The Bioremediation Potential of Ulva lactuca (Chlorophyta) Causing Green Tide in Marchica Lagoon (NE Morocco, Mediterranean Sea): Biomass, Heavy Metals, and Health Risk Assessment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
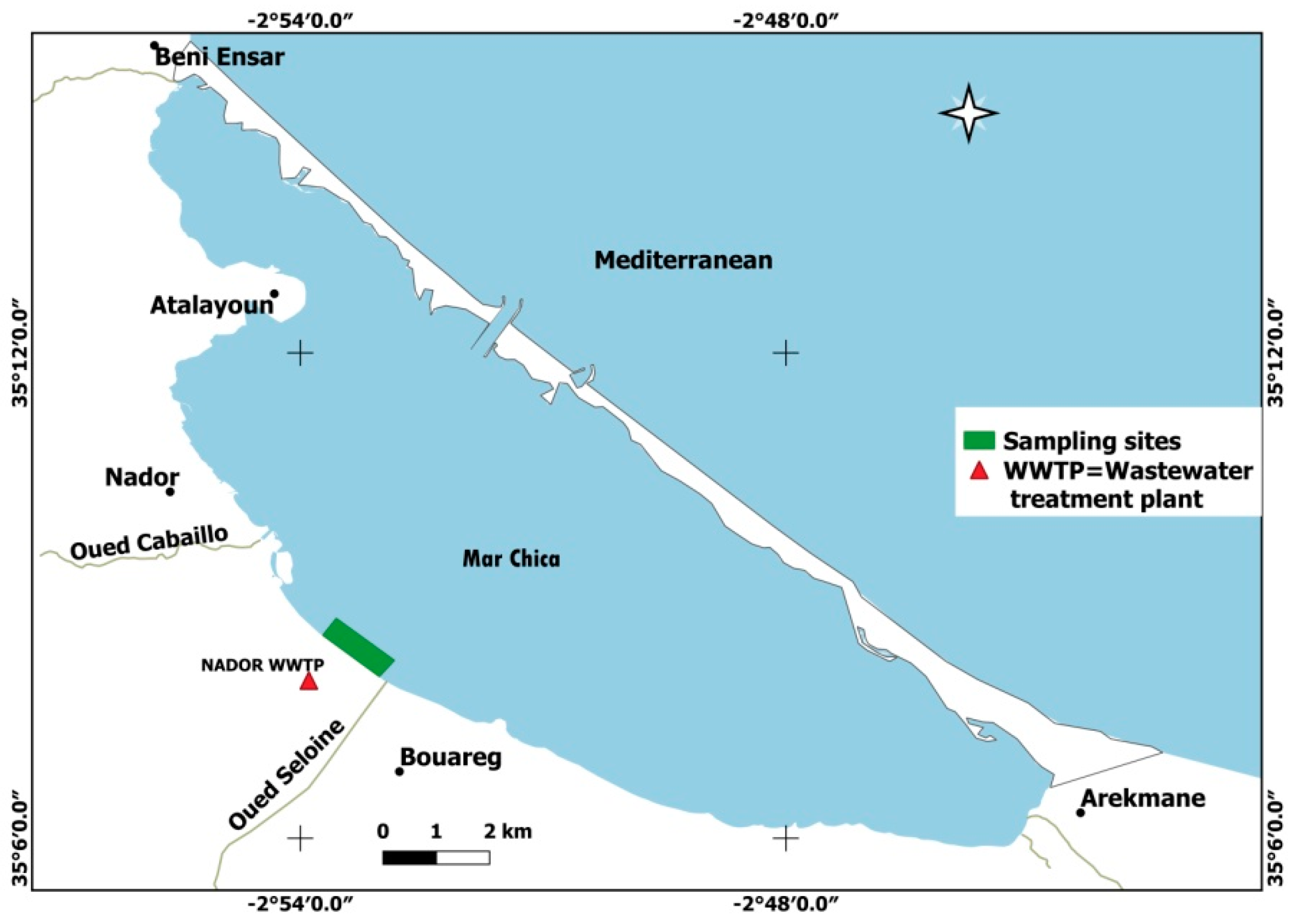
2.1. The Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection, Preparation, and Analysis
2.3. Metal Analysis Description
2.4. Health Risk Assessment
2.5. Determination of Intake
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Physicochemical Parameters of Water and Ulva lactuca
3.2. Heavy Metals in Water and Ulva lactuva
3.3. Health Risk Assessment
3.4. Comparative Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Areco, M.M.; Salomone, V.N.; dos Santos Afonso, M. Ulva Lactuca: A Bioindicator for Anthropogenic Contamination and Its Environmental Remediation Capacity. Mar. Environ. Res. 2021, 171, 105468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohra, B.S.; Habib, A. Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination Levels and Toxicity in Sediments and Fishes from the Mediterranean Sea (Southern Coast of Sfax, Tunisia). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 13954–13963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, G.; Orlando-Bonaca, M. Chemical Elements in Mediterranean Macroalgae. A Review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 44–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, G.; Veneziano, V.; Piccione, V. The Alga Ulva Lactuca (Ulvaceae, Chlorophyta) as a Bioindicator of Trace Element Contamination along the Coast of Sicily, Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, M.; Alprol, A.E.; Heneash, A.M.M.; Saleh, H.; Abualnaja, K.M.; Alhashmialameer, D.; Mansour, A.T. Ammonia Bioremediation from Aquaculture Wastewater Effluents Using Arthrospira Platensis NIOF17/003: Impact of Biodiesel Residue and Potential of Ammonia-Loaded Biomass as Rotifer Feed. Materials 2021, 14, 5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.T.; Alprol, A.E.; Abualnaja, K.M.; El-Beltagi, H.S.; Ramadan, K.M.A.; Ashour, M. Dried Brown Seaweed’s Phytoremediation Potential for Methylene Blue Dye Removal from Aquatic Environments. Polymers 2022, 14, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghour, M. Effect of Seaweeds in Phyto-Remediation. In Biotechnological Applications of Seaweeds; Nova Publishers Sciences: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 47–83. ISBN 978-1-5361-0983-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Chekroun, K.; Baghour, M. The Role of Algae in Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals: A Review. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2013, 4, 873–880. [Google Scholar]
- Ameen, F.; Al-Homaidan, A.A.; Almahasheer, H.; Dawoud, T.; Alwakeel, S.; AlMaarofi, S. Biomonitoring Coastal Pollution on the Arabian Gulf and the Gulf of Aden Using Macroalgae: A Review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 175, 113156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, G.; Orlando-Bonaca, M. Trace Elements in Mediterranean Seagrasses: Accumulation, Tolerance and Biomonitoring. A Review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 125, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackira, A.M.; Jazeel, K.; Puthur, J.T. Chapter 13—Phycoremediation and Phytoremediation: Promising Tools of Green Remediation. In Sustainable Environmental Clean-Up; Kumar Mishra, V., Kumar, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 273–293. ISBN 978-0-12-823828-8. [Google Scholar]
- Valiela, I.; Foreman, K.; LaMontagne, M.; Hersh, D.; Costa, J.; Peckol, P.; DeMeo-Andreson, B.; D’Avanzo, C.; Babione, M.; Sham, C.-H.; et al. Couplings of Watersheds and Coastal Waters: Sources and Consequences of Nutrient Enrichment in Waquoit Bay, Massachusetts. Estuaries 1992, 15, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, L.; Calizza, E.; Careddu, G.; Carlino, P.; Costantini, M.L.; Rossi, L. The Effects of Nitrogen Pollutants on the Isotopic Signal (Δ15N) of Ulva Lactuca: Microcosm Experiments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahhou, A.; Layachi, M.; Akodad, M.; El Ouamari, N.; Aknaf, A.; Skalli, A.; Oudra, B.; Baghour, M. Assessment of the Trophic Status of Marchica Lagoon (Ne Morocco, Mediterranean) After Restoration Activities Using Trophic Index (Trix): Seasonal and Spatial Variations. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2022, 20, 4667–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Seoane, R.; Fernández, J.A.; Villares, R.; Aboal, J.R. Use of Macroalgae to Biomonitor Pollutants in Coastal Waters: Optimization of the Methodology. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 84, 710–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, M.; Tomita-Yokotani, K.; Hashimoto, H.; Sawaki, N.; Notoya, M. Sodium and Potassium Uptake of Ulva—Application of Marine Macro-Algae for Space Agriculture. Adv. Space Res. 2009, 43, 1220–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.; Crespo, D.; Henriques, B.M.G.; Pereira, E.; Duarte, A.C.; Pardal, M.A. Kinetics of Mercury Accumulation and Its Effects on Ulva Lactuca Growth Rate at Two Salinities and Exposure Conditions. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 217, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.B. Ulva Lactuca as Bioindicator of Metal Contamination in Intertidal Waters in Hong Kong. Hydrobiologia 1990, 203, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haritonidis, S.; Malea, P. Bioaccumulation of Metals by the Green Alga Ulva Rigida from Thermaikos Gulf, Greece. Environ. Pollut. 1999, 104, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamala-Kannan, S.; Prabhu Dass Batvari, B.; Lee, K.J.; Kannan, N.; Krishnamoorthy, R.; Shanthi, K.; Jayaprakash, M. Assessment of Heavy Metals (Cd, Cr and Pb) in Water, Sediment and Seaweed (Ulva Lactuca) in the Pulicat Lake, South East India. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diop, M.; Howsam, M.; Diop, C.; Goossens, J.F.; Diouf, A.; Amara, R. Assessment of Trace Element Contamination and Bioaccumulation in Algae (Ulva Lactuca), Mussels (Perna Perna), Shrimp (Penaeus Kerathurus), and Fish (Mugil Cephalus, Saratherondon Melanotheron) along the Senegalese Coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 103, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuang, Q.; ShiJian, G.; Champagne, P.; Robertson, R.M. Potential of Ulva Lactuca for Municipal Wastewater Bioremediation and Fly Food. Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 91, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Farias, D.R.; Hurd, C.L.; Eriksen, R.S.; Simioni, C.; Schmidt, E.; Bouzon, Z.L.; Macleod, C.K. In Situ Assessment of Ulva Australis as a Monitoring and Management Tool for Metal Pollution. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 2489–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, G.; Orlando-Bonaca, M. Trace Elements in Mediterranean Seagrasses and Macroalgae. A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-Y.; Yang, F.; Jin, L.; Wang, Q.; Yin, J.; He, P.; Chen, Y. Safety and Quality of the Green Tide Algal Species Ulva Prolifera for Option of Human Consumption: A Nutrition and Contamination Study. Chemosphere 2018, 210, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, M.; Idrees, M.; Khan, M.M.A.; Moinuddin; Ansari, A.A. Task of Mineral Nutrients in Eutrophication. Eutrophication Causes Conseq. Control 2014, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Fur, I. Role of Macrophytes in the Restoration of Lagoon Environments: Ecological Succession. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Montpellier, Montpellier, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Oujidi, B.; Tahri, M.; Layachi, M.; Abid, A.; Bouchnan, R.; Selfati, M.; Bounakhla, M.; El Bouch, M.; Maanan, M.; Bazairi, H.; et al. Effects of the Watershed on the Seasonal Variation of the Surface Water Quality of a Post-Restoration Coastal Wetland: The Case of the Nador Lagoon (Mediterranean Sea, Morocco). Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 35, 101127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahhou, A.; Layachi, M.; Akodad, M.; Ouamari, N.E.; Aknaf, A.; Gueddari, H.; Oudra, B.; Baghour, M. The Potential Role of Sediments in Nutrients (N, P) Cycle in Marchica Lagoon (Mediterranean Sea, Morocco). IOP Conf. Ser.Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1090, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aknaf, A.; Akodad, M.; Layachi, M.; Baghour, M.; Oudra, B.; Vasconcelos, V. The Chemical Characterization and Its Relationship with Heavy Metals Contamination in Surface Sediment of Marchica Mediterranean Lagoon (North of Morocco). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 4159–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maicu, F.; Abdellaoui, B.; Bajo, M.; Chair, A.; Hilmi, K.; Umgiesser, G. Modelling the Water Dynamics of a Tidal Lagoon: The Impact of Human Intervention in the Nador Lagoon (Morocco). Cont. Shelf Res. 2021, 228, 104535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherib, A.; Bedouh, Y.; Messai, K.; Menad, A. Biomonitoring of Maritime Pollution by Heavy Metals (Pb and Zn) in the Coast of Jijel (Algeria). Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 73, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeroual, S.; El Bakkal, S.E.; Mansori, M.; Lhernould, S.; Faugeron-Girard, C.; El Kaoua, M.; Zehhar, N. Cell Wall Thickening in Two Ulva Species in Response to Heavy Metal Marine Pollution. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 35, 101125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.Y.A.; Idris, A.M.; Eltayeb, M.A.H.; El-Zahhar, A.A.; Ashraf, I.M. Bioaccumulation and Health Risk Assessment of Toxic Metals in Red Algae in Sudanese Red Sea Coast. Toxin Rev. 2021, 40, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arisekar, U.; Jeya Shakila, R.; Shalini, R.; Jeyasekaran, G.; Sivaraman, B.; Surya, T. Heavy Metal Concentrations in the Macroalgae, Seagrasses, Mangroves, and Crabs Collected from the Tuticorin Coast (Hare Island), Gulf of Mannar, South India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 163, 111971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żbikowski, R.; Szefer, P.; Latała, A. Comparison of Green Algae Cladophora Sp. and Enteromorpha Sp. as Potential Biomonitors of Chemical Elements in the Southern Baltic. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 387, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodier, J.; Bernard, L.; Nicole, M.; Bernard, L. Merlet Nicole L’analyse de l’eau/Jean Rodier, Bernard Legube, Nicole Merlet et Coll; Dunod: Paris, France, 2009; ISBN 978-2-10-007246-0. [Google Scholar]
- US EPA Integrated Risk Information System. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/iris (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Paz, S.; Rubio, C.; Frías, I.; Gutiérrez, Á.J.; González-Weller, D.; Martín, V.; Revert, C.; Hardisson, A. Toxic Metals (Al, Cd, Pb and Hg) in the Most Consumed Edible Seaweeds in Europe. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Véliz, K.; Toledo, P.; Araya, M.; Gómez, M.F.; Villalobos, V.; Tala, F. Chemical Composition and Heavy Metal Content of Chilean Seaweeds: Potential Applications of Seaweed Meal as Food and Feed Ingredients. Food Chem. 2023, 398, 133866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanisak, M.D. Nitrogen Limitation of Codium Fragile Ssp. Tomentosoides as Determined by Tissue Analysis. Mar. Biol. 1979, 50, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, P.A.; Björnsäter, B.R. Seasonal Fluctuations in Tissue Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and N:P for Five Macroalgal Species Common to the Pacific Northwest Coast. J. Phycol. 1992, 28, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesing, J.K.; Liu, D.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y. Abiotic Factors Influencing Biomass Accumulation of Green Tide Causing Ulva Spp. on Pyropia Culture Rafts in the Yellow Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 105, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Alstyne, K.L. Seawater Nitrogen Concentration and Light Independently Alter Performance, Growth, and Resource Allocation in the Bloom-Forming Seaweeds Ulva Lactuca and Ulvaria Obscura (Chlorophyta). Harmful Algae 2018, 78, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ale, M.T.; Mikkelsen, J.D.; Meyer, A.S. Differential Growth Response of Ulva Lactuca to Ammonium and Nitrate Assimilation. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 23, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yu, K.; Huo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, H.; Cai, C.; Liu, Y.; Shi, D.; He, P. Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Enrichment on Growth and Photosynthetic Assimilation of Carbon in a Green Tide-Forming Species (Ulva Prolifera) in the Yellow Sea. Hydrobiologia 2016, 776, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oujidi, B.; El Bouch, M.; Tahri, M.; Layachi, M.; Boutoumit, S.; Bouchnan, R.; Ouahidi, H.; Bounakhla, M.; El Ouamari, N.; Maanan, M.; et al. Seasonal and Spatial Patterns of Ecotoxicological Indices of Trace Elements in Superficial Sediments of the Marchica Lagoon Following Restoration Actions during the Last Decade. Diversity 2021, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Yang, K.; Lee, M.Y.; Youn, S.H.; Son, M.; Park, S.R.; Kim, T.-H. Factors Controlling Massive Green Tide Blooms on the Coasts of Jeju Island, Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 186, 114446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Q.; Gao, H.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Lek, S.; Xiao, J. Species-Specific Bioaccumulation and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal in Seaweeds in Tropic Coasts of South China Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 155031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosn, M.; Mahfouz, C.; Chekri, R.; Ouddane, B.; Khalaf, G.; Guérin, T.; Amara, R.; Jitaru, P. Assessment of Trace Element Contamination and Bioaccumulation in Algae (Ulva Lactuca), Bivalves (Spondylus Spinosus) and Shrimps (Marsupenaeus Japonicus) from the Lebanese Coast. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 39, 101478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano Muñoz, I.; Díaz, N.F. Minerals in Edible Seaweed: Health Benefits and Food Safety Issues. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1592–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, C.; Cardoso, C.; Ripol, A.; Varela, J.; Quental-Ferreira, H.; Pousão-Ferreira, P.; Ventura, M.S.; Delgado, I.M.; Coelho, I.; Castanheira, I.; et al. Composition and Bioaccessibility of Elements in Green Seaweeds from Fish Pond Aquaculture. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Pan, X.-D.; Huang, B.-F.; Han, J.-L. Distribution of Metals and Metalloids in Dried Seaweeds and Health Risk to Population in Southeastern China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roleda, M.Y.; Marfaing, H.; Desnica, N.; Jónsdóttir, R.; Skjermo, J.; Rebours, C.; Nitschke, U. Variations in Polyphenol and Heavy Metal Contents of Wild-Harvested and Cultivated Seaweed Bulk Biomass: Health Risk Assessment and Implication for Food Applications. Food Control 2019, 95, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, B.; Teixeira, A.; Figueira, P.; Reis, A.T.; Almeida, J.; Vale, C.; Pereira, E. Simultaneous Removal of Trace Elements from Contaminated Waters by Living Ulva Lactuca. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliceti, M.; Argese, E.; Sfriso, A.; Pavoni, B. Heavy Metal Contamination in the Seaweeds of the Venice Lagoon. Chemosphere 2002, 47, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özyiğit, İ.İ.; UYanık, Ö.L.; Şahin, N.R.; Yalçın, İ.E.; Demir, G. Monitoring the Pollution Level in Istanbul Coast of the Sea of Marmara Using Algal Species Ulva lactuca L. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akcali, I.; Kucuksezgin, F. A Biomonitoring Study: Heavy Metals in Macroalgae from Eastern Aegean Coastal Areas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaich, H.; Garna, H.; Besbes, S.; Paquot, M.; Blecker, C.; Attia, H. Chemical Composition and Functional Properties of Ulva Lactuca Seaweed Collected in Tunisia. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairy, H.M.; El-Sheikh, M.A. Antioxidant Activity and Mineral Composition of Three Mediterranean Common Seaweeds from Abu-Qir Bay, Egypt. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Masri, M.S.; Mamish, S.; Budier, Y. Radionuclides and Trace Metals in Eastern Mediterranean Sea Algae. J. Environ. Radioact. 2003, 67, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laib, E.; Leghouchi, E. Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, and Zn Concentrations in Ulva Lactuca, Codium Fragile, Jania Rubens, and Dictyota Dichotoma from Rabta Bay, Jijel (Algeria). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 1711–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherib, A.; Bounamous, A.; Aissaoui, A.; Charchar, N.; Bouchaala, L.; Bouaarouj, S.; Ahmed, M. Biomonitoring of Metallic Pollution in the Coast of Jijel (Algeria) by Using Algological Biomarkers. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 77, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Metals | Emission Wavelengths (nm) | Detection Limits (μg·L−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Cd | 214.439 | 0.3 |
| Cr | 267.716 | 1.0 |
| Cu | 327.395 | 1.0 |
| Fe | 238.204 | 1.0 |
| Mn | 257.610 | 0.3 |
| Ni | 231.604 | 3.0 |
| Pb | 220.353 | 3.0 |
| P | 213.618 | 10.0 |
| Zn | 13.857 | 1.0 |
| T° | Turbidity | Salinity | pH | DO (mg·L −1) | Chlorophyll a (µg·L−1) | DIN (mg·L−1) | PT (mg·L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30.60 ± 0.61 | 20.64 ± 17.09 | 35.64 ± 0.62 | 8.24 ± 0.05 | 9.72 ± 3.81 | 206.24 ± 164.1 | 0.09 ± 0.006 | 0.45 ± 0.05 |
| Sampling Sites | N° of Quadrat | Total Fresh Weight (kg) | Sub-Sample Fresh Weight (g) | Sub-Sample Dry Weight (g) | Dry Matter (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site 1 | 1 | 2.56 | 250 | 28.76 | 11.50 |
| Site 2 | 2 | 3.10 | 250 | 32.18 | 12.87 |
| Site 3 | 3 | 3.55 | 250 | 32.84 | 13.14 |
| Mean values (±Sd) | 3.07 ± 0.49 | 250 | 31.26 ± 2.19 | 12.50 ± 0.87 | |
| Pb | Ni | Zn | Cu | Mn | Fe | Cr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | 1.0 | ||||||
| Ni | 0.115 | 1.0 | |||||
| Zn | 0.567 | 0.883 | 1.0 | ||||
| Cu | 0.468 | 0.932 | 0.993 | 1.0 | |||
| Mn | −0.022 | 0.991 | 0.811 | 0.874 | 1.0 | ||
| Fe | 0.807 | 0.680 | 0.944 | 0.900 | 0.573 | 1.0 | |
| Cr | −0.684 | −0.803 | −0.989 | −0.965 | −0.714 | −0.983 | 1.0 |
| Pb | Cd | Cr | Ni | Zn | Cu | Mn | Fe | N | P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ulva lactuca | site 1 | 4.8 | - | 0.9 | 4.2 | 9.93 | 5.9 | 25.5 | 418 | 42.4 | 1.61 |
| site 2 | 2.7 | - | 1 | 4 | 8.52 | 1.9 | 164 | 213 | 52.17 | 1.84 | |
| site 3 | 3.2 | - | 0.9 | 4.5 | 10.2 | 7.4 | 49.2 | 378 | 37.67 | 1.86 | |
| Mean values in water (mg·L−1) | 0.0021 | - | 0.0334 | 0.0235 | 0.0283 | 0.0089 | 0.018 | 0.203 | 0.09 | 0.45 | |
| Mean values of BCF | 1728 | - | 27 | 179 | 336 | 568 | 1687 | 1656 | 48,986 | 3940 | |
| Uptake: mean values (mg·m2) | 43.77 | - | 11.45 | 51.95 | 117.19 | 62.17 | 976.4 | 4127.4 | 539 × 1000 | 21,762 | |
| Parameters | P | Mn | Fe | Cu | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimated daily intake (EDI) (mg·day−1) | site 1 | 8.38 | 0.132 | 2.173 | 0.031 | 0.051 |
| site 2 | 9.57 | 0.852 | 1.107 | 0.010 | 0.044 | |
| site 3 | 9.70 | 0.255 | 1.965 | 0.038 | 0.053 | |
| Dietary Reference Values (DRVs) (mg·day−1) | 550 | 3 | 11–16.0 | 1.6–1.3 | 12.7–6.3 | |
| Contribution (%) to the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) | site 1 | 1.52 | 4.42 | 13.585 | 2.36 | 0.43 |
| site 2 | 1.74 | 28.42 | 6.923 | 0.76 | 0.37 | |
| site 3 | 1.76 | 8.52 | 12.285 | 2.96 | 0.44 |
| Parameters | Cr | Mn | Fe | Ni | Cu | Zn | Cd | Pb | HI = ∑ THQ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RfD (µg·g−1·day−1) | 0.003 | 0.14 | 0.7 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.3 | 0.001 | 0.004 | ||
| Ulva lactuca | THQ | |||||||||
| site 1 | 0.025 | 0.013 | 0.044 | 0.015 | 0.011 | 0.002 | nd | 0.089 | 0.201 | |
| site 2 | 0.022 | 0.087 | 0.022 | 0.017 | 0.003 | 0.002 | nd | 0.050 | 0.204 | |
| site 3 | 0.022 | 0.026 | 0.040 | 0.016 | 0.013 | 0.002 | nd | 0.061 | 0.182 | |
| Reference | Location | Pb | Cr | Ni | Zn | Cu | Mn | Fe | Cd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This study | Morocco | 2.7–4.8 | 0.9–1 | 4.2–4.5 | 8.55–10.2 | 1.9–7.4 | 25.5–164 | 213–418 | nd |
| [60] | Egypt | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.46 ± 0.14 | nd | 0.31 ± 0.05 | 2.02 ± 0.13 | nd | 1.43 ± 0.05 | nd |
| [4] | Sicily coast, Italy | 0.67–5.77 | 0.25–2.21 | 0.97–8.12 | 8.21–85.1 | 1.48–10.4 | nd | nd | 0.06–0.26 |
| [63] | Algeria | nd–154.78 | 0.00 | nd | 16.6–106.88 | 0.33–44 | nd | nd | nd–7.02 |
| [61] | Syria | 0.55 ± 0.99 | 4.71 ± 0.02 | nd | 11.0 ± 0.33 | 5.48 ± 0.28 | nd | nd | 11.0 ± 0.33 |
| [57] | Marmara | 4.92–19.31 | nd | 15.15–41.29 | 6.67–18.31 | 8.26–25.31 | 553.31–989.32 | 0.451–3.21 | |
| [62] | Algeria | 1 ± 0.002 | 0.979 ± 0.002 | nd | 5.400 ± 0.001 | 2.587 ± 0.002 | nd | nd | 0.038 ± 0.008 |
| [32] | Algeria | 1.88–6.25 | 0.00 | nd | 92–178.9 | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| [50] | Lebanon | 1.04 ± 1.03 | 1.08 ± 0.90 | 2.13 ± 0.63 | 5.12 ± 2.29 | 2.30 ± 1.49 | 29.4 ± 37.8 | 516 ± 473 | 0.05 ± 0.03 |
| [56] | Italy | 0.7–17.6 | 0.7–8.6 | 2.2–5.0 | 25–179 | 4–29 | nd | 173–1630 | <0.1–0.7 |
| [59] | Tunisia | 12.6 | nd | nd | 68 | 8 | 13 | 410 | nd |
| [58] | Aegean coast | 0.94–5.65 | 0.78–4.78 | nd | 40.4–81 | 7.78–13.9 | nd | 146–307.5 | 14.9–54.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahhou, A.; Layachi, M.; Akodad, M.; El Ouamari, N.; Rezzoum, N.E.; Skalli, A.; Oudra, B.; El Bakali, M.; Kolar, M.; Imperl, J.; et al. The Bioremediation Potential of Ulva lactuca (Chlorophyta) Causing Green Tide in Marchica Lagoon (NE Morocco, Mediterranean Sea): Biomass, Heavy Metals, and Health Risk Assessment. Water 2023, 15, 1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071310
Rahhou A, Layachi M, Akodad M, El Ouamari N, Rezzoum NE, Skalli A, Oudra B, El Bakali M, Kolar M, Imperl J, et al. The Bioremediation Potential of Ulva lactuca (Chlorophyta) Causing Green Tide in Marchica Lagoon (NE Morocco, Mediterranean Sea): Biomass, Heavy Metals, and Health Risk Assessment. Water. 2023; 15(7):1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071310
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahhou, Abderrahmane, Mostafa Layachi, Mustapha Akodad, Najib El Ouamari, Nor Eddine Rezzoum, Ali Skalli, Brahim Oudra, Maryam El Bakali, Mitja Kolar, Jernej Imperl, and et al. 2023. "The Bioremediation Potential of Ulva lactuca (Chlorophyta) Causing Green Tide in Marchica Lagoon (NE Morocco, Mediterranean Sea): Biomass, Heavy Metals, and Health Risk Assessment" Water 15, no. 7: 1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071310






