Does Decentralized Food Crop Cultivation Threaten Water-Land-Food Nexus? A Spatial Econometric Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Evaluation and Measurement Methods for WLF Nexus
2.2. Methods for Measuring Decentralized Food Crop Cultivation
2.3. Prediction Method of WLF Nexus and Decentralized Food Crop Cultivation
2.4. Variables Selection
2.5. Model Design
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Measuring Results of the Decentralized Food Crop Cultivation and the WLF Nexus
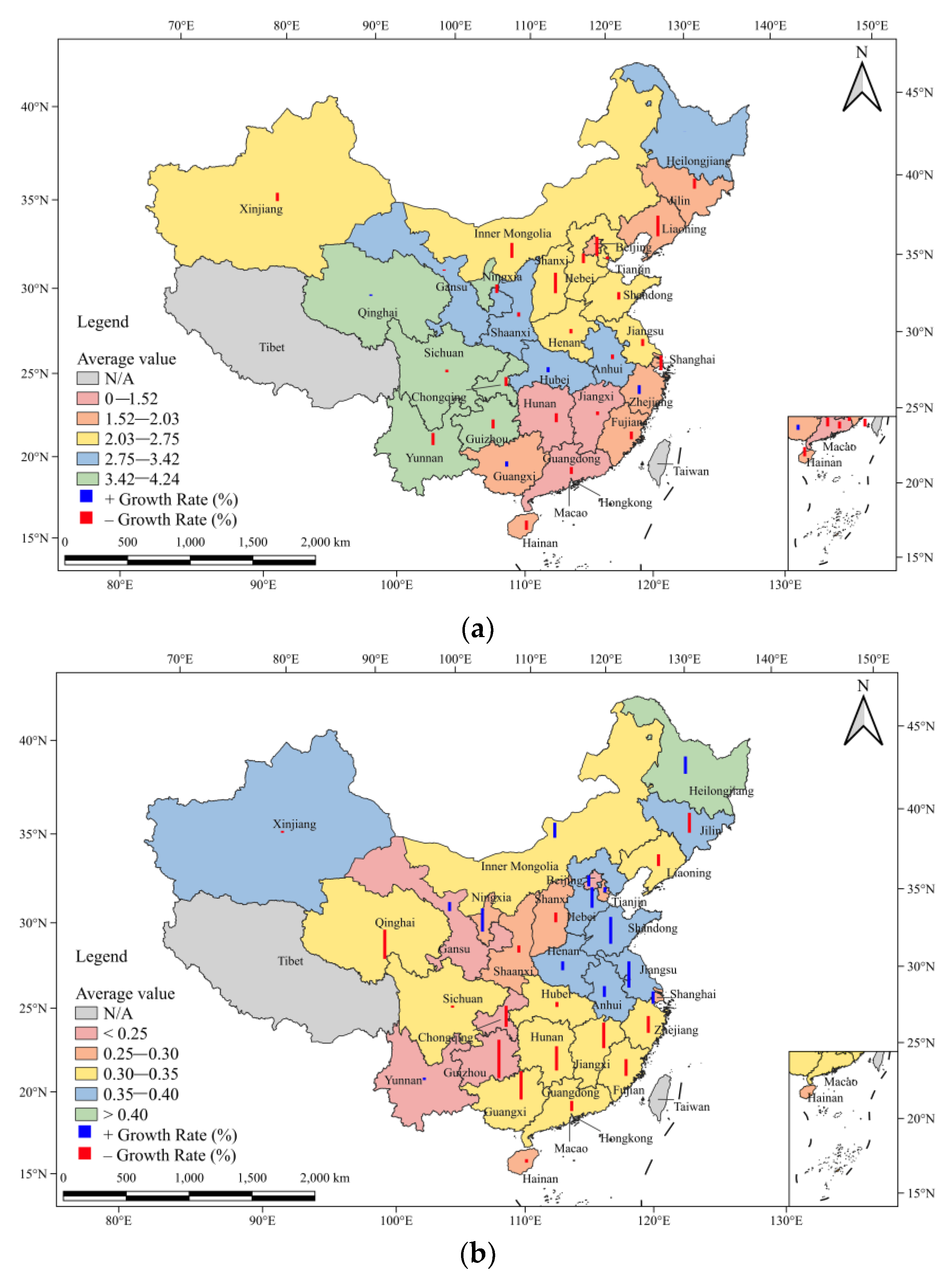
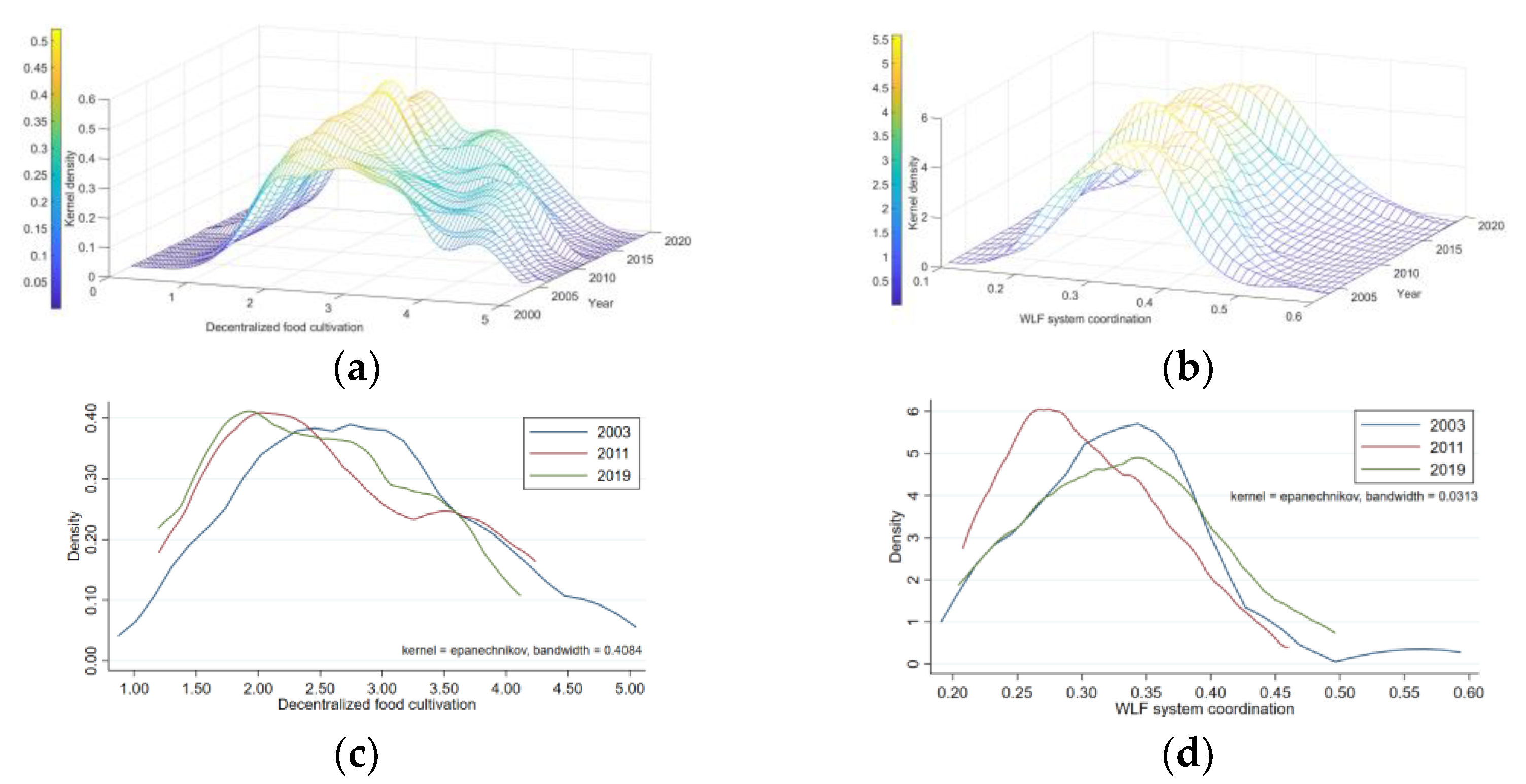
3.1.1. Analysis of Trend Characteristics of Water-Land-Food Nexus
3.1.2. Analysis of Trend Characteristics of Decentralized Food Crop Cultivation
3.2. Analysis of Empirical Test Results
3.2.1. Decentralized Food Crop Cultivation Affecting the WLF Nexus
3.2.2. A Sub-Sample Test of the Impact of Decentralized Food Crop Cultivation on the WLF Nexus
3.2.3. Quantile Test of the Impact of Decentralized Food Crop Cultivation on the WLF Nexus
3.2.4. Spatial Spillover Effect Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, W.S.; Elleby, C.; Zobbe, H. Food security policies in India and China: Implications for national and global food security. Food Secur. 2015, 7, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsogon, A.; Peres, L.E.P.; Xiao, Y.J.; Yan, J.B.; Fernie, A.R. Enhancing crop diversity for food security in the face of climate uncertainty. Plant J. 2022, 109, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.Z.; Yue, T.X.; Liu, Y.J.; Dong, J.W.; Sun, Z.G.; Chen, M.X.; Shi, W.J.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, Z.Y. Changes in China’s Food Self-Sufficiency Rate in the Context of a Changing Dietary Structure. J. Glob. Inf. Manag. 2022, 30, 298666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, G.V.; Atzori, R.; Acciaioli, A.; Giannetti, B.; Parrini, S.; Liu, G.Y. Agricultural landscape modification and land food footprint from 1970 to 2010: A case study of Sardinia, Italy. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 118097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzepczynski, M.S. Global Trends 2030: Alternative Worlds. Financ. Anal. J. 2014, 70, 60–63. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, L.C.; Tao, F.L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.C. Reducing agriculture irrigation water consumption through reshaping cropping systems across China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 312, 108707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Run, Y.D.; Li, M.D.; Qin, Y.C.; Shi, Z.F.; Li, Q.; Cui, Y.P. Dynamics of Land and Water Resources and Utilization of Cultivated Land in the Yellow River Beach Area of China. Water 2022, 14, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartres, C.J.; Noble, A. Sustainable intensification: Overcoming land and water constraints on food production. Food Secur. 2015, 7, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlamovitz, J.L.; Becker, P. Differentiated vulnerabilities and capacities for adaptation to water shortage in Gaborone, Botswana. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2021, 37, 278–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.Y.; Huang, X.J.; Song, Y.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Tan, Q.C. Response to urban land scarcity in growing megacities: Urban containment or inter-city connection? Cities 2020, 96, 102399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, P.; Asch, F. Rice production and food security in Asian Mega deltas-A review on characteristics, vulnerabilities and agricultural adaptation options to cope with climate change. J. Agron. Crop. Sci. 2020, 206, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.C.; Chiu, S.Y.; Chiu, Y.H.; Chang, T.H. Three-stage circular efficiency evaluation of agricultural food production, food consumption, and food waste recycling in EU countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 343, 130870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, J.M.E.; Urquiaga, S.; Jantalia, C.P.; Soares, L.H.D.; Alves, B.J.R.; Boddey, R.M.; Marchao, R.L.; Vilela, L. Energy balance for the production of grain, meat, and biofuel in specialized and mixed agrosystems. Pesqu. Agropecu. Bras. 2013, 48, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, E.G.; Zentner, R.P.; Campbell, C.A.; Lemke, R.; Brandt, K. Long-Term Crop Rotation Effects on Production, Grain Quality, Profitability, and Risk in the Northern Great Plains. Agron. J. 2017, 109, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.L.; Zhao, S.X.; Fu, X.M. Improved estimation model and empirical analysis of relationship between agricultural mechanization level and labor demand. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2016, 9, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.F.; Khan, S.U.; Xia, X.L.; Zhang, H.L.; Guo, C.H. Screening of agricultural land productivity and returning farmland to forest area for sensitivity to rural labor outward migration in the ecologically fragile Loess Plateau region. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 26442–26462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Li, X. The Impacts of Rural Labor Price Rising on Crop Structure among Provinces. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 39, 172–182. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Huang, Z.H.; Zhang, X.B.; Reardon, T. The Rapid Rise of Cross-Regional Agricultural Mechanization Services in China. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2013, 95, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Rizwan, M.; Abbas, A. Exploring the Role of Agricultural Services in Production Efficiency in Chinese Agriculture: A Case of the Socialized Agricultural Service System. Land 2022, 11, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, K.; Yamane, F.; Asano, K. Linkage between diversity and agro-ecosystem resilience: Nonmonotonic agricultural response under alternate regimes. Ecol. Econ. 2016, 126, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.L.; Li, X.Y.; Ruiz-Menjivar, J. The effect of crop diversity on agricultural eco-efficiency in China: A blessing or a curse? J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 124243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.Z.; Gibson, J. Improving eco-efficiency for the sustainable agricultural production: A case study in Shandong, China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2019, 144, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- .Jat, H.S.; Datta, A.; Choudhary, M.; Yadav, A.K.; Choudhary, V.; Sharma, P.C.; Gathala, M.K.; Jat, M.L.; McDonald, A. Effects of tillage, crop establishment and diversification on soil organic carbon, aggregation, aggregate associated carbon and productivity in cereal systems of semi-arid Northwest India. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 190, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Wang, S.L.; Wang, H.; Ning, F.; Zhang, Y.H.; Dong, Z.Y.; Wen, P.F.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.L.; Li, J. The effects of rotating conservation tillage with conventional tillage on soil properties and grain yields in winter wheat-spring maize rotations. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 263, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofori, S.A.; Cobbina, S.J.; Obiri, S. Climate change, land, water, and food security: Perspectives from Sub-Saharan Africa. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, A.S.; Nicholls, R.J.; Clarke, D.; Savin, C.; Harrison, P.A. Integrated assessment of the food-water-land-ecosystems nexus in Europe: Implications for sustainability. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Mohtar, R.H.; Yoo, S.H. Assessment of food trade impacts on water, food, and land security in the MENA region. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Psomas, A.; Vryzidis, I.; Spyridakos, A.; Mimikou, M. MCDA approach for agricultural water management in the context of water-energy-land-food nexus. Oper. Res. 2021, 21, 689–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Q.; Chen, B.; Su, M.R. Nonzero-Sum Relationships in Mitigating Urban Carbon Emissions: A Dynamic Network Simulation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11594–11603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, A.; Tsurita, I.; Burnett, K.; Orencio, P.M. A review of the current state of research on the water, energy, and food nexus. J. Hydrol. -Reg. Stud. 2017, 11, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clothier, B.; Jovanovic, N.; Zhang, X.Y. Reporting on water productivity and economic performance at the water food nexus. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 237, 106123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.X.; Zhang, G.J.; Li, Z.W.; Li, K. Interprovincial food trade and water resources conservation in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.K.; Zhong, X.Y.; Guo, S.; Liu, G.W.; Shen, G.Q.P.; Yu, T. Water-energy nexus and its efficiency in China’s construction industry: Evidence from province-level data. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 48, 101557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Song, J.; Wu, F. Modeling social-economic water cycling and the water-land nexus: A framework and an application. Ecol. Model. 2018, 390, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegmund-Schultze, M.; Sobral, M.D.; de Moraes, M.; Almeida-Cortez, J.S.; Azevedo, J.R.G.; Candeias, A.L.; Cierjacks, A.; Gomes, E.T.A.; Gunkel, G.; Hartje, V.; et al. The legacy of large dams and their effects on the water-land nexus. Reg. Environ. Change 2018, 18, 1883–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.Q.; Tian, Z.; He, X.G.; Wang, J.; Sun, L.X.; Fischer, G.; Fan, D.L.; Zhong, H.L.; Wu, W.; Pope, E.; et al. Future increases in irrigation water requirement challenge the water-food nexus in the northeast farming region of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.Y.; Liu, G.Y. Urban energy water food land climate change nexus in the flow and policy perspective: A review. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2018, 29, 4226–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.G.; Cao, T.; Chen, B. Urban energy-water nexus based on modified input-output analysis. Appl. Energy 2017, 196, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, A.A.; Crenna, E.; Sala, S.; Udias, A. A proposal for integration of the ecosystem-water-food-land-energy (EWFLE) nexus concept into life cycle assessment: A synthesis matrix system for food security. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 3874–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, V.J.; Kurniawan, J.H. Systematically linking qualitative elements of scenarios across levels, scales, and sectors. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 79, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.Q.; Chen, B. Changing Urban Carbon Metabolism over Time: Historical Trajectory and Future Pathway. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7560–7571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ye, W.; Jiang, H.; Song, H.; Zheng, C. Impact of the eco-efficiency of food production on the water–land–food system coordination in China: A discussion of the moderation effect of environmental regulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 857, 159641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hang, L.; Ding, X.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X. Spatial Heterogeneity and Influencing Factors of Agricultural Water Use Efficiency in China. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2019, 28, 817–828. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, R.D.; Ord, J.K.; Koehler, A.B. Prediction intervals for ARIMA models. J. Bus. Econ. Stat. 2001, 19, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhi, Y.L.; Chen, J.F.; Wang, H.M.; Liu, G.; Zhu, W.M. Evaluation of the suitability of the composite system of “water-energy-food” in China from the perspective of symbiosis. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2020, 30, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, D.; Tilman, D. National food production stabilized by crop diversity. Nature 2019, 571, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringler, C.; Bhaduri, A.; Lawford, R. The nexus across water, energy, land and food (WELF): Potential for improved resource use efficiency? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, G.; Rulli, M.C.; D’Odorico, P. European large-scale farmland investments and the land-water-energy-food nexus. Adv. Water Resour. 2017, 110, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moran, P.A. A test for the serial independence of residuals. Biometrika 1950, 37, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubin, R. Spatial lags and spatial errors revisited: Some Monte Carlo evidence. In Spatial and Spatiotemporal Econometrics; LeSage, J.P., Pace, R.K., Eds.; Advances in Econometrics; Emerald Group Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2004; Volume 18, pp. 75–98. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Xin, L.J.; Tan, M.H.; Li, X.B.; Wang, J.Y. Impact of spatiotemporal change of cultivated land on food-water relations in China during 1990–2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.C.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, Y.C.; Cao, J.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhuang, H.M.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, J.; Tao, F.L. Annual paddy rice planting area and cropping intensity datasets and their dynamics in the Asian monsoon region from 2000 to 2020. Agric. Sys. 2022, 200, 103437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Long, H.L.; Li, T.T.; Tu, S.S. Land use transitions and their effects on water environment in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, China. Land Use Policy 2015, 47, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.J.; Yan, D.H.; Qin, T.L.; Song, Y.F.; Weng, B.S.; Yuan, Y.; Dong, G.Q. Assessment of Drought Evolution Characteristics and Drought Coping Ability of Water Conservancy Projects in Huang-Huai-Hai River Basin, China. Water 2016, 8, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmerson, M.; Morales, M.B.; Onate, J.J.; Batry, P.; Berendse, F.; Liira, J.; Aavik, T.; Guerrero, I.; Bommarco, R.; Eggers, S.; et al. How Agricultural Intensification Affects Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. In Advances in Ecological Research, Vol 55: Large-Scale Ecology: Model Systems to Global Perspectives; Dumbrell, A.J., Kordas, R.L., Woodward, G., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 55, pp. 43–97. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.B.; Yang, J.; Thomas, R. Mechanization outsourcing clusters and division of labor in Chinese agriculture. China Econ. Rev. 2017, 43, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.H.; Cheng, E.J. Effects of land fragmentation and returns to scale in the Chinese farming sector. Appl. Econ. 2001, 33, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Chavas, J.P.; Barham, B.; Foltz, J. Specialization, diversification, and productivity: A panel data analysis of rice farms in Korea. Agric. Econ. 2012, 43, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelli, T.; Fleming, E. Diversification economies and specialisation efficiencies in a mixed food and coffee smallholder farming system in Papua New Guinea. Agric. Econ. 2004, 31, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.Y.; Shankar, S.; Li, L.H. Is specialization a strategy to improve farm efficiency in northwest China? Rev. Dev. Econ. 2021, 25, 1695–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.F.; Yang, Q.Y.; Li, Y.Q.; Sun, X.F. Mapping and evaluating cultivated land fallow in Southwest China using multisource data. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 987–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.Z.; Zhao, L.S.; Zou, W.; Zheng, D.F. Water resource utilization efficiency and spatial spillover effects in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 771–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, D.; Liu, Z.M. Does farmer economic organization and agricultural specialization improve rural income? Evidence from China. Econ. Model. 2012, 29, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variable Category | Variable | Symbol | Calculation Method | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent variable | WLF nexus | WLF | Referring to Li, et al. [42], Measured by entropy weighted TOPSIS and coupled coordination model | None |
| Independent variable | decentralized food crop cultivation | Defc | 1/Herfindahl index of planting area of wheat, rice, maize, beans and potatoes | None |
| Instrumental variable | Decentralized food yield | Grte | 1/Herfindahl index of yield of wheat, rice, maize, beans and potatoes | None |
| Control variables | Environmental regulation | Envi | Total investment in environmental pollution control | ×109 yuan |
| Degree of mechanization | Mach | Total agricultural machinery power/crop sown area | 102 kW·h/hm2 | |
| Disaster rate | Disa | Crop affected area/total crop sown area×100% | % | |
| Wetland area share | Welt | Wetland area/provincial land area | None | |
| Rural fixed asset investment | Inve | Investment in fixed assets of rural farm households/number of rural population | 103 yuan per person | |
| Technological environment | Tech | Technology market turnover × (total agricultural output value/GDP value)/number of rural employees | ×104 yuan per person | |
| Industrial structure level | Stru | (Value-added of the secondary industry + value-added of the tertiary industry)/gross GDP | km/hm2 |
| Producing Area | Variable | Decentralized Food Crop Cultivation | WLF Nexus | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 2003–2007 | 2008–2011 | 2012–2015 | 2016–2019 | 2003–2007 | 2008–2011 | 2012–2015 | 2016–2019 | |
| Province/National Average | 2.733 | 2.641 | 2.536 | 2.452 | 0.332 | 0.310 | 0.301 | 0.319 | |
| Main food producing areas | Hebei | 2.545 | 2.327 | 2.214 | 2.188 | 0.346 | 0.365 | 0.366 | 0.394 |
| Inner Mongolia | 3.199 | 2.869 | 2.324 | 2.315 | 0.321 | 0.345 | 0.343 | 0.367 | |
| Liaoning | 2.048 | 1.817 | 1.559 | 1.500 | 0.377 | 0.340 | 0.320 | 0.325 | |
| Jilin | 2.003 | 1.878 | 1.608 | 1.592 | 0.419 | 0.355 | 0.344 | 0.349 | |
| Heilongjiang | 2.987 | 3.153 | 2.769 | 2.936 | 0.435 | 0.458 | 0.482 | 0.494 | |
| Jiangsu | 2.832 | 2.748 | 2.723 | 2.675 | 0.365 | 0.390 | 0.403 | 0.435 | |
| Anhui | 3.467 | 3.473 | 3.472 | 3.241 | 0.363 | 0.358 | 0.371 | 0.391 | |
| Jiangxi | 1.217 | 1.200 | 1.213 | 1.170 | 0.397 | 0.306 | 0.303 | 0.312 | |
| Shandong | 2.424 | 2.308 | 2.281 | 2.188 | 0.359 | 0.387 | 0.411 | 0.430 | |
| Henan | 2.545 | 2.508 | 2.484 | 2.403 | 0.382 | 0.377 | 0.380 | 0.402 | |
| Hubei | 2.818 | 2.917 | 2.974 | 3.031 | 0.337 | 0.306 | 0.313 | 0.335 | |
| Hunan | 1.490 | 1.378 | 1.411 | 1.370 | 0.372 | 0.320 | 0.306 | 0.308 | |
| Sichuan | 4.342 | 4.259 | 4.226 | 4.108 | 0.312 | 0.322 | 0.302 | 0.313 | |
| Mean value of main producing area | 2.609 | 2.526 | 2.404 | 2.363 | 0.368 | 0.356 | 0.357 | 0.373 | |
| food main sales area | Beijing | 2.151 | 1.897 | 1.890 | 1.650 | 0.261 | 0.240 | 0.212 | 0.269 |
| Tianjin | 2.510 | 2.343 | 2.196 | 2.331 | 0.301 | 0.246 | 0.232 | 0.294 | |
| Shanghai | 1.786 | 2.030 | 1.966 | 1.498 | 0.271 | 0.283 | 0.290 | 0.297 | |
| Zhejiang | 1.814 | 1.779 | 2.089 | 2.188 | 0.376 | 0.325 | 0.295 | 0.301 | |
| Fujian | 1.917 | 1.885 | 2.015 | 1.682 | 0.383 | 0.314 | 0.305 | 0.306 | |
| Guangdong | 1.596 | 1.531 | 1.509 | 1.421 | 0.380 | 0.351 | 0.322 | 0.333 | |
| Chongqing | 1.758 | 1.734 | 1.771 | 1.598 | 0.250 | 0.210 | 0.200 | 0.217 | |
| Hainan | 4.107 | 3.856 | 3.750 | 3.571 | 0.291 | 0.333 | 0.280 | 0.283 | |
| The mean value of main sales area | 2.205 | 2.132 | 2.148 | 1.992 | 0.314 | 0.288 | 0.267 | 0.287 | |
| Production and sales balance area | Shanxi | 3.075 | 2.491 | 2.382 | 2.131 | 0.271 | 0.234 | 0.238 | 0.251 |
| Guangxi | 1.975 | 1.935 | 2.071 | 2.159 | 0.385 | 0.307 | 0.274 | 0.282 | |
| Guizhou | 4.447 | 4.126 | 3.188 | 3.912 | 0.293 | 0.256 | 0.184 | 0.192 | |
| Yunnan | 4.363 | 4.105 | 3.902 | 3.501 | 0.253 | 0.238 | 0.236 | 0.257 | |
| Shaanxi | 3.26 | 3.092 | 3.097 | 3.071 | 0.266 | 0.254 | 0.265 | 0.244 | |
| Gansu | 3.298 | 3.389 | 3.282 | 3.147 | 0.230 | 0.229 | 0.229 | 0.245 | |
| Qinghai | 3.682 | 3.782 | 3.747 | 3.588 | 0.370 | 0.262 | 0.249 | 0.309 | |
| Ningxia | 3.766 | 4.050 | 3.666 | 3.153 | 0.245 | 0.242 | 0.238 | 0.280 | |
| Xinjiang | 2.570 | 2.361 | 2.285 | 2.254 | 0.355 | 0.339 | 0.351 | 0.356 | |
| Mean value of equilibrium region | 3.382 | 3.259 | 3.069 | 2.991 | 0.297 | 0.262 | 0.252 | 0.269 | |
| Variable | WLF Nexus | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 (IV-Tobit) | Model 4 | |
| Defc | −0.011 * (−1.749) | −0.068 *** (−3.413) | ||
| Lag_Defc | −0.010 * (−1.648) | |||
| Envi | 0.072 *** (4.841) | 0.072 *** (4.840) | 0.067 *** (4.011) | 0.057 *** (3.949) |
| Mach | −0.196 (−1.170) | −0.192 (−1.155) | −0.054 (−0.260) | −0.165 (−1.013) |
| Disa | −0.013 (−0.875) | −0.013 (−0.899) | −0.016 (−0.965) | −0.002 (−0.173) |
| Wetl | 0.002 (0.165) | 0.002 (0.159) | 0.001 (0.088) | −0.009 (−0.628) |
| Inve | −0.072 (−1.581) | −0.069 (−1.521) | −0.074 (−1.453) | −0.053 (−1.208) |
| Tech | 0.000 (0.031) | 0.002 (0.165) | 0.019 (1.313) | −0.000 (−0.027) |
| Stru | 0.006 (0.496) | 0.006 (0.450) | 0.006 (0.443) | 0.009 (0.775) |
| Time | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Ind | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| One stage F test | 35.760 | |||
| Wald test | 112.080 *** | 115.370 *** | 35,584.100 *** | 113.820 *** |
| Cons | 0.336 *** (18.543) | 0.366 *** (14.706) | 0.523 *** (9.073) | 0.363 *** (15.029) |
| N | 510 | 510 | 510 | 480 |
| Variable | Major Food Producing Areas | Non-Food Main Producing Areas | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 5 | Model 6 | Model 7 | Model 8 | Model 9 | Model 10 (IV-Tobit) | Model 11 | |
| Defc | −0.006 (−0.686) | −0.019 *** (−2.653) | −0.070 ** (−2.527) | ||||
| Lag_Defc | −0.006 (−0.683) | −0.020 *** (−2.879) | |||||
| Envi | 0.123 *** (7.335) | 0.124 *** (7.368) | 0.117 *** (7.012) | 0.006 (0.238) | 0.003 (0.106) | −0.003 (−0.116) | −0.010 (−0.422) |
| Mach | −0.442 ** (−2.079) | −0.451 ** (−2.117) | −0.393 * (−1.898) | −0.089 (−0.400) | −0.104 (−0.498) | 0.095 (0.306) | −0.089 (−0.442) |
| Disa | −0.006 (−0.311) | −0.005 (−0.299) | 0.009 (0.525) | 0.001 (0.061) | 0.001 (0.055) | −0.005 (−0.202) | 0.004 (0.210) |
| Wetl | −0.001 (−0.042) | −0.001 (−0.051) | −0.001 (−0.057) | 0.004 (0.214) | 0.003 (0.149) | 0.004 (0.175) | −0.013 (−0.687) |
| Inve | −0.116 * (−1.902) | −0.113 * (−1.853) | −0.124 ** (−2.111) | −0.040 (−0.648) | −0.027 (−0.430) | −0.068 (−0.941) | 0.001 (0.022) |
| Tech | 0.024 (1.355) | 0.027 (1.481) | 0.027 (1.521) | 0.010 (0.619) | 0.007 (0.413) | 0.028 (1.382) | 0.003 (0.165) |
| Stru | 0.005 (0.524) | 0.005 (0.515) | 0.008 (0.960) | 0.023 (0.352) | −0.004 (−0.059) | 0.003 (0.033) | 0.004 (0.062) |
| Time | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Ind | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| One stage F test | 20.68 | ||||||
| Wald test | 96.820 *** | 97.580 *** | 95.950 *** | 81.170 *** | 87.690 *** | 11,594.010 *** | 90.000 *** |
| Cons | 0.370 *** (20.501) | 0.388 *** (12.389) | 0.392 *** (12.446) | 0.292 *** (4.982) | 0.370 *** (5.846) | 0.509 *** (4.276) | 0.367 *** (6.157) |
| N | 221 | 221 | 208 | 289 | 289 | 289 | 272 |
| Variable | Model 12 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QR_10 | QR_20 | QR_30 | QR_40 | QR_50 | QR_60 | QR_70 | QR_80 | QR_90 | |
| Defc | −0.024 *** (−5.132) | −0.023 *** (−6.054) | −0.024 *** (−6.901) | −0.025 *** (−6.861) | −0.026 *** (−7.153) | −0.025 *** (−6.279) | −0.020 *** (−4.973) | −0.018 *** (−4.042) | −0.010 (−1.120) |
| Envi | 0.105 ** (2.200) | 0.151 *** (3.246) | 0.205 *** (8.056) | 0.205 *** (13.315) | 0.196 *** (14.642) | 0.194 *** (12.750) | 0.185 *** (9.603) | 0.155 *** (5.874) | 0.093 ** (2.315) |
| Mach | −0.104 (−0.690) | −0.159 (−1.114) | −0.230 (−1.569) | −0.270 * (−1.891) | −0.266 * (−1.933) | −0.330 ** (−2.288) | −0.343 ** (−2.070) | −0.402 * (−1.851) | −0.477 * (−1.692) |
| Disa | −0.040 (−1.381) | −0.023 (−0.808) | −0.023 (−0.780) | −0.041 (−1.528) | −0.024 (−0.892) | −0.051 * (−1.871) | −0.039 (−1.369) | −0.056 * (−1.686) | −0.024 (−0.588) |
| Wetl | 0.013 (0.613) | −0.012 (−0.480) | 0.006 (0.231) | 0.000 (0.014) | −0.012 (−0.543) | −0.027 (−1.327) | −0.040 * (−1.922) | −0.048 (−1.570) | −0.032 (−0.421) |
| Inve | 0.181 *** (2.622) | 0.101 (1.409) | 0.111 * (1.696) | 0.077 (1.253) | 0.094 (1.606) | 0.115 * (1.668) | 0.120 (1.243) | 0.302 ** (1.967) | 0.730 *** (3.217) |
| Tech | −0.097 *** (−3.063) | −0.068 ** (−2.240) | −0.056 *** (−3.057) | −0.057 *** (−3.601) | −0.055 *** (−3.335) | −0.046 ** (−2.423) | −0.047 ** (−2.036) | −0.067 * (−1.897) | 0.002 (0.027) |
| Stru | −0.100 (−1.488) | −0.112 * (−1.683) | −0.112 (−1.499) | −0.103 (−1.205) | −0.113 (−1.200) | −0.116 (−1.091) | −0.095 (−0.689) | −0.036 (−0.217) | 0.001 (0.005) |
| Time | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Ind | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Cons | 0.421 *** (6.788) | 0.450 *** (7.884) | 0.460 *** (7.047) | 0.476 *** (6.380) | 0.501 *** (6.134) | 0.528 *** (5.690) | 0.497 *** (4.205) | 0.456 *** (3.196) | 0.431 *** (3.020) |
| Year | Moran’s I | Year | Moran’s I | Year | Moran’s I | Year | Moran’s I | Year | Moran’s I |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2003 | 0.210 ** (2.110) | 2007 | 0.340 *** (3.037) | 2011 | 0.348 *** (3.156) | 2015 | 0.319 *** (2.914) | 2019 | 0.371 *** (3.329) |
| 2004 | 0.148 * (1.503) | 2008 | 0.208 ** (1.974) | 2012 | 0.219 ** (2.107) | 2016 | 0.311 *** (2.855) | ||
| 2005 | 0.356 *** (3.180) | 2009 | 0.220 ** (2.100) | 2013 | 0.207 *** (2.553) | 2017 | 0.239 ** (2.247) | ||
| 2006 | 0.300 *** (3.468) | 2010 | 0.213 ** (2.032) | 2014 | 0.320 *** (2.931) | 2018 | 0.169 ** (1.687) |
| Variables and Tests | Dependent Variable: WLF Nexus | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Model 13 | |||
| ρ | 0.345 *** | ||
| Defc | −0.009 ** (−2.179) | ω_Defc | −0.017 *** (−2.914) |
| Envi | 0.118 *** (7.114) | ω_Envi | 0.044 (1.377) |
| Mach | −0.220 * (−1.664) | ω_Mach | −0.486 ** (−2.311) |
| Disa | −0.061 *** (−2.887) | ω_Disa | 0.134 *** (3.696) |
| Wetl | −0.021 (−0.966) | ω_Wetl | −0.064 (−1.316) |
| Inve | 0.211 *** (3.682) | ω_Inve | −0.084 (−0.683) |
| Tech | −0.046 *** (−3.253) | ω_Tech | 0.008 (0.257) |
| Stru | −0.048 ** (−2.546) | ω_Stru | 0.054** (2.063) |
| AIC | −1510.491 | ||
| BIC | −1434.272 | ||
| Observations | 510 | ||
| Variables | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Total Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Defc | −0.010 *** (−2.712) | −0.028 *** (−3.487) | −0.039 *** (−4.969) |
| Envi | 0.125 *** (7.812) | 0.122 *** (3.061) | 0.247 *** (5.484) |
| Mach | −0.260 ** (−2.060) | −0.809 *** (−2.942) | −1.069 *** (−3.530) |
| Disa | −0.051 ** (−2.543) | 0.161 *** (3.220) | 0.110 ** (2.069) |
| Wetl | −0.028 (−1.180) | −0.105 (−1.463) | −0.133 (−1.523) |
| Inve | 0.213 *** (3.522) | 0.001 (0.003) | 0.214 (0.979) |
| Tech | −0.046 *** (−2.936) | −0.013 (−0.290) | −0.059 (−1.099) |
| Stru | −0.046 ** (−2.465) | 0.049 (1.244) | 0.003 (0.065) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, Y. Does Decentralized Food Crop Cultivation Threaten Water-Land-Food Nexus? A Spatial Econometric Analysis. Water 2023, 15, 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061096
Li Z, Li X, Wang Y. Does Decentralized Food Crop Cultivation Threaten Water-Land-Food Nexus? A Spatial Econometric Analysis. Water. 2023; 15(6):1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061096
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ziqiang, Xiaoyun Li, and Yajie Wang. 2023. "Does Decentralized Food Crop Cultivation Threaten Water-Land-Food Nexus? A Spatial Econometric Analysis" Water 15, no. 6: 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061096





