Optimal Allocation of Water Resources Based on GWAS Model in Handan, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The GWAS Model: Computational Unit Division
2.2. Establishing the Topological Relationship between Water Supply and Consumption
2.3. Model Building
2.3.1. Objective Function
2.3.2. Restrictions
2.3.3. Configuration Parameters
2.3.4. Solution Method
2.4. Case Study
2.4.1. Study Area
2.4.2. Water Demand Forecasting
2.4.3. Prediction of Available Water Supply
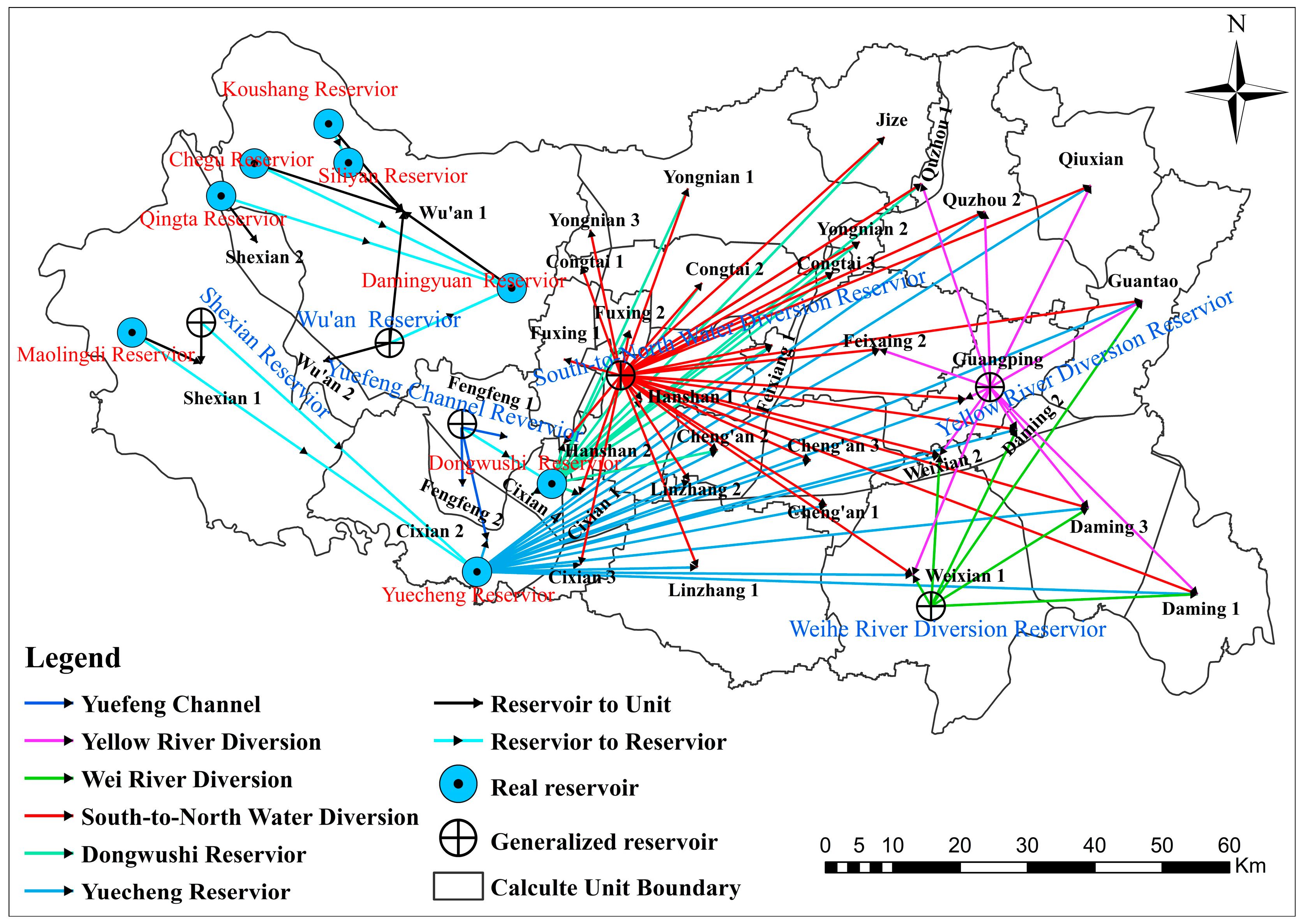
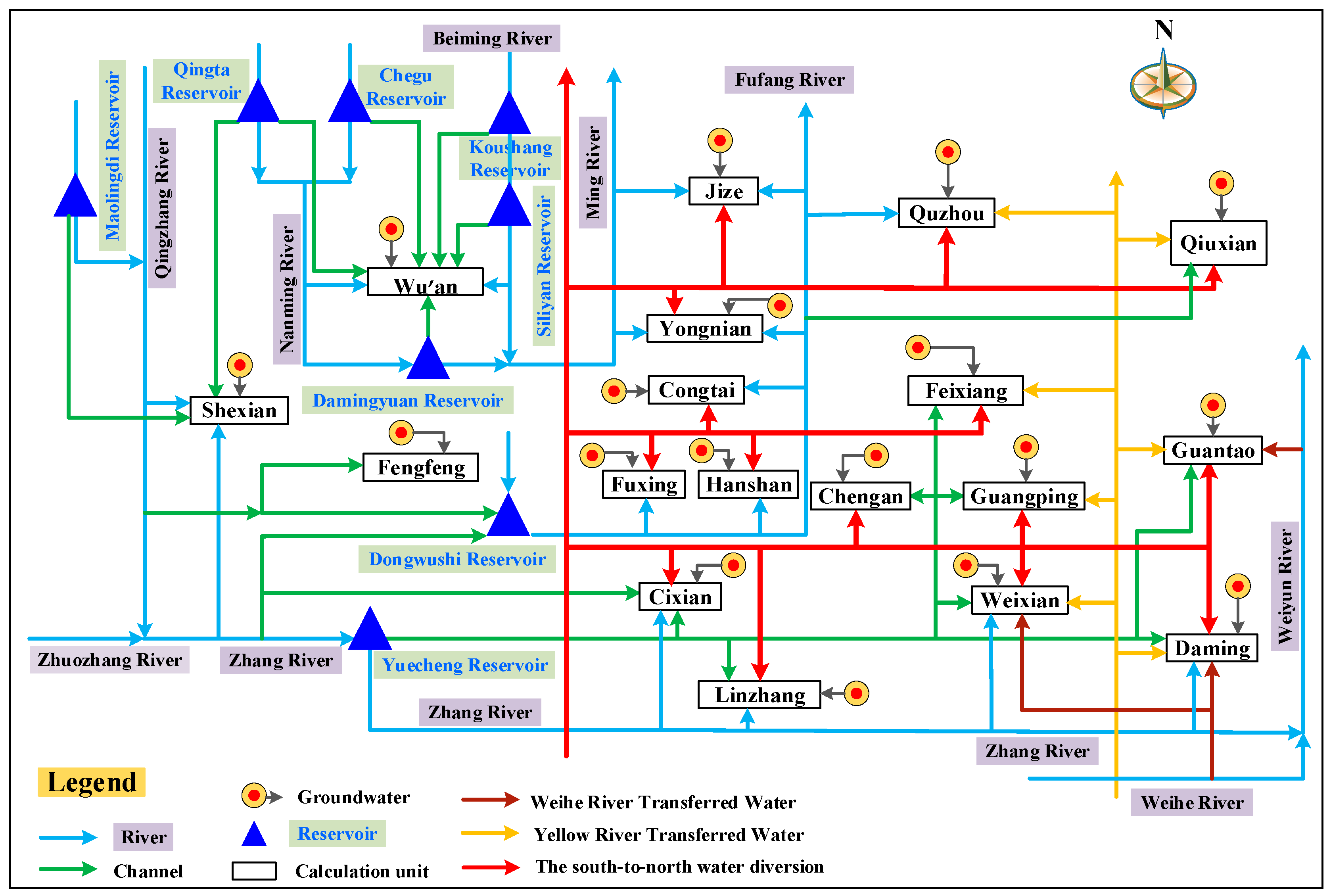
2.4.4. Determination of Topological Relationship and Model Parameters
Topological Relationship between Water Supply and Consumption
Parameters Setting
Reservoir Water Supply Characteristics
2.4.5. Model Validation
3. Analysis of Results and Discussion
3.1. Results and Analysis
3.1.1. Analysis of Industry Water Shortage Rate
3.1.2. Analysis of Water Allocation from Different Water Supply Sources
3.1.3. Analysis of Reservoir Water Allocation
3.1.4. Analysis of Water Distribution of Different Water Sources
3.1.5. Analysis of the Water Supply Ratio from Water Sources to Industry
3.2. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Sheng, L.X.; Li, K.; Sun, H.Y. Analysis of Present Situation of Water Resources and Countermeasures for Sustainable Development in China. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2008, 3, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.K. Sustainable Utilization of Water Resources in China. J. China Water Resour. 2000, 8, 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.P.; Xia, J.; Hu, Z.F. Situation and Problem Analysis of Water Resource Security in China. J. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2009, 18, 116–120. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.; Zhu, Y.Z. Measuring Water Resources Security: Research and Challenges of Water Resources Carrying Capacity. J. Nat. Resour. 2002, 3, 262–269. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.P. Overview of Research on Water Resource Allocation at Home and Abroad. J. Haihe Water Conserv. 2002, 5, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.J. Research on Synergetics Theory-Based Water Resource Allocation Model and Its Application. Doctoral Thesis, China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research, Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson, D. Optimum Allocation of Water Resources by Mathematical Programming. J. Hydrol. 1969, 9, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, N.J.; Howell, D.T.; Musgrave, W.F. Optimal Intraseasonal Irrigation Water Allocation. J. Water Resour. Res. 1971, 7, 770–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clyde, C.G.; King, A.B. Optimal allocation of water resources in Utah. J. Hydraul. Div. 1973, 99, 1777–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.V. Systems analysis and irrigation planning. J. Irrig. Drain. Div. 1973, 99, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, L.; Yeh, W.W.G. Optimization of real-time operation of a multiple-reservoir system. J. Water Resour. Res. 1974, 10, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haimes, Y.Y. Hierarchical modeling of regional total water resources systems. J. Autom. 1975, 11, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haimes, Y.Y.; Dreizin, Y.C. Management of groundwater and surface water via decomposition. J. Water Resour. Res. 1977, 13, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jønch-Clausen, T. Optimal allocation of regional water resources. J. Hydrol. Res. 1979, 10, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romijn, E.; Tamiga, M. Multi-objective optimal allocation of water resources. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. ASCE 1982, 108, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaron, D.; Dinar, A. Optimal allocation of farm irrigation water during peak seasons. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 1982, 64, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louie, P.W.F.; Yeh, W.W.G.; Hsu, N.S. Multi-objective water resources management planning. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1984, 110, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, R.; Liu, P. Optimization model for ground-water planning. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1984, 110, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, E.; Linnerud, K.; Banister, D. Sustainable Development: Our Common Future Revisited. J. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014, 26, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Wu, J. On the Initiation of the Idea of Sustainable Development and Its Meaning. J. Tongren Univ. 2014, 16, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; You, J.J. 30 Years of Water Resources Allocation in China. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 47, 265–271+282. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.L.; Hang, W.X.; Wang, H.J.; Lian, J.J. Study on Sustainable Development Oriented Optimal Allocation to Region Water Resources. J. Syst. Eng. Theory Pract. 2003, 23, 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.L. Research on Regional Sustainable Development and Optimum Allocation of Water Resources—Taking Chaidamu Basin in Arid Region of Northwest China as an Example. J. Nat. Resour. 2001, 16, 341–347. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.Y.; Gan, H. Remark on the Relationship between Water Resources Rational Allocation, Carrying Capacity and Sustainable Development. J. Adv. Water Sci. 2000, 11, 307–313. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.Y.; Wang, H.; Gan, H. Theory and Method of Macroeconomic Water Resources Planning in North China; Yellow River Water Conservancy Press: Zhengzhou, China, 1997. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chang, B.Y.; Xue, S.G.; Zhang, H.Y. Rational Allocation and Optimal Dispatch of Water Resources in the Yellow River Basin; Yellow River Water Conservancy Press: Zhengzhou, China, 1998. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.Y.; Liu, G.Q. Framework for Sustainable Utilization of Water Resources. J. Adv. Water Sci. 1997, 4, 2–8. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.Y.; Mei, Y.D. System Planning for Sustainable Utilization of Water Resources. J. Adv. Water Sci. 1998, 1, 2–7. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Wang, Z.F.; Chang, J.X.; Liang, Z.; Tian, F.W. Research on Joint Optimal Dispatch of Urban Water Supply Sources. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1999, 5, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- You, J.J.; Gan, H.; Wang, H. Research status and Prospect of Water Resource Allocation Model. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2005, 16, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, K.; Li, J.; Jia, P. Development and Application of Complex Reservoir Operation Program Based on MIKE BASIN Water Resource Model. J. Water Sci. Eng. Technol. 2008, 88, 19–22+39. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Dong, J.; Chen, X.Q.; Mo, Y.G.; Hong, Y.M.; Miao, J.Y. Research on Water Resources Allocation in Laizhou City Based on Mike Basin Model. J. Shandong Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 52, 984–989. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.N.; Wang, X.X.; Hou, L. Application of MIKE BASIN Model in Songhua River Basin. J. Water Resour. Hydropower Northeast China 2011, 29, 4–5+71. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, K. Application of MIKE BASIN for Water Resources Study of Daling River Basin in WRDMAP. J. Water Sci. Eng. Technol. 2008, 147(05), 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.X.; Li, Y.H.; He, D.M.; Cui, Y.L. Watershed Water Resources Three-allocation Based on MIKE BASIN. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2007, 18, 5–10+28. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Y. Research on Water Resources Allocation in Laizhou City Based on Mike Basin Model. Master’s Thesis, Shandong Agricultural University, Tai’an, Chian, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.C. A Water Resource Management Model for Shiyang Basin Based on MIKE BASIN; D. Tsinghua University: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Raskin, P.; Hansen, E.; Zhu, Z.; Stavisky, D. Simulation of Water Supply and Demand in the Aral Sea Region. J. Water Int. 1992, 17, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, D.; Sieber, J.; Purkey, D.; Huber-Lee, A. WEAP21—A Demand-, Priority-, and Preference-driven Water Planning Model: Part 1: Model Characteristics. J. Water Int. 2005, 30, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.H.; Jiang, Z.Y. Study on Water Resource Allocation Scheme in Tarim River Trunk Stream Based on WEAP Model. J. Pearl River 2019, 40, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.Z.; Xue, L.Q.; Zhen, G.; Lian, J.; Li, J.Y. Optimized allocation of Water Resources in Yarkand River Basin Based on WEAP Model. J. Hohai Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2013, 41, 493–499. [Google Scholar]
- Hatamkhani, A.; Moridi, A.; Asadzadeh, M. Water Allocation Using Ecological and Agricultural Value of Water. J. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 33, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.L.; Yang, R.X.; Hou, B.D.; Lu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Xao, W.H. Joint Allocation of Multiple Water Sources in Xiongan New Area Under Complex and Uncertain Environment. J. Water Resour. Hydropower Eng. 2022, 53, 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Hatamkhani, A.; KhazaiePoul, A.; Moridi, A. Sustainable water resource planning at the basin scale with simultaneous goals of agricultural development and wetland conservation. J. AQUA Water Infrastruct. Ecosyst. Soc. 2022, 71, 768–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.N. Water Resource System Resilience Assessment of Jinghuiqu Irrigation District Based on WEAP-MODFLOW. Master’s Thesis, Northwest A & F University, Yulin, Chian, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. Optimized Allocation of Water Resources in Ningxia Yellow River Basin Based on WEAP; D. Southwest University: Chongqing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.B. Urban Water Supply and Demand Balance Analysis Based on SWAT and WEAP Models. Master’s Thesis, Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sang, X.F.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Z.H. Water resources comprehensive simulation and allocation model WAS (Ⅰ): Model principle and construction. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2018, 49, 1451–1459. [Google Scholar]
- Sang, X.F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhai, Z.L.; Chang, H.Y. Water resources comprehensive simulation and allocation model WAS (Ⅱ): Application. J. Water Resour. 2019, 50, 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.Y. Development and Improvement of WAS Model and Application of Water Resources Allocation in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Master’s Thesis, China Institute of Water Resources & Hydropower Research, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.Q.; Zhou, Z.H.; Wang, H.; Jia, Y.W. Studies on Ecological Water Supplement in Pingshan River Basin Based on Generalized Water Allocation and Simulation Model. J. China Water Resour. 2020, 22, 28–30+33. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.B. Research on Water Resources Allocation in the Agro-Pastoral Ecotone of the Northern Shaanxi Province Based on WAS Model. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Technology, Xi’an, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.Y. Study on the Water Resources Regulation on the Suitable Scale Land Agricultural Utilization in Agro-Pastoral Ecotone of Northern Shaanxi. Doctoral’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Technology, Xi’an, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.Q.; Li, L. Simulation Analysis of Water Resources in Beijing Based on the Integrated Comprehensive Water Simulation and Allocation Model. J. Adv. Sci. Technol. Water Resour. 2021, 41, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Du, L.J.; Chen, G.F.; Liu, C.S.; Wang, X.N.; Liu, J.L.; Wang, H.L. GWAS Model Based on Allocation of Water Resources in Irrigated District. J. Water Resour. Hydropower Eng. 2020, 51, 26–35. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.X.Q. Optimal Allocation of Regional Water Resources From the Perspective of Water-Energy-Food Nexus: A Case Study of Yulin. Master’s Thesis, Northwest A & F University, Yulin, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Sang, X.F.; Li, H.H.; He, F.; Zhai, J.Q. Research on the Coordinated Regulation of Resources-Food-Energy-Ecology in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Ⅰ: Methods and Model. J. Water Resour. 2022, 53, 655–665. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Chang, H.Y.; Sang, X.F.; He, G.H.; Wang, Q.M.; Jiang, S. Research on the Coordinated Regulation of Resources-Food-Energy-Ecology in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region II: Application. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2022, 53, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar]
- Sang, X.F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhai, Z.L. The GWAS User Manual and Example Tutorial for General Configuration and Simulation Software of Water Resources; Publishing House of Electronics Industry: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, H.S. Handan Statistical Yearbook (2019); China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2020; pp. 33–316. [Google Scholar]
- Hebei Handan Hydrology and Water Resources Survey Bureau. Assessment of Water Resources in Handan (Third); Hebei Handan Hydrology and Water Resources Survey Bureau: Handan, China, 2019; pp. 71–165. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hebei University of Engineering. Research Report on Development and Utilization of Reclaimed Water in Handan; Hebei University of Engineering: Handan, China, 2018; pp. 213–219. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Handan Water Resources and Hydropower Survey and Design Institute. The Planning of Handan in the South to North Water Transfer Project (Middle Line) of Hebei Province; Handan Water Resources and Hydropower Survey and Design Institute: Handan, China, 2002; pp. 102–110. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Water Conservancy Bureau of Handan. Allocation and Utilization of Surface Water in Handan; Water Conservancy Bureau of Handan: Handan, China, 2020; pp. 1–22. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.P.; Wang, X.H.; Li, C.Y.; Yan, X.T.; Liu, H.L. Handan Water Resources Bulletin (2019); Handan Water Resources Management Center: Handan, China, 2020; pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Hebei University of Engineering. Research on Optimal Scheduling and Allocation Technology of Water Resources in Handan; Hebei University of Engineering: Handan, China, 2017; pp. 239–265. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Liu, H.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, S. Research on Optimal Allocation of Water Resources in Handan City Based on the Refined Water Resource Allocation Model. J. Water 2022, 15, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, M.Q.; Xia, F.; Fan, Y. A Fuzzy-Interval Dynamic Optimization Model for Regional Water Resources Allocation under Uncertainty. J. Sustain. 2022, 14, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Sha, J.; Liu, B.; Tian, W.; Lu, J. An ameliorative whale optimization algorithm for multi-objective optimal allocation of water resources in Handan, China. J. Water 2018, 10, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Subregion | Domestic | Ecology | Primary Industry | Secondary Industry | Tertiary Industry | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shexian | 16.75 | 9.83 | 25.00 | 10.21 | 11.49 | 73.28 |
| Wu’an | 32.14 | 17.02 | 154.29 | 61.39 | 30.22 | 295.06 |
| Cixian | 18.32 | 9.70 | 60.07 | 3.64 | 6.32 | 98.05 |
| Fengfeng | 17.41 | 11.11 | 20.29 | 16.38 | 9.35 | 74.54 |
| Hanshan | 29.45 | 19.66 | 90.33 | 10.54 | 23.20 | 173.18 |
| Fuxing | 16.07 | 11.24 | 21.62 | 17.37 | 13.37 | 79.67 |
| Congtai | 33.49 | 25.31 | 33.33 | 19.76 | 35.32 | 147.21 |
| Yongnian | 31.80 | 16.84 | 188.05 | 14.18 | 12.82 | 263.69 |
| Linzhang | 21.34 | 10.64 | 173.66 | 6.78 | 9.47 | 221.89 |
| Cheng’an | 14.63 | 7.74 | 104.84 | 10.02 | 8.37 | 145.60 |
| Weixain | 28.91 | 15.31 | 228.10 | 10.91 | 11.13 | 294.36 |
| Feixiang | 13.73 | 7.27 | 136.86 | 5.16 | 11.41 | 174.43 |
| Guangping | 10.26 | 5.43 | 69.65 | 3.88 | 6.60 | 95.82 |
| Quzhou | 15.92 | 7.73 | 103.79 | 6.33 | 6.89 | 140.66 |
| Daming | 29.56 | 15.65 | 271.03 | 3.70 | 9.94 | 329.88 |
| Guantao | 11.97 | 6.34 | 92.77 | 2.48 | 8.05 | 121.61 |
| Jize | 10.21 | 4.76 | 83.55 | 4.62 | 5.85 | 108.99 |
| Qiuxian | 8.88 | 4.70 | 82.59 | 4.08 | 5.72 | 105.97 |
| Total | 360.84 | 206.28 | 1939.82 | 211.43 | 225.52 | 2943.89 |
| Subunit | Ground Water | Recycled Water | South-to-North Water Diversion | Yellow River Transferred Water | Weihe River Transferred Water | Yuefeng Channel | Reservoir Water |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shexian | 70.46 | 17.81 | √ | ||||
| Wu’an | 122.51 | 45.02 | √ | ||||
| Cixian | 60.64 | 13.23 | √ | √ | |||
| Fengfeng | 91.57 | 18.61 | √ | √ | |||
| Hanshan | 53.09 | 33.77 | √ | ||||
| Fuxing | 16.12 | 21.06 | √ | ||||
| Congtai | 36.79 | 45.15 | √ | ||||
| Yongnian | 75.09 | 25.51 | √ | ||||
| Linzhang | 79.53 | 16.64 | √ | ||||
| Cheng’an | 40.26 | 13.93 | √ | √ | |||
| Weixain | 63.58 | 22.51 | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| Feixiang | 16.86 | 14.65 | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Guangping | 13.07 | 9.71 | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Quzhou | 5.35 | 12.33 | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Daming | 93.67 | 20.81 | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| Guantao | 43.09 | 11.20 | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| Jize | 29.62 | 8.76 | √ | √ | |||
| Qiuxian | 17.10 | 8.53 | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Total | 928.40 | 359.23 | 352.02 | 179.00 | 87.00 | 226.38 | 514.50 |
| Reservoir Name | Domestic | Ecology | Primary Industry | Secondary Industry | Tertiary Industry | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maolingdi | √ | 1 | √ | 2 | √ | 5 | √ | 3 | √ | 4 |
| Qingta | √ | 1 | √ | 2 | √ | 5 | √ | 3 | √ | 4 |
| Chegu | √ | 1 | √ | 2 | √ | 5 | √ | 3 | √ | 4 |
| Koushang | 5 | √ | 1 | √ | 4 | √ | 2 | √ | 3 | |
| Siliyan | √ | 1 | √ | 2 | √ | 5 | √ | 3 | √ | 4 |
| Damingyuan | 5 | √ | 1 | √ | 3 | √ | 2 | 4 | ||
| Yuecheng | 5 | √ | 1 | √ | 4 | √ | 2 | √ | 3 | |
| Dongwushi | 5 | √ | 1 | √ | 4 | √ | 2 | √ | 3 | |
| Wu’an | 5 | 4 | √ | 2 | √ | 1 | 3 | |||
| Shexian | 5 | 4 | √ | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| Yuefeng Channel | 5 | √ | 1 | √ | 3 | √ | 2 | 4 | ||
| South-to-North Water Diversion | √ | 1 | 4 | 5 | √ | 2 | √ | 3 | ||
| Weihe River Transferred | 5 | 4 | √ | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| Yellow River Transferred | 5 | √ | 1 | √ | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| Subunit | Domestic | Ecology | Primary Industry | Secondary Industry | Tertiary Industry | Total | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demand | Allocated | Shortage Rate | Demand | Allocated | Shortage Rate | Demand | Allocated | Shortage Rate | Demand | Allocated | Shortage Rate | Demand | Allocated | Shortage Rate | Demand | Allocated | Shortage Rate | |
| Shexian | 16.75 | 16.75 | 0 | 9.83 | 9.83 | 0 | 25.00 | 25.00 | 0 | 10.21 | 10.21 | 0 | 11.49 | 11.49 | 0 | 73.28 | 73.28 | 0 |
| Wu’an | 32.14 | 32.14 | 0 | 17.02 | 17.02 | 0 | 154.29 | 91.50 | 40.70 | 61.39 | 61.26 | 0.34 | 30.22 | 28.22 | 6.62 | 295.06 | 230.14 | 22.00 |
| Cixian | 18.32 | 18.32 | 0 | 9.70 | 9.70 | 0 | 60.07 | 60.07 | 0 | 3.64 | 3.64 | 0 | 6.32 | 6.32 | 0 | 98.05 | 98.05 | 0 |
| Fengfeng | 17.41 | 17.41 | 0 | 11.11 | 11.11 | 0 | 20.29 | 20.29 | 0 | 16.38 | 16.38 | 0 | 9.35 | 9.35 | 0 | 74.54 | 74.54 | 0 |
| Hanshan | 29.45 | 29.45 | 0 | 19.66 | 19.66 | 0 | 90.33 | 85.63 | 5.20 | 10.54 | 10.54 | 0 | 23.20 | 23.20 | 0 | 173.18 | 168.48 | 2.71 |
| Fuxing | 16.07 | 16.07 | 0 | 11.24 | 11.24 | 0 | 21.62 | 18.34 | 15.17 | 17.37 | 17.37 | 0 | 13.37 | 13.37 | 0 | 79.67 | 76.39 | 4.12 |
| Congtai | 33.49 | 33.49 | 0 | 25.31 | 25.31 | 0 | 33.33 | 33.33 | 0 | 19.76 | 19.76 | 0 | 35.32 | 35.32 | 0 | 147.21 | 147.21 | 0 |
| Yongnian | 31.80 | 31.80 | 0 | 16.84 | 16.84 | 0 | 188.05 | 147.48 | 21.57 | 14.18 | 14.18 | 0 | 12.82 | 12.82 | 0 | 263.69 | 223.12 | 15.39 |
| Linzhang | 21.34 | 21.34 | 0 | 10.64 | 10.64 | 0 | 173.66 | 97.04 | 44.12 | 6.78 | 6.78 | 0 | 9.47 | 9.47 | 0 | 221.89 | 145.27 | 34.53 |
| Cheng’an | 14.63 | 14.63 | 0 | 7.74 | 7.74 | 0 | 104.84 | 68.36 | 34.8 | 10.02 | 10.02 | 0 | 8.37 | 8.14 | 2.75 | 145.60 | 108.89 | 25.21 |
| Weixain | 28.91 | 28.91 | 0 | 15.31 | 15.31 | 0 | 228.1 | 164.97 | 27.68 | 10.91 | 10.91 | 0 | 11.13 | 11.13 | 0 | 294.36 | 231.23 | 21.45 |
| Feixiang | 13.73 | 13.73 | 0 | 7.27 | 7.27 | 0 | 136.86 | 87.10 | 36.36 | 5.16 | 5.16 | 0 | 11.41 | 11.02 | 3.42 | 174.43 | 124.28 | 28.75 |
| Guangping | 10.26 | 10.26 | 0 | 5.43 | 5.43 | 0 | 69.65 | 43.52 | 37.52 | 3.88 | 3.88 | 0 | 6.6 | 6.34 | 3.94 | 95.82 | 69.43 | 27.54 |
| Quzhou | 15.92 | 15.92 | 0 | 7.73 | 7.73 | 0 | 103.79 | 64.09 | 38.25 | 6.33 | 6.33 | 0 | 6.89 | 6.61 | 4.06 | 140.66 | 100.68 | 28.42 |
| Daming | 29.56 | 29.56 | 0 | 15.65 | 15.65 | 0 | 271.03 | 223.40 | 17.57 | 3.70 | 3.70 | 0 | 9.94 | 9.56 | 3.82 | 329.88 | 281.87 | 14.55 |
| Guantao | 11.97 | 11.97 | 0 | 6.34 | 6.34 | 0 | 92.77 | 69.84 | 24.72 | 2.48 | 2.48 | 0 | 8.05 | 7.74 | 3.85 | 121.61 | 98.37 | 19.11 |
| Jize | 10.21 | 10.21 | 0 | 4.76 | 4.76 | 0 | 83.55 | 61.73 | 26.12 | 4.62 | 4.62 | 0 | 5.85 | 5.85 | 0 | 108.99 | 87.17 | 20.02 |
| Qiuxian | 8.88 | 8.88 | 0 | 4.70 | 4.70 | 0 | 82.59 | 54.73 | 33.73 | 4.08 | 4.08 | 0 | 5.72 | 5.50 | 3.85 | 105.97 | 77.89 | 26.50 |
| Total | 360.84 | 360.84 | 0 | 206.28 | 206.28 | 0 | 1939.85 | 1416.42 | 26.98 | 211.43 | 211.30 | 0.10 | 225.52 | 221.45 | 1.80 | 2943.89 | 2416.29 | 17.92 |
| Subunit | Ground Water | Recycled Water | Reservoir Water | South-to-North Water Diversion | Yellow River Transferred Water | Weihe River Transferred Water | Yuefeng Channel | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shexian | 49.23 | 11.78 | 12.27 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 73.28 |
| Wu’an | 122.46 | 44.91 | 62.77 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 230.14 |
| Cixian | 58.37 | 10.65 | 2.01 | 12.59 | 0 | 0 | 14.43 | 98.05 |
| Fengfeng | 53.65 | 15.35 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5.54 | 74.54 |
| Hanshan | 53.07 | 33.66 | 41.83 | 39.92 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 168.48 |
| Fuxing | 16.12 | 21.03 | 17.00 | 22.24 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 76.39 |
| Congtai | 35.34 | 40.37 | 32.93 | 38.57 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 147.21 |
| Yongnian | 75.08 | 24.52 | 87.85 | 35.67 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 223.12 |
| Linzhang | 79.53 | 16.64 | 16.52 | 32.58 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 145.27 |
| Cheng’an | 40.25 | 13.93 | 36.75 | 17.96 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 108.89 |
| Weixain | 63.57 | 22.51 | 25.81 | 40.47 | 35.88 | 42.99 | 0 | 231.23 |
| Feixiang | 16.86 | 14.65 | 40.93 | 16.28 | 35.56 | 0 | 0 | 124.28 |
| Guangping | 13.06 | 9.71 | 17.23 | 11.65 | 17.78 | 0 | 0 | 69.43 |
| Quzhou | 5.33 | 12.32 | 36.41 | 17.57 | 29.05 | 0 | 0 | 100.68 |
| Daming | 93.67 | 20.67 | 71.45 | 31.31 | 30.73 | 34.04 | 0 | 281.87 |
| Guantao | 43.09 | 10.34 | 12.77 | 13.24 | 9.05 | 9.88 | 0 | 98.37 |
| Jize | 29.62 | 8.18 | 37.39 | 11.98 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 87.17 |
| Qiuxian | 17.10 | 8.52 | 21.53 | 9.97 | 20.77 | 0 | 0 | 77.89 |
| Total | 865.40 | 339.74 | 573.45 | 352.00 | 178.82 | 86.91 | 19.97 | 2416.29 |
| Reservoirs Name | Koushang | Qingta | Maolingdi | Shexian | Yuefeng Channel | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Siliyan | 12.00 | 12.00 | ||||
| Damingyuan | 0.12 | 0.12 | ||||
| Yuecheng | 42.96 | 1.49 | 44.45 | |||
| Dongwushi | 154.37 | 154.37 | ||||
| Total | 12.00 | 0.12 | 42.96 | 1.49 | 154.37 | 210.94 |
| Subunit | South-to-North Water Diversion | Yellow River Transferred Water | Weihe River Transferred Water | Yuefeng Channel | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GWAS | Tradition | GWAS | Tradition | GWAS | Tradition | GWAS | Tradition | |
| Shexian | ||||||||
| Wu’an | ||||||||
| Cixian | 12.59 | 30.74 | 14.43 | 15.00 | ||||
| Fengfeng | 5.54 | 5.00 | ||||||
| Hanshan | 39.92 | 77.49 | ||||||
| Fuxing | 22.24 | 44.56 | ||||||
| Congtai | 38.57 | 71.68 | ||||||
| Yongnian | 35.67 | 36.00 | ||||||
| Linzhang | 32.58 | 7.38 | ||||||
| Cheng’an | 17.96 | 6.74 | ||||||
| Weixain | 40.47 | 21.00 | 35.88 | 36.24 | 42.99 | 40.00 | ||
| Feixiang | 16.28 | 10.00 | 35.56 | 19.78 | 2.00 | |||
| Guangping | 11.65 | 7.00 | 17.78 | 22.53 | ||||
| Quzhou | 17.57 | 5.53 | 29.05 | 24.02 | ||||
| Daming | 31.31 | 7.90 | 30.73 | 24.46 | 34.04 | 25.00 | ||
| Guantao | 13.24 | 7.00 | 9.05 | 24.00 | 9.88 | 20.00 | ||
| Jize | 11.98 | 6.00 | ||||||
| Qiuxian | 9.97 | 13.00 | 20.77 | 27.93 | ||||
| Total | 352.00 | 352.02 | 178.82 | 178.96 | 86.91 | 87.00 | 19.97 | 20.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Y.; Sha, J.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J. Optimal Allocation of Water Resources Based on GWAS Model in Handan, China. Water 2023, 15, 1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061090
Luo Y, Sha J, Liu B, Zhang Y, Yang J. Optimal Allocation of Water Resources Based on GWAS Model in Handan, China. Water. 2023; 15(6):1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061090
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Yun, Jinxia Sha, Bin Liu, Yinqin Zhang, and Jie Yang. 2023. "Optimal Allocation of Water Resources Based on GWAS Model in Handan, China" Water 15, no. 6: 1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061090
APA StyleLuo, Y., Sha, J., Liu, B., Zhang, Y., & Yang, J. (2023). Optimal Allocation of Water Resources Based on GWAS Model in Handan, China. Water, 15(6), 1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061090







