Wave Effects on the Initial Dilution of Untreated Wastewater Discharge for Santa Marta’s Submarine Outfall (Colombia)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Effects of External Waves
2. Materials and Methods
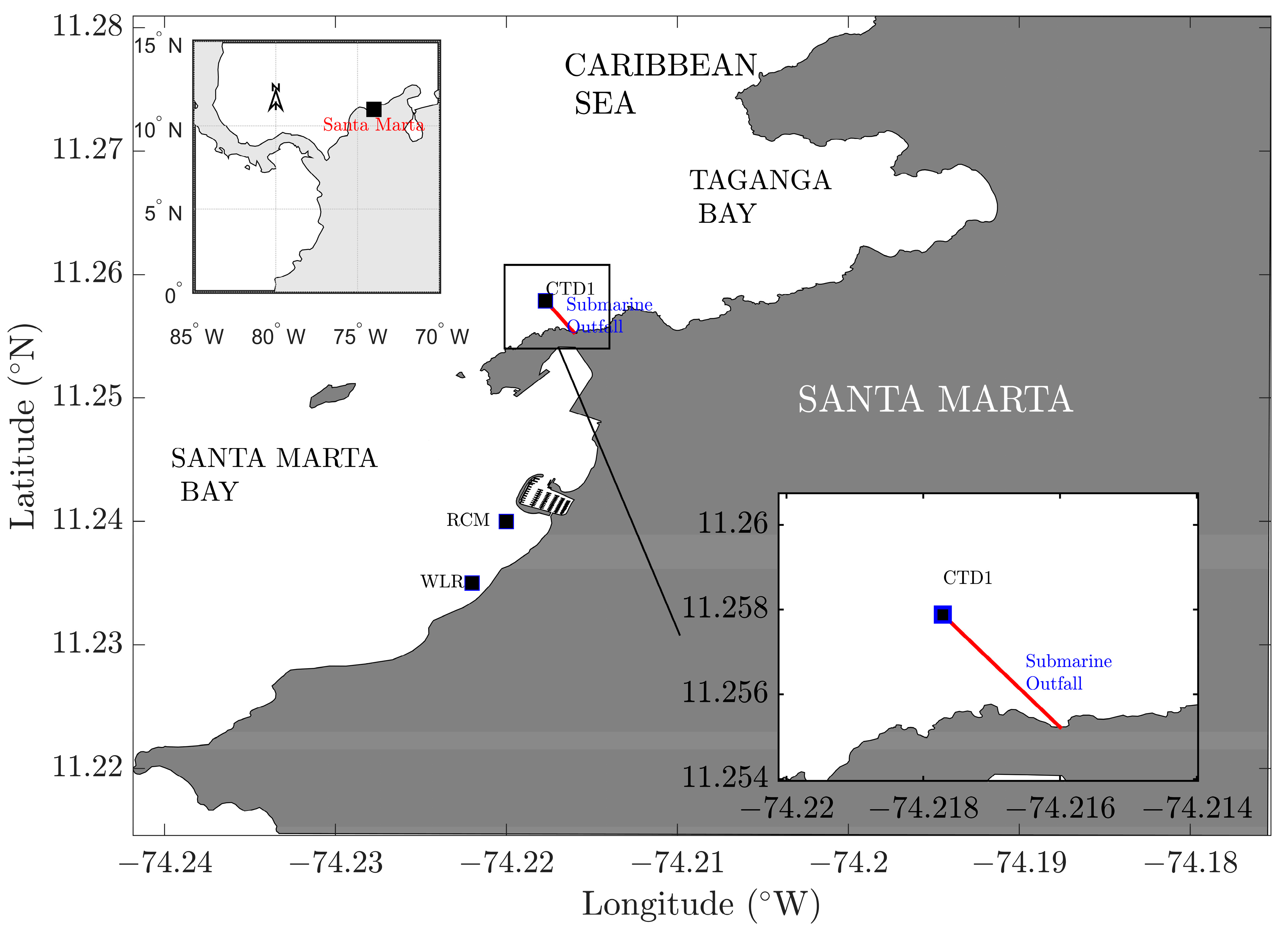
2.1. Study Area
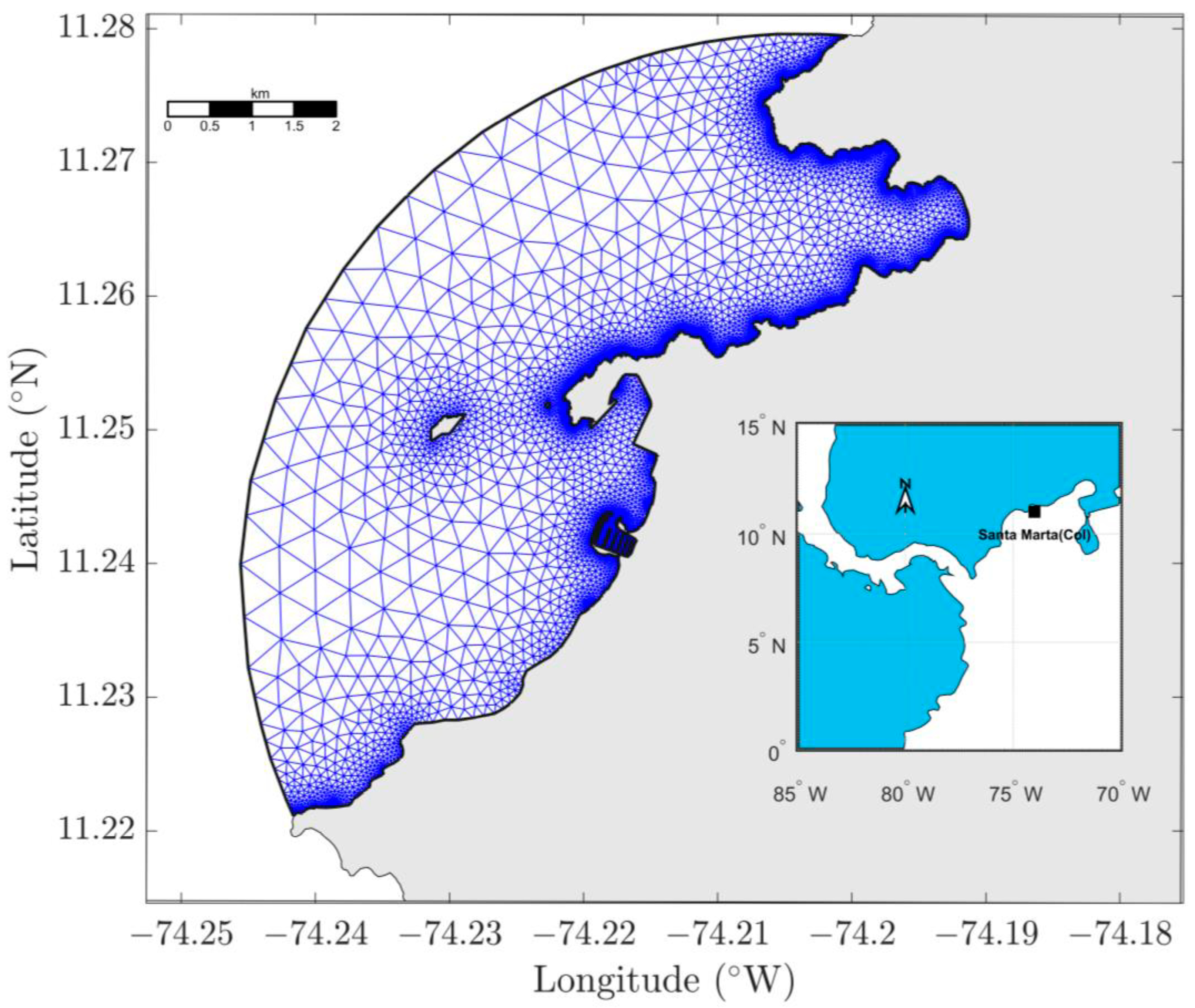
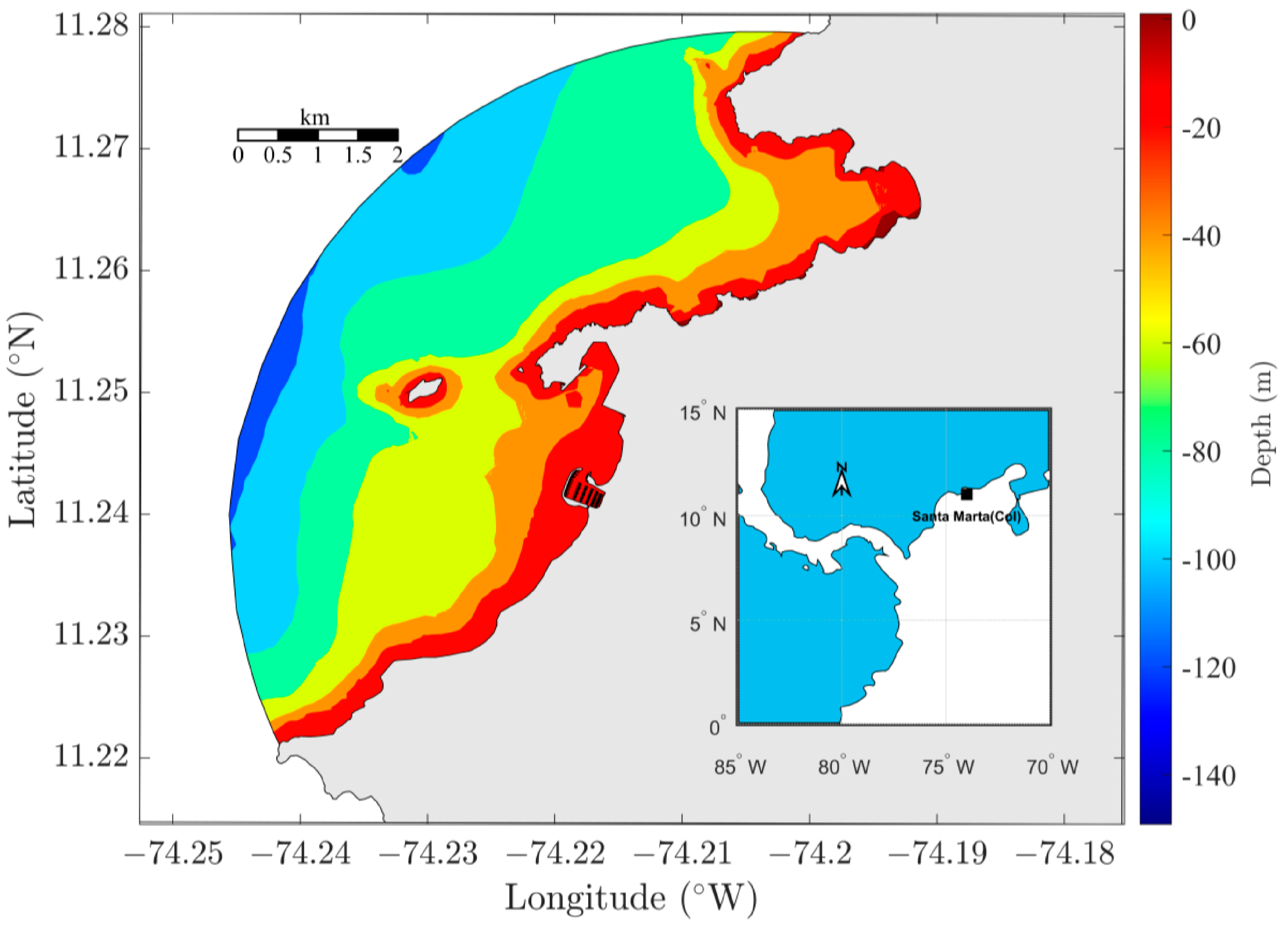
2.2. Hydrodynamic Model
3. Results
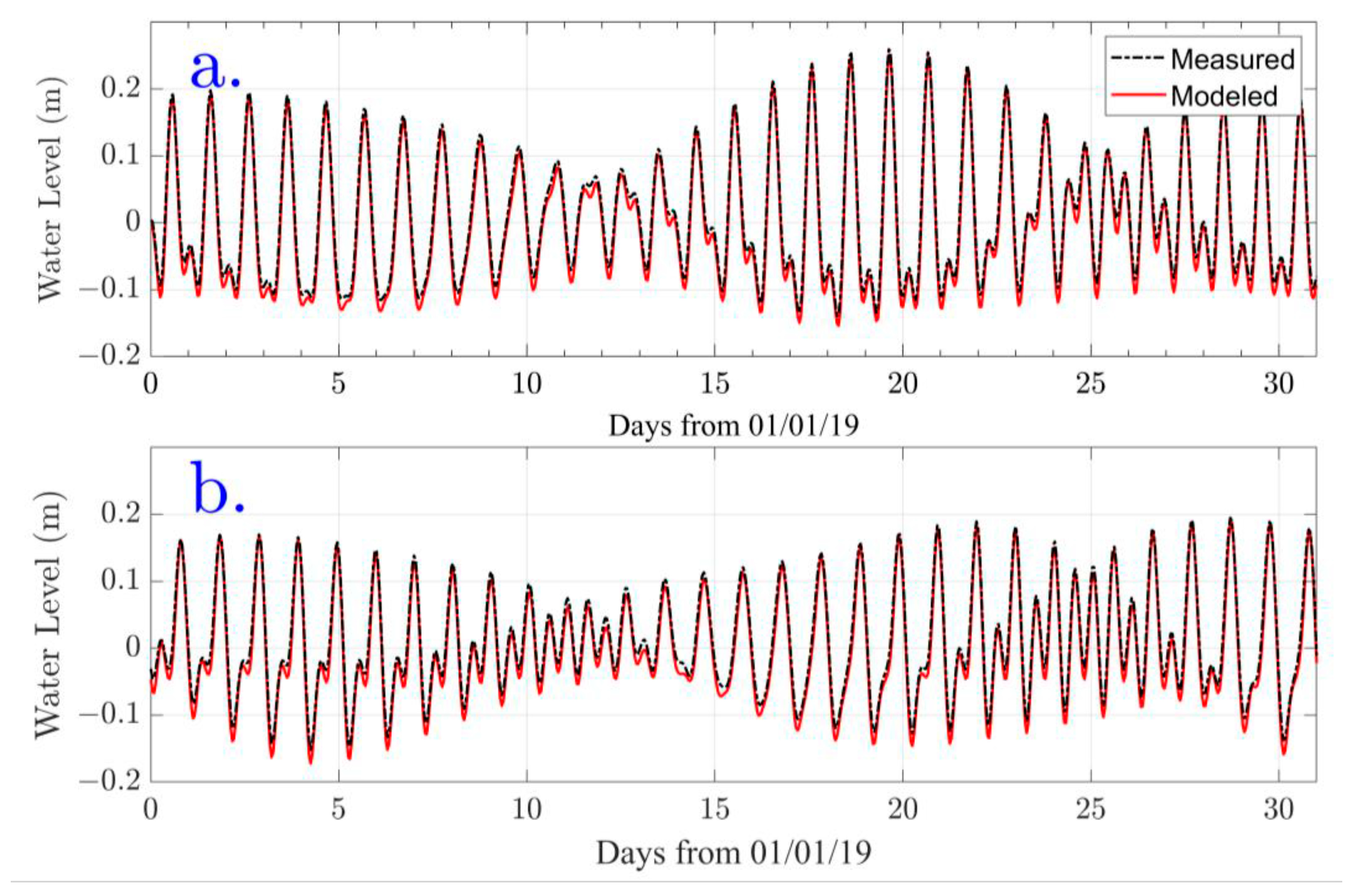
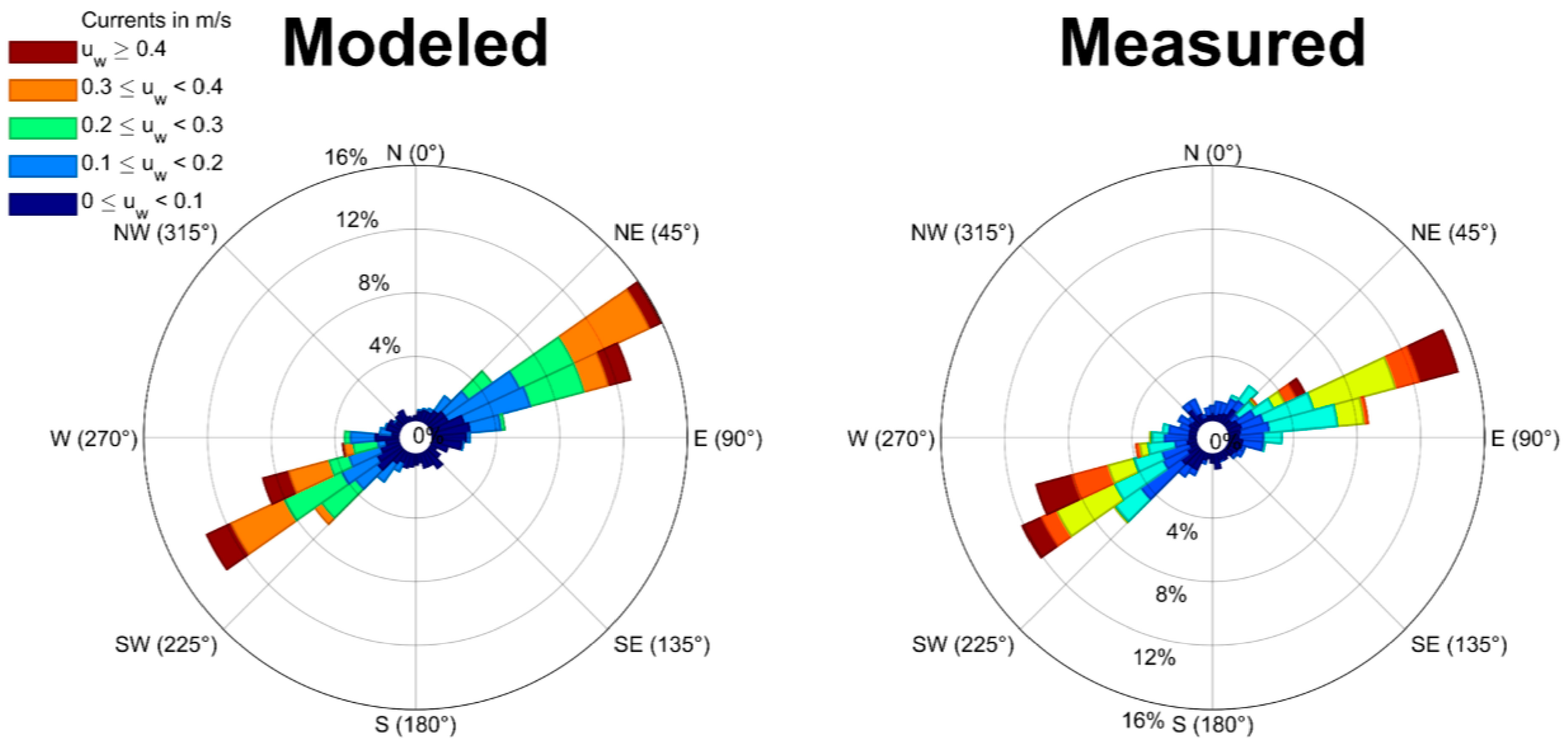
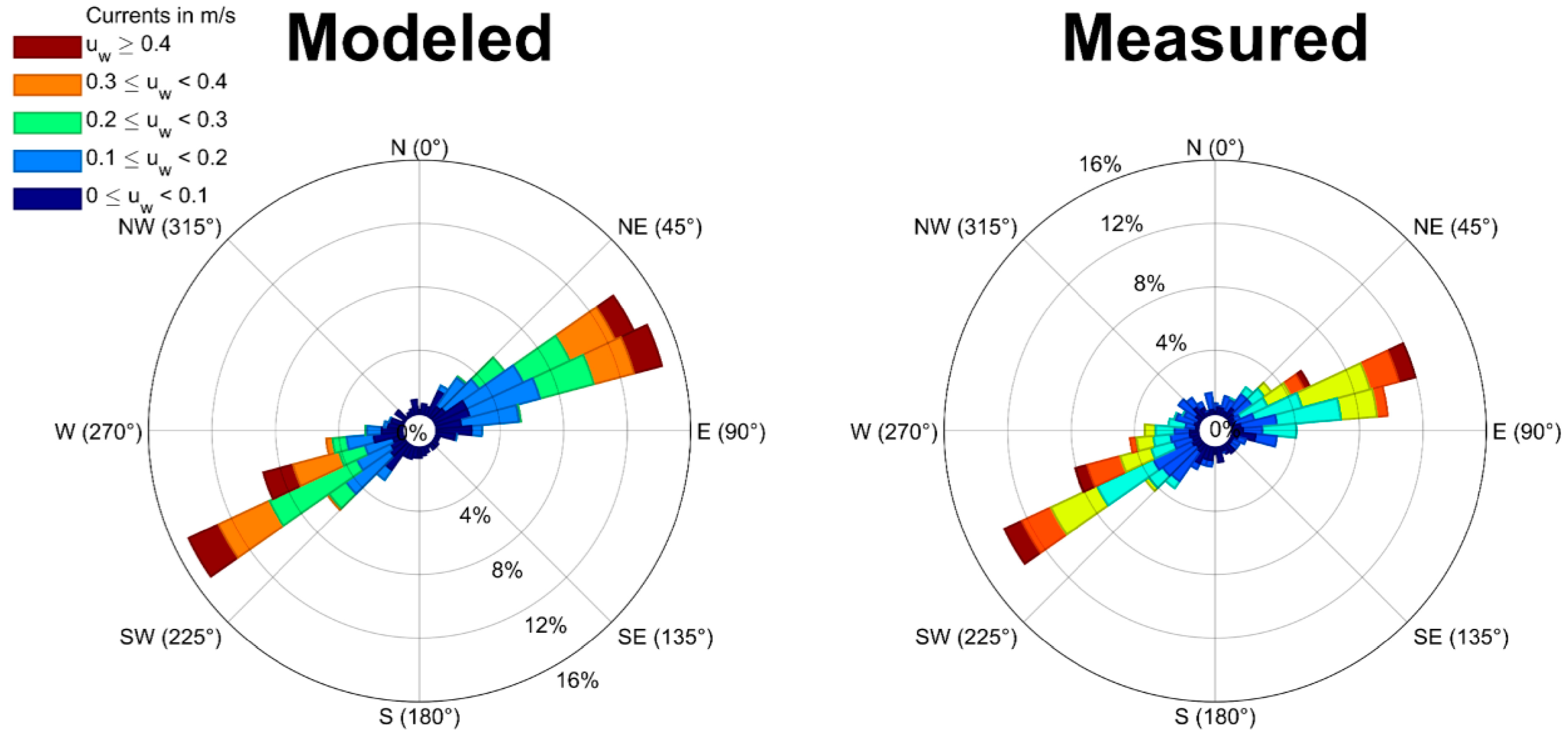
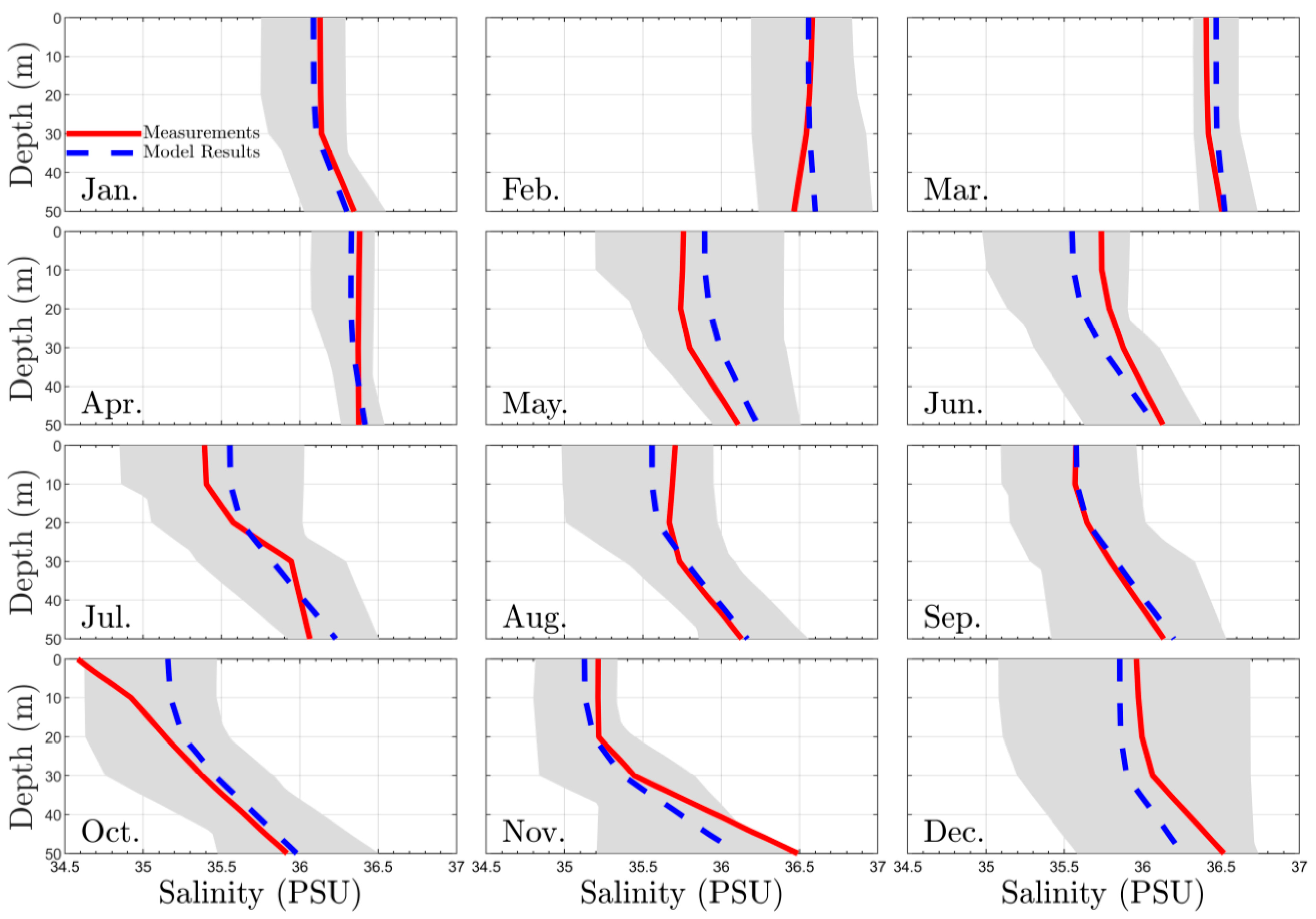
3.1. Calibration and Validation RMA10 Hydrodinamic Model
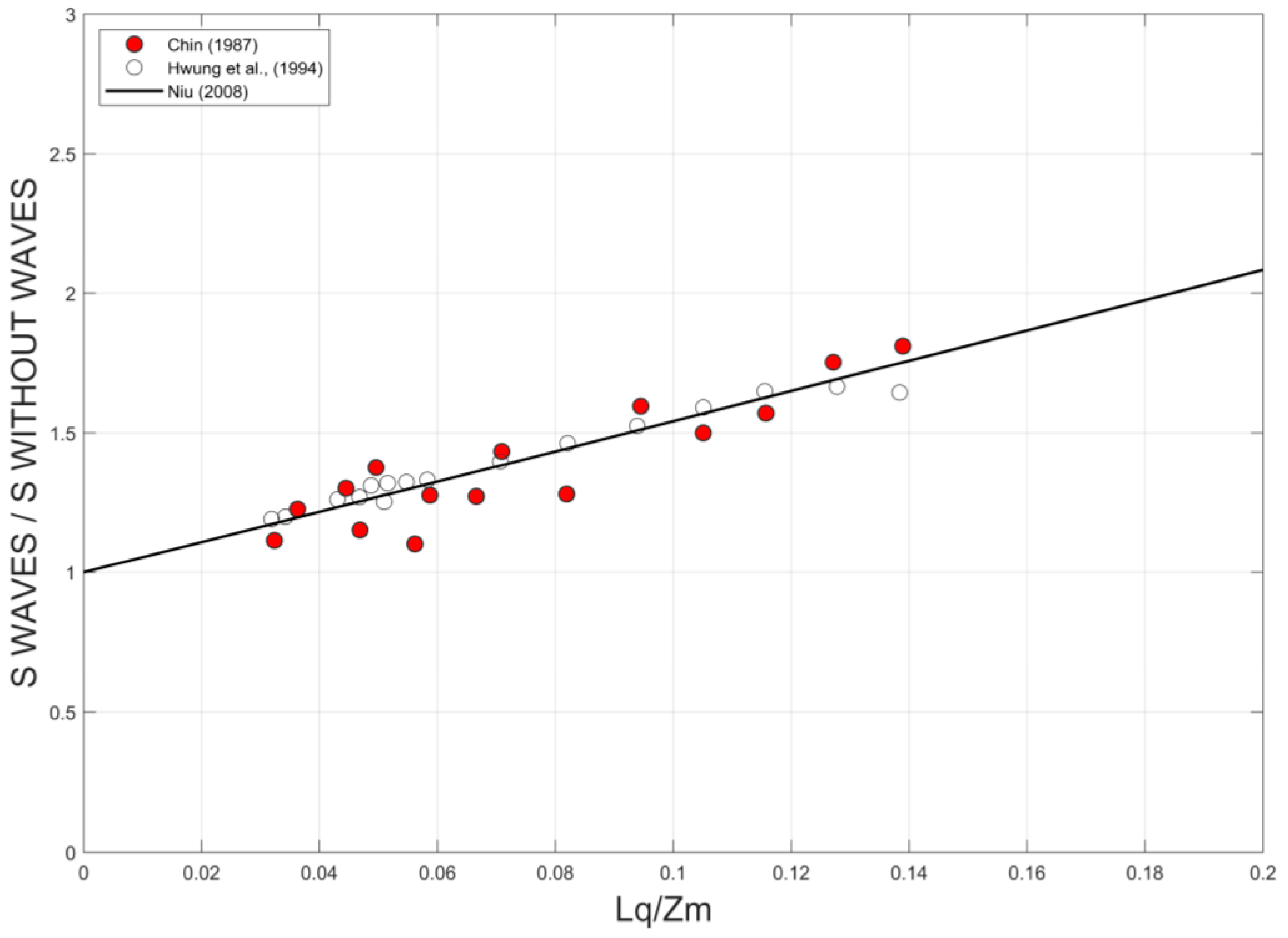
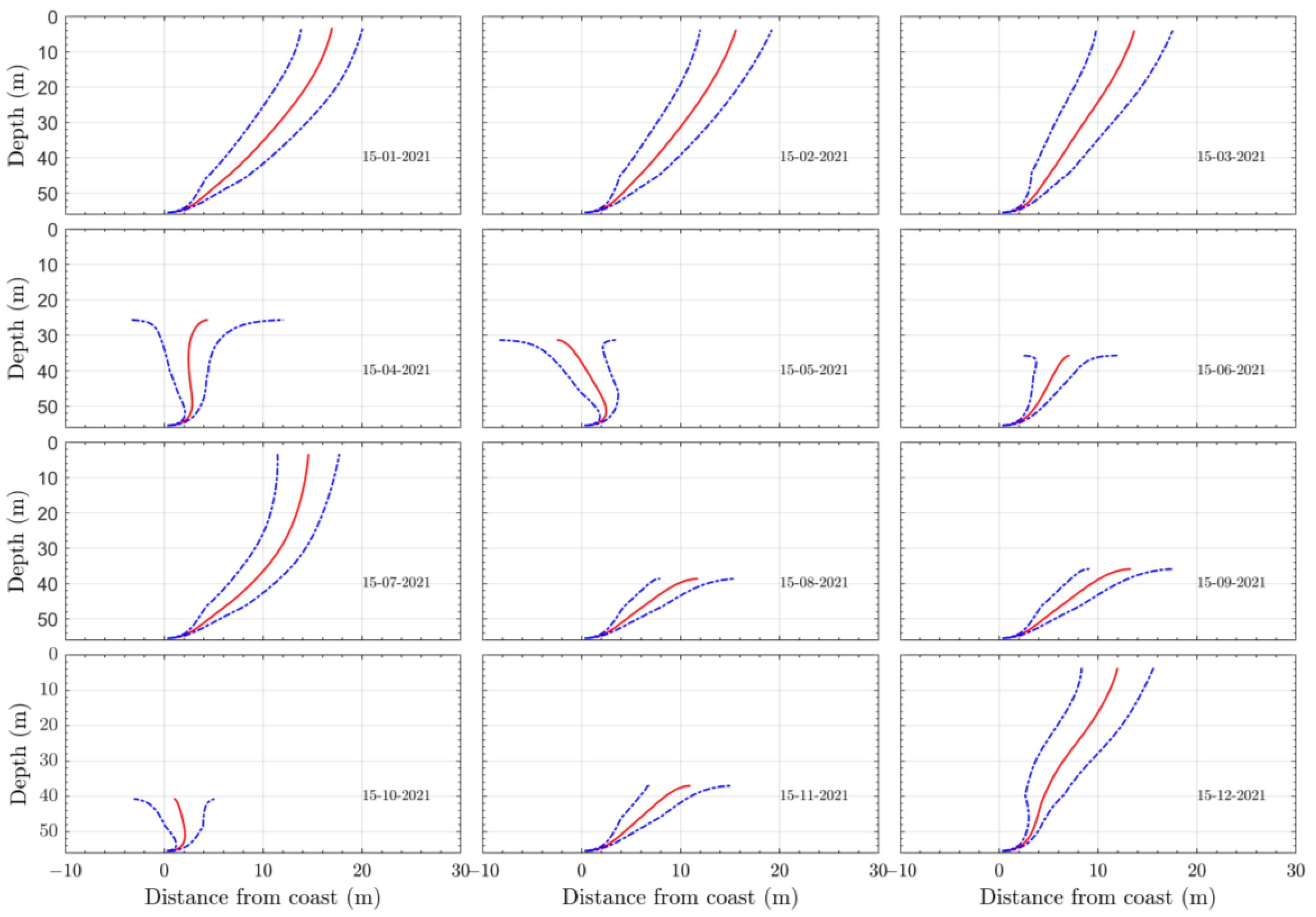
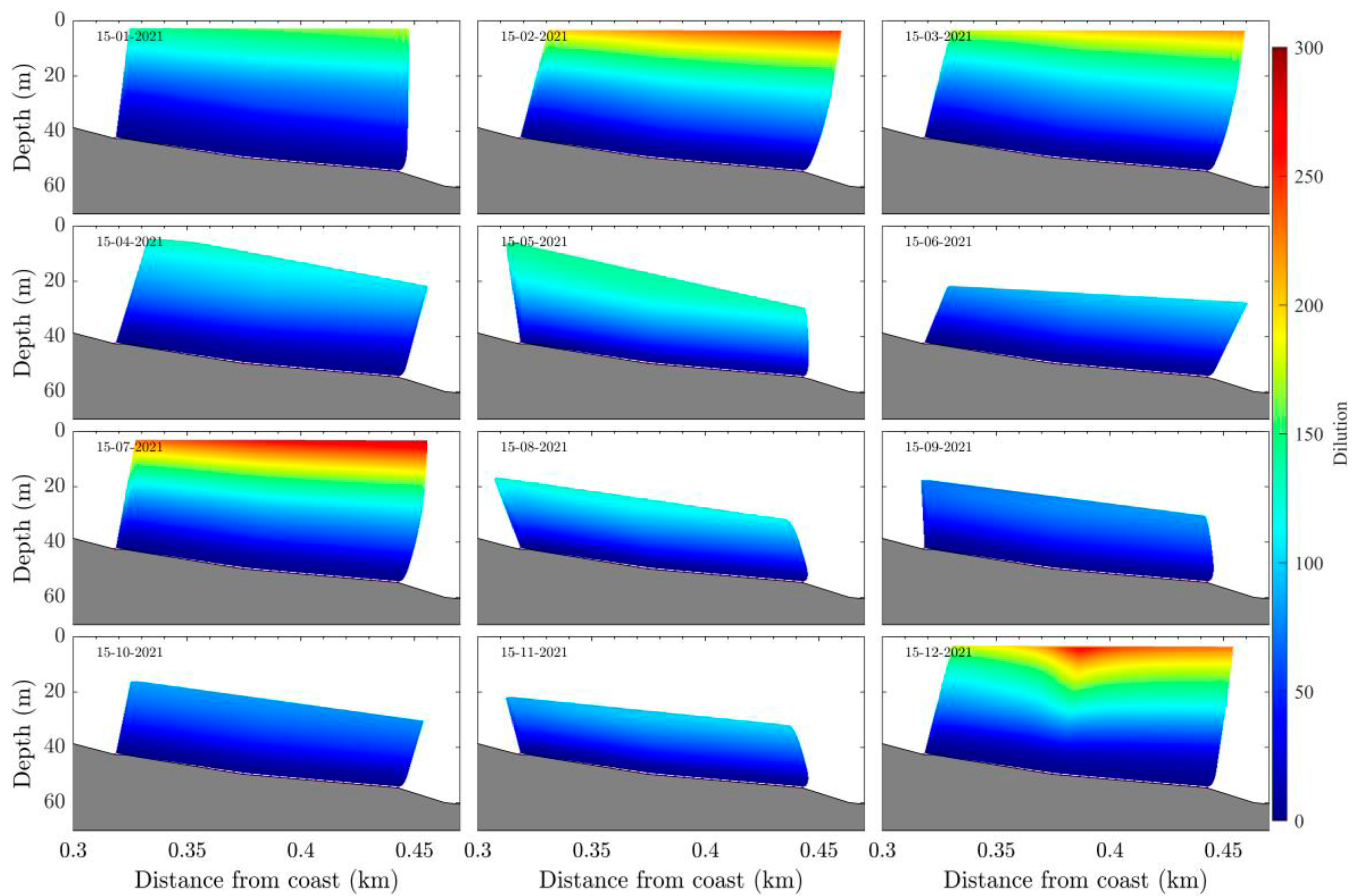
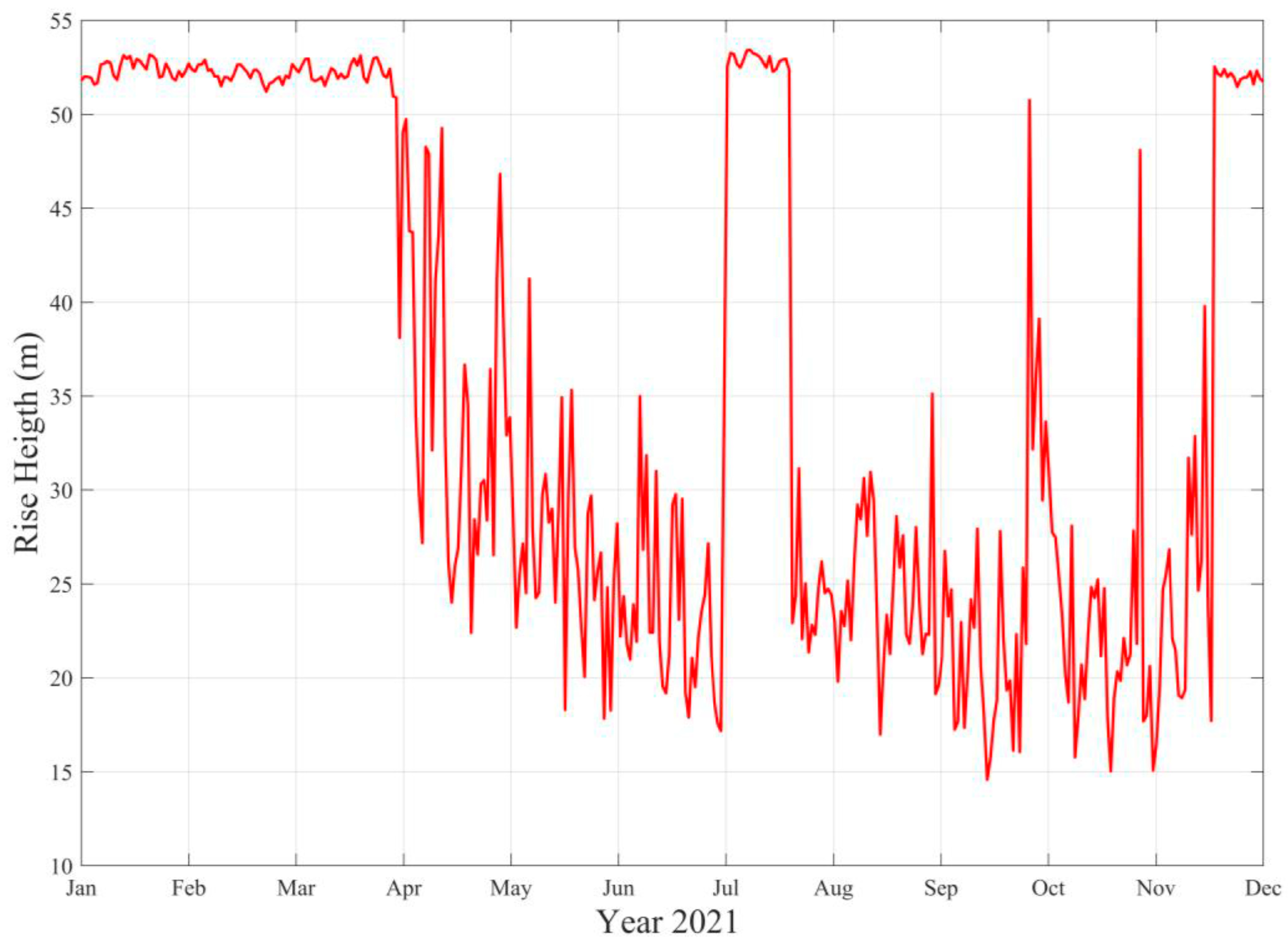
3.2. Wave Effects on the Initial Dilution of Santa Marta’s Submarine Outfall
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Birocchi, P.; Dottori, M.; de Godoi, R.C.; Bairão, L.J. Study of three domestic sewage submarine outfall plumes through the use of numerical modeling in the São Sebastião channel, São Paulo state, Brazil. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 44, 101647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamparelli, C.C.; Moura, D.O.; Pinto, K.C.; Camolez, A.C. Monitoring sea outfall discharges in São Paulo Coast—Brazil. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Outfall Systems, IAHR–IWA Joint Committee on Marine Outfall Systems, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 10–13 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lapointe, B.; Thacker, K.; Hanson, C.; Getten, L. Sewage pollution in Negril, Jamaica: Effects on nutrition and ecology of coral reef macroalgae. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2011, 29, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despland, L.M.; Vancov, T.; Aragno, M.; Clark, M.W. Diversity of microbial communities in an attached–growth system using Bauxsol™ pellets for wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 433, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.H.; Yang, J.Q.; Zhang, D.J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, C.D.; Su, X.R.; Li, T.W. Composition and structure of microbial communities associated with different domestic sewage outfalls. Genet. Mol. Res. 2012, 13, 7542–7552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FischerRoth, F.; Lessa, G.; Wild, C.; Kikuchi, R.; Naumann, M. Impacts of a high–discharge submarine sewage outfall on water quality in the coastal zone of Salvador (Bahia, Brazil). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 106, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Inan, A. Modeling of Hydrodynamics and Dilution in Coastal Waters. Water 2019, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, H.B.; List, E.J.; Koh, R.C.Y.; Imberger, J.; Brooks, N.H. Mixing in Inland and Coastal Waters; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, F.; Palacio, C.; Chang, G. Simulation of near field dilution of the submarine outfall of Santa Marta (Colombia). Dyna 2013, 182, 138–146. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, P.J.; Salas, H.J.; Reiff, F.M.; Libhaber, M.; Labbe, A.; Thomson, J.C. Marine Wastewater Outfalls and Treatment Systems, 2nd ed.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2011; pp. 51–134. [Google Scholar]
- Anghan, C.; Bade, M.; Banerjee, J. A review on fundamental properties of the jet in the wave environment. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 250, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otoo, E.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Chen, Y. Dilution characteristics of dual buoyant jets in wavy cross–flow environment. Water Sci. Eng. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, P.J.W. Ocean outfall dilution: Effects of currents. J. Hydraul. Div. ASCE 1980, 106, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, P.J.W. Modeling Mamala Bay outfall plumes. I: Near field. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1999, 125, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirka, G.H.; Doneker, R.L.; Barnwell, T.O. CORMIX: An expert system for mixing–zone analysis. Waterence Technol. 1991, 24, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L. Turbulent Buoyant Jets into Stratified or Flowing Ambient Fluids. California Institute of Technology, Pasadena. 1967. Available online: https://authors.library.caltech.edu/25955/1/KH–R–15.pdf (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Chin, D.A. Influence of surface waves on outfall dilution. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1987, 113, 1006–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, D. Experimental study on a buoyant jet in wavy crossflow. In Proceedings of the 28th International Ocean and Polar Engineering Conference, ISOPE, Sapporo, Japan, 10–15 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Otoo, E.; Chen, Y.P.; Ding, H.W. 2D PIV measurement of twin buoyant jets in wavy cross–flow environment. Water 2019, 11, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, R.; Gono, T.; Yamagata, T.; Fujisawa, N. Three–dimensional flow structure in highly buoyant jet by scanning stereo PIV combined with POD analysis. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2015, 52, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, L.L.; Tang, H.W.; Dai, H.C. Large eddy simulation of vertical turbulent jets under JONSWAP waves. Acta Mech. Sin. 2011, 27, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Otoo, E.; Lu, S. An Improved Integral Model for a Non–Buoyant Turbulent Jet in Wave Environment. Water 2019, 11, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tate, P.M. The Rise and Dilution of Buoyant Jets and Their Behaviour in an Internal Wave Field. Ph.D. Thesis, University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia, June 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, H. Dispersion of Offshore Discharged Produced Water in the Marine Environment: Hydrodynamic Modeling and Experimental Study. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Newfoundland, St. John’s, NL, Canada, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hwung, H.; Chyan, J.; Chang, C.; Chen, Y. The dilution processes of alternative horizontal buoyant jets in wave motions. Coast. Eng. Proc. 1994, 24, 3045–3059. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C. Near–field dilution of a turbulent jet discharged into coastal waters: Effect of regular waves. Ocean Eng. 2017, 140, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, D.A. Model of buoyant–jet–surface–wave interaction. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 1988, 114, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, B.-F.; Li, C.W. Flow induced by a turbulent jet under random waves. J. Hydraul. 2008, 46, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz–Rocca, L.H.; Causado–Rodríguez, E. La insostenibilidad del desarrollo urbano: El caso de Santa Marta–Colombia. Clío América 2007, 1, 64–100. [Google Scholar]
- Moscarella, M.V.; García, F.; Palacio, C. Microbiological water quality of Santa Marta Bay, Colombia. Dyna 2001, 167, 132–141. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, R.R.; Yang, W.C.; Chiang, T.P. Effects of Surface Waves on a Buoyant Jet. J. Mar. Environ. Eng. 1996, 3, 63–84. [Google Scholar]
- Chyan, J.M.; Hwung, H.H.; Chang, C.Y.; Chen, I.P. Effects of Discharge Angles on Dilution of Buoyant Jet in Wave Motions. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference of Hydrodynamics, Tainan, Taiwan, 31 October–2 November 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, C.A.; Barton, E.D. The guajira upwelling system. Cont. Shelf Res. 2005, 25, 1003–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arroyave, D.M.; Bartoli, M.; Bresciani, M.; Luciani, G.; Toro, M. Biogeochemical modelling of a tropical coastal area undergoing seasonal upwelling and impacted by untreated submarine outfall. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 172, 112771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, Y.; Medellín, J.; Navas, G. Contexto Climatológico y Oceanográfico del mar Caribe Colombiano. Biodiversidad del Margen Continental del Caribe Colombiano; Serie de Publicaciones Especiales; Instituto de Investigaciones Marinas y Costeras José Benito Vives de Andréis—INVEMAR: Santa Marta, Colombia, 2010; Volume 20, p. 4588. [Google Scholar]
- Tate, P.M.; Holden, C.J.; Tate, D.J. Influence of plume advection and particle settling on wastewater dispersion and distribution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 145, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tate, P.M.; Middleton, J.H. Unification of non–dimensional solutions to asymptotic equations for plumes of different shape. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2000, 94, 225–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, P.M.; Middleton, J.H. Buoyant jets of elliptical shape: An approximation for duckbill valves. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2004, 130, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossati, M.; Piedra, I. Numerical modelling of residual flow and salinity in the Rio de la Plata. Appl. Math. Model. 2008, 32, 1066–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, F.F.; Palacio, C.; Garcia, U. Uso de un modelo regional para el mar Caribe para obtener condiciones fronteras abiertas en un modelo local para la bahía de Santa Marta—Colombia. Boletín Científico CIOH 2008, 26, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, F.F.; Palacio, C.; Garcia, U. Simulation of hydrodynamic conditions at Santa Marta coastal area (Colombia). Dyna 2012, 174, 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, F.F.; Palacio, C.; Garcia, U. Calibración y validación de un modelo 3D para el área costera de Santa Marta (Colombia). Rev. Fac. Ing. Univ. Antioq. 2012, 62, 177–188. [Google Scholar]
- Simionato, C.; Meccia, V.; Dragani, W.; Nuñez, M. On the use of the NCEP/NCAR surface winds for modeling barotropic circulation in the Río de la Plata. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 70, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alewell, C.; Manderscheid, B. Use of objective criteria for the assessment of biogeochemical ecosystem models. Ecol. Model. 1998, 107, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Shore Protection Manual, Vol. I; 4th Edition. 1984. Available online: http://ft–sipil.unila.ac.id/dbooks/S%20P%20M%201984%20volume%201–1.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Ishikawa, M. Methodology to Classify and Visualize Time–Series Simulations Using Dilution Contour Maps. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal do Paraná, Curitiba, Brazil, March 2016. [Google Scholar]
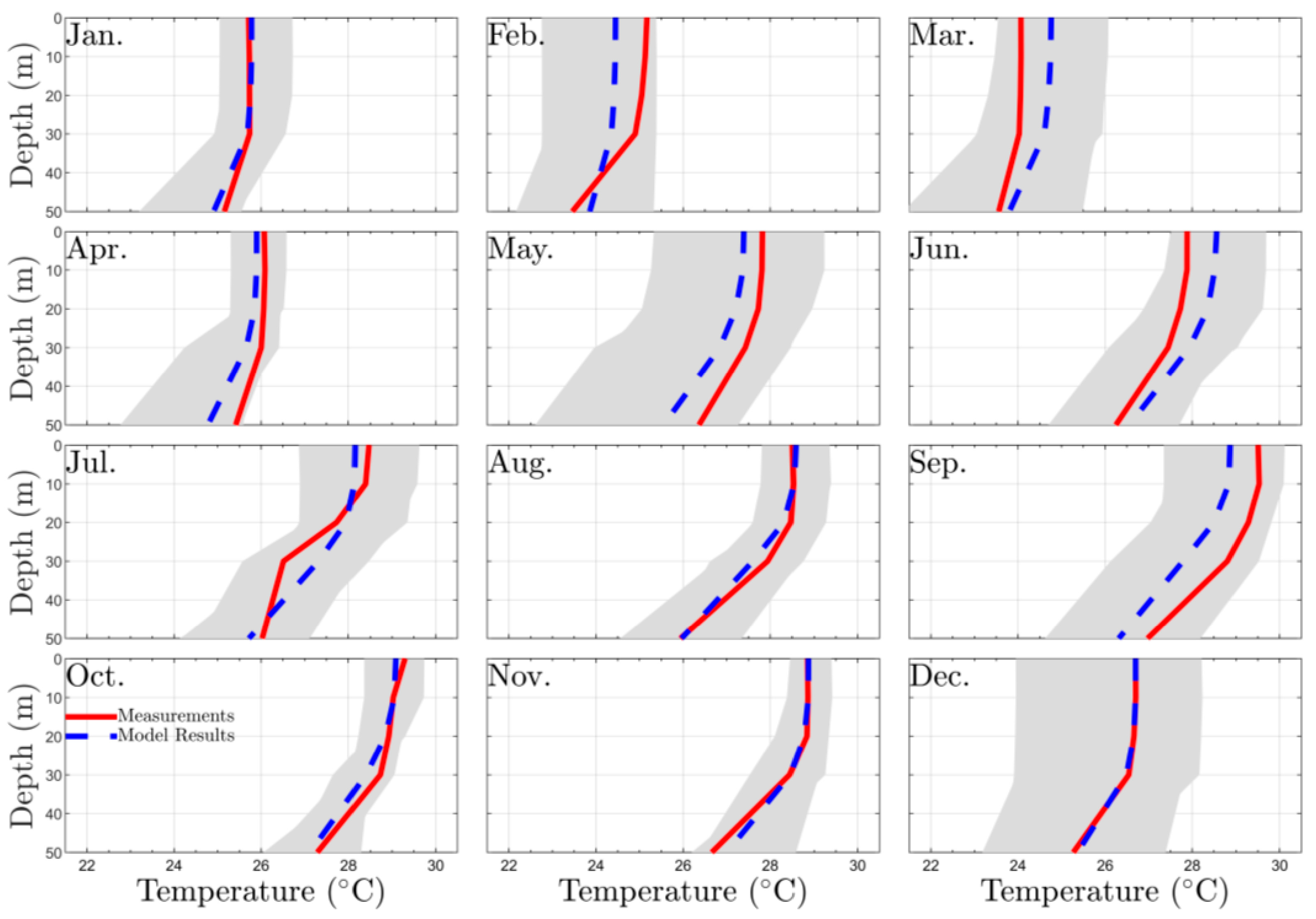
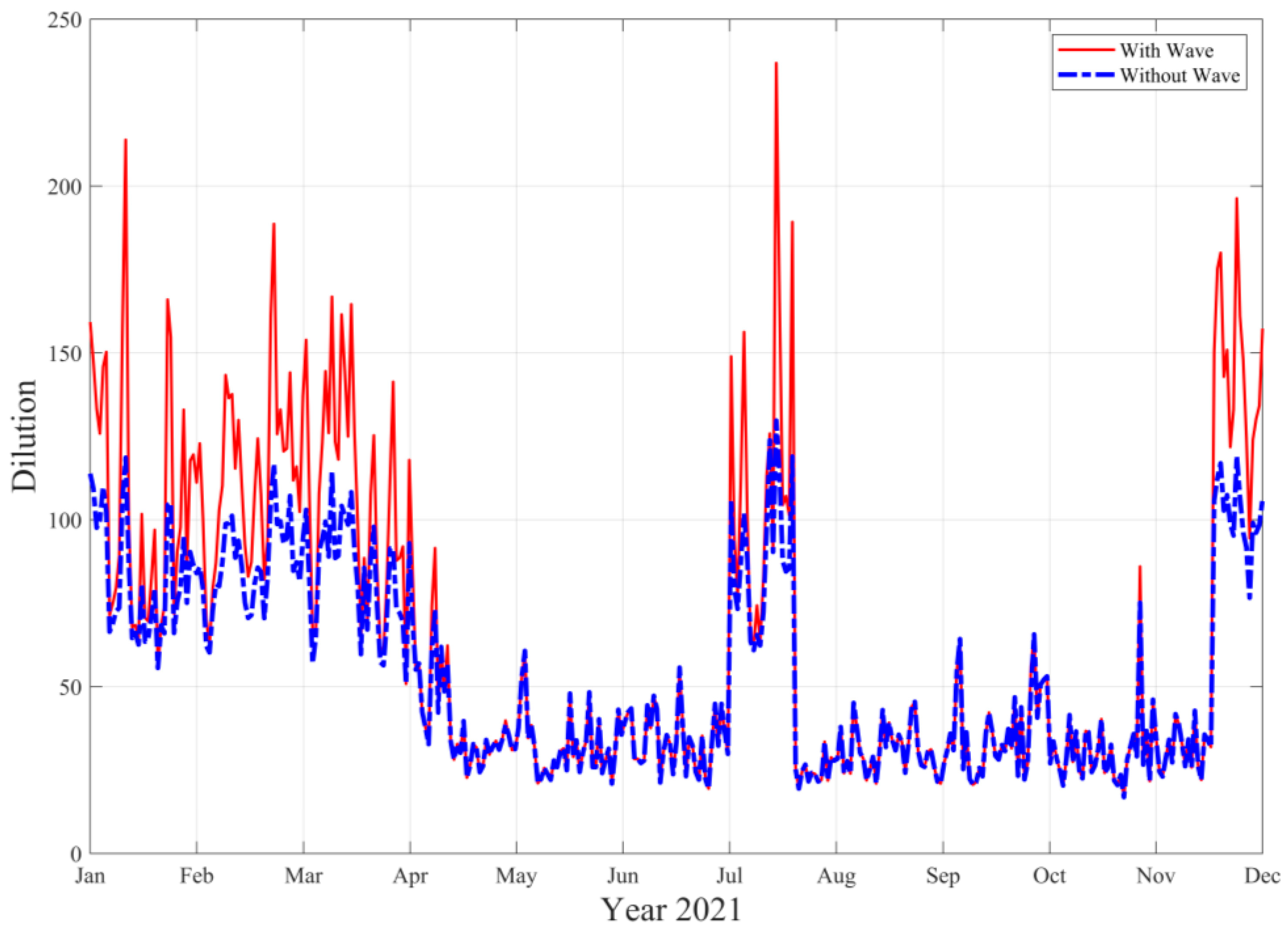
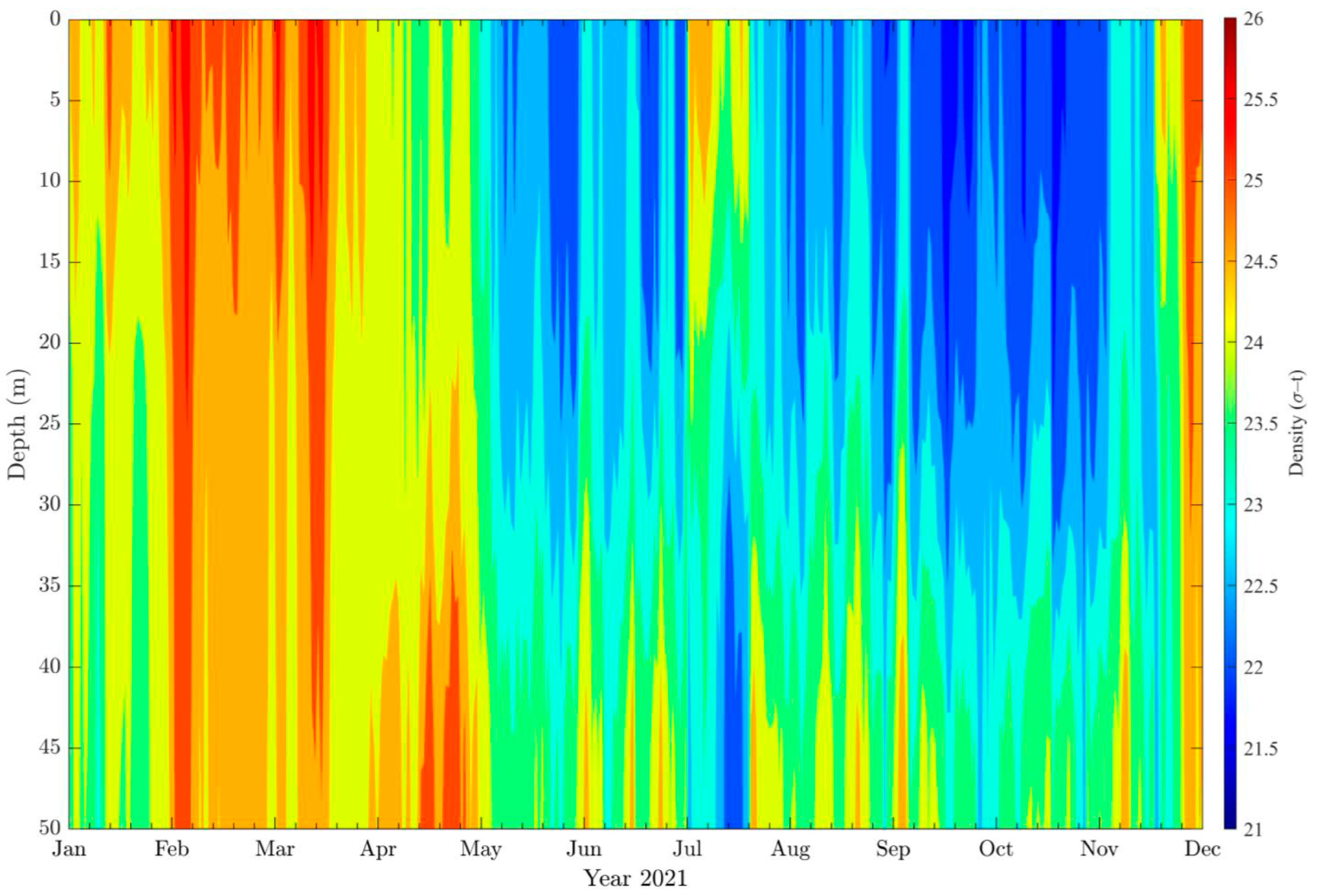
| January | February | March | April | May | June | July | August | September | October | November | December | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 0.0033 | 0.0202 | 0.0233 | 0.0134 | 0.0214 | 0.0191 | 0.0114 | 0.0041 | 0.0331 | 0.0051 | 0.0032 | 0.0001 |
| Salinity | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.0007 | 0.0048 | 0.0037 | 0.0045 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Rentería, F.-F.; Chang Nieto, G.A.; Cortés, G.H. Wave Effects on the Initial Dilution of Untreated Wastewater Discharge for Santa Marta’s Submarine Outfall (Colombia). Water 2023, 15, 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15050919
García-Rentería F-F, Chang Nieto GA, Cortés GH. Wave Effects on the Initial Dilution of Untreated Wastewater Discharge for Santa Marta’s Submarine Outfall (Colombia). Water. 2023; 15(5):919. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15050919
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Rentería, Francisco-Fernando, Gustavo Ariel Chang Nieto, and Gustavo Hernández Cortés. 2023. "Wave Effects on the Initial Dilution of Untreated Wastewater Discharge for Santa Marta’s Submarine Outfall (Colombia)" Water 15, no. 5: 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15050919





