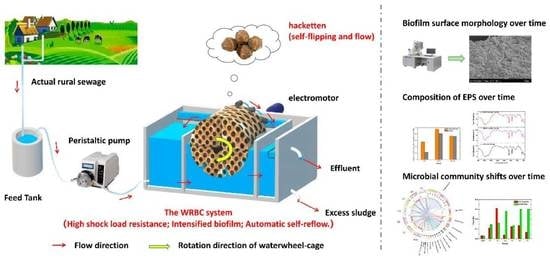
An Innovative Waterwheel-Rotating Biological Contactor (WRBC) System for Rural Sewage Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. WRBC System Set-Up
2.2. Preparation of Influents
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.3.1. N and COD Concentration
2.3.2. The Total Biofilm Amount Measurements
2.3.3. The SOUR Activity of Microorganism Measurements
2.3.4. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.3.5. EPS Extraction and Analysis
2.3.6. High-Throughput Sequencing
3. Results and Discussion
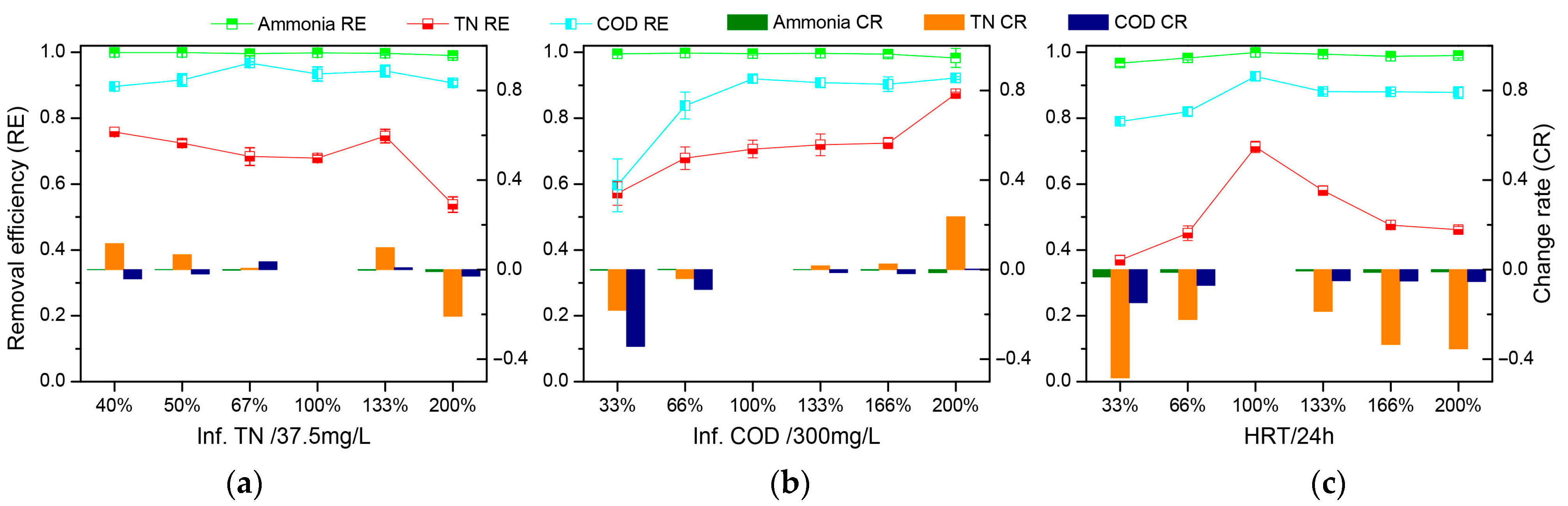
3.1. Performance of the WRBC System
3.1.1. The Start-Up
3.1.2. Actual Sewage Treatment Effect
3.1.3. Stability of the WRBC System
3.2. Biofilm Morphology and EPS Composition
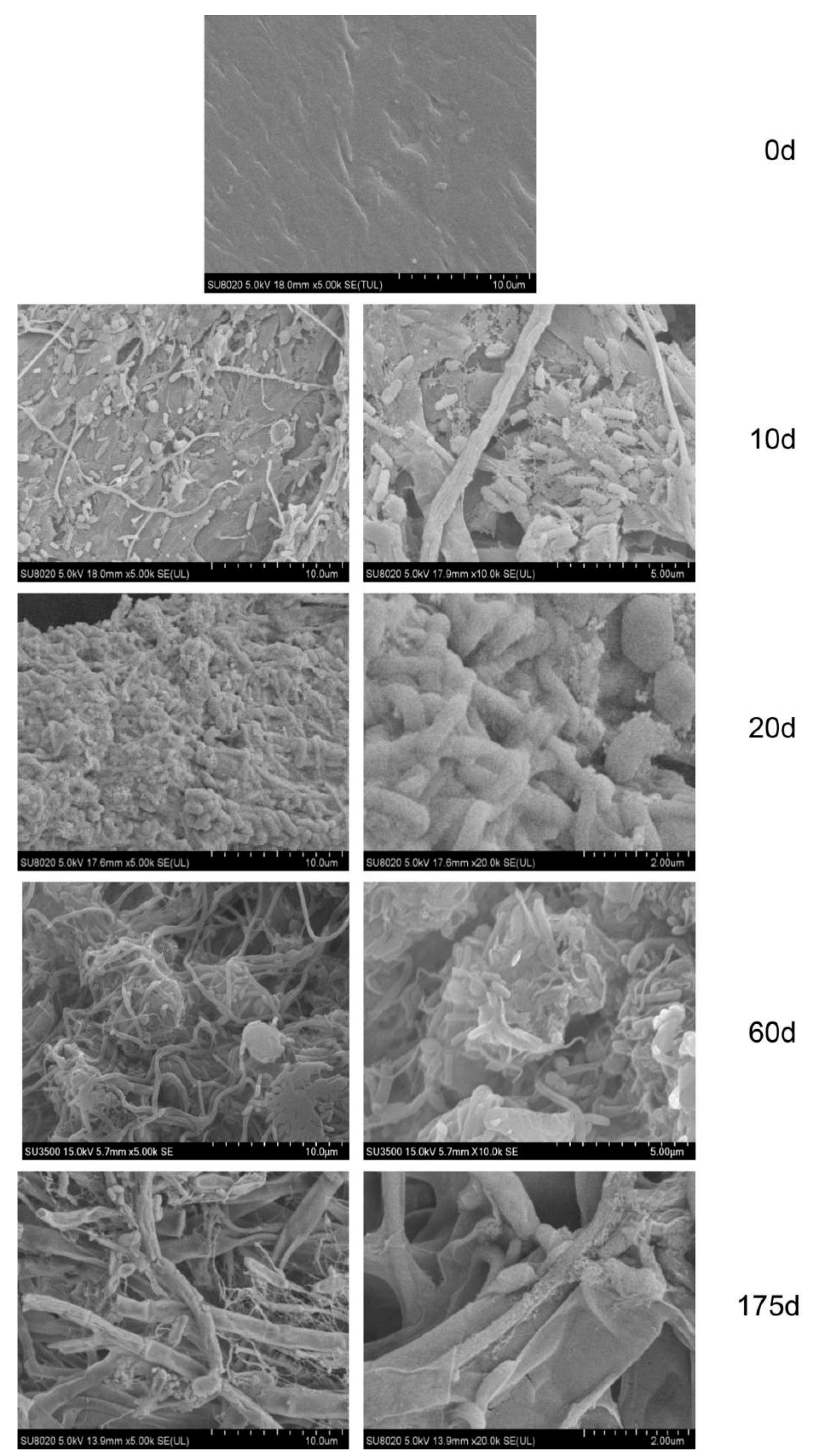
3.2.1. Surface Morphology of Biofilm
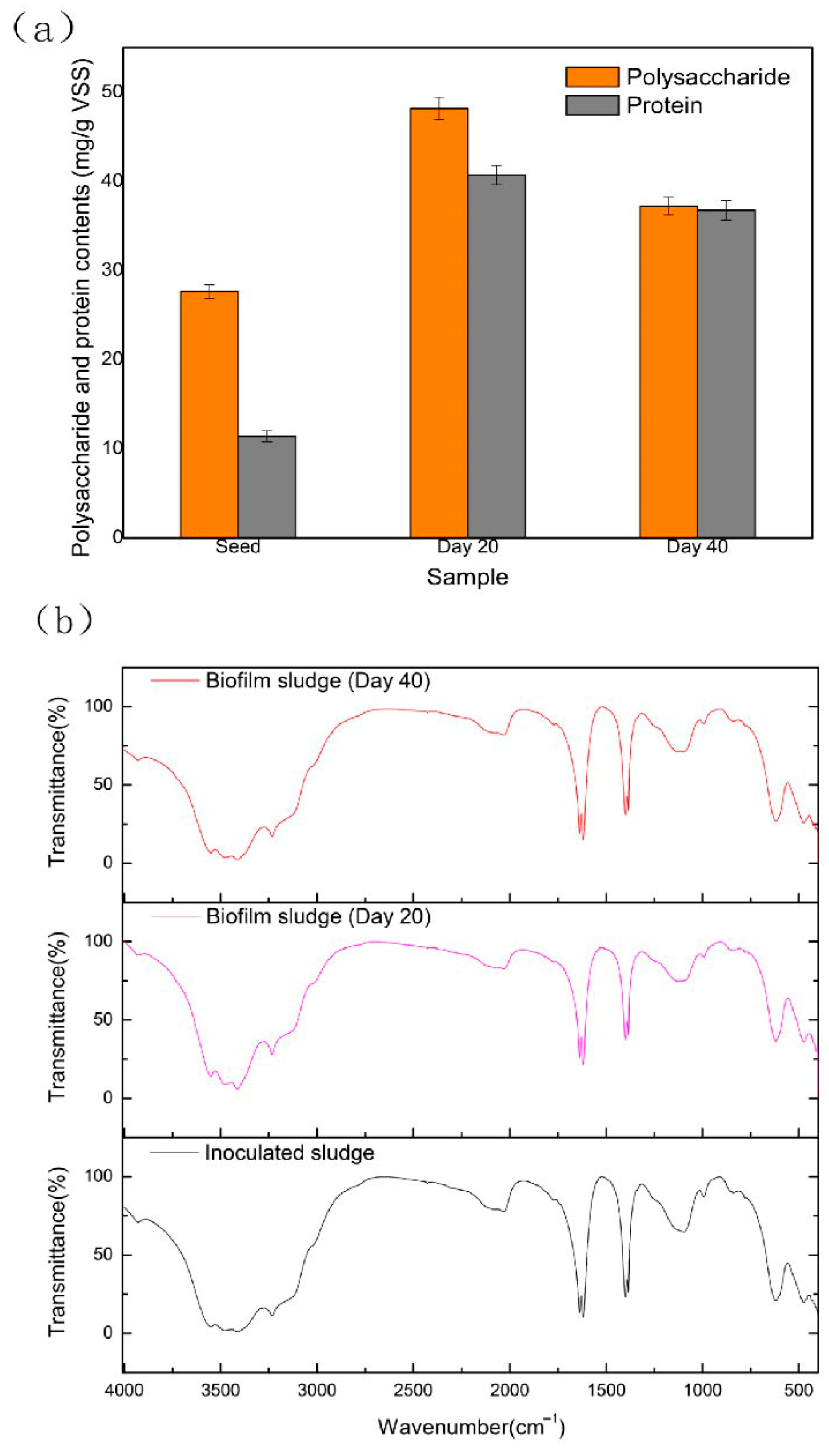
3.2.2. Composition of EPSs
3.3. Microbial Community
3.3.1. Bacterial Diversity
3.3.2. Microbial Community Structure
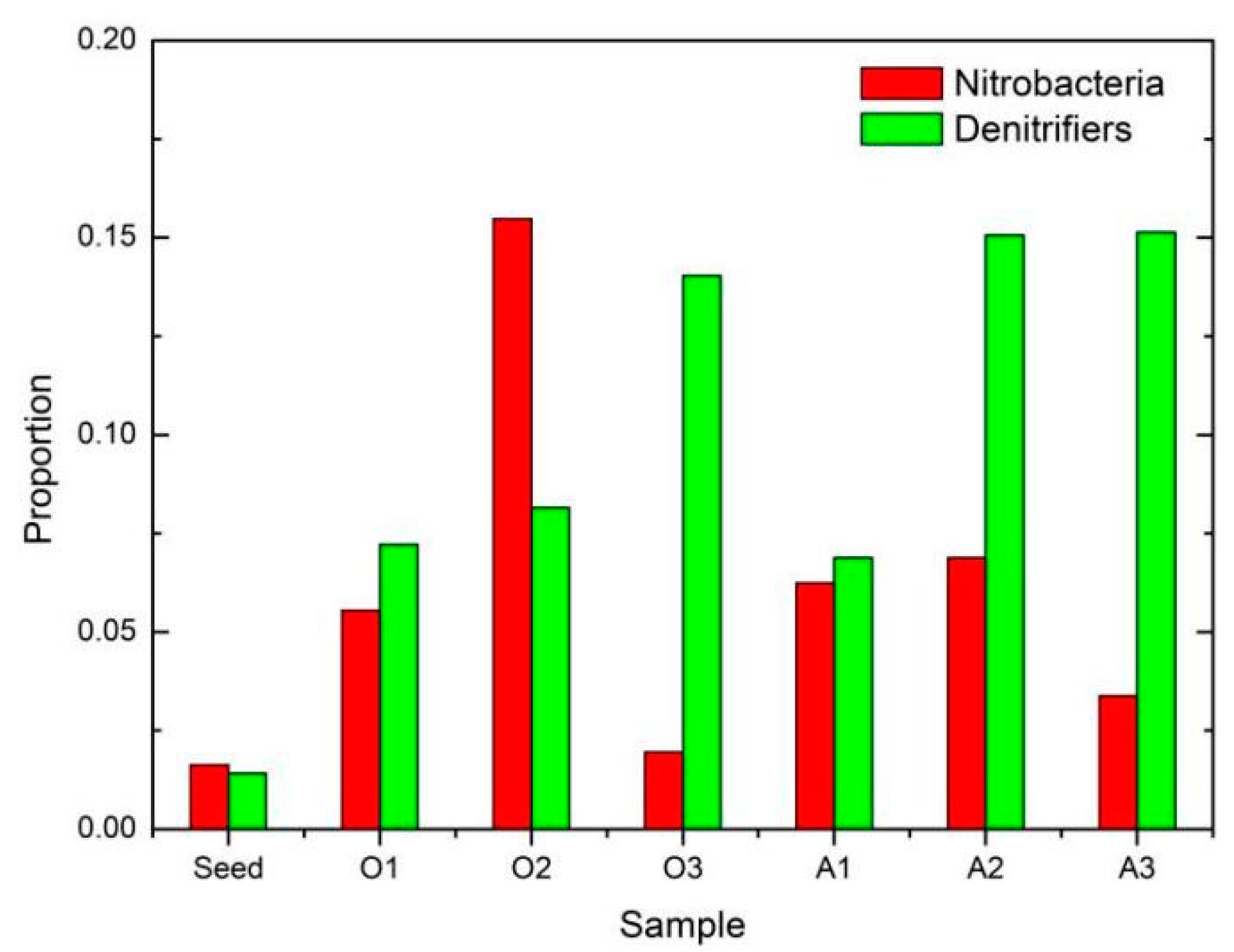
3.3.3. Functional Bacterium
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Yang, L.; Xu, K.; Bei, K.; Zheng, X.; Lu, S.; An, N.; Zhao, J.; Jin, Z. Application of constructed wetlands in treating rural sewage from source separation with high-influent nitrogen load: A review. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X.; Dai, C.; Xu, K.; Bei, K.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, M. Combined process of bio-contact oxidation-constructed wetland for blackwater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 316, 123891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wan, A.; Zhao, B.; Xue, S.; Xu, A. Single-stage MBBR using novel carriers to remove nitrogen in rural domestic sewage: The effect of carrier structure on biofilm morphology and SND. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zheng, T.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J. Fungi characteristics of biofilms from sewage and greywater in small diameter gravity sewers. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasecki, A. Water and sewage management issues in rural poland. Water 2019, 11, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadeghfam, S.; Abadi, B. Decision-making process of partnership in establishing and managing of rural wastewater treatment plants: Using intentional and geographical-spatial location data. Water Res. 2021, 197, 117096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Li, Y.; Yu, X.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, L. Characteristics of rural agritainment sewage in Sichuan, China. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 79, 1695–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Jiang, L.; Zheng, H.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, Q.; Mao, Y.; Ji, F.; Shi, D. Constructed wetlands for rural domestic wastewater treatment: A coupling of tidal strategy, in-situ bio-regeneration of zeolite and fe(Ⅱ)-oxygen denitrification. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-Barquero, L.G.; Luong, K.H.; Rudy, M.D.; Frank, R.A.; Hanson, M.L.; Wong, C.S. Attenuation of pharmaceuticals, nutrients and toxicity in a rural sewage lagoon system integrated with a subsurface filtration technology. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Jiang, L.; Cao, X.; Liao, Y.; Mao, Y.; Ji, F. A combined deodorization reflux system and tidal flow constructed wetland for sewage treatment performance. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 10, 106953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Sun, H.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, L.; Wu, W. Pilot-scale two-stage constructed wetlands based on novel solid carbon for rural wastewater treatment in southern china: Enhanced nitrogen removal and mechanism. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 292, 112750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Liang, Z.; Luo, A.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Lou, X.; Jia, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ping, S. Effect on simultaneous removal of ammonia, nitrate, and phosphorus via advanced stacked assembly biological filter for rural domestic sewage treatment. Biodegradation 2021, 32, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Ma, J.; Xiao, B.; Huo, X.; Guo, X. New integrated self-refluxing rotating biological contactor for rural sewage treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 217, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.; Wang, J.; Lin, D.; Tang, X.; Cheng, X.; Li, G.; Ren, N.; Liang, H. In situ coagulation versus pre-coagulation for gravity-driven membrane bioreactor during decentralized sewage treatment: Permeability stabilization, fouling layer formation and biological activity. Water Res. 2017, 126, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Dong, W.; Chang, Y.; Yan, G.; Chu, Z.; Ling, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fan, T.; Li, C. Nitrogen removal and microbial community for the treatment of rural domestic sewage with low C/N ratio by A/O biofilter with Arundo donax as carbon source and filter media. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 37, 101509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Huang, J.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, X.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, H. Microbial community succession and pollutants removal of a novel carriers enhanced duckweed treatment system for rural wastewater in Dianchi lake basin. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 276, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, W.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Q.; Xiang, W.; Qu, J.; Yang, C. Microbial community structure analysis in a hybrid membrane bioreactor via high-throughput sequencing. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 130989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guo, F.; Zheng, Z.; Luo, X.; Zhang, J. Enhancement of rural domestic sewage treatment performance, and assessment of microbial community diversity and structure using tower vermifiltration. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 9462–9470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barwal, A.; Chaudhary, R. To study the performance of biocarriers in moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) technology and kinetics of biofilm for retrofitting the existing aerobic treatment systems: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2014, 13, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, S.; Bilad, M.R. A review on rotating biological contactors. Indones. J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 4, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Glaskova, T.; Zarrelli, M.; Borisova, A.; Timchenko, K.; Aniskevich, A.; Giordano, M. Method of quantitative analysis of filler dispersion in composite systems with spherical inclusions. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2011, 71, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frølund, B.; Palmgren, R.; Keiding, K.; Nielsen, P.H. Extraction of extracellular polymers from activated sludge using a cation exchange resin. Water Res. 1996, 30, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, N.M.; Doganli, G.A.; Dogan, G.; Bozkaya, O. Characterization of extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) produced by thermal Bacillus and determination of environmental conditions affecting exopolysaccharide production. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2015, 9, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, G.P.; Yu, H.Q. Characterization of extracellular polymeric substances of aerobic and anaerobic sludge using three-dimensional excitation and emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Huang, J.; Zeng, G.; Liu, D.; Chen, S. Microbial activity along the depth of biofilm in simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox and denitrification (SNAD) system. Environ. Technol. 2022, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, C.; Yanagihara, H.; Wakaki, H. Improvement of the quality of the chi-square approximation for the ADF test on a covariance matrix with a linear structure. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 2011, 141, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Gong, B.; Zhou, J.; He, Q.; Qing, X. Efficient simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox and denitrification (SNAD) system equipped with a real-time dissolved oxygen (DO) intelligent control system and microbial community shifts of different substrate concentrations. Water Res. 2017, 119, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
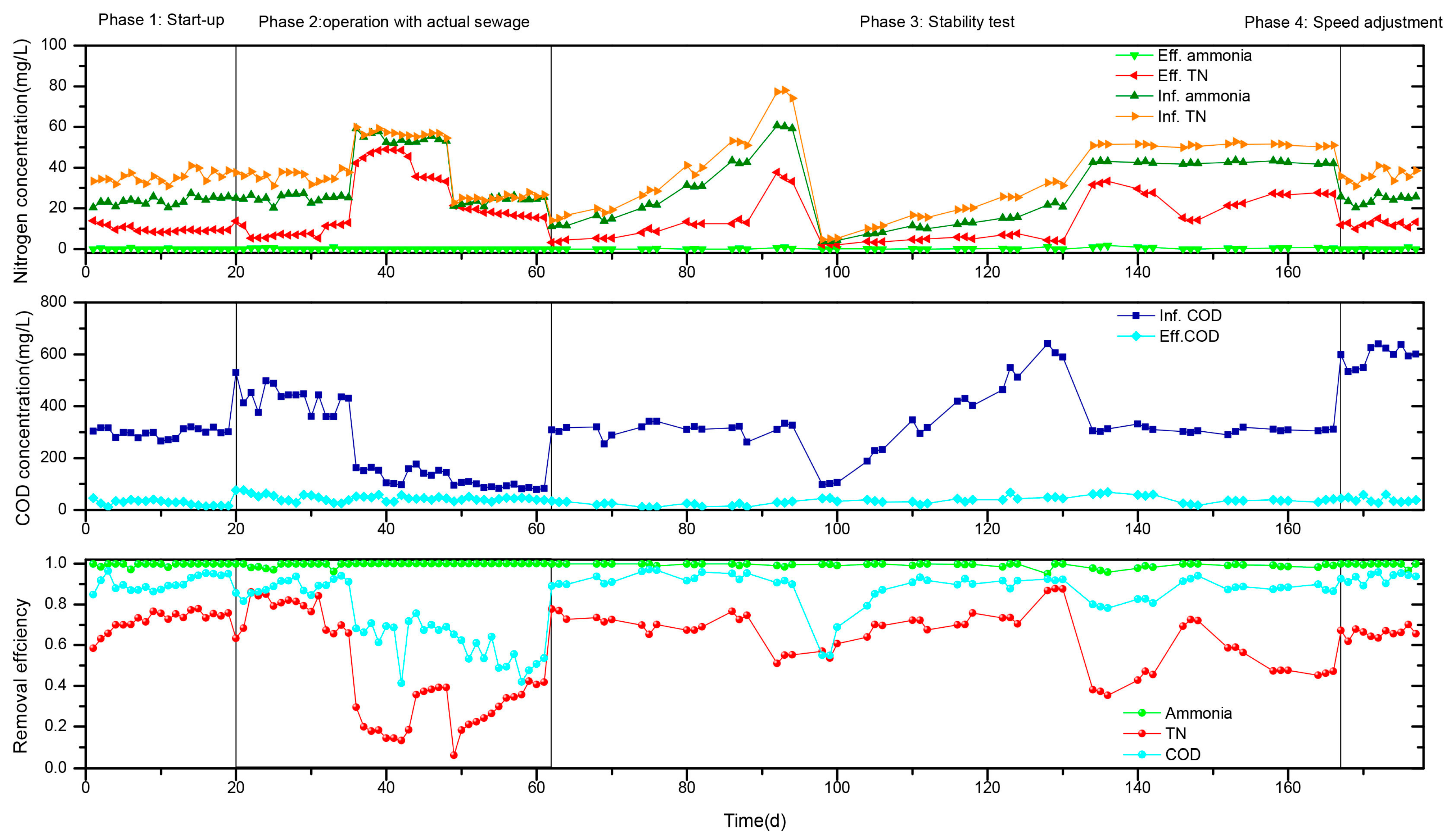

| Phase | Time | Influents | Inf. Ammonia | Inf. Nitrate | Inf. TN | Inf. COD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Days 1–19 | Artificial simulated sewage | 23.54 ± 1.95 | 11.65 ± 1.97 | 35.21 ± 2.75 | 298 ± 16 |
| 2 | Days 20–35 | Actual rural sewage from sampling point 1 | 25.10 ± 1.83 | 10.75 ± 1.36 | 35.89 ± 2.42 | 432 ± 50 |
| 2 | Days 36–48 | Actual rural sewage from sampling point 2 | 54.45 ± 2.30 | 2.30 ± 1.47 | 56.75 ± 1.49 | 142 ± 26 |
| 2 | Days 49–61 | Actual rural sewage from sampling point 2 (rainy) | 23.83 ± 1.70 | 1.42 ± 1.41 | 25.23 ± 1.30 | 91 ± 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Wen, X.; Tang, Q.; Liu, D.; Chen, S. An Innovative Waterwheel-Rotating Biological Contactor (WRBC) System for Rural Sewage Treatment. Water 2023, 15, 1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071323
Huang J, Wen X, Tang Q, Liu D, Chen S. An Innovative Waterwheel-Rotating Biological Contactor (WRBC) System for Rural Sewage Treatment. Water. 2023; 15(7):1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071323
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jiansheng, Xin Wen, Qian Tang, Deshao Liu, and Shuangkou Chen. 2023. "An Innovative Waterwheel-Rotating Biological Contactor (WRBC) System for Rural Sewage Treatment" Water 15, no. 7: 1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071323