Enrichment of Manganese at Low Background Level Groundwater Systems: A Study of Groundwater from Quaternary Porous Aquifers in Changping Region, Beijing, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
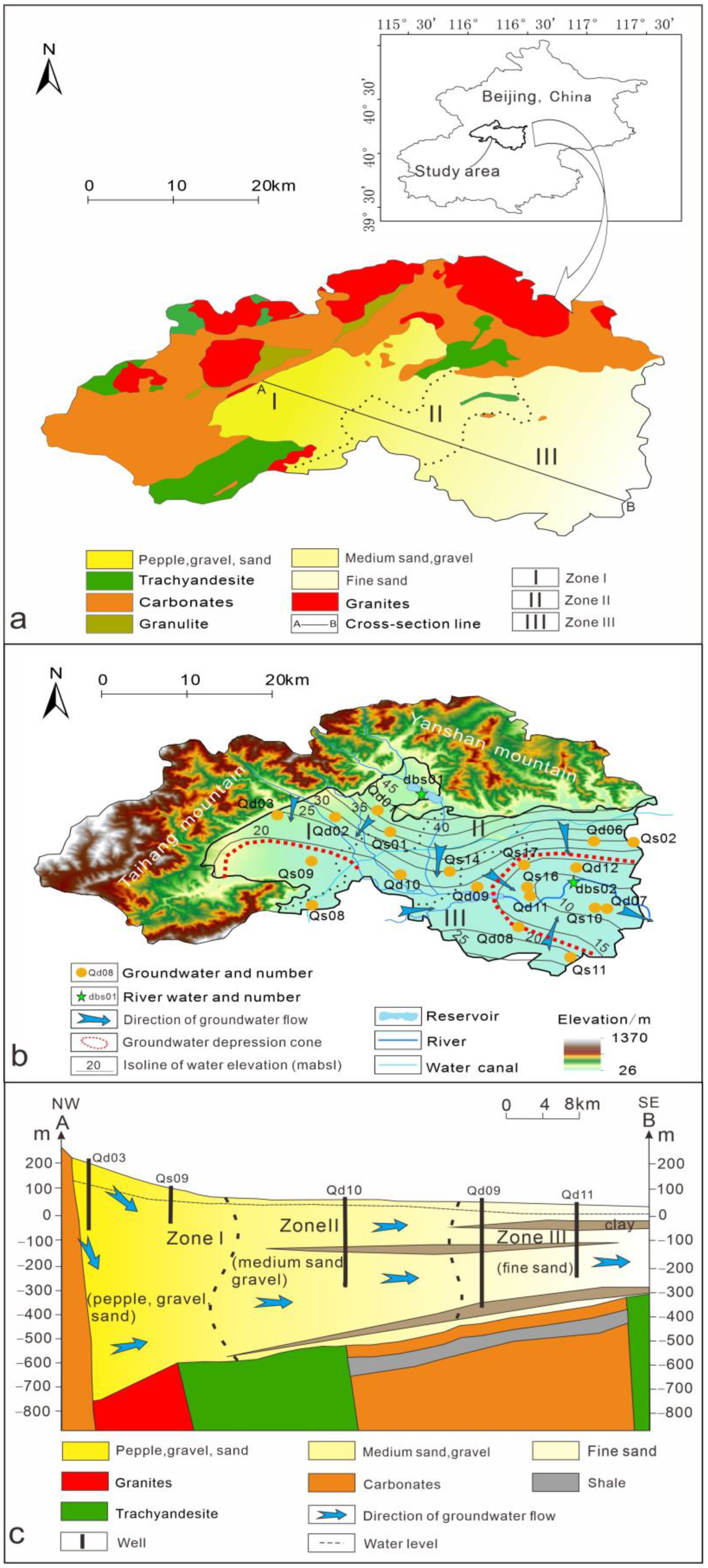
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Measurement
2.3. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
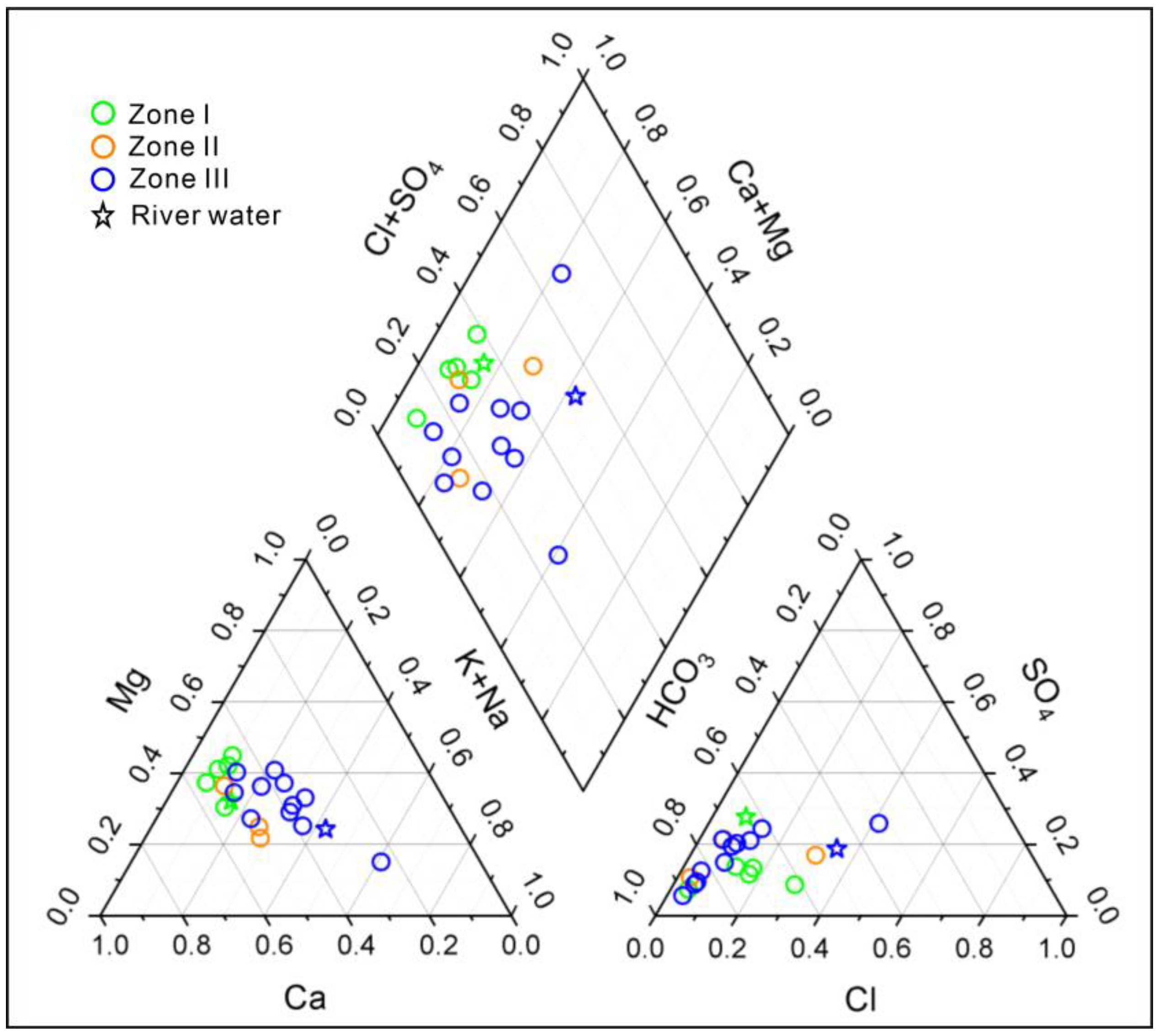
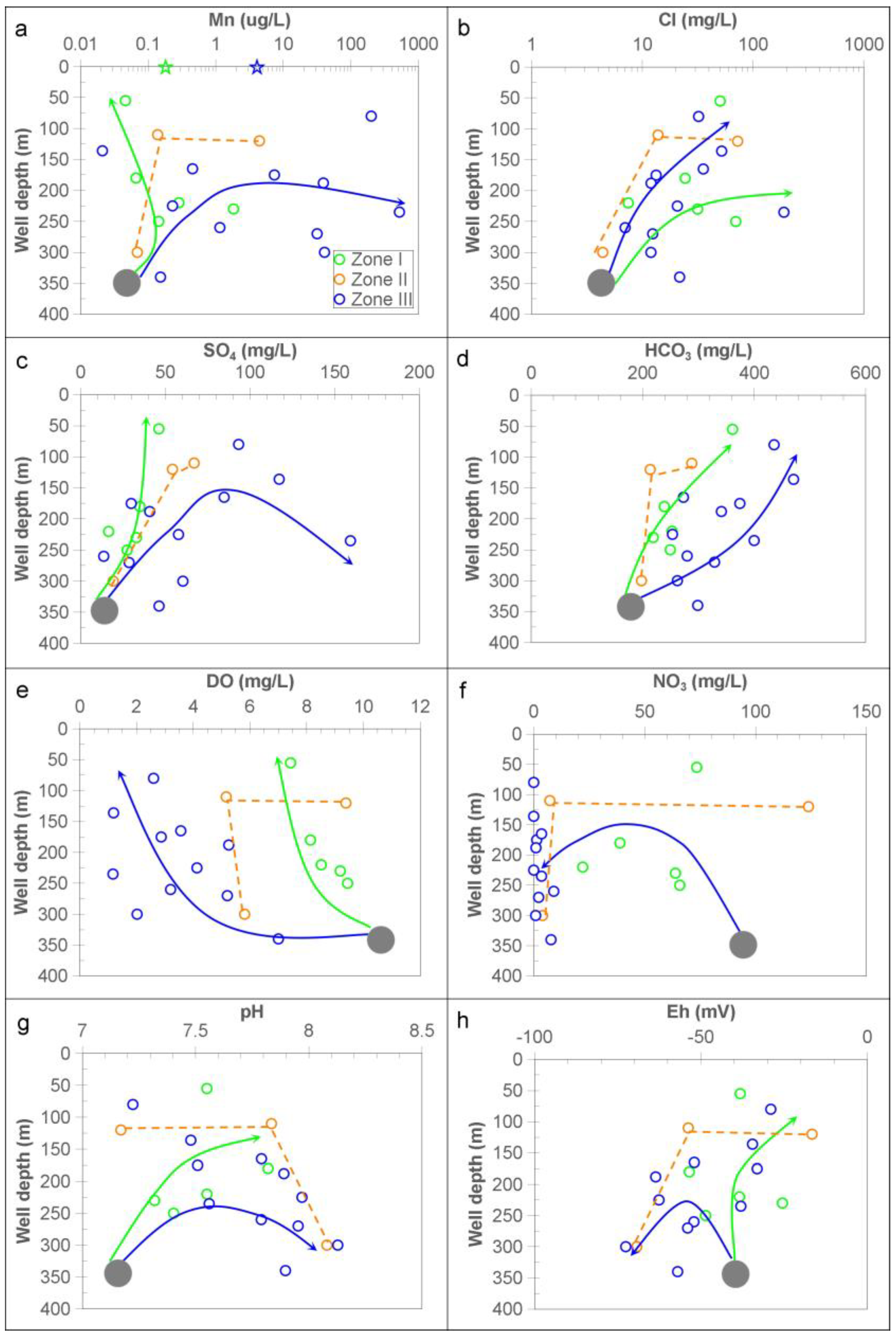
3.1. Hydrochemistry and Groundwater
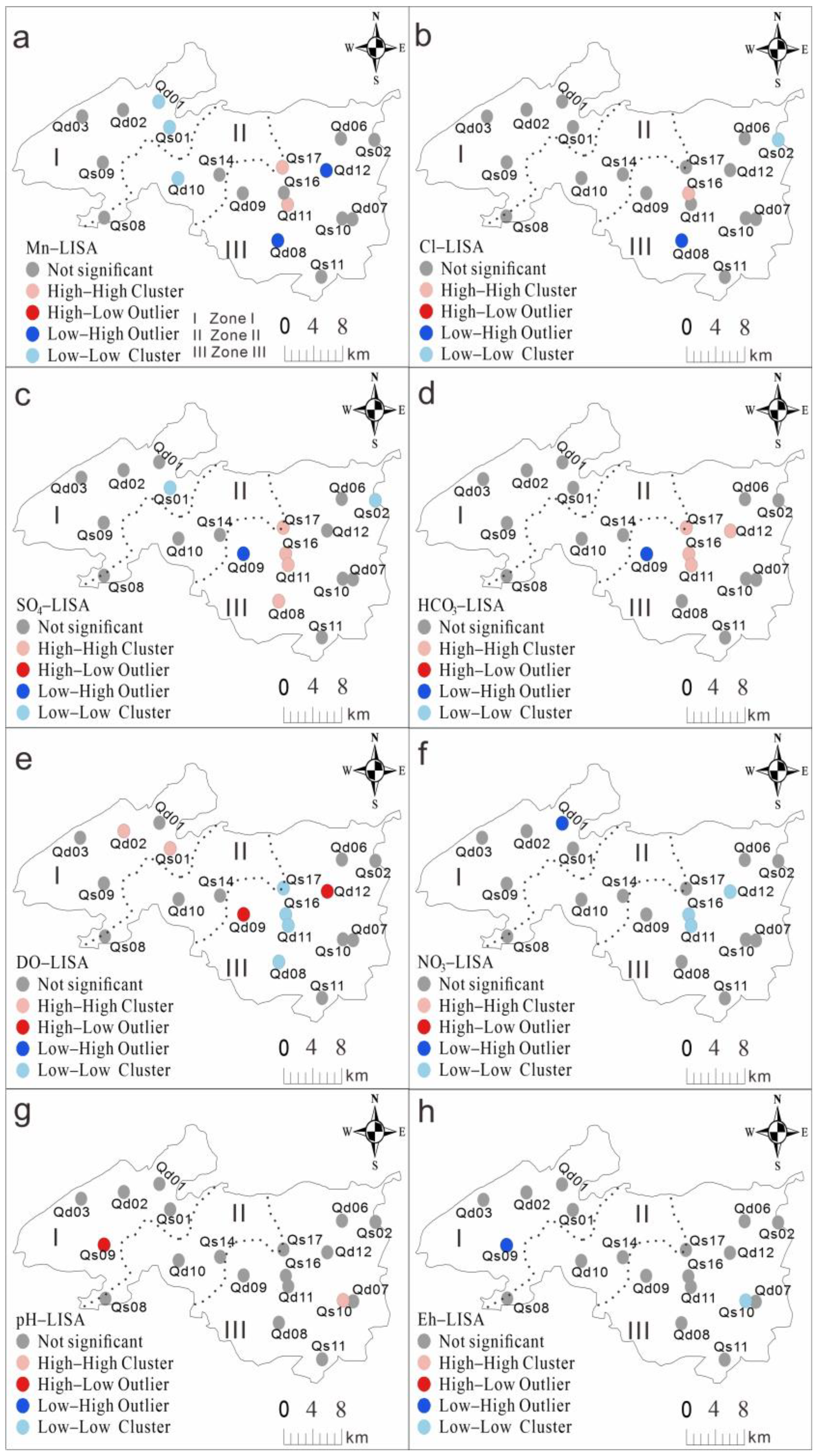
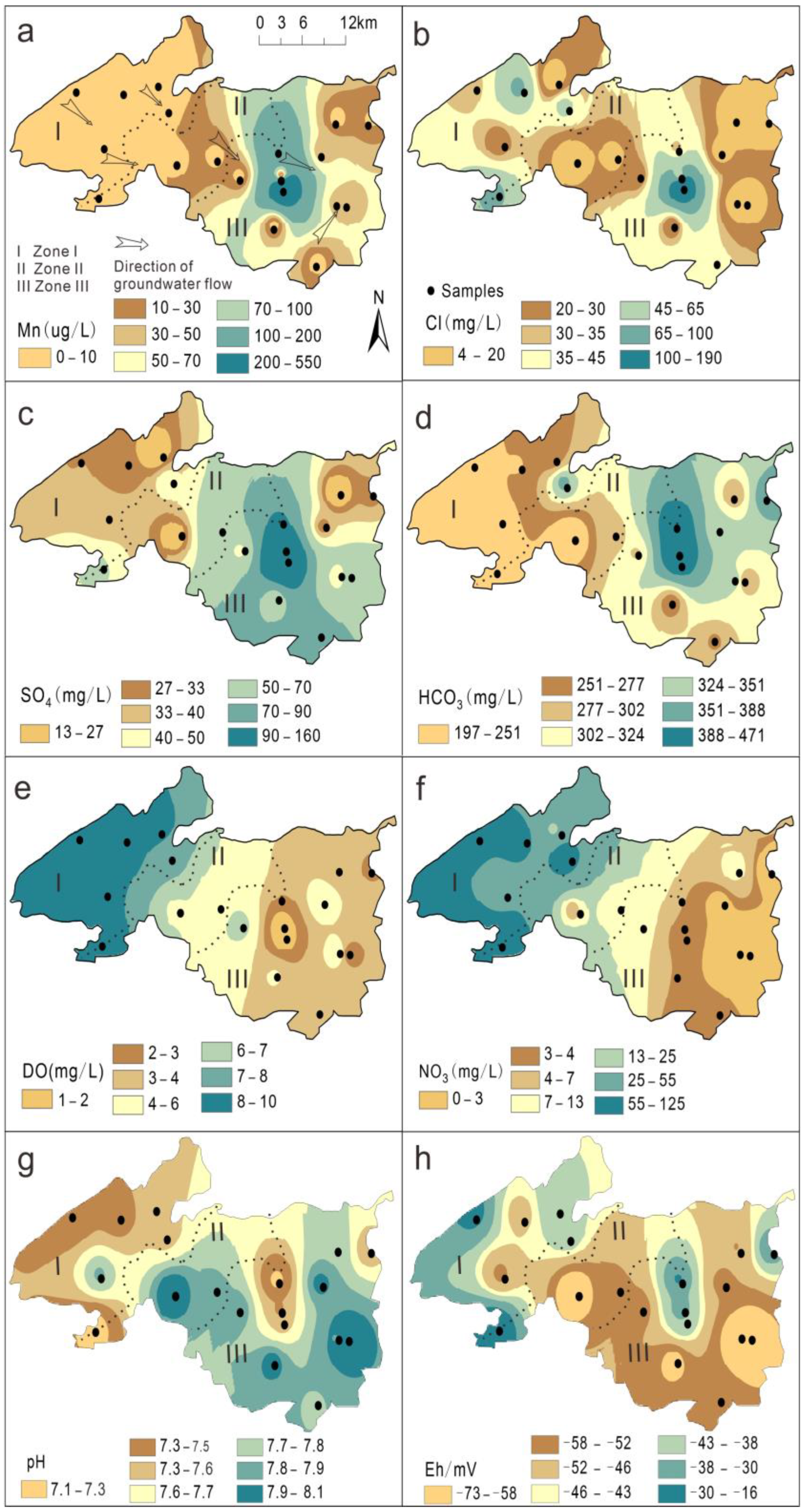
3.2. Spatial Correlation of Data and Ordinary Kriging Interpolation
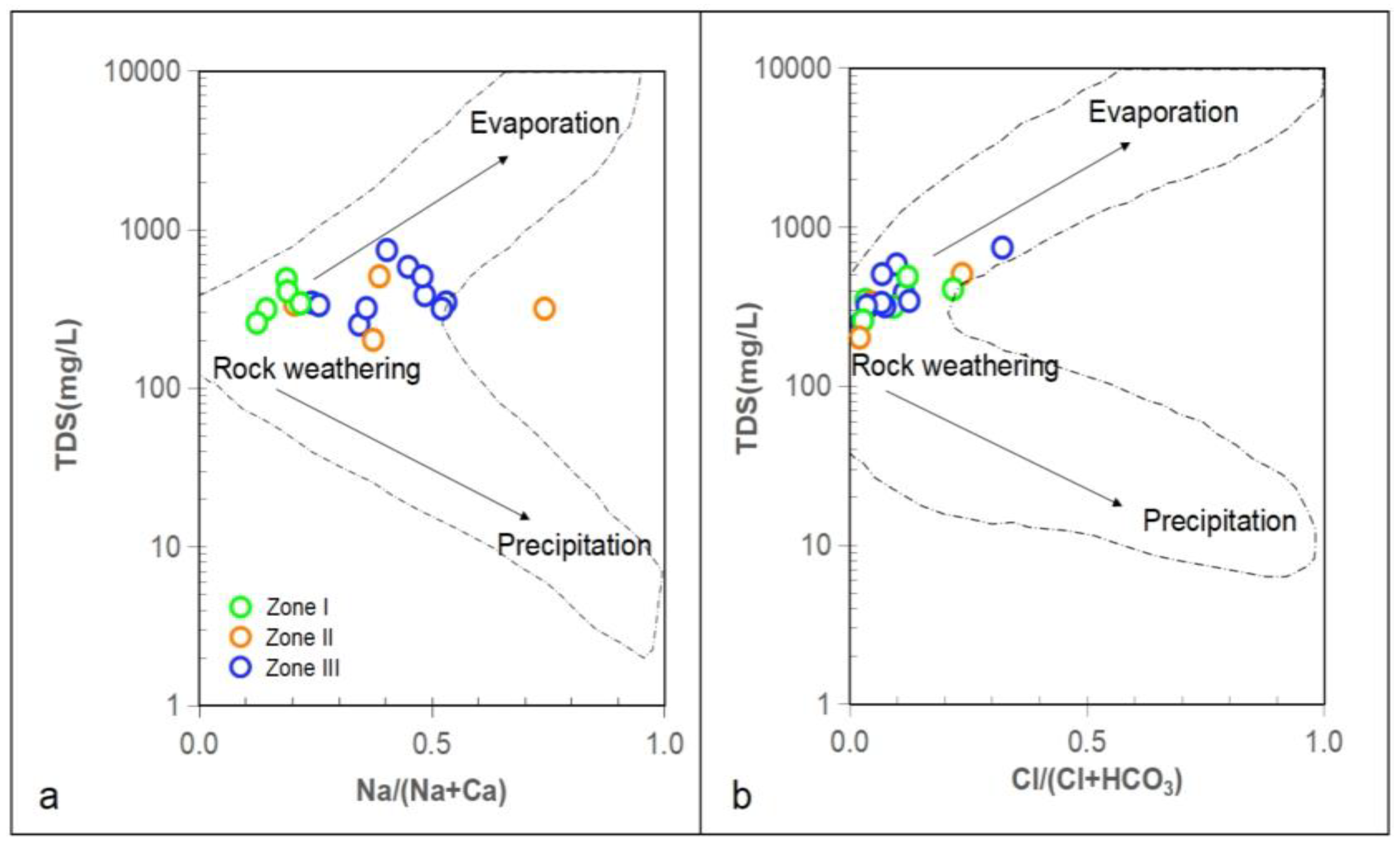
3.3. Potential Mn Sources
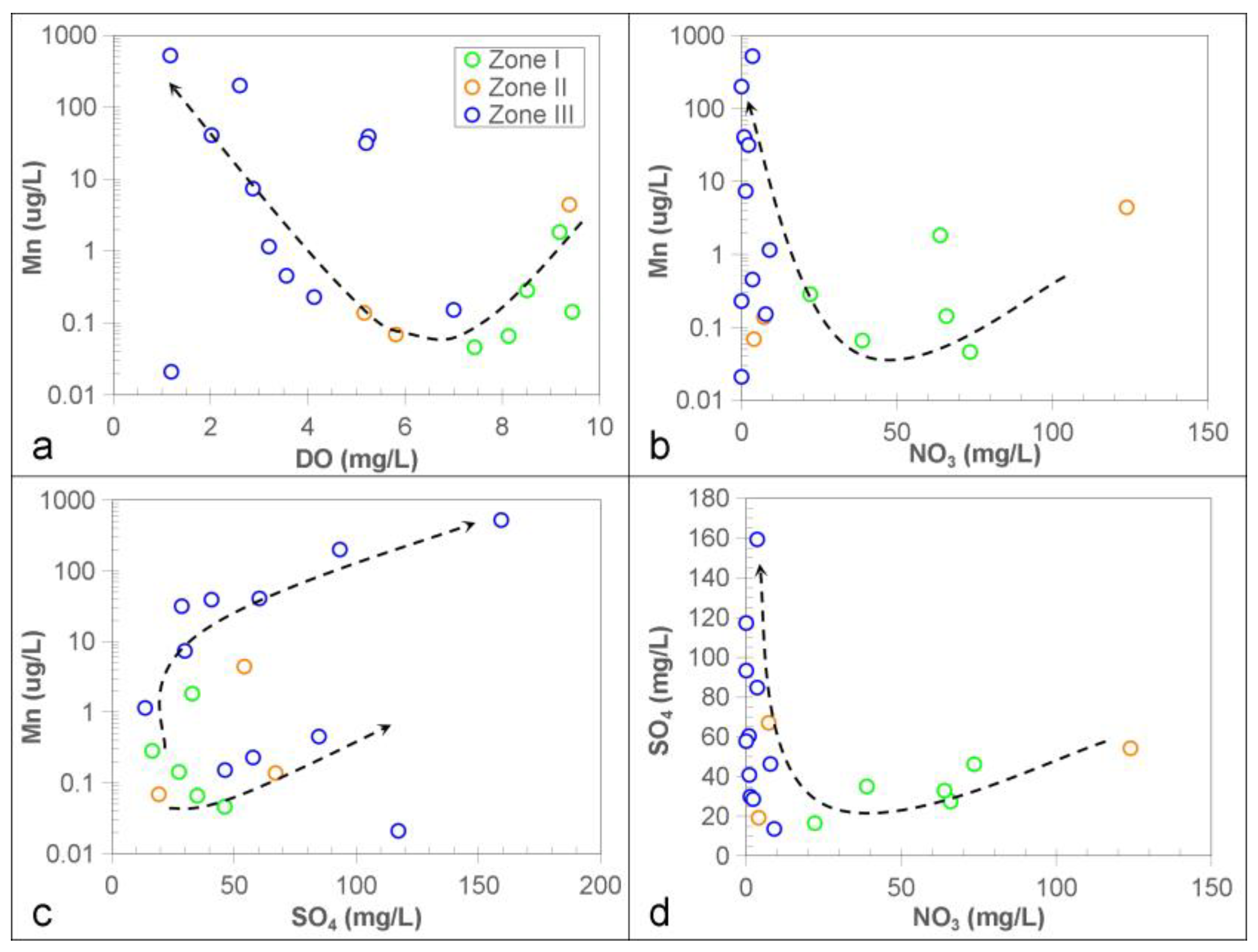
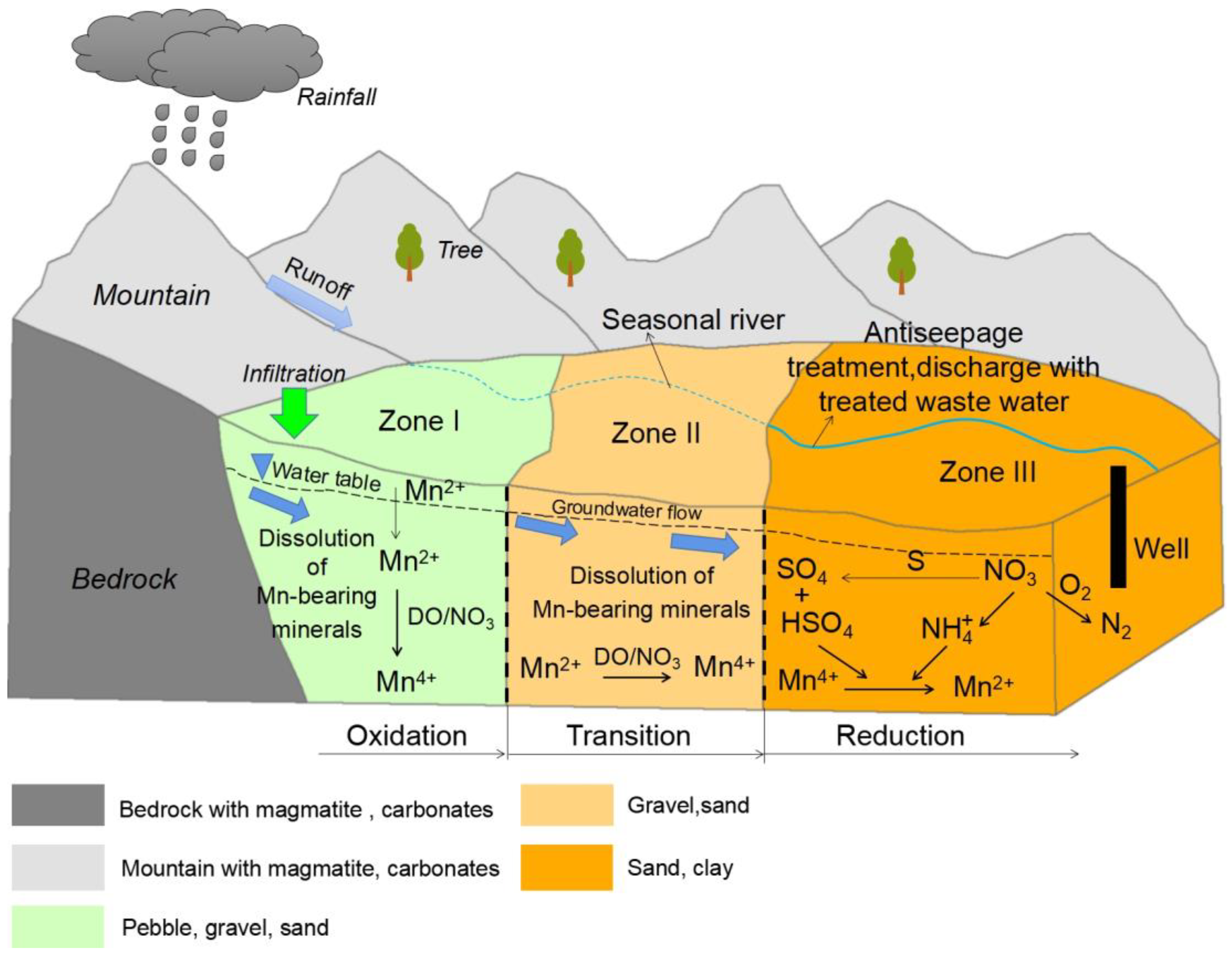
3.4. Redox Conditions for Controlling Groundwater Mn
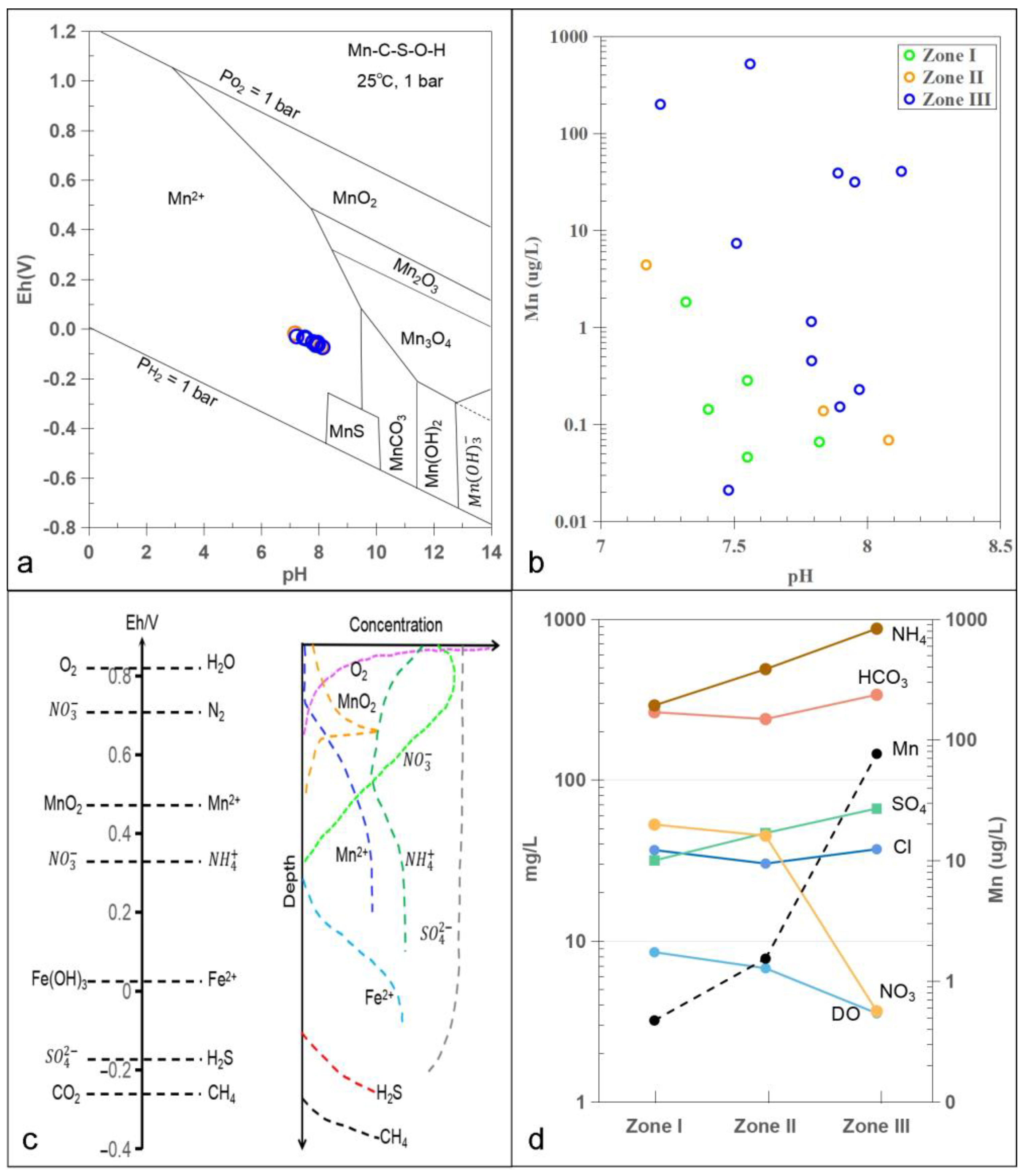
3.5. Implication for Groundwater Environment and Management
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anne, K.; Hannu, K.; Tarja, H.; Birgitta, B.; Sirpa, H. Variation in Groundwater Manganese in Finland. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 1193–1211. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Wang, X.; Yang, P. Analysis on the Characteristics of Mn Excess the Standard in Shallow Groundwater in the Plain Area of Northwestern Shandong Province. Shandong Land Resour. 2021, 37, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, G.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y. Elevated Manganese Concentrations in Shallow Groundwater of Various Aquifers in a Rapidly Urbanized Delta, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joode, B.V.W.D.; Barbeau, B.; Bouchard, M.F.; Mora, A.M.; Skytt, A.; Córdoba, L.; Quesada, R.; Lundh, T.; Lindh, C.H.; Mergler, D. Manganese Concentrations in Drinking Water from Villages near Banana Plantations with Aerial Mancozeb Spraying in Costa Rica: Results from the Infants’ Environmental Health Study (ISA). Environ. Pollut. 2016, 215, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshetrimayum, K.S.; Hegeu, H. The State of Toxicity and Cause of Elevated Iron and Manganese Concentrations in Surface Water and Groundwater Around Naga Thrust of Assam-Arakan Basin, Northeastern India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.; Factor-Litvak, P.; Wasserman, G.A.; Liu, X.; Ahmed, E.; Parvez, F.; Slavkovich, V.; Levy, D.; Mey, J.; Van Geen, A.; et al. Manganese Exposure from Drinking Water and Children’s Classroom Behavior in Bangladesh. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1501–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillispie, E.C.; Austin, R.E.; Rivera, N.A.; Bolich, R.; Duckworth, O.W.; Bradley, P.; Amoozegar, A.; Hesterberg, D.; Polizzotto, M.L. Soil Weathering as an Engine for Manganese Contamination of Well Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9963–9971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Qualtiy; Word Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; p. 226. [Google Scholar]
- Anjum, A.; Biswas, S.; Rahman, M.; Rahman, A.; Siddique, A.E.; Karim, Y.; Aktar, S.; Nikkon, F.; Haque, A.; Himeno, S.; et al. Butyrylcholinesterasea Potential Plasma Biomarker in Manganese-induced Neurobehavioral Changes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 6378–6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, S.; Dodd, C.A.; Hekmatyar, S.K.; Filipov, N.M. Brain Deposition and Neurotoxicity of Manganese in Adult Mice Exposed via the Drinking Water. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.; Wasserman, G.A.; Liu, X.; Ahmed, E.; Parvez, F.; Slavkovich, V.; Levy, D.; Mey, J.; Van Geen, A.; Graziano, J.H.; et al. Manganese Exposure from Drinking Water and Children’s Academic Achievement. Neurotoxicology 2012, 33, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, D.E.; Kristensen, E.; Bo, T. The Iron and Manganese Cycles. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2005, 48, 269–312. [Google Scholar]
- Gilkes, R.J.; Mckenzie, R.M. Geochemistry and Mineralogy of Manganese in Soils. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on ‘Manganese in Soils and Plants’, Waite Agricultural Research Institute, The University of Adelaide, Glen Osmond, SA, Australia, 22–26 August 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Kiracofe, Z.A.; Henika, W.S.; Schreiber, M.E. Assessing the Geological Sources of Manganese in the Roanoke River Watershed, Virginia. Environ. Eng. Geosci. 2017, 23, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J.J. Manganese in Natural Waters and Earth’s Crust: Its Availability to Organisms. In Metal Ions in Biological Systems, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; Volume 37, pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Binda, G.; Pozzi, A.; Livio, F. An integrated interdisciplinary approach to evaluate potentially toxic element sources in a mountainous watershed. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 1255–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisbie, S.H.; Mitchell, E.J.; Dustin, H.; Maynard, D.M.; Sarkar, B. World Health Organization Discontinues Its Drinking-Water Guideline for Manganese. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 775–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewusi, A.; Sunkari, E.D.; Seidu, J.; Coffie-Anum, E. Hydrogeochemical characteristics, sources and human health risk assessment of heavy metal dispersion in the mine pit water–surface water–groundwater system in the largest manganese mine in Ghana. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 26, 102312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, P.; Malcolm, H.; Dobson, S. Manganese and Its Compounds: Environmental Aspects; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; pp. 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Mcmahon, P.B.; Belitz, K.; Reddy, J.E.; Johnson, T.D. Elevated Manganese Concentrations in United States Groundwater, Role of Land Surface-Soil-Aquifer Connections. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteller, M.V.; Kondratenko, N.; Exposito, J.L.; Medina, M.; Del Campo, M.A.M. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of a Volcanic-sedimentary Aquifer with Special Emphasis on Fe and Mn Content: A Case Study in Mexico. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 180, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homoncik, S.C.; Macdonald, A.M.; Heal, K.V.; Dochartaigh, B.E.O.; Ngwenya, B.T. Manganese Concentrations in Scottish Groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 2467–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hem, J.D. Study and Interpretation of the Chemical Characteristics of Natural Water, 3rd ed.; Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1985; pp. 84–88.
- Hem, J.D. Chemical Factors that Influence the Availability of Iron and Manganese in Aqueous Systems. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1972, 83, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, H.; Sun, L.; Yu, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J. Experimental Analysis of Preferential Flow and its Effect on Nitrate Nitrogen Migration in Soil of Farmland at Changping District in Beijing. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 11, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Han, P.; Mi, N. Analysis of Nitrogen Spatial Distribution of Groundwater in Changping District Based on GIS. Beijing Water 2014, 1, 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, S.; Ma, M.; Wang, Z. Preliminary Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Drinking Waters in Beijing. Huan Jing Kexue 2004, 25, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, G.; Wang, Q.; Huang, Q. Evaluation of groundwater quality in Changping piedmont plain of Beijing based on BP neural network. Trans. Chi. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 150–156. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Shao, J.; Gu, X.; Zhao, W.; Hao, Q. Characteristics of Groundwater Pollution of Changping Plain in Beijing. South-North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 13, 252–256. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Qi, J.; Wang, M. Seasonal Variations of Hydrochemical Characteristics of Groundwater in Changping Plain, Beijing. J. Resour. Ecol. 2017, 8, 655–663. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Lu, S. The Evaluation of Groundwater Quality in Changping District. Beijing Water 2013, 2, 32–34. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, E.M.; Zhang, N.; Han, P.L. Analysis of Present Situation of Groundwater Level in Changping District Based on GIS. Beijing Water 2014, 4, 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y. Petrology and Zicon U-Pb Chronology of Dykes in Nankou Beijing. Master’s Thesis, China Universtiy of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Shuai, G.; Chen, Y.; Tang, W. Volcanic Rock Age of Tiaojishan Formation in Shisanling-Xishan of Beijing and Its Geological Significance. Geol. Rev. 2016, 62, 807–826. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.J.; Liu, Y.X.; Feng, H.; Sun, X.H.; Meng, M.S.; Cao, L. Geochemical Characteristics of Mesoproterozoic Xiamaling Formation Shales in Beijing and their Geological Significance. Acta Petrol. Mineral. 2018, 37, 230–240. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Jin, S.; Ye, H.; Zheng, S. Geothermometric and Barometric Studies of Metamorphism of the Miyun Group Near Beijing. Geochimica 1984, 1, 50–60. [Google Scholar]
- Song, T. Sedimentary Facies Indicators and Sedimentary Environments Models of the Changcheng System of Mesoproterozoic in Ming Tombs District, Beijing. J. Palaeogeogr. 2007, 5, 461–472. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Cui, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Hao, Q. Spatial Variability of Groundwater Levels of Piedmont in the Changping District. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2015, 42, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. A Model Study of Groundwater Sustainabiltiy in Beijing Plain. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- McGrory, E.R.; Brown, C.; Bargary, N.; Williams, N.H.; Mannix, A.; Zhang, C.; Henry, T.; Daly, E.; Nicholas, S.; Petrunic, B.M.; et al. Arsenic contamination of drinking water in Ireland: A spatial analysis of occurrence and potential risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1863–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matheron, G. Principles of geostatistics. Econ. Geol. 1963, 58, 1246–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbarats, A.J.; Logan, C.E.; Hinton, M.J.; Sharpe, D.R. On the kriging of water table elevations using collateral information from a digital elevation model. J. Hydrol. 2002, 255, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Huo, Z.; Feng, S.; Mao, X.; Kang, S.; Chen, J.; Xu, J.; Steenhuis, T.S. Evaluation of spatial interpolation methods for groundwater level in an arid inland oasis, northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 1911–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabandeh, S.M.; Kholghi, M.; Hosseini, S.A. Groundwater quality assessment in two shallow aquifers with different hydrogeological characteristics (case study: Lenjanat and Babol-Amol aquifers in Iran). Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryafar, A.; Khosravi, V.; Karami, S. Groundwater quality assessment of Birjand plain aquifer using kriging estimation and sequential Gaussian simulation methods. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Chand, S. Spatial Distribution of TDS in Drinking Water of Tehsil Jampur using Ordinary and Bayesian Kriging. Pak. J. Stat. Oper. Res. 2015, 11, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nas, B.; Berktay, A. Groundwater quality mapping in urban groundwater using GIS. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 160, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, N.; Hussain, I.; Faisal, M.; Hussain, T.; Shad, M.Y.; Abdel-Salam, N.M.; Shabbir, J. Spatial Distribution of Sulfate Concentration in Groundwater of South-Punjab, Pakistan. Water Qual. Expo. Health 2015, 7, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundogdu, K.S.; Guney, I. Spatial analyses of groundwater levels using universal kriging. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 116, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillé, Y.; Dickson, M.M.; Espa, G.; Giuliani, D. Measuring the spatial balance of a sample: A new measure based on Moran’s I index. Spat. Stat. 2018, 23, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueiros, B.B.; Machado, W.; Lisboa, S.D.; Lacerda, L.D. Manganese Behavior at the Sediment-Water Interface in a Mangrove Dominated Area in Sepetiba Bay, SE Brazil. J. Coast. Res. 2003, 19, 550–559. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Q. Soil Geochemical Characteristics and Influencing Factors in Beijing Plain. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 45, 502–516. [Google Scholar]
- Koopmann, S.; Froellje, H.; Hamer, K.; Kubier, A.; Pichler, T. Iron-manganese-anomalies of Groundwater:Analysis of Influencing Processes. Grundwasser 2020, 25, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.B. Eh-pH Diagrams for Geochemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Farnsworth, C.E.; Voegelin, A.; Hering, J.G. Manganese Oxidation Induced by Water Table Fluctuations in a Sand Column. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aller, R.C. Sedimentary Diagenesis, Depositional Environments, and Benthic Fluxes. In Treatise on Geochemistry, 2nd ed.; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 293–334. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, N.F.; Gary, P.K.; Michael, L.B.; Nile, A.L.; Heath, G.R.; Doug, C.; Paul, D.; Hammond, D.E.; Blayne, H.; Val, M. Early Oxidation of Organic Matter in Pelagic Sediments of the Eastern Equatorial Atlantic: Suboxic Diagenesis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1979, 43, 1075–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, P.; Kuypers, M.M.M. Microbial Nitrogen Cycling Processes in Oxygen Minimum Zones. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2011, 3, 317–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, B.; Peng, Z.; Zhu, M.; Feng, J.; Xie, Y. Progress and Problems in Understanding Sedimentary Manganese Carbonate Metallogenesis. Miner. Depos. 2020, 39, 237–255. [Google Scholar]
- Vandenabeele, J.; Debeer, D.; Germonpre, R.; Vandesande, R.; Verstraete, W. Influence of Nitrate on Manganese Removing Microbial Consortia from Sand Filters. Water Res. 1995, 29, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutting, T.; Huygens, D.; Mueller, C.; Cleemput, O.V.; Godoy, R.; Boeckx, P. Functional Role of DNRA and Nitrite Reduction in a Pristine South Chilean Nothofagus Forest. Biogeochemistry 2008, 90, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Deng, K.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, R. Effect of Nitrogen forms on Reduction of Manganese Oxides in an Oxisol by Plant Root Exudates. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2017, 63, 1725–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotowski, T.; Burkowska, A. The Influence of Bacterial Reduction on Concentrations of Sulphates in Deep Aquifers in River Drainage Basin. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2011, 20, 379–386. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhuang, L.; Zhou, S. Direct Uptake of Electrode Electrons for Autotrophic Denitrification by Thiobacillus Denitrificans. Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 60, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrentó, C.; Cama, J.; Urmeneta, J.; Otero, N.; Soler, A. Denitrification of groundwater with pyrite and Thiobacillus denitrificans. Chem. Geol. 2010, 278, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schedel, M.; Trüper, H.G. Anaerobic Oxidation of Thiosulfate and Elemental Sulfur in Thiobacillus Denitrificans. Arch. Microbiol. 1980, 124, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Rock Type | Granite * | Dacite & | Monzonite * | Syenite * | Shale # | Limestone ## | Granulite @ | Trachy- Andesite & | Upper Crust a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn (mg/kg) | 310 | 620 | 850 | 930 | 700 | 540 | 2000 | 770 | 650 |
| Zone | Sample | Water Type | Well Depth | pH | Eh | DO | TDS | Na | K | Mg | Ca | Cl | SO4 | NO3 | HCO3 | Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m | mV | mg/L | µg/L | |||||||||||||
| Zone I | Qs01 | Quaternary water | 55 | 7.6 | −38.2 | 7.4 | 485 | 16.7 | 1.9 | 43.3 | 72.3 | 50.4 | 46.2 | 73.5 | 361 | 0.05 |
| Qs09 | 180 | 7.8 | −53.5 | 8.1 | 314 | 9.6 | 1.6 | 27.9 | 56.8 | 24.3 | 35.0 | 38.9 | 239 | 0.07 | ||
| Qd01 | 220 | 7.6 | −38.4 | 8.5 | 257 | 7.7 | 0.7 | 22.1 | 54.2 | 7.5 | 16.5 | 22.1 | 253 | 0.28 | ||
| Qd02 | 250 | 7.4 | −48.6 | 9.4 | 406 | 15.5 | 1.1 | 35.4 | 66.0 | 69.7 | 27.5 | 65.9 | 250 | 0.14 | ||
| Qd03 | 230 | 7.3 | −25.5 | 9.2 | 342 | 17.2 | 4.3 | 20.8 | 61.5 | 31.5 | 32.9 | 63.9 | 219 | 1.83 | ||
| dbs01 | River water | 8.3 | −83 | 9.7 | 238 | 13.2 | 3.1 | 16.1 | 43.1 | 13.1 | 59.5 | 2.0 | 175 | 0.19 | ||
| Zone II | Qs08 | Quaternary water | 120 | 7.2 | −16.6 | 9.4 | 505 | 45.4 | 1.6 | 18.8 | 71.7 | 72.5 | 54.2 | 123.9 | 214 | 4.42 |
| Qs14 | 110 | 7.8 | −53.8 | 5.2 | 335 | 15.6 | 1.2 | 25.7 | 60.1 | 13.9 | 67.0 | 7.3 | 288 | 0.14 | ||
| Qd10 | 300 | 8.1 | −69.3 | 5.8 | 201 | 22.9 | 1.1 | 11.8 | 38.2 | 4.4 | 19.2 | 4.0 | 198 | 0.07 | ||
| Zone III | Qs02 | Quaternary water | 175 | 7.5 | −33.1 | 2.9 | 345 | 19.6 | 0.5 | 32.1 | 61.2 | 13.3 | 29.9 | 1.4 | 374 | 7.37 |
| Qs10 | 188 | 7.9 | −63.6 | 5.3 | 346 | 50.1 | 0.5 | 26.4 | 44.2 | 12.0 | 40.8 | 1.0 | 341 | 39.10 | ||
| Qs11 | 165 | 7.8 | −52 | 3.6 | 385 | 47.4 | 1.4 | 25.1 | 50.2 | 35.5 | 84.7 | 3.5 | 273 | 0.45 | ||
| Qs16 | 136 | 7.5 | −34.5 | 1.2 | 580 | 58.3 | 0.6 | 44.0 | 71.3 | 52.0 | 117.2 | 0.0 | 471 | 0.02 | ||
| Qs17 | 80 | 7.2 | −29 | 2.6 | 504 | 61.6 | 0.4 | 29.9 | 66.7 | 32.2 | 93.3 | 0.0 | 436 | 200 | ||
| Qd06 | 260 | 7.8 | −52.1 | 3.2 | 251 | 22.7 | 0.6 | 14.3 | 43.1 | 7.0 | 13.6 | 9.0 | 280 | 1.15 | ||
| Qd07 | 300 | 8.1 | −72.6 | 2.0 | 316 | 70.1 | 0.4 | 9.2 | 24.3 | 11.9 | 60.4 | 0.9 | 262 | 40.70 | ||
| Qd08 | 225 | 8.0 | −62.6 | 4.1 | 316 | 48.0 | 0.9 | 17.5 | 43.9 | 20.7 | 57.8 | 0.0 | 253 | 0.23 | ||
| Qd09 | 340 | 7.9 | −57 | 7.0 | 333 | 20.9 | 0.8 | 25.2 | 60.1 | 21.7 | 46.3 | 7.8 | 299 | 0.15 | ||
| Qd11 | 235 | 7.6 | −38 | 1.2 | 740 | 53.9 | 0.7 | 53.0 | 79.5 | 189.9 | 159.3 | 3.5 | 400 | 522 | ||
| Qd12 | 270 | 8.0 | −54 | 5.2 | 319 | 29.6 | 0.7 | 27.2 | 52.7 | 12.4 | 28.6 | 2.2 | 329 | 31.60 | ||
| dbs04 | River water | 8.3 | −82 | 9.3 | 460 | 67.0 | 15.1 | 22.8 | 51.2 | 109.0 | 79.4 | 26.0 | 200 | 4.03 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.; Qin, D.; Yang, Y.; Guo, G. Enrichment of Manganese at Low Background Level Groundwater Systems: A Study of Groundwater from Quaternary Porous Aquifers in Changping Region, Beijing, China. Water 2023, 15, 1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081537
Liu W, Qin D, Yang Y, Guo G. Enrichment of Manganese at Low Background Level Groundwater Systems: A Study of Groundwater from Quaternary Porous Aquifers in Changping Region, Beijing, China. Water. 2023; 15(8):1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081537
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wencai, Dajun Qin, Yong Yang, and Gaoxun Guo. 2023. "Enrichment of Manganese at Low Background Level Groundwater Systems: A Study of Groundwater from Quaternary Porous Aquifers in Changping Region, Beijing, China" Water 15, no. 8: 1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081537





