Assessment of Surface Water Quality Using Water Quality Index and Discriminant Analysis Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
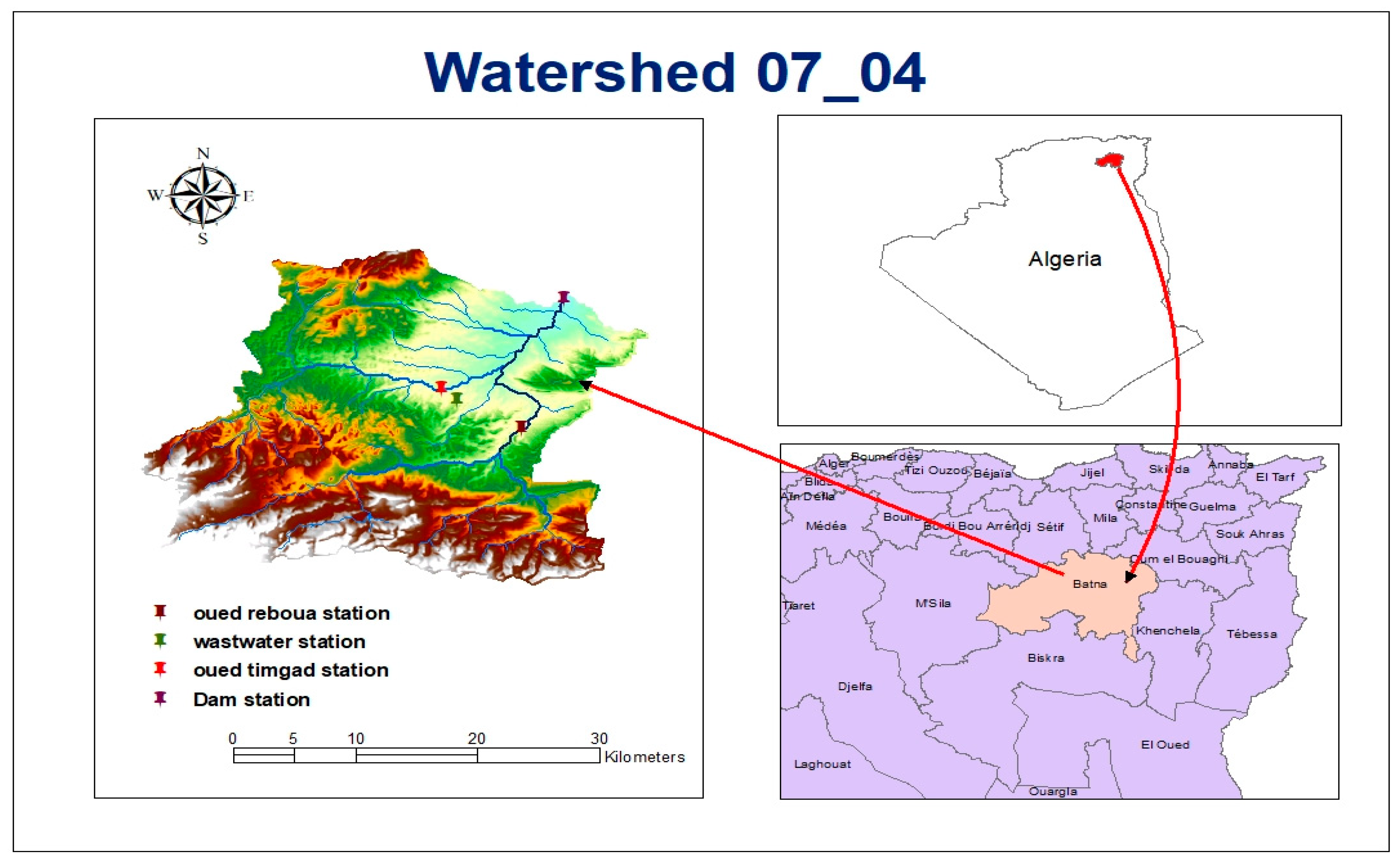
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling of Surface Water
2.3. Water Quality Index (WQI)
2.4. National Sanitation Foundation Water Quality Index
2.5. Discriminant Analysis (DA)
3. Results and Discussion
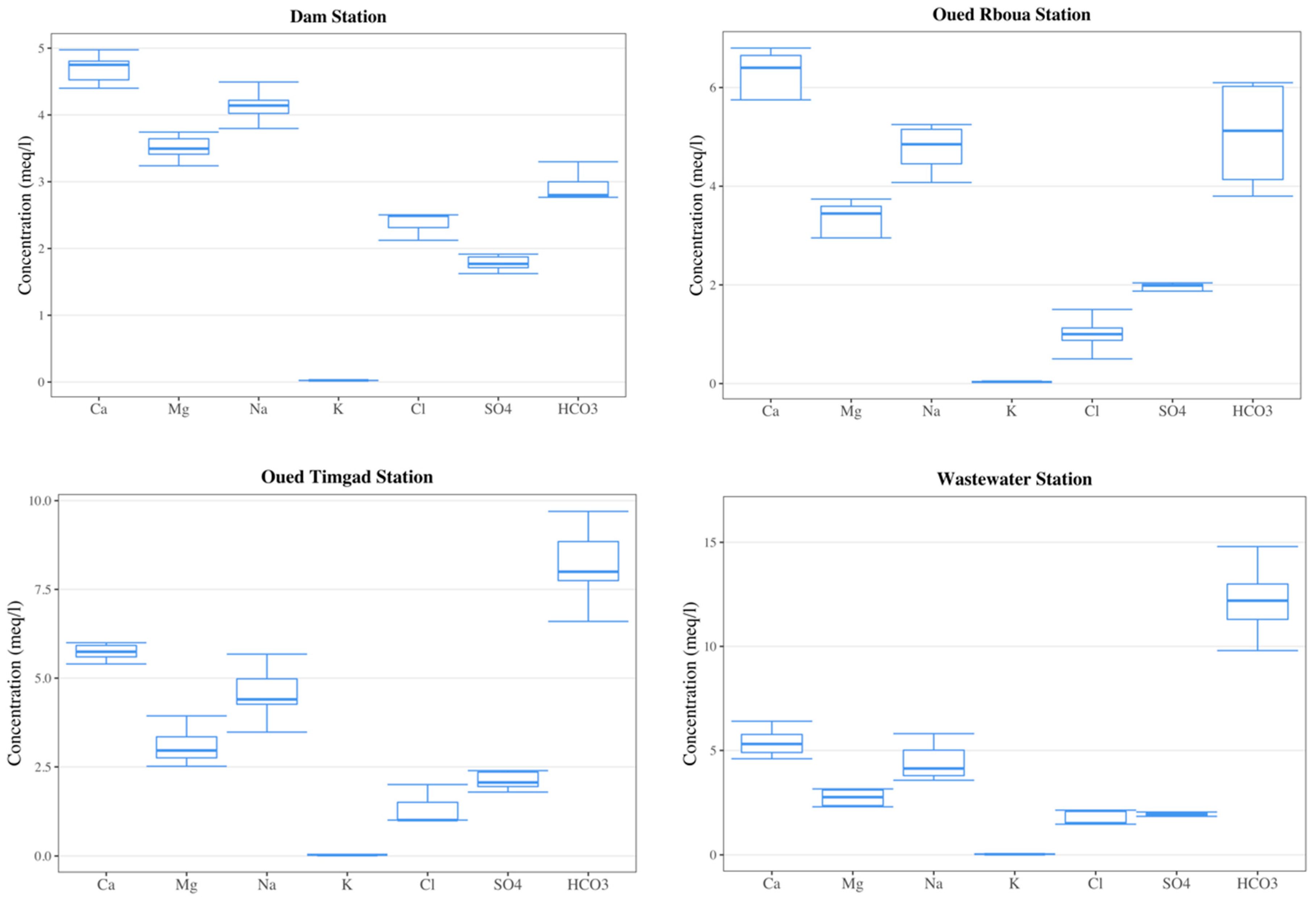
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
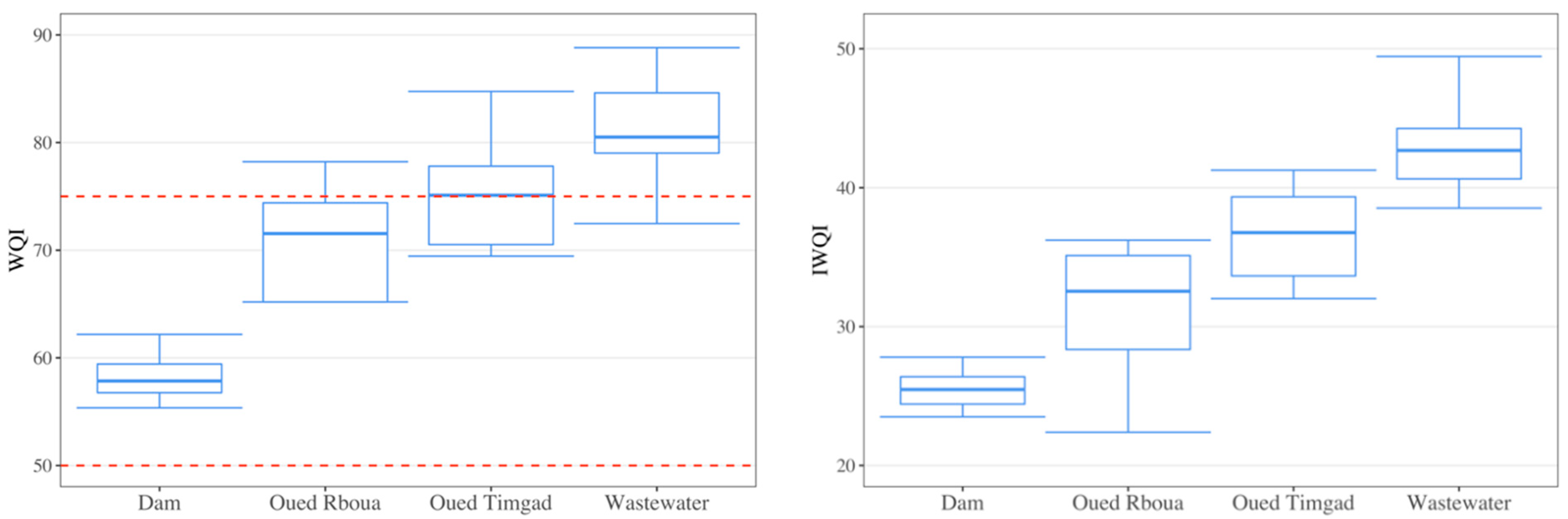
3.2. Evaluation of Surface Water Quality
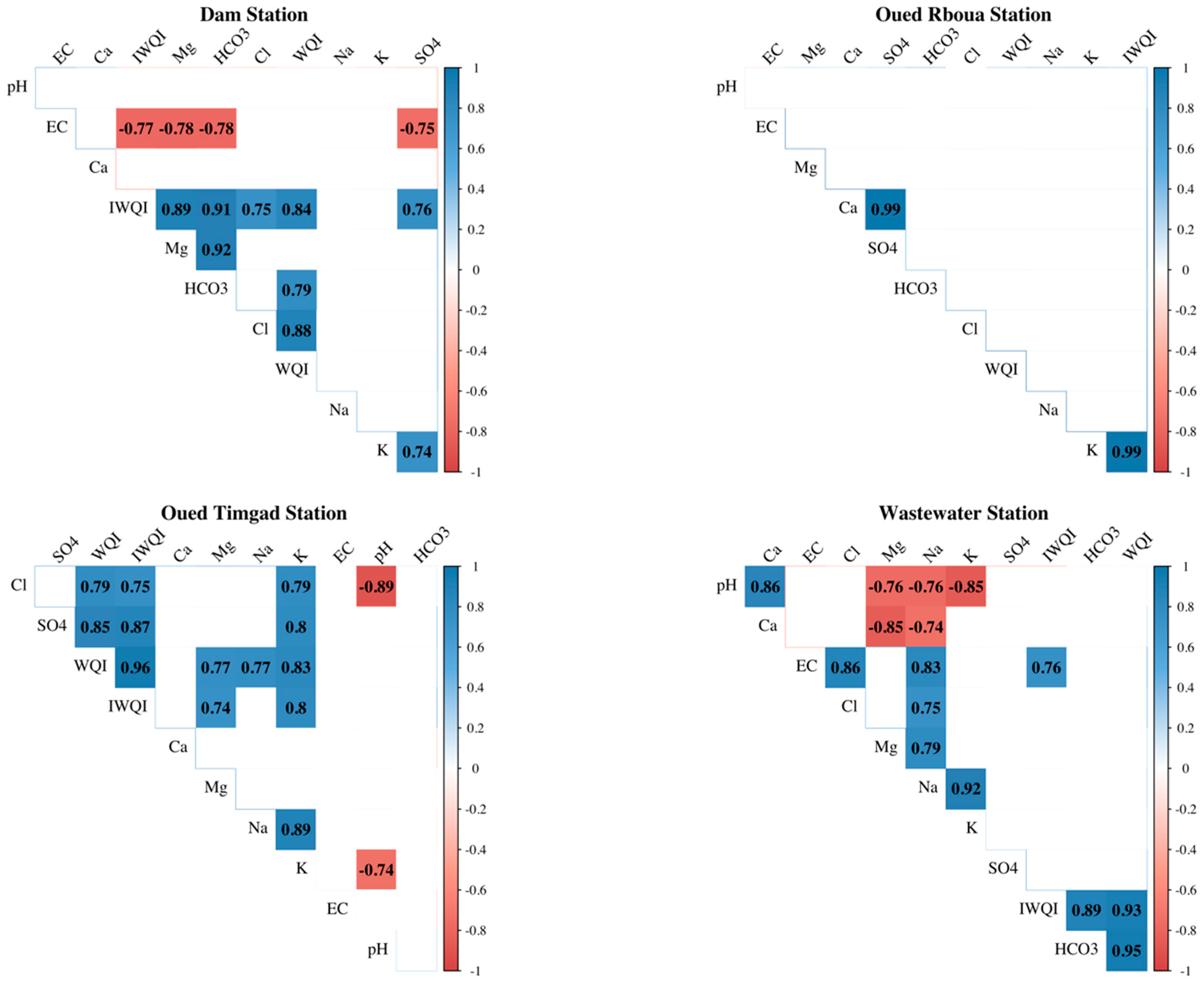
3.3. Correlation Analysis
3.3.1. Dam Station
3.3.2. Oued Reboua Station
3.3.3. Oued Timgad Station
3.3.4. Wastewater Station
3.4. Spatial Variation in Surface Water Quality
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdelwahab, O.; Amin, N.K. Adsorption of Phenol from Aqueous Solutions by Luffa Cylindrica Fibers: Kinetics, Isotherm and Thermodynamic Studies. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2014, 39, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahraoui, H.; Belhadj, A.-E.; Hamitouche, A.; Bouhedda, M.; Amrane, A. Predicting the Concentration of Sulfate (SO42−) in Drinking Water Using Artificial Neural Networks: A Case Study: Médéa-Algeria. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 217, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahraoui, H.; Belhadj, A.-E.; Hamitouche, A.-E. Prediction of the Bicarbonate Amount in Drinking Water in the Region of Médéa Using Artificial Neural Network Modelling. Kem. U Ind. Časopis Kemičara I Kem. Inženjera Hrvat. 2020, 69, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadadi, A.; Imessaoudene, A.; Bollinger, J.-C.; Bouzaza, A.; Amrane, A.; Tahraoui, H.; Mouni, L. Aleppo Pine Seeds (Pinus Halepensis Mill.) as a Promising Novel Green Coagulant for the Removal of Congo Red Dye: Optimization via Machine Learning Algorithm. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 331, 117286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadadi, A.; Imessaoudene, A.; Bollinger, J.-C.; Assadi, A.A.; Amrane, A.; Mouni, L. Comparison of Four Plant-Based Bio-Coagulants Performances against Alum and Ferric Chloride in the Turbidity Improvement of Bentonite Synthetic Water. Water 2022, 14, 3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadadi, A.; Imessaoudene, A.; Bollinger, J.-C.; Cheikh, S.; Assadi, A.A.; Amrane, A.; Kebir, M.; Mouni, L. Parametrical Study for the Effective Removal of Mordant Black 11 from Synthetic Solutions: Moringa Oleifera Seeds’ Extracts Versus Alum. Water 2022, 14, 4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahraoui, H.; Belhadj, A.-E.; Amrane, A.; Houssein, E.H. Predicting the Concentration of Sulfate Using Machine Learning Methods. Earth Sci. Inform. 2022, 15, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahraoui, H.; Amrane, A.; Belhadj, A.-E.; Zhang, J. Modeling the Organic Matter of Water Using the Decision Tree Coupled with Bootstrap Aggregated and Least-Squares Boosting. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 27, 102419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farch, S.; Yahoum, M.M.; Toumi, S.; Tahraoui, H.; Lefnaoui, S.; Kebir, M.; Zamouche, M.; Amrane, A.; Zhang, J.; Hadadi, A. Application of Walnut Shell Biowaste as an Inexpensive Adsorbent for Methylene Blue Dye: Isotherms, Kinetics, Thermodynamics, and Modeling. Separations 2023, 10, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imessaoudene, A.; Cheikh, S.; Hadadi, A.; Hamri, N.; Bollinger, J.-C.; Amrane, A.; Tahraoui, H.; Manseri, A.; Mouni, L. Adsorption Performance of Zeolite for the Removal of Congo Red Dye: Factorial Design Experiments, Kinetic, and Equilibrium Studies. Separations 2023, 10, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Imessaoudene, A.; Cheikh, S.; Bollinger, J.-C.; Belkhiri, L.; Tiri, A.; Bouzaza, A.; El Jery, A.; Assadi, A.; Amrane, A.; Mouni, L. Zeolite Waste Characterization and Use as Low-Cost, Ecofriendly, and Sustainable Material for Malachite Green and Methylene Blue Dyes Removal: Box–Behnken Design, Kinetics, and Thermodynamics. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, S.F.; Wunderlin, D.A. Use of Water Quality Indices to Verify the Impact of Córdoba City (Argentina) on Suquía River. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2915–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.; Vidyasagar, G.; Rao, P.; Bhanumurthy, P. Assessment of Hydrogeochemical Processes in a Coastal Region: Application of Multivariate Statistical Model. J. Geol. Soc. India 2014, 84, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahraoui, H.; Belhadj, A.-E.; Triki, Z.; Boudella, N.; Seder, S.; Amrane, A.; Zhang, J.; Moula, N.; Tifoura, A.; Ferhat, R.; et al. Mixed Coagulant-Flocculant Optimization for Pharmaceutical Effluent Pretreatment Using Response Surface Methodology and Gaussian Process Regression. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 169, 909–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchelkia, N.; Tahraoui, H.; Amrane, A.; Belkacemi, H.; Bollinger, J.-C.; Bouzaza, A.; Zoukel, A.; Zhang, J.; Mouni, L. Jujube Stones Based Highly Efficient Activated Carbon for Methylene Blue Adsorption: Kinetics and Isotherms Modeling, Thermodynamics and Mechanism Study, Optimization via Response Surface Methodology and Machine Learning Approaches. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 170, 513–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahraoui, H.; Belhadj, A.-E.; Moula, N.; Bouranene, S.; Amrane, A. Optimisation and Prediction of the Coagulant Dose for the Elimination of Organic Micropollutants Based on Turbidity. Kem. U Ind. 2021, 70, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H. Effects of Eutrophication on Maximum Algal Biomass in Lake and River Ecosystems. Inland Waters 2016, 6, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narsimha, A.; Taloor, A. Hydrogeochemical Investigation of Groundwater Quality in the Hard Rock Terrain of South India Using Geographic Information System (GIS) and Groundwater Quality Index (GWQI) Techniques. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 10, 100288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiri, A.; Belkhiri, L.; Asma, M.; Mouni, L. Suitability and Assessment of Surface Water for Irrigation Purpose. In Water Chemistry; Intechopen: London, UK, 2020; ISBN 978-1-78985-557-9. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/profiles/289828 (accessed on 17 January 2023).
- Alver, A. Evaluation of Conventional Drinking Water Treatment Plant Efficiency According to Water Quality Index and Health Risk Assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 27225–27238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Tizzani, R.; Zweers, H.; Rijnaarts, H.; Langenhoff, A.; Fernandes, T. Removal Processes of Individual and a Mixture of Organic Micropollutants in the Presence of Scenedesmus Obliquus. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghrebi, M.; Noori, R.; Bhattarai, R.; Mundher Yaseen, Z.; Tang, Q.; Al-Ansari, N.; Madani, K. Iran’s agriculture in the Anthropocene. Earth’s Future 2020, 8, e2020EF001547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, R.; Sabahi, M.S.; Karbassi, A.R.; Baghvand, A.; Zadeh, H.T. Multivariate statistical analysis of surface water quality based on correlations and variations in the data set. Desalination 2010, 260, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, R.; Karbassi, A.; Khakpour, A.; Shahbazbegian, M.; Badam, H.M.K.; Vesali-Naseh, M. Chemometric analysis of surface water quality data: Case study of the Gorganrud River Basin, Iran. Environ. Model. Assess. 2012, 17, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiri, A.; Belkhiri, L.; Mouni, L. Evaluation of Surface Water Quality for Drinking Purposes Using Fuzzy Inference System. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 6, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federation, W.E.; Aph Association. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Am. Public Health Assoc. 2005, 1, 541. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO). 1993. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso-iec:2382:-1:ed-3:v1:en (accessed on 17 January 2023).
- Water–Specification, I.S.D. Bureau of Indian Standards. New Delhi India. 2012. pp. 1–12. Available online: http://cgwb.gov.in/documents/wq-standards.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2023).
- Steduto, P.; Faurès, J.-M.; Hoogeveen, J.; Winpenny, J.; Burke, J. Coping with Water Scarcity: An Action Framework for Agriculture and Food Security. FAO Water Rep. 2012, 16, 78. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Progress on Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene: 2017 Update and SDG Baselines; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Noori, R.; Berndtsson, R.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Adamowski, J.F.; Abyaneh, M.R. A critical review on the application of the National Sanitation Foundation Water Quality Index. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkhiri, L.; Mouni, L.; Sheikhy Narany, T.; Tiri, A. Evaluation of Potential Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Groundwater Using the Integration of Indicator Kriging and Multivariate Statistical Methods. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 4, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiri, A.; Lahbari, N.; Abderrahmane, B. Assessment of the Quality of Water by Hierarchical Cluster and Variance Analyses of the Koudiat Medouar Watershed, East Algeria. Appl. Water Sci. 2015, 7, 4197–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization; WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; Volume 1, ISBN 92-4-154638-7. [Google Scholar]
- Raychaudhuri, S.; Jena; Kumar, M.; Ashwani; Srivastava, S. WQI to Monitor Water Quality for Irrigation and Potable Use; Indian Council of Agricultural Research Bhubaneswar: Bhubaneswar, Indian, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jehan, S.; Muhammad, S.; Khan, S.; Khattak, S.; Muhammad, N.; Rashid, A. Hydrochemical Properties of Drinking Water and Their Sources Apportionment of Pollution in Bajaur Agency, Pakistan. Measurement 2019, 139, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Yu, J.; Du, Y.; Li, H.; Su, C.-H. Artificial Intelligence Simulation of Pb(II) and Cd(II) Adsorption Using a Novel Metal Organic Framework-Based Nanocomposite Adsorbent. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 343, 117681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaba, E.; Jemna, D.; Viorica, E.-D.; Balan, C. Discriminant Analysis in the Study of Romanian Regional Economic Development. An. Ştiinţifice Ale Univ. “Alexandru Ioan Cuza” Din Iaşi Tomul LIV Ştiinţe Econ. 2007, 54, 147–153. [Google Scholar]
| Parameters | Characteristics | Analytical Method | Range | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General | pH | pH/EC/TDS meter | pH 4.7 and 9.2 | |
| Electrical conductivity | pH/EC/TDS meter | Potassium chloride | µS/cm | |
| Total dissolved solids (TDS) | Calculation | EC X (0.55–0.75) | mg/L | |
| Total hardness (CaCO3) | EDTA titrimetric | EDTA, ammonia buffer | mg/L | |
| and Eriochrome | ||||
| Black-T (EBT) indicator | ||||
| Major cations | Calcium (Ca) | EDTA titrimetric | EDTA, sodium hydroxide | mg/L |
| and murexide | ||||
| Magnesium (Mg) | Calculation | MgH = TH − CaH;Mg = MgH × Eq | mg/L | |
| Wt of Mg × Normality of EDTA | ||||
| Sodium (Na) | Flame photometric | Sodium chloride (NaCl) and KCl | mg/L | |
| Potassium (K) | Flame photometric | NaCl and KCl | mg/L | |
| Major anions | Bicarbonates (HCO3) | Titrimetric | Hydrosulfuric acide (H2SO4) | mg/L |
| phenlphthalein and methyl orange | ||||
| Chloride (Cl) | Titrimetric | Silver nitrate (AgNO3) | mg/L | |
| potassium chromate | ||||
| Sulfates (SO4) | UV-visible spectrophotometer | HCI, ethyl alcohl, NaCl | mg/L | |
| barium chloride, sodium sulfate | ||||
| Nitrate (NO3) | UV-visible spectrophotometer | Potassium nitrate (KNO3) | mg/L | |
| Phenol disulfonic acide, ammonia |
| WQI Values | Water Quality for Drinking Purpose |
|---|---|
| Less than 25 | Excellent |
| 26–50 | Good |
| 51–75 | Poor |
| 76–100 | Very poor |
| More than 100 | Unsuitable |
| IWQI Values | Class | Restriction |
|---|---|---|
| Less than 150 | I | None |
| 150–300 | II | Slight |
| 301–450 | III | Moderate |
| More than 450 | IV | Severe |
| Parameters | Ca | Mg | Na | K | Cl | SO4 | HCO3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WHO (2017) | 75 | 50 | 200 | 10 | 250 | 250 | 500 |
| FAO (1985) | 400 | 60 | 920 | 2 | 1065 | 1920 | 610 |
| Weight (wi) | |||||||
| Dam | 5 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 5 |
| Oued Rboua | 5 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Oued Timgad | 5 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Wastewater | 5 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Relative weight (Wi) | |||||||
| Dam | 0.1923 | 0.1154 | 0.1538 | 0.0769 | 0.1538 | 0.1154 | 0.1923 |
| Oued Rboua | 0.1923 | 0.1154 | 0.1538 | 0.0769 | 0.1154 | 0.1538 | 0.1923 |
| Oued Timgad | 0.1923 | 0.1154 | 0.1538 | 0.0769 | 0.1154 | 0.1538 | 0.1923 |
| Wastewater | 0.1923 | 0.1154 | 0.1538 | 0.0769 | 0.1154 | 0.1538 | 0.1923 |
| pH | EC | Ca | Mg | Na | K | Cl | SO4 | HCO3 | WQI | IWQI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dam | |||||||||||
| Min | 7.4 | 1040 | 88.18 | 39.36 | 80.00 | 0.812 | 75.25 | 78.00 | 134.20 | 55.36 | 23.50 |
| Max | 7.8 | 1800 | 99.70 | 45.49 | 103.30 | 1.289 | 124.25 | 92.00 | 201.30 | 62.18 | 27.80 |
| Mean | 7.5 | 1349 | 94.04 | 42.72 | 93.92 | 1.007 | 90.32 | 85.77 | 173.21 | 58.15 | 25.46 |
| SD | 0.14 | 302.44 | 4.14 | 2.07 | 6.22 | 0.14 | 13.74 | 4.97 | 19.87 | 1.98 | 1.45 |
| CV | 1.90 | 22.42 | 4.40 | 4.85 | 6.62 | 14.40 | 15.21 | 5.79 | 11.47 | 3.41 | 5.69 |
| Oued Rboua | |||||||||||
| Min | 7.5 | 680 | 88.18 | 21.48 | 93.70 | 0.908 | 17.75 | 75.00 | 231.80 | 50.88 | 22.39 |
| Max | 8.4 | 1230 | 136.27 | 45.44 | 120.70 | 1.638 | 53.25 | 98.00 | 372.10 | 78.22 | 36.22 |
| Mean | 7.75 | 1010 | 120.24 | 37.67 | 109.35 | 1.371 | 35.50 | 91.00 | 307.28 | 68.05 | 30.93 |
| SD | 0.44 | 258.07 | 21.95 | 10.97 | 12.38 | 0.35 | 14.49 | 10.74 | 72.25 | 11.94 | 6.21 |
| CV | 5.62 | 25.55 | 18.26 | 29.11 | 11.32 | 25.19 | 40.82 | 11.80 | 23.51 | 17.55 | 20.09 |
| Oued Timgad | |||||||||||
| Min | 7.1 | 1200 | 108.20 | 30.60 | 80.00 | 0.812 | 35.50 | 86.00 | 402.60 | 69.45 | 32.01 |
| Max | 8.6 | 1500 | 132.26 | 47.84 | 130.50 | 1.835 | 71.00 | 115.00 | 591.70 | 84.75 | 41.26 |
| Mean | 7.9 | 1326 | 116.93 | 37.49 | 105.64 | 1.257 | 45.18 | 101.32 | 500.51 | 75.30 | 36.51 |
| SD | 0.49 | 116.90 | 8.39 | 5.14 | 15.02 | 0.35 | 14.56 | 10.96 | 58.76 | 5.39 | 3.34 |
| CV | 6.30 | 8.81 | 7.17 | 13.72 | 14.22 | 28.09 | 32.22 | 10.82 | 11.74 | 7.16 | 9.15 |
| Wastewater | |||||||||||
| Min | 6.8 | 1010 | 92.18 | 27.84 | 82.00 | 0.830 | 51.57 | 88.00 | 597.80 | 72.47 | 38.53 |
| Max | 7.6 | 1660 | 128.30 | 38.28 | 133.50 | 1.815 | 106.50 | 98.00 | 1000.40 | 95.26 | 54.44 |
| Mean | 7.1 | 1173 | 107.84 | 33.48 | 101.53 | 1.30 | 65.87 | 92.27 | 758.38 | 82.07 | 43.68 |
| SD | 0.28 | 185.53 | 11.50 | 4.51 | 19.74 | 0.36 | 21.77 | 3.53 | 116.18 | 6.11 | 4.59 |
| CV | 3.96 | 15.82 | 10.67 | 13.48 | 19.44 | 27.71 | 33.06 | 3.83 | 15.32 | 7.44 | 10.52 |
| Variables | Ca | Mg | Na | K | Cl | SO4 | HCO3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weighting factor | |||||||
| Dam | 0.19 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.19 |
| Oued Reboua | 0.19 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.19 |
| Oued Timgad | 0.19 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.19 |
| Wastewater | 0.19 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.19 |
| Wi Ii Values | |||||||
| Dam | 13.31 | 8.24 | 12.73 | 4.52 | 8.24 | 12.73 | 13.05 |
| Oued Reboua | 13.06 | 8.53 | 12.29 | 2.89 | 7.61 | 11.15 | 13.02 |
| Oued Timgad | 13.58 | 8.95 | 11.61 | 1.98 | 6.81 | 10.32 | 12.66 |
| Wastewater | 10.08 | 6.32 | 7.43 | 1.03 | 5.35 | 9.28 | 11.09 |
| NSFWQI | |||||||
| Dam | 72.82 | ||||||
| Oued Reboua | 68.55 | ||||||
| Oued Timgad | 65.91 | ||||||
| Wastewater | 50.58 | ||||||
| Variables | Wilks’ Lambda | F | df1 | df2 | p-Level (Sig.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 0.555 | 8.808 | 3 | 33 | 0.000 |
| EC | 0.773 | 3.226 | 3 | 33 | 0.035 |
| Ca | 0.502 | 10.924 | 3 | 33 | 0.000 |
| Mg | 0.649 | 5.961 | 3 | 33 | 0.002 |
| Na | 0.868 | 1.674 | 3 | 33 | 0.192 |
| K | 0.823 | 2.361 | 3 | 33 | 0.089 |
| Cl | 0.388 | 17.358 | 3 | 33 | 0.000 |
| SO4 | 0.586 | 7.777 | 3 | 33 | 0.000 |
| HCO3 | 0.087 | 116.063 | 3 | 33 | 0.000 |
| WQI | 0.250 | 33.031 | 3 | 33 | 0.000 |
| IWQI | 0.193 | 45.914 | 3 | 33 | 0.000 |
| Function | Eigenvalue | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Canonical Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16.481 a | 77.2 | 77.2 | 0.971 |
| 2 | 4.324 a | 20.2 | 97.4 | 0.901 |
| 3 | 0.553 a | 2.6 | 100 | 0.597 |
| Test of Function(s) | Wilks’ Lambda | Chi-Square | df | p-Level (Sig.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 through 3 | 0.007 | 156.660 | 15 | 0.000 |
| 2 through 3 | 0.121 | 66.535 | 8 | 0.000 |
| 3 | 0.644 | 13.859 | 3 | 0.003 |
| Variables | Function | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| pH | 0.432 | 0.592 | 0.308 |
| K | −0.403 | 0.668 | −1.023 |
| Cl | 0.723 | −0.937 | 0.536 |
| SO4 | 0.305 | 0.650 | 0.995 |
| HCO3 | −1.057 | −0.272 | 0.136 |
| Variables | Function | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| HCO3 | −0.791 * | −0.157 | 0.497 |
| IWQI b | −0.529 * | −0.061 | 0.346 |
| Cl | 0.156 | −0.515 * | 0.244 |
| pH | 0.106 | 0.366 * | 0.252 |
| EC b | −0.039 | −0.110 * | −0.105 |
| SO4 | −0.106 | 0.291 | 0.529 * |
| WQI b | −0.370 | −0.042 | 0.472 * |
| Ca b | 0.072 | 0.172 | 0.363 * |
| Na b | −0.102 | −0.012 | −0.199 * |
| K | −0.095 | 0.103 | −0.193 * |
| Mg b | −0.013 | 0.027 | 0.117 * |
| Variables | Function | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| pH | 1.237 | 1.697 | 0.881 |
| K | −1.312 | 2.177 | −3.334 |
| Cl | 0.043 | −0.056 | 0.032 |
| SO4 | 0.040 | 0.085 | 0.130 |
| HCO3 | −0.014 | −0.004 | 0.002 |
| (Constant) | −7.777 | −18.124 | −17.580 |
| Variables | Station | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dam | Oued Rboua | Oued Timgad | Wastewater | |
| pH | 114.003 | 114.213 | 113.702 | 101.158 |
| K | 15.780 | 36.539 | 29.461 | 28.856 |
| Cl | 0.757 | 0.285 | 0.319 | 0.342 |
| SO4 | 2.816 | 2.761 | 2.983 | 2.370 |
| HCO3 | −0.158 | −0.117 | −0.089 | −0.019 |
| (Constant) | −580.199 | −581.729 | −602.609 | −493.412 |
| Station | Predicted Group Membership | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dam | Oued Rboua | Oued Timgad | Wastewater | ||||
| Original | Count | Dam | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 |
| Oued Rboua | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | ||
| Oued Timgad | 0 | 1 | 10 | 0 | 11 | ||
| Wastewater | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 11 | ||
| % | Dam | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | |
| Oued Rboua | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | ||
| Oued Timgad | 0 | 9.1 | 90.9 | 0 | 100 | ||
| Wastewater | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | ||
| Cross-validated b | Count | Dam | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 |
| Oued Rboua | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 4 | ||
| Oued Timgad | 0 | 1 | 10 | 0 | 11 | ||
| Wastewater | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 11 | ||
| % | Dam | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | |
| Oued Rboua | 0 | 75 | 25 | 0 | 100 | ||
| Oued Timgad | 0 | 9.1 | 90.9 | 0 | 100 | ||
| Wastewater | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mammeri, A.; Tiri, A.; Belkhiri, L.; Salhi, H.; Brella, D.; Lakouas, E.; Tahraoui, H.; Amrane, A.; Mouni, L. Assessment of Surface Water Quality Using Water Quality Index and Discriminant Analysis Method. Water 2023, 15, 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040680
Mammeri A, Tiri A, Belkhiri L, Salhi H, Brella D, Lakouas E, Tahraoui H, Amrane A, Mouni L. Assessment of Surface Water Quality Using Water Quality Index and Discriminant Analysis Method. Water. 2023; 15(4):680. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040680
Chicago/Turabian StyleMammeri, Asma, Ammar Tiri, Lazhar Belkhiri, Hichem Salhi, Djouhaina Brella, Elhadj Lakouas, Hichem Tahraoui, Abdeltif Amrane, and Lotfi Mouni. 2023. "Assessment of Surface Water Quality Using Water Quality Index and Discriminant Analysis Method" Water 15, no. 4: 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040680
APA StyleMammeri, A., Tiri, A., Belkhiri, L., Salhi, H., Brella, D., Lakouas, E., Tahraoui, H., Amrane, A., & Mouni, L. (2023). Assessment of Surface Water Quality Using Water Quality Index and Discriminant Analysis Method. Water, 15(4), 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040680









