Chromium Removal from Aqueous Solution Using Natural Clinoptilolite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Cr(VI) Aqueous Solutions
2.2. Treatment of Clinoptilolite with NaCl
2.3. Fixed Bed Study
2.4. Column Regeneration
2.5. Chemical Analysis of Cr Concentration
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Chemical Pretreatment
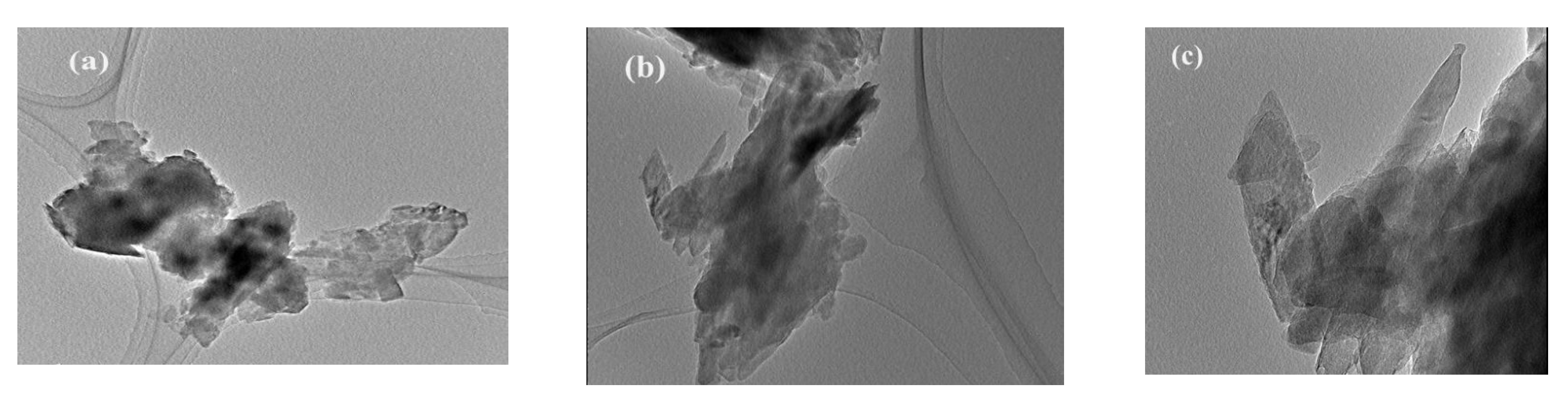
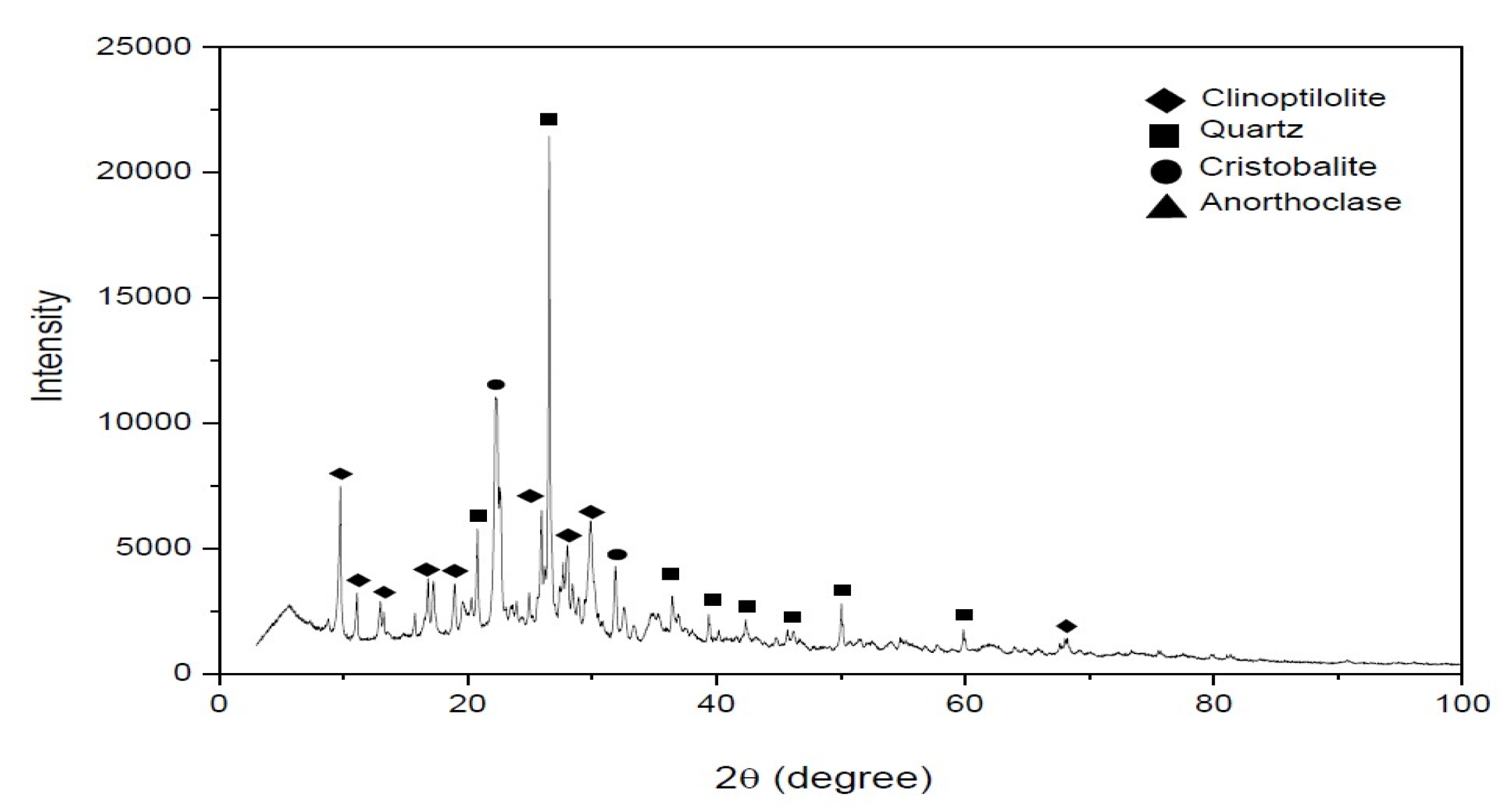
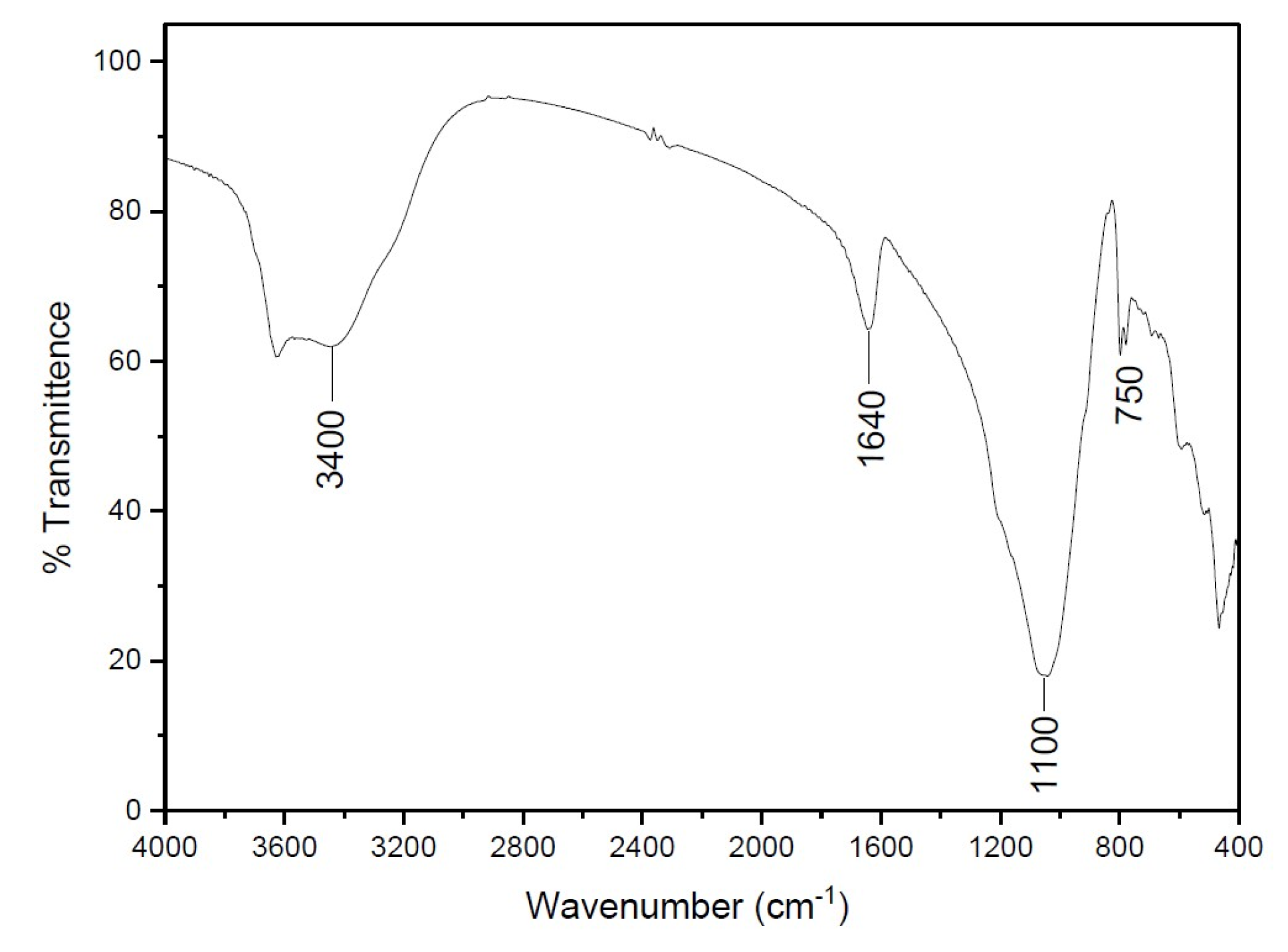
3.2. Characterization of Clinoptilolite before and after Pretreatment
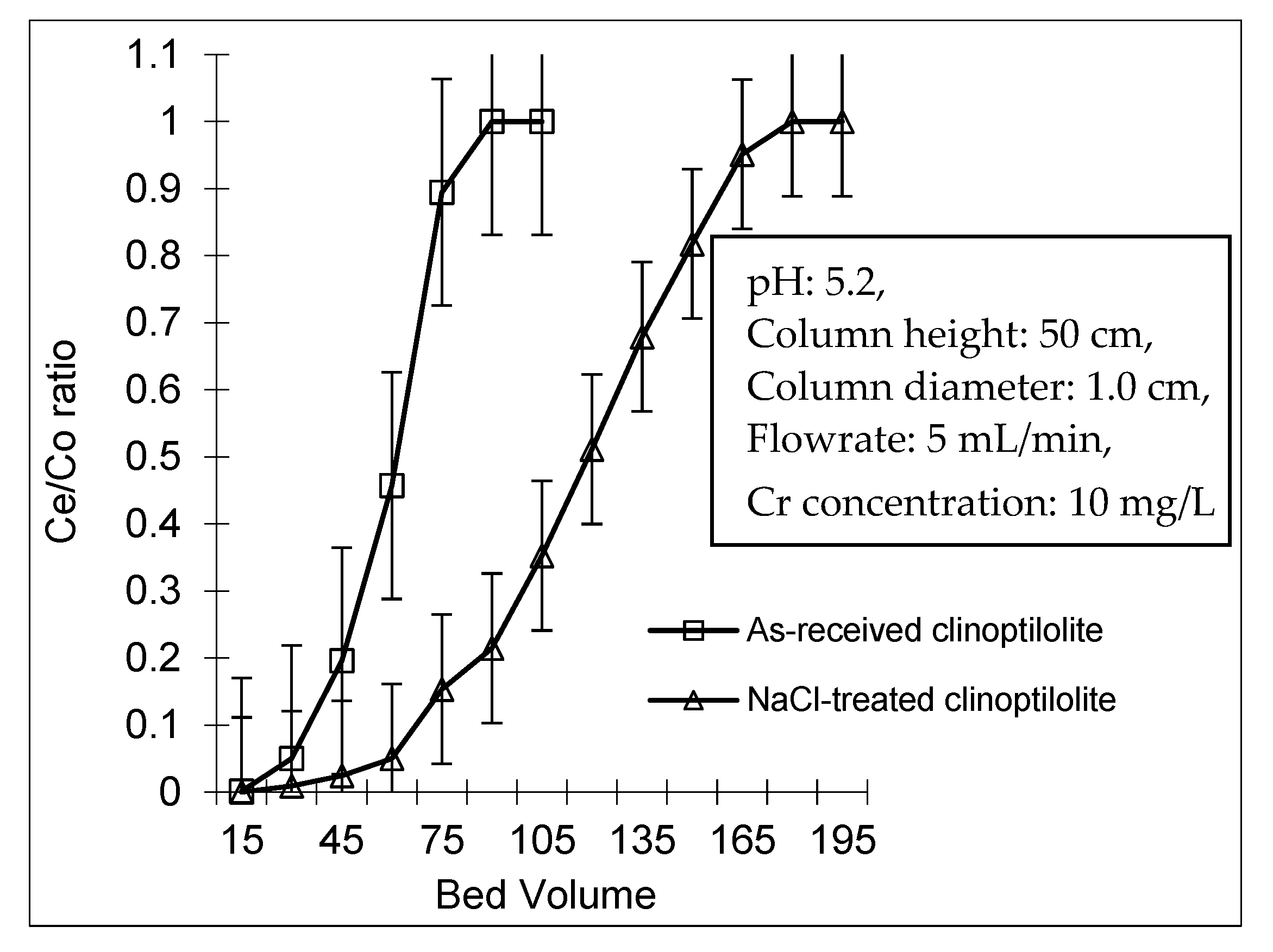
3.3. Fixed Bed Studies
3.3.1. Breakthrough
3.3.2. Regeneration
3.3.3. Cr Adsorption Capacity of Clinoptilolite
3.3.4. Adsorption Mechanism of Cr Removal by Clinoptilolite
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, M.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Duan, L.; Song, Y.; Hermanowicz, S.W.; Othman, M.H.D. Advances in BiOX-based ternary photocatalysts for water technology and energy storage applications: Research trends, challenges, solutions, and ways forward. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2022, 21, 331–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dun, F.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Ouyang, T. Uncovering potentials of integrated TiO2(B) nanosheets and H2O2 for removal of tetracycline from aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 248, 112–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Goh, H.H.; Zhang, D.; Dai, W.; Liu, H.; Goh, K.C.; Othman, M.H.D. Conversion of landfilled waste-to-electricity (WTE) for energy efficiency improvement in Shenzhen (China): A strategy to contribute to resource recovery of unused methane for generating renewable energy on-site. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 369, 133078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Goh, H.H.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Zhang, D.; Dai, W.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Goh, K.C. Utilizing landfill gas (LFG) to electrify digital data centers in China for accelerating energy transition in Industry 4.0 era. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 369, 133297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sniatala, B.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Sobotka, D.; Makinia, J.; Othman, M.H.D. Macro-nutrients recovery from liquid waste as a sustainable resource for production of recovered mineral fertilizer: Uncovering alternative options to sustain global food security cost-effectively. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiurova, A.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Kustikova, M.; Bykovskaia, E.; Othman, M.H.D.; Singh, D.; Goh, H.H. Promoting digital transformation in waste collection service and waste recycling in Moscow (Russia): Applying a circular economy paradigm to mitigate climate change impacts on the environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 354, 131604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Liang, X.; O’Callaghan, E.; Goh, H.; Othman, M.H.D.; Avtar, R.; Kusworo, T.D. Transformation of solid waste management in China: Moving towards sustainability through digitalization-based circular economy. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Guo, L.; Lan, J.; Zhang, L.; Cao, D. Heavy metal ion removal of wastewater by zeolite-imidazolate frameworks. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 194, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaid, S.S.; Gaikwad, D.K.; Sayyed, M.I.; Khader, A.R.; Pawar, P.P. Heavy metal ions removal from waste water bythe natural zeolites. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 17930–17934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Chen, H.; Lin, J.; Lin, Z.; Sun, J. Zeolite A synthesized from alkaline assisted pre-activated halloysite for efficient heavy metal removal in polluted river and industrial wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 56, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahnafi, A.; Elgamouz, A.; Tijani, N.; Jaber, L.; Kawde, A.N. Hydrothermal synthesis and electrochemical characterization of novel zeolite membranes supported on flat porous clay-based microfiltration system and its application of heavy metals removal of synthetic wastewaters. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 334, 111778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isawi, H. Using zeolite/polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate nanocomposite beads for removal of some heavy metals from wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 5691–5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloulou, W.; Aloulou, H.; Khemakhem, M.; Duplay, J.; Daramola, M.O.; Amar, R.B. Synthesis and characterization of clay-based ultrafiltration membranes supported on natural zeolite for removal of heavy metals from wastewater. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 18, 100794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurekli, Y. Removal of heavy metals in wastewater by using zeolite nano-particles impregnated polysulfone membranes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 309, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grba, N.; Baldermann, A.; Dietzel, M. Novel green technology for wastewater treatment: Geo-material/geopolymer applications for heavy metal removal from aquatic media. Int. J. Sediment. Res. 2022, 38, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjhi, F.A.; Ihsanullah, I.; Bilal, M.; Castro-Muñoz, R.; Boczkaj, G.; Gallucci, F. MXene-based materials for removal of antibiotics and heavy metals from wastewater–A review. Water Resour. Ind. 2023, 29, 100202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanin, E.; Scapinello, J.; de Oliveira, M.; Rambo, C.L.; Franscescon, F.; Freitas, L.; de Mello, J.M.M.; Fiori, M.A.; Oliveira, J.V.; Dal Magro, J. Adsorption of heavy metals from wastewater graphic industry using clinoptilolite zeolite as adsorbent. Process. Saf. Environ. 2017, 105, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, L.; Sun, S.; Gao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z. Disinfection and removal performance for Escherichia coli, toxic heavy metals and arsenic by wood vinegar-modified zeolite. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Law, W.W.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Yang, E.H. Hydrothermal synthesis of needle-like nanocrystalline zeolites from metakaolin and their applications for efficient removal of organic pollutants and heavy metals. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 272, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egashira, R.; Tanabe, S.; Habaki, H. Adsorption of heavy metals in mine wastewater by Mongolian natural zeolite. Procedia Eng. 2012, 42, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajiboye, T.O.; Oyewo, O.A.; Onwudiwe, D.C. Simultaneous removal of organics and heavy metals from industrial wastewater: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Tan, K.; Cai, J.; Hou, S.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, P.; Liang, M. Silica oxide encapsulated natural zeolite for high efficiency removal of low concentration heavy metals in water. Colloid. Surf. A 2019, 561, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dun, F.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q. Applicability of HDPC-supported Cu nanoparticles composite synthesized from unused waste digestate for octocrylene degradation in aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 355, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babel, S.; Kurniawan, T.A. Low-cost adsorbents for heavy metals uptake from contaminated water: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 97, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Babel, S. Cr(VI) removal from contaminated wastewater using natural zeolite. J. Ion Exch. 2003, 14, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Avtar, R.; Singh, D.; Xue, W.; Dzarfan Othman, M.H.; Hwang, G.H.; Iswanto, I.; Albadarin, A.B.; Kern, A.O. Reforming MSWM in Sukunan (Yogjakarta, Indonesia): A case-study of applying a zero-waste approach based on circular economy paradigm. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 284, 124775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Chan, G.; Lo, W.H.; Babel, S. Physico-chemical treatment techniques for wateswater laden with heavy metals. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 118, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Chan, G.Y.S.; Lo, W.H. Comparisons of low-cost adsorbents for treating wastewaters laden with heavy metals. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 366, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Lo, W.H.; Chan, G. Physico-chemical treatments for removal of recalcitrant contaminants from landfill leachate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 29, 80–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dun, F.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Gui, H.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q. Role of CuxO-anchored pyrolyzed hydrochars on H2O2-activated degradation of tetracycline: Effects of pyrolysis temperature and pH. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 8847–8857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Singh, D.; Avtar, R.; Dzarfan Othman, M.H.; Hwang, G.H.; Albadarin, A.B.; Rezakazemi, M.; Setiadi, T.; Shirazian, S. Resource recovery from landfill leachate: An experimental investigation and perspectives. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Liang, X.; Singh, D.; Othman, M.H.D.; Goh, H.H.; Gikas, P.; Kern, A.O.; Kusworo, T.D.; Shoqeir, J.A. Harnessing landfill gas (LFG) for electricity: A strategy to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions in Jakarta (Indonesia). J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dun, F.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Li, Q.; Gui, H.; Othman, M.H.D. Treatment of As(III)-contaminated water using iron-coated carbon fiber. Materials 2022, 15, 4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Othman, M.H.D.; Singh, D.; Avtar, R.; Goh, H.H.; Setiadi, T.; Lo, W.H. Technological solutions for long-term management of partially used nuclear fuel: A critical review. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2022, 166, 108736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Othman, M.H.D.; Hwang, G.H.; Gikas, P. Unlocking digital technology in waste recycling industry in Industry 4.0 era: A transformation towards digitalization-based circular economy in Indonesia. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 357, 131911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huuha, T.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Sillanpää, M. Removal of silicon from pulping whitewater using integrated treatment of chemical precipitation & evaporation. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 158, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Othman, M.H.D.; Adam, M.R.; Goh, H.H.; Mohyudin, A.; Avtar, R.; Kusworo, T.D. Treatment of pulping whitewater using membrane filtrations. Chem. Papers 2022, 76, 5001–5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Maiurova, A.; Kustikova, M.; Bykovskaia, E.; Othman, M.H.D.; Goh, H.H. Accelerating sustainability transition in St. Petersburg (Russia) through digitalization-based circular economy in waste recycling industry: A strategy to promote carbon neutrality in era of Industry 4.0. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Singh, D.; Xue, W.; Avtar, R.; Othman, M.H.D.; Hwang, G.H.; Setiadi, T.; Albadarin, A.B.; Shirazian, S. Resource recovery toward sustainability through nutrient removal from landfill leachate. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 287, 112265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premakumara, D.G.J.; Canete, A.L.M.L.; Nagaishi, M.; Kurniawan, T.A. Policy implementation of the Republic Act (RA) No. 9003 in the Philippines on MSW management: A case study of Cebu City. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulfat, W.; Mohyuddin, A.; Amjad, M.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Mujahid, B.; Nadeem, S.; Javed, M.; Amjad, A.; Ashraf, A.Q.; Othman, M.H.D.; et al. Reuse of buffing dust-laden tanning waste hybridized with polystyrene for fabrication of thermal insulation materials. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Othman, M.H.D.; Liang, X.; Ayub, M.; Goh, H.H.; Kusworo, T.D.K.; Mohyuddin, A.; Chew, K.W. Microbial fuel cells (MFC): A potential game changer in renewable energy development. Sustainability 2023, 14, 16847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Othman, M.H.D.; Liang, X.; Goh, H.H.; Chew, K.W. From liquid waste to mineral fertilizer: Recovery, recycle and reuse of high-value macro-nutrients from landfill leachate to contribute to circular economy, food security, and carbon neutrality. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 170, 791–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Meidiana, C.; Othman, M.H.D.; Goh, H.H.; Chew, K.W. Strengthening waste recycling industry in Malang (Indonesia): Lessons from waste management in the era of Industry 4.0. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 382, 135296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Lo, W.; Liang, X.; Goh, H.H.; Othman, M.H.D.; Chew, K.W. Remediation technologies for contaminated groundwater laden with arsenic (As), mercury (Hg), and/or fluoride (F): A critical review and ways forward to contribute to carbon neutrality. Separ. Purif. Technol. 2023, 314, 123474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Lo, W.H.; Liang, X.; Goh, H.H.; Othman, M.H.D.; Chong, K.K.; Mohyuddin, A.; Kern, A.O.; Chew, K.W. Heavy metal removal from aqueous solution using unused biomaterials and/or functional nanomaterials: Recent advances and ways forward in wastewater treatment. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.M.; Liu, M.; Pai, T.; Liu, W.; Wang, S.; Banks, C.; Hung, C.; Chiang, C.; Lin, K.; Chiu, H.; et al. Biostabilization assessment of MSW co-disposed with MSWI fly ash in anaerobic bioreactors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Othman, M.H.D.; Liang, X.; Goh, H.H.; Gikas, P.; Chong, K.K.; Chew, K.W. Challenges and opportunities for biochar management to promote circular economy and carbon neutrality. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 332, 117429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.M.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Pai, T.Y.; Liu, M.H.; Chiang, C.F.; Wang, S.C.; Wu, K.C. Effects of spiked metals on MSW anaerobic digestion. Waste Manag. Res. 2012, 30, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Daghistani, A.I.; Mohammad, B.T.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Singh, D.; Rabadi, A.D.; Xue, W.; Avtar, R.; Othman, M.H.D.; Shirazian, S. Characterization and applications of Thermomonas hydrothermalis isolated from Jordanian hot springs for biotechnological and medical purposes. Process Biochem. 2021, 104, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohyuddin, A.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Khan, Z.; Nadeem, S.; Javed, M.; Dera, A.A.; Iqbal, S.; Awwad, N.S.; Ibrahium, H.A.; Abourehab, M.A.S.; et al. Comparative insights into the antimicrobial, antioxidant, and nutritional potential of the Solanum Nigrum complex. Processes 2022, 10, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Haider, A.; Ahmad, H.M.; Mohyuddin, A.; Aslam, H.M.U.; Nadeem, S.; Javed, M.; Othman, M.H.D.; Goh, H.H.; Chew, K.W. Source, occurrence, distribution and implications of microplastic pollutants in freshwater ecosystem on sustainability: A critical review and the way forward. Chemosphere 2023, 325, 138367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.A.; Bishtawi, R.E. Removals of lead and nickel ions using zeolite tuff. J. Chem. Biotechnol. 1997, 69, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, G.; Maunaye, M.; Martin, G. Removal of heavy metals from water by means of natural zeolites. Water Res. 1984, 18, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curković, L.; Stefanovic, S.C.; Filipan, T. Metal ion exchange by natural and modified zeolites. Water Res. 1997, 31, 1379–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, D.C.; Skriba, M.C. Removal of radioactive contaminants from West Valley waste streams using natural zeolites. Environ. Prog. 1987, 6, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groffman, A.; Peterson, S.; Brookins, D. Removing lead from wastewater using zeolite. Water Environ. Technol. 1987, 4, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Leinonen, H.; Lehto, J. Purification of metal finishing wastewaters with zeolites and activated carbons. Water Manag. Res. 2001, 19, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshko, V.; Markovska, L.; Mincheva, M.; Rodrigues, A.E. Adsorption of basic dyes on granular activated carbon and natural zeolite. Water Res. 2001, 35, 3357–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondales, K.D.; Carland, R.M.; Aplan, F.F. The comparative ion-exchange capacities of natural sedimentary and synthetic zeolites. Min. Eng. 1995, 8, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouki, S.K.; Kavanagh, M. Performance of natural zeolites for the treatment of mixed metal-contaminated effluents. Waste Manag. Res. 1997, 15, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pansini, M.; Colella, C.; De’Gennaro, M. Chromium removal from water by ion exchange using zeolite. Desalination 1991, 83, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamzow, M.J.; Eichbaum, B.R.; Sandgren, K.R.; Shanks, D.E. Removal of heavy metal and other cations from wastewater using zeolites. Separ. Sci. Technol. 1990, 25, 1555–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A. Removal of Toxic Chromium from Wastewater; Nova Science Publisher: New York, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-1-60876-340-5. [Google Scholar]
- Dun, F.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q. Co-oxidative removal of As(III) and tetracycline (TC) from aqueous solutions based on a heterogeneous Fenton’s oxidation using Fe nanoparticles (Fe NP)-impregnated solid digestate. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglezakis, V.J.; Diamandis, N.A.; Loizidou, M.D.; Grigoropoulou, H.P. Effects of pore clogging on kinetics of lead uptake by clinoptilolite. J. Coll. Int. Sci. 1999, 215, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inglezakis, V.J.; Papadeas, C.D.; Loizidou, M.D.; Grigoropoulou, H.P. Effects of pretreatment on physical and ion exchange properties of natural clinoptilollite. Environ. Technol. 2001, 22, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malliou, E.; Loizidou, M.; Spyrellis, N. Uptake of lead and cadmium by clinoptilolite. Sci. Total Environ. 1994, 149, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouki, S.K.; Cheeseman, C.R.; Perry, R. Effects of conditioning and treatment of chabazite and clinoptilolite prior to lead and cadmium removal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmens, M.J.; Martin, W.P. The influence of pretreatment on the capacity and selectivity of clinoptilolite for metal removal. Water Res. 1988, 22, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaca-Mier, M.; Callejas, R.L.; Gehr, R.; Cisneros, B.E.J.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Heavy metal removal with Mexican clinoptilolite: Multi-component ionic exchange. Water Res. 2001, 35, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, K.M.; Nasser, E.T.; Khoury, H. Use of natural chabazite-philipsite tuff in wastewater treatment from electroplating factories in Jordan. Environ. Geol. 2002, 41, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dun, F.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Avtar, R.; Xu, P.; Othman, M.H.D. Recovering heavy metals from electroplating wastewater and their conversion into Zn2Cr-layered double hydroxide (LDH) for pyrophosphate removal from industrial wastewater. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dun, F.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Lan, L.; Yaqiong, L.; Avtar, R.; Othman, M.H.D. Arsenic removal from aqueous solution by FeS2. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Sun, G.; Quan, B.; Tang, J.; Zhang, C.; Jia, C.; Tang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, M.; Wang, W.; et al. An experimental study of fluoride removal from wastewater by Mn-Ti modified zeolite. Water 2021, 13, 3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamd, A.; Dryaz, A.R.; Shaban, M.; AlMohamadi, H.; Abu Al-Ola, K.A.; Soliman, N.K.; Ahmed, S.A. Fabrication and application of zeolite/Acanthophora Spicifera nanoporous composite for adsorption of Congo red dye from wastewater. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhuranthakam, C.M.R.; Thomas, A.; Akhter, Z.; Fernandes, S.Q.; Elkamel, A. Removal of chromium(VI) from contaminated water using untreated moringa leaves as biosorbent. Pollutants 2021, 1, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Nong, S.; Zhao, Y.; Riaz, M.S.; Xiao, Y.; Molokeev, M.S.; Huang, F. Renewable P-type zeolite for superior absorption of heavy metals: Isotherms, kinetics, and mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Yu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Dong, L.; Zan, Q.; Li, R. Heavy metal adsorption with zeolites: The role of hierarchical pore architecture. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bai, P.; Yan, Y.; Yan, W.; Shi, W.; Xu, R. Removal of Zn2+, Pb2+, Cd2+, and Cu2+ from aqueous solution by synthetic clinoptilolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 273, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahono, S.K.; Stalin, J.; Addai-Mensah, J.; Skinner, W.; Vinu, A.; Vasilev, K. Physico-chemical modification of natural mordenite-clinoptilolite zeolites and their enhanced CO2 adsorption capacity. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 294, 109871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, H.; Quintelas, C. Tailored zeolites for the removal of metal oxyanions: Overcoming intrinsic limitations of zeolites. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 274, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Lo, W.; Othman, M.H.D.; Goh, H.H.; Chong, K.K. Influence of Fe2O3 and bacterial biofilms on Cu(II) distribution in a simulated aqueous solution: A feasibility study to sediments in the Pearl River Estuary (PR China). J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 329, 117047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Lo, W.; Othman, M.H.D.; Goh, H.H.; Chong, K.K. Biosorption of heavy metals from aqueous solutions using activated sludge, Aeromasss hydrophyla, and Branhamella spp based on modeling with GEOCHEM. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 114070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Othman, M.H.D.; Goh, H.H.; Gikas, P.; Kusworo, T.D.; Anouzla, A.; Chew, K.W. Decarbonization in waste recycling industry using digital technologies to contribute to carbon neutrality and its implications on sustainability. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 338, 117765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velarde, L.; Nabavi, M.S.; Escalera, E.; Antti, M.L.; Akhtar, F. Adsorption of heavy metals on natural zeolites: A review. Chemosphere 2023, 328, 138508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.S.; Badawi, A.K.; Salama, R.S.; Mostafa, M.M.M. Design and development of novel composites containing nickel ferrites supported on activated carbon derived from agricultural wastes and its application in water remediation. Materials 2023, 16, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasri, T.M.; Ali, S.L.; Salama, R.S.; Alshorifi, F.T. Band-structure engineering of TiO2 photocatalyst by AuSe quantum dots for efficient degradation of malachite green and phenol. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baaloudj, O.; Nasrallah, N.; Kenfoud, H.; Bourkeb, K.W.; Badawi, A.K. Polyaniline/Bi12TiO20 hybrid system for cefixime removal by combining adsorption and photocatalytic degradation. ChemEngineering 2023, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, A.; Assadi, A.A.; El Jery, A.; Badawi, A.K.; Kenfoud, H.; Baaloudj, O.; Assadi, A.A. Advanced photocatalytic treatment of wastewater using immobilized titanium dioxide as a photocatalyst in a pilot-scale reactor: Process intensification. Materials 2022, 15, 4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, W.; Badawi, A.K.; Rehan, Z.A.; Khan, A.M.; Khan, R.A.; Shah, F.; Ali, S.; Ismail, B. Enhanced visible light photocatalytic performance of Sr0. 3 (Ba, Mn) 0.7 ZrO3 perovskites anchored on graphene oxide. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 24979–24988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Property | |
|---|---|
| Solid density (g/cm3) | 2.10 |
| Particle size (mm) | 0.68 |
| Packing density (g/cm3) | 2.25 |
| Total surface area (m2/g) | 800 |
| Cation exchange capacity (meq/g) | 2.50 |
| Oxide | Al2O3 | SiO2 | MgO | CaO | Fe2O3 | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition (%) | 12.0 | 73.0 | 1.9 | 2.1 | 4.3 | 6.7 |
| Types of Adsorbent | Cr Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Difference of Cr Adsorption Capacity (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Bed Studies | Batch Studies [25] | ||
| As-received clinoptilolite | 2.2 | 1.8 | 23 |
| NaCl-treated clinoptilolite | 4.5 | 3.2 | 41 |
| Types of Clinoptilolite | Cr before Regeneration (mg/g) | Cr after Regeneration (mg/g) | Regeneration Efficiency (%) * |
|---|---|---|---|
| As-received clinoptilolite | 2.2 | 2.0 | 91 |
| NaCl-treated clinoptilolite | 4.5 | 4.2 | 93 |
| Type of Clinoptilolite | BV Treated at 1st Run | Initial Cr Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Cr Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) At 2nd Run | Loss of Adsorption Capacity (%) * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| At Breakthrough | At Exhaustion | ||||
| As-received clinoptilolite | 32 | 91 | 2.2 | 1.7 | 23 |
| NaCl-treated clinoptilolite | 64 | 181 | 4.5 | 3.9 | 13 |
| Material | Reference | Cd2+ | Cr3+ | Cr6+ | Co2+ | Ni2+ | Zn2+ | Cu2+ | Pb2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinoptilolite | [64] | 2.4 | 0 | 1.4 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.6 | 1.6 | |
| [69] | 1.2 | 1.4 | |||||||
| [62] | 3.7 | 2.4 | 1.5 | 0.9 | 2.7 | 3.8 | 6.0 | ||
| Present study | 4.5 | ||||||||
| Chabazite | [70] | 137.0 | 175 | ||||||
| [62] | 6.7 | 3.6 | 5.8 | 4.5 | 5.5 | 5.1 | 6.0 | ||
| Chabazite− philipsite | [63] | 7.1 | |||||||
| [73] | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.04 | 0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kurniawan, T.A.; Othman, M.H.D.; Adam, M.R.; Liang, X.; Goh, H.; Anouzla, A.; Sillanpää, M.; Mohyuddin, A.; Chew, K.W. Chromium Removal from Aqueous Solution Using Natural Clinoptilolite. Water 2023, 15, 1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091667
Kurniawan TA, Othman MHD, Adam MR, Liang X, Goh H, Anouzla A, Sillanpää M, Mohyuddin A, Chew KW. Chromium Removal from Aqueous Solution Using Natural Clinoptilolite. Water. 2023; 15(9):1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091667
Chicago/Turabian StyleKurniawan, Tonni Agustiono, Mohd Hafiz Dzarfan Othman, Mohd Ridhwan Adam, Xue Liang, Huihwang Goh, Abdelkader Anouzla, Mika Sillanpää, Ayesha Mohyuddin, and Kit Wayne Chew. 2023. "Chromium Removal from Aqueous Solution Using Natural Clinoptilolite" Water 15, no. 9: 1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091667
APA StyleKurniawan, T. A., Othman, M. H. D., Adam, M. R., Liang, X., Goh, H., Anouzla, A., Sillanpää, M., Mohyuddin, A., & Chew, K. W. (2023). Chromium Removal from Aqueous Solution Using Natural Clinoptilolite. Water, 15(9), 1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091667








