Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Dyes from Clinical Laboratory Wastewater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
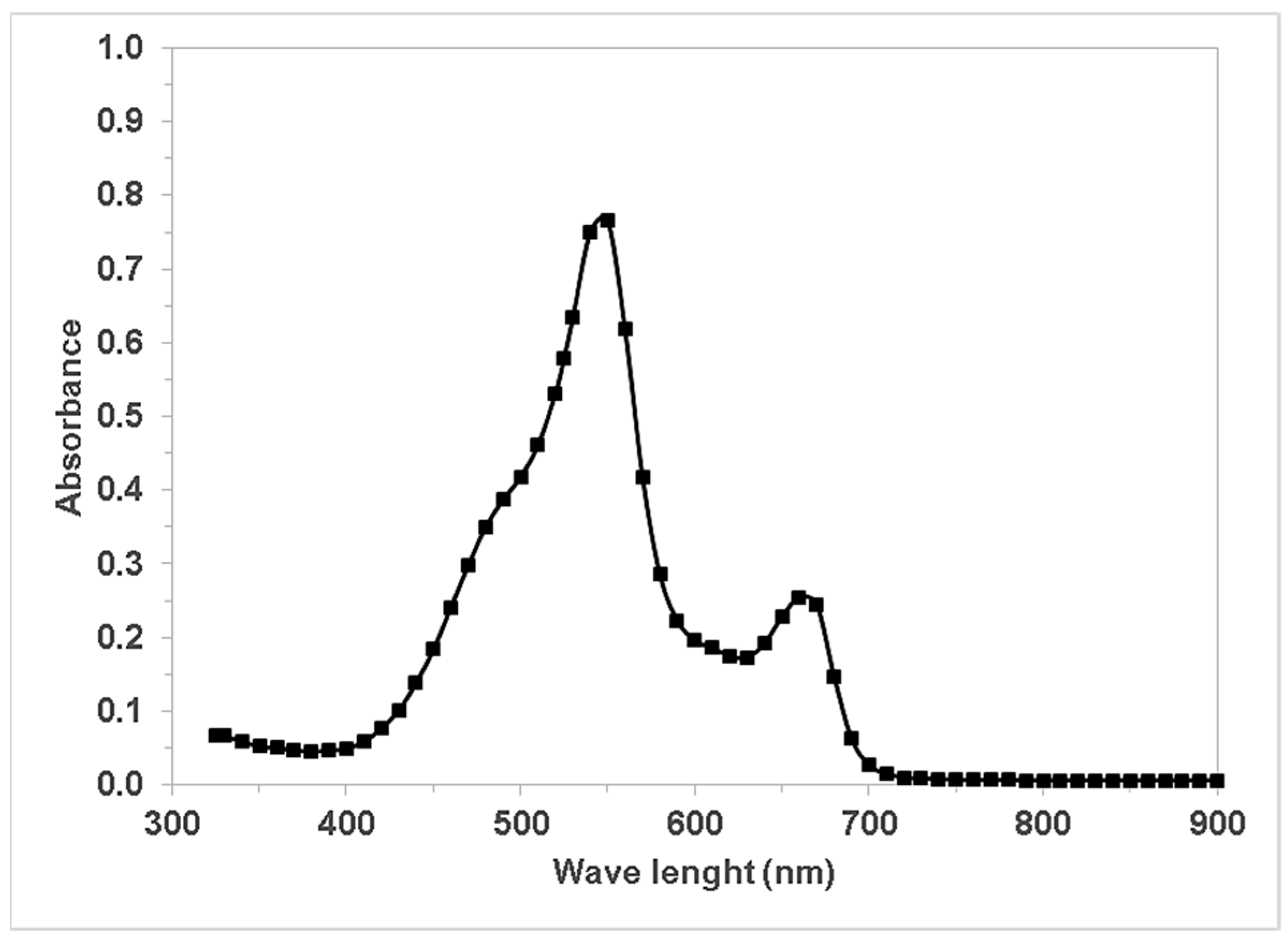
2.1. Clinical Laboratory Wastewater Characterization
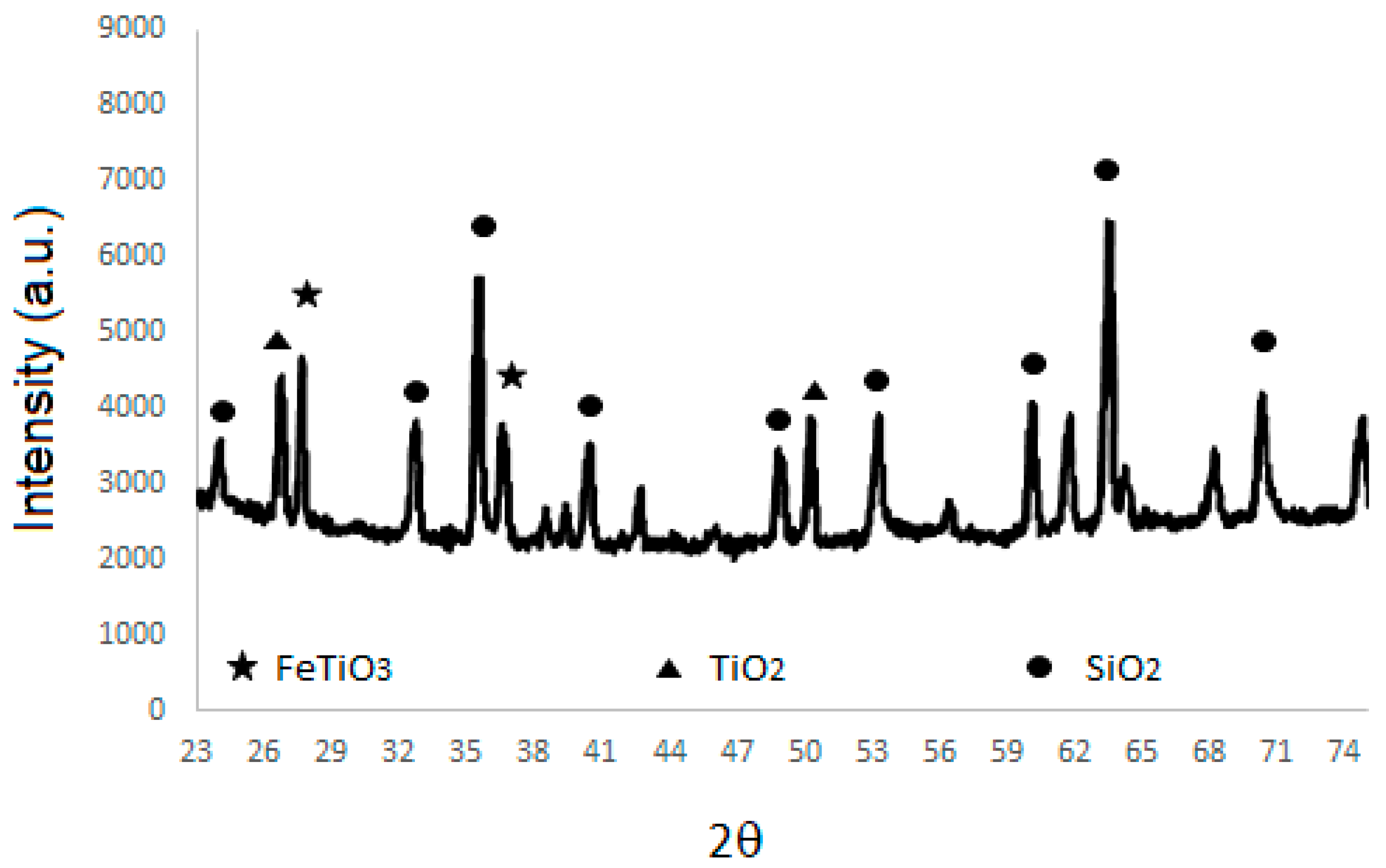
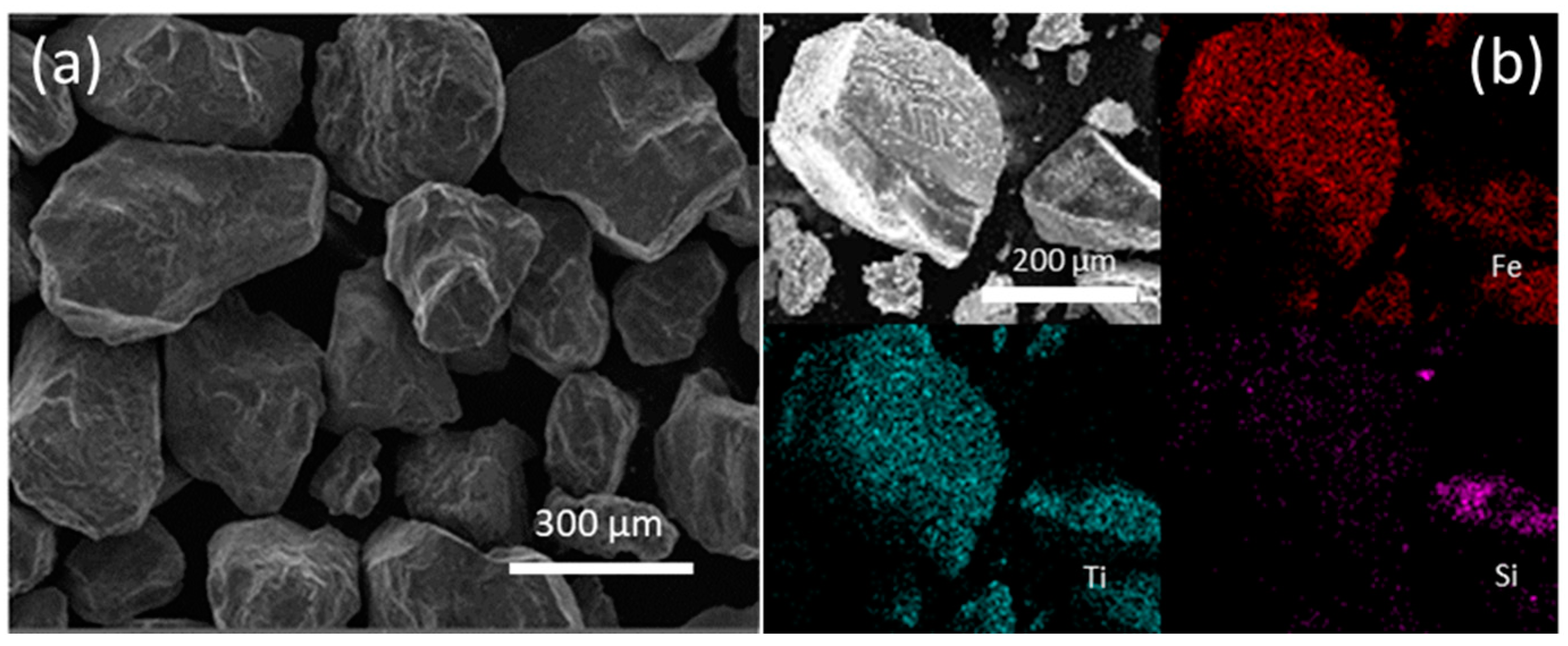
2.2. Ilmenite Characterization
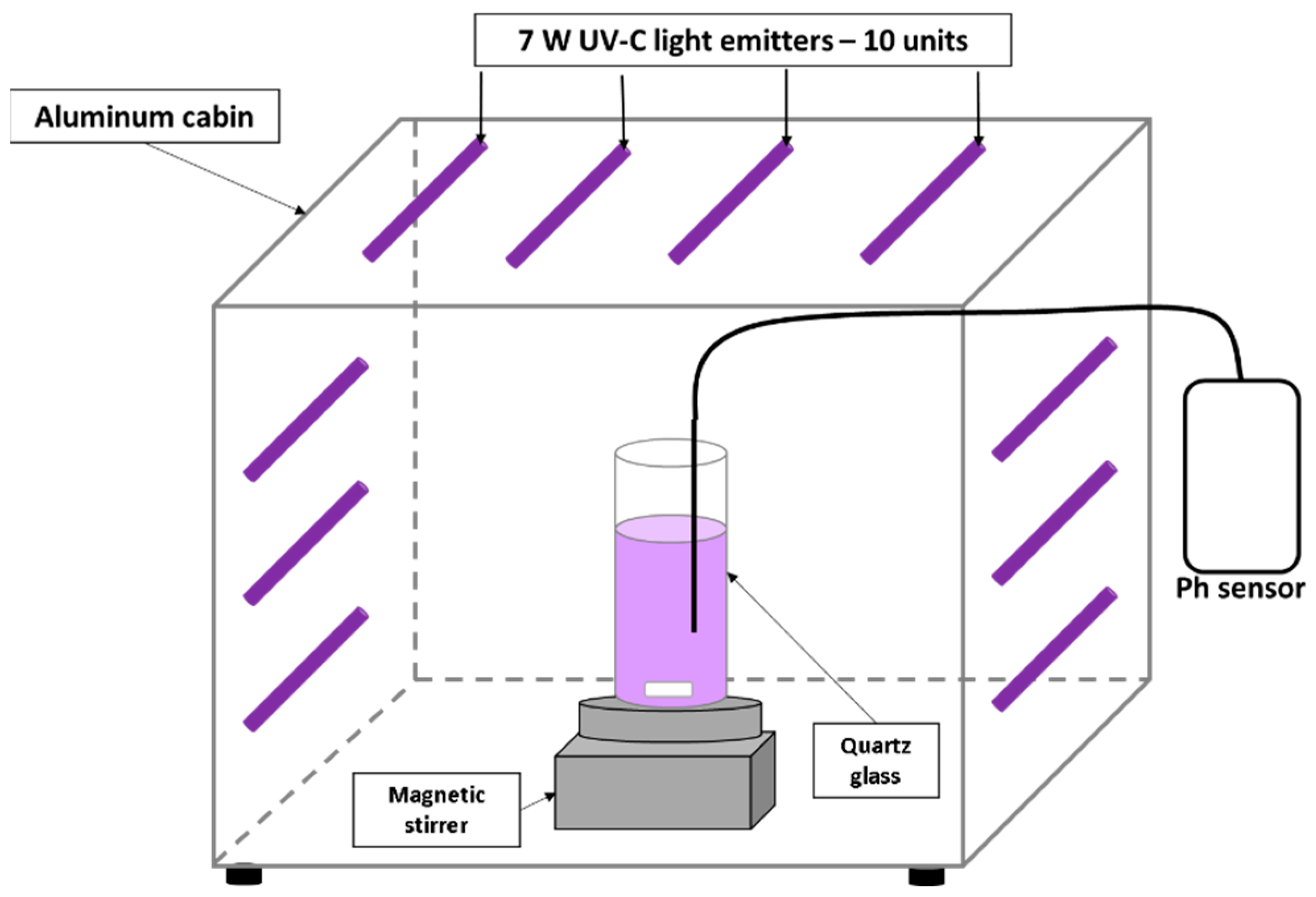
2.3. Experimental Reaction Process
3. Results
3.1. Ilmenite Characterization
3.2. Experimental Reaction Process
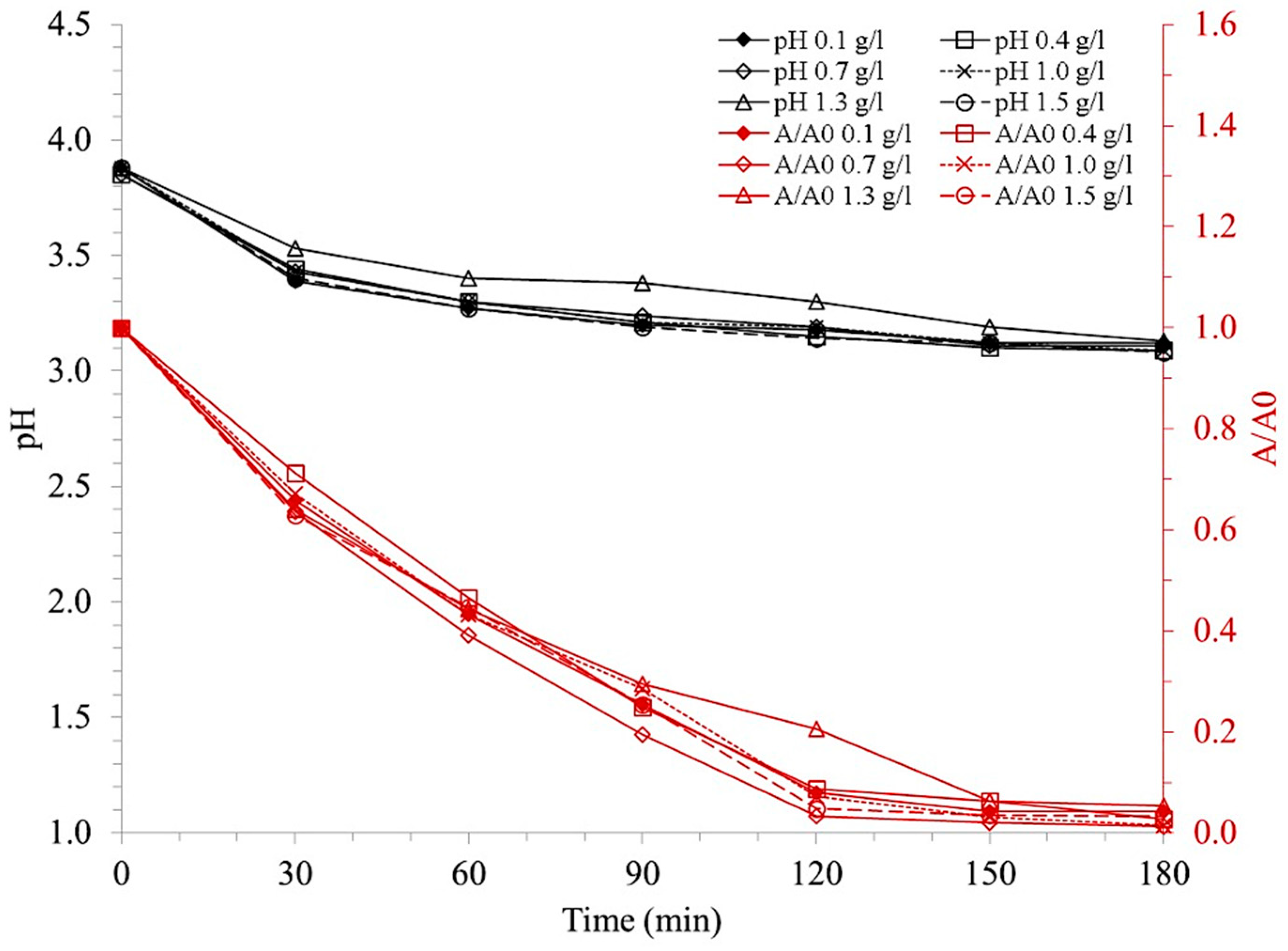
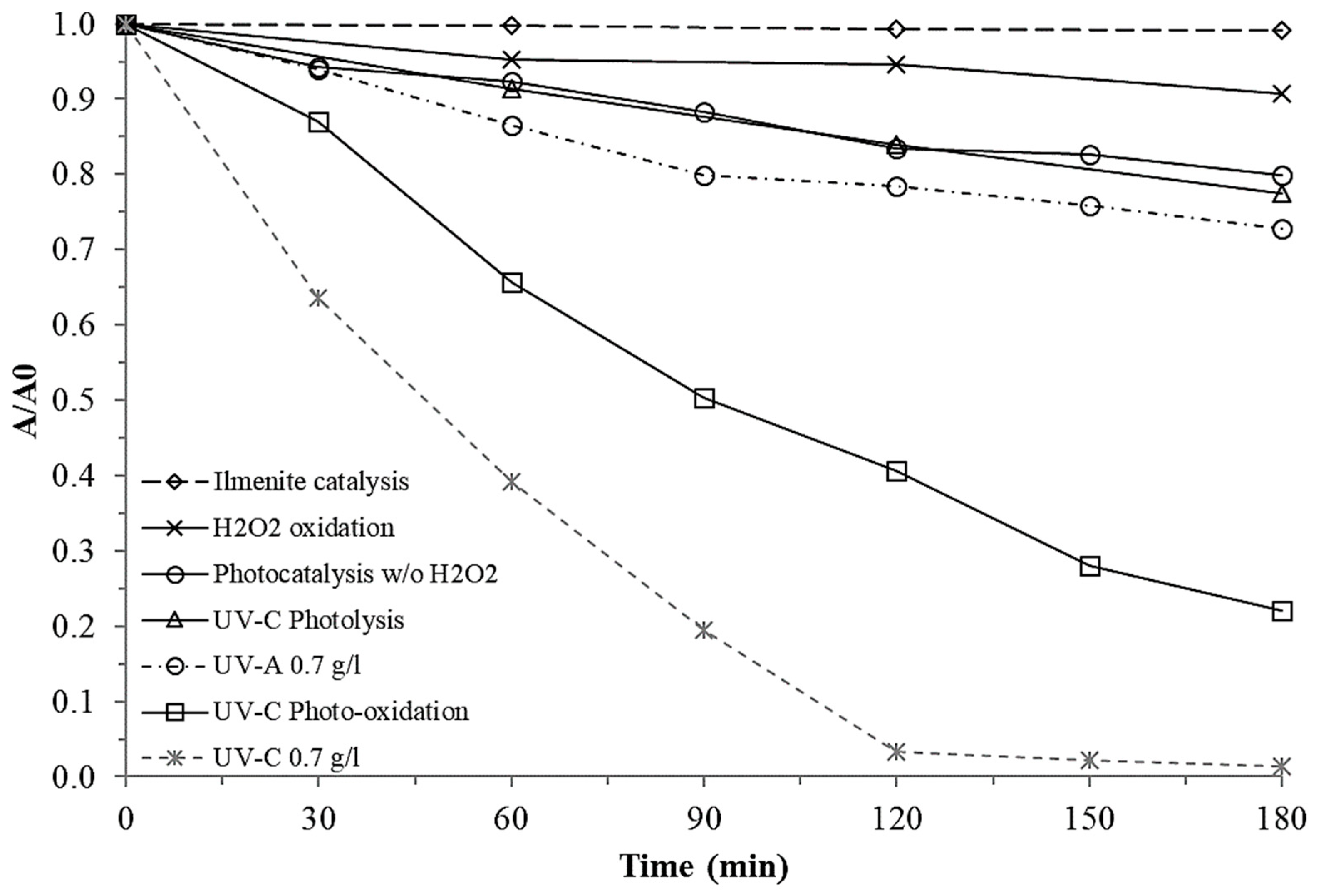
3.2.1. Effect of Ilmenite Concentration
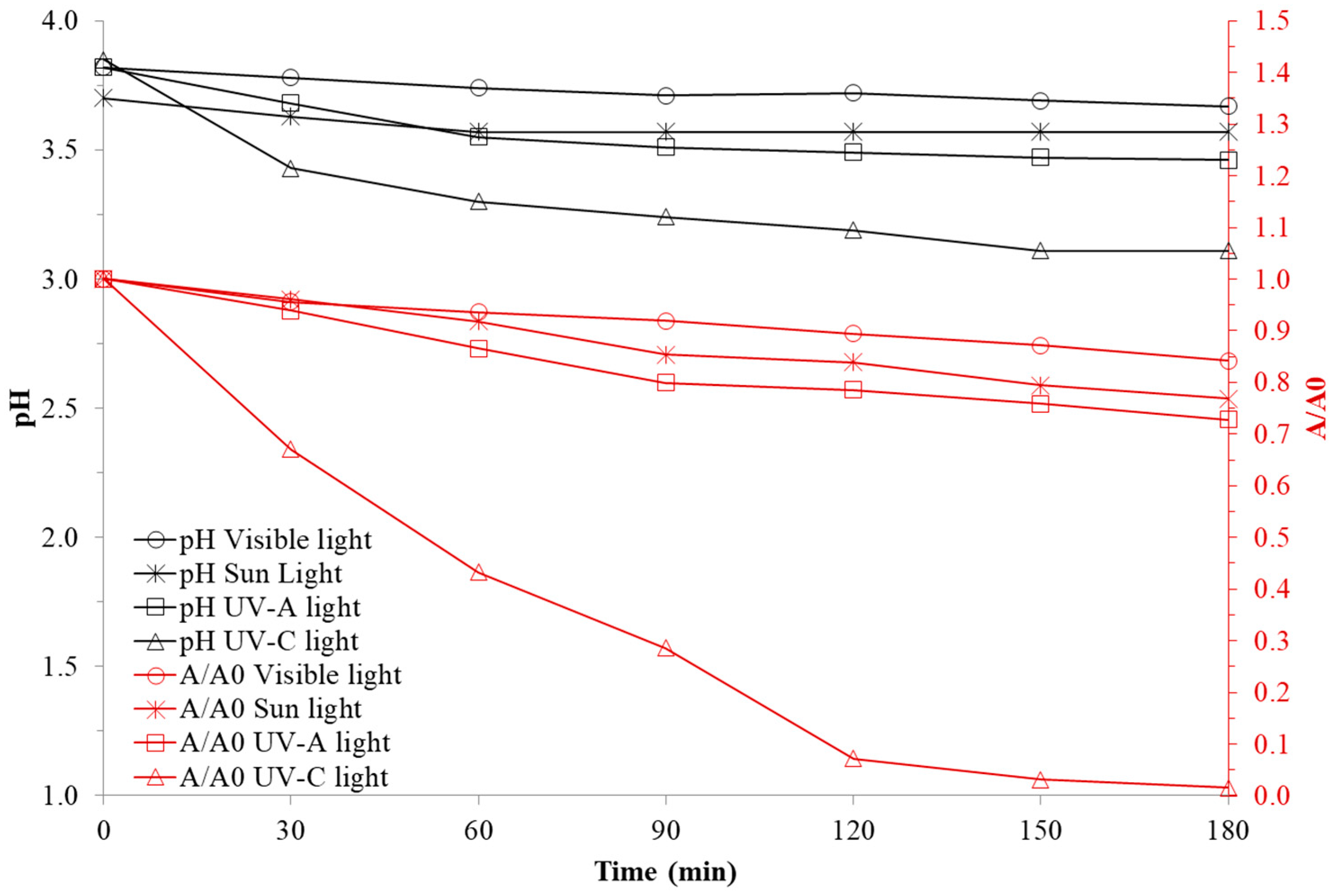
3.2.2. Effect of Light Type
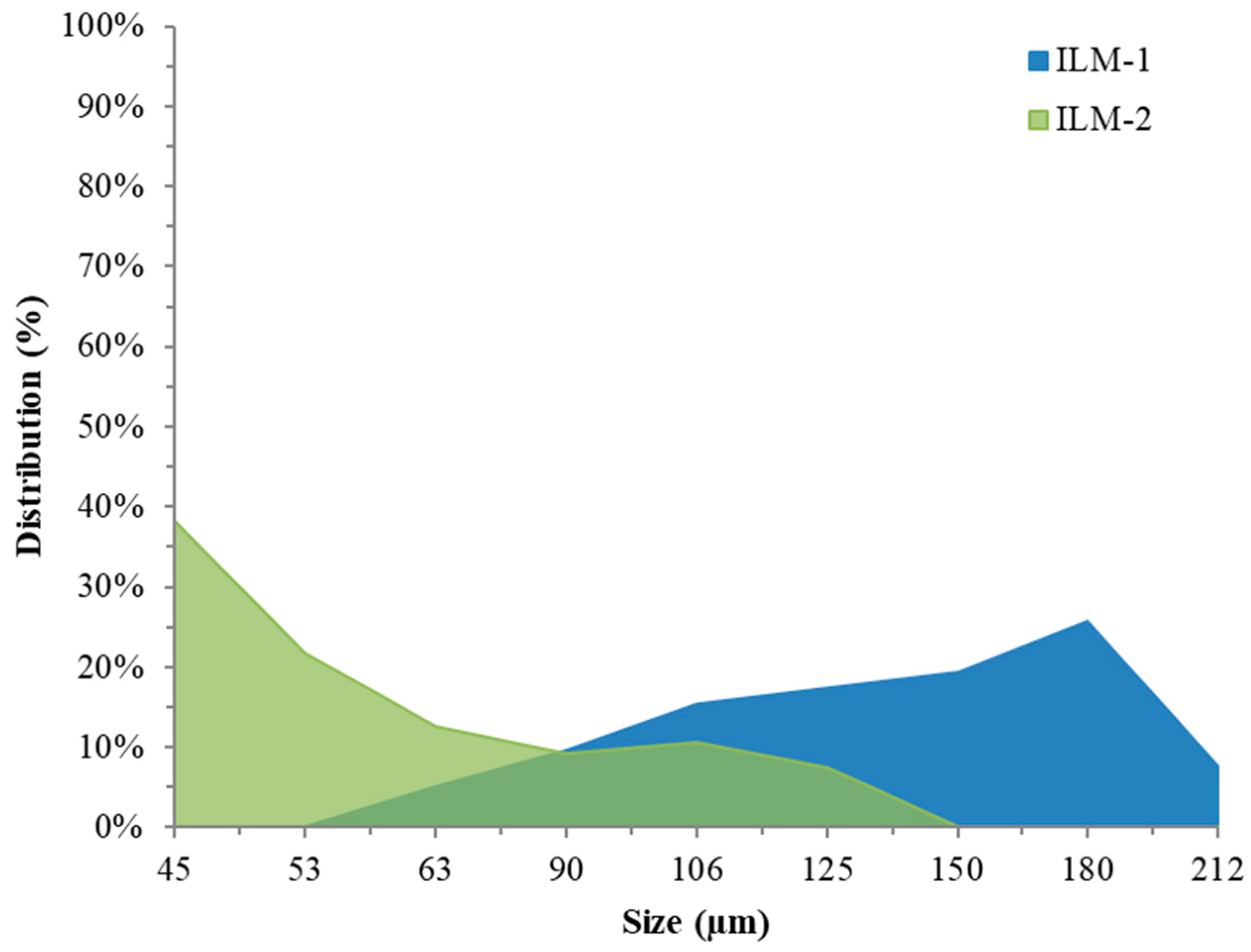
3.2.3. Effect of Ilmenite Particle Size
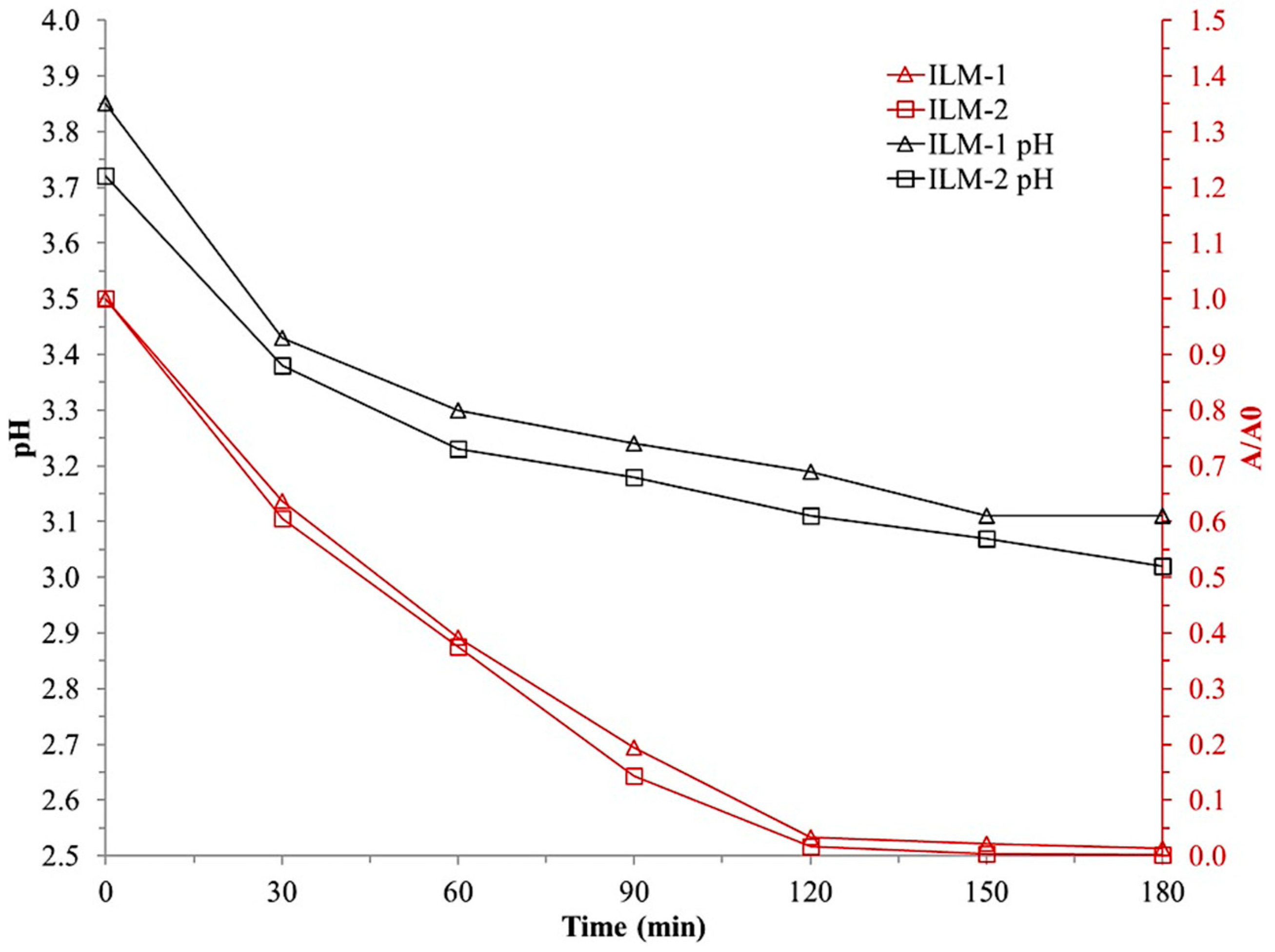
3.2.4. Ilmenite Stability
4. Discussion
4.1. Ilmenite Characterization
4.2. Experimental Reaction Process
4.2.1. Effect of Ilmenite Concentration
4.2.2. Light Type Effect
4.2.3. Ilmenite Particle Size Effect
4.2.4. Ilmenite Reuse Test
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IDEAM. Informe Nacional de Residuos o Desechos Peligrosos en Colombia; Ministerio de Ambiente y Desarrollo Sostenible: Bogotá, Colombia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Herney-Ramirez, J.; Lampinen, M.; Vicente, M.A.; Costa, C.A.; Madeira, L.M. Experimental Design to Optimize the Oxidation of Orange II Dye Solution Using a Clay-Based Fenton-like Catalyst. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herney-Ramirez, J.; Vicente, M.A.; Madeira, L.M. Heterogeneous Photo-Fenton Oxidation with Pillared Clay-Based Catalysts for Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 1–2, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, C.; Libra, J.A.; Sau, A. Ozonization of Water and Wastewater: A Practical Guide to Understanding Ozone and Its, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Vch Verlang GmbH & Co.: Weinheim, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Faisal, M.; Malick, T.; Muneer, M. Photocatalysed Degradation of Two Selected Dyes in UV-Irradiated Aqueous Suspensions of Titania. Dye. Pigment. 2007, 72, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, A.; Blangetti, N.; Sacco, O.; Freyria, F.S.; Bonelli, B.; Esposito, S.; Sannino, D.; Vaiano, V. Photocatalytic Degradation of Crystal Violet Dye under Visible Light by Fe-Doped TiO2 Prepared by Reverse-Micelle Sol–Gel Method. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudhoo, A.; Paliya, S.; Goswami, P.; Singh, M.; Lofrano, G.; Carotenuto, M.; Carraturo, F.; Libralato, G.; Guida, M.; Usman, M.; et al. Fabrication, Functionalization and Performance of Doped Photocatalysts for Dye Degradation and Mineralization: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 1825–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, U. Design of Heterogeneous Catalysts New Approaches Based on Synthesis, Characterization and Modeling; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Extraction and Beneficiation of Ores and Minerals; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; NTIS PB94-195203. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Tang, R.; Xiong, S.; Zheng, J.; Li, L.; Zhou, Z.; Gong, D.; Deng, Y.; Su, L.; Liao, C. Application of Natural Minerals in Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 152434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pataquiva-Mateus, A.Y.; Zea, H.R.; Ramirez, J.H. Degradation of Orange II by Fenton Reaction Using Ilmenite as Catalyst. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 6187–6194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Muñoz, P.; Pliego, G.; Zazo, J.A.; Bahamonde, A.; Casas, J.A. Sulfonamides Photoassisted Oxidation Treatments Catalyzed by Ilmenite. Chemosphere 2017, 180, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministerio de Ambiente y Desarrollo Sostenible. Resolución 631 de 2015 “Por la Cual se Establecen los Parámetros y los Valores Límites Máximos Permisibles en los Vertimientos Puntuales a Cuerpos de Aguas Superficiales y a los Sistemas de Alcantarillado Público y se Dictan otras Disposiciones; Ministerio de Ambiente y Desarrollo Sostenible: Bogotá, Colombia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hakki, A.; Dillert, R.; Bahnemann, D. Photocatalytic Conversion of Nitroaromatic Compounds in the Presence of TiO2. Catal. Today 2009, 144, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahnemann, W.; Muneer, M.; Haque, M.M. Titanium Dioxide-Mediated Photocatalysed Degradation of Few Selected Organic Pollutants in Aqueous Suspensions. Catal. Today 2007, 124, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; Ma, T.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y. Investigation on Degradation of Azo Fuchsine Using Visible Light in the Presence of Heat-Treated Anatase TiO2 Powder. Dye. Pigment. 2007, 75, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-Y.; Zheng, Z.; Mao, G.-J. Enhanced Photocatalytic Discoloration of Acid Fuchsine Wastewater by TiO2/Schorl Composite Catalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Muñoz, P.; Pliego, G.; Zazo, J.A.; Bahamonde, A.; Casas, J.A. Ilmenite (FeTiO3) as Low Cost Catalyst for Advanced Oxidation Processes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdilo, A.; Irannajad, M. Comparison of Microwave Irradiation and Oxidation Roasting as Pretreatment Methods for Modification of Ilmenite Physicochemical Properties. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 33, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.-J.; Huang, S.-T.; Chung, W.-H.; Jan, J.-L.; Lin, W.-Y.; Chen, C.-C. Degradation Pathways of Crystal Violet by Fenton and Fenton-like Systems: Condition Optimization and Intermediate Separation and Identification. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 1032–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carp, O.; Huisman, C.L.; Reller, A. Photoinduced Reactivity of Titanium Dioxide. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2004, 32, 33–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epling, G.A.; Lin, C. Investigation of Retardation Effects on the Titanium Dioxide Photodegradation System. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

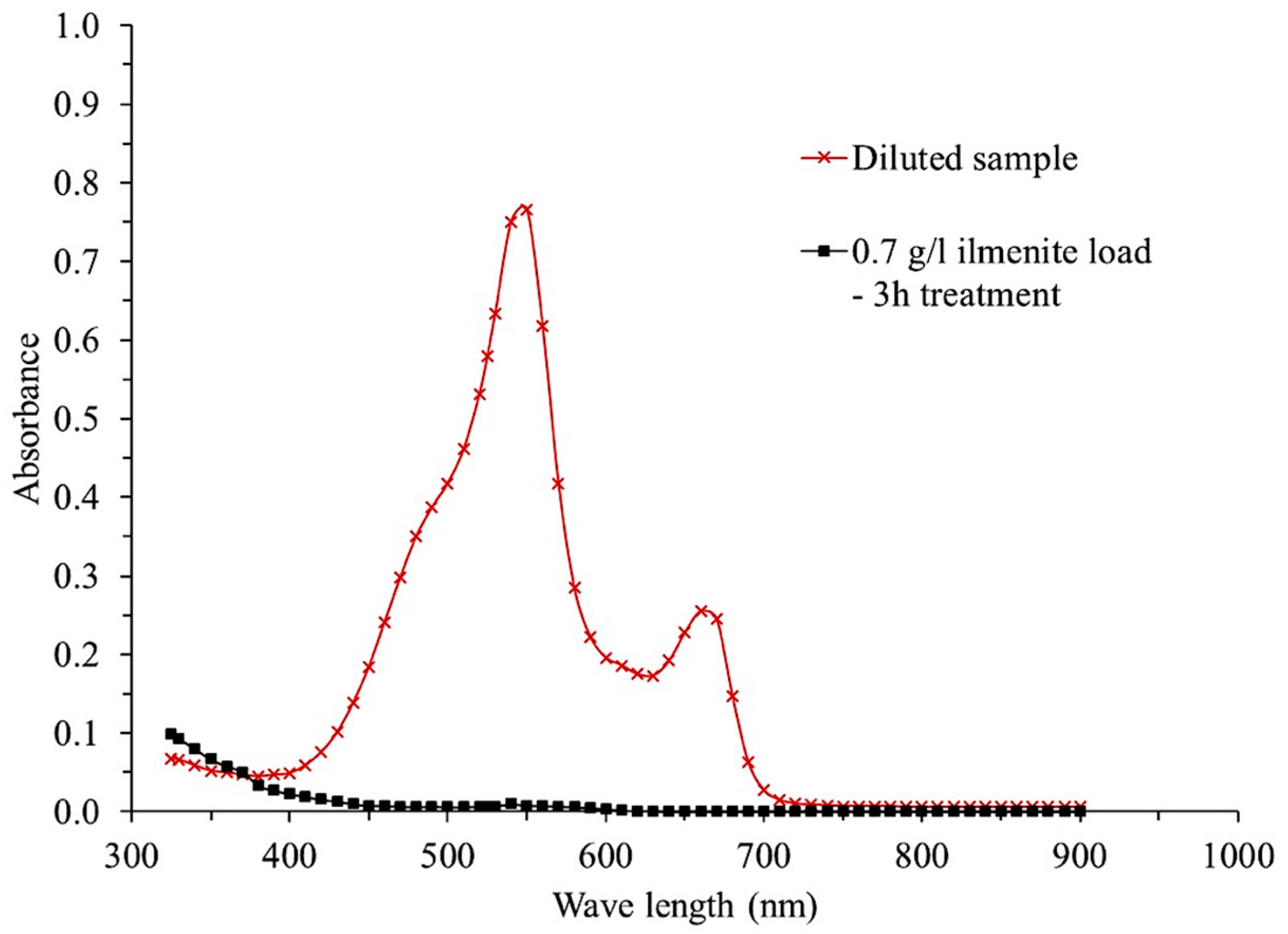
| Parameter | Undiluted | Diluted 5% (v/v) |
|---|---|---|
| COD (mg/L) | 27400 | 5240 |
| BOD5 (mg/L) | 5200 | N/A |
| pH (units) | 6.75 | 3.84 |
| Phenols (mg/L) | 5.4 | N/A |
| TSS (mg/L) | 242 | N/A |
| MBAS (mg/L) | <0.4 | N/A |
| SS (mg/L) | <0.5 | N/A |
| Element or Compound | (Weight %) |
|---|---|
| Fe2O3 | 42.645 |
| TiO2 | 41.250 |
| SiO2 | 12.273 |
| Al2O3 | 2.009 |
| MnO | 0.914 |
| V | 0.198 |
| MgO | 0.167 |
| K2O | 0.137 |
| Zr | 0.105 |
| P2O5 | 0.101 |
| Na2O | 0.090 |
| CaO | 0.060 |
| Cl | 0.020 |
| Nb | 0.012 |
| Zn | 0.010 |
| S | 0.009 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramírez Franco, J.H.; Castañeda Cárdenas, S.D.; Zea Ramírez, H.R. Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Dyes from Clinical Laboratory Wastewater. Water 2023, 15, 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061238
Ramírez Franco JH, Castañeda Cárdenas SD, Zea Ramírez HR. Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Dyes from Clinical Laboratory Wastewater. Water. 2023; 15(6):1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061238
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamírez Franco, J. H., S. D. Castañeda Cárdenas, and H. R. Zea Ramírez. 2023. "Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Dyes from Clinical Laboratory Wastewater" Water 15, no. 6: 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061238
APA StyleRamírez Franco, J. H., Castañeda Cárdenas, S. D., & Zea Ramírez, H. R. (2023). Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Dyes from Clinical Laboratory Wastewater. Water, 15(6), 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061238






