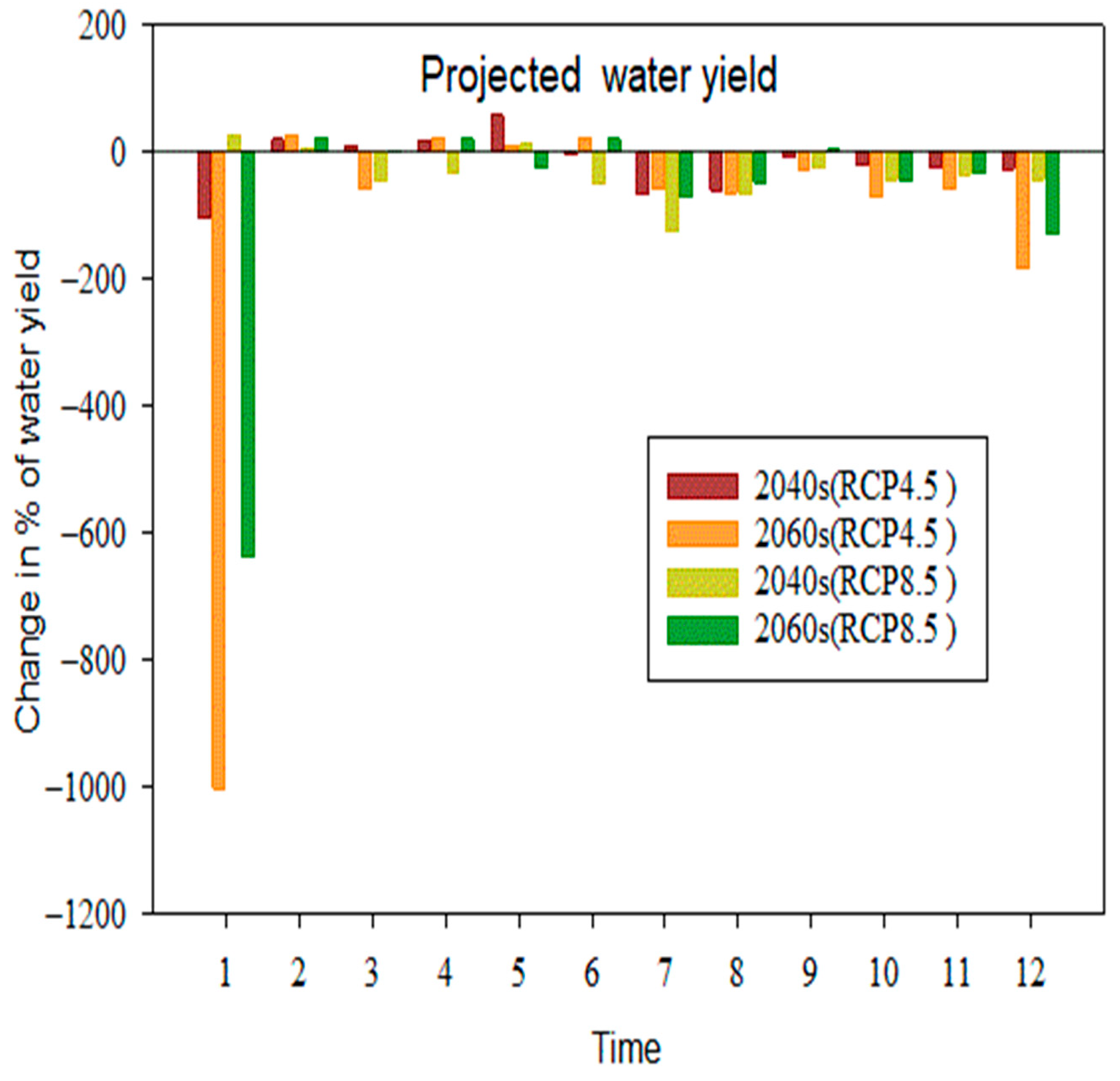
4.3.4. Change in Water Yield in the Sub-Basin
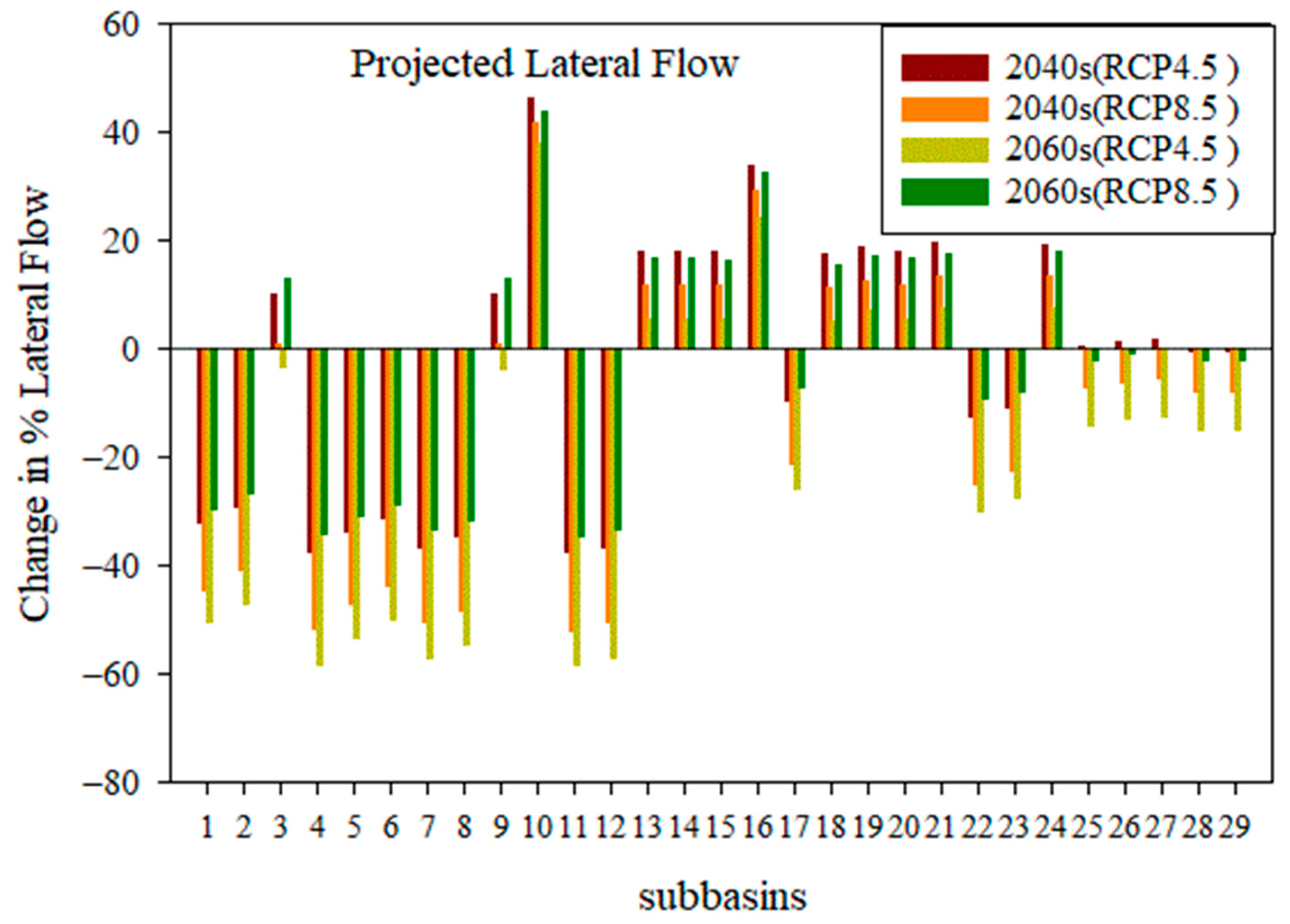
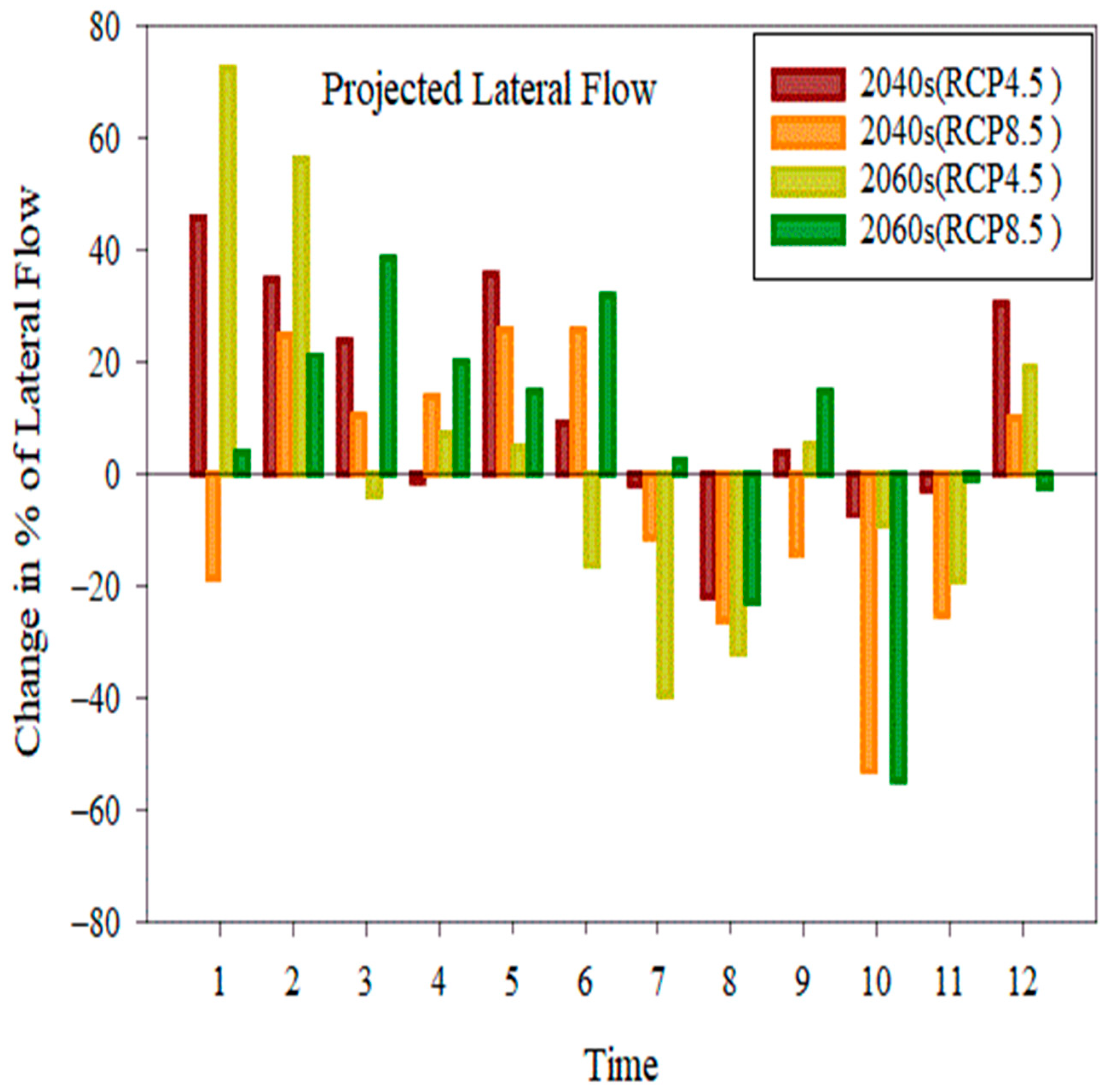
4.3.5. Change in Lateral Flow at the Sub-Basin
4.4. Monthly and Annual Water Balance Change
4.4.1. Change in Mean Monthly and Annual Evapotranspiration
4.4.2. Change in Mean Monthly and Annual Potential Evapotranspiration
4.4.3. Change in Mean Monthly and Annual Surface Runoff
4.4.4. Change in Mean Monthly and Annual Water Yield
4.4.5. Change in Mean Monthly and Annual Projected Lateral Flow
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
5.1. Conclusions
- ✓
- The CN2, ALPHA_BF, GW_DELAY, GWQMNm, GW_REVAP, and ESCO parameters were the most sensitive parameters among the 12 parameters proposed for calibration.
- ✓
- The performance of the model was excellent during the validation period (2002–2004) and the calibration period (1991–2001) according to the criterion mentioned in [69].
- ✓
- There is a change in minimum temperature by 1.22 °C to 4.23 °C, 1.68 °C to 6.21 °C and maximum temperature from 1.06 °C to 2.56 °C, 1.3 °C to 4.43 °C on the average monthly basis and 1.64 °C to 2.57 °C, 2.16 °C to 3.92 °C, 1.52 °C to 2.17 °C and 1.73 °C to 3.41 °C on a mean yearly basis under RCP4.5 and RCP8.5, respectively, and the change in rainfall is expected by −120.90% to 58.10%, −88.72% to 87.62% on a monthly basis and from 14.96% to 8.39% and 4.13% to 10.89% on a yearly basis in the Akaki catchment.
- ✓
- Compared to the baseline state, the effects of climate change on surface runoff range from −30.21% to −50.67%, potential evapotranspiration changes from 2.8% to 7.14%, evapotranspiration rises from 27.50% to 31.09%,l flow changes from −16.6% to –0.54%, and water yield changes from −31.1% to −55.73%.
- ✓
- Water yield, lateral flow, and surface runoff showed remarkable negative and positive changes under both scenarios, but evapotranspiration and potential evapotranspiration showed positive increments in RCP at the sub-basin level.
5.2. Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zerga, B.; Mengesha, G.G. Climate Change in Ethiopia Variability, Impact, Mitigation, and Adaptation Journal of Social Science and Humanities Research. Int. J. Sci. Humanit. Res. 2016, 2, 66–84. [Google Scholar]
- Abesh, B.F.; Jin, L.; Hubbart, J.A. Predicting Climate Change Impacts on Water Balance Components of a Mountainous Watershed in the Northeastern USA. Water 2022, 14, 3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayele, H.S.; Li, M.H.; Tung, C.P.; Liu, T.M. Impact of climate change on runoff in the Gilgel Abbay watershed, the upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Water 2016, 8, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, F.; Javadi, S.; Roozbahani, A.; Massah Bavani, A.R.; Golmohammadi, G.; Berndtsson, R.; Ghordoyee Milan, S.; Maghsoudi, R. Assessing Climate Change Impact on Water Balance Components Using Integrated Groundwater–Surface Water Models (Case Study: Shazand Plain, Iran). Water 2023, 15, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcha, S.K.; Awass, A.A.; Hulluka, T.A.; Bantider, A.; Ayele, G.T. Assessment of future climate change impact on water balance components in Central Rift Valley Lakes Basin, Ethiopia. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2023, 14, 175–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Githui, F.; Gitau, W.; Mutua, F.; Bauwens, W. Climate change impact on SWAT simulated streamflow in western Kenya. Int. J. Climatol. 2009, 29, 1823–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnisa, Z.; Govind, A.; Lasserre, B.; Marchetti, M. Water Balance Trends along Climatic Variations in the Mediterranean Basin over the Past Decades. Water 2023, 15, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathi, E.; Kastridis, A.; Myronidis, D. Analysis of Hydrometeorological Characteristics and Water Demand in Semi-Arid Mediterranean Catchments under Water Deficit Conditions. Climate 2023, 11, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todaro, V.; D’Oria, M.; Secci, D.; Zanini, A.; Tanda, M.G. Climate Change over the Mediterranean Region: Local Temperature and Precipitation Variations at Five Pilot Sites. Water 2022, 14, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahana, V.; Timbadiya, P.V. Spatiotemporal Variation of Water Availability under Changing Climate: Case Study of the Upper Girna Basin, India. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2020, 25, 05020004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, U.; Nejadhashemi, A.P. Impacts of Climate Change on Water Resources in Malawi. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2016, 21, 05016026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, U.; Nejadhashemi, A.P.; Woznicki, S.A. Climate change and eastern Africa: A review of impact on major crops. Food Energy Secur. 2015, 4, 110–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehan, S.; Kannan, N.; Neupane, R.P.; McDaniel, R.; Kumar, S. Climate change impacts on the hydrological processes of a small agricultural watershed. Climate 2016, 4, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negewo, T.F.; Sarma, A.K. Estimation of Water Yield under Baseline and Future Climate Change Scenarios in Genale Watershed, Genale Dawa River Basin, Ethiopia, Using SWAT Model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2021, 26, 05020051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshmidevi, T.V.; Nagesh Kumar, D.; Mehrotra, R.; Sharma, A. Estimation of the climate change impact on a catchment water balance using an ensemble of GCMs. J. Hydrol. 2018, 556, 1192–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Němečková, S.; Slámová, R.; Šípek, V. Climate change impact assessment on various components of the hydrological regime of the Malše river basin. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2011, 59, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasonova, O.N.; Gusev, Y.M.; Kovalev, E. Climate Change Impact on Water Balance Components in Arctic River Basins. Geogr. Environ. Sustain. 2022, 15, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, G.; Fuchs, M.; Nachtnebel, H.P.; Loibl, W. Semi-distributed modelling of the monthly water balance in an alpine catchment. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 2339–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Peng, S.; Wang, W.; Xu, J.; Yang, S. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of reference evapotranspiration trends in Karst area: A case study in Guizhou Province, China. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2016, 128, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stergiadi, M.; Di Marco, N.; Avesani, D.; Righetti, M.; Borga, M. Impact of geology on seasonal hydrological predictability in alpine regions by a sensitivity analysis framework. Water 2020, 12, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, M.C.; Hotchkiss, R.H.; Stone, A.B. Climate change impacts on missouri river basin water yields: The influence of temporal scales. In World Water Congress 2005: Impacts of Global Climate Change—Proceedings of the 2005 World Water and Environmental Resources Congress; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 2005; p. 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, T.; Yuan, R.; Liao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Gong, Z.; Zhao, X.; Chen, P.; Li, T.; Lin, Y.; Du, C.; et al. Characteristics of Potential Evapotranspiration Changes and Its Climatic Causes in Heilongjiang Province from 1960 to 2019. Agriculture 2022, 12, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xue, B.; Yinglan, A.; Sun, W.; Guo, Q. Water balance changes in response to climate change in the upper Hailar River Basin, China. Hydrology Research 2020, 51, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Shrestha, N.K.; Daggupati, P.; Rudra, R.; Shukla, R.; Kaur, B.; Hou, J. Quantifying the impacts of climate change on streamflow dynamics of two major rivers of the Northern Lake Erie basin in Canada. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Feng, Q.; Zou, S.; Yang, L. Assessing variation in water balance components in mountainous Inland River Basin experiencing climate change. Water 2016, 8, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uniyal, B.; Jha, M.K.; Verma, A.K. Assessing Climate Change Impact on Water Balance Components of a River Basin Using SWAT Model. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 4767–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, G. Impact of climate change on Lake Chamo Water Balance, Ethiopia. Int. J. Water Resour. Environ. Eng. 2017, 9, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taye, M.T.; Dyer, E.; Hirpa, F.A.; Charles, K. Climate change impact on water resources in the Awash basin, Ethiopia. Water 2018, 10, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelkeba Tumsa, B. Statistical and SWAT Model-Based Performance Evaluation of RCMs in Modeling Streamflow and Sediment Yield at Upper Awash Sub-Basin, Ethiopia. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2022, 2022, 9193516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilo, N.B.; Gebremariam, B.; Harka, A.E.; Woldemariam, G.W.; Behulu, F. Evaluation of the impacts of climate change on sediment yield from the Logiya Watershed, Lower Awash Basin, Ethiopia. Hydrology 2019, 6, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessema, N.; Kebede, A.; Yadeta, D. Modelling the effects of climate change on streamflow using climate and hydrological models: The case of the Kesem sub-basin of the Awash River basin, Ethiopia. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2021, 19, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endris, H.S.; Omondi, P.; Jain, S.; Lennard, C.; Hewitson, B.; Chang’a, L.; Awange, J.L.; Dosio, A.; Ketiem, P.; Nikulin, G.; et al. Assessment of the performance of CORDEX regional climate models in simulating East African rainfall. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 8453–8475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chala Daba, G.; Leta, G. Climate Change Induced Temperature Prediction and Bias Correction in Finchaa Watershed. Am. J. Agric. 2018, 18, 324–337. Available online: https://www.idosi.org/aejaes/jaes18(6)18/4.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Legese Jima, W.; Korecha, D.; Tur, K. Impact of Climate Change on Seasonal Rainfall Patterns over Bale Highlands, Southeastern Ethiopia. Int. J. Environ. Chem. 2019, 3, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangang, F.; Chung, J.X.; Juneng, L.; Supari; Salimun, E.; Ngai, S.T.; Jamaluddin, A.F.; Mohd, M.S.F.; Cruz, F.; Narisma, G.; et al. Projected future changes in rainfall in Southeast Asia based on CORDEX–SEA multi-model simulations. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 55, 1247–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashaley, J.; Anornu, G.K.; Awotwi, A.; Gyamfi, C.; Anim-Gyampo, M. Performance evaluation of Africa CORDEX regional climate models: Case of Kpong irrigation scheme, Ghana. Spatial Information Research 2020, 28, 735–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibaba, W.T.; Miegel, K.; Demissie, T.A. Evaluation of the CORDEX regional climate models performance in simulating climate conditions of two catchments in Upper Blue Nile Basin. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 2019, 87, 101104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, S.; Zango, B.S.; Seidou, O.; Perera, D.; Nagabhatla, N.; Tshimanga, R.M. Impacts of Climate Change on Hydrological Regimes in the Congo River Basin. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, N.; Wasimi, S.A.; Al-Ansari, N. Impacts of Climate Change on Water Resources in Diyala River Basin, Iraq. J. Civ. Eng. Archit. 2016, 10, 1059–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser Hilo, A.; Saeed, F.H.; Al-Ansari, N. Impact of Climate Change on Water Resources of Dokan Dam Watershed. Engineering 2019, 11, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leta, O.T.; El-Kadi, A.I.; Dulai, H.; Ghazal, K.A. Assessment of climate change impacts on water balance components of Heeia watershed in Hawaii. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2016, 8, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, G.H.; Samani, Z.A. Reference Crop Evapotranspiration from Temperature. Appl. Eng. Agric. 1985, 1, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neitsch, S.; Arnold, J.; Kiniry, J.; Williams, J. Soil & Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation Version 2009; Texas Water Resources Institute: College Station, TX, USA, 2011; pp. 1–647. Available online: https://swat.tamu.edu/docs/ (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Vaghefi, S.A.; Srinivasan, R. A guideline for successful calibration and uncertainty analysis for soil and water assessment: A review of papers from the 2016 international SWAT conference. Water 2017, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serur, A.B. Performance evaluation of hydrological model in simulating streamflow and water balance analysis: Spatiotemporal calibration and validation in the upper Awash sub-basin in Ethiopia. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Moriasi, D.N.; Gassman, P.W.; Abbaspour, K.C.; White, M.J. SWAT: Model use, calibration, and validation. Biol. Syst. Eng. 2012, 55, 1491–1508. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf Vaghefi, S.; Mousavi, S.J.; Abbaspour, K.C.; Srinivasan, R.; Arnold, J.R. Integration of hydrologic and water allocation models in basin-scale water resources management considering crop pattern and climate change: Karkheh River Basin in Iran. Reg. Environ. Change 2013, 15, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sao, D.; Kato, T.; Tu, L.H.; Thouk, P.; Fitriyah, A.; Oeurng, C. Evaluation of different objective functions used in the sufi-2 calibration process of swat-cup on water balance analysis: A case study of the pursat river basin, cambodia. Water 2020, 12, 2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, R.A.; Pereira, S.B.; Pinto, D.B.F. Calibration and validation of the SWAT hydrological model for the Mucuri river basin. Eng. Agric. 2018, 38, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jajarmizadeh, M.; Sidek, L.M.; Harun, S.; Salarpour, M. Optimal Calibration and Uncertainty Analysis of SWAT for an Arid Climate. Air Soil Water Res. 2017, 10, 1178622117731792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J. V River Flow Forecasting through Conceptual Models—Part I—A Discussion of Principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teutschbein, C.; Seibert, J. Is bias correction of regional climate model (RCM) simulations possible for non-stationary conditions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 5061–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.B.; Kwon, H.H.; Han, D. Intercomparison of joint bias correction methods for precipitation and flow from a hydrological perspective. J. Hydrol. 2022, 604, 127261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathjens, H.; Bieger, K.; Srinivasan, R.; Arnold, J.G. CMhyd User Manual Documentation for Preparing Simulated Climate Change Data for Hydrologic Impact Studies; SWAT: Huston, TX, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Brighenti, T.M.; Gassman, P.W.; Gutowski, W.J.; Thompson, J.R. Assessing the Influence of a Bias Correction Method on Future Climate Scenarios Using SWAT as an Impact Model Indicator. Water 2023, 15, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.; Masood, M.U.; Haider, S.; Anjum, M.N.; Hussain, F.; Ding, Y.; Shangguan, D.; Rashid, M.; Nadeem, M.U. Investigating the Effects of Climate and Land Use Changes on Rawal Dam Reservoir Operations and Hydrological Behavior. Water 2023, 15, 2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilahun, Z.A.; Bizuneh, Y.K.; Mekonnen, A.G. The impacts of climate change on hydrological processes of Gilgel Gibe catchment, southwest Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0287314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Srinivasan, R.; Williams, J.R.; Haney, E.B.; Neitsch, S.L. Swat-Io-Documentation-2012.Pdf. 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Majone, B.; Avesani, D.; Zulian, P.; Fiori, A.; Bellin, A. Analysis of high streamflow extremes in climate change studies: How do we calibrate hydrological models? Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 3863–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelkeba, B.; Feyessa, F.F.; Dibaba, W.T. Climate change in the upper Awash subbasin and its possible impacts on the stream flow, Oromiyaa, Ethiopia. Water Sci. 2023, 37, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekele, D.; Alamirew, T.; Kebede, A.; Zeleke, G.; Melesse, A.M. Modeling Climate Change Impact on the Hydrology of Keleta Watershed in the Awash River Basin, Ethiopia. Environ. Model. Assess. 2019, 24, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, M.G.; Wubneh, M.A.; Worku, T.A. Impact of climate change on hydrological response of Mojo river catchment, Awash river basin, Ethiopia. Geocarto Int. 2022, 2152497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emiru, N.C.; Recha, J.W.; Thompson, J.R.; Belay, A.; Aynekulu, E.; Manyevere, A.; Demissie, T.D.; Osano, P.M.; Hussein, J.; Molla, M.B.; et al. Impact of Climate Change on the Hydrology of the Upper Awash River Basin, Ethiopia. Hydrology 2022, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashu, A.B.; Lee, S. Il Assessing climate change effects on water balance in a monsoon watershed. Water 2020, 12, 2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaemiso, S.E.; Abebe, A.; Pingale, S.M. Assessment of the impact of climate change on surface hydrological processes using SWAT: A case study of Omo-Gibe river basin, Ethiopia. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakilu, G.G.; Sándor, S.; Zoltán, T. Change in stream flow of gumara watershed, upper blue nile basin, ethiopia under representative concentration pathway climate change scenarios. Water 2020, 12, 3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadese, M.T.; Kumar, L.; Koech, R. Climate change projections in the Awash River Basin of Ethiopia using Global and Regional Climate Models. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 3649–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurara, M.A.; Jilo, N.B.; Tolche, A.D.; Kassa, A.K. Climate change projection using the statistical downscaling model in Modjo watershed, upper Awash River Basin, Ethiopia. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 8885–8898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter Code | Fitted Value | Min Value | Max Value | t-Stat | P | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *CN2 | 0.07 | −0.25 | 0.25 | 30.03 | 0.00 | 1 |
| *ALPHA_BF | −0.11 | 0.04 | 0.69 | 13.25 | 0.00 | 2 |
| *GW_DELAY | 397.12 | 333.97 | 468.63 | 8.80 | 0.00 | 3 |
| *GWQMN | 0.55 | 0.24 | 1.03 | 8.43 | 0.00 | 4 |
| *GW_REVAP | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.18 | 7.75 | 0.00 | 5 |
| *ESCO | 0.82 | 0.80 | 0.88 | 7.09 | 0.00 | 6 |
| *CH_N2 | 0.13 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 5.76 | 0.01 | 7 |
| *CH_K2 | 45.63 | 10.51 | 80.07 | 5.55 | 0.01 | 8 |
| *ALPHA_BNK | 0.35 | 0.19 | 0.40 | 4.43 | 0.02 | 9 |
| *SOL_AWC | 0.32 | 0.24 | 0.49 | 4.19 | 0.03 | 10 |
| *SOL_K | 0.79 | 0.01 | 1.41 | 3.13 | 0.05 | 11 |
| *SOL_BD | 0.24 | 0.9 | 0.92 | 2.40 | 0.09 | 12 |
| Month | RCP4.5 (2040s) | RCP4.5 (2060s) | RCP8.5 (2040s) | RCP8.5 (2060s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | 45.42 | −120.90 | 87.62 | −88.77 |
| February | 57.30 | 73.54 | 59.89 | 68.48 |
| March | 45.48 | 24.55 | 24.30 | 43.02 |
| April | 27.11 | 46.32 | 27.27 | 35.96 |
| May | 58.10 | 52.89 | 41.44 | 34.77 |
| June | 10.60 | 21.77 | −15.14 | 23.65 |
| Jully | 1.84 | −4.13 | −26.62 | −9.40 |
| August | −0.60 | −3.74 | 2.02 | 2.48 |
| September | 21.66 | 5.65 | 27.38 | 29.03 |
| October | −1.26 | −73.32 | −35.69 | −81.06 |
| November | 24.44 | 46.11 | 40.28 | 55.52 |
| December | 51.84 | −7.44 | 35.46 | −10.25 |
| Annual | 14.96 | 8.39 | 4.13 | 10.89 |
| Month | RCP4.5 (2040s) | RCP4.5 (2060s) | RCP8.5 (2040s) | RCP8.5 (2060s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tmin | Tmax | Tmin | Tmax | Tmin | Tmax | Tmin | Tmax | |
| January | 1.50 | 1.99 | 2.63 | 2.91 | 2.13 | 2.59 | 3.96 | 4.43 |
| Februry | 1.23 | 2.23 | 1.78 | 3.09 | 2.00 | 2.65 | 3.24 | 4.60 |
| March | 1.45 | 1.71 | 2.16 | 2.17 | 2.29 | 1.76 | 3.35 | 3.67 |
| April | 1.22 | 1.12 | 2.27 | 2.25 | 1.77 | 1.88 | 3.42 | 3.34 |
| May | 1.45 | 1.81 | 2.21 | 2.28 | 1.65 | 1.81 | 2.96 | 2.95 |
| June | 1.79 | 1.17 | 2.71 | 2.56 | 1.70 | 1.32 | 4.03 | 3.47 |
| July | 2.78 | 1.06 | 4.23 | 2.28 | 3.09 | 1.39 | 6.02 | 4.28 |
| August | 2.80 | 1.64 | 4.10 | 2.11 | 3.07 | 1.80 | 6.21 | 3.97 |
| September | 1.79 | 1.31 | 2.82 | 1.27 | 2.16 | 1.39 | 4.34 | 2.38 |
| October | 1.44 | 1.75 | 2.41 | 1.71 | 2.24 | 1.50 | 3.46 | 2.62 |
| November | 1.11 | 1.22 | 1.69 | 1.59 | 1.68 | 1.30 | 2.89 | 2.59 |
| December | 1.14 | 1.25 | 1.79 | 1.77 | 2.12 | 1.40 | 3.14 | 2.59 |
| Annual | 1.64 | 1.52 | 2.57 | 2.17 | 2.16 | 1.73 | 3.92 | 3.41 |
| Annual Change (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenarios | Time | LAT_Q | WYLD | SURQ | PET | ET | |
| RCP4.5 | 2040s | −1.62 | −31.10 | −30.21 | 6.41 | 29.51 | |
| 2060s | −16.60 | −54.11 | −51.67 | 6.51 | 27.50 | ||
| RCP8.5 | 2040s | −11.09 | −55.73 | −46.86 | 7.14 | 31.09 | |
| 2060s | −0.54 | −37.02 | −42.47 | 2.80 | 30.46 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guyasa, A.K.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, D. Impact of Climate Change on the Water Balance of the Akaki Catchment. Water 2024, 16, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010054
Guyasa AK, Guan Y, Zhang D. Impact of Climate Change on the Water Balance of the Akaki Catchment. Water. 2024; 16(1):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010054
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuyasa, Alemayehu Kabeta, Yiqing Guan, and Danrong Zhang. 2024. "Impact of Climate Change on the Water Balance of the Akaki Catchment" Water 16, no. 1: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010054
APA StyleGuyasa, A. K., Guan, Y., & Zhang, D. (2024). Impact of Climate Change on the Water Balance of the Akaki Catchment. Water, 16(1), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010054








