Factors That Impact the Implementation of Water Safety Plans—A Case Study of Brazil
Abstract
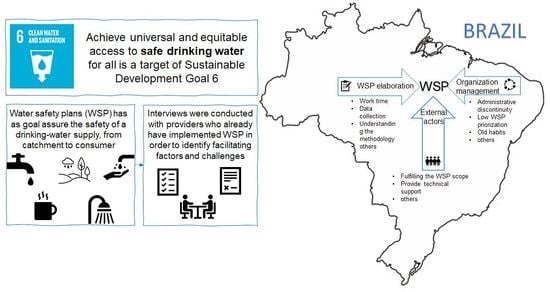
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Survey Regarding Existing WSPs in Brazil
2.2. Preparation of the Evaluation Tool
2.3. Identification of Facilitating/Challenging Factors of WSP
2.4. Systematization of the Information
3. Results and Discussion
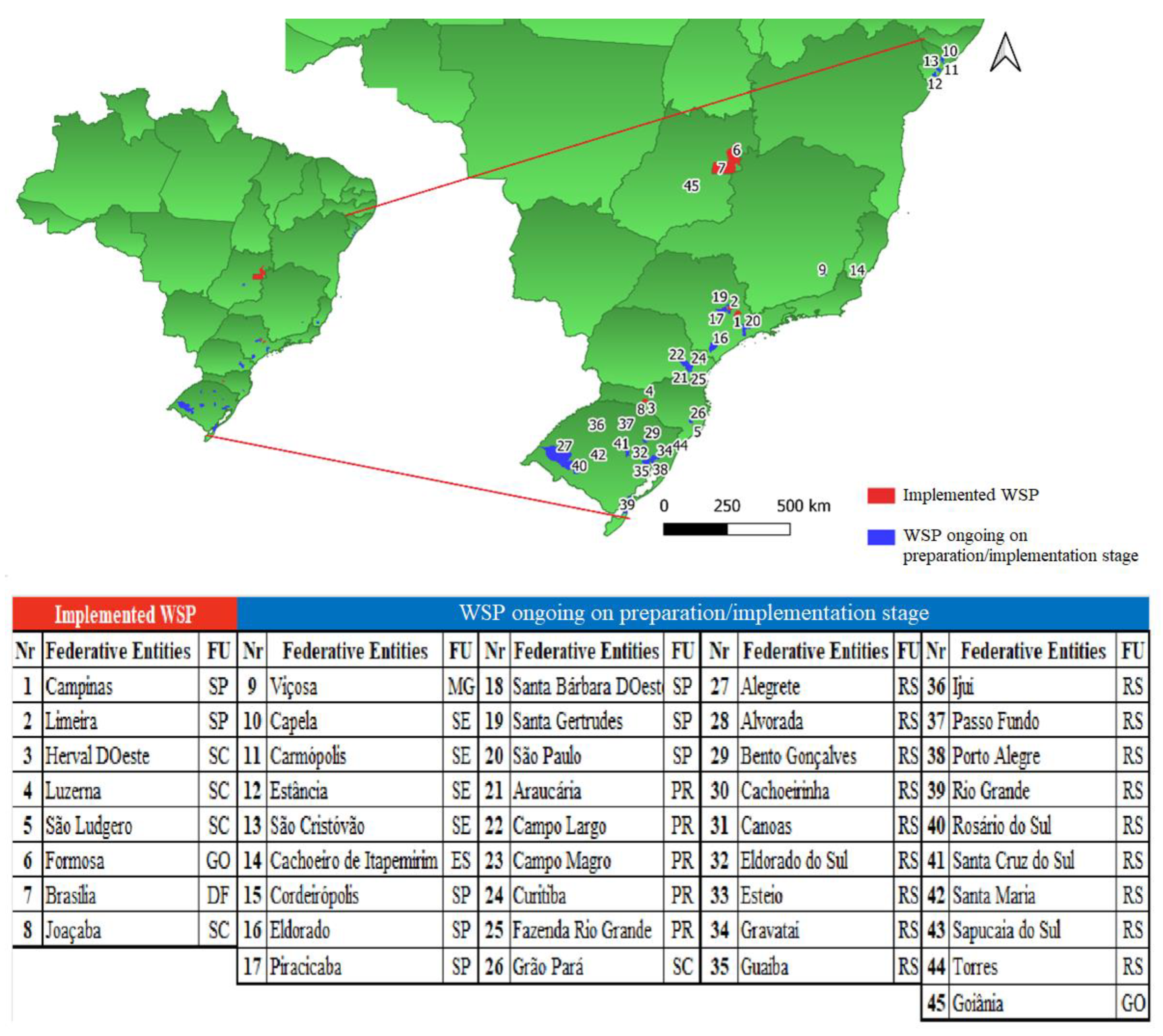
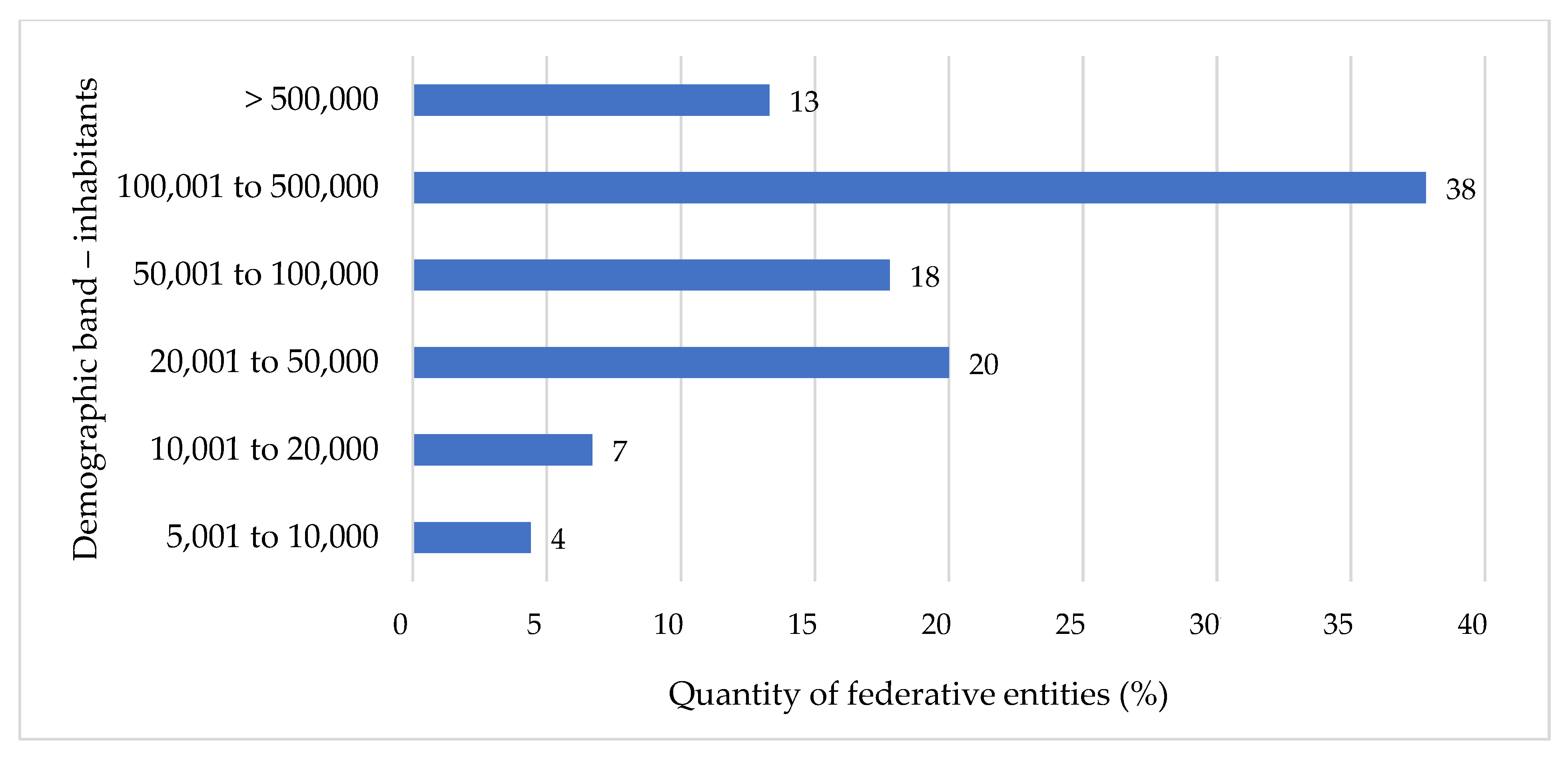
3.1. Overview of WSP in Brazil
3.2. Aspects related to Water Supply Public Service Providers
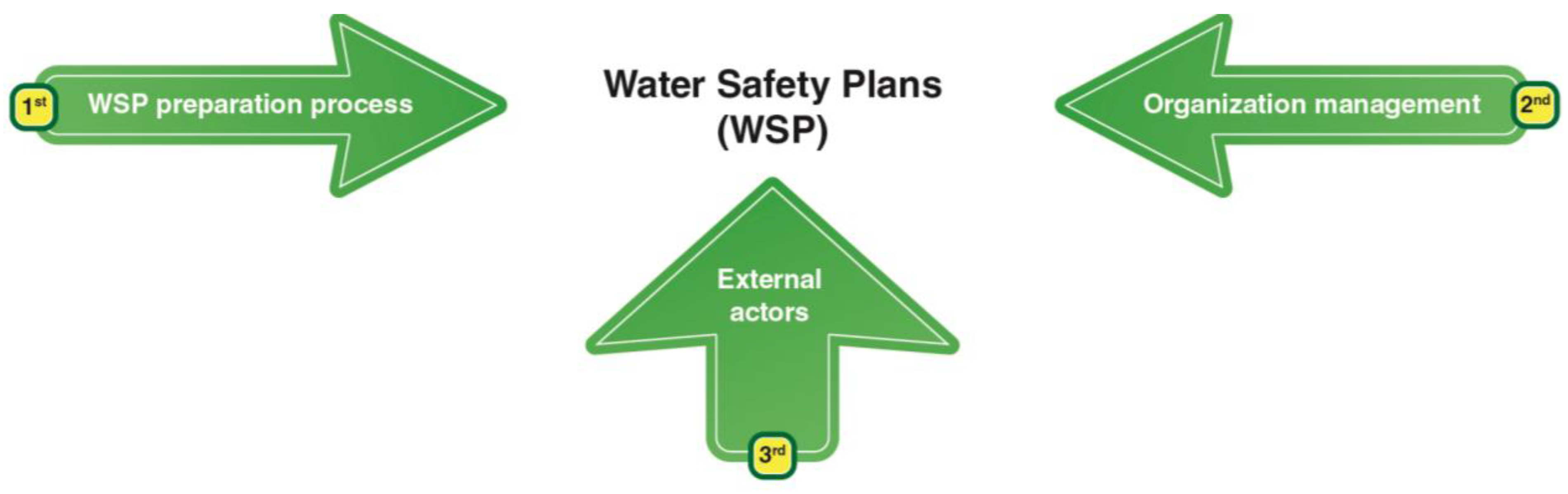
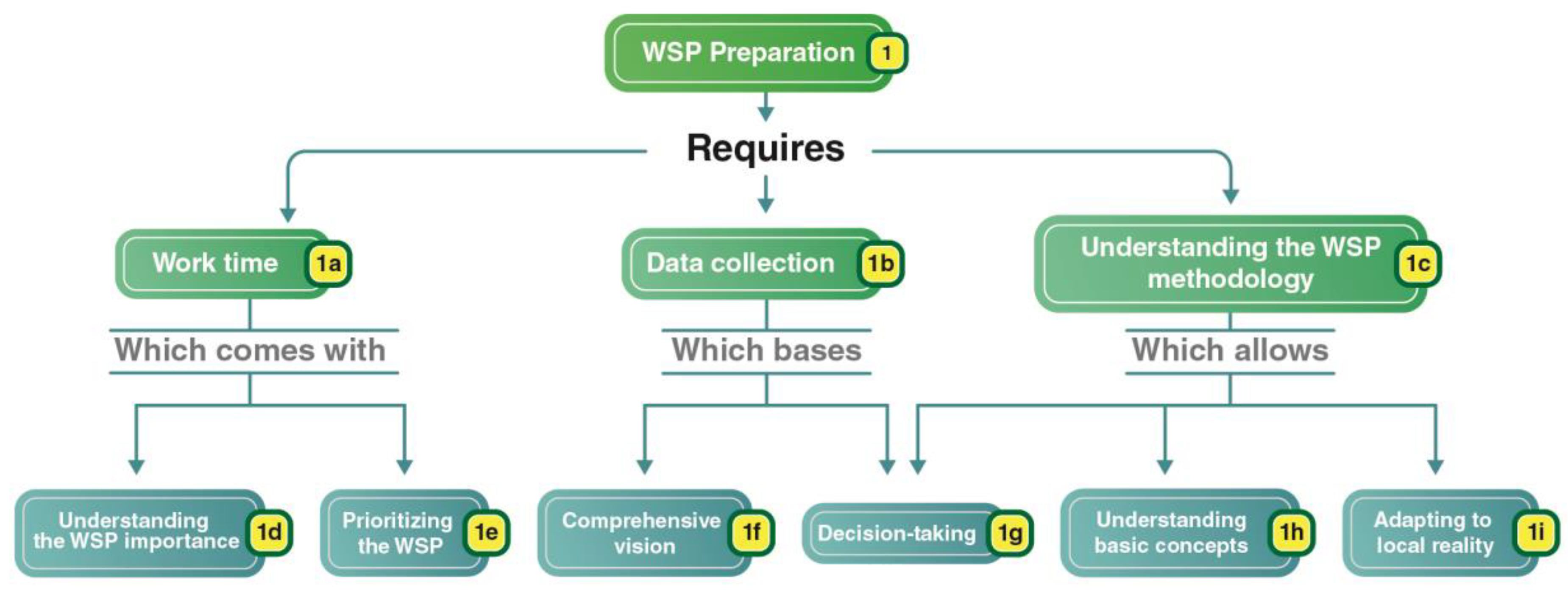
3.2.1. Aspects Related to WSPs’ Preparation
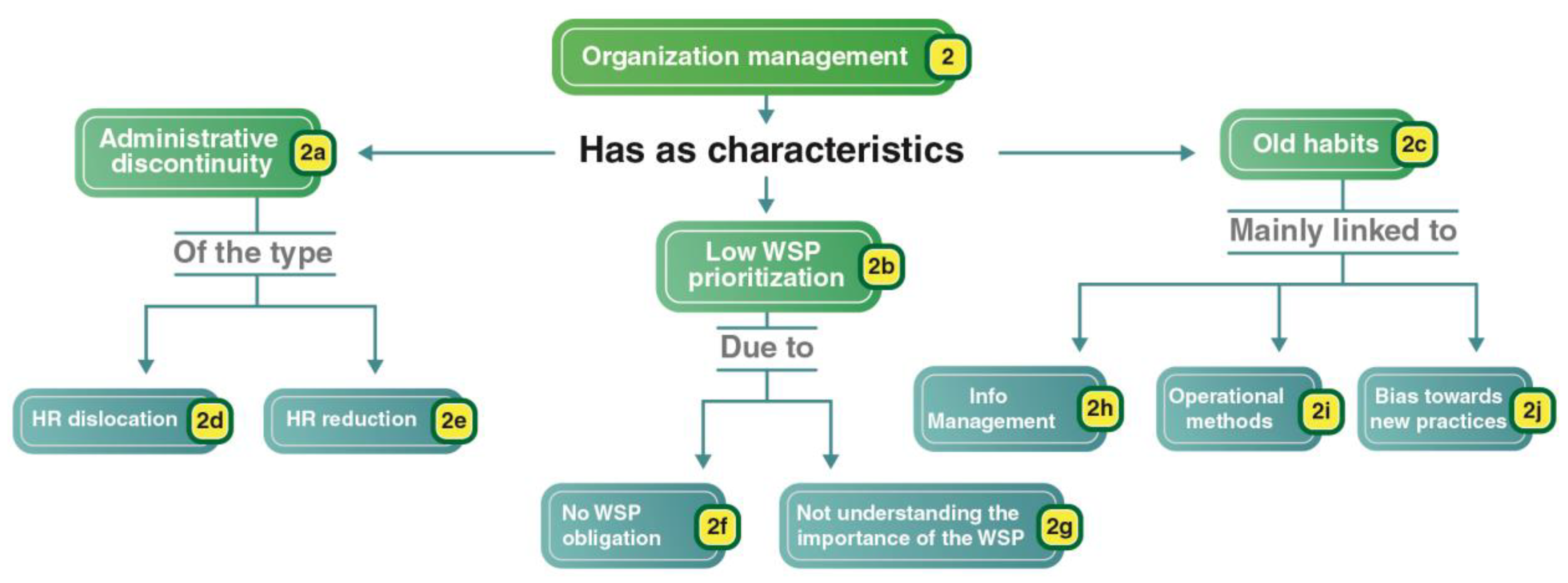
3.2.2. Aspects of Management
3.2.3. External Actors in WSP
3.3. Facilitating and/or Challenging Factors in the Implementation of WSP in Brazil
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Interview Script
- Researcher introduction, her research project, the terms of free consent of the research, guaranteeing of anonymity and opening space for eventual doubts in the interview or in the future, clarifying the means of communication described in the Free and Clarified Term of Consent;
- Present the day’s schedule and the procedures that will be done after the interview.
- Confirming the interviewees’ data: name, company, position and role in the preparation and implementing of the WSP.
- Confirming already obtained data regarding the WSP and about the city: year of the preparation beginning, year of implementing beginning; comprised systems, city population, existence of municipal basic sanitation plan, acting watershed committees in the region; type of service provider; if there is a preview in changing the type of service provider; if there is a regulatory entity to which the SAAE/SIMAE/CAESB answers to.
- What kinds of planning the SAAE/SIMAE/CAESB does daily? Did it take part in the preparation of the Municipal Basic Sanitation Program?
- Report how did the SAAE/SIMAE/CAESB learn of the existence of the Water Safety Plans and what was the motivation for implementing it.
- Report the WSP preparation process. What factors hindered the process of preparation? Which factors were crucial for facilitating the WSP preparation process?
- Did the SAAE/SIMAE/CAESB team have contact with risk evaluation methodologies yet?
- Did the SAAE/SIMAE/CAESB face hardships in understanding the WSP methodology proposed by the WHO, which involves a great step of system evaluation, operational surveillance and management plans definition? In which of those steps was there more difficulty and more ease?
- How was the process to move the WSP while written plan to its effective implementing?
- What were the challenges in WSP implementing? Was there a need for an adaptation period? Were there difficulties in convincing the workers to adopt the new procedures?
- What is the importance of the supporting institutions for the WSP preparation? And in the implementing, have you had aid of supporting institutions?
- The WSP collaborates to establish good relationship with the regulatory agency of basic sanitation services?
- Was there any kind of interference from the city hall fostering or culling the WSP preparation and implementing?
- Thanking the interviewee for making time for the interview.
- Reinforcing that the interview results will be sent to the interviewees.
- Interviewing other institutions.
- Researcher introduction, her research project, the terms of free consent of the research, guaranteeing of anonymity and opening space for eventual doubts in the interview or in the future, clarifying the means of communication described in the Free and Clarified Term of Consent.
- Confirming the interviewees’ data: name, organization, position, role in the support to WSP preparation and which service providers/city the interviewee has supported.
- Report how did you approach the WSP theme.
- What is the importance of the supporting institutions for the WSP preparation? And the implementing, have you had aid of the supporting institutions?
- How were the experiences of support to the mentioned cities (Joaçaba, Luzerna, Herval D’Oeste, Viçosa). How was your organization’s and your support performed, specifically?
- What difficulty did you notice that the service providers have shown in training and capacity building?
- Thanking the interviewee for making time for the interview.
References
- United Nations (UN). Progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals; Report of the Secretary-General UN: New York, NY, USA, 2022.
- Agência Nacional De Águas E Saneamento Básico (ANA). Conjuntura dos Recursos Hídricos No Brasil 2021–Relatório Pleno; ANA: Brasília, Brazil, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- SNS/MDR. Sistema Nacional de Informações Sobre Saneamento (SNIS): Diagnóstico dos Serviços de Água e Esgotos–2020; SNS/MDR: Brasília, Brazil, 2021.
- Bartram, J.; Corrales, L.; Davison, A.; Deere, D.; Drury, D.; Gordon, B.; Howard, G.; Rinehold, A.; Stevens, M. Water Safety Plan Manual: Step-by-Step Risk Management for Drinking-Water Suppliers; World Health Organization: Genéve, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Cohen, A.; Li, Z.; Lv, S.; He, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X. Intermittent Water Supply Management, Household Adaptation, and Drinking Water Quality: A Comparative Study in Two Chinese Provinces. Water 2020, 12, 1361. [Google Scholar]
- Diário Oficial da União. Portaria N. 2.914, de 12 de Dezembro de 2011; Diário Oficial da União: Brasília, Brazil, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Diário Oficial da União. Portaria N. 888, de 4 de Maio de 2021; Diário Oficial da União: Brasília, Brazil, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- World Healh Organization (WHO). Optimizing Regulatory Frameworks for Safe and Clean Drinking-Water-Water Safety Plans: Why Are They Important and How Can Their Implementation Be Supported by Regulations; WHO: Genéve, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, Y.Y.; Parker, A.; Smith, J.S.; Pollard, S.J.T. Risk management for drinking water safety in low and middle income countries-cultural influences on water safety plan (WSP) implementation in urban water utilities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roeger, A.; Tavares, A.F. Water safety plans by utilities: A review of research on implementation. Util. Policy 2018, 53, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Tsitsifli, S.; Tsoukalas, D.S. Water Safety Plans and HACCP implementation in water utilities around the world: Benefits, drawbacks and critical success factors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 28, 18837–18849. [Google Scholar]
- Ventura, K.S.; Vaz Filho, P.; Nascimento, S.G. Plano de segurança da água implementado na estação de tratamento de água de Guaraú, em São Paulo. Eng. Ambient. Sanit áRia 2019, 24, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murei, A.; Mogane, B.; Mothiba, D.P.; Mochware, O.T.W.; Sekgobela, J.M.; Mudau, M.; Musumuvhi, N.; Khabo-Mmekoa, C.M.; Moropeng, R.C.; Momba, M.N.B. Barriers to Water and Sanitation Safety Plans in Rural Areas of South Africa—A Case Study in the Vhembe District, Limpopo Province. Water 2022, 14, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-alvarez, M.S.; Gutiérrez-lópez, A.; Iribarnegaray, M.A.; Weir, M.H.; Seghezzo, L. Long-Term Assessment of a Water Safety Plan (WSP) in Salta, Argentina. Water 2022, 14, 2948. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrero, G.; Bichai, F.; Rusca, M. Experiential Learning through Role-Playing: Enhancing Stakeholder Collaboration in Water Safety Plans. Water 2018, 10, 227. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, R.K. Pesquisa Qualitativa do IníCio ao Fim; Penso: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Amjad, U.Q.; Luh, J.; Baum, R.; Bartram, J. Water safety plans: Bridges and barriers to implementation in North Carolina. J. Water Health 2016, 14, 816–826. [Google Scholar]
- Novak, J.D.; Cañas, A.J. The Theory Underlying Concept Maps and How to Construct and Use Them; Institute for Human and Machine Cognition: Pensacola, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bardin, L. Análise de Conteúdo; Edições 70: São Paulo, Brazil, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ministério do Desenvolvimento Regional. Diagnóstico Temático–Serviços de Água e Esgoto: Visão Geral; Ministério do Desenvolvimento Regional: Brasília, Brazil, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE). Malha Municipal 2015; IBGE: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2015.
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE). População Estimada: Estimativas da População Residente Com Data de Referência 1o de Julho de 2021; IBGE: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2021.
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE); Secretarias Estaduais de Governo e Superintendência da Zona Franca de Manaus (SUFRAMA). Produto Interno Bruto per Capta Dos Municípios; IBGE: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2016.
- IBGE. Pesquisa de Informações Básicas Municipais Saneamento–2017; IBGE: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2018.
- SUPERINTENDÊNCIA ESTADUAL DE SANTA CATARINA–SUEST-SC. In Relatório de Gestão 2014; FUNASA: Brasília, Brazil, 2014. Available online: http://www.funasa.gov.br/site/wp-content/uploads/2011/10/Relatorio-de-Gestao-2014_Funasa_Suest-SC.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- Shultz, G. Introdução à Gestão de Organizações; Editora da UFRGS: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kayser, G.; Loret, J.F.; Setty, K.; De Thé, C.B.; Martin, J.; Puigdomenech, C.; Bartram, J. Water safety plans for water supply utilities in China, Cuba, France, Morocco and Spain: Costs, benefits, and enabling environment elements. Urban Water J. 2019, 16, 277–288. [Google Scholar]
- Ncube, M.; Pawandiwa, M.N. Water safety planning and implementation: Lessons from South Africa. J. Water Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2013, 3, 557–563. [Google Scholar]
- Kanyesigye, C.; Marks, S.J.; Nakanjako, J.; Kansiime, F.; Ferrero, G. Status of water safety plan development and implementation in Uganda. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, A.; Summerill, C. Water safety plan implementation in East Africa: Motivations and barriers. Waterlines 2013, 32, 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Khatri, K.; Iddings, S.; Overmaps, M.; Hasan, T.; Gerber, F. Implementation of drinking water safety plans and lessons from the Pacific islands. Waterlines 2011, 30, 235–247. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Vidal, A.; Carlos Escobar-Rivera, J.; Torres-Lozada, P. Development and implementation of a water-safety plan for drinking-water supply system of Cali, Colombia. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 224, 113422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinehold, A.; Corrales, L.; Medlin, E.; Gelting, R.J. Water Safety Plan demonstration projects in Latin America and the Caribbean: Lessons from the field. Water Sci. Technol.-Water Supply 2011, 11, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KOT, M.; Castleden, H.; Gagnon, G.A. The human dimension of water safety plans: A critical review of literature and information gaps. Environ. Rev. 2015, 23, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Nijhawan, A.; Jain, P.; Sargaonkar, A.; Labhasetwar, P.K. Implementation of water safety plan for a large-piped water supply system. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 5547–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumpel, E.; Delaire, C.; Peletz, E.; Kisiangani, J.; Rinehold, A.; De France, J.; Sutherland, D.; Khush, R. Measuring the Impacts of Water Safety Plans in the Asia-Pacific Region. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gärtner, N.; Lindhe, A.; Wahtra, J.; Söderqvist, T.; Lång, L.-O.; Nordzell, H.; Norrman, J.; Rosén, L. Integrating Ecosystem Services into Risk Assessments for Drinking Water Protection. Water 2022, 14, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J. Avaliação e Gestão de Riscos No Controle da Qualidade da Água em Redes de Distribuição: Estudo de Caso. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo (USP), São Carlos, Brazil, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gradvohl, S.T.S. Análise de Riscos em Sistemas de Abastecimento de Água Sob a Perspectiva do Plano de Segurança da Água. Estudo de Caso: Região Metropolitana de Fortaleza No Estado do Ceará. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal do Ceará (UFC), Fortaleza, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bezerra, N.R. Aplicação de Redes Bayesianas na Identificação de Perigos em Sistemas de Abastecimento de Água Para Consumo Humano: Estudo de Caso No Município de Viçosa, Minas Gerais. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal de Viçosa (UFV), Viçosa, Brazil, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Perrier, E.; Kot, M.; Castleden, H.; Gagnon, G.A. Drinking water safety plans: Barriers and bridges for small systems in Alberta, Canada. Water Policy 2014, 16, 1140–1154. [Google Scholar]
- Summerill, C.; Pollard, S.J.T.; Smith, J.A.; Breach, B.; Williams, T. Securing executive buy-in for preventative risk management–lessons from water safety plans. Water Supply 2011, 11, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abolli, S.; Alimohammadi, M.; Zamanzadeh, M.; Yunesian, M.; Yaghmaeian, K.; Aghaei, M. Water safety plan: A novel approach to evaluate the efficiency of the water supply system in Garmsar. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 211, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, S.G.; Shamsuddin, S.A.J.; Feroze Ahmed, M.; Davison, A.; Deere, D.; Howard, G. Development and implementation of water safety plans for small water supplies in Bangladesh: Benefits and lessons learned. J. Water Health 2007, 5, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mälzer, H.-J.; Staben, N.; Hein, A.; Merkel, W. Identification, assessment, and control of hazards in water supply: Experiences from water safety plan implementations in Germany. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmoll, O.; Castell-exner, C.; Chorus, I. From international developments to local practice: Germany’s evaluation and dialogue process towards Water Safety Plan implementation. Water Sci. Technol.-Water Supply 2011, 11, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, M.C.; Alam, K.; Mushtaq, S. Water Policy Implementation In the State of São Paulo, Brazil: Key Challenges and Opportunities. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 60, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- String, G.; Lantagne, D. A systematic review of outcomes and lessons learned from general, rural, and country-specific Water Safety Plan implementations. Water Sci. Technol.-Water Supply 2016, 16, 1580–1594.general, rural, and country-specific Water Safety Plan implementations. Water Sci. Technol.-Water Supply 2016, 16, 1580–1594. [Google Scholar]


| Actor Interviewed | Main Topic | Examples of Questions |
|---|---|---|
| Service Provider | General information | Interviewee data, provider data, federal unity data, which planning the provider usually does, etc. |
| WSP preparation and implementation process | How did the interviewee found out about WSP, how did the preparation process happen, challenges in implementation, what are the harder steps, etc. | |
| Other stakeholders | If there is some external influence on the processes, if regulatory or other agencies help in the process. | |
| Members of Supporting Institutions | Experience with WSP | How the interviewed heard about WSP, how it was to support service providers in this process, etc. |
| External representatives importance | Importance and impact of stakeholders external to service providers in WSP preparation or implementation. | |
| Main challenges and facilitating factors identified | Challenges they have identified in training courses or workshops, main difficulties and factors that help service providers, etc. |
| Code | Actor | Covered City/Cities | Time since 1st WSP Implementation Tentative (Years) | Supporting Institutions | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suest (A1) | National Funasa (A2) | PAHO/WHO 1 (A3) | ||||
| S+ | Service provider (SP) covering state/district | 1 | 8 | - | - | - |
| M+ | Municipal SP | 1 | 10 | - | x | - |
| IM+ | Intermunicipal SP | 3 | 5 | x | x | - |
| S- | State/municipal SP whose WSP implementation did not happen | 1 | 5 | - | - | - |
| M- | Municipal SP whose WSP implementation did not happen | 1 | 13 | - | x | x |
| Service Provider | S+ | M+ | IM+ | M- | S- | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| City | All 1 | A 2 | B 3 | C 4 | All | ||
| WSSP-covered Population | 3,000,236 | 1,159,711 | 20,563 | 29,607 | 5329 | 75.246 | 11,279,793 |
| Produced Water Volume (m3) | 218,977 | 99,401.97 | 1713.2 | 2725.21 | 481.7 | 5883.1 | 944,611.5 |
| Revenue Losses (%) | 19.95 | 12.86 | 26.2 | 20,6 | 26.3 | 29 | Average of 27.8 |
| WSSP Coverage (%) | 98.71 | 98.08 | 91.6 | 100 | 93.4 | 96 | Average of 61.8 |
| WSP in the MBSP | No | Yes | No | ||||
| Regulatory Authority | Yes | ||||||
| WSSP Joint Venture | No | Yes | |||||
| Interviewee role in the WSP | Workgroups | Coordination | Data supplying | Coordination | |||
| City | Population 1 | GDP per Capita (USD) 2 | Type of Service Provider (SP)/Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Federal District | 3,094,325 | 15,153.21 | District/Regional Semi-Public Corporation (SPC) |
| Formosa | 125,705 | 3535.76 | SPC—State/Regional |
| Campinas | 1223,237 | 9554.91 | SPC Municipal/Local |
| Limeira | 310,783 | 7099.11 | Private/Local |
| Herval D’Oeste | 22,820 | 3379.65 | Intermunicipal/Micro-regional Autonomous Water and Sewage Service (SAAE) |
| Joaçaba | 30,684 | 9725.17 | |
| Luzerna | 5683 | 5229.54 | |
| São Ludgero | 13,886 | 8883.85 | Municipal/Local SAAE |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baracho, R.O.; Najberg, E.; Scalize, P.S. Factors That Impact the Implementation of Water Safety Plans—A Case Study of Brazil. Water 2023, 15, 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040678
Baracho RO, Najberg E, Scalize PS. Factors That Impact the Implementation of Water Safety Plans—A Case Study of Brazil. Water. 2023; 15(4):678. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040678
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaracho, Rafaella Oliveira, Estela Najberg, and Paulo Sérgio Scalize. 2023. "Factors That Impact the Implementation of Water Safety Plans—A Case Study of Brazil" Water 15, no. 4: 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040678