Comparison between Different Technologies (Zerovalent Iron, Coagulation-Flocculation, Adsorption) for Arsenic Treatment at High Concentrations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Experiments with Fe(0) and Natural Clay
2.3. Coagulation-Flocculation Experiments
2.4. Experiments of As Stability on the Generated Solids
2.5. Analytical Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Removal of As(V) with Fe(0)
3.2. Removal of As(III) with Fe(0)
3.3. Removal of As(V) and As(III) by Coagulation-Flocculation
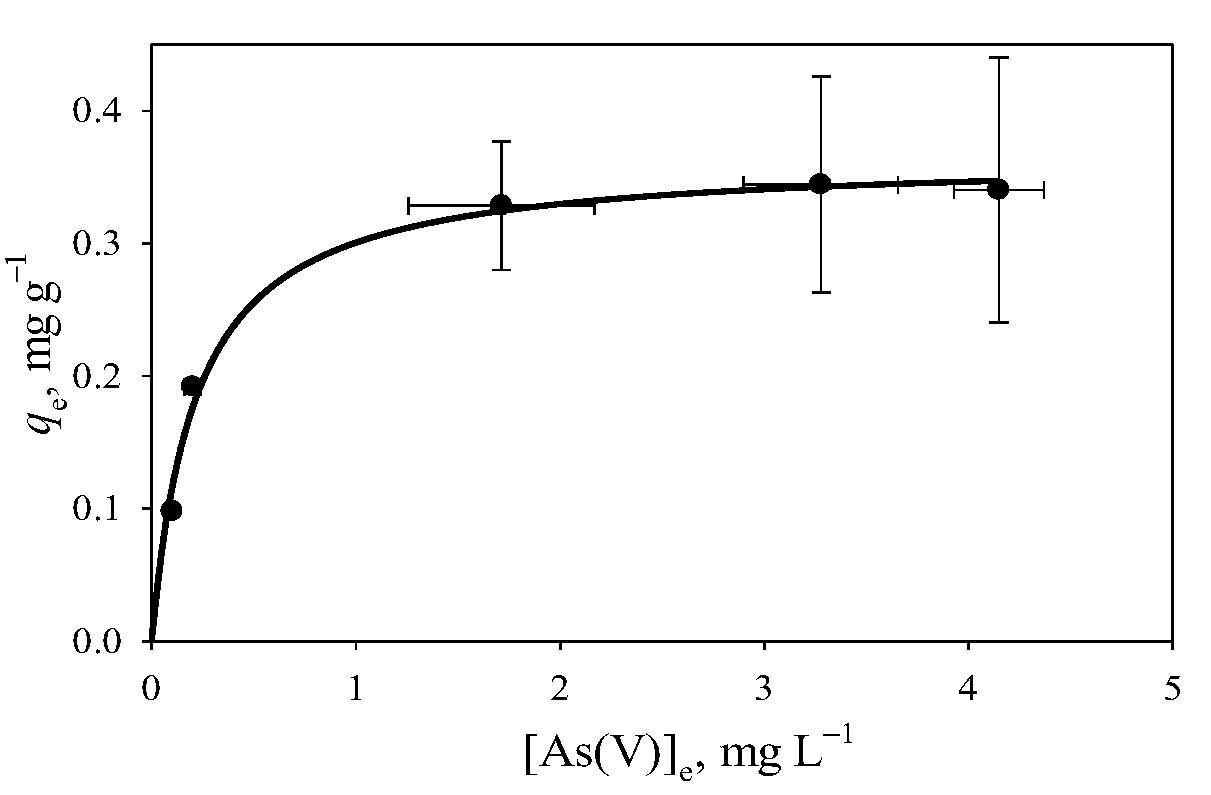
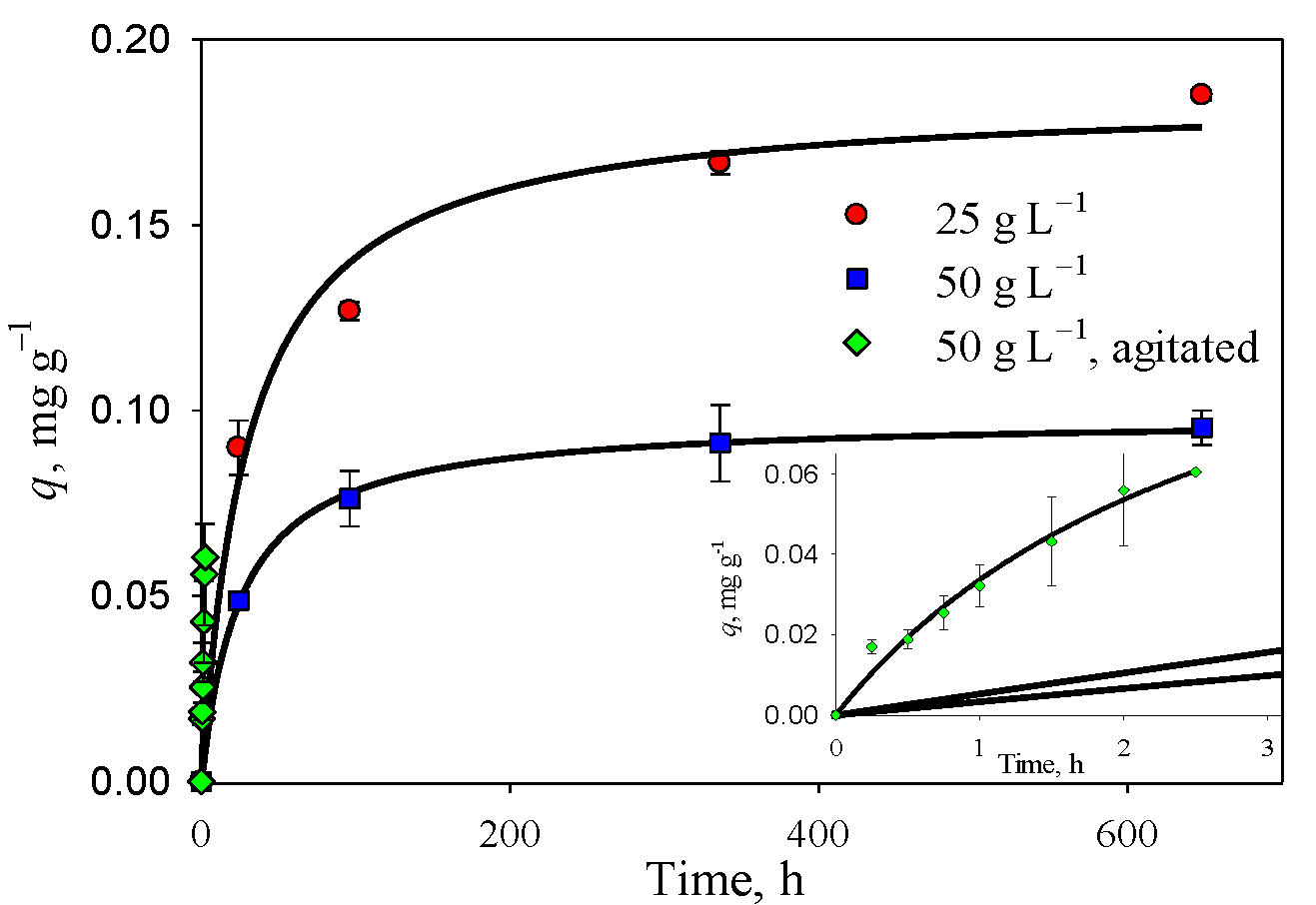
3.4. Removal of As(V) and As(III) with Clay
3.5. Comparison between the Technologies
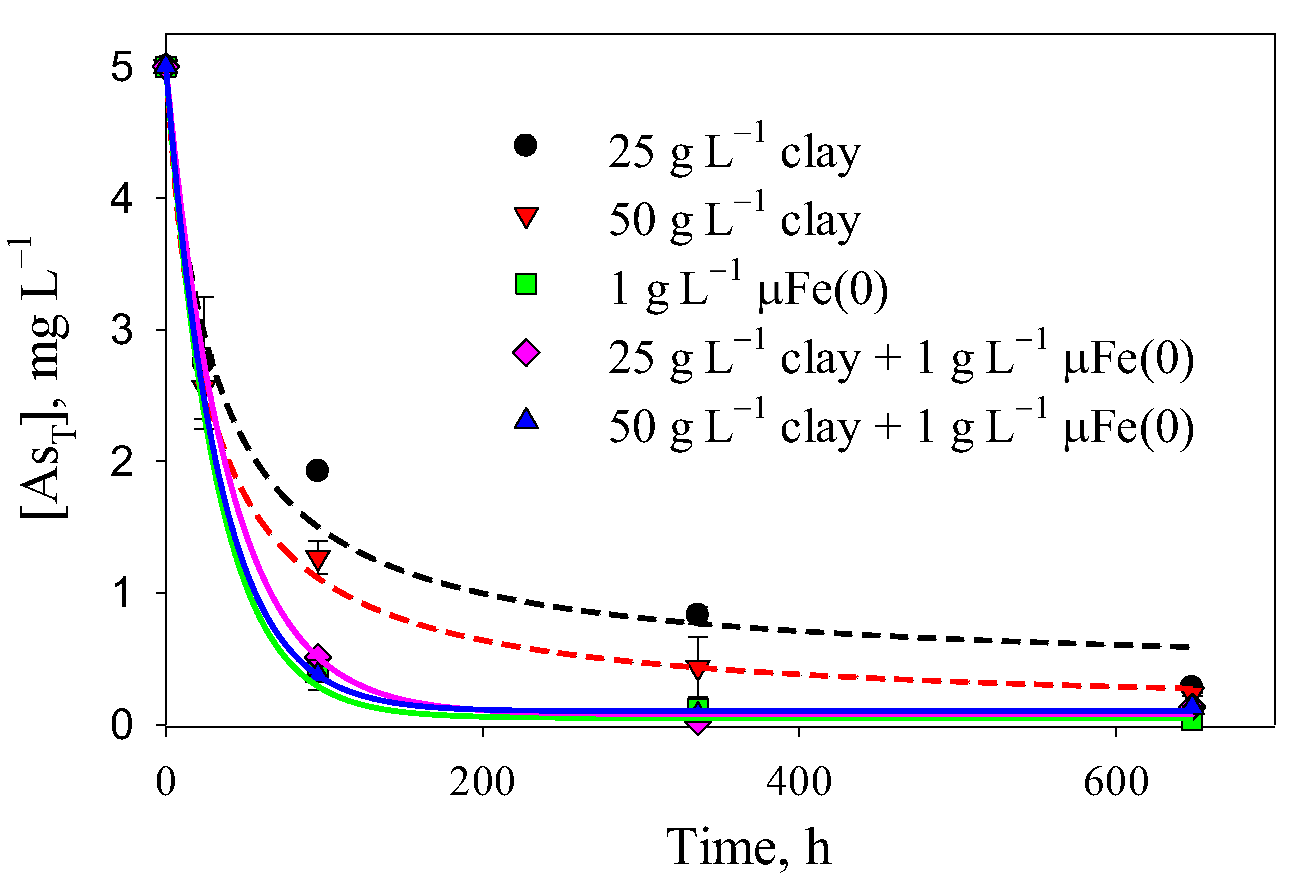
3.6. Stability of As Retained in the Clay and in Fe(0)
3.7. Suitability of Fe(0) Technology
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mandal, B.K.; Suzuki, K.T. Arsenic round the world: A review. Talanta 2002, 58, 201–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Sohn, M. Aquatic arsenic: Toxicity, speciation, transformations, and remediation. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 743–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, J.C. Environmental Contamination of arsenic and its toxicological impact on humans. Environ. Chem. 2005, 2, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.; Biswas, T. Arsenic: The largest mass poisoning of a population in history. BMJ 2013, 346, f3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.F.; Beck, B.D.; Chen, Y.; Lewis, A.S.; Thomas, D.J. Arsenic Exposure and Toxicology: A Historical Perspective. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 123, 305–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mandal, P. An insight of environmental contamination of arsenic on animal health. Emerg. Contam. 2017, 3, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Ryu, D.-Y. A short review of arsenic-induced toxicity. J. Prev. Vet. Med. 2016, 40, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATSDR. 2022 Priority List of Hazardous Substances. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/SPL/index.html (accessed on 22 February 2023).
- Litter, M.I.; Morgada, M.E.; Bundschuh, J. Possible treatments for arsenic removal in Latin American waters for human consumption. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1105–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedley, P.L.; Kinniburgh, D.G. A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 517–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shakoor, M.B.; Nawaz, R.; Hussain, F.; Raza, M.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Oh, S.-E.; Ahmad, S. Human health implications, risk assessment and remediation of As-contaminated water: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 756–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO (World Health Organization). Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; Available online: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2011/9789241548151_eng.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2023).
- Nicolli, H.B.; Bundschuh, J.; Blanco, M.D.C.; Tujchneider, O.C.; Panarello, H.O.; Dapeña, C.; Rusansky, J.E. Arsenic and associated trace-elements in groundwater from the Chaco-Pampean plain, Argentina: Results from 100 years of research. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 429, 36–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murcott, S. Arsenic Contamination in the World—An International Sourcebook; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/arsenic (accessed on 28 February 2023).
- Bundschuh, J.; Litter, M.I.; Parvez, F.; Román-Ross, G.; Nicolli, H.B.; Jean, J.-S.; Liu, C.-W.; López, D.; Armienta, M.A.; Guilherme, L.R.; et al. One century of arsenic exposure in Latin America: A review of history and occurrence from 14 countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 429, 2–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyenechea, M. Sobre la nueva enfermedad descubierta en Bell-Ville. Rev. Med. Rosario 1917, 7, 485. [Google Scholar]
- Bardach, A.E.; Ciapponi, A.; Soto, N.; Chaparro, M.R.; Calderon, M.; Briatore, A.; Cadoppi, N.; Tassara, R.; Litter, M.I. Epidemiology of chronic disease related to arsenic in Argentina: A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 802–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litter, M.I.; Ingallinella, A.M.; Olmos, V.; Savio, M.; Difeo, G.; Botto, L.; Torres, E.M.F.; Taylor, S.; Frangie, S.; Herkovits, J.; et al. Arsenic in Argentina: Occurrence, human health, legislation and determination. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hering, J.G.; Chen, P.-Y.; Wilkie, J.A.; Elimelech, M.; Liang, S. Arsenic removal by ferric chloride. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1996, 88, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoble, V. Arsenite oxidation and arsenate determination by the molybdene blue method. Talanta 2003, 61, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U., Jr. Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 142, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litter, M.I.; Sancha, A.M.; Ingallinella, A.M. Tecnologías Económicas para el Abatimiento de Arsénico en Aguas; CYTED Editorial: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, P.; Bhowmick, S.; Chatterjee, D.; Figoli, A.; Van der Bruggen, B. Remediation of inorganic arsenic in groundwater for safe water supply: A critical assessment of technological solutions. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, J.G.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Theoduloz, G.A.; Berg, M.; Hug, S.J. Arsenic Removal from Drinking Water: Experiences with Technologies and Constraints in Practice. J. Environ. Eng. 2017, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litter, M.I.; Ingallinella, A.M.; Olmos, V.; Savio, M.; Difeo, G.; Botto, L.; Torres, E.M.F.; Taylor, S.; Frangie, S.; Herkovits, J.; et al. Arsenic in Argentina: Technologies for arsenic removal from groundwater sources, investment costs and waste management practices. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, L.; Liu, M.; Wang, N.; Li, G. A critical review on arsenic removal from water using iron-based adsorbents. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 39545–39560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, H.R. A review on different arsenic removal techniques used for decontamination of drinking water. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2023, 35, 2165964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Li, R.; Zhao, B.; Liang, W. Arsenate removal from water by zero-valent iron/activated carbon galvanic couples. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noubactep, C. Metallic Iron for Safe Drinking Water Production; Freiberg Online Geoscience: Freiberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 27, ISSN 1434-7512. [Google Scholar]
- Ghauch, A. Iron-Based Metallic Systems: An Excellent Choice for Sustainable Water Treatment; Freiberg Online Geoscience: Freiberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 38, ISSN 1434-7512. [Google Scholar]
- Noubactep, C. Metallic iron for environmental remediation: A review of reviews. Water Res. 2015, 85, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noubactep, C.; Makota, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Rescuing Fe0 remediation research from its systemic flaws. Res. Rev. Insights 2017, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, C.; Tratnyek, P.G. Advances in metal(loid) oxyanion removal by zerovalent iron: Kinetics, pathways, and mechanisms. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Wang, L.; Zhu, H.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. Study on the Arsenate Removal from Raw As(V)-Rich Wastewater Using Zero-Valent Iron. Water 2022, 14, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamindy-Pajany, Y.; Hurel, C.; Marmier, N.; Roméo, M. Arsenic (V) adsorption from aqueous solution onto goethite, hematite, magnetite and zero-valent iron: Effects of pH, concentration and reversibility. Desalination 2011, 281, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackovic, J.A.; Nikolaidis, N.P.; Dobbs, G.M. Inorganic Arsenic Removal by Zero-Valent Iron. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2000, 17, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, J.; Wang, J.; O’Day, P.; Conklin, M. Electrochemical and Spectroscopic Study of Arsenate Removal from Water Using Zero-Valent Iron Media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 2026–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Puls, R.W. Arsenate and arsenite removal by zerovalent iron: Kinetics, redox transformation, and implications for in situ groundwater remediation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Puls, R.W. Arsenate and Arsenite Removal by Zerovalent Iron: Effects of Phosphate, Silicate, Carbonate, Borate, Sulfate, Chromate, Molybdate, and Nitrate, Relative to Chloride. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4562–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melitas, N.; Wang, J.; Conklin, M.; O’Day, P.; Farrell, J. Understanding Soluble Arsenate Removal Kinetics by Zerovalent Iron Media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2074–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaidis, N.P.; Dobbs, G.M.; Lackovic, J.A. Arsenic removal by zero-valent iron: Field, laboratory and modeling studies. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, S.; Korfiatis, G.P.; Meng, X. Removal of arsenic from water by zero-valent iron. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 121, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lien, H.-L.; Wilkin, R.T. High-level arsenite removal from groundwater by zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 2005, 59, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, S.; Johnson, M.D.; Korfiatis, G.P.; Meng, X. Chemical reactions between arsenic and zero-valent iron in water. Water Res. 2005, 39, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leupin, O.X.; Hug, S.J. Oxidation and removal of arsenic (III) from aerated groundwater by filtration through sand and zero-valent iron. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1729–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leupin, O.X.; Hug, S.J.; Badruzzaman, A.B.M. Arsenic Removal from Bangladesh Tube Well Water with Filter Columns Con-taining Zerovalent Iron Filings and Sand. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 8032–8037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, R.; Sui, J.; Xu, G. Treatment of groundwater polluted by arsenic compounds by zero valent iron. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 129, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triszcz, J.M.; Porta, A.; Einschlag, F.S.G. Effect of operating conditions on iron corrosion rates in zero-valent iron systems for arsenic removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, D.E.; Mohapatra, M.; Issa, T.B.; Anand, S.; Singh, P. Iron and aluminium based adsorption strategies for removing arsenic from water. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 3011–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Ruettimann, T.; Hug, S.J. pH Dependence of Fenton Reagent Generation and As(III) Oxidation and Removal by Corrosion of Zero Valent Iron in Aerated Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7424–7430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanel, S.R.; Manning, B.; Charlet, L.; Choi, H. Removal of Arsenic(III) from Groundwater by Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noubactep, C. Investigating the processes of contaminant removal in Fe0/H2O systems. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 29, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mondal, P.; Bhowmick, S.; Jullok, N.; Ye, W.; Van Renterghem, W.; Berghe, S.V.D.; Van der Bruggen, B. Behavior of As(V) with ZVI–H2O System and the Reduction to As(0). J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 21614–21621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voegelin, A.; Kaegi, R.; Frommer, J.; Vantelon, D.; Hug, S.J. Effect of phosphate, silicate, and Ca on Fe(III)-precipitates formed in aerated Fe(II)- and As(III)-containing water studied by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 164–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheju, M.; Balcu, I. Effect of Sand Co-Presence on CrVI Removal in Fe0-H2O System. Water 2023, 15, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Yang, Z.; Zeng, G.; Yang, X.; Xu, H.; Wang, L.; Xu, R.; Xiong, W.; Ahmad, K. Electrocoagulation treatment of arsenic in wastewaters: A comprehensive review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 707–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, J.G.; Chen, P.-Y.; Wilkie, J.A.; Elimelech, M. Arsenic Removal from Drinking Water during Coagulation. J. Environ. Eng. 1997, 123, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentahar, Y.; Hurel, C.; Draoui, K.; Khairoun, S.; Marmier, N. Adsorptive properties of Moroccan clays for the removal of arsenic(V) from aqueous solution. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 119, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudzielwana, R.; Gitari, M.W.; Ndungu, P. Performance evaluation of surfactant modified kaolin clay in As(III) and As(V) adsorption from groundwater: Adsorption kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamics. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bundschuh, J.; Litter, M.; Ciminelli, V.S.; Morgada, M.E.; Cornejo, L.; Hoyos, S.G.; Hoinkis, J.; Alarcón-Herrera, M.T.; Armienta, M.A.; Bhattacharya, P. Emerging mitigation needs and sustainable options for solving the arsenic problems of rural and isolated urban areas in Latin America—A critical analysis. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5828–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claesson, M.; Fagerberg, J. Arsenic in Groundwater of Santiago del Estero—Sources, Mobility Patterns and Remediation with Natural Materials. MScThesisTRITA-LWREX-03-05. Master’s Thesis, Department of Land and Water Research Engineering, KTH, Stockholm, Sweden, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bundschuh, J.; Bhattacharya, P.; Sracek, O.; Mellano, M.F.; Ramírez, A.E.; Storniolo, A.D.R.; Martín, R.A.; Cortés, J.; Litter, M.; Jean, J.-S. Arsenic removal from groundwater of the Chaco-Pampean Plain (Argentina) using natural geological materials as adsorbents. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox. Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2011, 46, 1297–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hergenreder, M.B.; Pereyra, F.N. Estudios Preliminares para la Remoción de Arsénico en Aguas Subterráneas Utilizando Mé-todos de Adsorción. Rev. Tecnol. Cienc. 2018, 32, 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Boglione, R.; Griffa, C.; Panigatti, M.C.; Keller, S.; Schierano, M.C.; Asforno, M. Arsenic adsorption by soil from Misiones province, Argentina. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2018, 13, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meichtry, J.M.; Castiglia, M.D.; Mugrabi, F.; Lan, L.E.; Reina, F.D.; De Seta, G.E.; López, A.R.; Domingo, E. Removal of arsenic in water by low-cost materials and safe final disposal. Proyecciones 2015, 13, 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, I.K.; Mizrahi, M.; Ruano, G.; Zampieri, G.; Requejo, F.G.; Litter, M.I. TiO2-Photocatalytic Reduction of Pentavalent and Trivalent Arsenic: Production of Elemental Arsenic and Arsine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2299–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Bose, P. Modeling Arsenite Adsorption on Rusting Metallic Iron. J. Environ. Eng. 2010, 136, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eljamal, O.; Sasaki, K.; Tsuruyama, S.; Hirajima, T. Kinetic Model of Arsenic Sorption onto Zero-Valent Iron (ZVI). Water Qual. Expo. Health 2010, 2, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liley, P.E.; Thomson, G.H.; Friend, D.G.; Daubert, T.E.; Buck, E. Physical and Chemical Data, Perry’s Chemical Engineering Handbook, 7th ed.; Perry, R.H., Green, D.W., Maloney, J.O., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1997; ISBN 0-07-115448-5. [Google Scholar]
- Biterna, M.; Arditsoglou, A.; Tsikouras, E.; Voutsa, D. Arsenate removal by zero valent iron: Batch and column tests. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusydi, A.F. Correlation between conductivity and total dissolved solid in various type of water: A review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 118, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanel, S.R.; Choi, H. Removal of Arsenic from Groundwater by Industrial Byproducts and Its Comparison with Zero-Valent Iron. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2017, 21, 04016028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trois, C.; Cibati, A. South African sands as an alternative to zero valent iron for arsenic removal from an industrial effluent: Batch experiments. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskan, M.B.; Pala, A. Determination of arsenic removal efficiency by ferric ions using response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmanan, D.; Clifford, D.; Samanta, G. Arsenic Removal by Coagulation With Aluminum, Iron, Titanium, and Zirconium. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2008, 100, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.C.; Hug, S.J.; Ruettimann, T.; Billah, M.; Khan, A.W.; Rahman, M.T. Arsenic Removal with Iron(II) and Iron(III) in Waters with High Silicate and Phosphate Concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 38, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.W.; Lounsbury, H.A.; Millero, F.J. Rates and Mechanism of Fe(II) Oxidation at Nanomolar Total Iron Concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.R.; Chaudhari, S.; Khilar, K.C.; Mahajan, S. Removal of arsenic from water by electrocoagulation. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Bang, S.; Korfiatis, G.P. Effects of silicate, sulfate, and carbonate on arsenic removal by ferric chloride. Water Res. 2000, 34, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abejón, R.; Garea, A. A bibliometric analysis of research on arsenic in drinking water during the 1992–2012 period: An outlook to treatment alternatives for arsenic removal. J. Water Process. Eng. 2015, 6, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K.N.; Green, J.F.; Do, H.D.; McLean, S.J. Arsenic removal by coagulation. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1995, 87, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzounis, K.; Katsoyiannis, I.; Zouboulis, A.; Mitrakas, M. Is the Coagulation-Filtration Process with Fe(III) Efficient for As(III) Removal from Groundwaters? Sep. Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 1587–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.N. Sketch of the History of Water Treatment. J. AWWA 1934, 26, 902–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.N. Ch. 13: Coagulation: Ancient and Modern. In The Quest For Pure Water: The History of Water Purification from the Earliest Records to the Twentieth Century, 2nd ed.; Ch. 13: Coagulation: Ancient and Modern; American Water Works Association: New York, NY, USA, 1949; pp. 299–320. [Google Scholar]
- Banerji, T.; Chaudhari, S. A cost-effective technology for arsenic removal: Case study of zerovalent iron-based IIT Bombay arsenic filter in West Bengal. In Water and Sanitation in the New Millennium; Nath, K., Sharma, V., Eds.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Seta, E.G.; Reina, F.D.; Mugrabi, F.I.; Lan, L.E.; Guerra, J.P.; Laburu, A.P.; Domingo, E.J.; Meichtry, J.M. Safe disposal of solid wastes generated during arsenic removal in drinking water. Int. J. Environ. Health 2018, 9, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretzler, A.; Nikiema, J.; Lalanne, F.; Hoffmann, L.; Biswakarma, J.; Siebenaller, L.; Demange, D.; Schirmer, M.; Hug, S.J. Arsenic removal with zero-valent iron filters in Burkina Faso: Field and laboratory insights. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussam, A.; Munir, A.K.M. A simple and effective arsenic filter based on composite iron matrix: Development and deployment studies for groundwater of Bangladesh. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2007, 42, 1869–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndé-Tchoupé, A.I.; Konadu-Amoah, B.; Gatcha-Bandjun, N.; Hu, R.; Gwenzi, W.; Noubactep, C. Kanchan Arsenic Filters for Household Water Treatment: Unsuitable or Unsustainable? Water 2022, 14, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indelicato, B.M. Comparison of Zerovalent Iron and Activated Carbon for Treating Chlorinated Contaminants in Groundwater. Master’s Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, S.J.; Metzler, D.R.; Dwyer, B.P. Removal of As, Mn, Mo, Se, U, V and Zn from groundwater by zero-valent iron in a passive treatment cell: Reaction progress modeling. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2001, 56, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, S.J.; Mushovic, P.S.; Niesen, P.L. Early Breakthrough of Molybdenum and Uranium in a Permeable Reactive Barrier. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 2018–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allred, B.J.; Martinez, L.R.; Gamble, D.L. Phosphate Removal from Agricultural Drainage Water Using an Iron Oxyhydroxide Filter Material. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allred, B.J.; Tost, B. Laboratory comparison of four iron-based filter materials for water treatment of trace element contaminants. Water Environ. Res. 2014, 86, 2221–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.H.; Rasul, S.B.; Munir, A.K.M.; Habibuddowla, M.; Alauddin, M.; Newaz, S.; Hussam, A. Appraisal of a simple arsenic removal method for ground water of Bangladesh. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2000, 35, 1021–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, S.J.; Spangler, R.R. Chemical barriers for controlling groundwater contamination. Environ. Prog. 1993, 12, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Hu, R.; Ndé-Tchoupé, A.I.; Gwenzi, W.; Ruppert, H.; Noubactep, C. Designing the Next Generation of Fe0-Based Filters for Decentralized Safe Drinking Water Treatment. Processes 2020, 8, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Hu, R.; Ruppert, H.; Noubactep, C. Modeling porosity loss in Fe0-based permeable reactive barriers with Faraday’s law. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agazzi, A.; Pirola, C. Fundamentals method and future trends of environmental microwave sample preparation. Microchem. J. 2000, 67, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
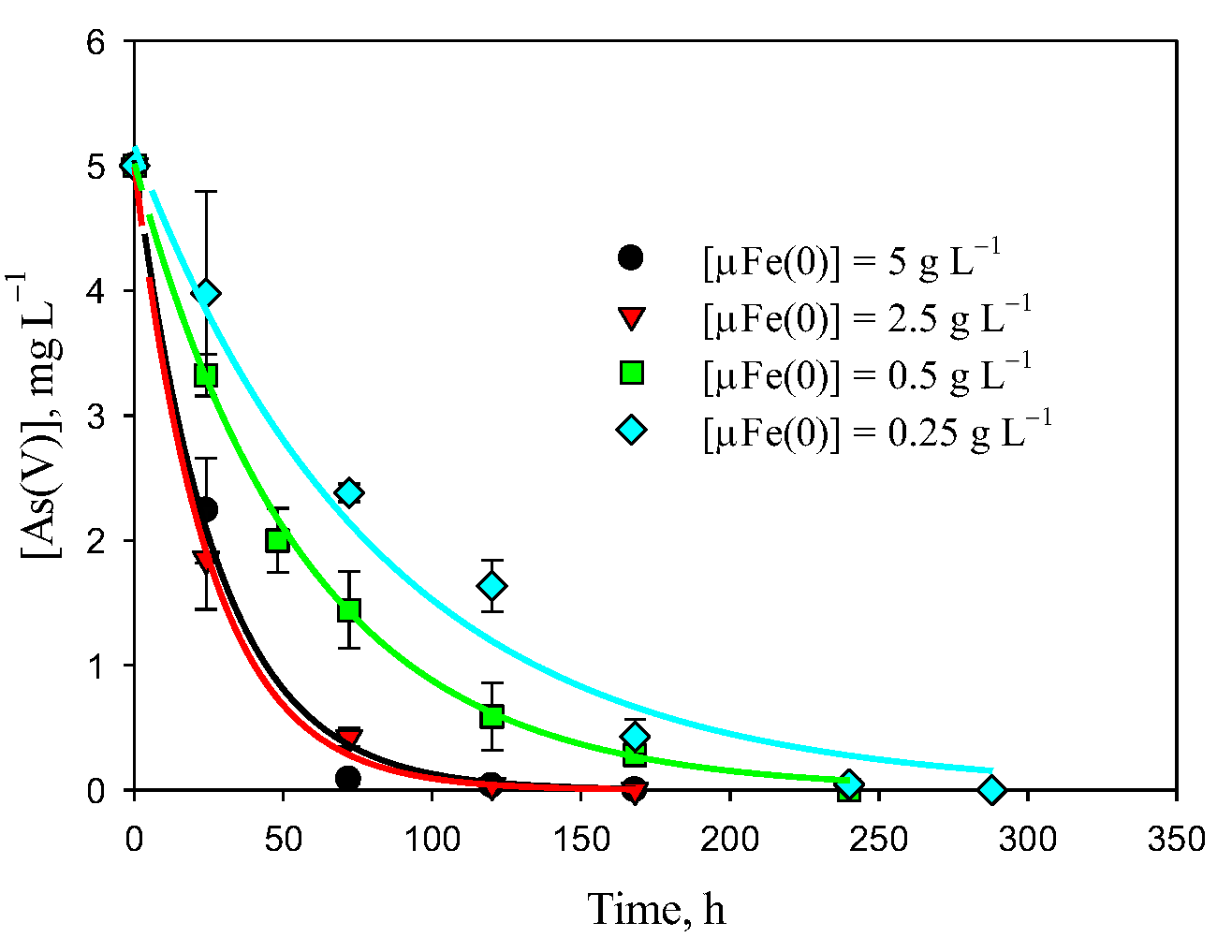
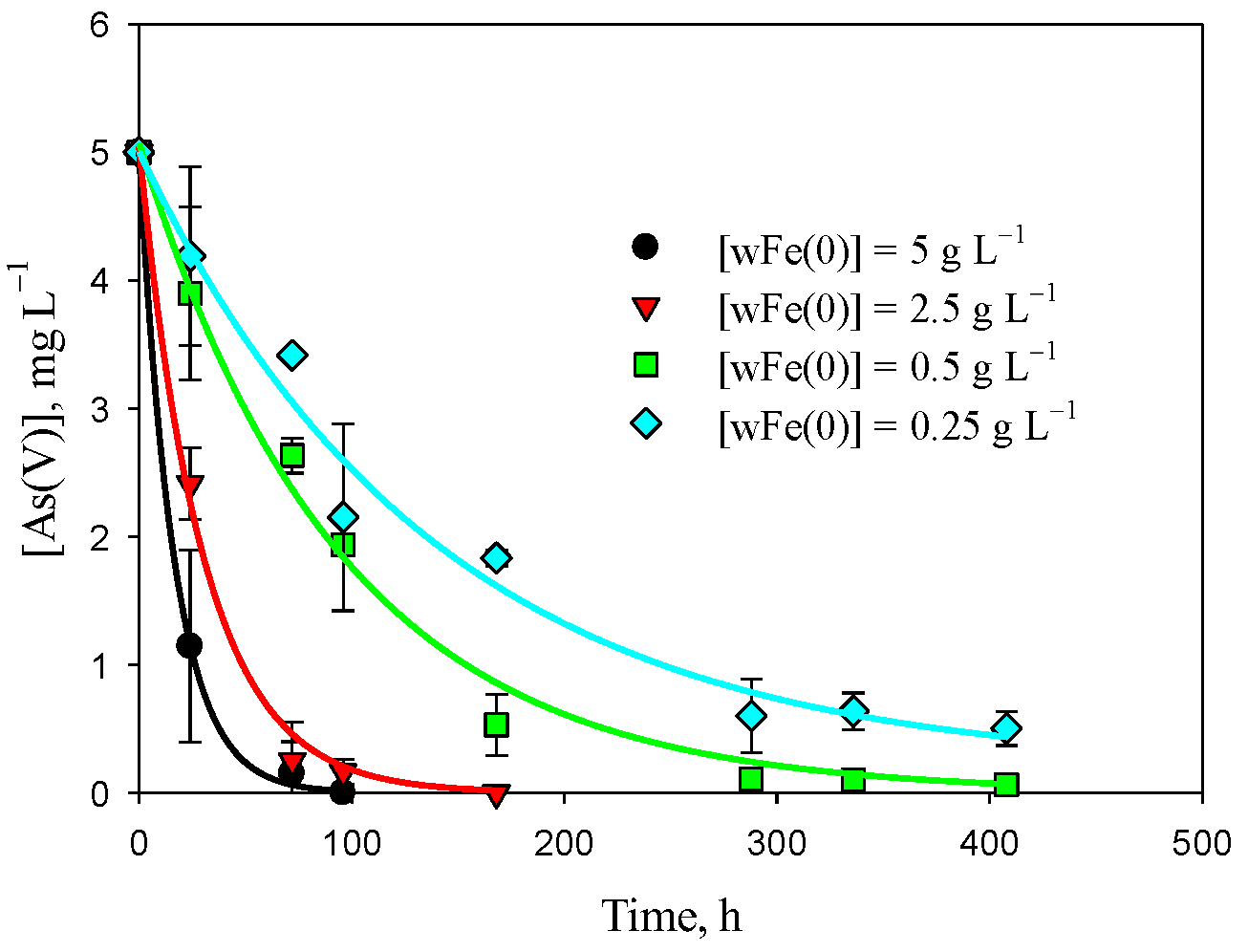
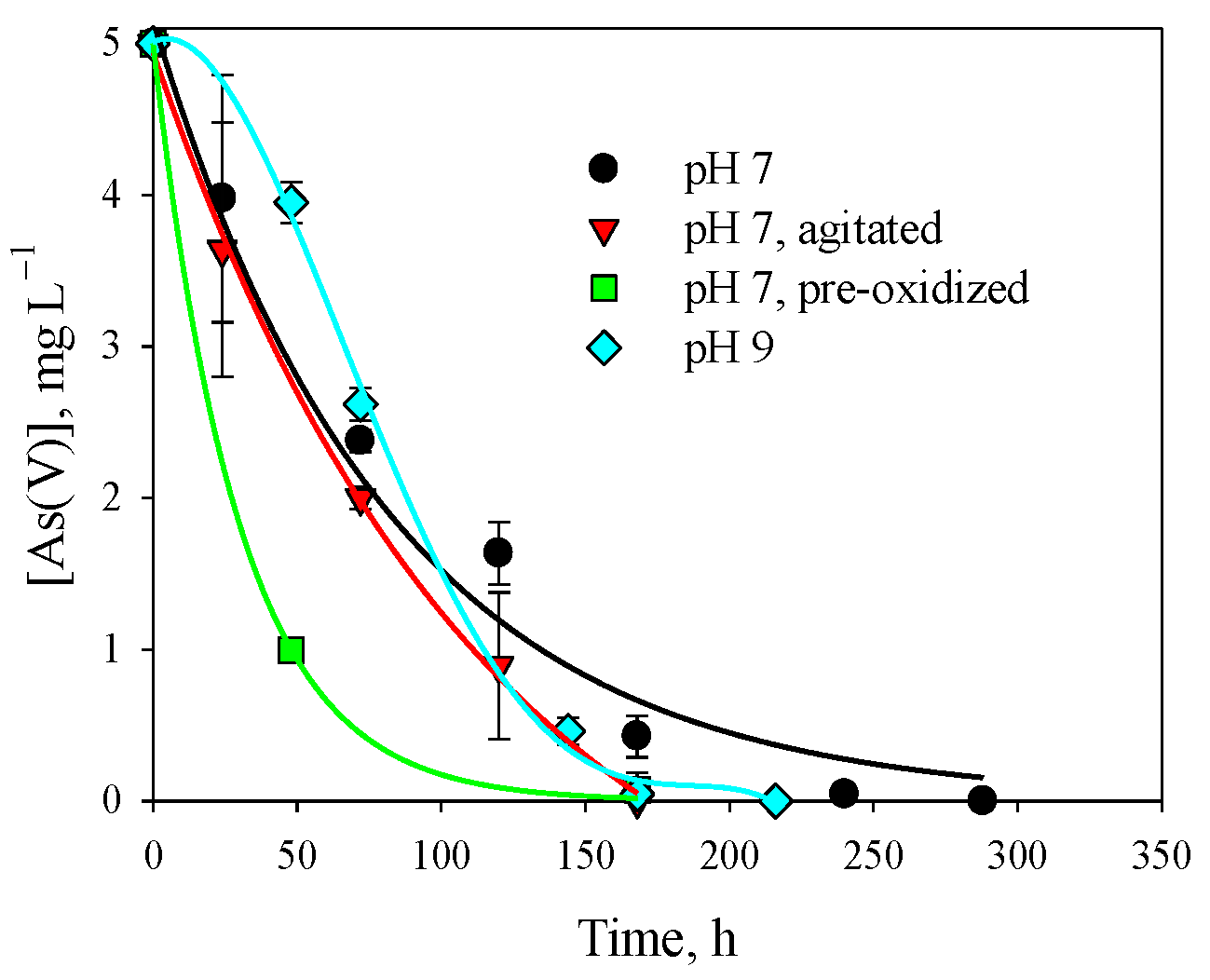
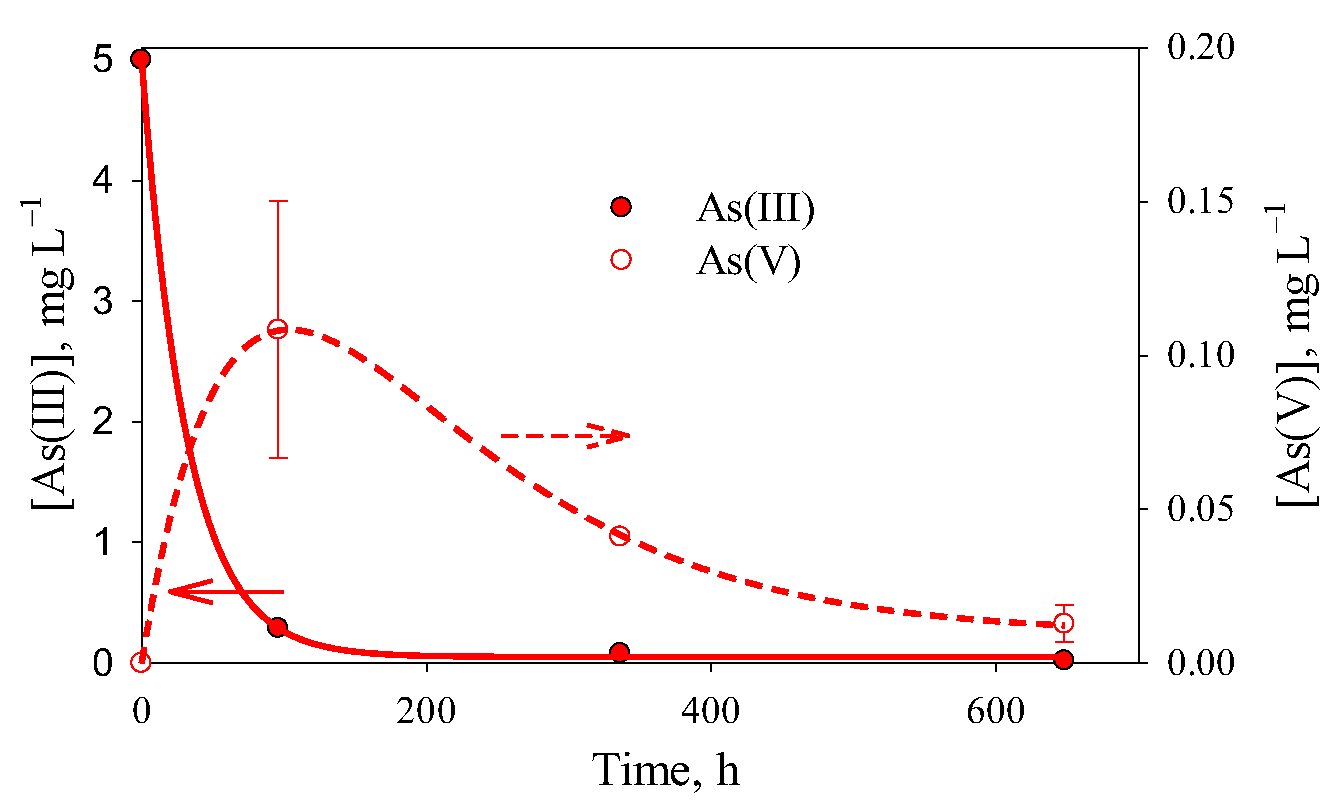

| Experiment | A, mg L−1 | k × 103, h−1 | [As(V)]∞, mg L−1 | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| µFe(0) | 0.25 g L−1 | 5.0 ± 0.2 | 12 ± 1 | 0 | 0.98 |
| 0.50 g L−1 | 5.00 ± 0.05 | 17 ± 0.3 | 0 | 1 | |
| 2.5 g L−1 | 5.0 ± 0.2 | 37 ± 3 | 0 | 0.99 | |
| 5.0 g L−1 | 5.0 ± 0.1 | 40 ± 2 | 0 | 1 | |
| 0.25 g L−1 a | 5.00 ± 0.05 | 34 ± 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| wFe(0) | 0.25 g L−1 | 4.8 ± 0.3 | 7.2 ± 1.5 | 0.2 ± 0.3 | 0.97 |
| 0.50 g L−1 | 5.00 ± 0.05 | 10.6 ± 0.7 | 0 | 0.99 | |
| 2.5 g L−1 | 5.0 ± 0.1 | 33 ± 2 | 0 | 1 | |
| 5.0 g L−1 | 5.0 ± 0.1 | 60 ± 2 | 0 | 1 | |
| Fe(0) Size (mm) | [As(V)]0 (mg L−1) | MR As:Fe | pH | EC (mS cm−1)a | Stirring | k × 103 (h−1) | ri (mg L−1 h−1) | tR (h) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.074–0.84(µFe(0)) | 5 | 1:67 | 7 | 0.03 | No | 12 | 0.06 | 288 | This work |
| 0.20(wFe(0)) | 5 | 1:1342 | 7 | 0.03 | No | 60 | 0.30 | 96 | This work |
| <0.149 | 100 | 1:13.4 | 7 | 0.05-0.8 | Magnetic | 79.5 | 7.95 | NR | [43] |
| <0.074 | 0.5 | 1:6708 | 8.28 | ≈3 a | NR | 348 | 0.174 | 8 | [48] |
| 0.125–0.177 | 5 | 1:134 | 7 | ≈2.7 a | Orbital, 180 rpm | 330 | 1.65 | NR | [29] |
| 0.149 | 2 | 1:16,109 | 6.4 | ≈0.9 a | Orbital, 50 rpm | 77.8 | 0.1556 | 72 | [39] |
| NR b | 2 | 1:16,109 | 6.4 | ≈0.9 a | Orbital, 50 rpm | 34.9 | 0.0698 | <96 | [39] |
| NR c | 2 | 1:16,109 | 6.4 | ≈0.9 a | Orbital, 50 rpm | 24.6 | 0.0492 | <96 | [39] |
| 0.045 | 2 | 1:16,109 | 6.4 | ≈0.9 a | Orbital, 50 rpm | 5.31 | 0.0106 | NR | [39] |
| 0.125–0.177 | 10 | 1:134 | 7 | ≈3.6 a | NR | --- | 10.5 | NR | [45] |
| 0–2–0.25 | 5 | 1:5366 | 9 | NR | Orbital, 100 rpm | --- | 2.8 | >120 | [69] |
| <0.044 | 0.2 | 1:13,416 | 7 | NR (no salt added) | Orbital | --- | 0.48 | 3 | [71] |
| <0.212 | 5 | 1:537 | 7 | ≈2.6 a | NR | --- | 3.2 | >50 | [54] |
| NR d | 0.1 | 1:40,247 | 7.1 | 1.50 | Magnetic, 300 rpm | --- | 0.12 | 2.7 | [49] |
| Coagulant | Dose (g L−1) | [AsT] Remaining Starting from As(V) (mg L−1) | [AsT] Remaining Starting from As(III) (mg L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al2(SO4)3 | 0.25 g L−1 | <LD | 5.00 |
| 0.50 g L−1 | <LD | --- | |
| 2.5 g L−1 | <LD | 3.91 | |
| 5.0 g L−1 | <LD | 3.60 | |
| FeCl3 | 0.25 g L−1 | <LD | 0.06 |
| 0.50 g L−1 | <LD | <LD | |
| 2.5 g L−1 | <LD | <LD | |
| 5.0 g L−1 | <LD | --- |
| Experiment | Minimum Dose (g L−1) | tR (h) | As:Fe or As:Al MR |
|---|---|---|---|
| As(V), µFe(0) | 0.25 | 288 | 1:67 |
| As(V), µFe(0) a | 0.25 | 168 | 1:67 |
| As(III), µFe(0) | 1 | >648 | 1:268 |
| As(V), wFe(0) | 2.50 | 168 | 1:670 |
| As(V), Al2(SO4)3 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 1:22 |
| As(III), Al2(SO4)3 | >5.00 | ND | >1:438 |
| As(V), FeCl3 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 1:23 |
| As(III), FeCl3 | 0.50 | 0.25 | 1:46 |
| As(V), clay | 50 | >168 | --- |
| As(III), clay | 50 | >648 | --- |
| Material | Dose (g L−1) | q (mg As g−1) | [As(III)] In the Leachate (mg L−1) | [As(V)] In the Leachate (mg L−1) | % AsT Leached |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μFe(0) | 1 | 5 | 0.007 | 0.119 | 0.063 |
| clay | 25 | 0.2 | 0.028 | 0.091 | 1.49 |
| clay | 50 | 0.1 | 0.007 | 0.119 | 3.15 |
| clay/μFe(0) | 25/1 | 0.192 | 0.021 | 0.084 | 1.36 |
| clay/μFe(0) | 50/1 | 0.098 | 0.028 | 0.076 | 2.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lan, L.E.; Reina, F.D.; De Seta, G.E.; Meichtry, J.M.; Litter, M.I. Comparison between Different Technologies (Zerovalent Iron, Coagulation-Flocculation, Adsorption) for Arsenic Treatment at High Concentrations. Water 2023, 15, 1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081481
Lan LE, Reina FD, De Seta GE, Meichtry JM, Litter MI. Comparison between Different Technologies (Zerovalent Iron, Coagulation-Flocculation, Adsorption) for Arsenic Treatment at High Concentrations. Water. 2023; 15(8):1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081481
Chicago/Turabian StyleLan, Luis E., Fernando D. Reina, Graciela E. De Seta, Jorge M. Meichtry, and Marta I. Litter. 2023. "Comparison between Different Technologies (Zerovalent Iron, Coagulation-Flocculation, Adsorption) for Arsenic Treatment at High Concentrations" Water 15, no. 8: 1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081481





