Field Evaluation of UF Filtration Pretreatment Impact on RO Membrane Scaling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
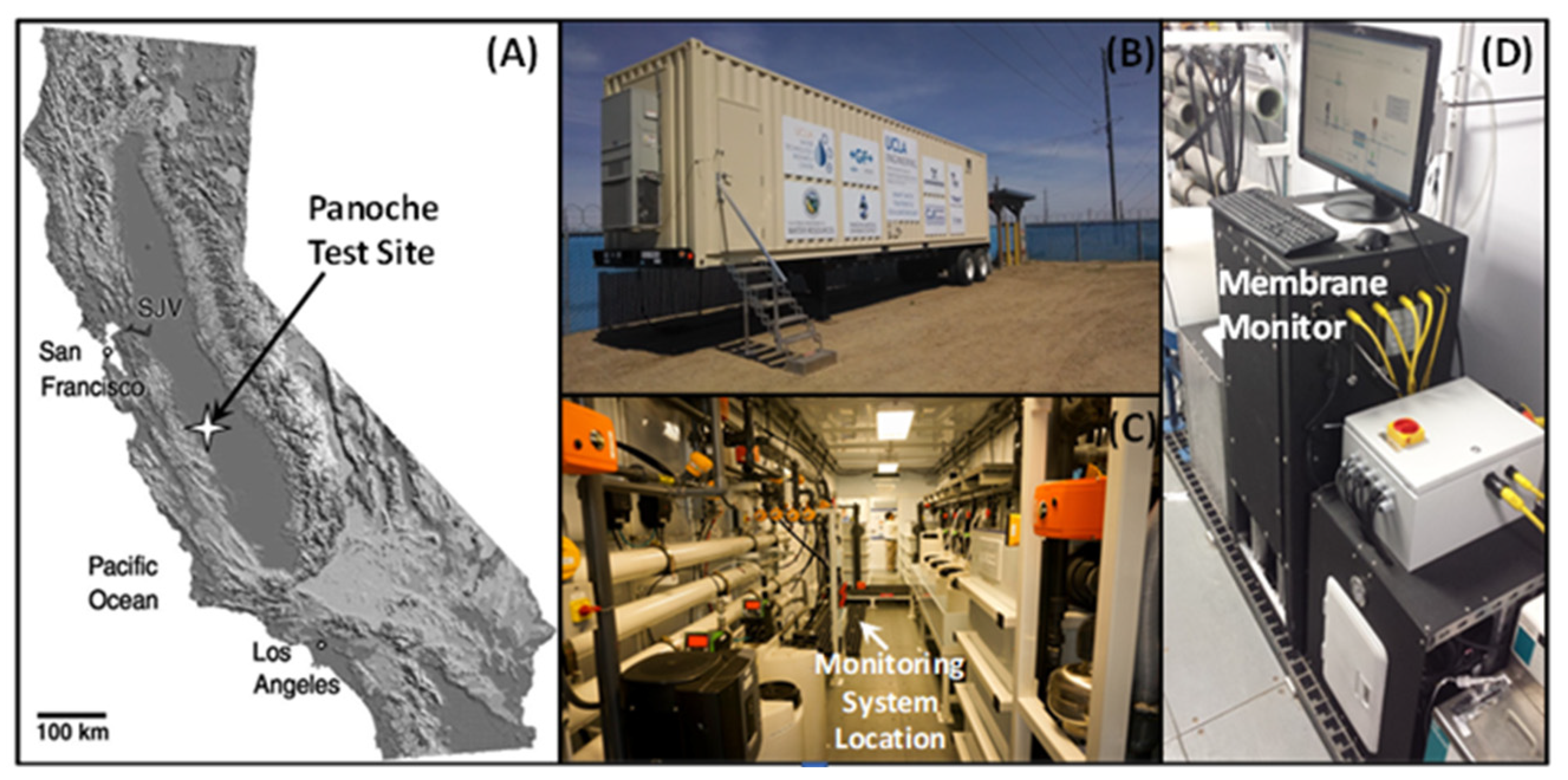
2.1. Field Brackish Water
2.2. Source Water Pretreatment
- (a)
- Media filtration using a standard silica sand filter (silver sand, US mesh #20, average sieve size 0.85 mm), a hydrocyclone (HC) separator (Lakos, Lindsay Corporation, Fresno, CA, USA), followed by an 80-mesh strainer for upstream failure to protect against large size debris. The media filtration served to reduce the burden of suspended particles prior to hydrocyclone.
- (b)
- Hydrocyclone centrifugal (HC) separator, followed by a 200 µm rotating self-cleaning disk microfilter (2” Brushaway Filter, Amiad, Mooresville, NC, USA) (Figure 2), and subsequent ultrafiltration (UF) modules consisting of two multi-bore inside-out hollow fiber ultrafiltration (UF) modules (Dizzer XL 0.9 MB 60 W; Inge GmbH, Greifenberg, Germany) arranged in parallel. UF pretreatment was assisted by inline coagulant dosing (using a metering pump, SMART Digital DDA; Grundfos, Bjerringbro, Denmark) of aluminum chlorohydrate (Qemipac 7580; Qemi International, Inc., Kingwood, TX, USA) at a dose of 0.8 mg/L. A rotating self-cleaning disk microfilter (200 μm) was used prior to UF in order to reduce the frequency of backwash cleaning of the UF unit. The UF modules were backwashed for 50 s every 60 min of operation. A strainer (80-mesh) was also installed after the UF for added protection of the RO elements to capture potential debris in the event of UF tubules breakage (Figure 2).
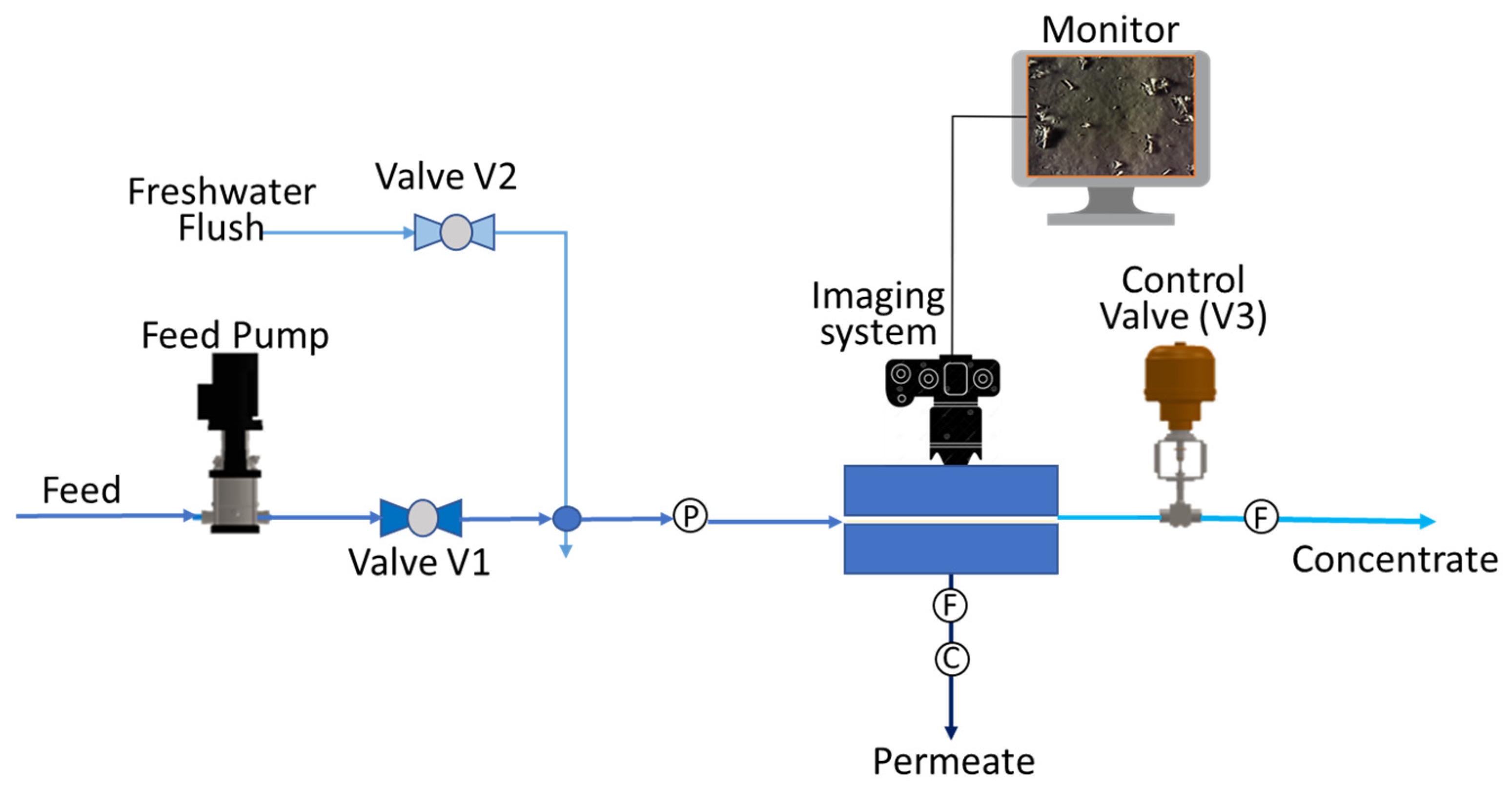
2.3. Membrane Monitoring System (MMS)
2.4. Evaluation of Feed Pretreatment on Downstream RO Membrane Scaling
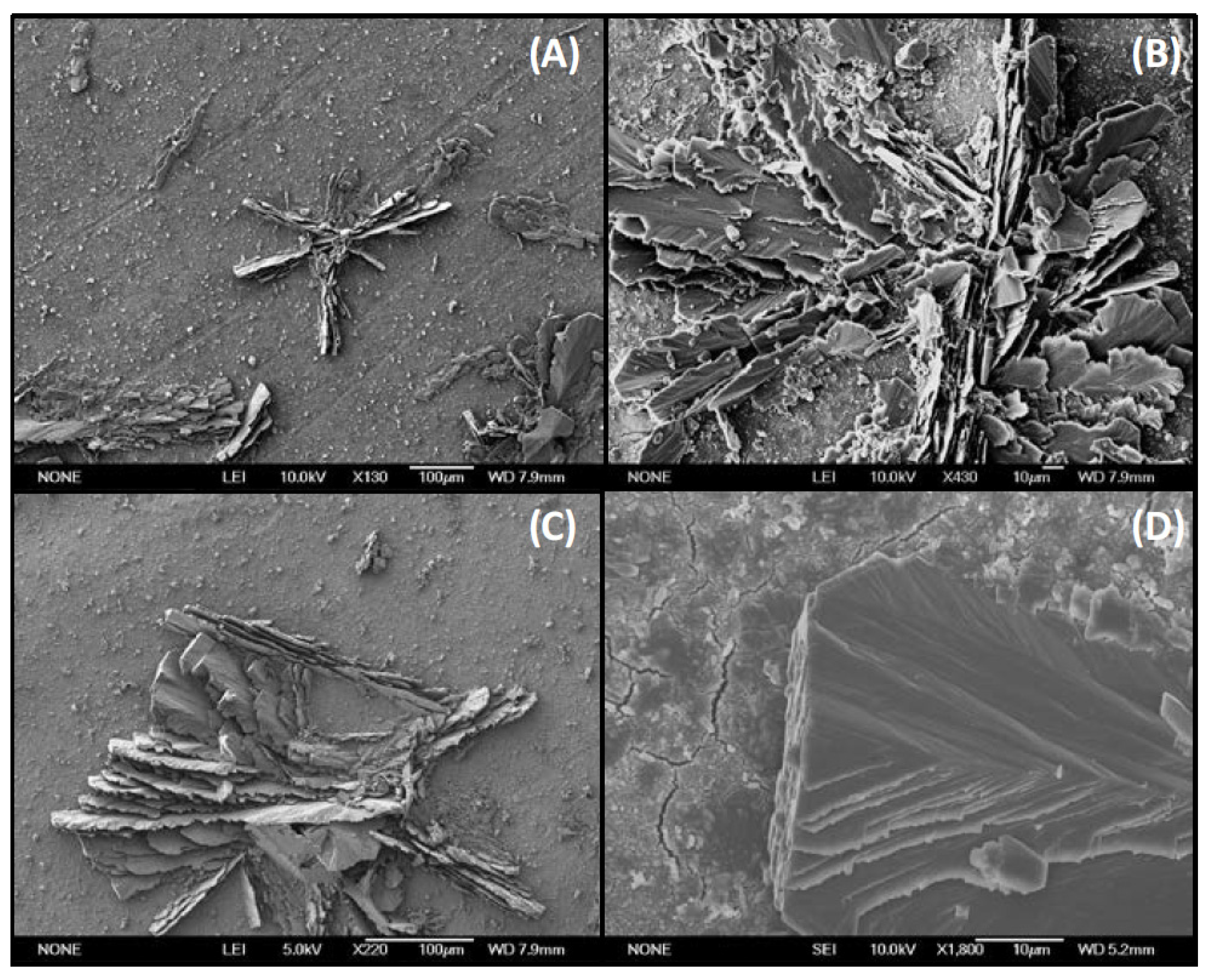
2.5. SEM/EDS Analysis of Scaled RO Membrane
3. Results
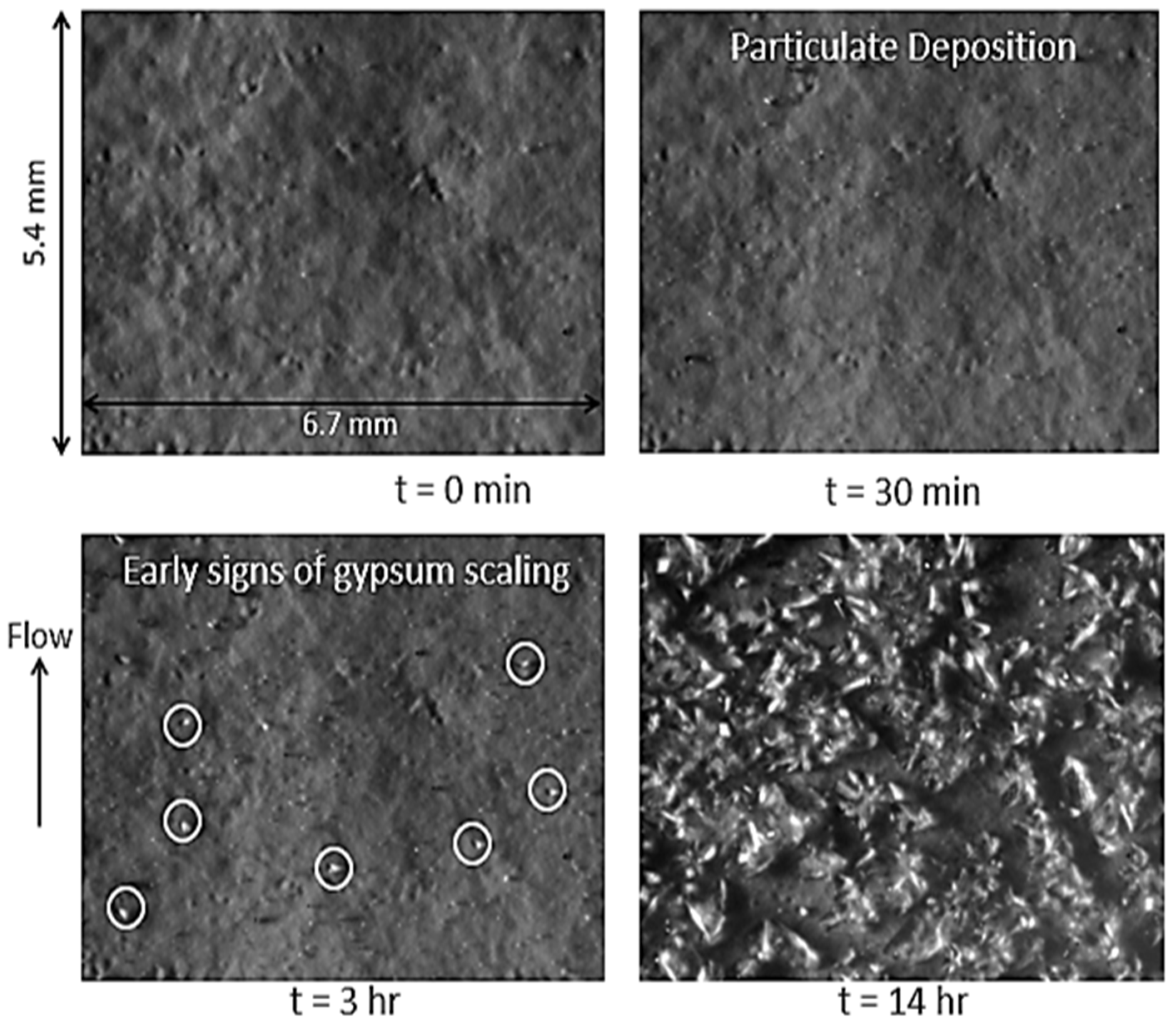
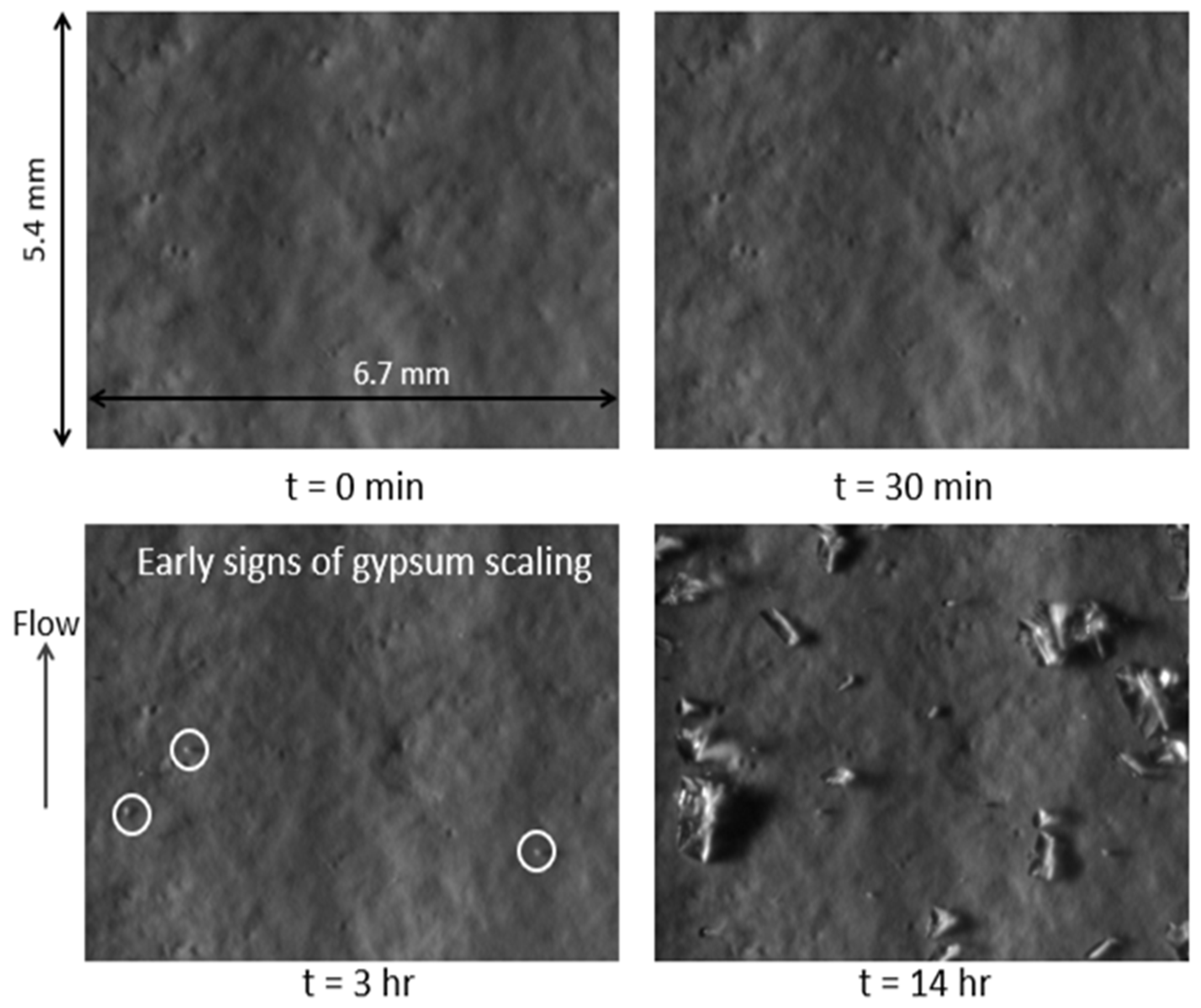
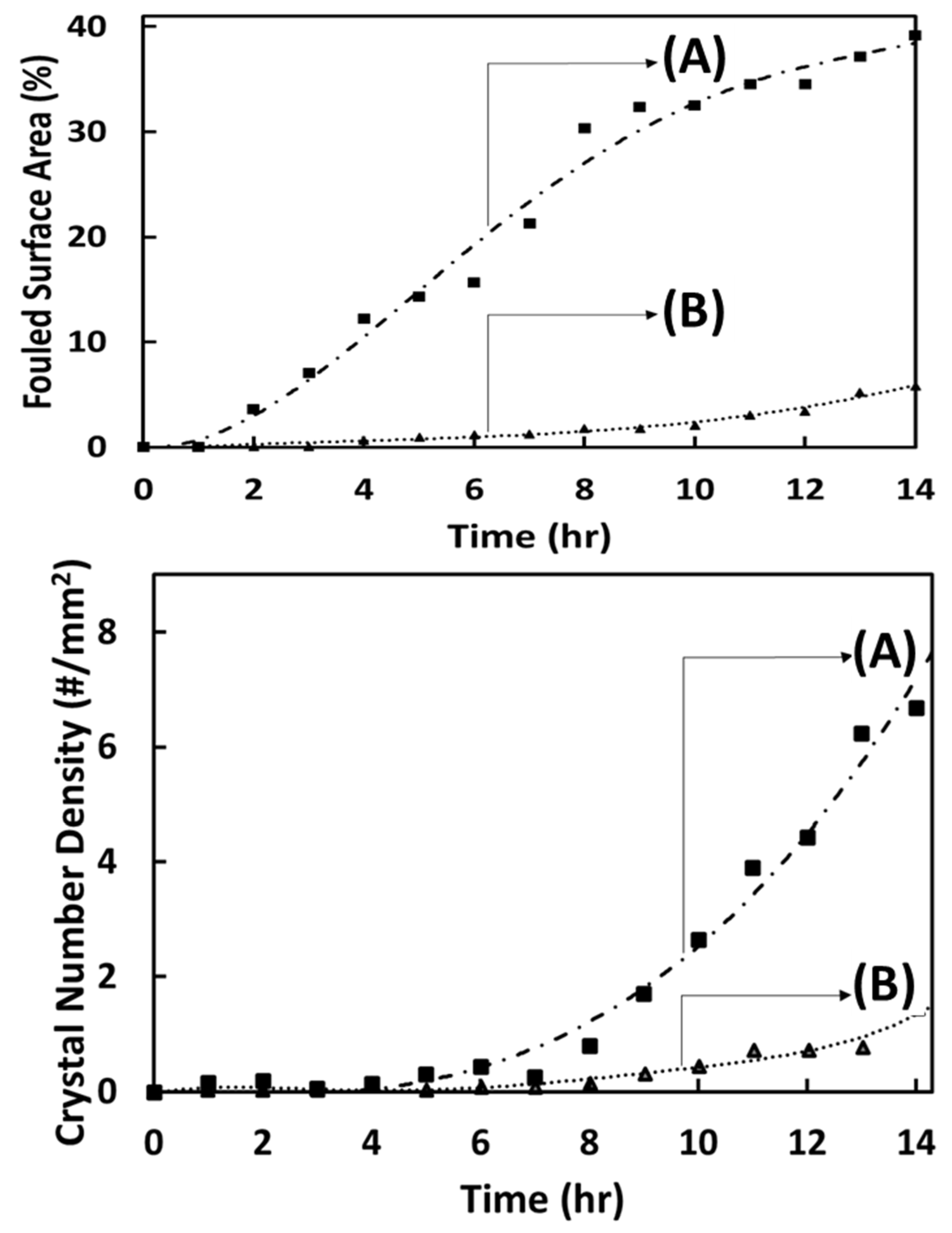
Impact of Feed Prefiltration Treatment on RO Permeate Flux and Surface Fouling/Scaling
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Bystrianský, M.; Nir, O.; Šír, M.; Honzajková, Z.; Vurm, R.; Hrychová, P.; Bervic, A.; van der Bruggen, B. The presence of ferric iron promotes calcium sulphate scaling in reverse osmosis processes. Desalination 2016, 393, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Rolf, J.; Wang, Z.; Violet, C.; Elimelech, M. Distinct impacts of natural organic matter and colloidal particles on gypsum crystallization. Water Res. 2022, 218, 118500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniz, G.L.; Camargo, A.P.; Signorelli, F.; Bertran, C.A.; Pereira, D.J.S.; Frizzone, J.A. Influence of suspended solid particles on calcium carbonate fouling in dripper labyrinths. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 273, 107890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Paudyal, S.; Wang, X.; Dai, C.; Ko, S.; Li, W.; Kan, A.T.; Tomson, M.B. Gypsum scale formation and inhibition kinetics with implications in membrane system. Water Res. 2022, 225, 119166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xu, G.-R.; Das, R. Inorganic scaling in reverse osmosis (RO) desalination: Mechanisms, monitoring, and inhibition strategies. Desalination 2019, 468, 114065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinthaki, A.; Kamaratou, M.; Skordalou, G.; Petratos, G.; Tramaux, A.; David, G.; Demadis, K.D. A universal scale inhibitor: A dual inhibition/dispersion performance evaluation under difficult brine stresses. Geothermics 2021, 89, 101972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, T.; Wallace, A.F.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Z. Mineral scaling in membrane desalination: Mechanisms, mitigation strategies, and feasibility of scaling-resistant membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 579, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melliti, E.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Elfil, H. Combined iron oxides and gypsum fouling of reverse osmosis membranes during desalination process. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 653, 120472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nthunya, L.N.; Bopape, M.F.; Mahlangu, O.T.; Mamba, B.B.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Quist-Jensen, C.A.; Richards, H. Fouling, performance and cost analysis of membrane-based water desalination technologies: A critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, A.; Rahman, F.; Shafi, H.Z.; Zubair, S.M. Scaling of reverse osmosis membranes used in water desalination: Phenomena, impact, and control; future directions. Desalination 2019, 455, 135–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Kaufmann, F.; Rahardianto, A.; Cohen, Y. Desupersaturation of RO concentrate and gypsum removal via seeded precipitation in a fluidized bed crystallizer. Water Res. 2021, 190, 116766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyllönen, H.; Grönroos, A.; Järvelä, E.; Heikkinen, J.; Tang, C. Experimental aspects of scaling control in membrane filtration of mine water. Mine Water Environ. 2017, 36, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrouli, S.; Karabelas, A.; Karanasiou, A.; Kostoglou, M. Incipient calcium carbonate scaling of desalination membranes in narrow channels with spacers—Experimental insights. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 425, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmulevsky, M.; Li, X.; Shemer, H.; Hasson, D.; Semiat, R. Analysis of the onset of calcium sulfate scaling on RO membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 524, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshchepkov, M.; Popov, K.; Kovalenko, A.; Redchuk, A.; Dikareva, J.; Pochitalkina, I. Initial Stages of Gypsum Nucleation: The Role of “Nano/Microdust”. Minerals 2020, 10, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Huang, H.; Han, Y. The role of diffusion in the nucleation of calcium carbonate. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 43, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapidot, T.; Matar, O.K.; Heng, J.Y. Calcium sulphate crystallisation in the presence of mesoporous silica particles: Experiments and population balance modelling. J. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 202, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Davis, T.E.; Tarabara, V.V. Crystillization of calcium sulfate dihydrate in the presence of colloidal silica. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 11344–11350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Z. Impact of gypsum supersaturated water on the uptake of copper and xanthate on sphalerite. Miner. Eng. 2013, 49, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trukhina, M.; Popov, K.; Oshchepkov, M.; Tkachenko, S.; Vorob’eva, A.; Rudakova, G. Impact of colloidal iron hydroxide and colloidal silicon dioxide on calcium sulfate crystallization in the presence of antiscalants. Int. J. Corros. Scale Inhib. 2022, 11, 1147–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Lee, T.; Cheng, Y.; Cohen, Y. Observed crystallization induction time in seeded gypsum crystallization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 23359–23365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCool, B.C.; Rahardianto, A.; Faria, J.I.; Cohen, Y. Evaluation of chemically-enhanced seeded precipitation of RO concentrate for high recovery desalting of high salinity brackish water. Desalination 2013, 317, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Starchenko, V.; Rampal, N.; Yang, F.; Yang, X.; Xiao, X.; Lee, W.-K.; Stack, A.G. Opposing Effects of Impurity Ion Sr2+ on the Heterogeneous Nucleation and Growth of Barite (BaSO4). Cryst. Growth Des. 2021, 21, 5828–5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnaseri, M.; Peyghambarzadeh, S.M. Interference effect of suspended particles on the crystallization fouling: A critical review. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Ladewig, B.P. A review of reverse osmosis membrane fouling and control strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.; Rahardianto, A.; Kim, S.; Bilal, M.; Breckenridge, R.; Cohen, Y. Real-time direct detection of silica scaling on RO membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 528, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AzadiAghdam, M.; Park, M.; Lopez-Prieto, I.J.; Achilli, A.; Snyder, S.A.; Farrell, J. Pretreatment for water reuse using fluidized bed crystallization. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 35, 101226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.; Walker, J.S.; Wolfe, T.; Coleman, K.; Cohen, Y. Scale up of polyamide reverse osmosis membranes surface modification with tethered poly(acrylic acid) for fabrication of low fouling spiral-wound elements. Desalination 2022, 536, 115762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.; Rahardianto, A.; Gu, H.; Uchymiak, M.; Bartman, A.; Hedrick, M.; Lara, D.; Cooper, J.; Faria, J.; Christofides, P.D.; et al. Rapid field assessment of RO desalination of brackish agricultural drainage water. Water Res 2013, 47, 2649–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCool, B.C.; Rahardianto, A.; Faria, J.; Kovac, K.; Lara, D.; Cohen, Y. Feasibility of reverse osmosis desalination of brackish agricultural drainage water in the San Joaquin Valley. Desalination 2010, 261, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Rahardianto, A.; Gao, L.; Caro, X.; Giralt, J.; Rallo, R.; Christofides, P.; Cohen, Y. Fouling indicators for field monitoring the effectiveness of operational strategies of ultrafiltration as pretreatment for seawater desalination. Desalination 2018, 431, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Khan, B.; Gu, H.; Christofides, P.; Cohen, Y. Modeling UF fouling and backwash in seawater RO feedwater treatment using neural networks with evolutionary algorithm and Bayesian binary classification. Desalination 2021, 513, 115129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartman, A.R.; Lyster, E.; Rallo, R.; Christofides, P.D.; Cohen, Y. Mineral scale monitoring for reverse osmosis desalination via real-time membrane surface image analysis. Desalination 2011, 273, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyster, E.; Au, J.; Rallo, R.; Giralt, F.; Cohen, Y. Coupled 3-D hydrodynamics and mass transfer analysis of mineral scaling-induced flux decline in a laboratory plate-and-frame reverse osmosis membrane module. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 339, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyster, E.; Cohen, Y. Numerical study of concentration polarization in a rectangular reverse osmosis membrane channel: Permeate flux variation and hydrodynamic end effects. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 303, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyster, E.; Kim, M.-M.; Au, J.; Cohen, Y. A method for evaluating antiscalant retardation of crystal nucleation and growth on RO membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 364, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchymiak, M.; Lyster, E.; Glater, J.; Cohen, Y. Kinetics of gypsum crystal growth on a reverse osmosis membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 314, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchymiak, M.; Rahardianto, A.; Lyster, E.; Glater, J.; Cohen, Y. A novel RO ex situ scale observation detector (EXSOD) for mineral scale characterization and early detection. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 291, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Y.; Rahardianto, A.; Christofides, P.; Thompson, J.; Gao, L. Pilot-Scale Evaluation of High Recovery Desalination of Agricultural Drainage Water with Smart Integrated Membrane Systems (SIMS), Desalination and Water Purification Research and Development Report No. 173; Bureau of Reclamation, Department of the Interior Denver Federal Center: Denver, CO, USA, 2016; pp. 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, H.; Bartman, A.R.; Uchymiak, M.; Christofides, P.D.; Cohen, Y. Self-adaptive feed flow reversal operation of reverse osmosis desalination. Desalination 2013, 308, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.; Woods, R. Digital Image Processing; Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing, Co. Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Krishna, A.; Rao, G.; Sravya, M. Contrast Enhancement Techniques Using Histogram Equalization on Color Images with Poor Lighting. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. Appl. 2013, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahardianto, A.; McCool, B.; Cohen, Y. Reverse osmosis desalting of inland brackish water of high gypsum scaling propensity: Kinetics and mitigation of membrane mineral scaling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4292–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, Y.; Korngold, E.; Daltrophe, N.; Messalem, R.; Volkman, Y.; Aronov, L.; Weismann, M.; Bouriakov, N.; Glueckstern, P.; Gilron, J. Pilot studies on high recovery BWRO-EDR for near zero liquid discharge approach. Desalination 2010, 261, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshchepkov, M.; Golovesov, V.; Ryabova, A.; Frolova, S.; Tkachenko, S.; Kamagurov, S.; Rudakova, G.; Popov, K. Synthesis and Visualization of a Novel Fluorescent-Tagged Polymeric Antiscalant during Gypsum Crystallization in Combination with Bisphosphonate Fluorophore. Crystals 2020, 10, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilron, J. Brine Treatment and High Recovery Desalination. In Emerging Membrane Technology for Sustainable Water Treatment; Singh, R., Hankins, N., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 3, pp. 297–324. [Google Scholar]
- Hydranautics. RO Water Chemistry. 2001. Available online: https://novoagua.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/04/RO_Water_Chemistry.pdf (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Dupont. FilmTec™ Reverse Osmosis Membranes Technical Manual. 2022. Available online: https://www.dupont.com/content/dam/dupont/amer/us/en/water-solutions/public/documents/en/RO-NF-FilmTec-Manual-45-D01504-en.pdf (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Gao, L.; Gu, H.; Rahardianto, A.; Christofides, P.; Cohen, Y. Self-adaptive cycle-to-cycle control of in-line coagulant dosing in ultrafiltration for pre-treatment of reverse osmosis feed water. Desalination 2017, 401, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Major Analytes/Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) (mg/L) | 14,160 |
| Total Suspended Solids (mg/L) | 8.6 |
| Total Organic Carbon (mg/L) | 8.3 |
| Barium (mg/L) | <0.1 |
| Boron (mg/L) | 49.8 |
| Calcium (mg/L) | 549 |
| Chloride (mg/L) | 3042 |
| Magnesium (mg/L) | 358 |
| Nitrate (mg/L) | 122 |
| Potassium (mg/L) | 15.1 |
| Silica (mg/L) | 37 |
| Sodium (mg/L) | 3772 |
| Strontium (mg/L) | 6.7 |
| Sulfate (mg/L) | 6047 |
| Turbidity (NTU) (a) | 1.1 |
| pH | 7.6 |
| SIcalcite(b) | 7.0 |
| SIgypsum(b) | 0.97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jarma, Y.A.; Thompson, J.; Khan, B.M.; Cohen, Y. Field Evaluation of UF Filtration Pretreatment Impact on RO Membrane Scaling. Water 2023, 15, 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15050847
Jarma YA, Thompson J, Khan BM, Cohen Y. Field Evaluation of UF Filtration Pretreatment Impact on RO Membrane Scaling. Water. 2023; 15(5):847. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15050847
Chicago/Turabian StyleJarma, Yakubu A., John Thompson, Bilal M. Khan, and Yoram Cohen. 2023. "Field Evaluation of UF Filtration Pretreatment Impact on RO Membrane Scaling" Water 15, no. 5: 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15050847
APA StyleJarma, Y. A., Thompson, J., Khan, B. M., & Cohen, Y. (2023). Field Evaluation of UF Filtration Pretreatment Impact on RO Membrane Scaling. Water, 15(5), 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15050847






