Assessment of Dams’ Failure and Flood Wave Hazards on the Downstream Countries: A Case Study of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Study Area Description
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Boundary and Initial Conditions
2.2.2. Defining Breach Parameters
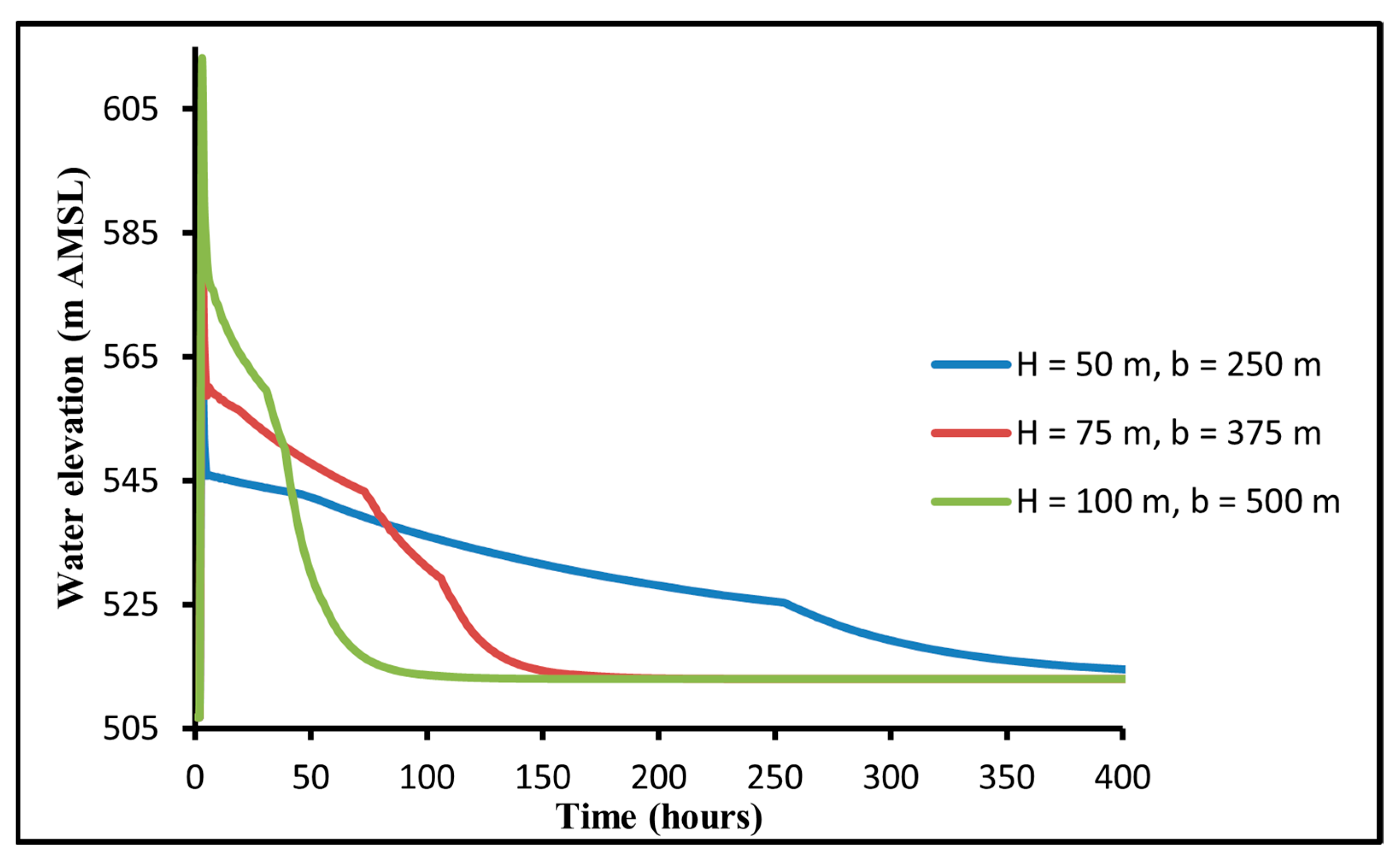
- The breach height (H) is equal to 50 m and it refers to the difference between the maximum operation level (640 m ASL) and the minimum operation level (590 m ASL);
- The breach is rectangular, with a width of 250 m. This width equalizes to five times the breach height (5H) according to Wetmore and Fread recommendations [36];
- Based on the previous guidelines, the breach formation time should be H/40 in minutes, but it is believed this period would really be shorter. Thus, as recommended by agencies such as HEC [37] and ICOLD [38], the time of breach formation ranges from 0.1 to 0.5 h for concrete dams. Therefore, the breach full time was assumed to be 0.1 h;
- The main dam will break when reservoir elevation reaches up to 645 m ASL;
- The failure mechanism is overtopping.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sensitivity of Results against Breach Parameters
3.1.1. Effect of Breach Size
3.1.2. Effect of Breach Formation Time
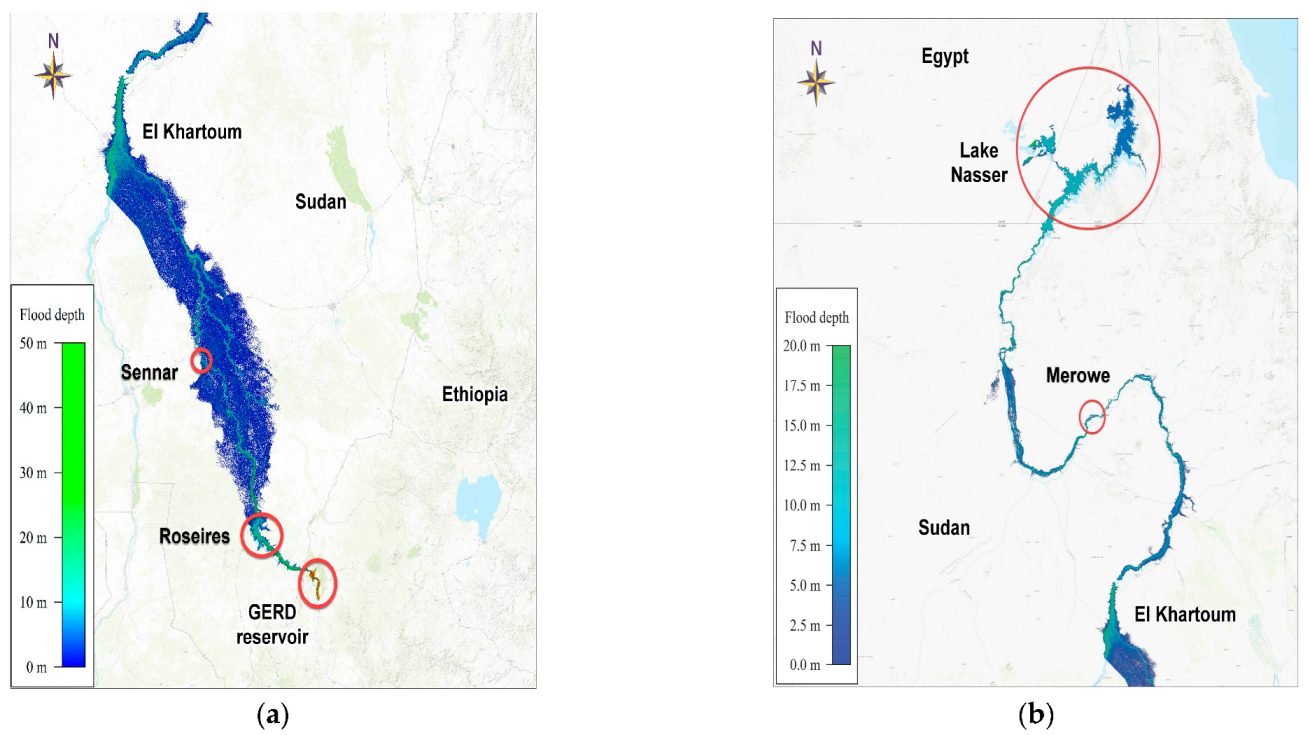
3.2. Emergency Plan and Inundation Map
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, M.; Zhang, L.; Chang, D.; Xu, Y. Dam Failure Mechanisms and Risk Assessment; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Azeez, O.; Elfeki, A.; Kamis, A.S.; Chaabani, A. Dam break analysis and flood disaster simulation in arid urban environment: The Um Al-Khair dam case study, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Nat. Hazards 2020, 100, 995–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Ge, W.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Pan, Y. Improved Set Pair Analysis and Its Application to Environmental Impact Evaluation of Dam Break. Water 2019, 11, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X. A dam break analysis using HEC-RAS. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2011, 3, 370–379. [Google Scholar]
- Cannata, M.; Marzocchi, R. Two-dimensional dam break flooding simulation: A GIS-embedded approach. Nat. Hazards 2012, 61, 1143–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskinas, A.; Tegos, A.; Tsira, P.; Dimitriadis, P.; Iliopoulou, T.; Papanicolaou, P.; Koutsoyiannis, D.; Williamson, T. Insights into the Oroville dam 2017 Spillway incident. Geosciences 2019, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotta, L.H.S.; Alcantara, E.; Park, E.; Negri, R.G.; Lin, Y.N.; Bernardo, N.; Mendes, T.S.G.; Souza Filho, C.R. The 2019 Brumadinho tailings dam collapse: Possible cause and impacts of the worst human and environmental disaster in Brazil. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 90, 102119. [Google Scholar]
- Latrubesse, E.M.; Park, E.; Sieh, K.; Dang, T.; Lin, Y.N.; Yun, S.-H. Dam failure and a catastrophic flood in the Mekong basin (Bolaven Plateau), southern Laos, 2018. Geomorphology 2020, 362, 107221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athens News. Available online: https://en.rua.gr/2023/02/06/cracks-in-the-ataturk-dam-after-earthquakes/ (accessed on 1 April 2023).
- Zin, W.W.; Kawasaki, A.; Takeuchi, W.; San, Z.M.L.T.; Htun, K.Z.; Aye, T.H.; Win, S. Flood hazard assessment of Bago river basin, Myanmar. J. Disaster Res. 2018, 13, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Wang, S.; Ni, J.; Xi, C.; Wang, J. Management system for dam-break hazard mapping in a complex basin environment. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.S.; Santos, M.A.; Santos, A.; Rocha, F. Dam-break flood emergency management system. Water Resour. Manag. 2002, 16, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincergok, T. The role of dam safety in dam-break induced flood management. In Proceedings of the International Congress on River Basin Management, Antalya, Turkey, 22–24 March 2007; p. 697. [Google Scholar]
- Duressa, J.N.; Jubir, A.K. Dam Break Analysis and Inundation Mapping, Case Study of Fincha’a Dam in Horro Guduru Wollega Zone, Oromia Region, Ethiopia. Sci. Res. 2018, 6, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, K.; Rostaminejad, M.; Cooper, J.R.; Mao, L.; Melesse, A.M. Dam break analysis and flood inundation mapping: The case study of Sefid-Roud Dam, Iran. In Extreme Hydrology and Climate Variability; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 395–405. [Google Scholar]
- Gouin, P. Earthquake History of Ethiopia and the Horn of Africa; IDRC: Ottawa, ON, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Kebede, F.; Van Eck, T. Probabilistic seismic hazard assessment for the Horn of Africa based on seismotectonic regionalisation. Tectonophysics 1997, 270, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbate, E.; Bruni, P.; Sagri, M. Geology of Ethiopia: A review and geomorphological perspectives. In Landscapes and Landforms of Ethiopia; Billi, P., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 33–64. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, A.H.; Zawahry, A.E.; Bekhit, H. GERD failure analysis and the impacts on downstream countries. In Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam versus Aswan High Da; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 149–171. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, H.A.N.; El-Moustafa, A.M.; Gad, M.A.E.-H. Hydrodynamic Modeling of Flood Wave Propagation in Major Rivers due to Dam Failures. Case Study: The Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD) on Nile River. Available online: http://azharcermjournal.com/CERMF1707/P17-07-07.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2023).
- Rendon, S.H.; Ashworth, C.E.; Smith, S.J. Dam-Breach Analysis and Flood-Inundation Mapping for Lakes Ellsworth and Lawtonka near Lawton, Oklahoma; US Department of Interior, US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- West, M.; Morris, M.; Hassan, M. A guide to breach prediction. Dams Reserv. 2018, 28, 150–152. [Google Scholar]
- Brunner, G.W. HEC-RAS River Analysis System 2D Modeling User’s Manual; US Army Corps of Engineers—Hydrologic Engineering Center: Davis, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 1–171. [Google Scholar]
- Özdemir, H.; Akbulak, C.; Özcan, H. Cokal Dam-break model and flood risk analysis (Canakkale). J. Hum. Sci. 2011, 8, 659–698. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.T.; Elsanabary, M.H. Environmental and hydrological impacts of grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam on the Nile River. Int. Water Technol. J. 2015, 5, 260–271. [Google Scholar]
- IPOE. International Panel of Experts for Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERDP); IPoE Final Report; IPoE: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Abtew, W.; Dessu, S.B. The Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam on the Blue Nile; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hassaballah, K.; Jonoski, A.; Popescu, I.; Solomatine, D. Model-based optimization of downstream impact during filling of a new reservoir: Case study of Mandaya/Roseires Reservoirs on the Blue Nile River. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 273–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, M. Hydrology and Water Resources of Africa; Springer Science & Business Media: Davis, CA, USA, 2006; Volume 41. [Google Scholar]
- Hafsaas-Tsakos, H. Ethical implications of salvage archaeology and dam building: The clash between archaeologists and local people in Dar al-Manasir, Sudan. J. Soc. Archaeol. 2011, 11, 49–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosshard, P. China’s role in financing African infrastructure. Int. Rivers Netw. 2007, 14, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Abul-Atta, A.A. Egypt and the Nile after the Construction of the High Aswan Dam; Egypt Ministry of Irrigation and Land Reclamation: Giza, Egypt, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- El Bastawesy, M.; Gabr, S.; Mohamed, I. Assessment of hydrological changes in the Nile River due to the construction of Renaissance Dam in Ethiopia. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2015, 18, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilania, S.; Chahar, B.R. A dam break analysis using HeC-RAs. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2019: Hydraulics, Waterways, and Water Distribution Systems Analysis, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 19–23 May 2019; pp. 382–389. [Google Scholar]
- Shahrim, M.; Ros, F. Dam break analysis of temenggor dam using hec-ras. Proc. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 479, 012041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetmore, J.N.; Fread, D.L. The NWS Simplified Dam-Break Flood Forecasting Model; National Weather Service: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 1981; pp. 164–197. [Google Scholar]
- Owen, H.J. Flood Emergency Plans: Guidelines for Corps Dams; Hydrologic Engineering Center: Davis, CA, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Mohr, J. Dam-Break Flood Analysis: Review and Recommendations; International Commission on Large Dams: Paris, France, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kansara, P.; Lakshmi, V. Water Levels in the Major Reservoirs of the Nile River Basin—A Comparison of SENTINEL with Satellite Altimetry Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Y.S.A. The Impact of Soil Erosion in the Upper Blue Nile on Downstream Reservoir Sedimentation; Citeseer: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Awal, R.; Nakagawa, H.; Kawaike, K.; Baba, Y.; Zhang, H. Experimental study on piping failure of natural dam. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. Ser. B1 (Hydraul. Eng.) 2011, 67, I_157–I_162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Elevation (m ASL) | Storage (109 m3) |
|---|---|
| 506 | 0 |
| 586 | 9.6 |
| 606 | 17.5 |
| 636 | 56 |
| 652 | 80.5 |
| 686 | 173 |
| Location Downstream | Distance from GERD (km) | Vmax (m/s) | Max. W.S.E (m ASL) | Max. Water Depth (m) | Arrival Time (hrs.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
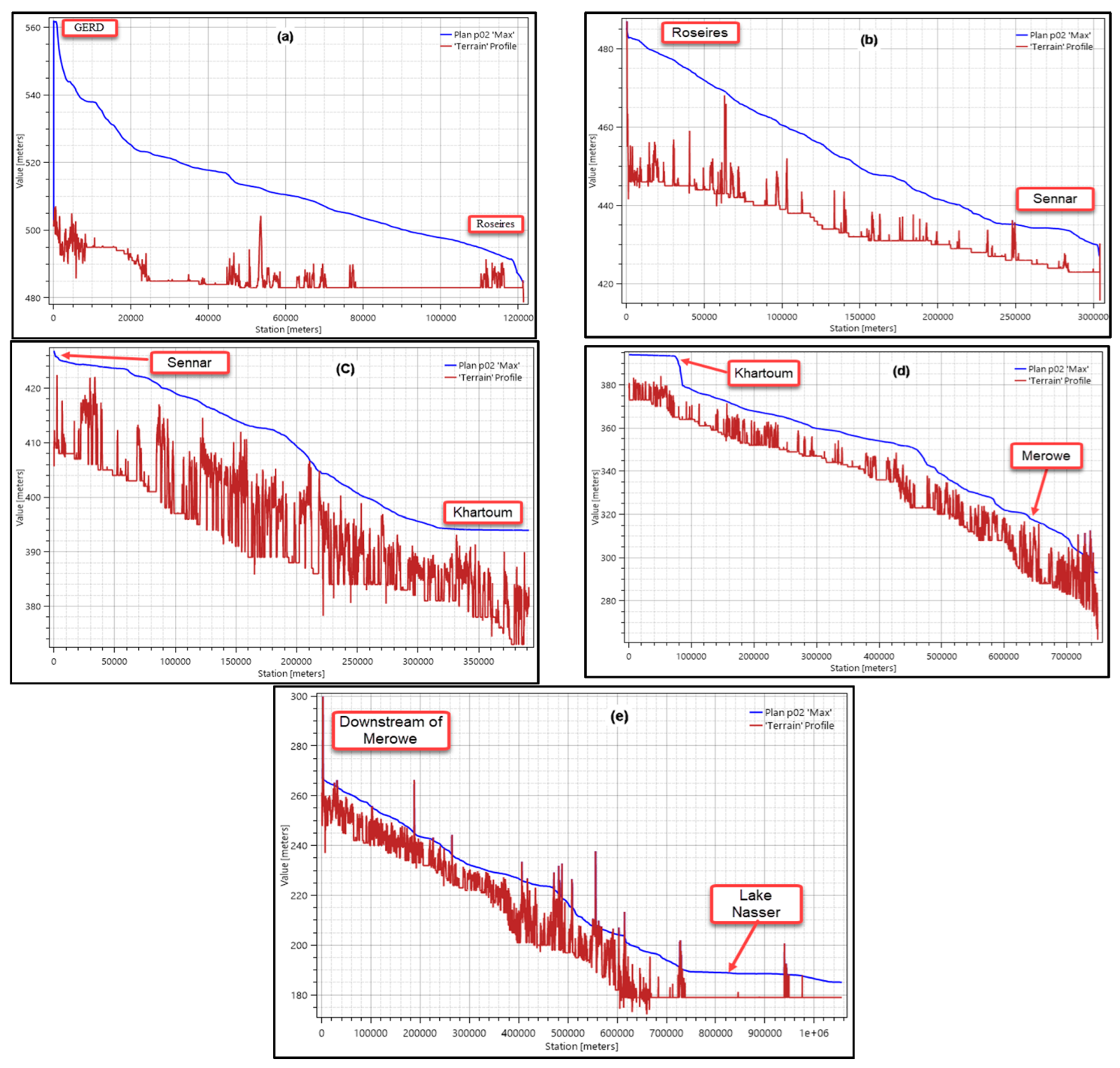
| Roseires dam | 123 | 5 | 490 | 11 | 8 |
| Sennar dam | 420 | 1.4 | 429 | 7 | 76 |
| Khartoum | 809 | 1 | 394 | 11 | 240 |
| Merowe dam | 1582 | 1.3 | 320 | 20 | 572 |
| Lake Nasser, AHD | 2670 | 0.8 | 188 | 10 | 960 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eldeeb, H.M.; Ibrahim, A.; Mowafy, M.H.; Zeleňáková, M.; Abd-Elhamid, H.F.; Pietrucha-Urbanik, K.; Ghonim, M.T. Assessment of Dams’ Failure and Flood Wave Hazards on the Downstream Countries: A Case Study of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD). Water 2023, 15, 1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081609
Eldeeb HM, Ibrahim A, Mowafy MH, Zeleňáková M, Abd-Elhamid HF, Pietrucha-Urbanik K, Ghonim MT. Assessment of Dams’ Failure and Flood Wave Hazards on the Downstream Countries: A Case Study of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD). Water. 2023; 15(8):1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081609
Chicago/Turabian StyleEldeeb, Hazem M., Ali Ibrahim, Magdy H. Mowafy, Martina Zeleňáková, Hany F. Abd-Elhamid, Katarzyna Pietrucha-Urbanik, and Mahmoud T. Ghonim. 2023. "Assessment of Dams’ Failure and Flood Wave Hazards on the Downstream Countries: A Case Study of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD)" Water 15, no. 8: 1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081609
APA StyleEldeeb, H. M., Ibrahim, A., Mowafy, M. H., Zeleňáková, M., Abd-Elhamid, H. F., Pietrucha-Urbanik, K., & Ghonim, M. T. (2023). Assessment of Dams’ Failure and Flood Wave Hazards on the Downstream Countries: A Case Study of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD). Water, 15(8), 1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081609










