Response Surface Optimization and Floc Structure Analysis of Magnetic Flocculation Technology for Anaerobic Digestion Reject Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Laboratory Water Quality
2.2. Agents and Instruments
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Response Surface Optimization
2.3.2. Analysis of Floc
Particle Size
SEM
FTIR
Influence of D2f of Flocs on FA
- (1)
- The determination of D2f
- (2)
- The determination of FA
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of SS and Fe3+ Contents in Sludge Dewatering Liquid
3.1.1. Model Variance Analysis of SS
3.1.2. Response Surface Diagram and Parameter Optimization of SS
3.1.3. Model Variance Analysis of Fe3+
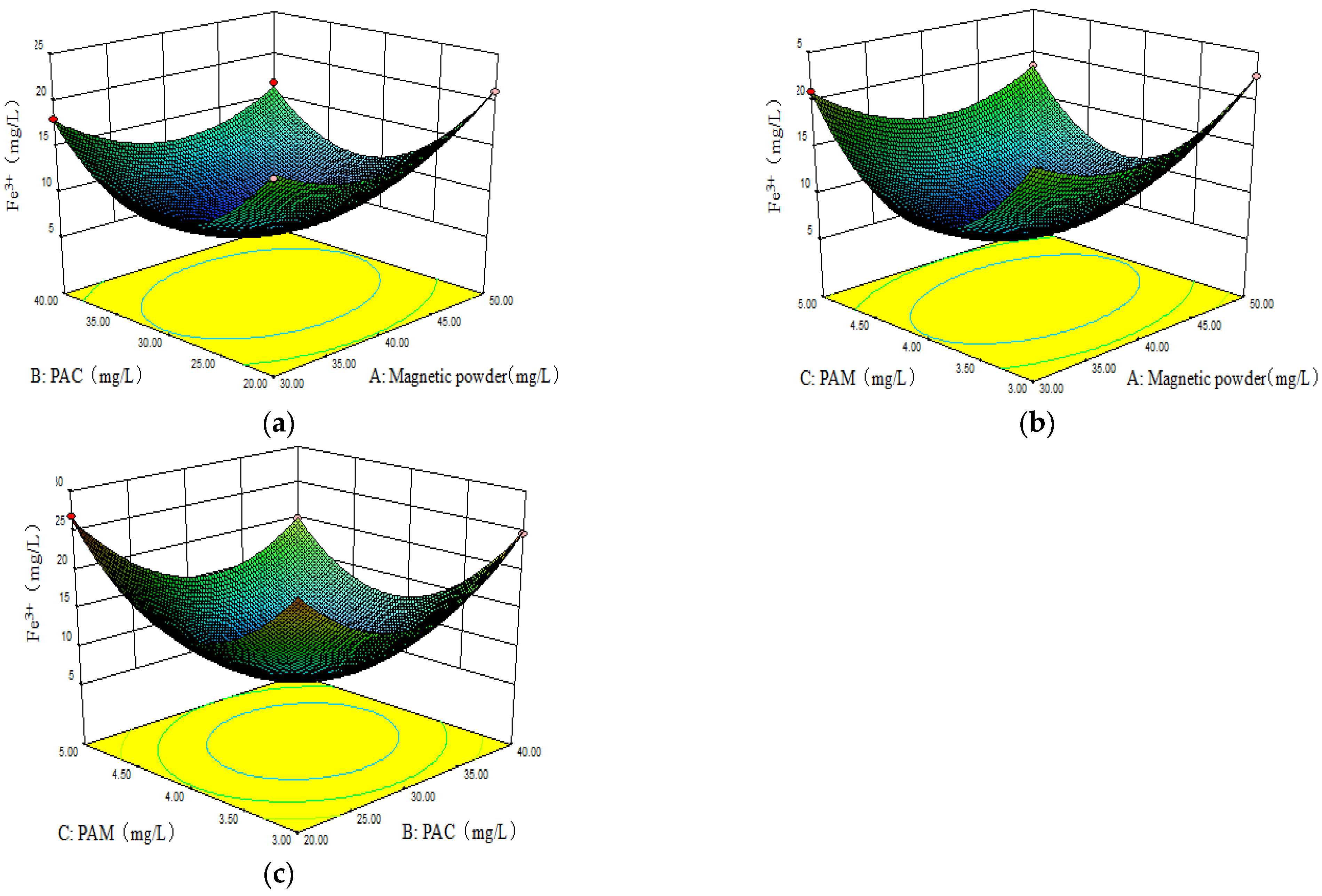
3.1.4. Response Surface Diagram and Parameter Optimization of Fe3+
3.1.5. Model Validation
3.2. Particle Size Analysis of Flocs
3.3. SEM Analysis of Flocs
3.4. FTIR Analysis of Flocs
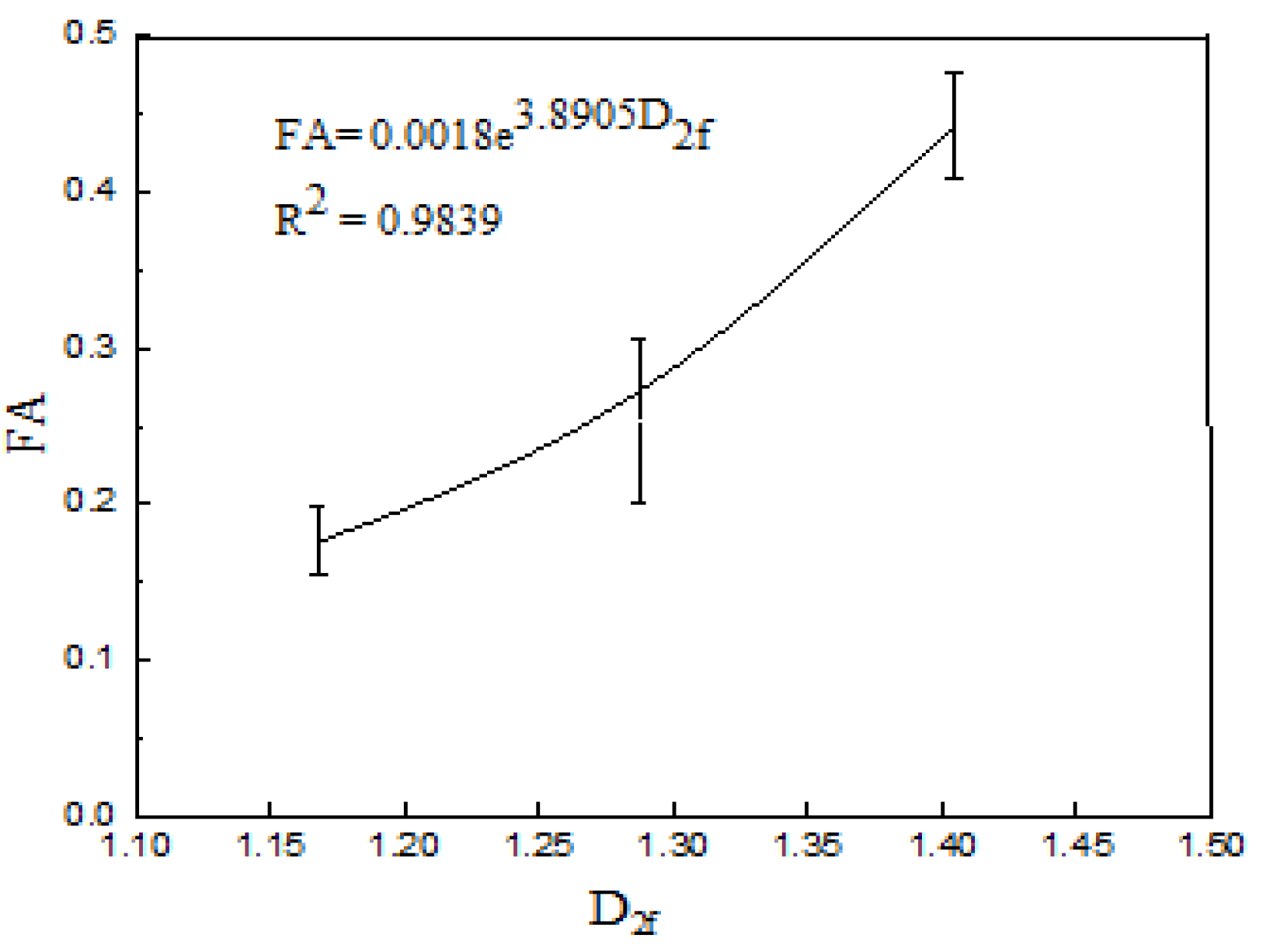
3.5. Influence of D2f of Flocs on FA
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chynoweth, D.P.; Owens, J.M.; Teixeire, A.A.; Pullammanappallil, P.; Luniya, S.S. Anaerobic digestion of space mission wastes. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 53, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierkiel, A.; Lanting, J. Membrane-coupled anaerobic digestion of municipal sewage sludge. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 52, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Shin, J.H.; Shin, S.G.; Lee, J.Y. Effect of magnetite supplementation on mesophilic anaerobic digestion of phenol and benzoate: Methane production rate and microbial communities. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 350, 126943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, P.; Steyer, J.-P.; Volcke, E.I.P.; Bernet, N.; Beline, F. Combined anaerobic digestion and biological nitrogen removal for piggery wastewater treatment: A modelling approach. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-C.; Peng, Y.-Z.; Zhang, J.-W.; Du, R. Multiple roles of complex organics in polishing THP-AD filtrate with double-line anammox: Inhibitory relief and bacterial selection. Water Res. 2022, 216, 118373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, K.I.; Choi, E. Nitrogen removal by recycle water nitritation as an attractive alternative for retrofit technologies in municipal wastewater treatment plants. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 49, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.H.; Choi, H.C. Autotrophic nitrogen removal from sludge digester liquids in up flow sludge bed reactor with external aeration. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 1945–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Xie, Y.; Fang, F.; Hu, H. Influences of Fe3+ on phosphorus removal andmicrobial products in denitrifying phosphorus removal system. Res. Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Mena, N.P.; Bulteau, A.L.; Salazar, J.; Hirsch, E.C.; Núñez, M.T. Effect of mitochondrial complex I inhibition on Fe–S cluster protein activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 409, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, M.; You, S.; Ma, D.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Z. Effect of Fe3+ on the sludge properties and microbial community structure in a lab-scale A2O process. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Sui, Q.W.; Yu, D.W.; Zheng, L.B.; Chen, M.X.; Ritigala, T.; Wei, Y.S. Development of a short-cut combined magnetic coagulation-sequence batch membrane bioreactor for swine wastewater treatment. Membranes 2021, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackner, S.; Gilbert, E.M.; Vlaeminck, S.E.; Joss, A.; Horn, H.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Full-scale partial nitritation/anammox experiences: An application survey. Water Res. 2014, 55, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Qin, Y.; Yang, S.; Lu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Q.; Zheng, L. Two-dimensional metal-organic framework nanobelts for selective Fe3+ removal from aqueous solution with high adsorption capacity. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 239, 116559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, H.; Sharma, K.; Saktaywin, W. Performance of an ultra-low-pressure reverse osmosis membrane (ULPROM) for separating heavy metal: Effects of interference parameters. Desalination 2002, 144, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Shabanian, M. Novel electrodialysis cation exchange membrane prepared by 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid; heavy metal ions removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 337, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, M.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zeng, J.Y.; Liu, J.F.; Sun, M.C.; Yadav, R.S.; Feng, Y.J. Roles of magnetic particles in magnetic seeding coagulation-flocculation process for surface water treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakawa, D.; Shirasaki, N.; Matsushita, T.; Matsui, Y.; Yamashita, R.; Matsumura, T.; Koriki, S. Evaluation of reduction efficiencies of pepper mild mottle virus and human enteric viruses in full-scale drinking water treatment plants employing coagulation-sedimentation–rapid sand filtration or coagulation–microfiltration. Water Res. 2022, 213, 118160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, J.K.; Jabin, S.; Bhatia, H.S. Optimization of coagulation-flocculation process for food industry waste water treatment using polyelectrolytes with inorganic coagulants. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2015, 92, 1697–1703. [Google Scholar]
- Bosak, V.K.; Vanderzaag, A.C.; Crolla, A.; Kinsley, C.; Chabot, D.; Miller, S.S.; Gordon, R.J. Treatment of potato farm wastewater with sand filtration. Environ. Technol. 2016, 37, 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.C.; Chang, C.C. Effectively recycling swine wastewater by coagulation-flocculation of nonionic polyacrylamide. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipus, L.C.; Krope, J.; Crepinsek, L. Dispersion destabilization in magnetic water treatment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 236, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisa, T.; Jason, L.S.; Andrew, H. Depositional remanent magnetization: Toward an improved theoretical and experimental foundation. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2006, 244, 515–529. [Google Scholar]
- Noor, M.H.M.; Wong, S.; Ngadi, N.; Inuwa, I.M.; Opotu, L.A. Assessing the effectiveness of magnetic nanoparticles coagulation/flocculation in water treatment: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 19, 6935–6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Y.-J.; Ouyang, Z.-Z.; Shen, T.T.; Wang, X.K. Preparation and characterization of polymer-coated Fe3O4 magnetic flocculant. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-Y.; Zheng, H.-L.; Xiang, W.-Y.; An, Y.Y.; Xu, B.C.; Zhao, C.L.; Zhang, S.X. Magnetic flocculation of anion dyes by a novel composite coagulant. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 143, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.J.; Li, C.-L.; Fu, X.-Y.; Wu, M.; Wen, S.-M. Beneficiation of micro-fine magnetic minerals from reductive iron ore with ultrafine grinding-magnetic flocculation separation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.-Q.; Nguyen, A.V. A review of principles and applications of magnetic flocculation to separate ultrafine magnetic particles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 172, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.-F.; Jin, W.-B.; Tu, R.-J.; Gao, S.-H.; Zhou, X. Microalgae harvesting by magnetic flocculation for biodiesel production: Current status and potential. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Luo, M.; Cai, W.-F. Influence of operating parameters on the performance of magnetic seeding flocculation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 2873–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Chen, P.; Wang, Z.C. Magnetic composite Ca(OH)2/Fe3O4 for highly efficient flocculation in papermaking black liquor without pH neutralization. Adv. Powder Technol. 2021, 32, 2457–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.L. Experimental study on deep treatment of coking wastewater by magnetic flocculation. Ind. Water Wastewater 2012, 43, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zielinski, M.; Rusanowska, P.; Debowski, M.; Hajduk, A. Influence of static magnetic field on sludge properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Chi, Y.-Z.; Zhang, H.-L.; Zhao, J.-H.; Ding, Y.-M.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Li, Y.-Y. Enhanced treatment of anaerobic digestion reject water by magnetic flocculation technology. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 2020, 39, 4693–4701. [Google Scholar]
- Bajpai, M.; Katoch, S.S. Techno-economical optimization using Box-Behnken (BB) design for chemical oxygen demand and chloride reduction from hospital wastewater by electro-coagulation. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 2140–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-Y.; Sun, J.; Zhou, J.; Chen, A.; Shah, K.J. Preparation and characterization of high-efficiency magnetic heavy metal capture flocculants. Water 2021, 13, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.; Nover, D.; Schladow, S.G. Using laser diffraction data to obtain accurate particle size distributions: The role of particle composition. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2010, 8, 507–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Qin, X.-L.; Yuan, J.-L.; Qiu, Y.; Tang, S.-H. Preparation, Characterization and decolorization performance of magnetic adsorbent pellets formed by the utilization of electric flocculation sludge. Chemistryselect 2021, 6, 7285–7294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.J.; Lu, S.C.; Yiacoum, S.; Tsouris, C. Fractal dimension of particle aggregates in magnetic fields. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2004, 39, 2839–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B.B. The Fractal Geometry of Nature; Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 1982; pp. 1–60. [Google Scholar]
- Meakin, P. Fractal Scaling and Growth Far from Equilibrium; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 1998; p. 83. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, B.; Wilén, B.M.; Lant, P. A comprehensive imsight into floc characteristics and their impact on compressibility and settleability of activated sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2003, 95, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.-Z.; Gregory, J.; Yang, Y.-L.; Sun, M.; Liu, T.; Li, G.-B. The effect of coagulation and applied breakage shear on the re-growth of kaolin flocs. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2010, 27, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborti, R.K.; Gardner, K.H.; Atkinson, J.F.; Van Benschoten, J.E. Changes in fractal dimension during aggregation. Water Res. 2003, 37, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorand, F.; Zartarian, F.; Thomas, F.; Block, J.C.; Manem, J. Chemical and structural (2D) linkage between bacteria within a within activated sludge flocs. Water Res. 1995, 29, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mietta, F.; Chassagne, C.; Verney, R.; Winterwerp, J.C. On the behavior of mud floc size distribution: Model calibration and model behavior. Ocean Dyn. 2011, 61, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-Y.; Yu, W.-Z.; Qu, J.-H.; Gregory, J. The variation of flocs activity during floc breakage and aging, adsorbing phosphate, humic acid and clay particles. Water Res. 2019, 155, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilén, B.M.; Jin, B.; Lant, P. The influence of key chemical constituents in activated sludge on surface and flocculating properties. Water Res. 2003, 37, 2127–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.-L.; Jiang, G.-C.; Li, X.-L.; Yang, L.-L.; Liu, F.; He, Y.-B. Flocculation of submicron particles in water-based drilling fluids by CMC-g-DMDAAC. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 162, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.J.; Chen, P.-W.; Wang, L.-J. Removal of nanoparticles from CMP wastewater by magnetic seeding aggregation. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 1809–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-M.; Li, X.; Zhan, P.; Hu, F.-P.; Ye, X. Removal of cadmium and copper from water by a magnetic adsorbent of PFM: Adsorption performance and micro-structural morphology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 206, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-M.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, F.-P.; Duan, X.-Y.; Ye, X. Adsorption performance and micro-structural morphology of a novel magnetic composite adsorbent for removing Cd2+ from water. Microchem. J. 2019, 146, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.-H.; Chang, Q.; Zeng, L.-Y. Velocity field structure and flocculation efficiency in Taylor-Couette flow. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Chu, Y.-B.; Gao, B.-Y.; Yue, Q.-Y. The dye or humic acid water treatment and membrane fouling by polyaluminum chloride composited with sodium alginate in coagulation-ultrafiltration process. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 2202–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.-L.; Wu, X.-G.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Zhang, D.-B. Application of response surface methodology to the treatment landfill leachate in a three-dimensional electrochemical reactor. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 2096–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Li, Q.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, L.; Wei, Y. Study on characteristics and mechanism of magnetic coagulationfor pollutants removal in black and odorous water. Technol. Water Treat. 2021, 47, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, D.; Kang, S.; Li, C.; Zheng, L.; Wei, Y. The application and coagulation mechanism of magnetic coagulation in treating mixed sewage from small towns. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2022, 42, 268–278. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.-Y.; Xia, W.; Fu, X.; Ding, L.; Kong, Y.-L.; Zhang, H.-W.; Fu, K. Magnetic flocculation of algae-laden raw water and removal of extracellular organic matter by using composite flocculant of Fe3O4/cationic polyacrylamide. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liang, W.-Y.; Liu, L.-J.; Li, F.-Z.; Fan, Q.-L.; Sun, X.-L. Harvesting Chlorella vulgaris by magnetic flocculation using Fe3O4 coating with polyaluminium chloride and polyacrylamide. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 198, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.-Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.-W.; Gao, Y.-X.; Naitoc, T.; Oinumac, G.; Inanagac, Y.; Yang, M. Rapid removal of polyacrylamide from wastewater by plasma in the gas-liquid interface. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 83, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.-X.; Feng, P.; Zhang, W. Rapid solidification of Portland cement/polyacrylamide hydrogel (PC/PAM) composites for diverse wastewater treatments. Rsc Adv. 2020, 10, 18936–18944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérin, L.; Coufort-Saudejaud, C.; Liné, A.; Frances, C. Dynamics of aggregate size and shape properties under sequenced flocculation in a turbulent Taylor-Couette reactor. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 491, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.-J.; Wen, S.-M.; Liu, D.-W.; Zhang, W.-B. Separation of phosphorus and magnetic mineral fines from siderite reductive ore by applying magnetic flocculation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 1434–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-L.; Liu, P.-K.; Xiao, L.-J.; Zhang, Y.-K.; Yang, X.-H.; Jiang, L.-Y. Experimental study on flocculation effect of tangential velocity in a cone-plate clarifier. Separations 2021, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.-B.; Han, Y.-X.; Li, W.-B.; Zhu, Y.-M. Study on polymer-bridging flocculation performance of ultrafine specular hematite ore and its high gradient magnetic separation behavior: Description of floc microstructure and flocculation mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 119304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edzwald, J.K.; Tobiason, J.E. Enhanced coagulation: US requirements and a broader view. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.-H.; Han, H.-S.; Wei, Z.; Sun, W.; Yue, T. Recovery of ultrafine scheelite particles by magnetic seeding flocculation and its mechanism. Colloids Serfaces A Hysicochemical Eng. Asp. 2021, 628, 127266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H.-W.; Guo, W.-S.; Ngo, H.H. Feasibility study on magnetic enhanced flocculation for mitigating membrane fouling. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 26, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zularisam, A.W.; Ismail, A.F.; Salim, M.R.; Sakinah, M.; Hiroaki, O. Fabrication, fouling and foulant analyses of asymmetric polysulfone (PSF) ultrafiltration membrane fouled with natural organic matter (NOM) source waters. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 299, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, W.; Shen, H.-Y.; Zhang, H.-Q.; Gu, N. Preparation and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles coated by amino silane. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2003, 212, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, J.; Jia, H.; Wen, H.-T.; Li, J.; Liu, W.-B.; Li, J.-Y. The investigation on Fe3O4 magnetic flocculation for high efficiency treatment of oily micro-polluted water. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 24, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Q. Correlations between floc physical properties and optimum polymer dosage in alum sludge condtioning and dewatering. Chem. Eng. J. 2003, 92, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.-Q.; Allen, D.G.; Droppo, I.G. Surface properties of sludge and their role in bioflocculation and settleability. Water Res. 2001, 35, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatasou, S.; Santamouris, M. Detection of low-dimensional chaos in buildings energy consumption time series. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2010, 15, 1603–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F. Study on focculation kinetics based on coagulation and precipitation integration process. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]







| Indicators | pH | SS (mg/L) | COD (mg/L) | Total Iron (mg/L) | Fe2+ (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw water | 7.0 ± 0.2 | 450 ± 80 | 387 ± 125 | 364 ± 32 | 129 ± 34 |
| Test water | 7.0 ± 0.2 | 450 ± 80 | 343 ± 62 | 364 ± 32 | <1 |
| Level | A /mg·L−1 | B /mg·L−1 | C /mg·L−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 30 | 20 | 3 |
| 0 | 40 | 30 | 4 |
| 1 | 50 | 40 | 5 |
| Number | A | B | C | SS /mg·L−1 | Fe3+ /mg·L−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 26.11 | 24.68 |
| 2 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 19.94 | 18.07 |
| 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 21.05 | 19.85 |
| 4 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 26.31 | 24.96 |
| 5 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 24.54 | 22.59 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10. 46 | 5.87 |
| 7 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 20.08 | 18.46 |
| 8 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 22.85 | 19.77 |
| 9 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 15.34 | 16.54 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10.39 | 6. 39 |
| 11 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 23.16 | 21.05 |
| 12 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 20.38 | 18.43 |
| 13 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 27.86 | 26.85 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10.32 | 5.1 |
| 15 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 23.37 | 20.94 |
| 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10. 15 | 6.12 |
| 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9.92 | 6.18 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | p | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 668.69 | 9 | 74.3 | 1262.49 | <0.0001 | 0.9994 |
| A | 1.46 | 1 | 1.46 | 24.84 | 0.0016 | |
| B | 29.15 | 1 | 29.15 | 495.26 | <0.0001 | |
| C | 6.94 | 1 | 6.94 | 117.89 | <0.0001 | |
| AB | 13.62 | 1 | 13.62 | 231.37 | <0.0001 | |
| AC | 6.2 | 1 | 6.2 | 105.35 | <0.0001 | |
| BC | 10.92 | 1 | 10.92 | 185.61 | <0.0001 | |
| A2 | 49.17 | 1 | 49.17 | 835.48 | <0.0001 | |
| B2 | 153.59 | 1 | 153.59 | 2609.89 | <0.0001 | |
| C2 | 344.45 | 1 | 344.45 | 5852.99 | <0.0001 | |
| Residual | 0.41 | 7 | 0.059 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 0.22 | 3 | 0.075 | 1.6 | 0.3232 | |
| Pure Error | 0.19 | 4 | 0.047 | |||
| Total | 669.1 | 16 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | p | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 895.41 | 9 | 99.49 | 713.49 | <0.0001 | 0.9989 |
| A | 0.26 | 1 | 0.26 | 1.83 | 0.2178 | |
| B | 18.45 | 1 | 18.45 | 132.33 | <0.0001 | |
| C | 4.35 | 1 | 4.35 | 31.2 | 0.0008 | |
| AB | 4.31 | 1 | 4.31 | 30.88 | 0.0009 | |
| AC | 7.02 | 1 | 7.02 | 50.36 | 0.0002 | |
| BC | 11.29 | 1 | 11.29 | 80.96 | <0.0001 | |
| A2 | 81.21 | 1 | 81.21 | 582.39 | <0.0001 | |
| B2 | 271.96 | 1 | 271.96 | 1950.31 | <0.0001 | |
| C2 | 417.21 | 1 | 417.21 | 2991.99 | <0.0001 | |
| Residual | 0.98 | 7 | 0.14 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 0.8 | 3 | 0.27 | 5.91 | 0.0595 | |
| Pure Error | 0.18 | 4 | 0.045 | |||
| Total | 896.39 | 16 |
| Methods | D2f | FA |
|---|---|---|
| PAC | 1.1681 ± 0.0851 | 0.1762 ± 0.0221 |
| PAC + PAM | 1.2876 ± 0.1092 | 0.2534 ± 0.0523 |
| Magnetic flocculation | 1.4046 ± 0.0936 | 0.4425 ± 0.0345 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, B.; Chi, Y.; Chi, Y.; Zhao, J.; Fu, C.; Wang, X.; Tian, S.; Ding, Y. Response Surface Optimization and Floc Structure Analysis of Magnetic Flocculation Technology for Anaerobic Digestion Reject Water. Water 2023, 15, 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040707
Xu B, Chi Y, Chi Y, Zhao J, Fu C, Wang X, Tian S, Ding Y. Response Surface Optimization and Floc Structure Analysis of Magnetic Flocculation Technology for Anaerobic Digestion Reject Water. Water. 2023; 15(4):707. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040707
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Bo, Yongzhi Chi, Yiyang Chi, Jianhai Zhao, Cuilian Fu, Xueke Wang, Sufeng Tian, and Yanmei Ding. 2023. "Response Surface Optimization and Floc Structure Analysis of Magnetic Flocculation Technology for Anaerobic Digestion Reject Water" Water 15, no. 4: 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040707





