Utilizing Satellite Data to Establish Rainfall Intensity-Duration-Frequency Curves for Major Cities in Iraq
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
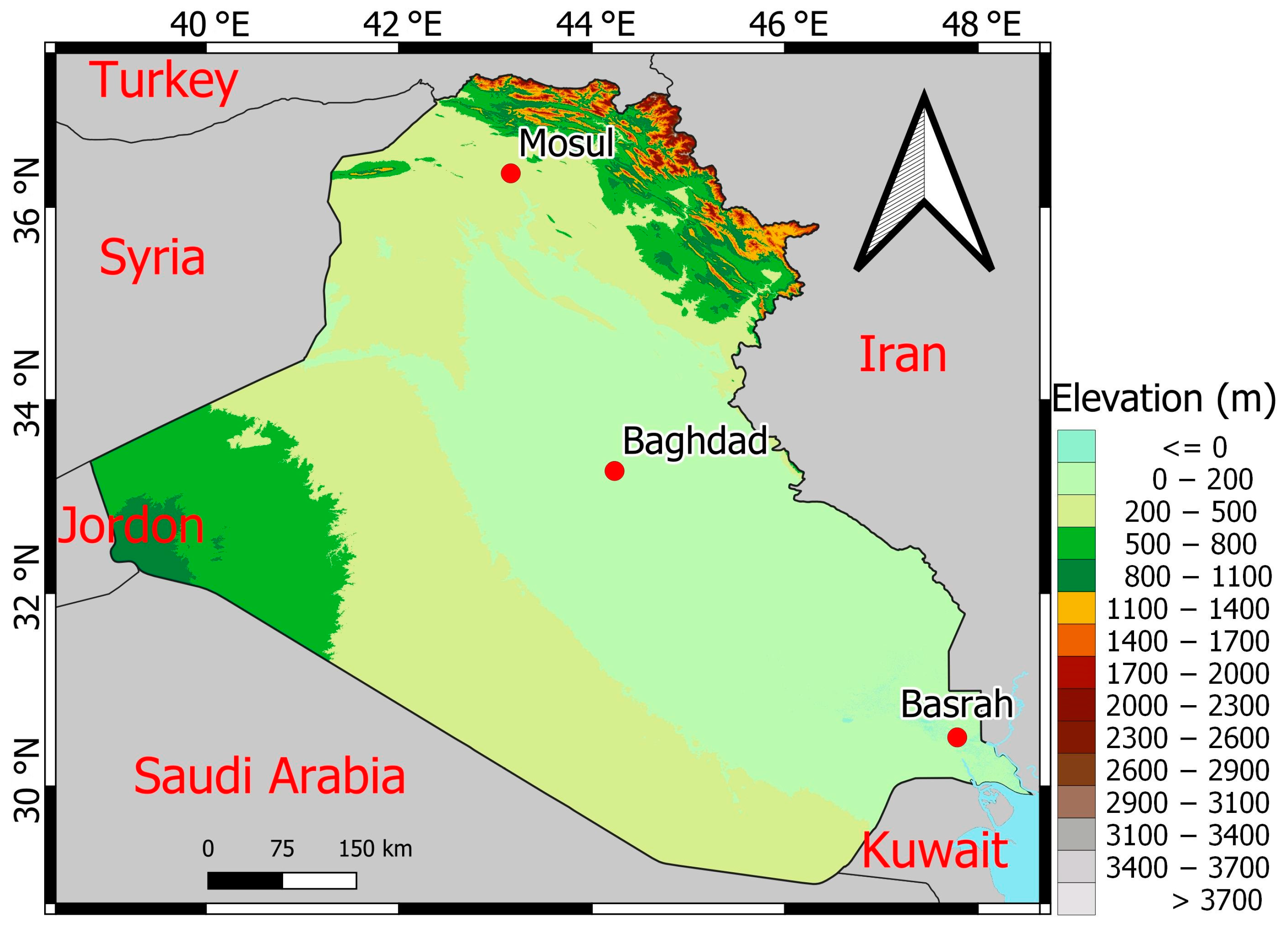
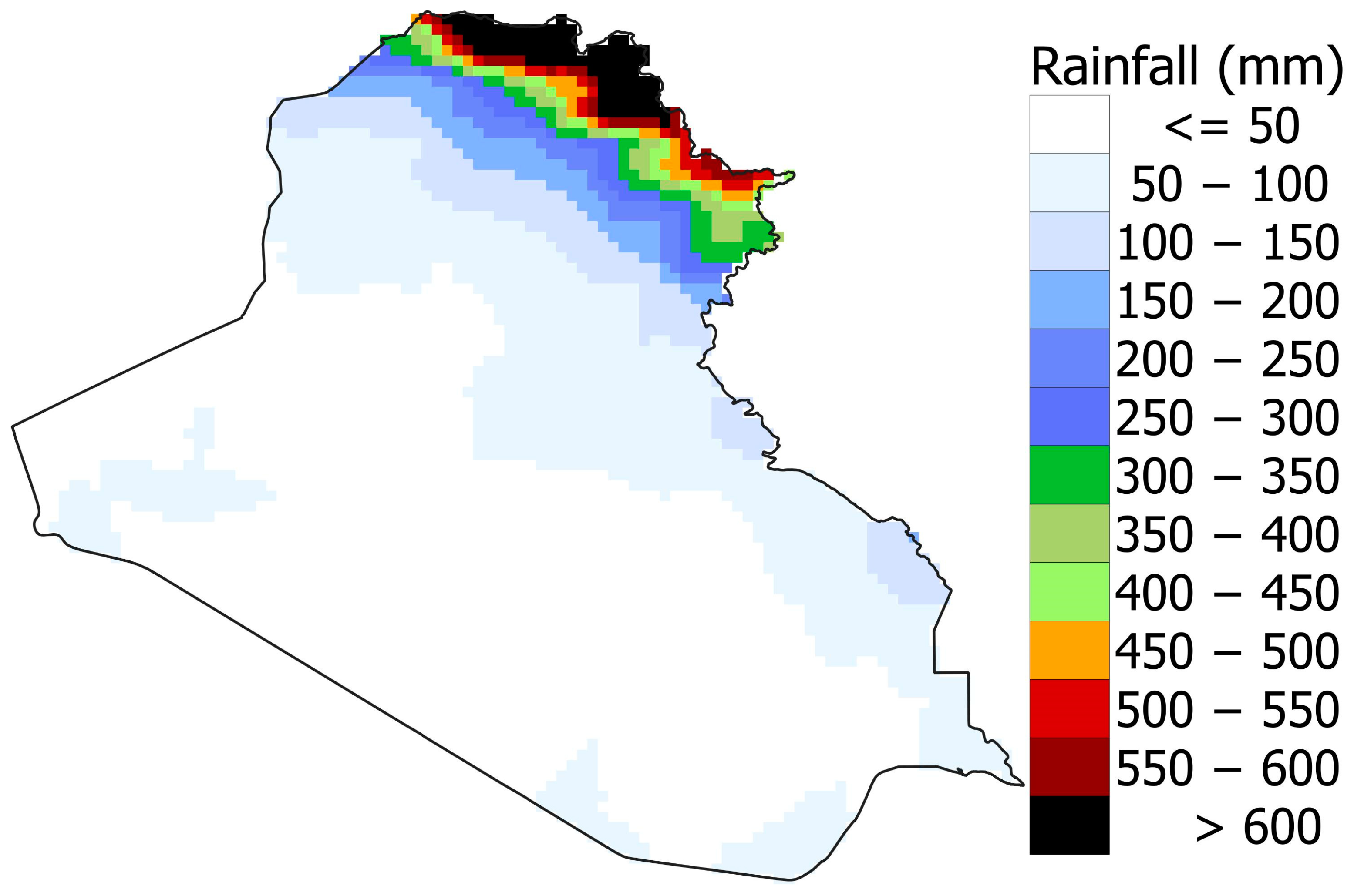
2.1. Physical and Climatological Properties of Iraq
2.2. Dataset
3. Methodology
3.1. Research Steps
- Estimate the maximum annual rainfall intensity (ARI) for the study period (2000–2021);
- Determine probability distribution functions (PDFs) best fit the ARI time series;
- Use the best-fit PDF for estimating rainfall intensity for each duration and return period;
- Apply regression techniques to generate the IDF curves using the Sherman equation;
- Repeat steps 1–4 to generate IDF curves for all locations using all three satellite-based precipitation datasets, repeat;
- Quantify the discrepancy between each city’s satellite and observed dataset IDF curves;
- Select the satellite rainfall with the lowest IDF bias and correct it based on the observed dataset IDF.
3.2. Distribution Functions
3.3. Sherman Equation
3.4. Evaluation of Satellite Precipitation Data
4. Results
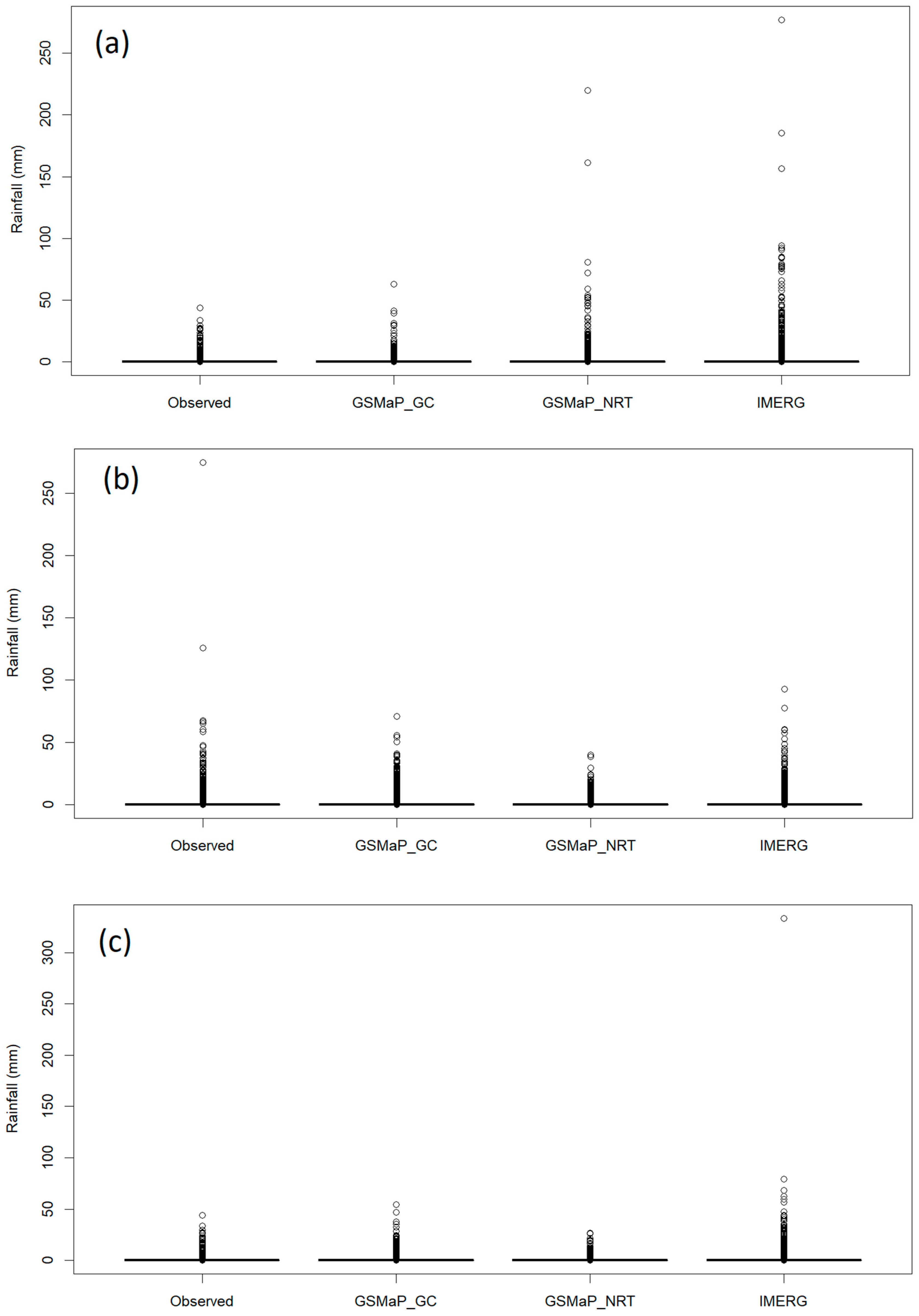
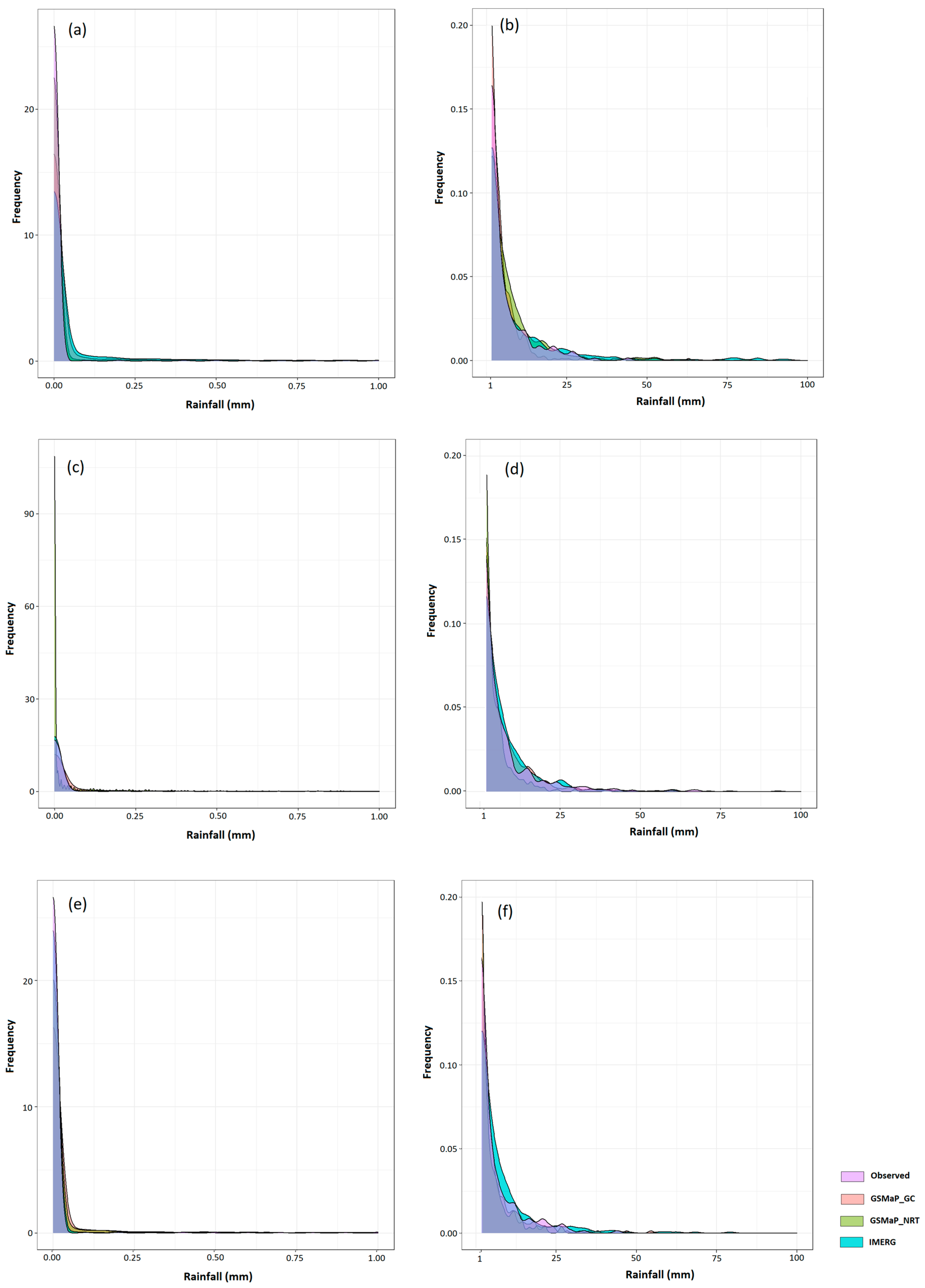
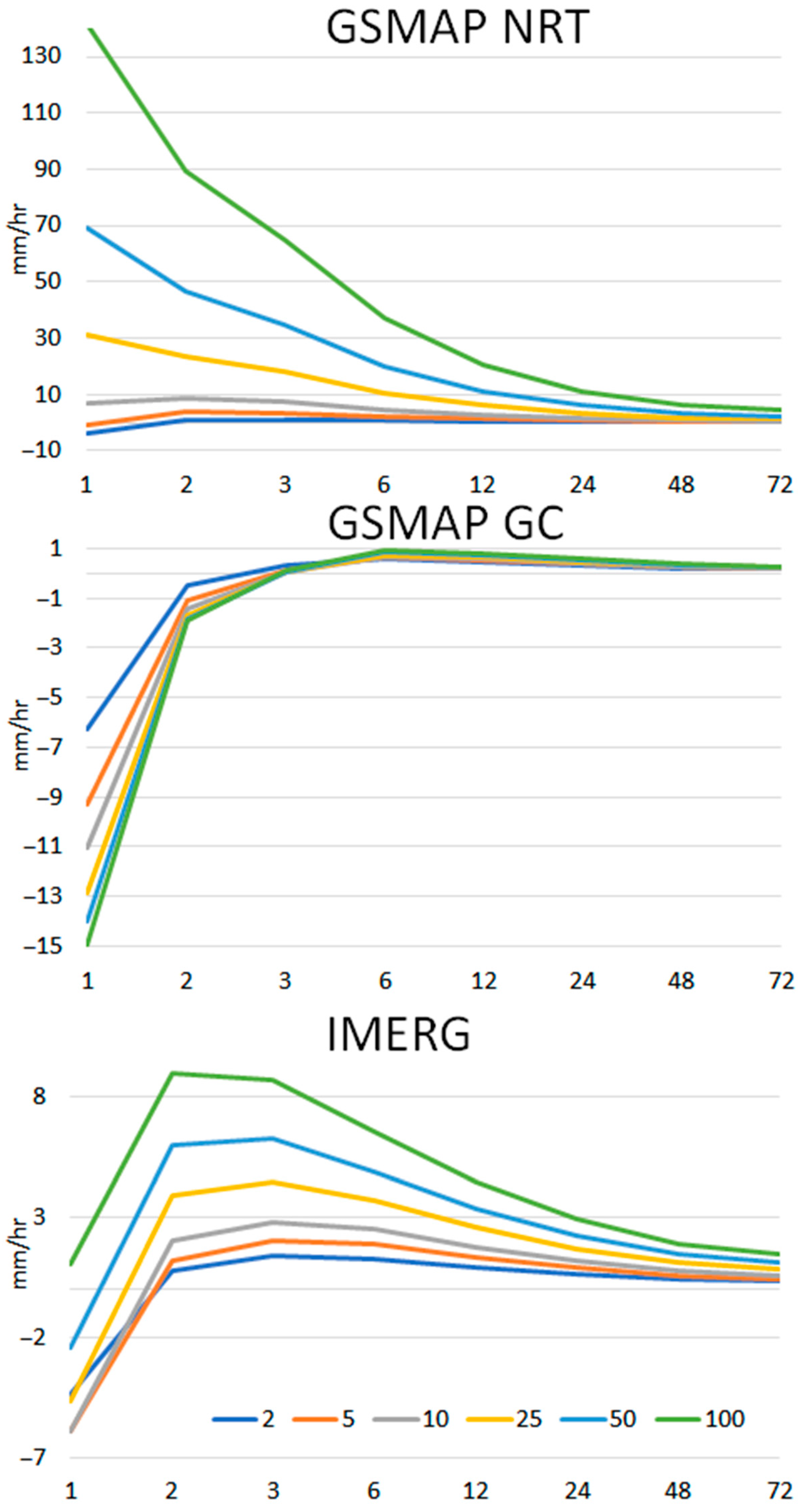
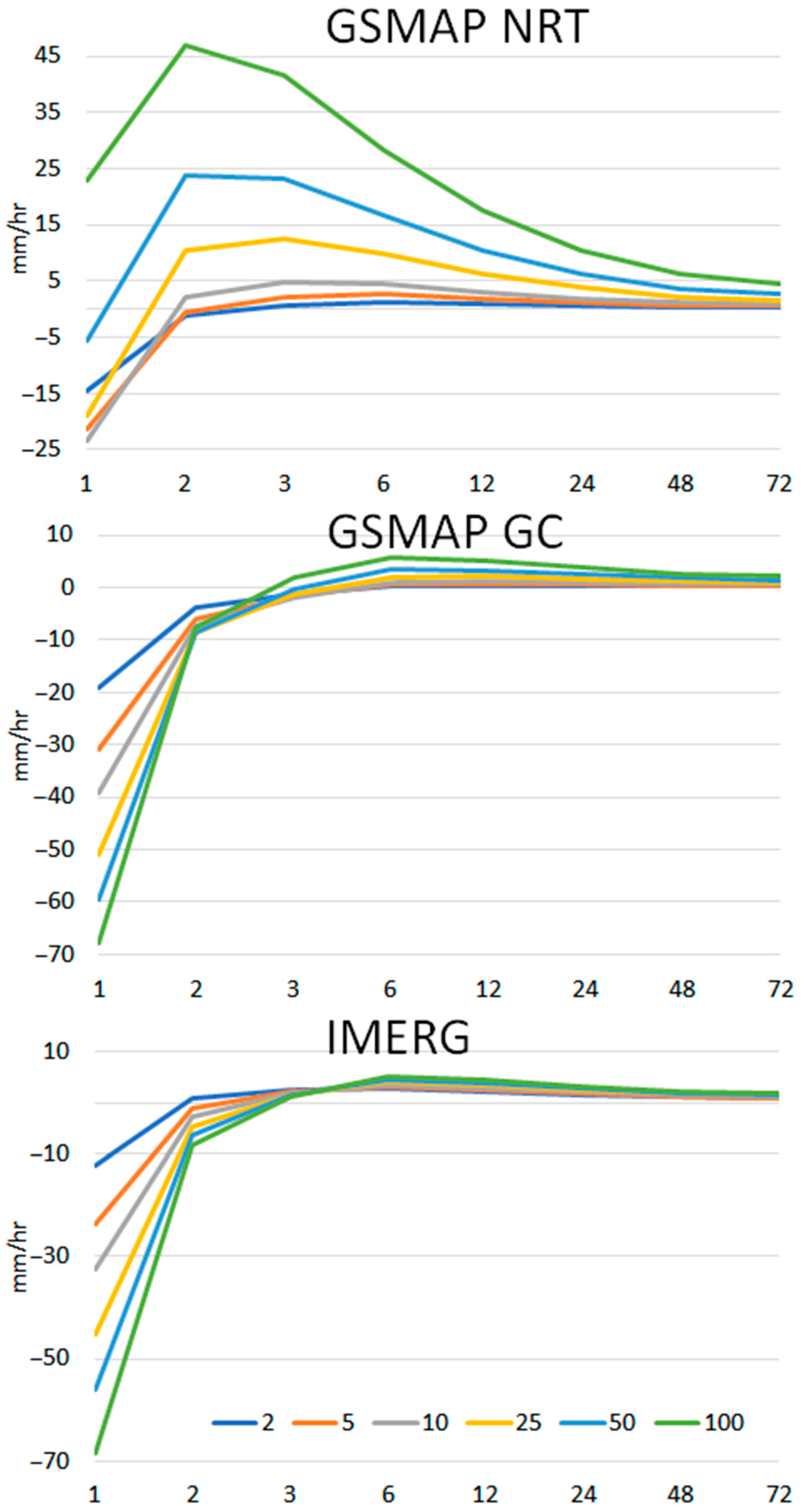
4.1. Performance of Satellite Precipitation Data
4.2. The Goodness of Fit Test
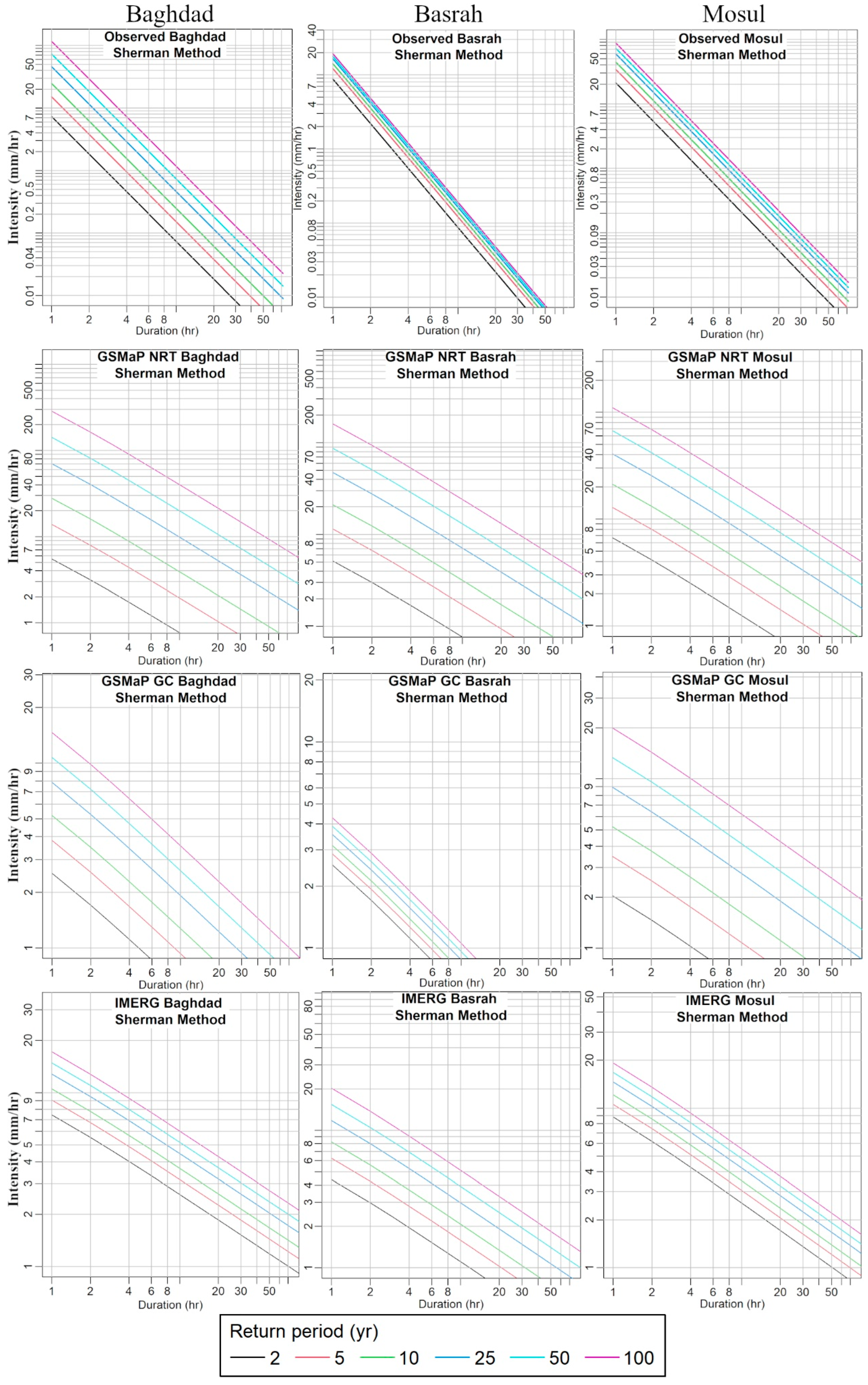
4.3. Generation of IDF Curves
4.4. IDF Curved Based on Sherman Equation
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Symbol | Definition |
| IDF | Intensity-duration-frequency |
| PDFs | Probability distribution functions |
| SWMS | Stormwater management systems |
| MENA | Middle East and North Africa |
| IMERG | Integrated Multi-Satellite Retrievals for Global Precipitation Measurement |
| GSMaP | Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation |
| GSMaP NRT | Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation Near Real-Time |
| GSMaP GC | Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation gauge corrected |
| GPM | Global Precipitation Measurement |
| CREST | Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology |
| JSTA | Japan Science and Technology Agency |
| JAXA | Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency |
| PMM | Precipitation Measuring Mission |
| ARI | Annual rainfall intensity |
| GEV | Generalized Extreme Value |
| GP | Gumbel and General Pareto |
| MLE | Maximum Likelihood |
| R2 | Spearman coefficient of determination |
| %BIAS | percentage of bias |
| SS | Perkin’s skill score |
References
- Aly, M.M.; Refay, N.H.; Elattar, H.; Morsy, K.M.; Bandala, E.R.; Zein, S.A.; Mostafa, M.K. Ecohydrology and flood risk management under climate vulnerability in relation to the sustainable development goals (SDGs): A case study in Nagaa Mobarak Village, Egypt. Nat. Hazards 2022, 112, 1107–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, S.H.; Wahab, A.K.A.; Shahid, S. Spatiotemporal changes in precipitation indicators related to bioclimate in Iran. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 141, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, S.C.; Raghavan, S.V.; Liong, S.Y. Development of Intensity-Duration-Frequency curves at ungauged sites: Risk management under changing climate. Geosci. Lett. 2014, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhatti, A.S.; Wang, G.; Ullah, W.; Ullah, S.; Fiifi Tawia Hagan, D.; Kwesi Nooni, I.; Lou, D.; Ullah, I. Trend in Extreme Precipitation Indices Based on Long Term In Situ Precipitation Records over Pakistan. Water 2020, 12, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IPCC. IPCC. IPCC SR15: Summary for Policymakers. In IPCC Special Report Global Warming of 1.5 °C; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Angel, S.; Parent, J.; Civco, D.L.; Blei, A.; Potere, D. The dimensions of global urban expansion: Estimates and projections for all countries, 2000–2050. Prog. Plann. 2011, 75, 53–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kineber, A.F.; Mohandes, S.R.; Hamed, M.M.; Singh, A.K.; Elayoty, S. Identifying and Assessing the Critical Criteria for Material Selection in Storm Drainage Networks: A Stationary Analysis Approach. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filazzola, A.; Shrestha, N.; MacIvor, J.S. The contribution of constructed green infrastructure to urban biodiversity: A synthesis and meta-analysis. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 56, 2131–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ren, Y.; Shen, L.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Shi, F. A novel evaluation method for urban infrastructures carrying capacity. Cities 2020, 105, 102846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nashwan, M.S.; Shahid, S. Future precipitation changes in Egypt under the 1.5 and 2.0 °C global warming goals using CMIP6 multimodel ensemble. Atmos. Res. 2022, 265, 105908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, S.A.; Hamed, M.M.; Shahid, S.; Ahmed, K.; Sharafati, A.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Ziarh, G.F.; Ismail, T.; Chung, E.-S.; Wang, X.-J.; et al. Projecting spatiotemporal changes of precipitation and temperature in Iraq for different shared socioeconomic pathways with selected Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 9032–9050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, M.M.; Sammen, S.S.; Nashwan, M.S.; Shahid, S. Spatiotemporal variation of drought in Iraq for shared socioeconomic pathways. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, S.A.; Shahid, S.; Ismail, T.; Rahman, N.b.A.; Wang, X.; Chung, E.S. Unidirectional trends in daily rainfall extremes of Iraq. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 134, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faihan, S.M. Urban policy in Iraq for the period 1970–2012, evaluation study. J. Adv. Soc. Res. 2014, 4, 58–76. [Google Scholar]
- Gámez-Balmaceda, E.; López-Ramos, A.; Martínez-Acosta, L.; Medrano-Barboza, J.P.; Remolina López, J.F.; Seingier, G.; Daesslé, L.W.; López-Lambraño, A.A. Rainfall intensity-duration-frequency relationship. Case study: Depth-duration ratio in a semi-arid zone in Mexico. Hydrology 2020, 7, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paola, F.; Giugni, M.; Topa, M.E.; Bucchignani, E. Intensity-Duration-Frequency (IDF) rainfall curves, for data series and climate projection in African cities. SpringerPlus 2014, 3, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdulrazzaq, Z.; Aziz, N.; Mohammed, A. Flood modelling using satellite-based precipitation estimates and digital elevation model in eastern Iraq. Int. J. Adv. Geosci. 2018, 6, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Najmaddin, P.M.; Whelan, M.J.; Balzter, H. Application of satellite-based precipitation estimates to rainfall-runoff modelling in a data-scarce semi-arid catchment. Climate 2017, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Awchi, T.A.; Suliman, A.H. Spatiotemporal assessment of meteorological drought using satellite-based precipitation data over Iraq. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 779, 012052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliman, A.H.A.; Awchi, T.A.; Al-Mola, M.; Shahid, S. Evaluation of remotely sensed precipitation sources for drought assessment in Semi-Arid Iraq. Atmos. Res. 2020, 242, 105007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, A.R.; Nile, B.K.; Al-Baidhani, J.H. Selection of suitable PDF model and build of IDF curves for rainfall in Najaf city, Iraq. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1973, 12184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamkhi, M.; Jawad, A.; Jameel, T. Comparison between Satellite Rainfall Data and Rain Gauge Stations in Galal-Badra Watershed, Iraq. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Developments in eSystems Engineering (DeSE), Kazan, Russia, 7–10 October 2019; pp. 340–344. [Google Scholar]
- Schardong, A.; Simonovic, S.P.; Gaur, A.; Sandink, D. Web-based tool for the development of intensity duration frequency curves under changing climate at gauged and ungauged locations. Water 2020, 12, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amri, N.S.; Subyani, A.M. Generation of Rainfall Intensity Duration Frequency (IDF) Curves for Ungauged Sites in Arid Region. Earth Syst. Environ. 2017, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ombadi, M.; Nguyen, P.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K. lin Developing Intensity-Duration-Frequency (IDF) Curves from Satellite-Based Precipitation: Methodology and Evaluation. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 7752–7766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valjarević, A.; Morar, C.; Živković, J.; Niemets, L.; Kićović, D.; Golijanin, J.; Gocić, M.; Bursać, N.M.; Stričević, L.; Žiberna, I.; et al. Long Term Monitoring and Connection between Topography and Cloud Cover Distribution in Serbia. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, M.; Ismail, T.; Shahid, S.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Dewan, A. Evaluating intensity-duration-frequency (IDF) curves of satellite-based precipitation datasets in Peninsular Malaysia. Atmos. Res. 2021, 248, 105203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapountzis, M.; Kastridis, A.; Kazamias, A.P.; Karagiannidis, A.; Nikopoulos, P.; Lagouvardos, K. Utilization and uncertainties of satellite precipitation data in flash flood hydrological analysis in ungauged watersheds. Glob. NEST J. 2021, 23, 388–399. [Google Scholar]
- Alsumaiti, T.S.; Hussein, K.; Ghebreyesus, D.T.; Sharif, H.O. Performance of the CMORPH and GPM IMERG Products over the United Arab Emirates. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashwan, M.S.; Shahid, S.; Dewan, A.; Ismail, T.; Alias, N. Performance of five high resolution satellite-based precipitation products in arid region of Egypt: An evaluation. Atmos. Res. 2020, 236, 104809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falah, G.; Shahid, S.; Bin, T. Correcting bias of satellite rainfall data using physical empirical model. Atmos. Res. 2021, 251, 105430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyaw, A.K.; Shahid, S.; Wang, X. Remote Sensing for Development of Rainfall Intensity–Duration–Frequency Curves at Ungauged Locations of Yangon, Myanmar. Water 2022, 14, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, S.A.; Shahid, S.; Ismail, T.; Chung, E.S.; Al-Abadi, A.M. Long-term trends in daily temperature extremes in Iraq. Atmos. Res. 2017, 198, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarazah, A. Assessment of the Hydrological Status of Iraq Using a Combination of Remote Sensing and Drought Indices Declaration of original Authorship Declaration; University of Reading: Reading, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Aboodi, A.H.; Hassan, A.A.; Ibrahim, H.T. Rainfall intensity probability for design of drainage system in Basrah City, south of Iraq. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2019, 14, 954–961. [Google Scholar]
- Jalut, Q.H. Generation of Rainfall Intensity Duration Curves Using Disaggregation Technique. Diyala J. Eng. Sci. 2018, 11, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, E.; Steinacker, R.; Saghafian, B. Multi time-scale evaluation of high-resolution satellite-based precipitation products over northeast of Austria. Atmos. Res. 2018, 206, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aonashi, K.; Awaka, J.; Hirose, M.; Kozu, T.; Kubota, T.; Liu, G.; Shige, S.; Kida, S.; Seto, S.; Takahashi, N. GSMaP passive microwave precipitation retrieval algorithm: Algorithm description and validation. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan. Ser. II 2009, 87, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ushio, T.; Sasashige, K.; Kubota, T.; Shige, S.; Okamoto, K.; Aonashi, K.; Inoue, T.; Takahashi, N.; Iguchi, T.; Kachi, M. A Kalman filter approach to the Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) from combined passive microwave and infrared radiometric data. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan. Ser. II 2009, 87, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okamoto, K.I.; Ushio, T.; Iguchi, T.; Takahashi, N.; Iwanami, K. The global satellite mapping of precipitation (GSMaP) project. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS ’05, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 29 July 2005; IEEE: Manhattan, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 5, pp. 3414–3416. [Google Scholar]
- Nashwan, M.S.; Shahid, S. Symmetrical uncertainty and random forest for the evaluation of gridded precipitation and temperature data. Atmos. Res. 2019, 230, 104631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mega, T.; Ushio, T.; Kubota, T.; Kachi, M.; Aonashi, K.; Shige, S. Gauge adjusted global satellite mapping of precipitation (GSMaP_Gauge). In Proceedings of the 2014 XXXIth URSI General Assembly and Scientific Symposium (URSI GASS), Beijing, China, 16–23 August 2014; IEEE: Manhattan, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kubota, T.; Shige, S.; Hashizume, H.; Aonashi, K.; Takahashi, N.; Seto, S.; Hirose, M.; Takayabu, Y.N.; Ushio, T.; Nakagawa, K.; et al. Global Precipitation Map Using Satellite-Borne Microwave Radiometers by the GSMaP Project: Production and Validation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 2259–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Stocker, E.F.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Jackson, T. GPM IMERG Final Precipitation L3 1 Day 0.1 Degree x 0.1 Degree V06; Savtchenko, A., Ed.; Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC): Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Koutsoyiannis, D.; Baloutsos, G. Analysis of a long record of annual maximum rainfall in Athens, Greece, and design rainfall inferences. Nat. Hazards 2000, 22, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastridis, A.; Stathis, D. The effect of rainfall intensity on the flood generation of mountainous watersheds (Chalkidiki Prefecture, North Greece). In Proceedings of the Perspectives on Atmospheric Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 341–347. [Google Scholar]
- AL-Dulaimi, M.H.A.; Alfatlawi, T.J.M.; Mohammed, W.A. Developing (IDF) Curves Models for Babylon City And Alluvial Fertile Zone, Iraq. Solid State Technol. 2020, 63, 2585–2598. [Google Scholar]
- Ihsan Hasan, Y.S. Analysis of Rainfall Data for a Number of Stations in Northern Iraq. Al-Rafidain Eng. J. 2020, 25, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, M.; Ismail, T.; Shahid, S.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Dewan, A. Projection of Rainfall Intensity-Duration-Frequency Curves at Ungauged Location under Climate Change Scenarios. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 83, 103951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.S.; Rahman, A.; Zaman, M.A.; Haddad, K.; Ahsan, A.; Imteaz, M. A study on selection of probability distributions for at-site flood frequency analysis in Australia. Nat. Hazards 2013, 69, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, C.W. Maximum rates of rainfall at Boston. Trans. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1905, 54, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.V.; Kling, H.; Yilmaz, K.K.; Martinez, G.F. Decomposition of the mean squared error and NSE performance criteria: Implications for improving hydrological modelling. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamed, M.M.; Nashwan, M.S.; Shahid, S. Performance Evaluation of Reanalysis Precipitation Products in Egypt using Fuzzy Entropy Time Series Similarity Analysis. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 5431–5446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, D.A.; M Amen, A.R.; Mustafa, A.; Yüce, M.I.; Szydłowski, M. Comparative Analysis of Developed Rainfall Intensity–Duration–Frequency Curves for Erbil with Other Iraqi Urban Areas. Water 2022, 14, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, E.S.; Mohamedmeki, M.Z. Analysis of rainfall intensity-duration-frequency (IDF) curves of Baghdad city. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 888, 12066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, F.; Morin, E.; Peleg, N.; Mei, Y.; Anagnostou, E.N. Intensity-duration-frequency curves from remote sensing rainfall estimates: Comparing satellite and weather radar over the eastern Mediterranean. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 2389–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaber, H.S.; Mansor, S.; Pradhan, B.; Ahmad, N. Rainfall–runoff modelling and water balance analysis for Al-Hindiyah barrage, Iraq using remote sensing and GIS. Geocarto Int. 2016, 32, 1407–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abushandi, E.; Merkel, B. Modelling rainfall runoff relations using HEC-HMS and IHACRES for a single rain event in an arid region of Jordan. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 2391–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darand, M.; Fathi, H. Evaluation of high resolution global satellite precipitation mapping during meteorological drought over Iran. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 145, 1421–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Areeq, A.M.; Al-Zahrani, M.A.; Sharif, H.O. Assessment of the performance of satellite rainfall products over Makkah watershed using a physically based hydrologic model. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Areeq, A.M.; Abba, S.I.; Yassin, M.A.; Benaafi, M.; Ghaleb, M.; Aljundi, I.H. Computational Machine Learning Approach for Flood Susceptibility Assessment Integrated with Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques from Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, M.; Yilmaz, K.K. Evaluation and bias correction of satellite-based rainfall estimates for modelling flash floods over the Mediterranean region: Application to Karpuz River Basin, Turkey. Water 2018, 10, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Yong, B.; Kirstetter, P.-E.; Wang, L.; Hong, Y. Global component analysis of errors in three satellite-only global precipitation estimates. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 3087–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sh, M.S.; Tabark, J.A.; Atyaf, J.M. comparison Between Satellite Rainfall Data and Dain Gauge Stations in The Al-Adhaim Watershed, Iraq. Plant Arch. 2020, 20, 625–629. [Google Scholar]
- Abd Elhamid, A.M.I.; Eltahan, A.M.H.; Mohamed, L.M.E.; Hamouda, I.A. Assessment of the two satellite-based precipitation products TRMM and RFE rainfall records using ground based measurements. Alex. Eng. J. 2020, 59, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanian, A.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Jamali, S.; Duan, Z. Performance Evaluation of Six Gridded Precipitation Products throughout Iran Using Ground Observations over the Last Two Decades (2000–2020). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Extreme Rainfall and Floods | Date | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Heavy rainfall and flash flood in central Iraq | 11 November 2013 | 11 death and heavy damages to building and civil structures |
| Flash flood in Baghdad | 28 October 2015 | 58 people died, and 84,000 were evacuated. Emergency was declared |
| Heavy rainfall driven flood in south Iraq | 5 May 2019 | 20,00 people were evacuated, and a hundred thousand were out of water supply |
| Heavy rainfall driven flood in Erbil | 17 December 2021 | 14 people died, and 7000 evacuated. Damage to residential buildings, infrastructure, and vehicles |
| Extreme rainfall in northern Iraq | 30 October 2021 | 3180 people were evacuated. Damages to roads |
| Heavy storms throughout the country | 24 March 2019 | 1173 families have been displaced |
| Heavy rainfall and flash floods in southern governorates | 22 November 2018 | 21 people have died, and 180 were injured as a result of the flooding |
| Recorded 67 mm of rainfall in a day in the bordering region of Iraq | 07 November 2018 | Heavy damage to infrastructure |
| Data | Time | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSMaP NRT | 2000 to present | 0.1° × 0.1° | 1-h | [41] |
| GSMaP GC | 2000 to present | 0.1° × 0.1° | 1-h | [44] |
| IMERG | 2000 to present | 0.1° × 0.1° | 30 min | [46] |
| Function | Equation | Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| GEV | k: shape μ: location σ: scale | |
| Gumbel | ||
| GP |
| Index | Optimum Value |
|---|---|
| 1 | |
| 0 | |
| 1 |
| Indices | City | GSMaP_GC | GSMaP_NRT | IMERG |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spearman | Baghdad | 0.339 | 0.259 | 0.292 |
| Basrah | 0.505 | 0.519 | 0.521 | |
| Mosul | 0.624 | 0.593 | 0.539 | |
| %Bias | Baghdad | 65.3 | 213.8 | 453.6 |
| Basrah | 37.6 | −16.1 | 196 | |
| Mosul | 27.7 | −29.4 | 18.5 | |
| Skill Score | Baghdad | 0.278 | 0.159 | 0.137 |
| Basrah | 0.419 | 0.545 | 0.278 | |
| Mosul | 0.466 | 0.325 | 0.371 |
| Negative Log-Likelihood Statistics (MLE Estimator) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product | Distribution | Duration (h) | ||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 12 | 24 | 48 | 72 | 96 | 144 | ||
| GSMAP NRT | GEV | 93.1 | 101.5 | 106.7 | 110.5 | 113.4 | 117.7 | 120.6 | 123.0 | 123.1 | 123.5 | 123.8 |
| Gumbel | 110.7 | 116.3 | 118.4 | 121.1 | 121.1 | 122.4 | 124.2 | 125.3 | 125.1 | 125.2 | 125.4 | |
| GP | 101.0 | 108.9 | 112.7 | 115.8 | 118.3 | 121.4 | 123.6 | 125.2 | 126.5 | 126.1 | 126.6 | |
| GSMAP GC | GEV | 49.9 | 63.1 | 69.4 | 74.6 | 81.8 | 87.6 | 91.6 | 93.9 | 94.9 | 95.8 | 97.8 |
| Gumbel | 50.7 | 64.8 | 72.2 | 77.7 | 83.7 | 88.4 | 92.7 | 94.2 | 95.1 | 95.9 | 97.8 | |
| GP | 54.4 | 69.4 | 76.2 | 81.1 | 86.7 | 92.7 | 96.6 | 97.6 | 97.3 | 96.9 | 96.4 | |
| IMERG | GEV | 62.1 | 75.8 | 84.1 | 89.1 | 93.4 | 102.6 | 111.0 | 117.9 | 119.8 | 122.1 | 122.4 |
| Gumbel | 62.1 | 75.9 | 84.2 | 89.1 | 93.5 | 103.1 | 112.9 | 120.2 | 121.6 | 123.9 | 123.9 | |
| GP | 53.6 | 79.2 | 88.3 | 89.1 | 101.4 | 114.0 | 122.8 | 127.2 | 127.9 | 129.1 | 129.4 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeri, S.J.; Hamed, M.M.; Wang, X.; Shahid, S. Utilizing Satellite Data to Establish Rainfall Intensity-Duration-Frequency Curves for Major Cities in Iraq. Water 2023, 15, 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15050852
Zeri SJ, Hamed MM, Wang X, Shahid S. Utilizing Satellite Data to Establish Rainfall Intensity-Duration-Frequency Curves for Major Cities in Iraq. Water. 2023; 15(5):852. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15050852
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeri, Sarah Jabbar, Mohammed Magdy Hamed, Xiaojun Wang, and Shamsuddin Shahid. 2023. "Utilizing Satellite Data to Establish Rainfall Intensity-Duration-Frequency Curves for Major Cities in Iraq" Water 15, no. 5: 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15050852
APA StyleZeri, S. J., Hamed, M. M., Wang, X., & Shahid, S. (2023). Utilizing Satellite Data to Establish Rainfall Intensity-Duration-Frequency Curves for Major Cities in Iraq. Water, 15(5), 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15050852








