Abstract
Agriculture has significantly aided in meeting the food needs of growing population. In addition, it has boosted economic development in irrigated regions. In this study, an assessment of the groundwater (GW) quality for agricultural land was carried out in El Kharga Oasis, Western Desert of Egypt. Several irrigation water quality indices (IWQIs) and geographic information systems (GIS) were used for the modeling development. Two machine learning (ML) models (i.e., adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) and support vector machine (SVM)) were developed for the prediction of eight IWQIs, including the irrigation water quality index (IWQI), sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), soluble sodium percentage (SSP), potential salinity (PS), residual sodium carbonate index (RSC), and Kelley index (KI). The physicochemical parameters included T°, pH, EC, TDS, K+, Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Cl−, SO42−, HCO3−, CO32−, and NO3−, and they were measured in 140 GW wells. The hydrochemical facies of the GW resources were of Ca-Mg-SO4, mixed Ca-Mg-Cl-SO4, Na-Cl, Ca-Mg-HCO3, and mixed Na-Ca-HCO3 types, which revealed silicate weathering, dissolution of gypsum/calcite/dolomite/ halite, rock–water interactions, and reverse ion exchange processes. The IWQI, SAR, KI, and PS showed that the majority of the GW samples were categorized for irrigation purposes into no restriction (67.85%), excellent (100%), good (57.85%), and excellent to good (65.71%), respectively. Moreover, the majority of the selected samples were categorized as excellent to good and safe for irrigation according to the SSP and RSC. The performance of the simulation models was evaluated based on several prediction skills criteria, which revealed that the ANFIS model and SVM model were capable of simulating the IWQIs with reasonable accuracy for both training “determination coefficient (R2)” (R2 = 0.99 and 0.97) and testing (R2 = 0.97 and 0.76). The presented models’ promising accuracy illustrates their potential for use in IWQI prediction. The findings indicate the potential for ML methods of geographically dispersed hydrogeochemical data, such as ANFIS and SVM, to be used for assessing the GW quality for irrigation. The proposed methodological approach offers a useful tool for identifying the crucial hydrogeochemical components for GW evolution assessment and mitigation measures related to GW management in arid and semi-arid environments.
1. Introduction
The Nubian sandstone aquifer is located within the eastern Sahara desert, which is considered one of the world’s largest fossil GW reservoirs. It is shared by Egypt, Libya, Sudan, and Chad and covers an area of more than 2 × 106 km2. GW is critical to Egypt’s economic growth and long-term development, particularly in desert areas [1]. The estimated water storage in the Egyptian side of the aquifer is approximately 40,000 × 109 m3, but this is nonrenewable due to the negligible GW recharge in the Western Desert [1,2]. The Western Desert’s largest oasis was the first to start utilizing Egypt’s Nubian sandstone aquifer on a massive basis, and it is anticipated that the amount of GW extracted will be approximately 2.8 × 109 m3/y by 2020 [1]. GW is the unique resource of the water needed for irrigation and residential usage in El Kharga Oasis. Before 1960, springs and freely flowing shallow wells were used to draw GW for extensive irrigation. Since then, GW use has continuously grown, leading to GW level depletion, necessitating the construction of deeper wells. Because the GW resources in El Kharga Oasis have substantially decreased, proper GW extraction management is strongly advised [3]. Furthermore, a challenge for sustainable GW resource management is the lack of the hydrogeological data required to estimate GW flow and predict the impacts of GW abstraction [3,4,5].
GW is an important water resource for a country’s socioeconomic development. Agriculture, on the other hand, is the world’s largest GW consumer [1]. Irrigation water supply is the essential factor influencing agricultural output growth in arid and semi-arid countries, influencing both sustainable crop productivity and irrigated area expansion. These water resources are threatened by a number of issues, including the effects of environmental issues, human interventions, and natural occurrences [2,6]. Generally, these factors deteriorate the chemical and physical compositions of GW, rendering it unfit for agricultural use.
GW chemistry studies have been widely applied to evaluate water quality. As a result, the physicochemical elements in irrigation water could have negative impacts on crop productivity and soil depletion [7]. Throughout many hydrochemical investigations, the various water quality indicators have also been compared to established values to assess the GW quality. This assessment does not provide decision makers with immediate information and a comprehensive description of the GW quality, especially when multiple water quality degraders are observed. Application programming interfaces, such as the United States Salinity Laboratory (USSL), Doneen, and Wilcox plots, have aided in determining GW suitability for irrigation water [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. In addition, IWQIs are derived from the chemical composition of water, which are considered effective methods for evaluating the suitability of water by combining multiple water key indicators into a single value, which is intended to assist decision makers in water quality management [16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. The IWQIs for agricultural purposes are typically assessed using various indices and variables in accordance with Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) guidelines [23]. The IWQI, KI, SAR, SSP, PS, and RSC are all commonly used to classify GW irrigation suitability, which aids in defining the infiltration capacity of the rock formation [11,24,25,26]. Numerous studies have been conducted worldwide to evaluate the suitability of GW for agricultural purposes by implementing IWQIs and GIS technology, which allow for the separation of quality zones for irrigation by producing GW quality maps [27,28,29,30,31,32,33].
For agricultural production, traditional methods for assessing the quality of irrigation water are frequently expensive and time consuming. This problem can be solved by evaluating and forecasting IWQIs with respect to the physicochemical parameters using ML implementations, such as ANFIS and SVM. In addition, long-term GW management strategies demand the development of fresh, affordable technologies for analyzing and forecasting GW quality. It is essential for secure environmental management to handle this issue through the prediction of water quality indicators. Consequently, a number of deterministic models have been applied in this field recently [13,34,35,36,37].
In water quality modeling, there are typically a number of characteristics that are either very expensive to measure or cannot be measured at all [38]. With regard to water-related issues, a considerable increase has been achieved in the development and use of ML tools. Examples of these tools include ML models. Without knowing the physical behavior explicitly, ML is based on the analysis of data describing the system by mimicking the inter-relationship between the input and output parameters [39]. Traditional models, such as statistical modeling (e.g., ARMA-ARIMA and seasonal ARMA) or ML modeling, such as artificial neural networks (ANNs) and SVM, are examples of ML simulation models [40,41]. The most effective ML models are ANN models, which are often used because of their high predicted accuracy and adaptability [34,35]. The literature reports that ANN models have been effectively used to address a number of challenges in water management [42]. This is because complicated hydrological data and nonlinear functions may be correctly simulated and estimated by these types of models. ANNs have been successfully utilized for forecasting rivers inflows, with a fair level of competence [34,37,38]. Another extensively used ML approach is the SVM model, which is frequently used in modeling hydrology datasets [33,39,40,41]. The SVM model is a technique for reducing the complexity of dynamic systems, modeling nonlinear behaviors, and collecting the information required for making pertinent decisions with a respectable level of accuracy [42]. There are several studies conducted in the study area that focused on the monitoring of the water level, measuring hydraulic parameters, assessing the health risk from the drinking water, and determining the soil quality deterioration with time. For this reason, El Kharga Oasis requires regular monitoring and assessment of the irrigation water quality to investigate how the rapid drawdown of the water level, the geological composition, and anthropogenic activities could affect the irrigation water quality, which affects the quality of the soil as well as crop production, in order to provide recommendations for the sustainable management of water resources in the study area according to the IWQIs [6,43,44].
The major objectives of this work were to (i) define the GW chemistry, GW categories, and their geochemical controlling processes employing physicochemical metrics and imitative techniques; (ii) evaluate the GW’s appropriateness for agricultural purposes utilizing various IWQIs; (iii) investigate the performance of ANFIS and SVM models in the reliable prediction of IWQIs, such as IWQI, SAR, SSP, KI, PS, and RSC.
2. Case Study and Applied Machine Learning
2.1. Site Description and Hydrogeological Settings
El Kharga Oasis is a geomorphologic valley inside the south of the Western Desert (Figure 1). The depression is situated along an anticline with a major axis that stretches north to south and is associated with the fault zones and an elevation ranges from 0 to 120 m [45]. El Kharga Oasis is among the extremely dry regions of the Eastern Sahara, if not the driest place on the planet [46]. The summer seasons are extremely hot, with maximum daily temperatures exceeding 40 degrees Celsius, but winters are mild, with temperatures dropping below zero in the evening. The rainfall is relatively low, averaging <1 mm/y, though torrential storms do occur on occasion [47,48]. El Kharga Oasis is a farming community with roughly 11,400 ha of agricultural land, with date palm being the major cash crop in addition to the olive and other fruits [49]. Groundwater is pumped to the surface by 1100 producer shallow wells with an overall abstraction of 8.3 × 106 m3/y and approximately 300 governmental wells with 198.1 × 106 m3/y. The wells’ locations vary across the considered site, but they are mainly concentrated around main sites, primarily El Kharga, Ghormachine, Paris, and Darb Elarbien [1].
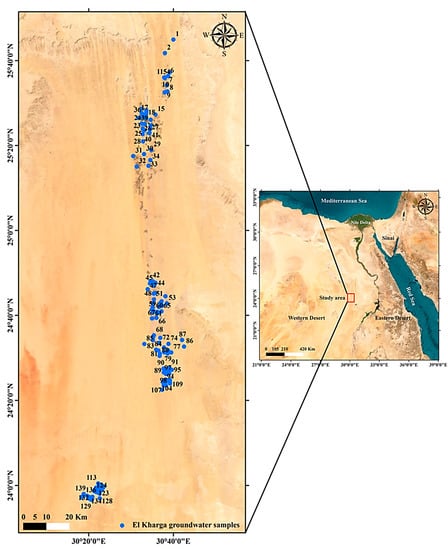
Figure 1.
The location sites of the GW samples in the representative case study.
This study chose the dry land area of El Kharga Oasis to verify the interactions of the hydrogeochemical condition and agriculture systems on the hydrochemical change of the GW. The research area is situated between the longitudes 30°10′ and 30°48′ E and latitudes 24°0′ and 25°48′ N (Table S1). The production wells were established for sustainable agriculture and drinkable water use. Upper Cretaceous sediments (the Quseir Formation) underpin a large portion of the study region, particularly in the east, while only the northeast has outcrops of Tertiary deposits (marly and chalky limestones). Quaternary formations (sand dunes and sabkha sediments) with thicknesses ranging from 2 to 10 m are found in the western part of the region. Furthermore, Precambrian basement rocks (granites) are exposed in the southeast part of the study area.
The New Valley project is regarded as one of Egypt’s significant programs in agriculture development, relying on GW withdrawal from the NSSA. The investigated aquifer represents a relatively small zone from the broad Nubian Aquifer System (NAS), which spans four countries and cover a wide land area (Egypt, Sudan, Libya, and Chad) [50,51,52].
In the study region, the regional direction of the GW flow is a northerly to northeasterly direction (Figure 2). Furthermore, several GW flow directions were recorded. The GW flow direction in the northern part of the study region comes from the southwest to east direction, while from the west to east direction in the central region. Another local GW flow direction from south to northeast was observed in the southern part of the studied area. Large decreases in the GW heads were recorded in some areas due to the effect of over pumping and rapid drawdown. The study area’s severe hydraulic gradients are most likely caused by the region’s high GW abstraction rates, the Nubian aquifer’s comparatively thin saturation thickness, and the sediments’ low hydraulic conductivity [53,54]. The GW is an under unconfined condition in the Baris Oasis and south area of NAS, while it is an under confined system in El Kharga Oasis (Figure 2). Therefore, the potentiality of the northern parts is less than the northern parts. Excessive GW utilization in these areas might result in significant reductions in the aquifer potentiometric head and the water quality deteriorating. The correlation between the different stratigraphic logs from north to south across El Kharga Oasis showed that the NSSA is located above basement rocks and overly by shale layer. The aquifer thickness increases gradually from the north to south direction of the study area. The NSSA is divided to several layers separated from each other by thin layer of shale, which could be connected through the fault plain (Figure 2).
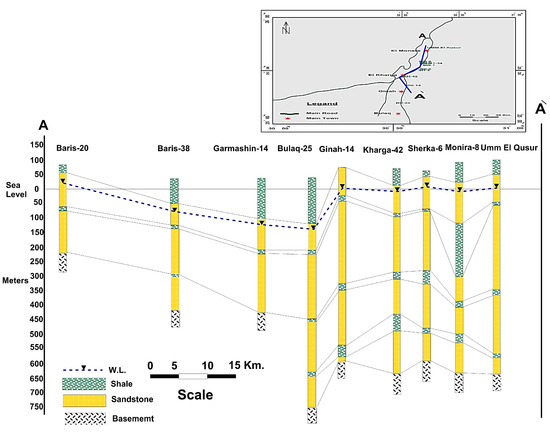
Figure 2.
Hydrogeological setting for the NSSA aquifer in El Kharga Oasis.
2.2. Sampling and Analysis
The GW samples were collected in July 2020 from 140 production wells with depths of GW varying from 8 to 75 m (Table S1), penetrating the Nubian sandstone aquifer. The temperature, pH, EC, and TDS parameters, as well as ground surface elevation, were measured on site. A mobile multimeter was used to monitor the EC and pH (HI 9829 type). After filtration, each sample was taken in polyethylene bottles to investigate chemical parameters, such as Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, K+, Cl−, HCO3−, CO32−, and SO42−. SO42− and Cl− were analyzed using a spectrophotometer HACH (DR2000 type); however, a flame spectrophotometer was used to monitor K+, Ca+, and Na+. Mg2+ was analyzed using the complexometric method, and the titrimetric approach was used to measure CO32− and HCO3−. According to Equation (1), the charge-balance error (CBE) with a limit of 5% was used to crosscheck the analytic errors of the measured ions concentrations in meq/L−1 [55].
The analytical procedures were verified in terms of quality control by carrying out adequate devices calibrations and evaluating the precision of each sample that was being examined.
2.3. Indexing Approach
2.3.1. Irrigation Water Quality Indices (IWQIs)
The calculations of the IWQIs were performed using the equations presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Equation used to calculate the IWQIs.
2.3.2. Irrigation Water Quality Index (IWQI)
The IWQI, which is a dimensionless index, has a limit between 0 and 100, and it is calculated using several parameters, including EC, SAR, Na+, Cl−, and HCO32− [60,61], as follows in Equations (2) and (3):
Qi is a metric for measuring the quality based on the tolerance limits, and Wi is the predefined weight of the parameters (Table 2).
where Xij is the measured values of the parameters, Xinf is the value that refers to the lower limits of the classes, Qimap is the classes amplitudes, and Xamp is the classes amplitudes which involve the considered parameter.

Table 2.
Upper and lower limits of the parameters used in the quality evaluation (Qi).
Finally, Wi is obtained as follows:
where F is the auto record of element j, A is the mostly limited of parameter i by factor j, i is the number of the selected physicochemical parameters (1 ≤ i ≤ n), and j is the number of the selected factors (1 ≤ j ≤ k. ij).
2.4. Simulation Models
Support Vector Machine (SVM) Model
SVM is a well-known ML approach that is dependent on mathematical learning theory. It is useful for classifying large amounts of data, identifying features, and performing regression analyses [62]. From the datasets (x, y) provided, SVR sought to create functions where x is the input parameter and y is the output parameter of the “IWQIs”.
Equation (5) presents the regression description of the SVM function:
where f(x) indicates the output of the SVM, and indicates a nonlinear mapping function. The weighting array ω and bias factor b, correspondingly, are to be adjusted utilizing the following regularized functions:
where C represents the adjustment value needed for the stability component and the normalization component . and are the positive slack variables. Based on Lagrange multipliers, the SVR model is determined by:
In this case, the kernel function is , and the positive Lagrange multipliers are and , accordingly.
The parameters of the SVM are eventually defined after obtaining the desired outcome for the objective function; thus, the following regression formula is used to represent an input vector x.
2.5. Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System
The ANFIS modeling combines the advantages of FIS with deep learning models [14]. The ANFIS model is hypothesized using various output–input data, and the backpropagation process is then used to update the model’s membership criteria. The relationships between the IWQIs and the water quality parameters were derived herein using ANFIS, and they were described as if–then fuzzy rules (Figure 3). The ANFIS models involved the Sugeno-type FIS of bell input membership functions, with 5 functions for the 9 inputs; however, the outputs had linear memberships functions. Figure 4 illustrates an ANFIS model that has a multilayer feed-forward architecture.
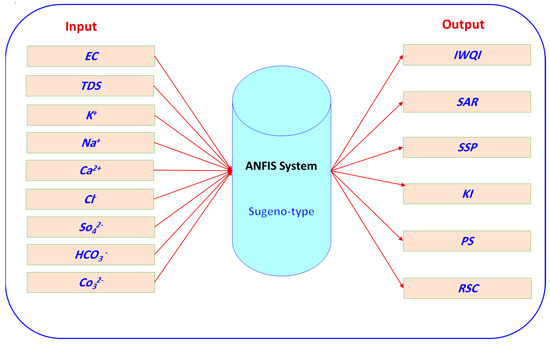
Figure 3.
An ANFIS architecture for IWQIs prediction.
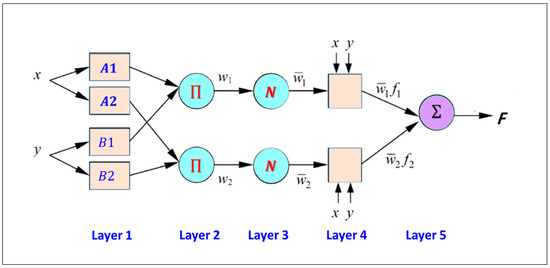
Figure 4.
The structure of the adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system model.
Figure 5 illustrates the ANFIS model, which has an incoherent x and y input network and a multilayer feed-forward architecture. The rule foundation for the Sugeno model (Figure 4) is as follows:
where A and B are the memberships orders of magnitude, a and b indicate indirect identifying function. p, q, and r are relevant constraints modified in the training algorithm’s forward pass, and fi is the output falling inside the inconsistent region determined by the FIS concept. Figure 5 illustrates the five layers that comprise ANFIS where the memberships function of the fuzzy set A and B are and , respectively. Further information regarding ANFIS is provided in Khadr [63].
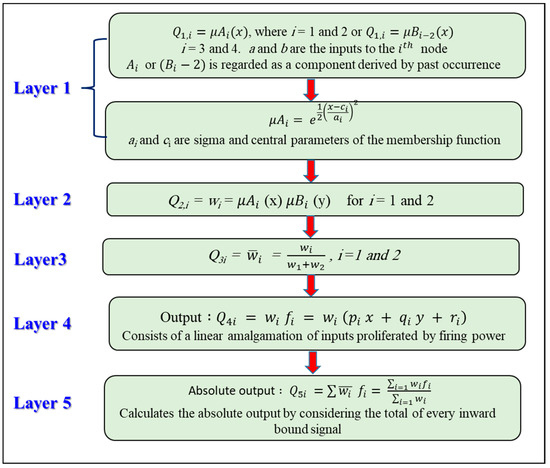
Figure 5.
Conceptual illustration of the five layers that comprise ANFIS.
2.6. Performance Evaluation of the Simulation Models
The performance of the ANFIS and SVM models in predicting the IWQIs was evaluated using the following statistical measures:
- (a)
- Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency coefficient (NSE):
- (b)
- The mean absolute error (MAD):
- (c)
- The absolute variance fraction, R2:
- (d)
- The root mean square error (RMSE):
In this investigation, EC, K+, Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cl−, SO42−, and HCO3− were found to be relatively the most influential parameters to forecast the IWQIs. The model architecture used in the ML algorithms is presented in Figure 6.
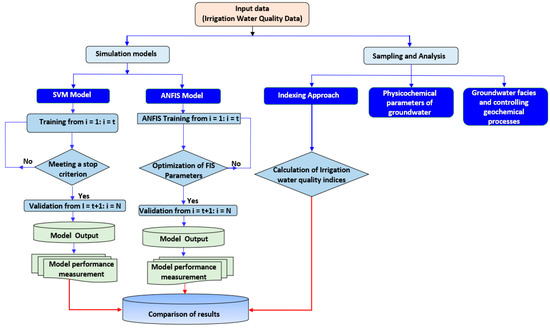
Figure 6.
Methodology flow chart of this study.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Physicochemical Parameters of the Groundwater
The subsequent GW classification was performed using physicochemical factors suitabile for irrigation purposes in the NSSA, including T °C, pH, EC, TDS, K+, Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Cl−, SO42−, HCO3−, and CO32−, which are affecting soil quality and crops productivity. Table 3 shows the statistical properties of the physical and the chemical parameters for 140 GW samples.

Table 3.
Statistical characteristics of the physicochemical parameters of the investigated GW samples.
In accordance with the FAO [23], the max. and min. values were calculated based on statistical evaluations of the water quality. The highest value of the electrical conductivity was 2610 S/cm, which fell below FAO limits (3000 μS/cm). The maximum TDS value was 1870 mg/L, which is within the standard limitations [23]. According to [64], the GW in the actual area of the research ranges from fresh to brackish. The values of pH ranged from 6.1 to 8.1, which is within the acceptable limits based on the irrigation water standard [31]. The concentration of calcium for all samples met the water irrigation standard (from 8 to 180 mg/L) [23]. Only 1.42% of the samples had higher Mg2+ concentrations above the irrigation water’s acceptable levels, while the rest of the samples had a mean concentration of 21.90 mg/L [23]. The K+ concentrations in all locations exceeded the allowable irrigation water standards, with a min. value of 3.50 mg/L and a max. value of 53 mg/L.
The Na+ concentration was observed to be within the acceptable value for the examined GW ranged between 4 and 460 mg/L. The Cl− (175.53 mg/L) and SO42− (143.47 mg/L) were the most abundant anions in the GW. Their concentrations were overall permissible for irrigation water. The HCO3− concentrations in all of the water samples were acceptable for irrigation water, with a max. of 300 mg/L [23].
3.2. Groundwater Facies and Controlling Geochemical Processes
For the categorization of the GW hydrochemical facies, a piper plot was established (Figure 7a) [65]. The cationic triangle showed that approximately 82.14% of the total water samples were Na+ and K+ dominant, while approximately 17.14% were nondominant, and the rest of samples were Mg2+ dominant. The water samples were divided into five hydrochemical facies based on the presentation of the pipe plot (Figure 7a). One sample fell within the Ca-Mg-SO4 facies zone (Type 1) with permanent hardness. Approximately 88 samples belonged to the Na-Cl facies (type 2), while five samples belong to the Ca-Mg-HCO3 facies zone (Type 3), and 15 samples belonged to the mixed Na-Ca-HCO3 facies zone (Type 4). The rest were in the mixed Ca-Mg-Cl-SO4 zone (type 5). The majority of the selected samples revealed that the salinity indices (SO42− + Cl−) were generally higher than the alkalinity (HCO3− + CO32−), and the alkalis (Na+ + K+) were higher than the alkaline earths (Ca2+ + Mg2+), as the overarching factor dictating the NSSA’s hydrochemistry in this region.
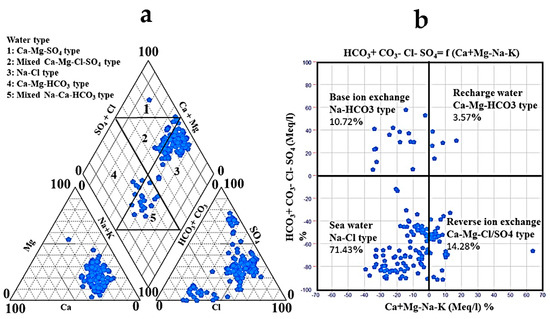
Figure 7.
The presentation of the hydrochemical faces of the GW and the water chemistry mechanism: (a) Piper plot, and (b) Chadha diagram.
The primary dominating geochemical processes controlling the water chemistry was further confirmed using the Chadha diagram, as shown in Figure 7b [66]. According to Chadha diagram, most samples (71.43%) were located in the region of the Na-Cl type, which indicates the dissolution of halite minerals as a significant factor in the GW chemistry. Approximately 14.28% fell in the reverse ion exchange zone (Ca-Mg-Cl/SO4), while 10.72% of the water samples located within the base ion exchange zone (Na-HCO3). The rest of samples 3.57% fell within the recharge water zone (Ca-Mg-HCO3). It is worth noting that the evolution of GW quality and its appropriateness for irrigation water use depends on the control mechanism and geochemical processes. The chemical characteristics of the analyzed GW samples showed Ca-Mg-HCO3 and Na-HCO3 water types, which reflects the meteoric/initial water stages in the recharge areas, while the Ca-Mg-Cl/SO4 water type reflected the intermediate water stages of evolution, especially in the northern and central parts of the study area. Moreover, the majority of samples fell in the Na-Cl water type, indicating last stage of geochemical evolution in the discharge areas, especially in southern parts of the study area with the direction of GW flow. These findings could confirm previous work in the study area through the application of the geochemical modeling to detect the mineral saturation state [53].
The Durov graph may be used to demonstrate three primary processes: ion exchange, mixing/dissolution, and reverse ion exchange (Figure 8). The majority of the samples were located within the mixing/dissolution zone, while the rest fell between the ion exchange and reverse ion exchange zones, confirming the previous statistical explanation.
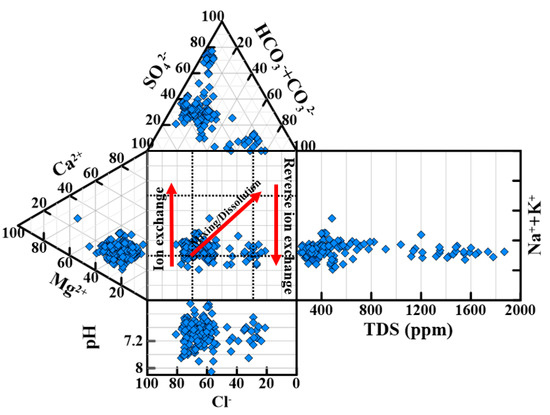
Figure 8.
The visualization of the main geochemical mechanism, which controls the water chemistry.
The tatistical analysis was utilized to demonstrate the primary mechanisms governing the GW chemistry in the research region by utilizing the correlations and ratios between the various major ions (Figure 9). Utilizing the link between the EC and Na+/Cl− ratio, the influence of the dissolution and evaporation processes in the research region could be explained [67]. The ratio of Na+/Cl− had an almost constant trend line with the increase in the electrical conductivity owing to halite dissolution; in addition, the samples above and below the 1:1 line indicate direct ion exchange and reverse ion exchange, respectively (Figure 9a). To validate the role of dissolution, direct ion exchange, and reverse ion exchange as key features in the water chemistry of El Kharga Oasis, several ionic plots and a Chadha diagram were used.
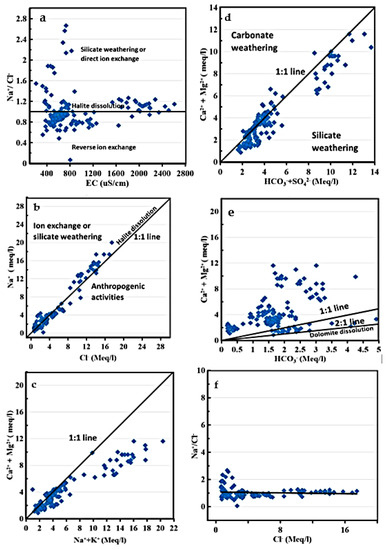
Figure 9.
Ionic relationships between various physicochemical variables: (a) Na+/Cl− and EC; (b) Na+ and Cl−; (c) Ca2+ + Mg2+ and Na+ + K+; (d) Ca2+ + Mg2+ and SO42− + HCO3−; (e) Ca2+ + Mg2+ and HCO3−; (f) Na+/Cl− and Cl−.
The linear correlations between Na+ and Cl- illustrate that these two ions were in balance, and the majority of the water samples were close to the 1:1 line graph, with the same R2 = 0.96% because of a similar source, such as halite dissolution (Figure 9b). The influences of halite dissolution, particularly in the unsaturated zone, are characteristic of arid and semi-arid areas that have average annual rainfalls below 600 mm [68,69]. The samples that were found below the 1:1 line graph may have had their chloride levels enriched as a sign of an additional source of chloride ions, or they may have had their sodium levels reduced by eliminating Na+ from the GW. The surplus irrigation water from agricultural land and trash disposal are two anthropogenic activities that may be to blame for the high chloride content [70,71] or atmospheric deposition of chloride [72]. The Na+/Cl− ratio in some samples was higher than 1, indicating silicate weathering or ion exchange [73]. The relationship between Na+ + K+ and Ca2+ + Mg2+ (Figure 9c) showed a significant amount of the water samples near the 1:1 line as an indication of the minerals’ dissolution and few samples above the line because of reverse ion exchange. The dominance of Na+ and K+ over Ca2+ and Mg2+ in most of the water samples reveals that Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions were replaced by Na+ and K+ ions through the ion exchange process and silicate weathering [74]. Few of the GW samples exceeded the 1:1 line, indicating the reverse ion exchange process, according to a linear graph (Figure 9d) plotting the sum of Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions vs. the sum of HCO3− and SO42−. Because of the breakdown of gypsum, calcite, and dolomite, the samples crossed the 1:1 line. The relative increase in the number of SO42− + HCO3− ions compared to Ca2+ + Mg2+ ions resulted from silicate weathering [75], which appears clearly in the ratio of Na/Cl, where the water was enriched in Na+ more than Cl−.
The proportion of Ca2+ + Mg2+ to HCO3− could be utilized to determine the source of calcium and magnesium in the samples (Figure 9e). If the ratio is near 0.5, this indicates that the weathering of carbonate and silicate minerals produced the Ca2+ + Mg2+ [76]. If the ratio is less than 0.5, the major cause of the depletion of calcium and magnesium may be ion exchange or bicarbonates enrichment. Most of the water samples had a very high Ca2+ + Mg2+/HCO3− ratio that was greater than 0.5, while only a few samples had a ratio that was close to 0.5. Therefore, different hydrochemical processes in addition to the sole dissolution of carbonates (calcite and dolomite) should have an impact on the high levels of Ca2+ and Mg2+. Since the water was in a moderately alkaline condition and the depletion of HCO3- (carbonic acid) was not considered to be a contributing factor to the majority of samples falling significantly over the 1:1 line (ratio = 0.5), silicate weathering and/or reverse ion exchange were the main causes [77]. The Ca2+ + Mg2+/HCO3− ratio can be used to identify the meteoric nature and the fresh GW recharge. When this ratio is lower than 1, this indicates that the water is meteoric and that GW recharge existed [78]. In the study area, 15% of the GW samples had a ratio less than 1, referring to the meteoric nature and presence of recharge, while 85% of the samples had a value greater than 1, relating to the lack of meteorological activity and GW recharge. The relationship between Na+/Cl− and Cl− (Figure 9f) reveals a reversible link showing that the clay minerals in the aquifer’s clay replaced the sodium that was released when the halite disintegrated with calcium and magnesium [75]. The results of the ionic ratio interpretation confirmed with the same findings of the previous study that was conducted by El Osta et al. [53].
3.3. Water Quality Indices for Agricultural Purposes
Due to the fact that agricultural practices, soil types, and water quality all impact the most appropriate irrigation techniques [79,80], a number of indices were used herein in order to monitor the water quality suitability for agriculture, including the irrigation-specific IWQI, SAR, SSP, KI, PS, and RSC. These procedures highlight the possibility of soil salinization, as well as negatively the impact of irrigation on soil and plant health. The data from the IWQIs were statistically analyzed, and the water’s suitability for agriculture was determined (Table 4 and Table 5).

Table 4.
Statistical characteristics of the different IWQIs.

Table 5.
Classification of the IWQIs for irrigation purposes.
3.3.1. Irrigation Water Quality Index (IWQI)
A comprehensive assessment of GW quality in regard to the irrigation systems were performed utilizing IWQIs. The process of GW evaluation is conducted by utilizing either individual chemical indices [81,82] or a combination of numerous indices [60,83] to evaluate the GW for irrigation purposes using IWQIs. Although GW assessment for irrigation based on individual parameters is important, combined indices provide more valuable information for decision makers. Five hazards’ groups were used for the evaluation of the safety of the GW for irrigation purposes [84]. The IWQI values varied from 29.61 to 99.50, with an average of 80.34 (Table 4). According to the IWQI values for the study area, the majority of investigated samples (67.85%) were classified as no restriction range, which prevents crops that tolerate salinity, while approximately 12.84% of the investigated samples were classified from low to moderate restriction, and approximately 19.28% of the samples were classified from high to severe restriction for irrigation, which can be used to irrigate crops that are moderately to severely salt sensitive in loose soil without compacted layers (Table 5).
The overall index map (Figure 10a) is helpful for validating GW for irrigation, since it shows how suitable water is for irrigation based on physical and chemical criteria. According to the IWQI readings, there was a decline in the water quality in the southern regions of the study area as a result of anthropogenic activities and geogenic sources.
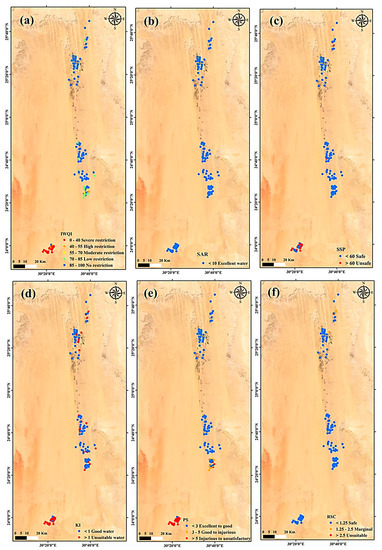
Figure 10.
Spatial distribution maps of the IWQIs in the study area: (a) IWQI, (b) SAR, (c) SSP, (d) KI, (e) PS, and (f) RSC.
3.3.2. Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR)
In irrigation water, the term “SAR parameter” refers to the soil matrix’s capability to release Ca2+ and Mg2+ and absorb Na+ ions at the locations of ion exchange, which spreads soil particles and reduces infiltration capacities [85,86]. Highly saline water can be beneficial for the soil structure by accelerating infiltration, but it puts plants under higher water stress to draw water from the soil in the case that the irrigation water has a high salinity, and plants and crops must expend more energy (water stress condition). The USSL diagram categorizes and demonstrates the relation between SAR and EC (Figure 11) [54]. Most of the samples fell between C2-S1 and C3-S1 (low SAR and medium to high salinity), 20 samples belonged to C3-S2 class (high salinity and medium SAR), 5 samples of NSSA fell in the C4-S2 class (very high salinity and medium SAR), and only 1 sample was in the C1-S1 class (low salinity and low SAR). The maximum value of SAR, for all of the investigated samples, was less than 10, indicating an excellent class for irrigation (Figure 10b).
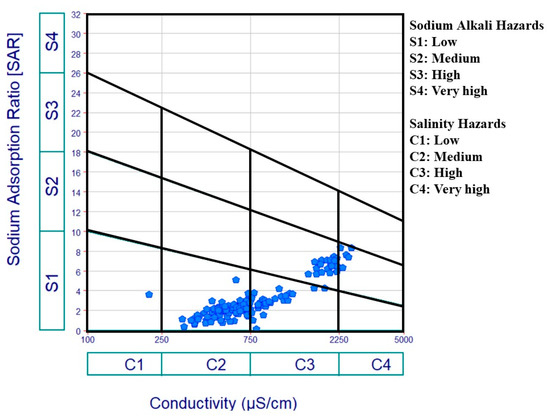
Figure 11.
USSL diagram for irrigation purposes.
The results present that the excessive salinity of the irrigation water will negatively impact plants, although the low to medium SAR values (Figure 11) and the absence of calcium conditions have no effect on the soil infiltration capacity. The best strategy for managing the use of GW for irrigation in the degraded region is to choose plants and crops that can resist the water’s high salinity.
3.3.3. Soluble Sodium Percentage (SSP)
The SSP was used to determine salinity through a comparison between the Mg concentration and the ratio of the sodium to calcium concentrations. A high-level sodium concentration in water compared to calcium and Mg causes harmful substances, which are responsible for deteriorated leaves and dead plant tissues [87]. The SSP values ranged from 3.80 to 66.39 with an average value of 48.54. According to the SSP results, 83.57% of the GW samples fell within the safe category for irrigation, and 16.42% belonged to the unsafe category (Figure 10c).
3.3.4. Potential Salinity (PS)
The concentration of chloride ions and half of the sulfate concentration are important parameters to assess the suitability of GW for irrigation through the potential salinity index. PS values are generally divided into two categories: unsuitable if greater than three (>3) and suitable (<3) for irrigation [58]. The PS ranged from −0.85 to 12.11, with a mean of 3.41. Based on the PS values, 92 samples fell within the excellent to good category, while the remaining belonged to the good to injurious class (Figure 10d).
3.3.5. Kelley Index (KI)
The Kelley index was calculated to evaluate the suitability of GW for irrigation use, where it was revealed an excess of sodium ions in the water [88]. The KI value varied between 0.08 and 0.62, with an average of 0.25. According to the KI results obtained, 57.85% of the GW samples were categorized as suitable (good class) for irrigation and the rest as not suitable (unsuitable class) (Table 3). A KI value greater than one (KI > 1) reveals that there is an excess of sodium in the water, while a value less than one (KI < 1) demonstrates that the water is suitable for irrigation [57,89]. The unsuitable GW samples were distributed in the southern parts of the study area (Figure 10e).
3.3.6. Residual Sodium Carbonate (RSC)
An excess of carbonate and bicarbonate concentration levels in relation to calcium and magnesium ions is one popular method for irrigation water determination. By precipitating, alkali metals can lower the quality of the irrigation water, primarily Ca2+ and Mg2+. The Ca2+ and Mg2+ precipitations as carbonate minerals could increase the Na+ concentration levels and, thus, the SAR values [59]. The soil physical properties can be deteriorated with the high magnitude of the RSC causing the dissociation of organic matter. This leads to a black stain on the soil surface when it is dry [24,90]. The RSC was computed in order to predict the possibility of calcium and magnesium precipitating on soil surface particles and their removal from the soil solution. According to reports, RSC levels in GW are high in dry and semi-arid areas, which results in soil salinization and sodification [91]. Using the RSC value, the GW was divided into three types [91]. Water for irrigation with an RSC less than 1.25 and between 1.25 and 2.5 is acceptable, while water with an RSC greater than 2.5 is not acceptable. In the current investigation, 134 water samples had an RSC value of less than 1.25, indicating that the water was acceptable for irrigation and of good and safe quality. Three samples were in the borderline class, while the other samples were in the unsuitable class (Figure 10f).
According to the IWQIs’ results, there was a gradual degradation in the GW quality from north to south of the study area, which can cause sodification, deterioration of the soil’s physical properties, dissociation of organic matter, and soil salinization. The best management of the water resources in the southern part of the study area is using calcium fertilizers for the soil that can be affected by sodification and using the plant that can be more resistant for salinity. Additionally, the GW in the research area’s southern region can be employed to irrigate crops with moderate to high salt sensitivity on loose soil that does not have any compacted layers. The land resources and soil classification revealed that the soils were classified as fair, poor, and very poor according to the salinity, alkalinity, and texture of the soil, which has been confirmed in previous works [44].
3.4. Simulation of Models
3.4.1. SVM Model
The SVM and ANFIS coding was carried out using MATLAB, and the radial basis function (RFB) the parameters (C, σ, and ε) was implemented for the IWQI prediction. The shuffled complex evolution algorithm (SCE-UA), which is commonly applied in hydrological applications, was implemented herein to achieve the accurate predictive performances for the SVM model [92,93]. The predicted values of the identified IWQIs were computed following the selection of the best performing SVM model during the training procedure, and the predicted and observed records were then compared. The results of the model’s performance are presented in Table 6 in terms of the R2, RMSE, MAE and E. For the training period of the IWQI, the values of the performance measures were R2 = 0.97, RMSE = 1.57, MAE = 0.64, and E = 0.98; the values for the testing period were R2 = 0.76, RMSE = 12.45, MAE = 8.48, and E = 0.70. Figure 12 shows the measured and predicted IWQI values and scatter diagram for the SVM model. A significant drop in the performance level can be noticed, as shown in Figure 12, in terms of the testing results. The results demonstrate further that the SVM model overestimated the values of the predicted IWQI in the testing period. In the case of the SAR index, in the training period the performance measures were R2 = 0.93, RMSE = 0.57, MAE = 0.28, and E = 0.91; the values for the testing period were R2 = 0.36, RMSE = 2.23, MAE = 148, and E = 0.20. In general, the performance of the SVM model decreased in the testing period for all indices (Figure 12 and Figure 13).

Table 6.
Performance criteria of the simulation models for IWQI prediction.
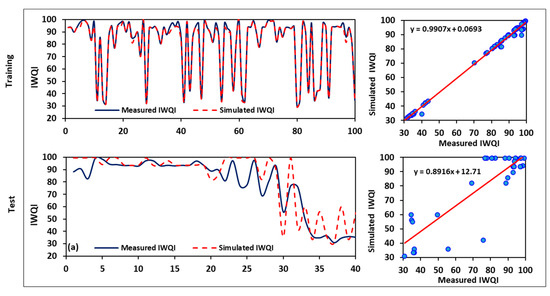
Figure 12.
Results of the simulated IWQIs using the SVM model.
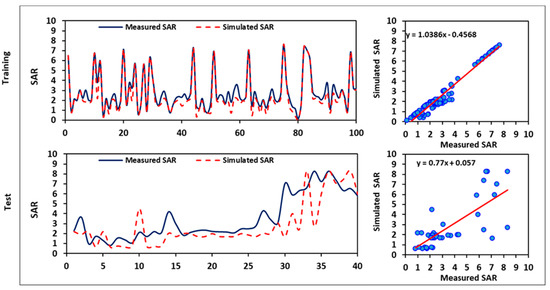
Figure 13.
Results of the simulated SAR based using SVM model.
3.4.2. ANFIS Model
After determining the model with the greatest performance using the ANFIS training, the predicted estimates of the IWQIs were calculated. Figure 14 and Figure 15 compare the predicted values of IWQI and SAR in both the training and testing stages with the actual data. It is apparent that the two curves strongly overlapped and, except for some values that diverged even quite far from the measured values, the trend of both the predicted and observed datasets was closely similar. The significant R2 value (0.99) shows that there was perfect agreement between the predicted and observed IWQI. The developed ANFIS model had a perfect fit for the IWQIs in both the testing and training stages, as shown by the E values in Table 6, which were more than 0.90. Table 6 illustrates that for all indices, the ANFIS model outperformed the SVM model in terms of the accuracy. From the training to the testing phases, the ANFIS model’s performance quality (R2, RMSE, and MAD) decreased only slightly. A much more distinctive description arises in Figure 14 and Figure 15, which illustrate the disparity between the forecasted and measured IWQIs in the training and testing phases, as well as the comparative scatter plots. The time series plots reveal that the ANFIS model was adept at identifying the varying patterns of the observed IWQI data.
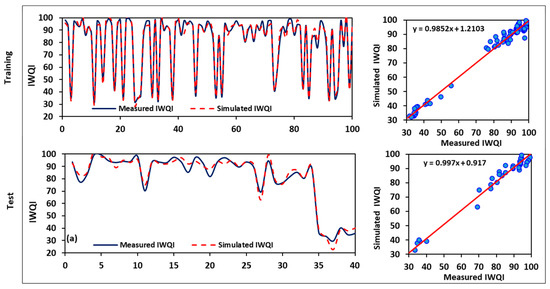
Figure 14.
Results of the simulated IWQI using the ANFIS model.
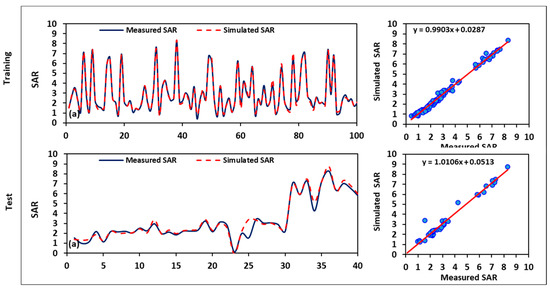
Figure 15.
Results of the simulated SAR using the ANFIS model.
As one of the main objectives of this study was to evaluate groundwater appropriateness for agricultural purpose utilizing various IWQIs, which are traditionally calculated using classical mathematical equations that are time consuming, especially in calculating IWQIs because of the large amount of data and several steps needed to obtain the final results, we proposed the ANFIS and SVM models to analyze the large amount of data for the nonlinear systems, quickly and accurately identifying patterns, making predictions for the IWQIs with an acceptable accuracy and efficiency, optimizing the processes, and determining the results based on the simulations. Furthermore, simulation models are useful for predicting outcomes in situations where experimentation is not possible or practical.
The results confirm the viability of applying the ANFIS and SVMR models for the assessment and control of the GW quality for irrigation throughout the NSS aquifer in El Kharga Oasis. Finally, combining IWQIs, ANFIS, and SVMR proved to be a useful and practical tool for determining and predicting irrigation water quality in both arid and semi-arid environments.
3.4.3. Theoretical and Practical Implications
The impacts of the suggested technique rely on the size of the survey and the availability of the datasets. It might be broadened further to incorporate a regional scope and to offer strategic data to decision makers and stakeholders. To support relevant and accurate outcomes, however, an understanding of the important hydrogeological conditions is always necessary. Decision makers and stakeholders may benefit from using the suggested preliminary assessment process, since it will significantly save their time and resources needed for traditional complex strategies. By creating management strategies specifically for the situations identified by the study, its results might be rendered more valuable. The natural environment and socioeconomic structure of a region may eventually benefit as a result over the long run.
4. Conclusions
This study used physicochemical parameters, IWQIs, and GIS tools to recognize GW hydrogeochemical classes and their controlling processes to examine the suitability of the GW for the NSSA in El Kharga Oasis for agricultural uses. According to the collected physicochemical data, the hydrochemical facies of the GW resources were of Ca-Mg-SO4, mixed Ca-Mg-Cl-SO4, Na-Cl, Ca-Mg-HCO3, and mixed Na-Ca-HCO3 types, which reveals silicate weathering, dissolution of gypsum/calcite/dolomite, halite dissolution rock–water interaction, and reverse ion exchange processes. For instance, the IWQI showed that 67.85% of the GW samples were categorized for irrigation purposes into no restriction, 11.42% in the low restriction class, 1.42% in the moderate restriction class, 5% in the high restriction class, and the rest of the samples in the severe restriction class. Two simulation models were developed to predict the IWQIs based on the collected physicochemical parameters. The results of the performance assessment for the proposed simulation models show that the ANFIS model and SVM model were capable of simulating the IWQI with reasonable accuracy in the learning phase (R2 = 0.99 and 0.97) and validation phase (R2 = 0.97 and 0.76). The proposed models’ accurate performance indicates that they have the potential to be used for IWQI prediction. Therefore, the combination of physicochemical parameters, IWQIs, GIS, and the feasibility of the ML models can contribute in an efficient manner to the utilization of GW for irrigation purposes. The research attempted to overcome the constraints of traditional methods by using ANFIS and SVM models to predict the quality of the GW used for irrigation under extensive salinization. The preliminary findings of this effort will contribute to the provision of knowledge for the coordinated and precise management of water resources in El Kharga Oasis. This work offers a reliable technology for water resources risk contingency plans. Thus, it will be useful to manage the environmental safety of the water environment in the future. Additionally, the method put out in this work has the potential to be further studied to increase its accuracy for GW under various conditions, and it enables decision makers to combine various technologies for water quality management and planning. Because of this, we used ML models in this study to anticipate the groundwater quality for irrigation purposes under significant salinization in an effort to go beyond the constraints of conventional approaches. Finally, the integration of IWQIs, ML, and GIS approaches offers an alternative data analysis approach for acquiring quick results with a less time-consuming process that achieves satisfactory results from the perspective of GW quality management.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w15040694/s1, Table S1. Locations of the collected samples and depths to GW in El Kharga Oasis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.I., M.G. and M.M.K.; Investigation, H.I. and M.M.K.; Methodology, Z.M.Y., M.K., H.H. and H.H.I.; Project administration, H.I., M.G., S.E. and M.M.K.; Resources, M.S., A.K. and S.P.; Software M.H.E., H.I., M.M.K. and M.G.; Supervision, Z.M.Y. and M.S.; Validation, M.A. and S.E.; Visualization, H.I., M.S., M.A. and H.H.I.; Writing—original draft, H.I., M.G., M.H.E., S.E. and M.K.; Writing—review and editing, H.I., M.G., S.E., M.M.K. and M.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by WATERAGRI (European Union Horizon 2020 research and innovation action under Grant Agreement Number 858375).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data are provided as tables and figures.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest to any party. The statements and opinions expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect those of any institutions mentioned in the list of affiliations.
References
- El-Rawy, M.; De Smedt, F. Estimation and Mapping of the Transmissivity of the Nubian Sandstone Aquifer in the Kharga Oasis, Egypt. Water 2020, 12, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinl, M.; Thorweihe, U.; Meisner, B.; Wycisk, P. Geopotential and Ecology–Analysis of a Desert Region; Schweizerbart Science Publishers: Stuttgart, Germany, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmod, W.E.; Watanabe, K. Modified Grey Model and Its Application to Groundwater Flow Analysis with Limited Hydrogeological Data: A Case Study of the Nubian Sandstone, Kharga Oasis, Egypt. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 1063–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebraheem, A.; Riad, S.; Wycisk, P.; Seif El-Nasr, A. Simulation of Impact of Present and Future Groundwater Extraction from the Non-Replenished Nubian Sandstone Aquifer in Southwest Egypt. Environ. Geol. 2002, 43, 188–196. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmod, W.E.; Watanabe, K.; Zahr-Eldeen, A.A. Analysis of Groundwater Flow in Arid Areas with Limited Hydrogeological Data Using the Grey Model: A Case Study of the Nubian Sandstone, Kharga Oasis, Egypt. Hydrogeol. J. 2013, 21, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaagai, A.; Aouissi, H.A.; Bencedira, S.; Hinge, G.; Athamena, A.; Haddam, S.; Gad, M.; Elsherbiny, O.; Elsayed, S.; Eid, M.H.; et al. Application of Water Quality Indices, Machine Learning Approaches, and GIS to Identify Groundwater Quality for Irrigation Purposes: A Case Study of Sahara Aquifer, Doucen Plain, Algeria. Water 2023, 15, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Ghosh, N.C.; Gurjar, S.; Krishan, G.; Kumar, S.; Berwal, P. Index-Based Assessment of Suitability of Water Quality for Irrigation Purpose under Indian Conditions. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, P.; Qian, H. Hydrochemical Characterization of Drinking Groundwater with Special Reference to Fluoride in an Arid Area of China and the Control of Aquifer Leakage on Its Concentrations. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 8575–8588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswaran, S.; Ayyandurai, R. Groundwater Characterization and Quality Assesment for Irrigational Purpose Using Gis-A Case Study of Kadavanar Watershed Tamilnadu, India. J. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 17, 488–496. [Google Scholar]
- Sridharan, M.; Senthil Nathan, D. Groundwater Quality Assessment for Domestic and Agriculture Purposes in Puducherry Region. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 4037–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.F.; Srinivasamoorthy, K.; Rabina, C. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Quality Assessment of Groundwater along the Coastal Tracts of Tamil Nadu and Puducherry, India. Appl. Water. Sci. 2020, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Wang, B.; Heck, K.; Guo, S.; Clark, C.A.; Arredondo, J.; Wang, M.; Senftle, T.P.; Westerhoff, P.; Wen, X.; et al. Efficient Photocatalytic PFOA Degradation over Boron Nitride. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, S.; Ibrahim, H.; Hussein, H.; Elsherbiny, O.; Elmetwalli, A.H.; Moghanm, F.S.; Ghoneim, A.M.; Danish, S.; Datta, R.; Gad, M. Assessment of Water Quality in Lake Qaroun Using Ground-Based Remote Sensing Data and Artificial Neural Networks. Water 2021, 13, 3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadr, M.; Gad, M.; El-Hendawy, S.; Al-Suhaibani, N.; Dewir, Y.H.; Tahir, M.U.; Mubushar, M.; Elsayed, S. The Integration of Multivariate Statistical Approaches, Hyperspectral Reflectance, and Data-Driven Modeling for Assessing the Quality and Suitability of Groundwater for Irrigation. Water 2020, 13, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.; Dahab, K.; Ibrahim, H. Applying of a Geochemical Model on the Nubian Sandstone Aquifer in Siwa Oasis, Western Desert, Egypt. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, B.G.; Nata, T.; Elias, J. Application of Water Quality Index to Assess Suitablity of Groundwater Quality for Drinking Purposes in Hantebet Watershed, Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. ISABB J. Food Agric. Sci. 2011, 1, 22–30. [Google Scholar]
- Rajankar, P.N.; Tambekar, D.H.; Wate, S.R. Groundwater Quality and Water Quality Index at Bhandara District. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 179, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravikumar, P.; Aneesul Mehmood, M.; Somashekar, R.K. Water Quality Index to Determine the Surface Water Quality of Sankey Tank and Mallathahalli Lake, Bangalore Urban District, Karnataka, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2013, 3, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo-Duque, W.; Osorio, C.; Piamba, C.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L. Water Quality Analysis in Rivers with Non-Parametric Probability Distributions and Fuzzy Inference Systems: Application to the Cauca River, Colombia. Environ. Int. 2013, 52, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutadian, A.D.; Muttil, N.; Yilmaz, A.G.; Perera, B.J.C. Development of River Water Quality Indices—A Review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, M.; El Osta, M.; Alqarawy, A.; Elsayed, S.; Gad, M. Evaluation of Groundwater Quality for Agricultural under Different Conditions Using Water Quality Indices, Partial Least Squares Regression Models, and GIS Approaches. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Osta, M.; Masoud, M.; Alqarawy, A.; Elsayed, S.; Gad, M. Groundwater Suitability for Drinking and Irrigation Using Water Quality Indices and Multivariate Modeling in Makkah Al-Mukarramah Province, Saudi Arabia. Water 2022, 14, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, R.; Westcott, D. Water Quality for Agriculture. FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 29 Rev. 1; Food and Agricultural Organisation of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasamoorthy, K.; Gopinath, M.; Chidambaram, S.; Vasanthavigar, M.; Sarma, V.S. Hydrochemical Characterization and Quality Appraisal of Groundwater from Pungar Sub Basin, Tamilnadu, India. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2014, 26, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, S.; Srinivasamoorthy, K.; Saravanan, K.; Prakash, R.; Suma, C.S.; Khan, F.; Senthilnathan, D.; Sarma, V.S.; Devi, P. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Coastal Groundwater in Nagapattinam and Karaikal Aquifers: Implications for Saline Intrusion and Agricultural Suitability. J. Coast. Sci. 2015, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Aravinthasamy, P.; Karunanidhi, D.; Subba Rao, N.; Subramani, T.; Srinivasamoorthy, K. Irrigation Risk Assessment of Groundwater in a Non-Perennial River Basin of South India: Implication from Irrigation Water Quality Index (IWQI) and Geographical Information System (GIS) Approaches. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.T.; Hasan, M.Y.; Monir, M.U.; Samad, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam Rifat, M.S.; Islam, M.N.; Khan, A.A.S.; Biswas, P.K.; Jamil, A.H.M.N. Evaluation of Hydrochemical Properties and Groundwater Suitability for Irrigation Uses in Southwestern Zones of Jashore, Bangladesh. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, G.S.; Keshavarzi, A.; Shit, P.K.; Omran, E.-S.E.; Bagherzadeh, A. Evaluation of Groundwater Quality and Its Suitability for Drinking and Irrigation Using GIS and Geostatistics Techniques in Semiarid Region of Neyshabur, Iran. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.; Gupta, S.; Reddy, D.V.; Kaur, H. An Evaluation of Irrigation Water Suitability in the Dwarka River Basin through the Use of GIS-Based Modelling. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqarawy, A.; El Osta, M.; Masoud, M.; Elsayed, S.; Gad, M. Use of Hyperspectral Reflectance and Water Quality Indices to Assess Groundwater Quality for Drinking in Arid Regions, Saudi Arabia. Water 2022, 14, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.; Abou El-Safa, M.M.; Farouk, M.; Hussein, H.; Alnemari, A.M.; Elsayed, S.; Khalifa, M.M.; Moghanm, F.S.; Eid, E.M.; Saleh, A.H. Integration of Water Quality Indices and Multivariate Modeling for Assessing Surface Water Quality in Qaroun Lake, Egypt. Water 2021, 13, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.; Saleh, A.H.; Hussein, H.; Farouk, M.; Elsayed, S. Appraisal of Surface Water Quality of Nile River Using Water Quality Indices, Spectral Signature and Multivariate Modeling. Water 2022, 14, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, S.; Hussein, H.; Moghanm, F.S.; Khedher, K.M.; Eid, E.M.; Gad, M. Application of Irrigation Water Quality Indices and Multivariate Statistical Techniques for Surface Water Quality Assessments in the Northern Nile Delta, Egypt. Water 2020, 12, 3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.J.; Shimizu, Y.; Kamiya, A.; Maneechot, L.; Bharambe, K.P.; Fong, C.S.; Nik Sulaiman, N.M. Application of Artificial Intelligence Methods for Monsoonal River Classification in Selangor River Basin, Malaysia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.J.; Shimizu, Y.; He, K.; Nik Sulaiman, N.M. Comparison among Different ASEAN Water Quality Indices for the Assessment of the Spatial Variation of Surface Water Quality in the Selangor River Basin, Malaysia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eid, M.H.; Elbagory, M.; Tamma, A.A.; Gad, M.; Elsayed, S.; Hussein, H.; Moghanm, F.S.; Omara, A.E.-D.; Kovács, A.; Péter, S. Evaluation of Groundwater Quality for Irrigation in Deep Aquifers Using Multiple Graphical and Indexing Approaches Supported with Machine Learning Models and GIS Techniques, Souf Valley, Algeria. Water 2023, 15, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Hameed, M.M.; Marhoon, H.A.; Zounemat-Kermani, M.; Salim, H.; Sungwon, K.; Sulaiman, S.O.; Tan, M.L.; Sa’adi, Z.; Mehr, A.D.; et al. Groundwater level prediction using machine learning models: A comprehensive review. Neurocomputing 2022, 489, 271–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rode, M.; Arhonditsis, G.; Balin, D.; Kebede, T.; Krysanova, V.; van Griensven, A.; van der Zee, S.E.A.T.M. New Challenges in Integrated Water Quality Modelling. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 3447–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadr, M.; Elshemy, M. Data-Driven Modeling for Water Quality Prediction Case Study: The Drains System Associated with Manzala Lake, Egypt. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2017, 8, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-Y.; Qiu, J.; Li, F.-F. Hybrid Models Combining EMD/EEMD and ARIMA for Long-Term Streamflow Forecasting. Water 2018, 10, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Peng, T.; Zhang, C.; Sun, N. Data Pre-Analysis and Ensemble of Various Artificial Neural Networks for Monthly Streamflow Forecasting. Water 2018, 10, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, R.; Karbassi, A.R.; Mehdizadeh, H.; Vesali-Naseh, M.; Sabahi, M.S. A Framework Development for Predicting the Longitudinal Dispersion Coefficient in Natural Streams Using an Artificial Neural Network. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2011, 30, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, M.I.; Sturchio, N.C. Elevated Radium Levels in Nubian Aquifer Groundwater of Northeastern Africa. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, M.M. Land and Water Resources Assessment for Sustainable Agricultural Development in EL-kharga Oases by Using Remote Sensing and Geographic Information System. Menoufia J. Soil Sci. 2020, 5, 55–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaad, F.A. Hydrogeological Aspects and Environmental Concerns of the New Valley Project, Western Desert, Egypt, with Special Emphasis on the Southern Area. Environ. Geol. Water Sci. 1988, 12, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehl, H.; Bornkamm, R. Landscape Ecology and Vegetation Units of the Western Desert of Egypt. Catena Suppl. 1993, 155–178. Available online: http://geoprodig.cnrs.fr/items/show/85519 (accessed on 29 January 2023).
- Salman, A.B.; Howari, F.M.; El-Sankary, M.M.; Wali, A.M.; Saleh, M.M. Environmental Impact and Natural Hazards on Kharga Oasis Monumental Sites, Western Desert of Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2010, 58, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoreaux, P.E.; Memon, B.A.; Idris, H. Groundwater Development, Kharga Oases, Western Desert of Egypt: A Long-Term Environmental Concern. Environ. Geol. Water Sci. 1985, 7, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahran, M.A.; Willis, A.J. The Vegetation of Egypt; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2008; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Fathy, R.G.; El Nagaty, M.; Atef, A.; El Gammal, N. Contributions to the Hydrogeological and Hydrochemical Characteristics of Nubia Sandstone Aquifer in Darb Al-Arbeain, South Western Desert, Egypt. Al-Azhar Bull. Sci. 2002, 13, 69–100. [Google Scholar]
- Elewa, H.H.; Fathy, R.G.; Qaddah, A.A. The Contribution of Geographic Information Systems and Remote Sensing in Determining Priority Areas for Hydrogeological Development, Darb El-Arbain Area, Western Desert, Egypt. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 1157–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Osta, M.; Hussein, H.; Tomas, K. Numerical Simulation of Groundwater Flow and Vulnerability in Wadi El-Natrun Depression and Vicinities, West Nile Delta, Egypt. J. Geol. Soc. India 2018, 92, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Osta, M.; Masoud, M.; Ezzeldin, H. Assessment of the Geochemical Evolution of Groundwater Quality near the El Kharga Oasis, Egypt Using NETPATH and Water Quality Indices. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Saeed, G.H.; Abdelmageed, N.B.; Riad, P.; Komy, M. Confined Aquifer Piezometric Head Depletion in the Dynamic State. JOKULL J. 2019, 69, 56–67. [Google Scholar]
- Domenico, P.A.; Schwartz, F.W. Physical and Chemical Hydrogeology; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998; Volume 506. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, L.A. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils; LWW: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1954; p. 78. [Google Scholar]
- Kelley, W.P. Permissible Composition and Concentration of Irrigation Water. In Proceedings of the American Society of Civil Engineers 1940. Volume 66, pp. 607–613. Available online: https://www.scirp.org/(S(351jmbntvnsjt1aadkposzje))/reference/ReferencesPapers.aspx?ReferenceID=1927054 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Doneen, L.D. Water Quality for Agriculture; Department of Irrigation, University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 1964; p. 48. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, F.M. Significance of Carbonates in Irrigation Waters. Soil Sci. 1950, 69, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meireles, A.C.M.; Andrade, E.M.D.; Chaves, L.C.G.; Frischkorn, H.; Crisostomo, L.A. A New Proposal of the Classification of Irrigation Water. Rev. Ciênc. Agron. 2010, 41, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasnia, A.; Yousefi, N.; Mahvi, A.H.; Nabizadeh, R.; Radfard, M.; Yousefi, M.; Alimohammadi, M. Evaluation of Groundwater Quality Using Water Quality Index and Its Suitability for Assessing Water for Drinking and Irrigation Purposes: Case Study of Sistan and Baluchistan Province (Iran). Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2019, 25, 988–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, K.-R.; Smola, A.J.; Rätsch, G.; Schölkopf, B.; Kohlmorgen, J.; Vapnik, V. Predicting Time Series with Support Vector Machines. In Artificial Neural Networks—ICANN’97; Gerstner, W., Germond, A., Hasler, M., Nicoud, J.-D., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; Volume 1327, pp. 999–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Khadr, M. Water Resources Management in the Context of Drought (an Application to the Ruhr River Basin in Germany); Shaker: Düren, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Freeze, R.A.; Cherry, J. Groundwater; Prenctice Hall. Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Piper, A.M. A Graphic Procedure in the Geochemical Interpretation of Water-Analyses. Trans. AGU 1944, 25, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, D.K. A Proposed New Diagram for Geochemical Classification of Natural Waters and Interpretation of Chemical Data. Hydrogeol. J. 1999, 7, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonakos, A.; Lambrakis, N. Hydrodynamic Characteristics and Nitrate Propagation in Sparta Aquifer. Water Res. 2000, 34, 3977–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elango, L.; Kannan, R. Chapter 11 Rock–Water Interaction and Its Control on Chemical Composition of Groundwater. In Dev. Environ. Sci. 2007, 5, 229–243. [Google Scholar]
- Jalali, M. Salinization of Groundwater in Arid and Semi-Arid Zones: An Example from Tajarak, Western Iran. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 1133–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasamoorthy, K.; Chidambaram, S.; Prasanna, M.V.; Vasanthavihar, M.; Peter, J.; Anandhan, P. Identification of Major Sources Controlling Groundwater Chemistry from a Hard Rock Terrain—A Case Study from Mettur Taluk, Salem District, Tamil Nadu, India. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 117, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacks, G.; Sefe, F.; Carling, M.; Hammar, M.; Letsamao, P. Tentative Nitrogen Budget for Pit Latrines-Eastern Botswana. Environ. Geol. 1999, 38, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.S.; Mullican, W.F., III. Hydrochemical Evolution of Sodium-Sulfate and Sodium-Chloride Groundwater Beneath the Northern Chihuahuan Desert, Trans-Pecos, Texas, USA. Hydrogeol. J. 1997, 5, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meybeck, M. Global Chemical Weathering of Surficial Rocks Estimated from River Dissolved Loads. Am. J. Sci. 1987, 287, 401–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, J.; Acworth, R.I. Impact of Debris-Flow Deposits on Hydrogeochemical Processes and the Developement of Dryland Salinity in the Yass River Catchment, New South Wales, Australia. Hydrogeol. J. 1997, 5, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajmohan, N.; Elango, L. Identification and Evolution of Hydrogeochemical Processes in the Groundwater Environment in an Area of the Palar and Cheyyar River Basins, Southern India. Environ. Geol. 2004, 46, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sami, K. Recharge Mechanisms and Geochemical Processes in a Semi-Arid Sedimentary Basin, Eastern Cape, South Africa. J. Hydrol. 1992, 139, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spears, D.A. Mineralogical Control of the Chemical Evolution of Groundwater. Solute Process. 1986, 512. [Google Scholar]
- Nazzal, Y.; Ahmed, I.; Al-Arifi, N.S.N.; Ghrefat, H.; Zaidi, F.K.; El-Waheidi, M.M.; Batayneh, A.; Zumlot, T. A Pragmatic Approach to Study the Groundwater Quality Suitability for Domestic and Agricultural Usage, Saq Aquifer, Northwest of Saudi Arabia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 4655–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.; El-Hendawy, S.; Al-Suhaibani, N.; Tahir, M.U.; Mubushar, M.; Elsayed, S. Combining Hydrogeochemical Characterization and a Hyperspectral Reflectance Tool for Assessing Quality and Suitability of Two Groundwater Resources for Irrigation in Egypt. Water 2020, 12, 2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaka, E.A.; Akiti, T.T.; Nartey, V.K.; Bam, E.K.P.; Adomako, D. Hydrochemistry and Evaluation of Groundwater Suitability for Irrigation and Drinking Purposes in the Southeastern Volta River Basin: Manyakrobo Area, Ghana. Elixir Agric. 2011, 39, 4793–4807. [Google Scholar]
- Kawo, N.S.; Karuppannan, S. Groundwater Quality Assessment Using Water Quality Index and GIS Technique in Modjo River Basin, Central Ethiopia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 147, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, J.; Qian, H. Assessment of Groundwater Quality for Irrigation Purposes and Identification of Hydrogeochemical Evolution Mechanisms in Pengyang County, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 2211–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RamyaPriya, R.; Elango, L. Evaluation of Geogenic and Anthropogenic Impacts on Spatio-Temporal Variation in Quality of Surface Water and Groundwater along Cauvery River, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture; FAO irrigation and drainage paper; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ozdemir, O.; Hampton, M.A.; Nguyen, A.V.; Do, D.D. The Effect of Zeolite Treatment by Acids on Sodium Adsorption Ratio of Coal Seam Gas Water. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5247–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, B.; Grattan, S.R.; Fulton, A. Agricultural Salinity and Drainage; University of California Irrigation Program; University of California Davis: Davis, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, M.A.; Grewal, M.S.; Rajpaul, R.; Wani, S.A.; Dar, E.A. Assessment of Groundwater Quality for Irrigation Purposes Using Chemical Indices. Indian J. Ecol. 2016, 43, 574–579. [Google Scholar]
- Sudhakar, A.; Narsimha, A. Suitability and Assessment of Groundwater for Irrigation Purpose: A Case Study of Kushaiguda Area, Ranga Reddy District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 2013, 4, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Sundaray, S.K.; Nayak, B.B.; Bhatta, D. Environmental Studies on River Water Quality with Reference to Suitability for Agricultural Purposes: Mahanadi River Estuarine System, India—A Case Study. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 155, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Kumari, K.; Ramanathan, A.; Saxena, R. A Comparative Evaluation of Groundwater Suitability for Irrigation and Drinking Purposes in Two Intensively Cultivated Districts of Punjab, India. Environ. Geol. 2007, 53, 553–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Kumar, D.; Singh, D.V. Effect of Residual Sodium Carbonate in Irrigation Water on the Soil Sodication and Yield of Palmarosa (Cymbopogon Martinni) and Lemongrass (Cymbopogon Flexuosus). Agric. Water Manag. 2001, 50, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisi, O. Streamflow Forecasting and Estimation Using Least Square Support Vector Regression and Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Embedded Fuzzy c-Means Clustering. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 5109–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsaie, A.; Yonesi, H.A.; Najafian, S. Predictive Modeling of Discharge in Compound Open Channel by Support Vector Machine Technique. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2015, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).