Hydropower Dam Development and Fish Biodiversity in the Mekong River Basin: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Fish Biodiversity in the Mekong River Basin
3. Hydropower Dam Development in the Mekong River Basin
4. The Impacts of Hydropower Dam Development on Mekong Fish Biodiversity: Past, Present and Future
5. Uncertainty
6. Preventing and Mitigating Hydropower Dam Impacts on Fish Biodiversity
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soukhaphon, A.; Baird, I.G.; Hogan, Z.S. Hydropower dams and impacts in the Mekong River Basin: A review. Water 2021, 13, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, A.V.; Hortle, K.G.; Nguyen, D.N. Factors driving long term declines in inland fishery yields in the Mekong Delta. Water 2021, 13, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welcomme, R.L.; Baird, I.G.; Dudgeon, D.; Halls, A.; Lamberts, D.; Mustafa, M.G. Fisheries of the rivers of Southeast Asia. In Freshwater Fisheries Ecology; Craig, J.F., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Winemiller, K.; McIntyre, P.B.; Castello, L.; Fluet-Chouinard, E.; Giarrizzo, T.; Nam, S.; Baird, I.G.; Darwall, W.; Lujan, N.K.; Harrison, I.; et al. Hydropower expansion in the Amazon, Congo and Mekong—A looming threat to global biodiversity. Science 2016, 351, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baran, E.; Myschowoda, C. Dams and fisheries in the Mekong Basin. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2009, 12, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, S.R.; Hirsch, P. Framing fisheries decline. Aquat. Resour. Cult. Dev. 2005, 1, 79–90. [Google Scholar]
- Cooney, P.B.; Kwak, T.J. Spatial extent and dynamics of dam impacts on tropical island freshwater fish assemblages. BioScience 2013, 63, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.J.; Jordan, A.; Frisk, M.G. The historic influence of dams on diadromous fish habitat with a focus on river herring and hydrologic longitudinal connectivity. Landscape Ecol. 2011, 26, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, L. Yangtze dams increasingly threaten the survival of the Chinese sturgeon. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 3640–3647.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phomikong, P.; Udduang, S.; Fukushima, M.; Srichareondham, B.; Rattanachamnong, D.; Jutagate, T. Larval fish assemblage patterns in three tributaries of Mekong River in Thailand. Indian J. Fish. 2018, 65, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziv, G.; Baran, E.; Nam, S.; Rodríguez-Iturbe, I.; Levin, S.A. Trading-off fish biodiversity, food security, and hydropower in the Mekong River Basin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5609–5614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orr, S.; Pittock, J.; Chapagain, A.; Dumaresq, D. Dams on the Mekong River: Lost fish protein and the implications for land and water resources. Glob. Environ. Change 2012, 22, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, I.G. The Don Sahong dam: Potential impacts on regional fish migrations, livelihoods and human health. Crit. Asian Stud. 2011, 43, 211–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, A.J.; Baumgartne, L.J.; Boys, C.A.; Conallin, J.; Cowx, I.G.; Finlayson, M.C.; Franklin, P.A.; Hogan, Z.S.; Koehn, J.D.; McCartney, M.P.; et al. Speaking the same language: Can the sustainable development goals translate the needs of inland fisheries into irrigation decisions? Mar. Freshw. Res. 2019, 70, 1211–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kottelat, M.; Whitten, A.J. Freshwater Biodiversity in Asia, with Special Reference to Fish; World Bank Technical Paper No. 343; World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, I.G. Aquatic biodiversity in the Siphandone wetlands. Siphandone Wetlands. In Environmental Protection and Community Development in Siphandone Wetland Project; Daconto, G., Ed.; CESVI: Bergamo, Italy, 2001; pp. 61–74. [Google Scholar]
- Coates, D.; Poeu, O.; Suntornratana, U.; Thanh Tung, N.; Viravong, S. Biodiversity and fisheries in the Lower Mekong Basin. In Mekong Development Series No. 2; Mekong River Commission: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2003; p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Pittock, J. Limiting the effects of hydropower dams on freshwater biodiversity: Options on the Lancang River, China. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2018, 70, 169–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorella, K.J.; Bageant, E.R.; Kim, M.; Sean, V.; Try, V.; MacDonell, H.J.; Baran, E.; Kura, Y.; Brooks, A.C.; Barrett, C.B.; et al. Analyzing drivers of fish biomass and biodiversity within community fish refuges in Cambodia. Ecol. Soc. 2019, 24, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kominoski, J.S.; Ruhí, A.; Hagler, M.M.; Petersen, K.; Sabo, J.L.; Sinha, T.; Sankarasubramanian, A.; Olden, J.D. Patterns and drivers of fish extirpations in rivers of the American Southwest and Southeast. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhuoy, S.; Hogan, Z.S.; Chandra, S.; Chheng, P.; Touch, B.; Utsugi, K.; Ngor, P.B. Daily otolith ring validation, age composition, and origin of the endangered striped catfish in the Mekong. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 33, e01953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Du, W.; Lucas, M.C.; Ding, C.; Chen, J.; Tao, J.; He, D. River fragmentation and barrier impacts on fishes have been greatly underestimated in the upper Mekong River. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 327, 116817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taki, Y. Fishes of the Lao Mekong Basin; U.S. A.I.D. Mission to Laos: Vientiane, Laos, 1974; p. vi + 232.
- Kottelat, M. Zoogeography of the fishes from Indochinese inland waters with an annotated check-list. Bull. Zool. Mus. Univ. 1989, 12, 1–55. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, T.R. Revision of the Southeast Asian cyprinid fish genus Probarbus, with two new species threatened by proposed construction of dams on the Mekong River. Ichthyol. Explor. Freshw. 1992, 3, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, I.G. Probarbus jullieni and Probarbus labeamajor: The management and conservation of two of the largest fish species in the Mekong River in southern Laos. Aquat. Conserv. Freshw. Mar. Ecosyst. 2006, 16, 517–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.R. Osphronemus exodon, a new species of giant gouramy with extraordinary dentition from the Mekong. Nat. Hist. Bull. Siam Soc. 1994, 42, 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Monkolprasit, S.; Roberts, T.R. Himantura chaophraya, a new giant freshwater stingray from Thailand. Jpn. J. Ichthyol. 1990, 37, 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, T.R. Artisinal fisheries and fish ecology below the great waterfalls of the Mekong River in Southern Laos. Nat. Hist. Bull. Siam Soc. 1993, 41, 31–62. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, I.G.; Inthaphaisy, V.; Kisouvannalat, P.; Phylaivanh, B.; Mounsouphom, B. The Fishes of Southern Lao; Lao Community Fisheries and Dolphin Protection Project, Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry: Pakse, Laos, 1999; p. 162.
- Last, P.R.; Naylor, G.; Manjaji-Matsumoto, B.M. A revised classification of the family Dasyatidae (Chondrichthyes: Myliobatiformes) based on new morphological and molecular insights. Zootaxa 2016, 4139, 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.T.; Last, P.R. A review of the taxonomy of chondrichthyan fishes: A modern perspective. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 80, 901–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottelat, M. Fishes of the Nam Theun and Xe Bangfai basins, Laos, with diagnoses of twenty-two new species (Teleostei: Cyprinidae, Balitoridae, Cobitidae, Coiidae and Odontobutidae). Ichthyol. Explor. Freshwaters. 1998, 9, 1–128. [Google Scholar]
- Rainboth, W.J. Fishes of the Cambodian Mekong; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1996; Volume 265, p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- Vidthayanon, C.; Karnasuta, J.; Nabhitabhata, J. Diversity of Freshwater Fishes in Thailand; Fisheries Department, the Office of Environmental Policy and Planning and Danced: Bangkok, Thailand, 1998.
- ICEM. MRC Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA) of Hydropower on the Mekong Mainstream: Summary of the Final Report; International Centre for Environmental Management: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kottelat, M.; Baird, I.G.; Kullander, S.O.; Ng, H.H.; Parenti, L.R.; Rainboth, W.J.; Vidthayanon, C. The status and distribution of freshwater fishes of Indo-Burma. In The Status and Distribution of Freshwater Biodiversity in Indo-Burma; Allen, D.J., Smith, K.G., Darwall, W.R.T., Eds.; IUCN: Cambridge, UK; Gland, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 36–65. [Google Scholar]
- Rainboth, W.J. Fishes of the Greater Mekong Ecosystem with Species List and Photographic Atlas; Miscellaneous Publications of the University of Michigan Museum of Zoology: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2012; p. 293. [Google Scholar]
- Jerde, C.L.; Mahon, A.R.; Campbell, T.; McElroy, M.E.; Pin, K.; Childress, J.N.; Armstrong, M.N.; Zehnpfennig, J.R.; Kelson, S.J.; Koning, A.A.; et al. Are Genetic Reference Libraries Sufficient for Environmental DNA Metabarcoding of Mekong River Basin Fish? Water 2021, 13, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 28 New Species Discovered in Laos, WWF reveals. Vientiane Times, 28 May 2015.
- Ng, H.H.; Kottelat, M. Clarias serniosus, a new walking catfish (Teleostei: Clariidae) from Laos. Zootaxa 2014, 3884, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.H.; Kottelat, M. The Glyptothorax of the Bolaven Plateau, Laos (Teleostei: Sisoridae): New and endangered. Zootaxa 2017, 4238, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.H.; Kottelat, M. Description of Bagarius vegrandis, a new species of sisorid catfish from Indochina (Actinopterygii: Siluriformes), with notes on the identity of Bagarius. Zootaxa 2021, 4926, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kottelat, M. Speolabeo, a new genus name for the cave fish Bangana musaei (Teleostei: Cyprinidae). Zootaxa 2017, 4254, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kottelat, M. Schistura epixenos, a new species of loach from the Nakai Plateau, Laos (Teleostei: Nemacheilidae). Zootaxa 2017, 4300, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottelat, M. Schistura systomos, a new species of loach from southern Laos (Teleostei: Nemacheilidae). Ichthyol. Explor. Freshw. 2017, 28, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kottelat, M. Schistura titan, a new species of loach from Dakchung Plateau, southern Laos (Teleostei: Nemacheilidae). Ichthyol. Explor. Freshw. 2017, 28, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Kottelat, M. Schistura thavonei, a new species of loach from northwestern Laos (Teleostei: Nemacheilidae). Raffles Bull. Zool. 2017, 65, 395–403. [Google Scholar]
- Kottelat, M. Schistura colossa and S. klydonion, two new species of loaches from Bolaven Plateau, southern Laos (Teleostei: Nemacheilidae). Raffles Bull. Zool. 2017, 65, 341–356. [Google Scholar]
- Kottelat, M. Three new species of loaches of the genus Schistura from the Nam Ngiep drainage, central Laos (Teleostei: Nemacheilidae). Raffles Bull. Zool. 2017, 65, 691–706. [Google Scholar]
- Kottelat, M. Vanmanenia orcicampus, a new species of loach from the Plain of Jars, Laos (Teleostei: Gastromyzontidae). Ichthyol. Explor. Freshwaters. 2017, 28, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Kottelat, M. Rhyacoschistura larreci, a new genus and species of loach from Laos and redescription of R. suber (Teleostei: Nemacheilidae). Zootaxa 2019, 4612, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottelat, M. ‘Nemacheilus’ argyrogaster, a new species of loach from southern Laos (Teleostei: Nemacheilidae). Zootaxa 2021, 4933, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlen, J.; Petrtýl, M.; Chaloupková, P.; Borin, C. Schistura kampucheensis, a new species of loach from Cambodia (Teleostei: Nemacheilidae). Ichthyol. Explor. Freshw. 2016, 26, 353–362. [Google Scholar]
- Page, L.M.; Pfeiffer, J.M.; Suksri, S.; Randall, Z.S.; Boyd, D.A. Variation in the arrow loach, Nemacheilus masyae (Cypriniformes: Nemacheilidae), in mainland Southeast Asia with description of a new species. Copeia 2020, 108, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao Natural Environment Foundation. Fishes of Indochinese Mekong; Nagao Natural Environment Foundation: Tokyo, Japan, 2021; p. xii + 546. [Google Scholar]
- Zakaria-Ismail, M. Zoogeography and biodiversity of the freshwater fishes of Southeast Asia. Hydrobiologia 1994, 285, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, E.; Samadee, S.; Shwu Jiau, T.; Thanh Cong, T. Fish and fisheries in the Sesan River Basin—Catchment baseline, fisheries section. In Mekong Challenge Program Project MK3 “Optimizing the Management of a Cascade of Reservoirs at the Catchment Level”; Project Report; WorldFish Center: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2011; p. 61. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, B.; Huang, X. Mekong Fishes: Biogeography, Migration, Resources, Threats, and Conservation. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2022, 30, 170–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, I.C.; Poole, C.; Giesen, W.; Valbo-Jorgensen, J. Species diversity and ecology of Tonle Sap Great Lake, Cambodia. Aquat. Sci. 2006, 68, 355–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anadromous species spend part of their lives at sea but spawn in freshwater. Catadromous species, on the other hand, spend most of their lives in freshwaters but spawn in salt waters.
- Vu, A.V.; Baumgartner, L.G.; Mallen-Cooper, M.; Howitt, J.A.; Robinson, W.A.; So, N.; Cowx, I.G. Diadromy in a large tropical river, the Mekong: More common than assumed, with greater implications for management. J. Ecohydraulics. 2020, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, A.V.; Baumgartner, L.J.; Doran, G.S.; Limburg, K.E.; Gillanders, B.M.; Thiem, J.D.; Howitt, J.A.; Kewish, C.M.; Reinhardt, J.; Cowx, I.G. Diverse migration tactics of fishes within the large tropical Mekong river system. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2022, 29, 708–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, Z.; Baird, I.G.; Radtke, R.; Vander Zanden, M.J. Long distance migration and marine habitation in the Asian catfish, Pangasius krempfi. J. Fish Biol. 2007, 71, 818–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, I.G. Best Practices in Compensation and Resettlement for Large Dams: The Case of the Planned Lower Sesan 2 Hydropower Project in Northeastern Cambodia; RCC: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2009; p. 138. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, I.G.; Flaherty, M.S.; Phylavanh, B. Mekong River Pangasiidae catfish migrations and the Khone Falls wing trap fishery in southern Laos. Nat. Hist. Bull. Siam Soc. 2004, 52, 81–109. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, T.R.; Warren, T.J. Observations on fisheries and fisheries in southern Laos and northeaster Cambodia, October 1993-February 1994. Nat. Hist. Bull. Siam Soc. 1994, 42, 87–115. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, T.R.; Baird, I.G. Traditional fisheries and fish ecology on the Mekong River At Rhone Waterfalls in Southern Laos. Nat. Hist. Bull. Siam Soc. 1995, 43, 219–262. [Google Scholar]
- Rainboth, W.J. Aaptosyax grypus, a new genus and species of large piscivorous cyprinids from the middle Mekong River. Jpn. J. Ichthyol. 1991, 38, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, T.; Pin, K.; Ngor, P.B.; Hogan, Z. Conserving Mekong megafishes: Current status and critical threats in Cambodia. Water 2020, 12, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, J.D.; Abell, R.; Hogan, Z.; Revenga, C.; Taylor, B.W.; Welcomme, R.L.; Winemiller, K. Overfishing of inland waters. BioScience 2005, 55, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hogan, Z.; Ngor, P.B.; van Zalinge, N. Status and conservation of two endangered fish species, the Mekong giant catfish Pangasianodon gigas and the giant carp Catlocarpio siamensis, in Cambodia’s Tonle Sap River. Nat. Hist. Bull. Siam Soc. 2001, 49, 269–282. [Google Scholar]
- Hogan, Z.S.; Moyle, P.B.; May, B.; Vander Zanden, M.J.; Baird, I.G. The imperiled giants of the Mekong. Ecologists struggle to understand—And protect—Southeast Asia’s large migratory catfish. Am. Sci. 2004, 92, 228–237. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.I.; Jarić, I.; Roberts, D.L.; He, H.; Du, C.; Wu, J.; Wang, C.; Wei, Q. Extinction of one of the world’s largest freshwater fishes: Lessons for conserving the endangered Yangtze fauna. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, I.L.; Bunnefeld, N.; Jump, A.S.; Peres, C.A.; Dent, D.H. Extinction debt on reservoir land-bridge islands. Biol. Conserv. 2016, 199, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuussaari, M.; Bommarco, R.; Heikkinen, R.K.; Helm, A.; Krauss, J.; Lindborg, R.; Öckinger, E.; Pärtel, M.; Pino, J.; Rodà, F.; et al. Extinction debt: A challenge for biodiversity conservation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, Z.; Na-Nakorn, U.; Kong, H. Threatened fishes of the world: Pangasius sanitwongsei Smith 1931 (Siluriformes: Pangasiidae). Environ. Biol. Fishes 2009, 84, 303–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneddon, C. Concrete Revolution: Large Dams, Cold War Geopolitics, and the US Bureau of Reclamation; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Molle, F.; Floch, P.; Promphakping, B.; Blake, D.J.H. The ‘greening of Isaan’: Politics, ideology and irrigation development in the northeast of Thailand. In Contested Waterscapes in the Mekong Region: Hydropower, Livelihoods and Governance; Molle, F., Foran, T., Käkönen, M., Eds.; Eartchscan: London, UK, 2009; pp. 253–282. [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch, P. The changing political dynamics of dam building on the Mekong. Water Altern. 2010, 3, 312–323. [Google Scholar]
- Foran, T.; Manorom, K. Pak Mun dam: Perpetually contested. In Contested Waterscapes in the Mekong Region: Hydropower, Livelihoods and Governance; Molle, F., Foran, T., Käkönen, M., Eds.; Eartchscan: London, UK, 2009; pp. 55–80. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, I.G.; Manorom, K.; Phenow, A.; Gaja-Svasti, S. Opening the gates of the Pak Mun Dam: Fish migrations, domestic water supply, irrigation projects and politics. Water Altern. Interdiscip. J. Water Politics Dev. 2020, 13, 141–159. [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon, C. Reconfiguring scale and power: The Khong-Chi-Mun Project in northeast Thailand. Environ. Plan. 2003, 35, 2229–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Rivers Network. Power Struggle: The Impacts of Hydro-Development in Laos; International Rivers Network: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Whitington, J. Anthropogenic Rivers: The Production of Uncertainty in Lao Hydropower; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, K.D.; He, D.M.; Lu, X.X. Sedimentation in the Manwan reservoir in the Upper Mekong and its downstream impacts. Quart. Int. 2008, 186, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, A.B.; Baird, I.G. Transboundary impact assessment in the Sesan River Basin: The case of the Yali Falls dam. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2007, 23, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magee, D. Powershed politics: Hydropower and interprovincial relations under Great Western Development. China Q. 2006, 185, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Commission on Dams (WCD). Dams and Development: A New Framework for Decision-Making; Earthscan Publications: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker, B.; Robichaud, W. Dead in the Water: Global Lessons from the World Bank’s Model Hydropower Project in Laos; University of Wisconsin Press: Madison, WI, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xinhua. Available online: http://www.xinhuanet.com/english/asiapacific/2019-02/14/c_137821006.htm (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Wyatt, A.B. Infrastructure Development and BOOT in Laos and Vietnam: A Case Study of Collective Action and Risk in Transitional Developing Economies. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Board, J. Southeast Asia’s hydropower boom grinds to a halt as COVID-19 stalls projects. CNA, 22 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, I.G. Non-government organizations, villagers, political culture and the Lower Sesan 2 dam in northeastern Cambodia. Crit. Asian Stud. 2016, 48, 257–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Associated Press. Cambodia’s biggest hydropower dam now producing electricity. Bangkok Post, 17 December 2018.
- Chen, X.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, B.; Wang, L.; Han, F.; Zhang, C. Balancing competing interests in the Mekong River Basin via the operation of cascade hydropower reservoirs in China: Insights from systems modeling. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 119967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyler, B.; Weatherby, C. New Evidence: How China Turned off the Tap on the Mekong River; Stimson Center: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Phomikong, P.; Fukushima, M.; Srichareondham, B.; Nohara, S.; Jutagate, T. Diversity and community structure of fishes in the regulated versus unregulated tributaries of the Mekong River. River Res. Applic. 2015, 31, 1262–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEARIN; AoP. Mae Mun: The Return of Fisherman; South East Asian Rivers Network and Assembly of the Poor: Chiang Mai, Thailand, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins, P.R.; Hortle, K.G.; Phommanivong, S.; Singsua, Y. Underwater video monitoring of fish passage in the Mekong River at Sadam Channel, Khone Falls, Laos. River Res. Appl. 2018, 34, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal-Quintero, J.D.; Januchowski-Hartley, S.R.; Maldonado-Ocampo, J.A.; Jézéquel, C.; Delgado, J.; Tedesco, P.A. Damming fragments species’ ranges and heightens extinction risk: Damming increases fish extinction risk. Conserv. Lett. 2007, 10, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, F.; Thieme, M.; Zarfl, C.; Grill, G.; Lehner, B.; Hogan, Z.; Tockner, K.; Jahnig, S.C. Impacts of loss of free-flowing rivers on global freshwater megafauna. Biol. Conserv. 2021, 263, 109335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekong River Commission Secretariat. Fisheries in the Lower Mekong Basin: Review of the Fishery Sector in the Lower Mekong Basin; Interim Committee for Coordination of Investigations of the Lower Mekong Basin: Thailand, 1992; p. 92. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, M.T.; Hill, S.A. Fisheries Ecology and Hydropower in the Mekong River: An Evaluation of Run-of-the-River Projects. Mekong Secretariat: Bangkok, Thailand, 1994; p. x + 106. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, B. What do the occurrences of migratory fishes in the Upper Mekong mean? Ambio 2013, 42, 877–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baird, I.G. Pa Souay Hang Leuang Pangasius krempfi. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2011. e.T181328A7668262. International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources. 2013. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/181328/7668262 (accessed on 4 February 2023).
- Tran, N.T.; Labonne, M.; Chung, M.-T.; Wang, C.-H.; Huang, K.-F.; Durand, J.-D.; Grudpan, C.; Chan, B.; Hoang, H.D.; Panfili, J. Natal origin and migration pathways of Mekong catfish (Pangasius krempfi) using strontium isotopes and trace element concentrations in environmental water and otoliths. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, I.G.; Flaherty, M.S. Beyond national borders: Important Mekong River medium sized migratory carps (Cyprinidae) and fisheries in Laos and Cambodia. Asian Fish. Sci. 2004, 17, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, I.G.; Hogan, Z.; Phylavanh, B.; Moyle, P. A communal fishery for the migratory catfish Pangasius macronema in the Mekong River. Asian Fish. Sci. 2001, 14, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffels, R.J.; Humphries, P.; Bond, N.R.; Price, A.E. Fragmentation of lateral connectivity and fish population dynamics in large rivers. Fish Fish. 2022, 23, 680–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumsteiger, J.; Moyle, P.B. Assessing extinction. Bioscience 2017, 67, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCully, P. Silenced Rivers: The Ecology and Politics of Large Dams, 2nd ed.; Zed Books: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Tromboni, F.; Dilts, T.E.; Null, S.E.; Lohani, S.; Ngor, P.B.; Soum, S.; Hogan, Z.; Chandra, S. Changing land use and population density are degrading water quality in the Lower Mekong Basin. Water 2021, 13, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondolf, G.M.; Rubin, Z.K.; Minear, J.T. Dams on the Mekong: Cumulative sediment starvation. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 5158–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, I.G.; Silvano, R.; Parlee, B.; Poesch, M.; Maclean, B.; Napoleon, A.; Lepine, M.; Hallwass, G. The downstream impacts of hydropower dams and indigenous and local knowledge: Examples from the Peace-Athabasca, Mekong and Amazon. Environ. Manag. 2021, 67, 682–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Räsänen, T.A.; Koponen, J.; Lauri, H.; Kummu, M. Downstream hydrological impacts of hydropower development in the Upper Mekong Basin. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 3495–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, E.; Guerin, E.; Nasiel, J. Sediments and Dams in the Mekong; WorldFish, and CGIAR Research Program on Water, Land and Ecosystems (WLE): Penang, Malaysia, 2015; p. 108. [Google Scholar]
- Welcomme, R.L.; Vidthayanon, C. The impacts of introductions and stocking of exotic species in the Mekong basin and policies for their control. MRC Tech. Pap. 2003, 9, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson, R.G.; Waples, R.S.; Myers, J.M.; Weitkamp, L.A.; Bryant, G.J.; Johnson, O.W.; Hard, J.J. Pacific salmon extinctions: Quantifying lost and remaining diversity. Conserv. Biol. 2007, 21, 1009–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiruba-Sankar, R.; Praveen Raj, J.; Saravanan, K.; Lohith, K.; Kumar, J.; Jani Angel, R.; Velmurugan, A.; Dam Roy, S. Chapter 9—Invasive Species in Freshwater Ecosystems. In Threats to Ecosystem Services. Biodiversity and Climate Change Adaptation in Tropical Islands; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 257–296. [Google Scholar]
- Predator fish species appear in Laos. Vientiane Times, 23 December 2014.
- Roberts, T.R. Just another dammed river? Negative impacts of Pak Mun Dam on fishes of the Mekong Basin. Nat. Hist. Bull. Siam Soc. 1993, 41, 105–133. [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell, J.F. Vegetation in the Siphandone Wetlands. In Siphandone Wetlands; Daconto, G., Ed.; CESVI: Bergamo, Italy, 2001; pp. 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Dugan, P.J.; Barlow, C.; Agostinho, A.A.; Baran, E.; Cada, G.F.; Chen, D.; Marmulla, G. Fish migration, dams, and loss of ecosystem services in the Mekong basin. AMBIO J. Hum. Environ. 2010, 39, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, T.R. On the river of no returns: Thailand’s Pak Mun Dam and its fish ladder. Nat. Hist. Bull. Siam Soc. 2001, 49, 189–230. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, I.G.; Manorom, K.; Phenow, A.; Gaja-Svasti, S. What about the tributaries of the tributaries? Fish migrations, fisheries, dams and fishers’ knowledge in northeastern Thailand. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2020, 36, 170–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.R. Mekong mainstream hydropower dams: Run-of-the-River or ruin-of-the-river? Nat. Hist. Bull. Siam Soc. 1995, 43, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, I.G.; Shoemaker, B.P.; Manorom, K. The people and their river, the World Bank and its dam: Revisiting the Xe Bang Fai River in Laos. Dev. Change 2015, 46, 1080–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; He, D.; Perrett, L.; Wang, H.; Hu, W.; Deng, W.; Wu, Y. Fish and fisheries in the Upper Mekong: Current assessment of the fish community, threats and conservation. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2009, 19, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, J.W.; Healey, M.; Dugan, P.; Barlow, C. Potential effects of dams on migratory fish in the Mekong River: Lessons from salmon in the Fraser and Columbia Rivers. Environ. Manag. 2011, 47, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, Z. Imperiled Giant Fish and Mainstream Mekong Dams in the Lower Mekong Basin: Assessment of Current Status, Threats, and Mitigation; University of Nevada: Reno, NV, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, B.D.; Thomas, G.A. Restoring environmental flows by modifying dam operations. Ecol. Soc. 2007, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, M.; Bergkamp, G.; Scanlon, J. Flow: The Essentials of Environmental Flows; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, B.D.; Postel, S.; Revenga, C.; Scudder, T.; Lehner, B.; Churchill, A.; Chow, M. Lost in development’s shadow: The downstream human consequences of dams. Water Altern. 2010, 3, 14–42. [Google Scholar]
- Halls, A.S.; Moyle, P.B. Comment on “Designing river flows to improve food security futures in the Lower Mekong Basin”. Science 2018, 361, eaat1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limburg, K.E.; Waldman, J.B. Dramatic declines in North Atlantic diadromous fishes. BioScience 2009, 59, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, M.; Foote, K.J.; McNie, P.; Piria, M. The decline of New Zealand’s freshwater fish fauna: The influence of land-use. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2019, 70, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.R. Fluvicide: An independent Environmental Assessment of the Nam Theun 2 Hydropower Project in Laos, with Particular Reference to Aquatic Biology and Fishes; Institute for Development Anthropology: Bangkok, Thailand, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Deap, L.; Degen, P.; Van Zalinge, N. Fishing gears of the Cambodian Mekong; Fisheries Technical Paper; Inland Fisheries Research and Development Institute of Cambodia: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2003; Volume 4, p. 269. [Google Scholar]
- Cooke, S.J.; Paukert, C.; Hogan, Z. Endangered river fish: Factors hindering conservation and restoration. Endanger. Species Res. 2012, 17, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dvorák, T.; Šlechtová, V.; Bohlen, J. Using species groups to approach the large and taxonomically unresolved freshwater fish family Nemacheilidae (Teleostei: Cypriniformes). Biology 2022, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, D.T.; Vinh, N.T. Genetic diversity of Pangasius krempfi in the Mekong River estuaries. Can Tho Univ. J. Sci. 2019, 11, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Eva, B.; Harmony, P.; Thomas, G.; Francois, G.; Alice, V.; Claude, M.; Tony, D. Trails of river monsters: Detecting critically endangered Mekong giant catfish Pangasianodon gigas using environmental DNA. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2016, 7, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hurwood, D.A.; Adamson, E.A.S.; Mather, P.B. Evidence for strong genetic structure in a regionally important, highly vagile cyprinid (Henicorhynchus lobatus) in the Mekong River Basin. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2008, 17, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, I.G.; Flaherty, M.S. Mekong River fish conservation zones in southern Laos: Assessing effectiveness using local ecological knowledge. Environ. Manag. 2005, 36, 439–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, I.G. Strength in diversity: Fish sanctuaries and deep-water pools in Laos. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2006, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loury, E.; Ainsley, S.M. Identifying indicators to evaluate community-managed freshwater protected areas in the Lower Mekong Basin: A review of marine and freshwater examples. Water 2020, 12, 3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loury, E.K.; Ainsley, S.M.; Bower, S.D.; Chuenpagdee, R.; Farrell, T.; Guthrie, A.G.; Heng, S.; Lunn, Z.; Mamun, A.A.; Oanedel, R.; et al. Salty stories, fresh spaces: Lessons for aquatic protected areas from marine and freshwater experiences. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2018, 28, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koning, A.A.; Perales, K.M.; Fluet-Chouinard, E.; McIntyre, P.B. Success of small reserves for river fishes emerges from local, network, and cultural contexts. Nature 2020, 12, 3530. [Google Scholar]
- Koning, A.A.; McIntyre, P.B. Grassroots reserves rescue a river food web from cascading impacts of overharvest. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2021, 19, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loury, E.K.; Elliott, V.L.; Ainsley, S.M.; Baird, I.G.; Baumgartner, L.J.; Chhuoy, S.; Lee, D.J.; Ngor, P.B.; Touch, B.; Vu, A.V.; et al. Priority knowledge needs for management of migratory fish species in Cambodia. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2021, 28, 393–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naughton, G.P.; Hogan, Z.S.; Campbell, T.; Graf, P.J.; Farwell, C.; Sukumasavin, N. Acoustic telemetry monitors movements of wild adult catfishes in the Mekong River, Thailand and Laos. Water 2021, 13, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolding, J.; Viravong, S.; Phounsavath, S.; Photthitai, C.; Sverdrup-Jensen, S.; Warren, T.J. Monitoring of deep pools in the Mekong River: The potential of hydro-acoustic methods. Catch Cult. 2002, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Johannes, R.E.; Freeman, M.M.R.; Hamilton, R.J. Ignore fishers’ knowledge and miss the boat. Fish Fish. 2000, 1, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggan, N.; Neis, B.; Baird, I.G. Fishers’ Knowledge in Fisheries Science and Management; In Coastal Management Sourcebooks Series; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, I.G. Fishes and forests: The importance of seasonally flooded riverine habitat for Mekong River fish feeding. Nat. Hist. Bull. Siam Soc. 2007, 55, 121–148. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, I.G.; Manorom, K. Migrating fish and mobile knowledge: Situated fishers’ knowledge and social networks in the Lower Mekong River Basin in Thailand, Laos and Cambodia. Mobilities 2019, 14, 762–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvano, R.A.M.; Baird, I.G.; Begossi, A.; Hallwass, G.; Huntington, H.P.; Lopes, P.F.M.; Parlee, B.; Berkes, F. Fishers’ multidimensional knowledge advances in fisheries and aquatic science. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2022, 38, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tickner, D.; Opperman, J.J.; Abell, R.; Acreman, M.; Arthington, A.H.; Bunn, S.E.; Cooke, S.J.; Dalton, J.; Darwall, W.; Edwards, G.; et al. Bending the curve of global freshwater biodiversity loss: An emergency recovery plan. Bioscience 2020, 70, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maasri, A.; Jähnig, S.C.; Adamescu, M.C.; Adrian, R.; Baigun, C.; Baird, D.J.; Batista-Morales, A.; Bonada, A.; Brown, L.E.; Cai, Q.; et al. A global agenda for advancing freshwater biodiversity research. Ecol. Lett. 2022, 25, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthington, T.A.; van Soesbergen, A.; Berkhuysen, A.; Brink, K.; Royte, J.; Thieme, M.; Wanningen, H.; Darwall, W. Global swimways for the conservation of migratory freshwater fishes. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2022, 20, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilpern, S.A.; Sethi, S.A.; Barthem, R.B.; Batista, V.d.; Doria, C.R.C.; Duponchelle, F.; Vasquez, A.G.; Goulding, M.; Isaac, V.; Naeem, S.; et al. Biodiversity underpins fisheries resilience to exploitation in the Amazon river basin. Proceddings R. Soc. B 2022, 163, 2892022072620220726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
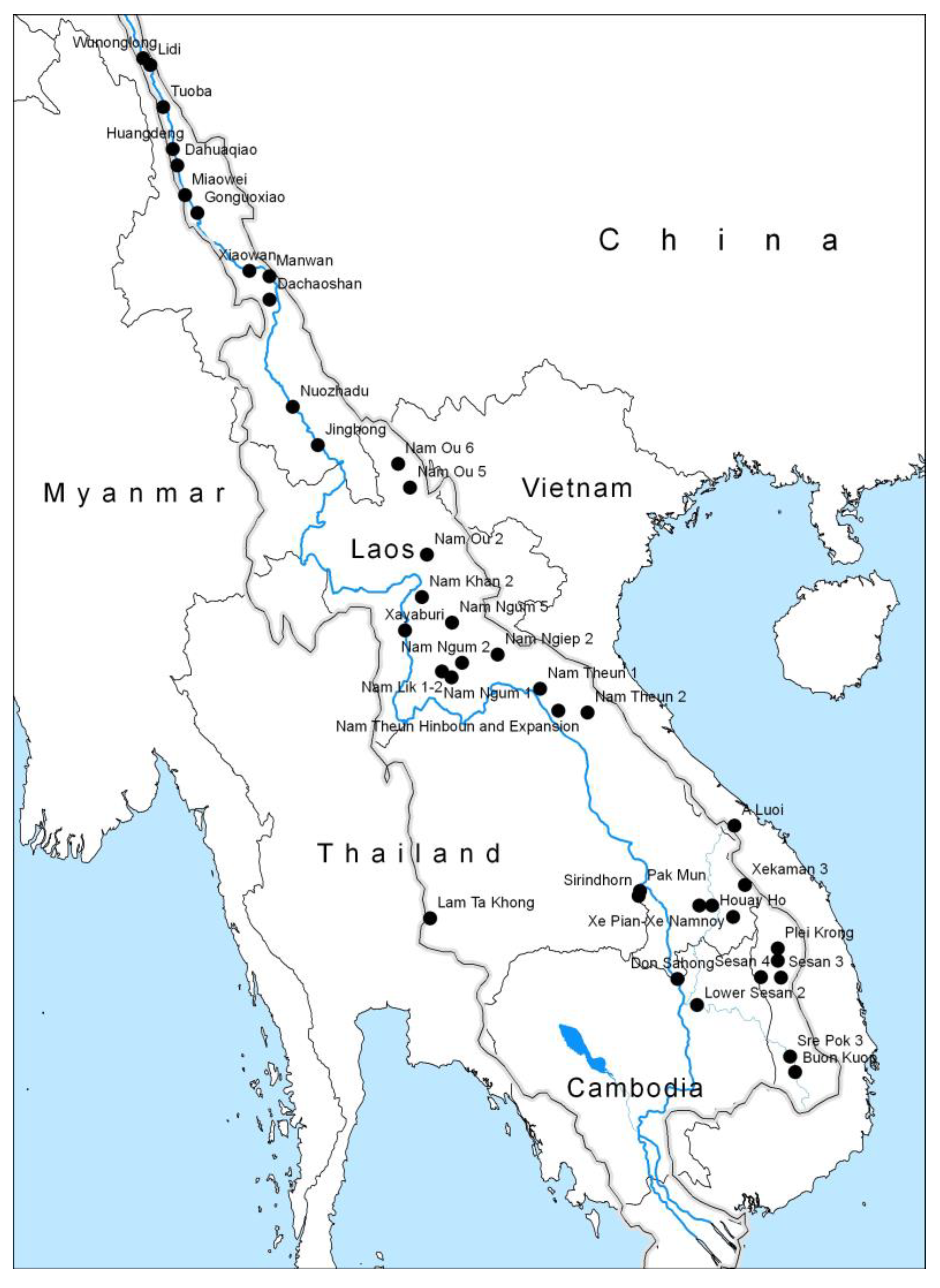
| Project | Location | Developer | Power Capacity (MW) | Reservoir Area (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wunonglong | Lancang/Mekong mainstream, China | PRC | 990 | |
| Lidi | Lancang/Mekong mainstream, China | PRC | 420 | 3.7 |
| Tuoba | Lancang/Mekong mainstream, China | PRC | ||
| Huangdeng | Lancang/Mekong mainstream, China | PRC | 1900 | |
| Dahuaqiao | Lancang/Mekong mainstream, China | PRC | 920 | |
| Miaowei | Lancang/Mekong mainstream, China | PRC | 1400 | |
| Gonguoxiao | Lancang/Mekong mainstream, China | PRC | 900 | 343 |
| Xiaowan | Lancang/Mekong mainstream, China | PRC | 4200 | 194 |
| Manwan | Lancang/Mekong mainstream, China | PRC | 1550 | 415 |
| Dachaoshan | Lancang/Mekong mainstream, China | PRC | 1500 | 26.25 |
| Nuozhadu | Lancang/Mekong mainstream, China | PRC | 5850 | 320 |
| Jinghong | Lancang/Mekong mainstream, China | PRC | 1750 | 510 |
| Xayaburi | Mekong River, northern Laos. 150 km downstream from Luang Prabang | CK Power PLC, Thailand | 1280 | 55.9 |
| Don Sahong | Mekong River, southern Laos. Channel just above Cambodia border | Mega First Corporation Berhad, Malaysia and EdL | 240 | 0.29 |
| Nam Theun 2 | Mekong tributary, Central Laos, Nakai Plateau | Electricite du France, EdL and others | 1075 | 450 |
| Nam Theun Hinboun and Expansion | Mekong tributary, Central Laos, Theun and Hinboun Rivers | EdL, GMS Power and Scatect | 220 and 222 | 49 and 49 |
| Nam Ngum 1 | Mekong tributary, Central Laos, Nam Ngum River | EdL (Royal Lao Government) | 155 | 370 |
| Nam Theun 1 | Mekong tributary, Central Laos, Theun River | Phonesack, EGCO and EdL | 650 | 93.6 |
| Houay Ho | Mekong tributary, Bolaven Plateau, southern Laos | Daewoo (original developer) | 152 | 37 |
| Nam Khan 2 | Mekong tributary, northern Laos | China’s Sinohydro Corporation | 130 | 30.5 |
| Nam Lik 1-2 | Mekong tributary, northern Laos | China Water and Energy, Ltd. holding (90%) and EDL holding (10%) | 100 | 24.4 |
| Nam Ngiep 2 | Mekong tributary, northern Laos | China Water and Energy, Ltd. holding (90%) and EDL holding (10%) | 180 | |
| Nam Ngum 2 | Mekong tributary, central Laos | Ch Karnchang and Ratchaburi Holdings | 615 | 122.2 |
| Nam Ngum 5 | Mekong tributary, central Laos | Sinhydro Corporation | 120 | 15 |
| Nam Ou 2 | Mekong tributary, northern Laos | Sinohydro Corporation | 120 | 15.7 |
| Nam Ou 5 | Mekong tributary, northern Laos | Sinohydro Corporation | 240 | 17.22 |
| Nam Ou 6 | Mekong tributary, northern Laos | Sinohydro Corporation | 180 | 17.01 |
| Xe Pian-Xe Namnoy | Mekong tributary, Bolaven Plateau, southern Laos | SK Engineering and Construction, Korea Western Power, Ratchaburi Electricity Generating Holdings | 410 | 533 |
| Xekaman 1 and Xekaman Sanxay | Mekong tributary, southern Laos | Songda Corporation | 322 | |
| Xekaman 3 | Mekong tributary, Sekong River Basin, southern Laos | EVN, EdL | 250 | 5.2 |
| A Luoi | Mekong tributary, Sekong River Basin, Vietnam | EVN | 170 | |
| Buon Kuop | Mekong tributary, Sesan River Basin, Vietnam | EVN | 280 | 47 |
| Plei Krong | Mekong tributary, Sesan River Basin, Vietnam | EVN | 100 | 53 |
| Sesan 3 | Mekong tributary, Sesan River Basin, Vietnam | EVN | 260 | 6.4 |
| Sesan 4 | Mekong tributary, Sesan River Basin, Vietnam | EVN | 360 | |
| Sre Pok 3 | Mekong tributary, Srepok River Basin, Vietnam | EVN | 220 | |
| Yali Falls | Mekong tributary, Sesan River Basin, Vietnam | EVN | 720 | 64.5 |
| Lower Sesan 2 | Mekong tributary, Sesan River, Stung Treng, Cambodia, 25 km upstream from Mekong | China’s Hydrolancang International Energy, Royal Group, Electricite du Vietnam | 400 | 75 |
| Pak Mun | Mekong tributary, Mun River, Ubon Ratchathani, Thailand, 6 m upstream from Mekong | EGAT | 136 (part of year) | 60 |
| Lam Ta Khong | Mekong tributary, Nakorn Ratchasima, Thailand | EGAT | 500 | 37 |
| Scientific Name | Common Name | IUCN Red List Category |
|---|---|---|
| Aaptosyax grypus | Giant salmon carp | CR |
| Balantiocheilos ambusticauda | Burnt-tail fish | CR |
| Catlocarpio siamensis | Giant barb | CR |
| Datniodes pulcher | Siamese tiger perch | CR |
| Pangasianodon gigas | Mekong giant catfish | CR |
| Pangasius sanitwongsei | Giant pangasius | CR |
| Probarbus jullieni | Jullien’s golden carp | CR |
| Schistura bairdi | Baird’s Schistura | CR |
| Hemitrygon laosensis | Mekong stingray | EN |
| Luciocyprinus striolatus | Giant wolf barb | EN |
| Pangasianodon hypophthalmus | Striped river catfish | EN |
| Probarbus labeamajor | Thick-lipped barb | EN |
| Scleropages formosus | Asian bony-tongue | EN |
| Urogymnus polylepis | Giant freshwater whipray | EN |
| Bangana behri | Two-headed carp | VU |
| Cirrhinus microlepis | Small-scaled mud carp | VU |
| Datnioides undecimradiatus | Mekong tiger perch | VU |
| Hypsibarbus lagleri | Trey chhpin thom (Khmer) | VU |
| Mystus bocourti | Trey kanchos kdaung (Khmer) | VU |
| Osphronemus exodon | Elephant ear goramy | VU |
| Oygaster pointoni | Bamboo leaf fish | VU |
| Pangasius krempfi | Kremp’s catfish | VU |
| Scaphognathops bandanensis | Bandan sharp-mouth | VU |
| Tenualosa thibaudeaui | Laotian shad | VU |
| Wallago attu | Wallago | VU |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baird, I.G.; Hogan, Z.S. Hydropower Dam Development and Fish Biodiversity in the Mekong River Basin: A Review. Water 2023, 15, 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071352
Baird IG, Hogan ZS. Hydropower Dam Development and Fish Biodiversity in the Mekong River Basin: A Review. Water. 2023; 15(7):1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071352
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaird, Ian G., and Zeb S. Hogan. 2023. "Hydropower Dam Development and Fish Biodiversity in the Mekong River Basin: A Review" Water 15, no. 7: 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071352






