Research Progress of Zebrafish Model in Aquatic Ecotoxicology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
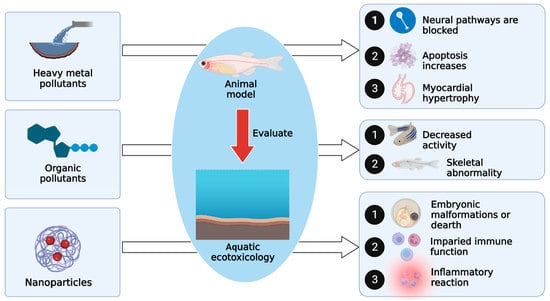
2. Evaluating the Effect of Ecological Water Pollution on Zebrafish
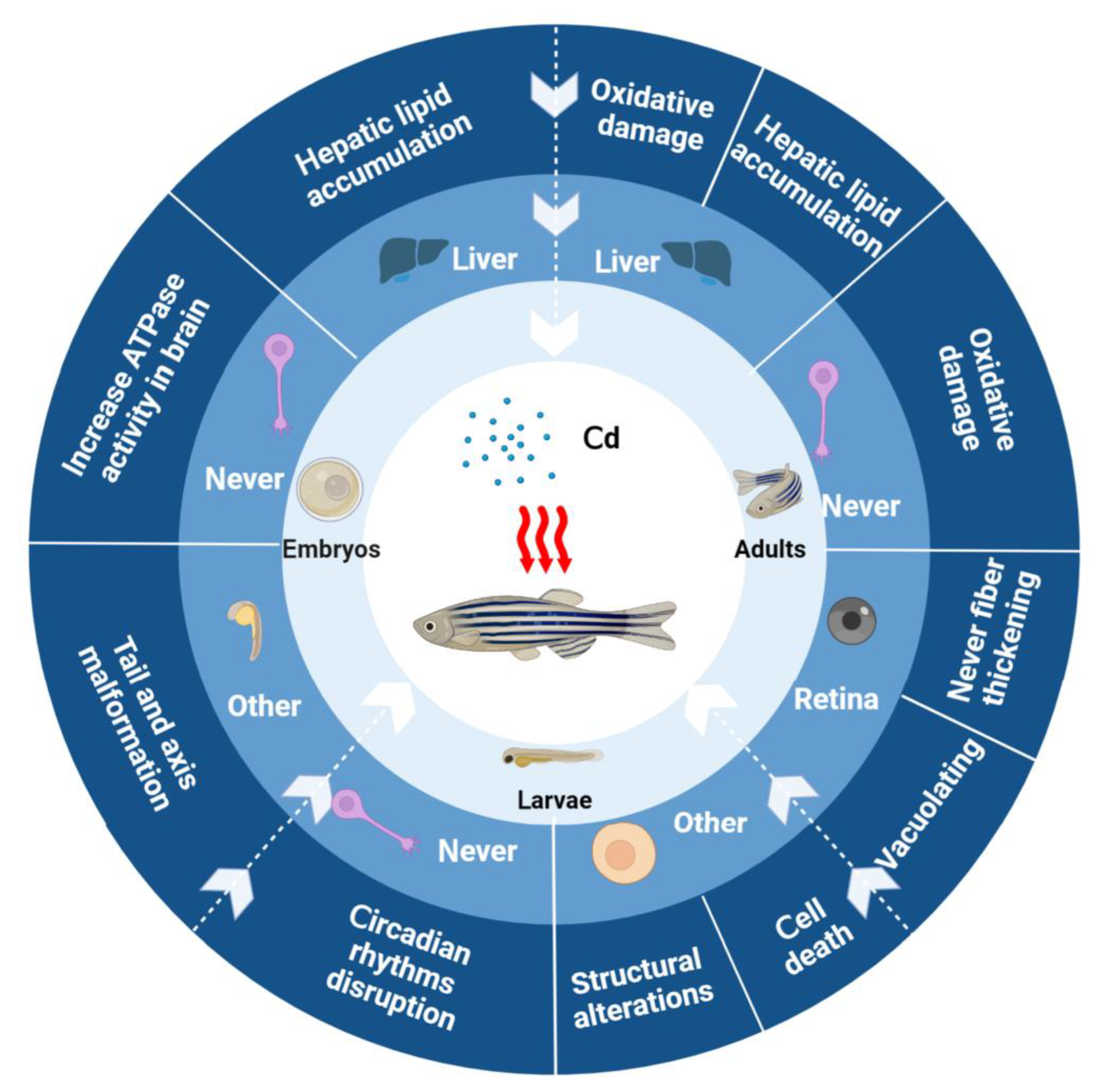
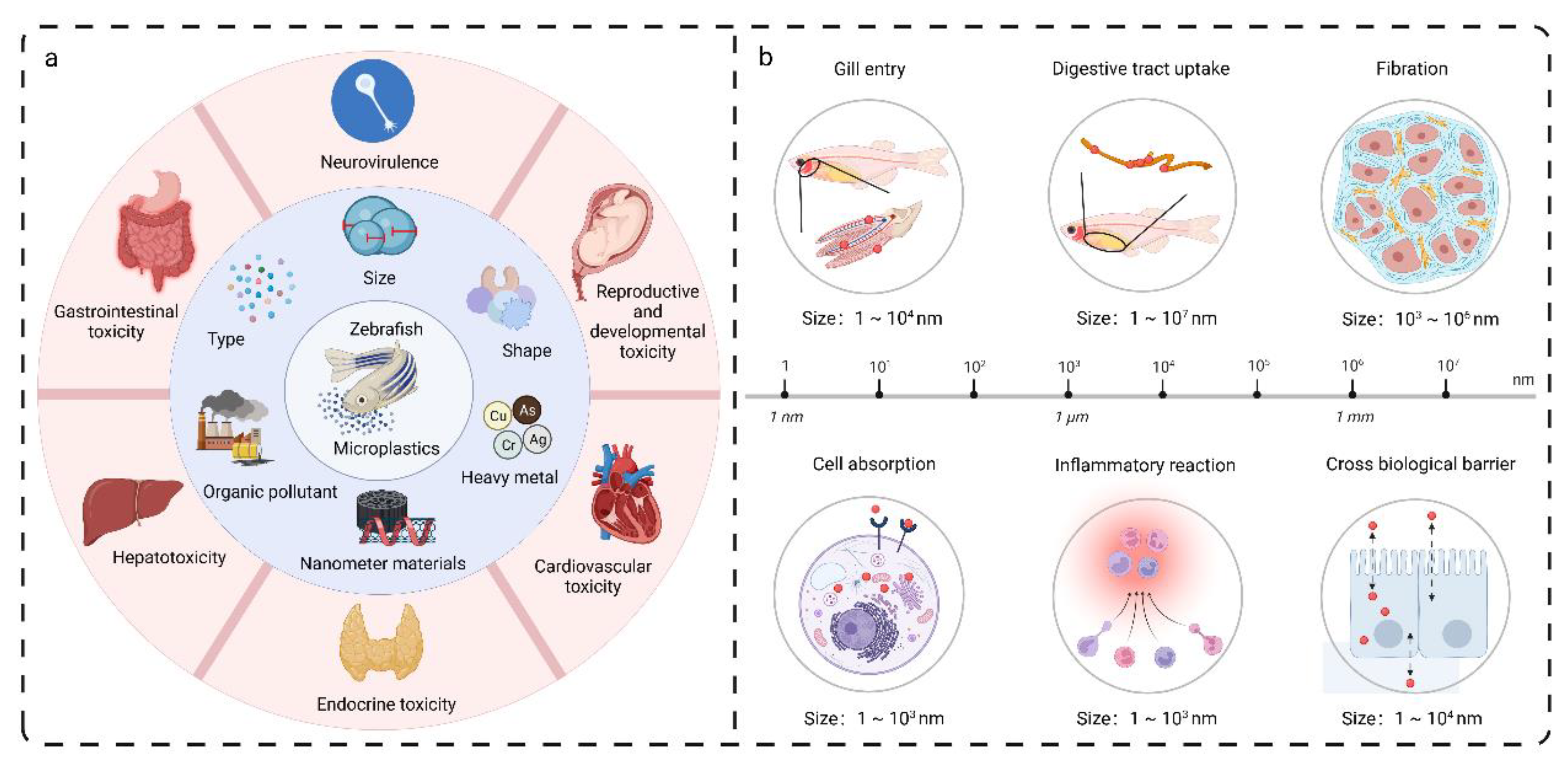
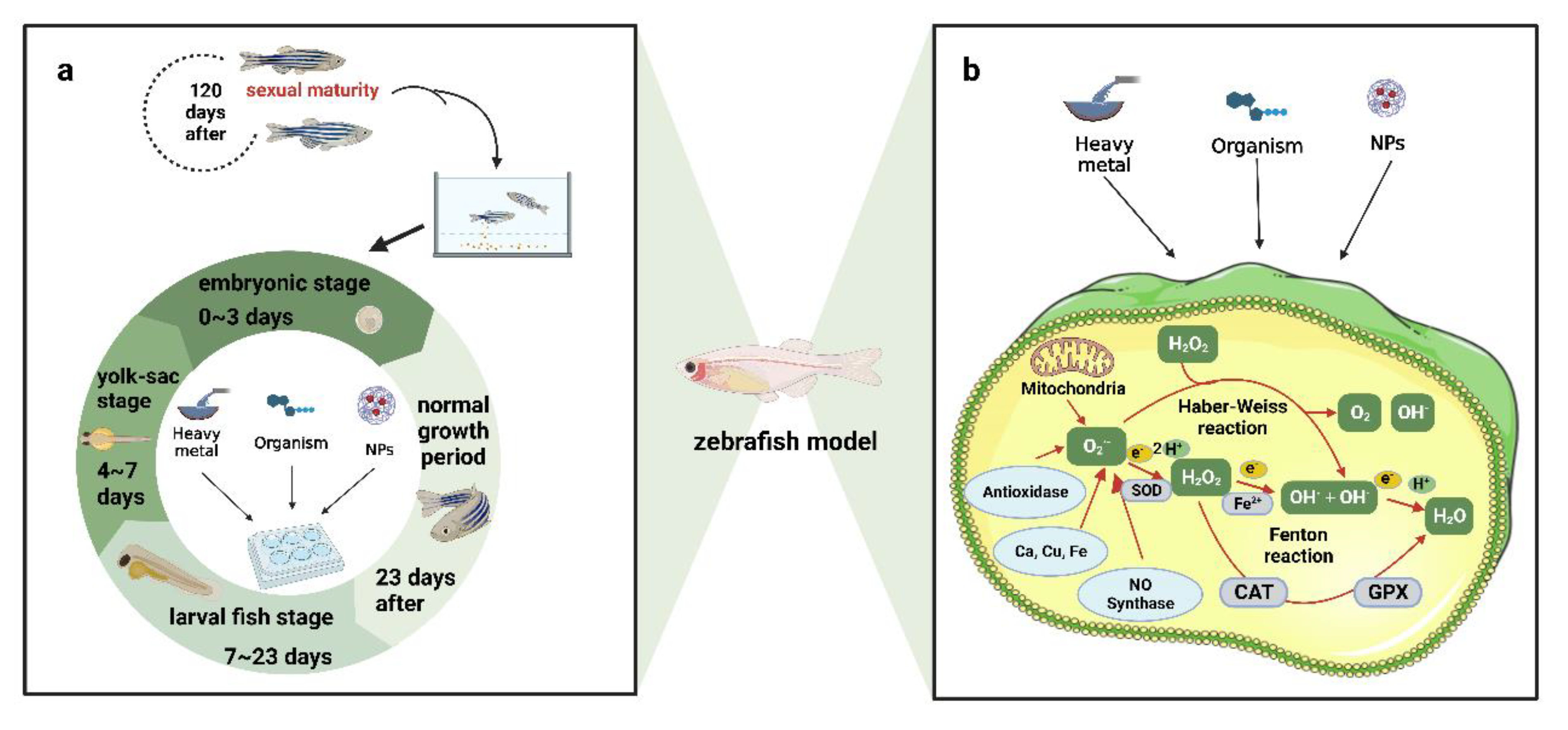
2.1. Evaluating the Toxicological Effects of Heavy Metal Pollution on Zebrafish in Water Environments
2.2. Evaluating the Toxicological Effects of Organic Pollutants on Zebrafish in Water Environments
2.3. Evaluating the Toxicity of Nanoparticles and Microplastics on Zebrafish in Water Environments
3. Aquatic Ecotoxicological Evaluation Methods Based on Zebrafish
3.1. Aquatic Ecotoxicological Evaluation Based on the Physiological Toxicity of Zebrafish
3.2. Evaluation of Water Ecotoxicology Based on Molecular Biomarkers in Zebrafish
3.3. Aquatic Ecotoxicological Evaluation Based on Genomic and Phenotypic Analysis of Zebrafish Toxicology
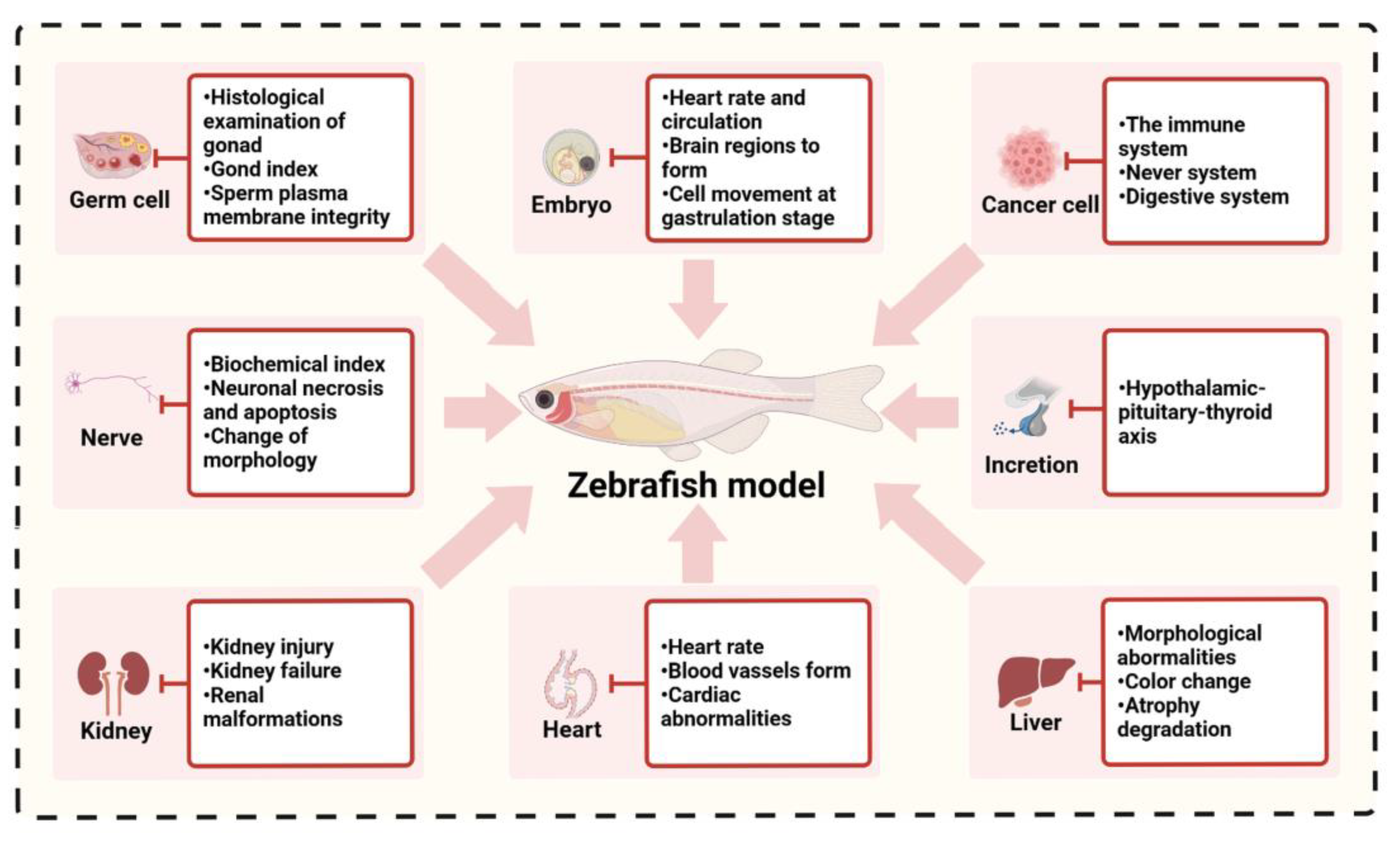
4. Application of the Zebrafish Model in Environmental Toxicology Evaluation
4.1. Reproductive Toxicity
4.2. Teratogenic Toxicity of Embryos
4.3. Neurodevelopmental Toxicity and Behavioral Changes
4.4. Cardiac and Cardiovascular Developmental Toxicity
4.5. Hepatorenal Toxicity
4.6. Endocrine-Disrupting Toxicity
4.7. Environmental Carcinogenicity
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Ledón-Rettig, C.C.; Pfennig, D.W. Emerging Model Systems in Eco-Evo-Devo: The Environmentally Responsive Spadefoot Toad. Evol. Dev. 2011, 13, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Huang, X.; Wu, Q.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X.; Ouyang, L.; Crump, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R. Acute Toxicity of Polychlorinated Diphenyl Ethers (PCDEs) in Three Model Aquatic Organisms (Scenedesmus Obliquus, Daphnia Magna, and Danio Rerio) of Different Trophic Levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bambino, K.; Chu, J. Zebrafish in Toxicology and Environmental Health. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2017, 124, 331–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacRae, C.A.; Peterson, R.T. Zebrafish as Tools for Drug Discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanandrea, R.; Bonan, C.D.; Campos, M.M. Zebrafish as a Model for Inflammation and Drug Discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 2201–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raldúa, D.; Piña, B. In Vivo Zebrafish Assays for Analyzing Drug Toxicity. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2014, 10, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanungo, J.; Cuevas, E.; Ali, S.F.; Paule, M.G. Zebrafish Model in Drug Safety Assessment. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 5416–5429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantz-McPeak, S.; Guo, X.; Cuevas, E.; Dumas, M.; Newport, G.D.; Ali, S.F.; Paule, M.G.; Kanungo, J. Developmental Toxicity Assay Using High Content Screening of Zebrafish Embryos. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 35, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, B.; Mally, A.; Liedtke, D. Zebrafish Embryos and Larvae as Alternative Animal Models for Toxicity Testing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audira, G.; Siregar, P.; Chen, J.-R.; Lai, Y.-H.; Huang, J.-C.; Hsiao, C.-D. Systematical Exploration of the Common Solvent Toxicity at Whole Organism Level by Behavioral Phenomics in Adult Zebrafish. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266 Pt 1, 115239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, J.; Astrinidis, P.; Astrinides, P.; Frohnhöfer, H.G.; Walderich, B.; Nüsslein-Volhard, C. Transparent, a Gene Affecting Stripe Formation in Zebrafish, Encodes the Mitochondrial Protein Mpv17 That Is Required for Iridophore Survival. Biol. Open 2013, 2, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blechinger, S.R.; Warren, J.T.; Kuwada, J.Y.; Krone, P.H. Developmental Toxicology of Cadmium in Living Embryos of a Stable Transgenic Zebrafish Line. Environ. Health Perspect 2002, 110, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Bi, L.; Lin, S.; Ji, H.; Sun, D.; Jin, L.; Peng, R. Hydrogen Sulfide-Induced Oxidative Stress Mediated Apoptosis via Mitochondria Pathway in Embryo-Larval Stages of Zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 239, 113666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingues, I.; Oliveira, R.; Lourenço, J.; Grisolia, C.K.; Mendo, S.; Soares, A.M.V.M. Biomarkers as a Tool to Assess Effects of Chromium (VI): Comparison of Responses in Zebrafish Early Life Stages and Adults. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharm. 2010, 152, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richetti, S.K.; Rosemberg, D.B.; Ventura-Lima, J.; Monserrat, J.M.; Bogo, M.R.; Bonan, C.D. Acetylcholinesterase Activity and Antioxidant Capacity of Zebrafish Brain Is Altered by Heavy Metal Exposure. Neurotoxicology 2011, 32, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, A.J.; Cyphers, T.; Gerrish, G.; Belby, C.; King-Heiden, T.C. Using Morphological, Behavioral, and Molecular Biomarkers in Zebrafish to Assess the Toxicity of Lead-Contaminated Sediments from a Retired Trapshooting Range within an Urban Wetland. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2018, 81, 924–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Wang, A.-P.; Li, W.-F.; Shi, R.; Jin, H.-T.; Wei, J.-F. Sensitive Biomarkers Identification for Differentiating Cd and Pb Induced Toxicity on Zebrafish Embryos. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 56, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.-L.; Peng, L.-B.; Xia, L.-P.; Li, J.; Zhu, Q.-L. Effects of Continuous and Intermittent Cadmium Exposure on HPGL Axis, GH/IGF Axis and Circadian Rhythm Signaling and Their Consequences on Reproduction in Female Zebrafish: Biomarkers Independent of Exposure Regimes. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 130879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomo, M.M.; Fernandes, J.B.; Carlos, R.M.; Fernandes, M.N. Biochemical and Genotoxic Biomarkers and Cell Cycle Assessment in the Zebrafish Liver (ZF-L) Cell Line Exposed to the Novel Metal-Insecticide Magnesium-Hespiridin Complex. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, I.; Oliveira, R.; Musso, C.; Cardoso, M.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Loureiro, S. Prochloraz Effects on Biomarkers Activity in Zebrafish Early Life Stages and Adults. Environ. Toxicol. 2013, 28, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.-J.; Lee, Y.-H.; Kim, M.-J.; Choi, S.-D.; Park, B.-J.; Lee, S.-E. Integrated Biomarkers Induced by Chlorpyrifos in Two Different Life Stages of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) for Environmental Risk Assessment. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 43, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, R.; McDonough, S.; Ladewig, J.C.L.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Nogueira, A.J.A.; Domingues, I. Effects of Oxytetracycline and Amoxicillin on Development and Biomarkers Activities of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 36, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, R.; Sheng, C.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, H.; Lemos, B. Microplastics Induce Intestinal Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Disorders of Metabolome and Microbiome in Zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasamma, S.; Audira, G.; Siregar, P.; Malhotra, N.; Lai, Y.-H.; Liang, S.-T.; Chen, J.-R.; Chen, K.H.-C.; Hsiao, C.-D. Nanoplastics Cause Neurobehavioral Impairments, Reproductive and Oxidative Damages, and Biomarker Responses in Zebrafish: Throwing up Alarms of Wide Spread Health Risk of Exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyadarshini, E.; Priyadarshini, S.S.; Pradhan, N. Heavy Metal Resistance in Algae and Its Application for Metal Nanoparticle Synthesis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 3297–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Pandit, S.; Mokkapati, V.R.S.S.; Garg, A.; Ravikumar, V.; Mijakovic, I. Gold Nanoparticles in Diagnostics and Therapeutics for Human Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy Metal Toxicity and the Environment. Exp. Suppl. 2012, 101, 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, O.; Green, J.M.; Tyler, C.R. Transgenic Fish Systems and Their Application in Ecotoxicology. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2015, 45, 124–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liang, J.; Meng, H.; Yin, Y.; Zhen, H.; Zheng, X.; Shi, H.; Wu, X.; Zu, Y.; Wang, B.; et al. Rare Earth Elements Lanthanum and Praseodymium Adversely Affect Neural and Cardiovascular Development in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Bi, L.; Jin, L.; Peng, R. Toxic Effects of Cadmium on Fish. Toxics 2022, 10, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, E.K.; Lee, A.N.; Lee, J.-Y.; Shim, I.; Kim, P.; Kim, T.-Y.; Kim, K.-T.; Lee, S. Advantages of Omics Technology for Evaluating Cadmium Toxicity in Zebrafish. Toxicol. Res. 2021, 37, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olisah, C.; Adams, J.B.; Rubidge, G. The State of Persistent Organic Pollutants in South African Estuaries: A Review of Environmental Exposure and Sources. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 219, 112316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, L.; Shi, M.; Liu, G. Persistent Organic Pollutants in Typical Lake Ecosystems. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brody, J.G.; Rudel, R.A. Environmental Pollutants and Breast Cancer. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaan, K.; Haigis, A.-C.; Weiss, J.; Legradi, J. Effects of 25 Thyroid Hormone Disruptors on Zebrafish Embryos: A Literature Review of Potential Biomarkers. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 1238–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Poopal, R.-K.; Ramesh, M. Synthetic Organic Chemicals (Flame Retardants and Pesticides) with Neurotoxic Potential Induced Behavioral Impairment on Zebrafish (Danio Rerio): A Non-Invasive Approach for Neurotoxicology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 37534–37546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-C.; Shields, J.N.; Akemann, C.; Meyer, D.N.; Connell, M.; Baker, B.B.; Pitts, D.K.; Baker, T.R. The Phenotypic and Transcriptomic Effects of Developmental Exposure to Nanomolar Levels of Estrone and Bisphenol A in Zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdörster, G.; Oberdörster, E.; Oberdörster, J. Nanotoxicology: An Emerging Discipline Evolving from Studies of Ultrafine Particles. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; You, H.; Lv, L. Acute ZnO Nanoparticles Exposure Induces Developmental Toxicity, Oxidative Stress and DNA Damage in Embryo-Larval Zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 136–137, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fent, K.; Weisbrod, C.J.; Wirth-Heller, A.; Pieles, U. Assessment of Uptake and Toxicity of Fluorescent Silica Nanoparticles in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Early Life Stages. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 100, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdineaud, J.-P.; Rossignol, R.; Brèthes, D. Zebrafish: A Model Animal for Analyzing the Impact of Environmental Pollutants on Muscle and Brain Mitochondrial Bioenergetics. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisselier, E.; Astruc, D. Gold Nanoparticles in Nanomedicine: Preparations, Imaging, Diagnostics, Therapies and Toxicity. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1759–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Leifert, A.; Graf, M.; Schiefer, F.; Thoröe-Boveleth, S.; Broda, J.; Halloran, M.C.; Hollert, H.; Laaf, D.; Simon, U.; et al. High-Sensitivity Real-Time Analysis of Nanoparticle Toxicity in Green Fluorescent Protein-Expressing Zebrafish. Small 2013, 9, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsden, C.S.; Henry, T.B.; Handy, R.D. Sub-Lethal Effects of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on the Physiology and Reproduction of Zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 126, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Stegeman, J.J.; Fleming, L.E.; Allemand, D.; Anderson, D.M.; Backer, L.C.; Brucker-Davis, F.; Chevalier, N.; Corra, L.; Czerucka, D.; et al. Human Health and Ocean Pollution. Ann. Glob. Health 2020, 86, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajith, N.; Arumugam, S.; Parthasarathy, S.; Manupoori, S.; Janakiraman, S. Global Distribution of Microplastics and Its Impact on Marine Environment-a Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 25970–25986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagat, J.; Zang, L.; Nishimura, N.; Shimada, Y. Zebrafish: An Emerging Model to Study Microplastic and Nanoplastic Toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Duan, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wei, Y.; Sun, H. Immunotoxicity Responses to Polystyrene Nanoplastics and Their Related Mechanisms in the Liver of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Larvae. Environ. Int. 2022, 161, 107128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lai, H.; Huang, J.; Sun, L.; Mennigen, J.A.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Tu, W. Polystyrene Microplastics Decrease F-53B Bioaccumulation but Induce Inflammatory Stress in Larval Zebrafish. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 127040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami, A.; Groman, D.B.; Wilson, S.P.; Ismail, P.; Neela, V.K. Biomarker Responses in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Larvae Exposed to Pristine Low-Density Polyethylene Fragments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cózar, A.; Martí, E.; Duarte, C.M.; García-de-Lomas, J.; van Sebille, E.; Ballatore, T.J.; Eguíluz, V.M.; González-Gordillo, J.I.; Pedrotti, M.L.; Echevarría, F.; et al. The Arctic Ocean as a Dead End for Floating Plastics in the North Atlantic Branch of the Thermohaline Circulation. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1600582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, X.; Heng, X.; Chu, W. Polystyrene Nano/Microplastics Induce Microbiota Dysbiosis, Oxidative Damage, and Innate Immune Disruption in Zebrafish. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 163, 105387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, Y.; Inoue, A.; Sasagawa, S.; Koiwa, J.; Kawaguchi, K.; Kawase, R.; Maruyama, T.; Kim, S.; Tanaka, T. Using Zebrafish in Systems Toxicology for Developmental Toxicity Testing. Congenit. Anom. 2016, 56, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dooley, K.; Zon, L.I. Zebrafish: A Model System for the Study of Human Disease. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2000, 10, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, S.; Chow, H.; Tsang, B.; Facciol, A.; Gandhi, P.; Desai, P.; Gerlai, R. Zebrafish Are Able to Detect Ethanol in Their Environment. Zebrafish 2017, 14, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.D.; Mirbahai, L.; Chipman, J.K. The Toxicological Application of Transcriptomics and Epigenomics in Zebrafish and Other Teleosts. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2014, 13, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, R.; Jin, Y. Differential Responses of Larval Zebrafish to the Fungicide Propamocarb: Endpoints at Development, Locomotor Behavior and Oxidative Stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Su, M.; Ba, H.; Chen, G.; Luo, J.; Liu, F.; Liao, X.; Cao, Z.; Zeng, J.; Lu, H.; et al. ZIF-8 Nanoparticles Induce Neurobehavioral Disorders through the Regulation of ROS-Mediated Oxidative Stress in Zebrafish Embryos. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, S.; Qian, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Xu, Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y. The Assessment of the Eco-Toxicological Effect of Gabapentin on Early Development of Zebrafish and Its Antioxidant System. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 22777–22784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Wang, A.-P.; Li, W.-F.; Shi, R.; Jin, H.-T.; Wei, J.-F. Time-Response Characteristic and Potential Biomarker Identification of Heavy Metal Induced Toxicity in Zebrafish. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 72, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Zheng, M.; Li, X.; Qiu, L. Acute and Short-Term Developmental Toxicity of Cyhalofop-Butyl to Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 10080–10089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, F.S.; Souza, T.M.; Vieira, L.R.; Marchi, F.C.; Nascimento, A.P.; Farias, D.F. Toxicity Testing of Pesticides in Zebrafish-a Systematic Review on Chemicals and Associated Toxicological Endpoints. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 10185–10204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, D.; Ibrahim, K.E.; Hussain, S.A.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Role of ROS Generation in Acute Genotoxicity of Azoxystrobin Fungicide on Freshwater Snail Lymnaea luteola L. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 5566–5574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Z.; Duan, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Gong, Z.; Wang, L. Barrier Function of Zebrafish Embryonic Chorions against Microplastics and Nanoplastics and Its Impact on Embryo Development. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 395, 122621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.-Y.; Yu, X.-Y.; Wang, D.-L.; Yan, H.-J.; Liu, X.-J. Acute Toxicity to Zebrafish of Two Organophosphates and Four Pyrethroids and Their Binary Mixtures. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Techer, D.; Milla, S.; Fontaine, P.; Viot, S.; Thomas, M. Acute Toxicity and Sublethal Effects of Gallic and Pelargonic Acids on the Zebrafish Danio Rerio. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 5020–5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Xie, Y.; Guo, Y.; Dai, J. 6:2 Fluorotelomer Sulfonamide Alkylbetaine (6:2 FTAB), a Novel Perfluorooctane Sulfonate Alternative, Induced Developmental Toxicity in Zebrafish Embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 195, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köktürk, M.; Altindağ, F.; Ozhan, G.; Çalimli, M.H.; Nas, M.S. Textile Dyes Maxilon Blue 5G and Reactive Blue 203 Induce Acute Toxicity and DNA Damage during Embryonic Development of Danio Rerio. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 242, 108947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Huang, C.; Wang, L.; Ye, X.; Bai, C.; Simonich, M.T.; Tanguay, R.L.; Dong, Q. Toxicity, Uptake Kinetics and Behavior Assessment in Zebrafish Embryos Following Exposure to Perfluorooctanesulphonicacid (PFOS). Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 98, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, W.S.; Chan, W.K.-L.; Chan, K.M. Toxicity Assessment and Vitellogenin Expression in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Embryos and Larvae Acutely Exposed to Bisphenol A, Endosulfan, Heptachlor, Methoxychlor and Tetrabromobisphenol A. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2013, 33, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Feng, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, L. Role of Toxicokinetic and Toxicodynamic Parameters in Explaining the Sensitivity of Zebrafish Larvae to Four Metals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 8965–8976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasqualetti, S.; Banfi, G.; Mariotti, M. The Effects of Strontium on Skeletal Development in Zebrafish Embryo. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2013, 27, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Chen, S.; Du, M.; Tang, S.; Chen, M.; Wang, W.; Yang, H.; Chen, Q.; Chen, J. Toxic Effect of Palladium on Embryonic Development of Zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 159, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trestrail, C.; Walpitagama, M.; Hedges, C.; Truskewycz, A.; Miranda, A.; Wlodkowic, D.; Shimeta, J.; Nugegoda, D. Foaming at the Mouth: Ingestion of Floral Foam Microplastics by Aquatic Animals. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.A.; Hall, L.W. Environmental Concentrations and Aquatic Toxicity Data on Diflubenzuron (Dimilin). Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1992, 22, 45–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Péan, S.; Daouk, T.; Vignet, C.; Lyphout, L.; Leguay, D.; Loizeau, V.; Bégout, M.-L.; Cousin, X. Long-Term Dietary-Exposure to Non-Coplanar PCBs Induces Behavioral Disruptions in Adult Zebrafish and Their Offspring. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2013, 39, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, S.H.; Hlaing, M.M.; Zhang, X.; Yan, C.; Duan, Z.; Zhu, L.; Ung, C.Y.; Mathavan, S.; Ong, C.N.; Gong, Z. Toxicogenomic and Phenotypic Analyses of Bisphenol-A Early-Life Exposure Toxicity in Zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Shi, X.; Liu, C.; Yu, K.; Zhou, B. Chronic Effects of Water-Borne PFOS Exposure on Growth, Survival and Hepatotoxicity in Zebrafish: A Partial Life-Cycle Test. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinnberg, K.L.; Petersen, G.I.; Albrektsen, M.; Minghlani, M.; Awad, S.M.; Holbech, B.F.; Green, J.W.; Bjerregaard, P.; Holbech, H. Endocrine-Disrupting Effect of the Ultraviolet Filter Benzophenone-3 in Zebrafish, Danio Rerio. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 2833–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakos, K.; Kovacs, R.; Balogh, E.; Sipos, D.K.; Reining, M.; Gyomorei-Neuberger, O.; Balazs, A.; Kriszt, B.; Bencsik, D.; Csepeli, A.; et al. Estrogen Sensitive Liver Transgenic Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Line (Tg(Vtg1:MCherry)) Suitable for the Direct Detection of Estrogenicity in Environmental Samples. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 208, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, T.K.; Perkins, E.; Ferguson, D.C.; Cropek, D.M. Tissue Explant Coculture Model of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal-Liver Axis of the Fathead Minnow (Pimephales Promelas) as a Predictive Tool for Endocrine Disruption. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 2530–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirbisky, S.E.; Freeman, J.L. Atrazine Exposure and Reproductive Dysfunction through the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Gonadal (HPG) Axis. Toxics 2015, 3, 414–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetter, E.; Smetanová, S.; Baldauf, L.; Lidzba, A.; Altenburger, R.; Schüttler, A.; Scholz, S. Identification and Characterization of Androgen-Responsive Genes in Zebrafish Embryos. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11789–11798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Sheng, N.; Wang, M.; Zhang, H.; Dai, J. Zebrafish Reproductive Toxicity Induced by Chronic Perfluorononanoate Exposure. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 175, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Dai, X.; Chen, X.; He, J.; Yin, Z. Zebrafish Pituitary Gene Expression before and after Sexual Maturation. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 221, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Fan, L.; Hu, H.; Yin, S. Ciprofloxacin and Enrofloxacin Can Cause Reproductive Toxicity via Endocrine Signaling Pathways. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 244, 114049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhong, Y.; Tian, H.; Wang, W.; Ru, S. Impairment of the Cortisol Stress Response Mediated by the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Interrenal (HPI) Axis in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Exposed to Monocrotophos Pesticide. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 176–177, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gründker, C.; Emons, G. Role of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) in Ovarian Cancer. Cells 2021, 10, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recchia, K.; Jorge, A.S.; Pessôa, L.V.d.F.; Botigelli, R.C.; Zugaib, V.C.; de Souza, A.F.; Martins, D.d.S.; Ambrósio, C.E.; Bressan, F.F.; Pieri, N.C.G. Actions and Roles of FSH in Germinative Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, E.; Menuet, A.; Lethimonier, C.; Adrio, F.; Gueguen, M.-M.; Tascon, C.; Anglade, I.; Pakdel, F.; Kah, O. Relationships between Aromatase and Estrogen Receptors in the Brain of Teleost Fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2005, 142, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.-K.; Chung, B. Analysis of Zebrafish Cyp19 Promoters. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 86, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luu-The, V. Assessment of Steroidogenesis and Steroidogenic Enzyme Functions. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 137, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsop, D.; Vijayan, M.M. Molecular Programming of the Corticosteroid Stress Axis during Zebrafish Development. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2009, 153, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Peng, L.-B.; Wang, D.; Zhu, Q.-L.; Zheng, J.-L. Combined Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics and Cadmium on Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis, and GH/IGF Axis in Zebrafish Early Life Stages. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 140396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Gu, A.; Ji, G.; Li, Y.; Di, J.; Jin, J.; Hu, F.; Long, Y.; Xia, Y.; Lu, C.; et al. Developmental Toxicity of Cypermethrin in Embryo-Larval Stages of Zebrafish. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wu, R.; Wang, X.; Huang, W.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, J.; Tan, W.; Wu, K. Effects of 2,2′,4,4′-Tetrabromodiphenyl Ether (BDE-47) on Reproductive and Endocrine Function in Female Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 248, 114326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Bi, L.; Jin, L.; Xu, K.; Peng, R. High Glucose-Induced ROS-Accumulation in Embryo-Larval Stages of Zebrafish Leads to Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis. Apoptosis 2022, 27, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Zhu, L.; Li, H.; Yu, S.; Wang, C.; Qiu, L. Reproductive Toxicity of Azoxystrobin to Adult Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 1109–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, F.M.; Varela Junior, A.S.; Corcini, C.D.; da Silva, A.C.; Guazzelli, V.G.; Tavares, G.; da Rosa, C.E. Effect of Glyphosate on the Sperm Quality of Zebrafish Danio Rerio. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 155, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islinger, M.; Willimski, D.; Völkl, A.; Braunbeck, T. Effects of 17a-Ethinylestradiol on the Expression of Three Estrogen-Responsive Genes and Cellular Ultrastructure of Liver and Testes in Male Zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 62, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, H.; Song, H. Exposure to 17alpha-Ethynylestradiol Impairs Reproductive Functions of Both Male and Female Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 88, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Hu, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Jiang, Q.; Gong, Y.; Gu, Y.; Song, H. Generation of a Fluorescent Transgenic Zebrafish for Detection of Environmental Estrogens. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 96, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsakran, A.; Kudoh, T. Zebrafish as a Model for Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 721924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Ruiz, M.; De la Vieja, A.; Gonzalez, M.d.A.; Lopez, M.E.; Calvo, A.C.; Portilla, A.I.C. Toxicity of Nanoplastics for Zebrafish Embryos, What We Know and Where to Go Next. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 149125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Liu, W.; Chen, X.; Meng, P.; Lin, Q.; Chi, Y.; Xu, M.; Ma, N.; et al. Large-Scale Forward Genetic Screening Analysis of Development of Hematopoiesis in Zebrafish. J. Genet. Genom. 2012, 39, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, E.; Barenys, M.; Hermsen, S.A.B.; Verhoef, A.; Ossendorp, B.C.; Bessems, J.G.M.; Piersma, A.H. Comparison of the Mouse Embryonic Stem Cell Test, the Rat Whole Embryo Culture and the Zebrafish Embryotoxicity Test as Alternative Methods for Developmental Toxicity Testing of Six 1,2,4-Triazoles. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 253, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brannen, K.C.; Panzica-Kelly, J.M.; Danberry, T.L.; Augustine-Rauch, K.A. Development of a Zebrafish Embryo Teratogenicity Assay and Quantitative Prediction Model. Birth Defects Res. B Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 2010, 89, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selderslaghs, I.W.T.; Blust, R.; Witters, H.E. Feasibility Study of the Zebrafish Assay as an Alternative Method to Screen for Developmental Toxicity and Embryotoxicity Using a Training Set of 27 Compounds. Reprod Toxicol. 2012, 33, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotzmann, K.; Wolterbeek, A.; Kroese, D.; Braunbeck, T. Neurotoxic Effects in Zebrafish Embryos by Valproic Acid and Nine of Its Analogues: The Fish-Mouse Connection? Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 641–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, A.; McHenry, M.J. Zebrafish Learn to Forage in the Dark. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219 Pt 4, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashina, K.; Tejero-Cantero, Á.; Herz, A.; Baier, H. Zebrafish Exploit Visual Cues and Geometric Relationships to Form a Spatial Memory. iScience 2019, 19, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facciol, A.; Bailleul, C.; Nguyen, S.; Chatterjee, D.; Gerlai, R. Developmental Stage-Dependent Deficits Induced by Embryonic Ethanol Exposure in Zebrafish: A Neurochemical Analysis. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 99, 109859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, E.S.H.; Hui, M.N.Y.; Lin, C.C.; Cheng, S.H. Cadmium Inhibits Neurogenesis in Zebrafish Embryonic Brain Development. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 87, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, C.S.; Korzh, V.; Strahle, U. Zebrafish Embryos Are Susceptible to the Dopaminergic Neurotoxin MPTP. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 21, 1758–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kong, A.; Shelton, D.; Dong, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, F.; Bai, C.; Huang, K.; Mo, W.; Chen, S.; et al. Early Life Stage Transient Aristolochic Acid Exposure Induces Behavioral Hyperactivity but Not Nephrotoxicity in Larval Zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 238, 105916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Guo, M.; Huang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Fan, D.; Shi, L.; et al. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle Affects Motor Behavior, Neurodevelopment and Axonal Growth in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Larvae. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, J.; Wu, W.; Fang, Y.; Liu, F.; Yang, Q.; Hu, X.; Gu, X.; He, Z.; Sun, D.; et al. Effect of Aerobic Exercise as a Treatment on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Depression-like Behavior Zebrafish. Life Sci. 2022, 300, 120578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, M.; Bedrossiantz, J.; Ramírez, J.R.R.; Mayol, M.; García, G.H.; Bellot, M.; Prats, E.; Garcia-Reyero, N.; Gómez-Canela, C.; Gómez-Oliván, L.M.; et al. Glyphosate Targets Fish Monoaminergic Systems Leading to Oxidative Stress and Anxiety. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Wu, M.; Chen, C.; Xu, H.; Wu, X.; Qiu, X. Impacts of Chronic Exposure to Sublethal Diazepam on Behavioral Traits of Female and Male Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalcin, H.C.; Amindari, A.; Butcher, J.T.; Althani, A.; Yacoub, M. Heart Function and Hemodynamic Analysis for Zebrafish Embryos. Dev. Dyn. 2017, 246, 868–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Ding, R.; Ma, Y.; Sun, Q.; Ren, X.; Sun, Z.; Duan, J. Cardiovascular Toxicity Assessment of Polyethylene Nanoplastics on Developing Zebrafish Embryos. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 131124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Fan, Z.; Fang, Y.; He, L.; Peng, M.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, H.; et al. Cardiac Developmental Toxicity and Transcriptome Analyses of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Embryos Exposed to Mancozeb. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 226, 112798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cj, G.; Lp, W. Comparison of the Acute Effects of Benzo-a-Pyrene on Adult Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Cardiorespiratory Function Following Intraperitoneal Injection versus Aqueous Exposure. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 165, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eimon, P.M.; Rubinstein, A.L. The Use of in Vivo Zebrafish Assays in Drug Toxicity Screening. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2009, 5, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.-J.; Xu, Y.-Q.; He, J.-H.; Yu, H.-P.; Huang, C.-J.; Gao, J.-M.; Dong, Q.-X.; Xuan, Y.-X.; Li, C.-Q. Human Cardiotoxic Drugs Delivered by Soaking and Microinjection Induce Cardiovascular Toxicity in Zebrafish. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2014, 34, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoch, S.; Patial, V. Zebrafish: An Emerging Model System to Study Liver Diseases and Related Drug Discovery. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 41, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Yeung, K.; Chan, K.M. Toxic Effects of Octocrylene on Zebrafish Larvae and Liver Cell Line (ZFL). Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 236, 105843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Dang, Y.; Gong, Z.; Letcher, R.J.; Liu, C. Progression of Liver Tumor Was Promoted by Tris(1,3-Dichloro-2-Propyl) Phosphate through the Induction of Inflammatory Responses in KrasV12 Transgenic Zebrafish. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255 Pt 2, 113315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.L.; Liu, S.Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, C.X.; Li, D.H.; Liu, Y.D. Antioxidative Responses in Zebrafish Liver Exposed to Sublethal Doses Aphanizomenon Flos-Aquae DC-1 Aphantoxins. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 113, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, I.A.; Davidson, A.J. Zebrafish Kidney Development. Methods Cell Biol. 2016, 134, 391–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.-J.; Chen, Y.-H. Developmental Nephrotoxicity of Aristolochic Acid in a Zebrafish Model. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 261, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, M.; Fagman, H. Development of the Thyroid Gland. Development 2017, 144, 2123–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; Li, X.; Qiu, Y.; Zeng, X.; Yu, X.; Wang, W.; Yi, X.; Huang, L. Low-Dose Effects on Thyroid Disruption in Zebrafish by Long-Term Exposure to Oxytetracycline. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 227, 105608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Dang, J.; Paudel, Y.N.; Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Wang, L.; Li, P.; Sun, C.; Liu, K. The Possible Hormetic Effects of Fluorene-9-Bisphenol on Regulating Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Thyroid Axis in Zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazio, M.; Ablain, J.; Chuan, Y.; Langenau, D.M.; Zon, L.I. Zebrafish Patient Avatars in Cancer Biology and Precision Cancer Therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.-W.; Hsia, Y.; Tu, H.-C.; Hsiao, Y.-C.; Yang, W.-Y.; Wang, H.-D.; Yuh, C.-H. Liver Development and Cancer Formation in Zebrafish. Birth Defects Res. Part C Embryo Today Rev. 2011, 93, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.L.; Goessling, W. Baiting for Cancer: Using the Zebrafish as a Model in Liver and Pancreatic Cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 916, 391–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitsbergen, J.M.; Tsai, H.W.; Reddy, A.; Miller, T.; Arbogast, D.; Hendricks, J.D.; Bailey, G.S. Neoplasia in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Treated with 7,12-Dimethylbenz[a]Anthracene by Two Exposure Routes at Different Developmental Stages. Toxicol. Pathol. 2000, 28, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitsbergen, J.M.; Buhler, D.R.; Peterson, T.S. Neoplasia and Neoplasm-Associated Lesions in Laboratory Colonies of Zebrafish Emphasizing Key Influences of Diet and Aquaculture System Design. ILAR J. 2012, 53, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitsbergen, J.M.; Tsai, H.W.; Reddy, A.; Miller, T.; Arbogast, D.; Hendricks, J.D.; Bailey, G.S. Neoplasia in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Treated with N-Methyl-N’-Nitro-N-Nitrosoguanidine by Three Exposure Routes at Different Developmental Stages. Toxicol. Pathol. 2000, 28, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pollutants Classes | Contaminants | Biomarkers/Endpoints | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy metal | Cr (VI) | Cholinesterase, glutathione S-transferase and lactate dehydrogenase | [14] |
| Cadmium acetate, lead acetate, mercury chloride, zinc chloride | Acetylcholinesterase activity, gene expression pattern, antioxidant competence in the brain | [15] | |
| Lead contaminated sediments | Survival rate, C-start response, skeletal malformations and bent spines, pericardial edema and yolk sacmalformations, ALA-D gene expression | [16] | |
| Cd, Pb | Embryo lethality and teratogenicity, oxygen species (ROS), Nrf2 and IFN-γ gene expression | [17] | |
| Cd | specific growth rate (SGR), 17β-estradiol (E2) and vitellogenin (VTG) concentrations in plasma, gonadosomatic index (GSI), egg-laying amount, spawning percentage, and hatching and mortality rate of embryos, vtg1 gene expression | [18] | |
| Organic pollutant | MgHP | Catalase (CAT), reactive oxygen species (ROS), glutathione, metallothionein values | [19] |
| Prochloraz (PCZ) | Cholinesterase, glutathione S-transferase, and lactate dehydrogenase | [20] | |
| Chlorpyrifos (CHL) | Rate of deformity, cytochrome P450 (CYP450), NR1I2 gene, UGT1a1, and MDR1 expression level | [21] | |
| Oxytetracycline, amoxicillin | Premature hatch, delayed hatching of embryos, CAT, glutathione-S-transferases, lactate dehydrogenase | [22] | |
| NPs | MPs | CAT, superoxide dismutase (SOD), D-lactate, Diamine oxidase (DAO) activity | [23] |
| PS-NPs | Acetylcholinesterase (AChE), ROS, oxytocin, Adenosine triphosphate (ATP), malondialdehyde (MDA), single stranded DNA (ssDNA), VTG, dopamine (DA), CYP1A1, γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) | [24] |
| Pollutant | Time | LC50 | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic pollutant | Permethrin | 24 h | 0.0052 (0.0041–0.0066) mg/L | [65] |
| 48 h | 0.0030 (0.0019–0.0038) mg/L | |||
| 72 h | 0.0026 (0.0018–0.0033) mg/L | |||
| 96 h | 0.0025 (0.0017–0.0032) mg/L | |||
| Tetramethrin | 24 h | 0.0782 (0.0728–0.0838) mg/L | ||
| 48 h | 0.0517 (0.0470–0.0572) mg/L | |||
| 72 h | 0.0484 (0.0436–0.0596) mg/L | |||
| 96 h | 0.0460 (0.0436–0.0481) mg/L | |||
| Bifenthrin | 24 h | 0.0065 (0.0051–0.0093) mg/L | ||
| 48 h | 0.0039 (0.0026–0.0050) mg/L | |||
| 72 h | 0.0034 (0.0020–0.0046) mg/L | |||
| 96 h | 0.0032 (0.0021–0.0041) mg/L | |||
| Etofenprox | 24 h | 0.0969 (0.0701–0.121) mg/L | ||
| 48 h | 0.0865 (0.0613–0.109) mg/L | |||
| 72 h | 0.0825 (0.0561–0.105) mg/L | |||
| 96 h | 0.0791 (0.0564–0.0988) mg/L | |||
| Dichlorvos | 24 h | 51.3 (47.2–55.8) mg/L | ||
| 48 h | 32.3 (28.7–36.0) mg/L | |||
| 72 h | 15.0 (12.1–18.4) mg/L | |||
| 96 h | 13.0 (10.4–16.1) mg/L | |||
| Gallic acid | 96 h | >100 mg/L | [66] | |
| Pelargonic acid | 96 h | 81.2 mg/L | ||
| 6:2 fluorotelomer sulfonamide alkylbetaine (6:2 FTAB) | 120 h | 43.73 ± 3.24 mg/L | [67] | |
| Maxilon blue 5G (MB-5G) | 96 h | 166.04 | [68] | |
| Reactive Blue 203 (RB-203) | 96 h | 278.32 | ||
| perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) | 120 h | 2.20 mg/L | [69] | |
| Bisphenol A(BPA) | 96 h | 8.041 mg/L | [70] | |
| Endosulfan | 96 h | 0.238 mg/L | ||
| Heptachlor | 96 h | 1.738 mg/L | ||
| Heavy metal | Cd | 72 h | 1.823 ± 0.125 μmol/L | [71] |
| Pb | 72 h | 292.6 μg/L | ||
| Cu | 72 h | 0.38 ± 0.092 μmol/L | ||
| Zn | 72 h | 12.432 ± 0.497 μmol/L | ||
| 90Sr | 6 d | 6 mM | [72] | |
| Pd | 48 h | 292.6 μg/L | [73] | |
| NPs | Regular foam Phenol-formaldehyde microplastics | 96 h (170.4 ± 147.5 µm) | 27.1 mg/mL | [74] |
| Biofoam Phenol-formaldehydemicroplastics | 96 h (155.9 ± 56.4 µm) | 43.8 mg/mL | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Jin, L.; Peng, R. Research Progress of Zebrafish Model in Aquatic Ecotoxicology. Water 2023, 15, 1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091735
Li H, Liu Y, Chen Q, Jin L, Peng R. Research Progress of Zebrafish Model in Aquatic Ecotoxicology. Water. 2023; 15(9):1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091735
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Huiqi, Yinai Liu, Qianqian Chen, Libo Jin, and Renyi Peng. 2023. "Research Progress of Zebrafish Model in Aquatic Ecotoxicology" Water 15, no. 9: 1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091735