Euryhalinity and Geographical Origin Aid Global Alien Crayfish Invasions
Abstract
1. Introduction
- to analyse whether the euryhalinity of American crayfishes was higher than that of crayfishes from other geographical regions;
- to determine global alien crayfish invasion in both fresh and saline waters, and assess their ability to tolerate, osmoregulate, reproduce and grow in different saline regimes.
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Alien Crayfishes
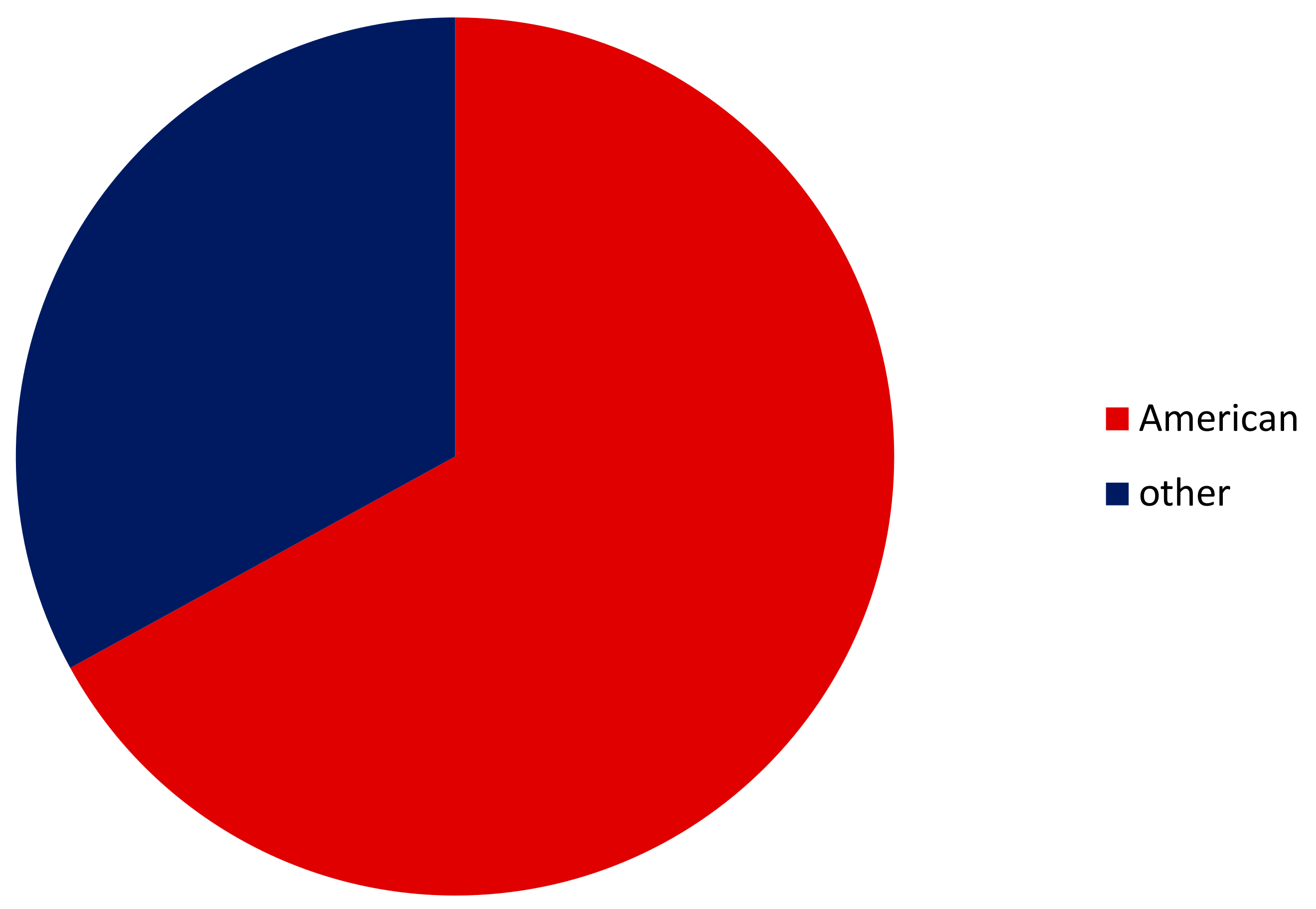
3.2. Euryhalinity of All Alien versus American Crayfishes
3.3. Distribution of Invasive Alien Crayfishes That Can Live in Freshwater and Saline Environments Based on Field Observations
3.4. Is Salinity a Barrier to the Dispersal of Crayfishes?
3.5. Experimental Evaluation of Salinity Tolerance and Osmoregulation
3.6. Experimental Evaluation of Growth in Fresh and in Saline Waters
3.7. Experimental Evaluation of Reproduction in Fresh and in Saline Waters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rode, A.L.; Babcock, L.E. Phylogeny of fossil and extant freshwater crayfish and some closely related Nephropid lobsters. J. Crust. Biol. 2003, 23, 418–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crandall, K.; Buhay, J.E. Global diversity of crayfish (Astacidae, Cambaridae, and Parastacidae-Decapoda) in freshwater. Hydrobiologia 2008, 595, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crandall, K.A.; De Grave, S. An updated classification of the freshwater crayfishes (Decapoda: Astacidea) of the world, with a complete species list. J. Crust. Biol. 2017, 37, 615–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowery, R. Growth, moulting, and reproduction. In Freshwater Crayfish: Biology, Management and Exploitation; Holdich, D.M., Lowery, R.S., Eds.; Croom Helm: London, UK, 1988; pp. 83–113. [Google Scholar]
- Crandall, K.A.; Harris, D.J.; Fetzner, J.W. The monophyletic origin of freshwater crayfish estimated from nuclear and mitochondrial DNA sequences. Proc. R. Soc. 2000, 267, 1679–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieluch, U.; Anger, K.; Aujolat, F.; Buchholz, F.; Charmantier-Daures, M.; Charmantie, G. Ontogeny of osmoregulatory structures and functions in the green crab Carcinus maenas (Crustacea, Decapoda). J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 207, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anger, K.; Spivak, E.; Luppi, T. Effects of reduced salinities on development and bioenergetics of early larval shore crab, Carcinus maenas. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1998, 220, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anger, K. Salinity as a key parameter in the larval biology of decapod crustaceans. Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 2003, 43, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, A.; Petrusek, A.; Kozak, P. Continental-wide distribution of crayfish species in Europe. Update and maps. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2014, 413, 05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szaniawska, A.; Dobrzycka-Krahel, A.; Jaszczołt, J. Spiny-cheek crayfish Orconectes limosus (Rafinesque, 1817) on its way to the open coastal waters of the Baltic Sea. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2017, 46, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GRIIS. Global Register of Introduced and Invasive Species. 2021. Available online: http://www.griis.org (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- CABI. Centre for Agriculture and Bioscience International. 2021. Available online: https://www.cabi.org (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- GBIF. Global Biodiversity Information Facility. 2021. Available online: https://www.gbif.org (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- NEMESIS. Smithsonian Environmental Research Center’s National Estuarine and Marine Exotic Species Information System. 2021. Available online: https://invasions.si.edu/nemesis (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Venice System. Symposium on the classification of brackish waters, Venice, 8–14 April 1958. Arch. Oceanogr. Limnol. 1958, 11, 1–248. [Google Scholar]
- Souty-Grosset, C.; Holdich, D.M.; Noël, P.Y.; Reynolds, J.D.; Haffner, P. (Eds.) Atlas of Crayfish in Europe; Patrimoines naturels, 64; Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle: Paris, France, 2006; 187p. [Google Scholar]
- Burba, A. Orconectes limosus found along the Lithuanian Coastal zone of the Baltic Sea. Crayfish News IAA Newsl. 2008, 30, 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wiktor, J. Rak Amerykański Cambarus Limosus Raf. Wszechświat. 1955, pp. 31–32. Available online: http://rcin.org.pl/Content/23966/WA058_36365_K14248_Kat-Faun-Polski-t53.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2022).
- Gajewski, Z.; Terlecki, W. Raki; PWRiL: Warszawa, Poland, 1956; 196p. [Google Scholar]
- Żmudziński, L. Crustacean decapods (Decapoda) of the Baltic Sea. Przegląd Zool. 1961, 5, 352–360. [Google Scholar]
- Jażdżewski, K.; Konopacka, A. Survey and distribution of Crustacea, Malacostraca in Poland. Crustaceana 1993, 65, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruszka, P. The river Odra estuary as a gateway for alien species immigration to the Baltic Sea basin. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 1999, 27, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaszczołt, J.; Szaniawska, A. The spiny-cheek crayfish Orconectes limosus (Rafinesque, 1817) as an inhabitant of the Baltic Sea—Experimental evidences from its invasions of brackish waters. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2011, 40, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- iswinoujscie.pl. Był Bóbr, Teraz Są Raki. 2021. Available online: http://www.iswinoujscie.pl (accessed on 27 March 2021).
- Jansen, W.; Geard, N.; Mosindy, T.; Olson, G.; Turner, M. Relative abundance and habitat association of three crayfish (Orconectes virilis, O. rusticus, and O. immunis) near an invasion front of O. rusticus, and long-term changes in their distribution in Lake of the Woods, Canada. Aquat. Invasions 2009, 4, 627–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, K.M.; Green, R.H. Seasonal patterns in trap catches of the crayfish Cambarus bartoni and Orconectes virilis in six south-central Ontario lakes. Can. J. Zool. 1993, 71, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, L.M.; Warren, A.H. A new crayfish of the genus Orconectes Cope, 1872 from southern New England (Crustacea: Decapoda: Cambariidae). Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash 2008, 121, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, L.M.; Adams, L.; Anderson, E.; Basile, M.; Gottardi, E.; Buckholt, M.A. Genetic and morphological evidence for substantial hidden biodiversity in a freshwater crayfish species complex. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 48, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipová, L.; Holdich, D.M.; Lesobre, J.; Grandjean, F.; Petrusek, A. Cryptic diversity within the invasive virile crayfish Orconectes virilis (Hagen, 1870) species complex: New lineages recorded in both native and introduced ranges. Biol. Invasions 2010, 12, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzycka-Krahel, A.; Skóra, M.; Raczyński, M.; Szaniawska, A. Signal crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus—Distribution and invasion in the southern Baltic coastal river. Pol. J. Ecol. 2017, 65, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cukersis, J. Presnovodnje Raki (Freshwater Crayfishes); Mokslas Publish: Vilnius, Lithuania, 1989; 143p. [Google Scholar]
- Maguire, I.; Klobucar, G.I.V.; Marcic, Z.; Zanella, D. The first record of Pacifastacus leniusculus in Croatia. Crayfish News 2008, 30, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Petrusek, A.; Petruskova, T. Invasive American crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus (Decapoda: Astacidae) in the Morava River (Slovakia). Biologia 2007, 62, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, J.M.; Bruxelas, S.; Bochechas, J.; Costa, A.M. Freshwater crayfish in Portugal: A new Astacidae, Pacifastacus leniusculus (Dana), and less perspectives for the rehabilitation of the native. In Austropotamobius Pallipes. Actas do 2º Congresso Nacional de Conservação da Natureza; CD edition; Instituto de Conservação da Natureza: Lisboa, Portugal, 2001; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardo, J.M.; Costa, A.M.; Bruxelas, S.; Teixeira, A. Dispersal and coexistence of two non-native crayfish species (Pacifastacus leniusculus and Procambarus clarkii) in NE Portugal over a 10-year period. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2011, 401, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundquist, J.C.; Goldman, C.R. Growth and food conversion efficiency of juvenile Pacifastacus leniusculus along a salinity gradient. Freshw. Crayfish 1978, 4, 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- NOBANIS. European Network on Invasive Species. 2021. Available online: https://www.nobanis.org (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Walls, J.G. Crawfishes of Louisiana; Louisiana State University Press: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2009; 240p. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, C.A.; Schuster, G.A.; Wylie, D.B. Field Guide to Crayfishes of the Midwest; Illinois Natural History Survey Press: Champaign, IL, USA, 2015; pp. 130–131. [Google Scholar]
- Sharfstein, B.A.; Chafin, C. Red swamp crawfish: Short-term effects of salinity on survival and growth. Prog Fish Cult 1979, 41, 156–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oficialdegui, F.J.; Clavero, M.; Sánchez, M.I.; Green, A.J.; Boyero, L.; Michot, T.C.; Klose, K.; Kawai, T.; Lejeusne, C. Unravelling the global invasion routes of a worldwide invader, the red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Freshw. Biol. 2019, 64, 1382–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Torrijos, L.; Correa-Villalona, A.J.; Pradillo, A.; Diéguez-Uribeondo, J. Coexistence of two invasive species, Procambarus clarkii and Aphanomyces astaci, in brackish waters of a Mediterranean Coastal Lagoon. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 8, 622434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalici, M.; Chiesa, S.; Scuderi, S.; Celauro, D.; Gibertini, G. Population structure and dynamics of Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852) in a Mediterranean brackish wetland (Central Italy). Biol. Invasions 2010, 12, 1415–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.A.; Pereira, T. Um novo Astacidae para a fauna portuguesa: Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852). Bol. Inst. Nac. Investig. Pescas 1981, 6, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Fidalgo, M.L.; Carvalho, A.P.; Santos, P. Population dynamics of the red swamp crayfish, Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852) from the Aveiro region, Portugal (Decapoda, Cambaridae). Crustaceana 2001, 74, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, A.M.; Costa, A.C. Introduction of the red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii (Crustacea, Decapoda) in São Miguel, Azores, Portugal. Arquipélago. Life Mar. Sci. 1994, 12, 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Maciaszek, R.; Bonk, M.; Strużyński, W. New records of the invasive red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852) (Decapoda: Cambaridae) from Poland. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2019, 420, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, H.H. On the distribution of the crayfish genus Procambarus (Decapoda: Cambaridae). J. Crust. Biol. 1984, 4, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, H.H., Jr. An illustrated checklist of the American crayfishes (Decapoda: Astacidae, Cambaridae, and Parastacidae). Smithson. Contrib. Zool. 1989, 1–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vershinina, T. The blue crayfish. Rybolov. Rybovod. 1983, 9, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Shuranova, Z.P.; Burmistrov, Y.M. The Neurophysiology of the Crayfish; Nauka: Moskva, Rossia, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Patoka, J.; Kalous, L.; Kopecky, O. Risk assessment of the crayfish pet trade based on data from the Czech Republic. Biol. Invasions 2014, 16, 2489–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotovska, G.; Khrystenko, D.; Patoka, J.; Kouba, A. East European crayfish stocks at risk: Arrival of non-indigenous crayfish species. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2016, 417, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiperth, A.; Gal, B.; Kuříková, P.; Langrová, I.; Kouba, A. Risk assessment of pet-traded decapod crustaceans in Hungary with evidence of Cherax quadricarinatus (von Martens, 1868) in the wild. North-West. J. Zool. 2019, 15, 42–47, Article No: e171303. [Google Scholar]
- Ojaveer, H.; Jaanus, A.; MacKenzie, B.R.; Martin, G.; Olenin, S.; Radziejewska, T.; Telesh, I.; Zettler, M.L.; Zaiko, A. Status of Biodiversity in the Baltic Sea. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubart, C.D.; Diesel, R. Osmoregulation and the transition from marine to freshwater and terrestrial life: A comparative study of Jamaican crabs of the genus Sesarma. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1999, 145, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łapucki, T.; Normant, M. Physiological responses to salinity changes of the isopod Idotea chelipes from the Baltic brackish waters. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2008, 149, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, B.T.; Bailey, P.; Edwards, R.; Hortle, K.; James, K.; McMahon, A.; Meredith, C.; Swadling, K. A review of the salt sensitivity of the Australian freshwater biota. Hydrobiologia 1991, 210, 105–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteley, N.M.; Scott, J.L.; Breeze, S.J.; McCann, L. Effects of water salinity on acid–base balance in decapod Crustaceans. J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 204, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meineri, E.; Rodriguez-Perez, H.; Hilaire, S.; Mesleard, F. Distribution and reproduction of Procambarus clarkii in relation to water management, salinity and habitat type in the Camargue. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2014, 24, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesely, L.; Hrbek, V.; Kozák, P.; Buřič, M.; Sousa, R.; Kouba, A. Salinity tolerance of marbled crayfish Procambarus fallax f. virginalis. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2017, 418, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paital, B.G.; Chainy, B.N. Antioxidant defenses and oxidative stress parameters in tissues of mud crab (Scylla serrata) with reference to changing salinity. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2010, 151, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppäkoski, E.; Olenin, S. Non-native species and rates of spread: Lessons from the brackish Baltic Sea. Biol. Invasions 2000, 2, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ginneken, V.J.T.; Maes, G.E. The European eel (Anguilla anguilla, Linnaeus), its life cycle, evolution and reproduction: A literature review. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2005, 15, 367–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornis, M.S.; Mercado-Silva, N.; Vander Zanden, M.J. Twenty years of invasion: A review of round goby Neogobius melanostomus biology, spread and ecological implications. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 80, 235–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdich, D.M.; Harlioglu, M.M.; Firkins, I. Salinity Adaptations of Crayfish in British Waters with particular reference to Austropotamobius pallipes, Astacus leptodactylus and Pacifastacus leniusculus. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1997, 44, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schram, F.R. The fossil record and evolution of the Crustacea. In Biology of Crustacea; Abele, L.G., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1982; pp. 93–147. [Google Scholar]
- Mantel, L.H.; Farmer, L.L. Osmotic and ionic regulation. In The Biology of Crustacea; Bliss, D.E., Mantel, L.H., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1983; Volume 5, pp. 54–126. [Google Scholar]
- Péqueux, P.A. Osmotic regulations in crustaceans. J. Crust. Biol. 1995, 15, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsom, J.E.; Davis, K.B. Osmotic responses of haemolymph in red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) and white river crayfish (P. zonangulus) to changes in temperature and salinity. Aquaculture 1994, 126, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casellato, S.; Masiero, L. Does Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852) represent a threat for estuarine and lagoonal ecosystems for northeastern Adriatic coast (Italy)? J. Life Sci. 2011, 5, 549–554. [Google Scholar]
- Bissattini, A.M.; Traversetti, L.; Bellavia, G.; Scalici, M. Tolerance of increasing water salinity in the red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852). J. Crustac. Biol. 2015, 35, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörr, A.J.M.; Scalici, M.; Caldaroni, B.; Magara, G.; Scoparo, M.; Goretti, E.; Elia, A.C. Salinity tolerance of the invasive red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852). Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 2065–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerley, D.E.; Pritchard, A.W. Osmotic regulation in the crayfish, Pacifastacus leniusculus, stepwise acclimated to dilutions of seawater. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1967, 20, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerley, D.E. Osmotic and Ionic Regulation in the North American Crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus (Dana). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Oregon State, Corvallis, OR, USA, 1970; 108p. [Google Scholar]
- Susanto, G.N.; Charmantier, G. Ontogeny of osmoregulation in the crayfish Astacus leptodactylus. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 2000, 73, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherkasina, N.Y.A. Distribution and biology of crayfishes of genus Astacus (Crustacea, Decapoda, Astacidae) in the Turkmen waters of the Caspian Sea. Freshw. Crayfish 1975, 2, 553–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köksal, G. Astacus leptodactylus in Europe. In Freshwater Crayfish: Biology, Management and Exploitation; Holdich, D.M., Lowery, R.S., Eds.; Chapman Hall: London, UK, 1988; pp. 365–400. [Google Scholar]
- Yildiz, H.Y.; Köksal, G.; Benli, A.C.K. Physiological Response of the crayfish Astacus leptodactylus to saline water. Crustaceana 2004, 77, 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesni, M.A.; Shabanipour, N.; Zahmatkesh, A.; Toutouni, M.M. Effects of temperature and salinity on survival and moulting of the narrow-clawed crayfish, Astacus leptodactylus Eschscholtz, 1823 (Decapoda, Astacidea). Crustaceana 2009, 82, 1495–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jussila, J.; Paganini, M.; Mansfield, S.; Evans, L.H. On physiological responses, plasma glucose, total hemocyte counts and dehydration, of marron (Cherax tenuimanus (Smith)) to handling and transportation under simulated conditions. Freshw. Crayfish 1999, 12, 154–167. [Google Scholar]
- Elia, A.C.; Dörr, A.J.M.; Mastrangelo, C.; Prearo, M.; Abete, M.C. Glutathione and antioxidant enzymes in the hepatopancreas of crayfish Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852) of lake Trasimeno (Italy). Bull. Français Pêche Piscic. 2006, 380–381, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, G. Functional anatomy. In Biology of Freshwater Crayfish; Holdich, D.M., Ed.; Blackwell Science: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 64–87. [Google Scholar]
- Sarver, R.G.; Flynn, M.A.; Hollyday, C.W. Renal Na, K-ATPase and osmoregulation in the crayfish, Procambarus clarkii. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Physiol. 1994, 107, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanawi, J.; Saoud, I.P. Molting, reproductive biology, and hatchery management of redclaw crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus (von Martens 1868). Aquaculture 2012, 358, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, S.S.; Likens, G.E.; Pace, M.L.; Reimer, J.E.; Maas, C.M.; Galella, J.G.; Utz, R.M.; Duan, S.; Kryger, J.R.; Yaculak, A.M.; et al. Freshwater salinization syndrome: From emerging global problem to managing risks. Biogeochemistry 2021, 154, 255–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | Origin [12,13] | Habitat | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freshwater [11] | Saline [11,12,14] | |||
| 1 | Austropotamobius fulcisianus orientalis (Karaman, 1929) | Europe | + (I) | – |
| 2 | Astacus astacus (Linnaeus, 1758) | Europe | + (UK) | – |
| 3 | Cherax albidus (Clark, 1936) | Australia | + (SA) | – |
| 4 | Cherax destructor (Clark, 1936) | Australia | + (Ch, G, S, M, SA) | – |
| 5 | Cherax quadricarinatus (von Martins, 1868) | Australia | + (A, B, Ch, C, G, Eq, Is, Ja, Ma, Me, Mal, Na, P, Ph, Pa, Si, Slo, Th, Tri, V, SA, Z, Zi) | – |
| 6 | Cherax tenuimenus (Smith, 1912) | Australia | + (Ch, G, Mau, Mal, NZ, Pan, P, T, SA) | – |
| 7 | Faxonius immunis (Hagen, 1870) | North America | + (G, F, Sw) | – |
| 8 | Faxonius juvenilis (Hagen, 1870) | North America | + (F) | – |
| 9 | Faxonius limosus (Rafinesque, 1817) | North America | + (Au, Be, Bel, Cro, F, G, Hu, I, La, Lux, Li, E, Mar, Ne, Po, Ro, S, Se, Slo, Sl, Sw, Swit, UK) | + [12] |
| 10 | Faxonius obscurus (Hagen, 1870) | North America | + (Ca) | – |
| 11 | Faxonius rusticus (Girard, 1852) | North America | + (Sw) | – |
| 12 | Faxonius virilis (Hagen, 1870) | North America | + (Sw) | + (USA) [14] |
| 13 | Pacifastacus leniusculus (Dana, 1852) | North America | + (Au, Be, Swit, Cz, G, D, E, S, Fi, F, UK, Gr, Cro, Hu, I, J, Li, Lux, La, No, Po, Por, Ro, Sw, Slo, Sl) | + (USA) [12,14] |
| 14 | Pontastacus (Astacus) leptodactylus (Eschscholtz, 1823) | Eastern Europe | + (Be, Ma, Ne, Sw, Swit, U, Cz, G, D, Fi, UK, I, La, R) | + (Swit, U, Cz, G, D, Fi, F, UK, I, La, R) [11] |
| 15 | Procambarus acutus (Girard, 1852) | North America | + (UK, Ne, Sw, Eg) | – |
| 16 | Procambarus alleni (Faxon, 1884) | North America | + (Eq) | – |
| 17 | Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852) | North America | + (Sw, A, Be, Br, Bl, Swit, Ch, CR, C, G, DR, Eq, Eg, S, F, UK, Ge, Gu, Is, I, J, K, Mar, Ma, Ni, Nic, Ne, Pan, Ph, Po, Por, Su, Th, Ug, Ve, V, SA, Z, Zi) | + (Au, Be, Br, Bl, Swi, Ch, Co, CR, C, G, Do, Eq, Eg, S, F, UK, Ge, Gu, Is, I, J, K, Ma, Ni, Nic, Ne, Pan, Ph, Po, Por, Su, Th, Ug, Ve, V, SA, Z, Zi [11] |
| 18 | Procambarus cubensis (Erichson, 1846) | Central America | + (G) | + (G) [11] |
| 19 | Procambarus fallax (Hagen, 1870) | North America | + (G, E, Ne, Po, Ro, U, Sw) | – |
| 20 | Procambarus virginalis (Lyko, 2017) | North America | + (Mad, Mal, Ne) | – |
| 21 | Procambarus zonangulus (Hobbs and Hobbs III, 1990) | North America | + (Eg) | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dobrzycka-Krahel, A.; Fidalgo, M.L. Euryhalinity and Geographical Origin Aid Global Alien Crayfish Invasions. Water 2023, 15, 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030569
Dobrzycka-Krahel A, Fidalgo ML. Euryhalinity and Geographical Origin Aid Global Alien Crayfish Invasions. Water. 2023; 15(3):569. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030569
Chicago/Turabian StyleDobrzycka-Krahel, Aldona, and Maria Leonor Fidalgo. 2023. "Euryhalinity and Geographical Origin Aid Global Alien Crayfish Invasions" Water 15, no. 3: 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030569
APA StyleDobrzycka-Krahel, A., & Fidalgo, M. L. (2023). Euryhalinity and Geographical Origin Aid Global Alien Crayfish Invasions. Water, 15(3), 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030569






