Modeling of Soil Loss by Water Erosion and Its Impacts on the Cantareira System, Brazil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
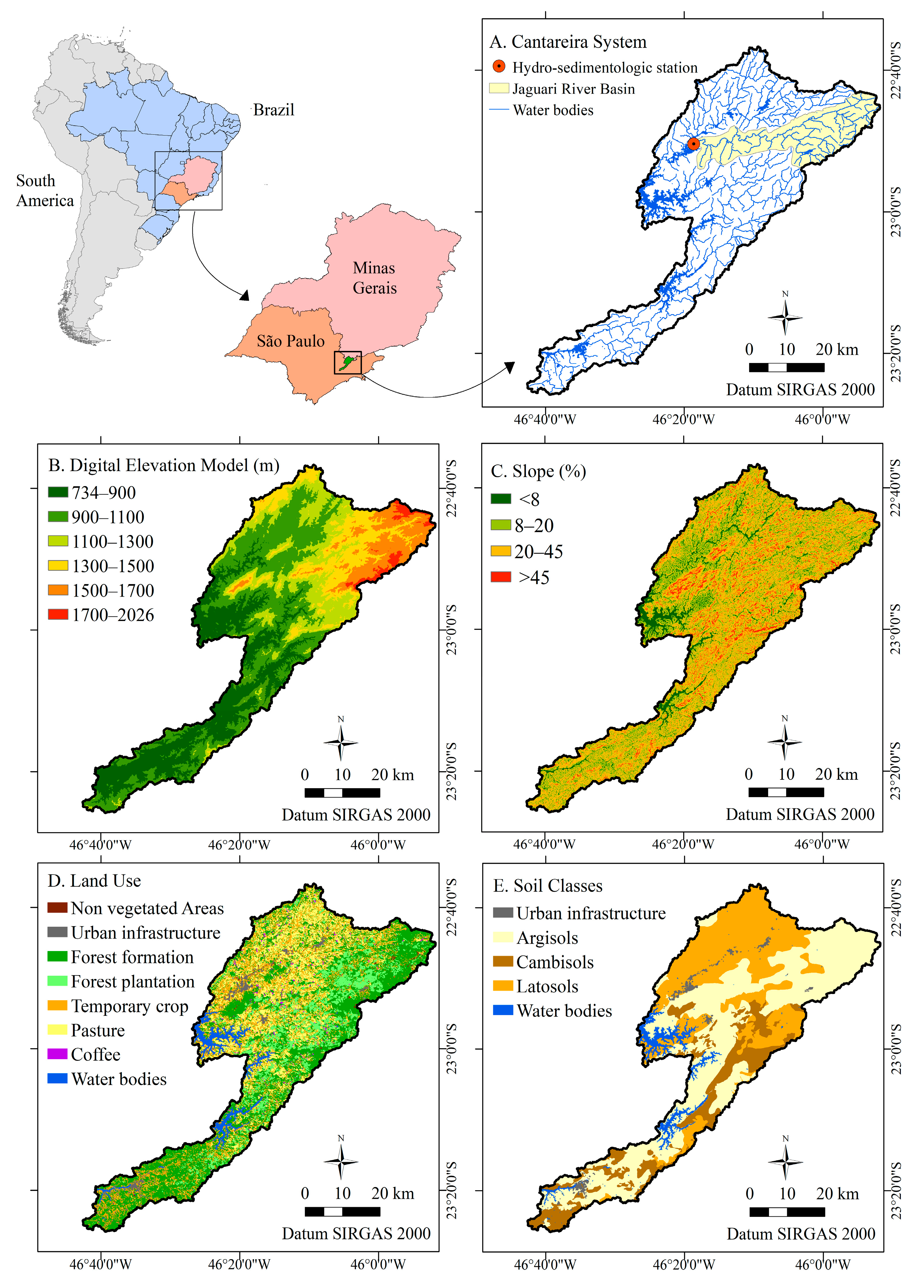
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE)
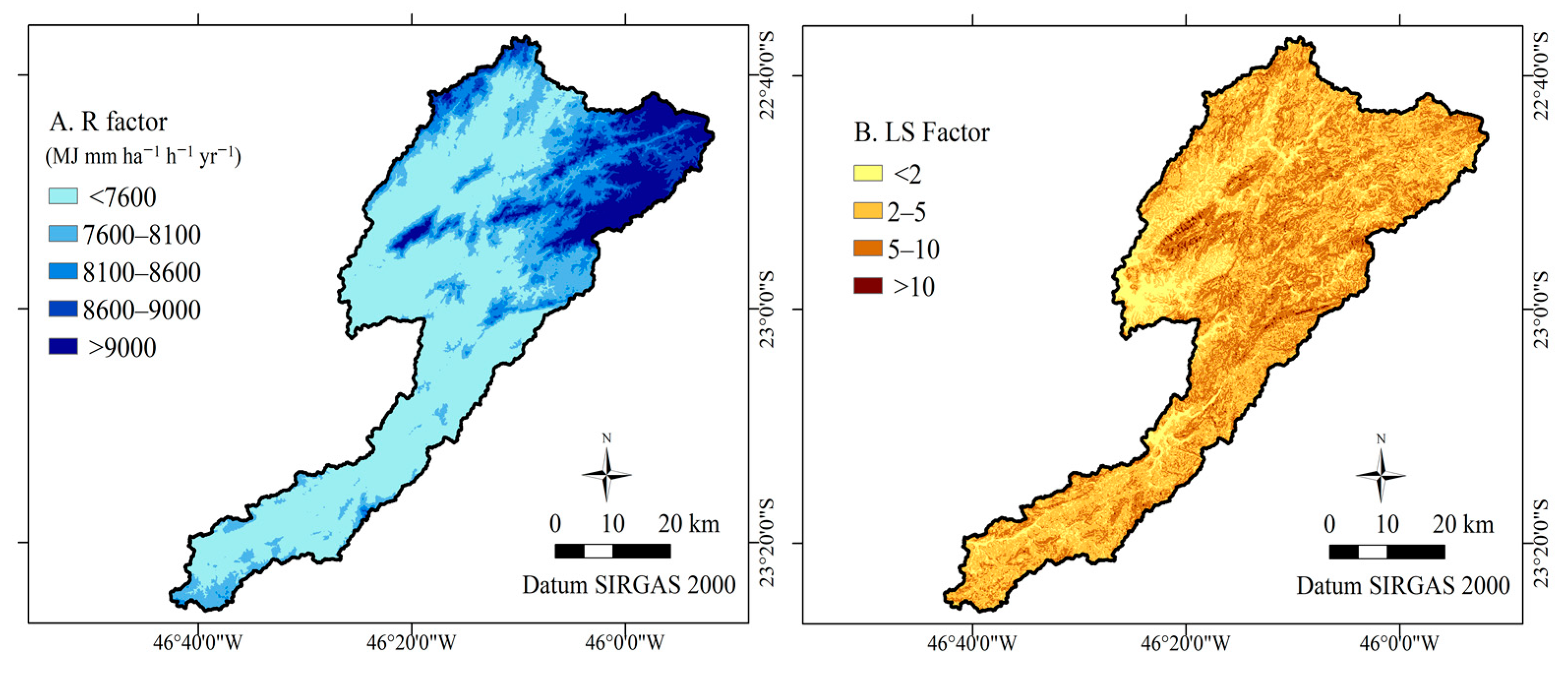
2.2.1. Rain Erosivity (R)
2.2.2. Soil Erodibility (K)
2.2.3. Topographic Factor (LS)
2.2.4. Soil Use and Management Factor (C) and Factor of Conservation Practices (P)
2.3. Geoprocessing and Spatial Analysis
2.4. Data Validation
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. RUSLE Factors
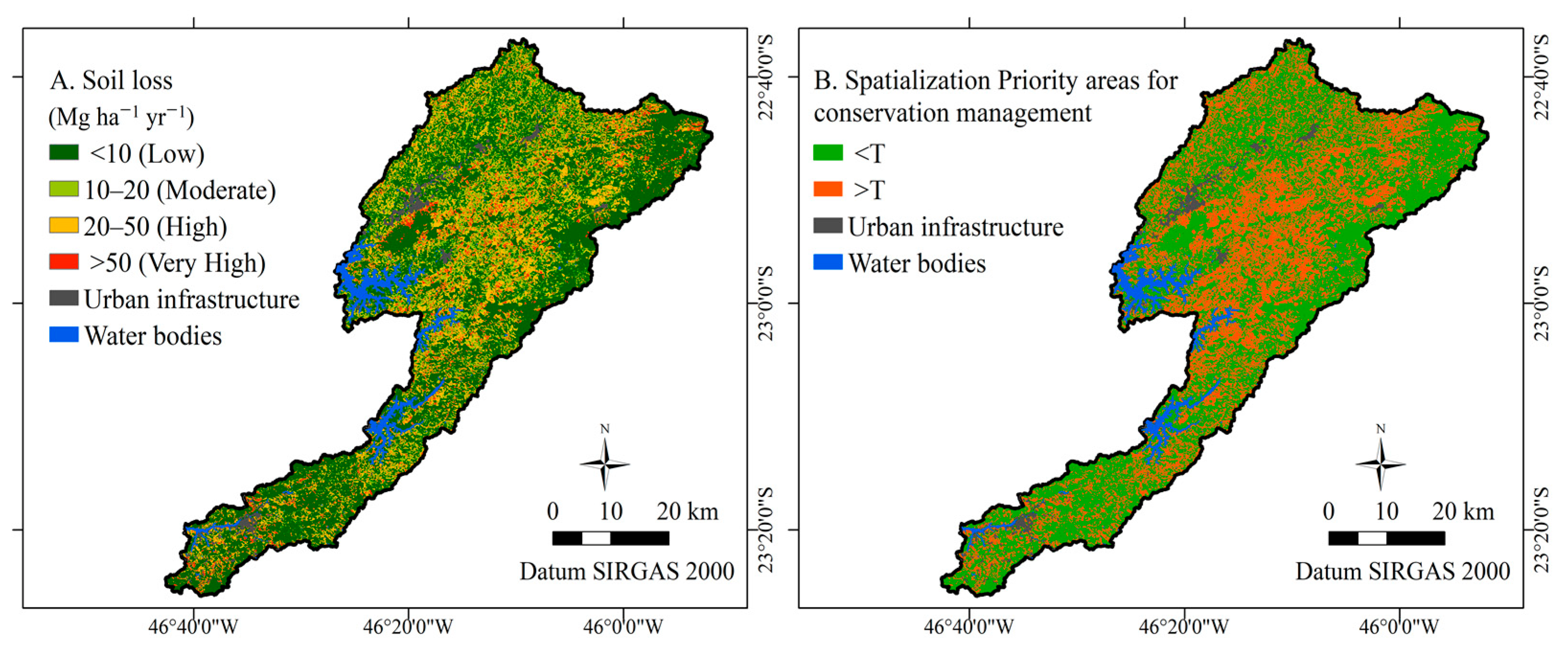
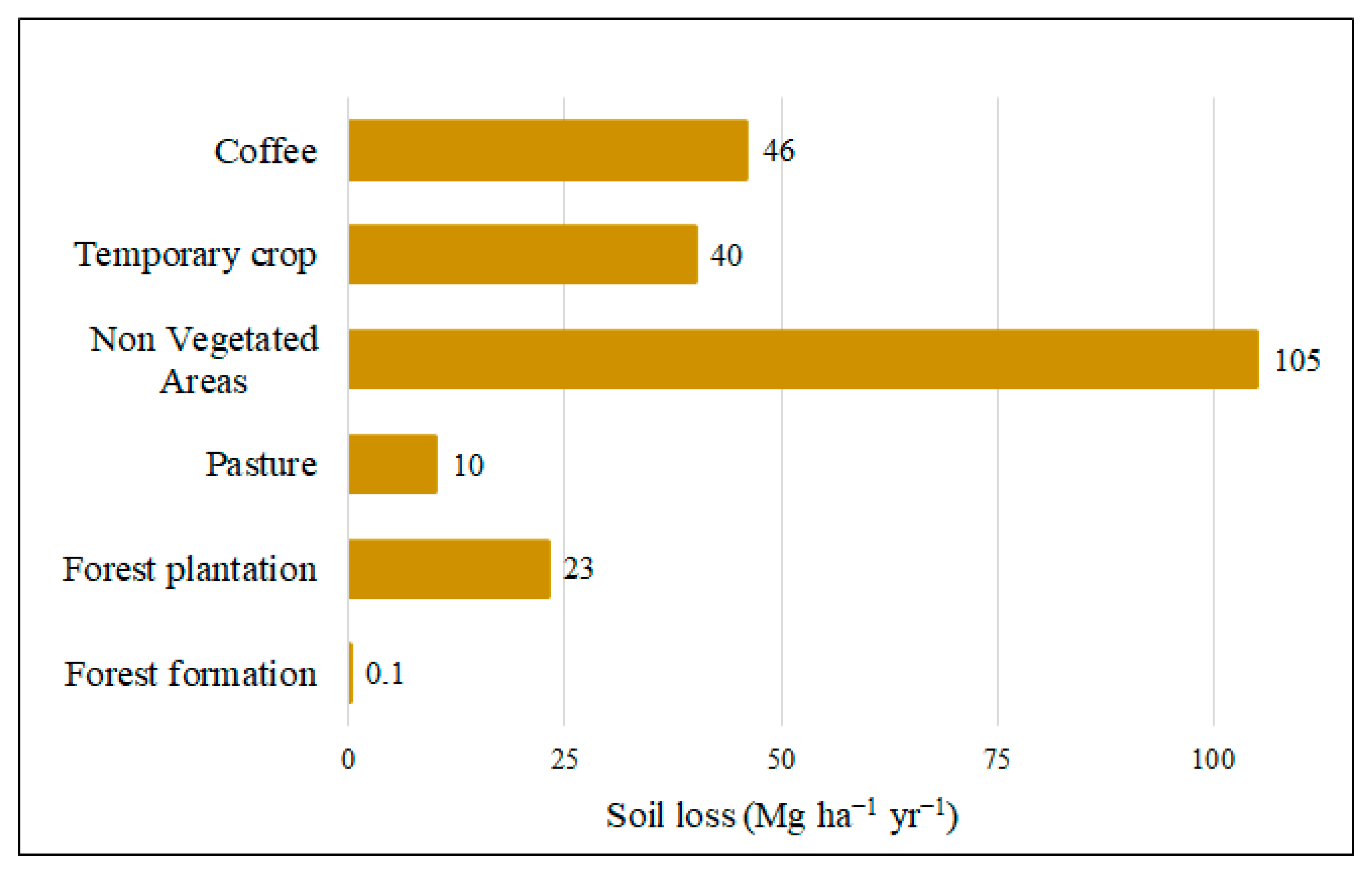
3.2. Soil Losses and Priority Areas for Conservation Management
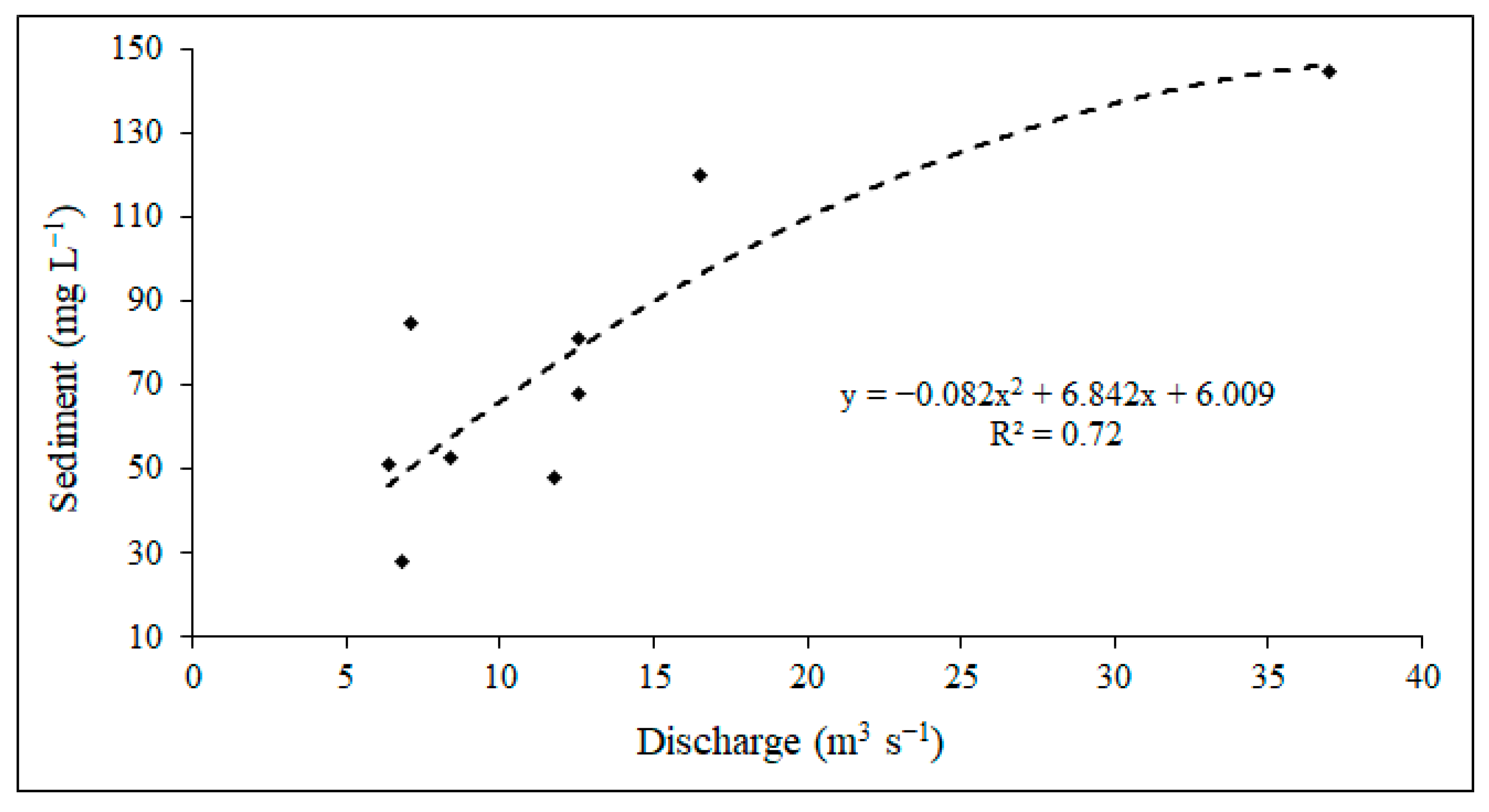
3.3. Validation of Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lisetskii, F.; Stolba, V.F.; Marinina, O. Indicators of Agricultural Soil Genesis under Varying Conditions of Land Use, Steppe Crimea. Geoderma 2015, 239–240, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.-Z.; Tan, M.-Z.; Gong, Z.T. Soil Degradation: A Global Problem Endangering Sustainable Development. J. Geogr. Sci. 2002, 12, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, R.; Ghosh, B.N.; Mishra, P.K.; Mandal, B.; Rao, C.S.; Sarkar, D.; Das, K.; Anil, K.S.; Lalitha, M.; Hati, K.M.; et al. Soil Degradation in India: Challenges and Potential Solutions. Sustainability 2015, 7, 3528–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pena, S.B.; Abreu, M.M.; Magalhães, M.R.; Cortez, N. Water Erosion Aspects of Land Degradation Neutrality to Landscape Planning Tools at National Scale. Geoderma 2020, 363, 114093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, C.; Berggren, K. Alterations of Riparian Ecosystems Caused by River Regulation: Dam Operations Have Caused Global-Scale Ecological Changes in Riparian Ecosystems. How to Protect River Environments and Human Needs of Rivers Remains One of the Most Important Questions of Our Time. BioScience 2000, 50, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lama, G.F.C.; Crimaldi, M.; Pasquino, V.; Padulano, R.; Chirico, G.B. Bulk Drag Predictions of Riparian Arundo Donax Stands through UAV-Acquired Multispectral Images. Water 2021, 13, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Chaube, U.C.; Mishra, S.K.; Kumar, D. Assessment of Reservoir Sedimentation Using Remote Sensing and Recommendations for Desilting Patratu Reservoir, India. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, X.; Lin, R. Integrated Study on Soil Erosion Using RUSLE and GIS in Yangtze River Basin of Jiangsu Province (China). Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chafai, A.; Brahim, N.; Shimi, N.S. Mapping of Water Erosion by GIS/RUSLE Approach: Watershed Ayda River—Tunisia Study. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asthana, B.N.; Khare, D. Reservoir Sedimentation. In Recent Advances in Dam Engineering; Asthana, B.N., Khare, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 265–288. ISBN 978-3-030-32278-6. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanidis, P.; Stefanidis, S. Reservoir Sedimentation and Mitigation Measures. Lakes Reserv. Sci. Policy Manag. Sustain. Use 2012, 17, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, J.C.; Landwehr, T.; Alencar, P.H.L.; Paulino, W.D. Water Management Causes Increment of Reservoir Silting and Reduction of Water Yield in the Semiarid State of Ceará, Brazil. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2023, 121, 104102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.C.; Pereira Filho, A.J. Water Demand Forecasting Model for the Metropolitan Area of São Paulo, Brazil. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 4401–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozment, S.; Gray, E.; Padovezi, A.; Hamel, P.; Ribeiro, J.B.; Barrêto, S.R.; Valente, T.P.; Feltran-Barbieri, R. Infraestrutura Natural para Água no Sistema Cantareira, em São Paulo; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; 92p, ISBN 978-1-56973-943-3. [Google Scholar]
- Taffarello, D.; Samprogna Mohor, G.; do Carmo Calijuri, M.; Mendiondo, E.M. Field Investigations of the 2013–14 Drought through Quali-Quantitative Freshwater Monitoring at the Headwaters of the Cantareira System, Brazil. Water Int. 2016, 41, 776–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padulano, R.; Lama, G.F.C.; Rianna, G.; Santini, M.; Mancini, M.; Stojiljkovic, M. Future Rainfall Scenarios for the Assessment of Water Availability in Italy. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Agriculture and Forestry (MetroAgriFor), Trento, Italy, 4–6 November 2020; pp. 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, V.R.; Teixeira Filho, J. Identificação das áreas susceptíveis aos processos erosivos em duas bacias do Sistema Cantareira por meio de diferentes cenários. Acta Sci. Agron. 2009, 31, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pompêo, M.; Moschini-Carlos, V.; Bitencourt, M.D.; Sòria-Perpinyà, X.; Vicente, E.; Delegido, J. Water Quality Assessment Using Sentinel-2 Imagery with Estimates of Chlorophyll a, Secchi Disk Depth, and Cyanobacteria Cell Number: The Cantareira System Reservoirs (São Paulo, Brazil). Enviorn. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 34990–35011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taffarello, D.; Srinivasan, R.; Mohor, G.S.; Guimarães, J.L.B.; do Carmo Calijuri, M.; Mendiondo, E.M. Modeling Freshwater Quality Scenarios with Ecosystem-Based Adaptation in the Headwaters of the Cantareira System, Brazil. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 4699–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mortatti, B.C.; Enzweiler, J. Major Ions and Rare Earth Elements Hydrogeochemistry of the Atibaia and Jaguari Rivers Subbasins (Southeast Brazil). Appl. Geochem. 2019, 111, 104461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igwe, P.U.; Onuigbo, A.A.; Chinedu, O.C.; Ezeaku, I.I.; Muoneke, M.M. Soil erosion: A review of models and applications. IJAERS 2017, 4, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, E.; Spalevic, V.; Boukdir, A.; Karaoui, I.; Ouallali, A.; Luiz Mincato, R.; Sestras, P. Estimation of soil losses and reservoir sedimentation: A case study in tillouguite sub-basin (high atlas-morocco). Agric. For. 2022, 68, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganasri, B.P.; Ramesh, H. Assessment of Soil Erosion by RUSLE Model Using Remote Sensing and GIS—A Case Study of Nethravathi Basin. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imamoglu, A.; Dengiz, O. Determination of Soil Erosion Risk Using RUSLE Model and Soil Organic Carbon Loss in Alaca Catchment (Central Black Sea Region, Turkey). Rend. Fis. Acc. Lincei 2017, 28, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvares, C.A.; Stape, J.L.; Sentelhas, P.C.; de Moraes Gonçalves, J.L.; Sparovek, G. Köppen’s Climate Classification Map for Brazil. Meteorol. Z. 2013, 22, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uezu, A.; Sarcinelli, O.; Chiodi, R.; Jenkins, C.N.; Martins, C.S. Atlas Dos Serviços Ambientais Do Sistema Cantareira, 1st ed.; Memnon Edições Científicas; IPÊ—Instituto de Pesquisas Ecológicas: São Paulo, Brazil, 2017; ISBN 978-85-7954-113-1. [Google Scholar]
- Mapbiomas. Coleções MapBiomas. Available online: https://mapbiomas.org/colecoes-mapbiomas-1 (accessed on 13 February 2023).
- UFV—Universidade Federal de Viçosa; CETEC—Fundação Centro Tecnológico de Minas Gerais; UFLA—Universidade Federal de Lavras; FEAM—Fundação Estadual do Meio Ambiente. Mapa de solos do Estado de Minas Gerais: Legenda Expandida; Fundação Estadual do Meio Ambiente: Belo Horizonte, MG, Brasil, 2010; 49p, Available online: http://www.feam.br/noticias/1/949-mapas-de-solo-do-estado-de-minas-gerais (accessed on 19 December 2022).
- Rossi, M. Mapa Pedológico do Estado de São Paulo: Revisado e Ampliado; Instituto Florestal: São Paulo, SP, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dias-Filho, M.B. Diagnóstico das Pastagens No Brasil; Embrapa Amazônia Oriental: Belém, PA, Brazil, 2014; 36p. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, L.C.P.; Pimenta, F.M.; Santos, A.B.; Costa, M.H.; Ladle, R.J. Patterns of Land Use, Extensification, and Intensification of Brazilian Agriculture. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 2887–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses—A Guide to Conservation Planning; Agriculture Handbook No. 537; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978; 67p.
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); Agriculture Handbook No. 703; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; 384p.
- Lense, G.; Servidoni, L.; Parreiras, T.; Santana, D.; Bolleli, T.; Ernesto, J.; Spalevic, V.; Mincato, R. Modeling of Soil Loss by Water Erosion in the Tietê River Hydrographic Basin, São Paulo, Brazil. Semin. Cienc. Agrar. 2022, 43, 1403–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, S.; Pradhan, B.; Alamri, A.; Park, H.-J. A New Application of Deep Neural Network (LSTM) and RUSLE Models in Soil Erosion Prediction. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 845, 157220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, C.R.; Viola, M.R.; Beskow, S.; Norton, L.D. Multivariate Models for Annual Rainfall Erosivity in Brazil. Geoderma 2013, 202–203, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, A.A.; Cassalho, F.; Caldeira, T.L.; de Oliveira, V.A.; Beskow, S.; Timm, L.C. Assessment of Soil Loss Vulnerability in Data-Scarce Watersheds in Southern Brazil. Ciênc. Agrotec. 2018, 42, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanchin, M.; Moura, M.M.; Nunes, M.C.M.; Tuchtenhagen, I.K.; Lima, C.R.L. Assessment of soil loss susceptibility in Santa Rita Watershed in southern Brazil. Eng. Agríc. 2021, 41, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannigel, A.; De Passos, M.; Moreti, D.; Da, L.; Medeiros, R. Fator erodibilidade e tolerância de perda dos solos do Estado de São Paulo. Acta Scientiarum. Agron. 2002, 24, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.M.; Alvares, C.A. Levantamento de informações e estruturação de um banco dados sobre a erodibilidade de classes de olos no Estado de São Paulo. Geociências 2007, 24, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Mitasova, H.; Mitas, L.; Brown, W.M.; Johnston, D.M. Terrain Modeling and Soil Erosion Simulations for Fort Hood and Fort Polk Test Areas; U.S. Army Construction Engineering Research Laboratories: Champaign, IL, USA, 1999; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, F.G.B.; Minotti, R.T.; Lombardi Neto, F.; Primavesi, O.; Crestana, S. Previsão da perda de solo na Fazenda Canchim—SP (EMBRAPA) utilizando geoprocessamento e o USLE 2D. Eng. Sanit. Ambient. 2010, 15, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ESRI—Environmental Systems Research Institute. ARCGIS Professional GIS for the Desktop Version 10.5. Available online: https://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/10.5/get-started/setup/arcgis-desktop-quick-start-guide.htm (accessed on 13 February 2023).
- USGS—United States Geological Survey. Earth Explorer. Available online: https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 13 February 2023).
- Nunes, S.; Oliveira, L.; Siqueira, J.; Morton, D.C.; Souza, C.M. Unmasking Secondary Vegetation Dynamics in the Brazilian Amazon. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 034057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alencar, A.A.C.; Arruda, V.L.S.; da Silva, W.V.; Conciani, D.E.; Costa, D.P.; Crusco, N.; Duverger, S.G.; Ferreira, N.C.; Franca-Rocha, W.; Hasenack, H.; et al. Long-Term Landsat-Based Monthly Burned Area Dataset for the Brazilian Biomes Using Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, C.; Ferro, V. Establishing soil loss tolerance: An overview. J. Agric. Eng. 2016, 47, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demarchi, J.C.; Zimback, C.R.L. Mapeamento, erodibilidade e tolerância de perda de solo na sub-bacia do Ribeirão das Perobas. Energ. NA Agric. 2014, 29, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanoni, V.A. Sedimentation Engineering; American Society of Civil Engineers: Charleston, SC, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-7844-0823-0. [Google Scholar]
- Beskow, S.; Mello, C.R.; Norton, L.D.; Curi, N.; Viola, M.R.; Avanzi, J.C. Soil Erosion Prediction in the Grande River Basin, Brazil Using Distributed Modeling. Catena 2009, 79, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes, L.M.; Batista, P.V.G.; Silva, B.P.C.; Viola, M.R.; da Rocha, H.R.; Silva, M.L.N. Assessing Sediment Yield and Streamflow with SWAT Model in a Small Sub-Basin of the Cantareira System. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Solo 2021, 45, e0200140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, G.d.O.R.; Giarolla, A.; Sampaio, G.; de Andrade Marinho, M. Estimates of Annual Soil Loss Rates in the State of São Paulo, Brazil. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Solo 2016, 40, e0150497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertol, I.; Almeida, J.A. Tolerância De Perda De Solo Por Erosão Para Os Principais Solos Do Estado De Santa Catarina. Rev. Bras. Ciência Solo 2000, 24, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nunes, J.G.; Campos, M.C.C.; Oliveira, F.P.; Nunes, J.C.; Macedo, J.A.B. Tolerância de perda de solo por erosão na região sul do Amazonas. Ambiência 2012, 8, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amorim, R.S.S.; da Silva, D.D.; Pruski, F.F.; Matos, A.T. de Avaliação do desempenho dos modelos de predição da erosão hídrica USLE, RUSLE e WEPP para diferentes condições edafoclimáticas do Brasil. Eng. Agríc. 2010, 30, 1046–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polidoro, J.C.; de Freitas, P.L.; Hernani, L.C.; dos Anjos, L.H.C.; Rodrigues, R.d.A.R.; Cesário, F.V.; de Andrade, A.G.; Ribeiro, J.L. Potential Impact of Plans and Policies Based on the Principles of Conservation Agriculture on the Control of Soil Erosion in Brazil. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 3457–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthimiou, N.; Lykoudi, E.; Karavitis, C. Comparative Analysis of Sediment Yield Estimations Using Different Empirical Soil Erosion Models. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2017, 62, 2674–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebrahimzadeh, S.; Motagh, M.; Mahboub, V.; Mirdar Harijani, F. An Improved RUSLE/SDR Model for the Evaluation of Soil Erosion. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alewell, C.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Panagos, P. Using the USLE: Chances, challenges and limitations of soil erosion modelling. WASWAC 2019, 7, 203–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alewell, C.; Egli, M.; Meusburger, K. An attempt to estimate tolerable soil erosion rates by matching soil formation with denudation in Alpine grasslands. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 1383–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meusburger, K.; Konz, N.; Schaub, M.; Alewell, C. Soil erosion modelled with USLE and PESERA using QuickBird derived vegetation parameters in an alpine catchment. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2010, 12, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lense, G.H.E.; Lämmle, L.; Ayer, J.E.B.; Lama, G.F.C.; Rubira, F.G.; Mincato, R.L. Modeling of Soil Loss by Water Erosion and Its Impacts on the Cantareira System, Brazil. Water 2023, 15, 1490. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081490
Lense GHE, Lämmle L, Ayer JEB, Lama GFC, Rubira FG, Mincato RL. Modeling of Soil Loss by Water Erosion and Its Impacts on the Cantareira System, Brazil. Water. 2023; 15(8):1490. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081490
Chicago/Turabian StyleLense, Guilherme Henrique Expedito, Luca Lämmle, Joaquim Ernesto Bernardes Ayer, Giuseppe Francesco Cesare Lama, Felipe Gomes Rubira, and Ronaldo Luiz Mincato. 2023. "Modeling of Soil Loss by Water Erosion and Its Impacts on the Cantareira System, Brazil" Water 15, no. 8: 1490. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081490
APA StyleLense, G. H. E., Lämmle, L., Ayer, J. E. B., Lama, G. F. C., Rubira, F. G., & Mincato, R. L. (2023). Modeling of Soil Loss by Water Erosion and Its Impacts on the Cantareira System, Brazil. Water, 15(8), 1490. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081490









