Predictive Model Based on K-Nearest Neighbor Coupled with the Gray Wolf Optimizer Algorithm (KNN_GWO) for Estimating the Amount of Phenol Adsorption on Powdered Activated Carbon
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Solution Preparation
2.3. Adsorption Kinetics Experiments
2.4. Adsorption Isotherms
2.5. K-Nearest Neighbor
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Phenol
3.2. Characterization of PAC
3.3. Effect of Operating Parameters
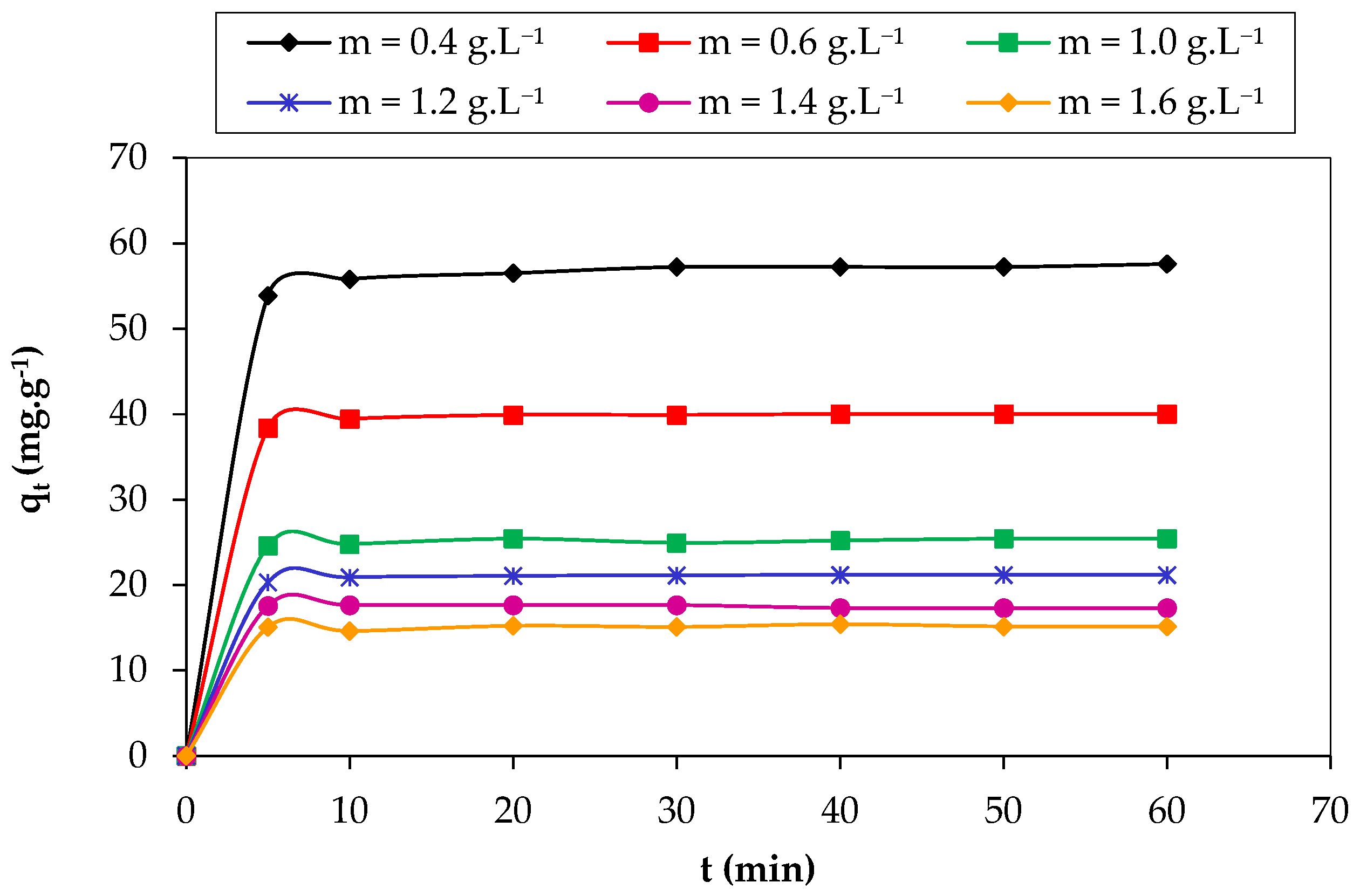
3.3.1. Effect of the Adsorbent Mass to Volume
3.3.2. Effect of the Initial Concentration of Phenol
3.3.3. Effect of Temperature
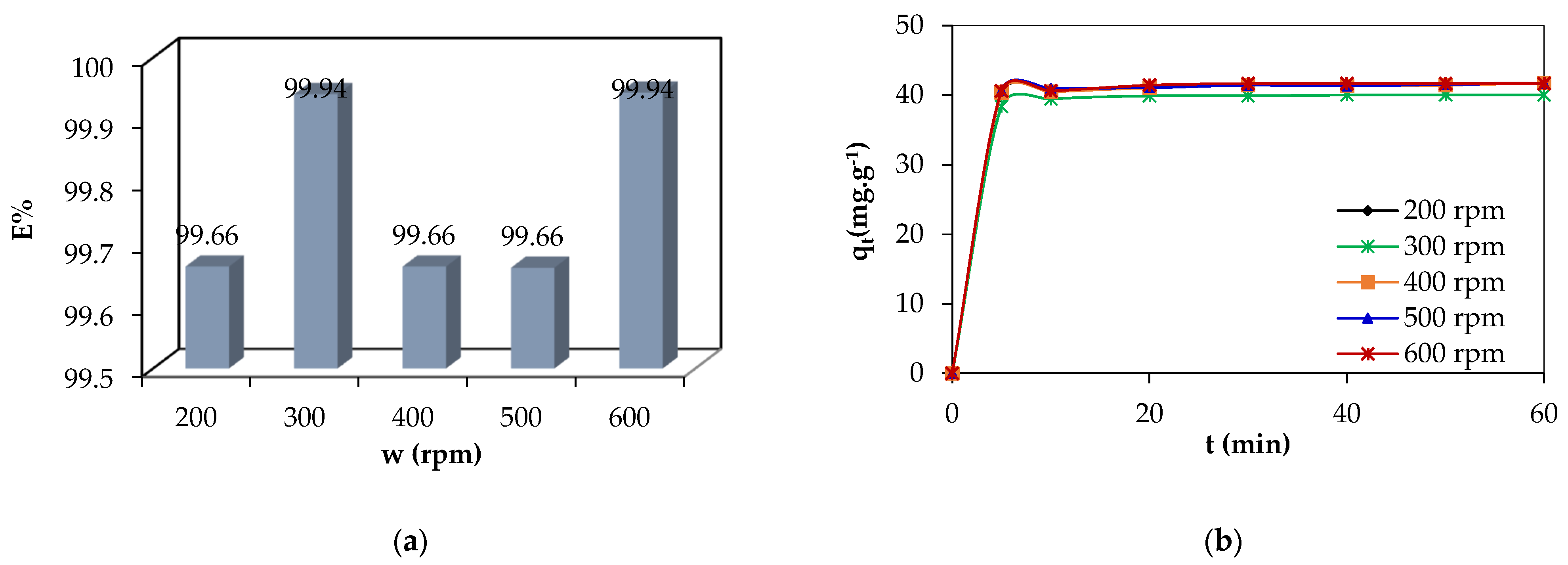
3.3.4. Effect of the Stirring Speed
3.3.5. Effect of the pH
3.4. Kinetics Study
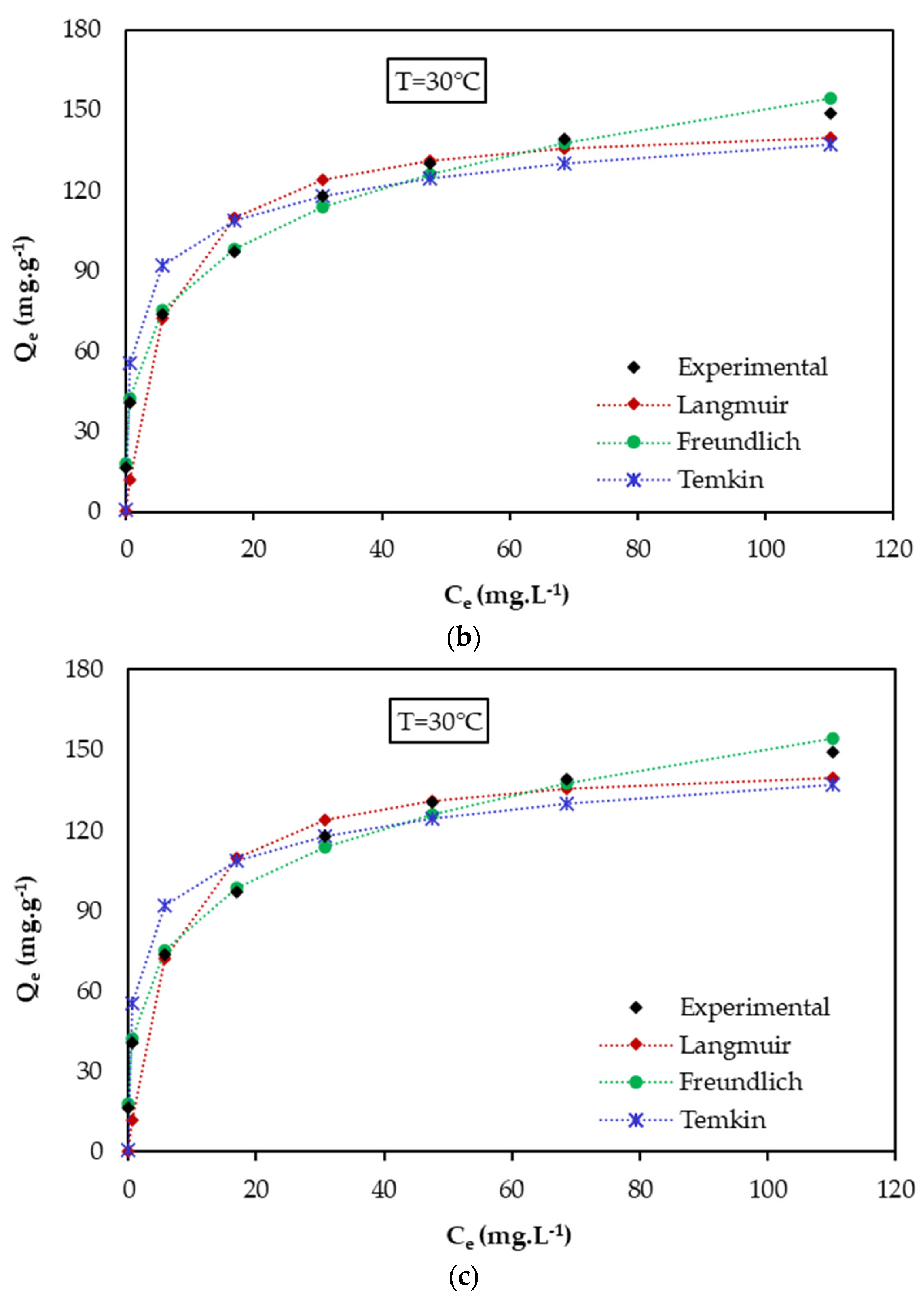
3.5. Isotherms Study
- C0: initial concentration of phenol (mg.L−1)
- KL: the constant related to the energy of adsorption (Langmuir constant)
- RL: value indicates the adsorption nature to be either unfavorable if RL > 1, linear if RL = 1, favorable if 0 < RL < 1 and irreversible if RL = 0.
3.6. Thermodynamics Study
3.7. KNN Model
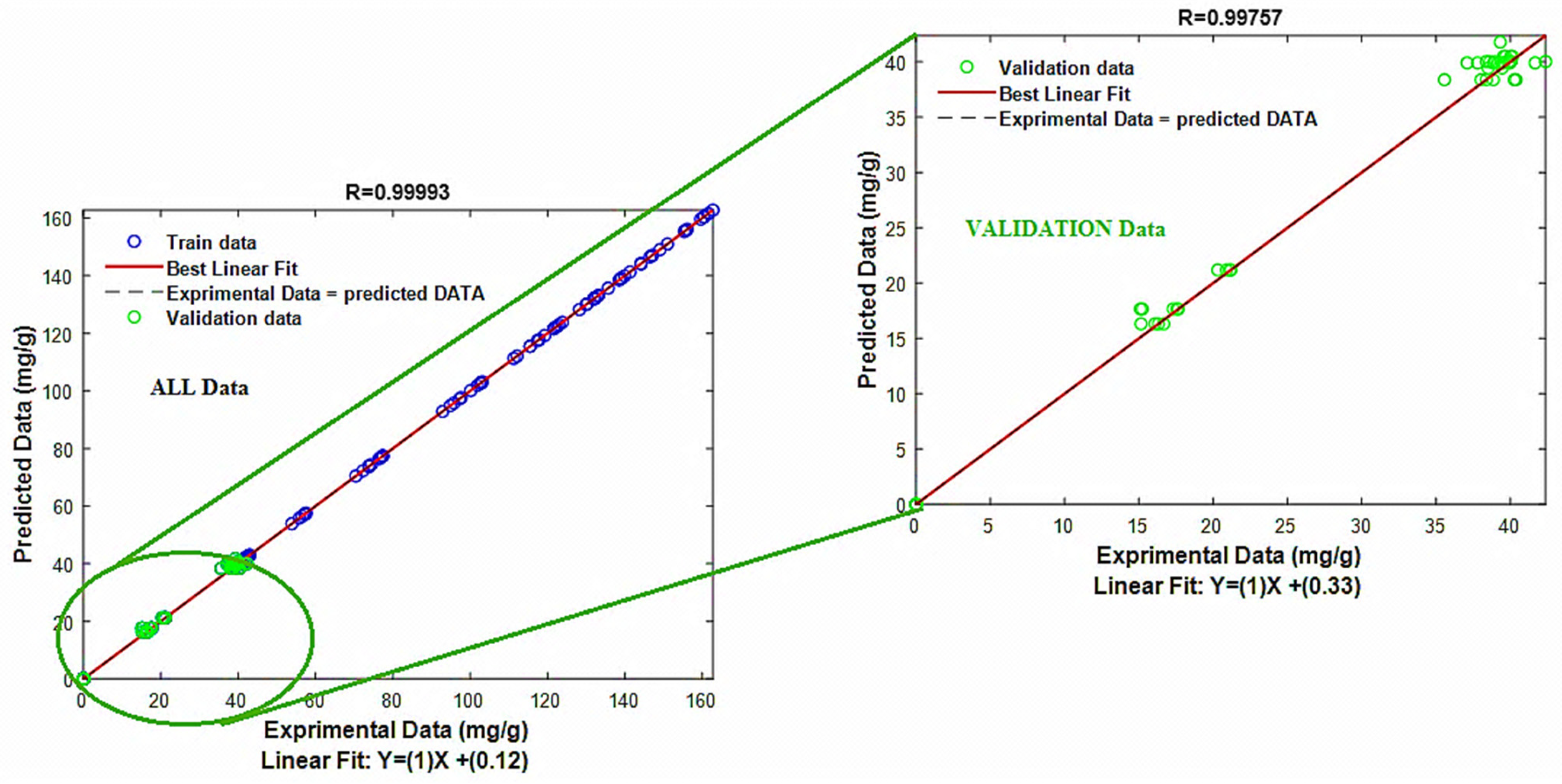
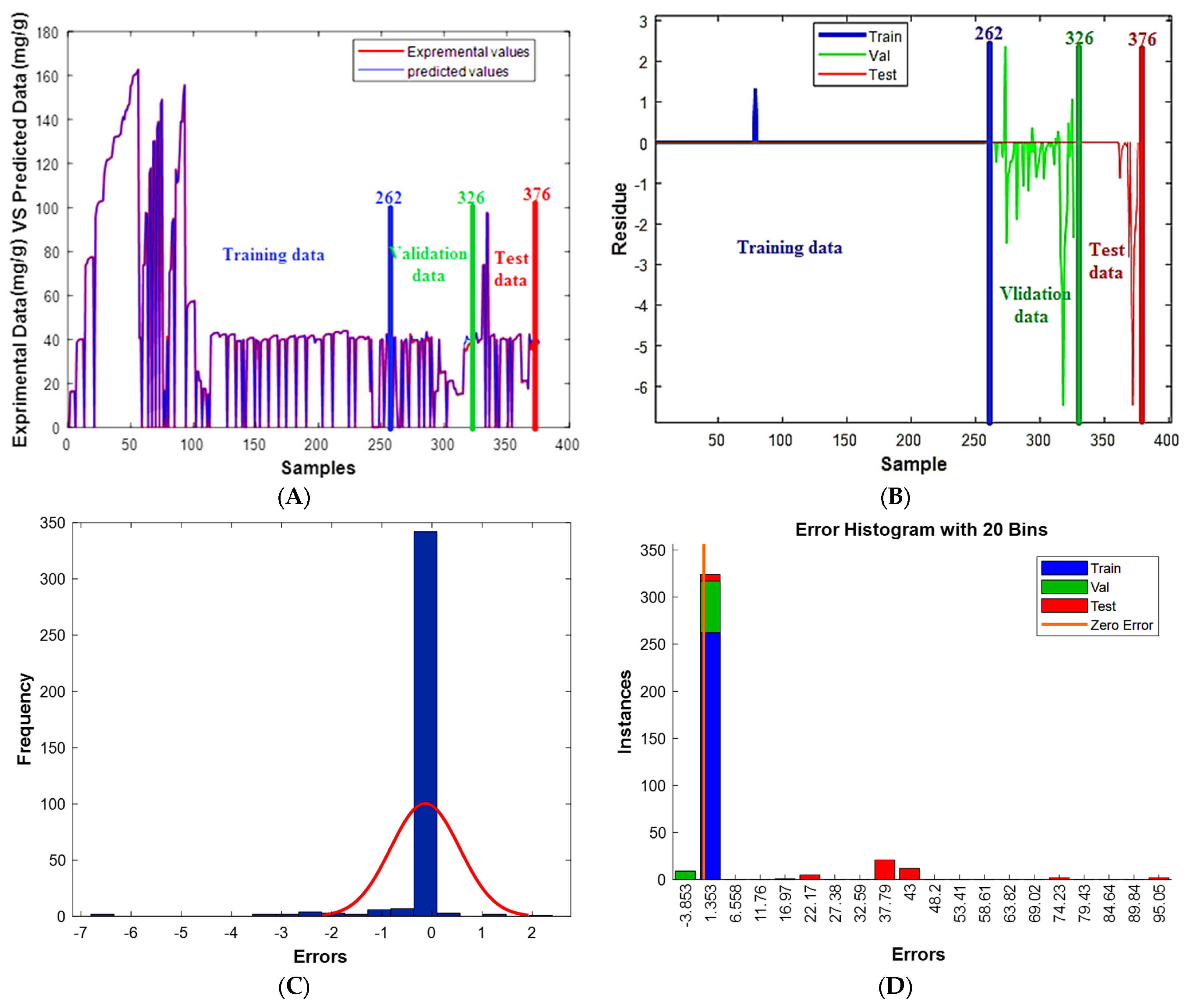
3.7.1. Model Performance Test
3.7.2. Residues Study
3.7.3. Optimization of the Optimal Analysis and Validation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mishra, R.; Dubey, S. Fresh Water Availability and It’s Global Challenge. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Invent. Res. Dev. 2015, 2, 351–407. [Google Scholar]
- Bruce, R.M.; Santodonato, J.; Neal, M.W. Summary Review of the Health Effects Associated with Phenol. Toxicol. Ind. Health 1987, 3, 535–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimuka, L.; Nefale, F.; Masevhe, A. Determination of phenols in water samples using a supported liquid membrane extraction probe and liquid chromatography with photodiode array detection. S. Afr. J. Chem. 2007, 60, 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Puszkarewicz, A.; Kaleta, J.T.; Papciak, D. Adsorption of Phenol from Water on Natural Minerals. J. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 19, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehmani, Y.; Khalki, O.E.; Mezougane, H.; Abouarnadasse, S. Comparative study on adsorption of cationic dyes and phenol by natural clays. Chem. Data Collect. 2021, 33, 100674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehmani, Y.; Dridi, D.; Lamhasni, T.; Abouarnadasse, S.; Chtourou, R.; Lima, E.C. Review of phenol adsorption on transition metal oxides and other adsorbents. J. Water Process. Eng. 2022, 49, 102965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammini, A.; Dehbi, A.; Omari, H.; Elazhari, K.; Mehanned, S.; Bengamra, Y.; Dehmani, Y.; Rachid, O.; Alrashdi, A.A.; Gotore, O.; et al. Experimental and theoretical evaluation of synthetized cobalt oxide for phenol adsorption: Adsorption isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehmani, Y.; Lainé, J.; Daouli, A.; Sellaoui, L.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Lamhasni, T.; Abouarnadasse, S.; Badawi, M. Unravelling the adsorption mechanism of phenol on zinc oxide at various coverages via statistical physics, artificial neural network modeling and ab initio molecular dynamics. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahangar, R.M.; Farmanzadeh, D. Theoretical study for exploring the adsorption behavior of aniline and phenol on pristine and Cu-doped phosphorene surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 614, 156194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougna, A.A.; Gombert, B.; Kodom, T.; Djaneye-Boundjou, G.; Boukari, S.O.B.; Leitner, N.K.V.; Bawa, L.M. Photocatalytic removal of phenol using titanium dioxide deposited on different substrates: Effect of inorganic oxidants. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2015, 305, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmina, M.; Mourad, K.; Mohammed, S.H.; Khaoula, C. Treatment Heterogeneous Photocatalysis; Factors Influencing the Photocatalytic Degradation by TiO2. Energy Procedia 2014, 50, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, H.; Araki, S.; Yamamoto, H. Evaluation of advanced oxidation processes (AOP) using O3, UV, and TiO2 for the degradation of phenol in water. J. Water Process Eng. 2015, 7, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ballesteros, S.; Mora, M.; Vicente, R.; Vercher, R.F.; Sabater, C.; Castillo, M.A.; Amat, A.M.; Arques, A. A new methodology to assess the performance of AOPs in complex samples: Application to the degradation of phenolic compounds by O3 and O3/UV-A–Vis. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chedri Mammar, A.; Mouni, L.; Bollinger, J.-C.; Belkhiri, L.; Bouzaza, A.; Assadi, A.A.; Belkacemi, H. Modeling and optimization of process parameters in elucidating the adsorption mechanism of Gallic acid on activated carbon prepared from date stones. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 3113–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ververi, M.; Goula, A.M. Pomegranate peel and orange juice by-product as new biosorbents of phenolic compounds from olive mill wastewaters. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2019, 138, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, J.N.; Karri, R.R.; Jayakumar, N.S. Improvement in phenol adsorption capacity on eco-friendly biosorbent derived from waste Palm-oil shells using optimized parametric modelling of isotherms and kinetics by differential evolution. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 164, 113333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, D.S.P.; Georgin, J.; Netto, M.S.; Allasia, D.; Oliveira, M.L.S.; Foletto, E.L.; Dotto, G.L. Highly effective adsorption of synthetic phenol effluent by a novel activated carbon prepared from fruit wastes of the Ceiba speciosa forest species. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-H.; Balathanigaimani, M.S.; Shim, W.-G.; Lee, J.-W.; Moon, H. Adsorption characteristics of phenol on novel corn grain-based activated carbons. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 127, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adithiyaa, T.; Chandramohan, D.; Sathish, T. Optimal prediction of process parameters by GWO-KNN in stirring-squeeze casting of AA2219 reinforced metal matrix composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 21, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parul Sinha, P.S. Comparative Study of Chronic Kidney Disease Prediction using KNN and SVM. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2015, 4, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Grey Wolf Optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tahraoui, H.; Amrane, A.; Belhadj, A.-E.; Zhang, J. Modeling the organic matter of water using the decision tree coupled with bootstrap aggregated and least-squares boosting. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 27, 102419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahraoui, H.; Belhadj, A.-E.; Amrane, A.; Houssein, E.H. Predicting the concentration of sulfate using machine learning methods. Earth Sci. Inform. 2022, 15, 1023–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahraoui, H.; Belhadj, A.-E.; Hamitouche, A.-e.; Bouhedda, M.; Amrane, A. Predicting the concentration of sulfate (SO42-) in drinking water using artificial neural networks: A case study: Médéa-Algeria. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 217, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahraoui, H.; Belhadj, A.; Moula, N.; Bouranene, S.; Amrane, A. Optimisation and Prediction of the Coagulant Dose for the Elimination of Organic Micropollutants Based on Turbidity. Kem. Ind. 2021, 70, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Qin, J.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Sun, H.; Chen, W. Adsorption of Phenol on Commercial Activated Carbons: Modelling and Interpretation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, J.; Wen, J.; Li, H.; Yang, Y. Surface functional groups determine adsorption of pharmaceuticals and personal care products on polypropylene microplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.C.; Sher, F.; Guleria, A.; Saeb, M.R.; Anastopoulos, I.; Tran, H.N.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A. Is one performing the treatment data of adsorption kinetics correctly? J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonin, J.-P. On the comparison of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws in the modeling of adsorption kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.; Wang, J. Comparison of linearization methods for modeling the Langmuir adsorption isotherm. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 296, 111850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.-J.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Chao, H.-P. Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Water Res. 2017, 120, 88–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamouche, M.; Mouni, L.; Ayachi, A.; Merniz, I. Use of commercial activated carbon for the purification of synthetic water polluted by a pharmaceutical product. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 172, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atunwa, B.T.; Dada, A.O.; Inyinbor, A.A.; Pal, U. Synthesis, physiochemical and spectroscopic characterization of palm kernel shell activated carbon doped AgNPs (PKSAC@AgNPs) for adsorption of chloroquine pharmaceutical waste. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 65, 3538–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girish, C.R.; Ramachandra Murty, V. Adsorption of Phenol from Aqueous Solution Using Lantana camara, Forest Waste: Kinetics, Isotherm, and Thermodynamic Studies. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 2014, 201626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelwahab, O.; Amin, N.K. Adsorption of phenol from aqueous solutions by Luffa cylindrica fibers: Kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2013, 39, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Gaidoumi, A.; Benabdallah, A.; Lahrichi, A.; Kherbeche, A. Adsorption of phenol in aqueous medium by a raw and treated moroccan pyrophyllite. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2015, 6, 2247–2259. [Google Scholar]
- De la Luz-Asunción, M.; Sánchez-Mendieta, V.; Martínez-Hernández, A.L.; Castaño, V.M.; Velasco-Santos, C. Adsorption of Phenol from Aqueous Solutions by Carbon Nanomaterials of One and Two Dimensions: Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 405036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gundogdu, A.; Duran, C.; Senturk, H.B.; Soylak, M.; Ozdes, D.; Serencam, H.; Imamoglu, M. Adsorption of Phenol from Aqueous Solution on a Low-Cost Activated Carbon Produced from Tea Industry Waste: Equilibrium, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Study. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2012, 57, 2733–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudaib, B. Treatment of real industrial wastewater with high sulfate concentrations using modified Jordanian kaolin sorbent: Batch and modelling studies. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of Adsorption on Carbon from Solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. 1963, 89, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiki, C.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ifon, B.E.; Qin, D.; Chabi, K.; Yu, C.-P.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Sun, Q. Induced aging, structural change, and adsorption behavior modifications of microplastics by microalgae. Environ. Int. 2022, 166, 107382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jnr, M.H.; Spiff, A.I. Effects of temperature on the sorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ from aqueous solution by Caladium bicolor (Wild Cocoyam) biomass. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 8, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Fierro, V.; Torné-Fernández, V.; Montané, D.; Celzard, A. Adsorption of phenol onto activated carbons having different textural and surface properties. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 111, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dada, A.O.; Olalekan, A.P.; Olatunya, A.M.; Dada, O.J.I.J.C. Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin–Radushkevich Isotherms Studies of Equilibrium Sorption of Zn 2+ Unto Phosphoric Acid Modified Rice Husk. J. Appl. Chem. 2012, 3, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Das, S. Kinetics and adsorption isotherm model of 2-thiouracil adsorbed onto the surface of reduced graphene oxide-copper oxide nanocomposite material. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1268, 133723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, S.; Sen, T.K. Removal of anionic dye Congo red from aqueous solution by raw pine and acid-treated pine cone powder as adsorbent: Equilibrium, thermodynamic, kinetics, mechanism and process design. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1933–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N. Improper estimation of thermodynamic parameters in adsorption studies with distribution coefficient KD (qe/Ce) or Freundlich constant (KF): Conclusions from the derivation of dimensionless thermodynamic equilibrium constant and suggestions. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 5553212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouni, L.; Belkhiri, L.; Bollinger, J.-C.; Bouzaza, A.; Assadi, A.; Tirri, A.; Dahmoune, F.; Madani, K.; Remini, H. Removal of Methylene Blue from aqueous solutions by adsorption on Kaolin: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 153, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imessaoudene, A.; Cheikh, S.; Bollinger, J.-C.; Belkhiri, L.; Tiri, A.; Bouzaza, A.; El Jery, A.; Assadi, A.; Amrane, A.; Mouni, L. Zeolite Waste Characterization and Use as Low-Cost, Ecofriendly, and Sustainable Material for Malachite Green and Methylene Blue Dyes Removal: Box-Behnken Design, Kinetics, and Thermodynamics. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, N.A.S.; Abu-Zurayk, R.A.; Hamadneh, I.; Al-Dujaili, A.H. Phenol adsorption on biochar prepared from the pine fruit shells: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamics studies. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 226, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, H.H.C.; Maniezzo, R.S.; Llop, M.E.G.; Kupfer, V.L.; Arroyo, P.A.; Guilherme, M.R.; Rubira, A.F.; Girotto, E.M.; Rinaldi, A.W. Synthesis and characterization of pecan nutshell-based adsorbent with high specific area and high methylene blue adsorption capacity. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 276, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbhar, P.; Narale, D.; Bhosale, R.; Jambhale, C.; Kim, J.-H.; Kolekar, S. Synthesis of tea waste/Fe3O4 magnetic composite (TWMC) for efficient adsorption of crystal violet dye: Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasbaji, M.; Mennani, M.; Grimi, N.; Barba, F.J.; Oubenali, M.; Simirgiotis, M.J.; Mbarki, M.; Moubarik, A. Implementation and physico-chemical characterization of new alkali-modified bio-sorbents for cadmium removal from industrial discharges: Adsorption isotherms and kinetic approaches. Process Biochem. 2022, 120, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahraoui, H.; Belhadj, A.; Hamitouche, A.-E. Prediction of the Bicarbonate Amount in Drinking Water in the Region of Médéa Using Artificial Neural Network Modelling. Kem. Ind. 2020, 69, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousselma, A.; Abdessemed, D.; Tahraoui, H.; Amrane, A. Artificial Intelligence and Mathematical Modelling of the Drying Kinetics of Pre-treated Whole Apricots. Kem. Ind. 2021, 70, 651–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| pHPZC | 7.5 |
| S(BET) (m2.g−1) | 463.4 |
| Ø (pore size) (Å) | 27.36 |
| ṽ (total pore volume) (cm3.g−1) | 0.13 |
| Iodine number (mg.g−1) | 752 |
| Methylene blue number (mg.g−1) | 244 |
| Strong acid carboxylic group (meq.g−1) | 0.026 |
| Hydroxyl and phenol groups (meq.g−1) | 0.725 |
| C0 (mg.L−1) | qeexp (mg.g−1) | Lagergren | Blanchard | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (1.min−1) | qetheo (mg.g−1) | R2 | k2 (g.mg−1.min−1) | qetheo (mg.g−1) | R2 | ||
| 10 | 16.31 | 0.290 | 0.004 | 0.477 | 0.339 | 16.36 | 1 |
| 25 | 40.02 | 0.246 | 13.335 | 0.896 | 0.135 | 40.16 | 1 |
| 50 | 77.34 | 0.379 | 141.58 | 0.854 | 0.036 | 78.125 | 1 |
| 75 | 103.1 | 0.095 | 18.24 | 0.774 | 0.025 | 104.2 | 1 |
| 100 | 123.1 | 0.196 | 101.25 | 0.632 | 0.021 | 123.5 | 1 |
| 125 | 133.2 | 0.081 | 13.56 | 0.589 | 0.038 | 133.3 | 1 |
| 150 | 146.95 | 0.191 | 159.62 | 0.624 | 0.01 | 147.0 | 0.999 |
| 200 | 162.7 | 0.069 | 26.08 | 0.648 | 0.014 | 163.9 | 0.999 |
| C0 (mg.L−1) | 10 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 200 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kd1 (mg.mg−1 min−1/2) | 5.457 | 13.338 | 25.283 | 33.723 | 40.285 | 44.635 | 47.874 | 53.08 |
| Cd1 (mg.g−1) | 0.666 | 1.938 | 3.917 | 4.614 | 5.757 | 6.439 | 7.124 | 8.30 |
| R1² | 0.951 | 0.931 | 0.923 | 0.939 | 0.933 | 0.932 | 0.928 | 0.921 |
| Kd2 (mg.mg−1 min−1/2) | −1 × 10−14 | 0.044 | 0.506 | 0.351 | 0.450 | 0.349 | 2.051 | 0.893 |
| Cd2 (mg.g−1) | 16.315 | 39.704 | 74.135 | 100.45 | 119.36 | 130.34 | 131.56 | 155.4 |
| R2² | −7 × 10−15 | 0.773 | 0.998 | 0.913 | 0.902 | 0.714 | 0.902 | 0.886 |
| Type | Langmuir | Freundlich | Temkin | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm (mg.g−1) | KL (L.mg−1) | RL | R² | KF [(mg.g−1)/ ((mg/L)1/n)] | n | R² | bT (J.mol−1) | AT (L.g−1) | R² | |
| T = 20 °C | 156.26 | 0.196 | 0.170 | 0.976 | 61.31 | 4.79 | 0.992 | 42.60 | 361.0 | 0.962 |
| T = 30 °C | 146.99 | 0.174 | 0.187 | 0.981 | 49.88 | 4.16 | 0.998 | 39.80 | 74.96 | 0.963 |
| T = 40 °C | 150.8 | 0. 118 | 0.001 | 0.975 | 47.64 | 4.08 | 0.998 | 43.00 | 88.00 | 0.958 |
| T (°K) | KL (L.mg−1) | KL° (×104) (Dimensionless) | Ln KL° | ΔG° (kJ.mol−1) | ΔH° (KJ.mol−1) | ΔS° (J.mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 293 | 0.196 | 1.84 | 9.823 | −24.04 | −19.23 | 16.433 |
| 303 | 0.174 | 1.64 | 9.704 | −24.20 | ||
| 313 | 0.118 | 1.11 | 9.315 | −24.37 |
| GWO | Max_iteration = 100 SearchAgents_no = 50 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distance | Distance Weight | Num Neighbors | Exponent | loss | R/R2/R2adj | RMSE/MSE/MAE | ||||
| Train | VAL | ALL | Train | VAL | ALL | |||||
| Euclidean | Equal | 8 | / | 0.5356 | 0.7938 0.6302 0.6199 | 0.7183 0.5159 0.4565 | 0.8002 0.6403 0.6324 | 0.3553 0.1262 0.1606 | 0.1448 0.0210 0.0659 | 0.3244 0.3317 0.3605 |
| Inverse | 8 | / | 0.0271 | 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 | 0.6632 0.4398 0.3711 | 0.9896 0.9792 0.9788 | 0.0010 0.0000 0.0001 | 0.1650 0.0272 0.0808 | 0.0737 0.2768 0.3237 | |
| Squared Inverse | 15 | / | 0.0271 | 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 | 0.7221 0.5214 0.4627 | 0.9919 0.9838 0.9835 | 0.0010 0.0000 0.0001 | 0.1463 0.0214 0.0725 | 0.0653 0.2455 0.2905 | |
| bychev | Equal | 12 | / | 0.6102 | 0.7405 0.5483 0.5358 | 0.6528 0.4262 0.3557 | 0.7482 0.5597 0.5500 | 0.3988 0.1591 0.1964 | 0.1556 0.0242 0.0718 | 0.3636 0.2202 0.2836 |
| Inverse | 7 | / | 0.0237 | 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 | 0.7036 0.4951 0.4330 | 0.9900 0.9802 0.9797 | 0.0010 0.0000 0.0001 | 0.1629 0.0266 0.0842 | 0.0728 0.2153 0.2767 | |
| Squared Inverse | 11 | / | 0.0305 | 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 | 0.8005 0.6408 0.5967 | 0.9932 0.9864 0.9861 | 0.0010 0.0000 0.0001 | 0.1332 0.0177 0.0662 | 0.0595 0.2977 0.3528 | |
| Minkowski | Equal | 11 | 4 | 0.5627 | 0.7172 0.5143 0.5009 | 0.8218 0.6753 0.6355 | 0.7322 0.5361 0.5259 | 0.4156 0.1727 0.1920 | 0.1149 0.0132 0.0426 | 0.3754 0.2907 0.3370 |
| Inverse | 14 | 2 | 0.0271 | 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 | 0.7220 0.5214 0.4626 | 0.9921 0.9843 0.9840 | 0.0010 0.0000 0.0001 | 0.1426 0.0203 0.0627 | 0.0637 0.2129 0.2830 | |
| Squared Inverse | 29 | 2 | 0.0237 | 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 | 0.7511 0.5642 0.5107 | 0.9927 0.9854 0.9851 | 0.0010 0.0000 0.0001 | 0.1387 0.0192 0.0647 | 0.0619 0.2603 0.3026 | |
| Mahalanobis | Equal | 3 | / | 0.3932 | 0.8902 0.7925 0.7868 | 0.7330 0.5372 0.4804 | 0.8920 0.7956 0.7911 | 0.2531 0.0640 0.0732 | 0.1360 0.0185 0.0507 | 0.2344 0.2661 0.3091 |
| Inverse | 4 | / | 0.0271 | 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 | 0.6717 0.4512 0.3838 | 0.9909 0.9818 0.9814 | 0.0010 0.0000 0.0001 | 0.1537 0.0236 0.0697 | 0.0686 0.2444 0.3133 | |
| Squared Inverse | 25 | / | 0.0203 | 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 | 0.6895 0.4755 0.4110 | 0.9904 0.9810 0.9805 | 0.0010 0.0000 0.0001 | 0.1584 0.0251 0.0724 | 0.0707 0.1528 0.2224 | |
| Cosine | Equal | 6 | / | 0.5220 | 0.7670 0.5883 0.5770 | 0.6574 0.4321 0.3624 | 0.7714 0.5950 0.5861 | 0.3746 0.1403 0.1598 | 0.1533 0.0235 0.0698 | 0.3421 0.3488 0.3663 |
| Inverse | 7 | / | 0.0305 | 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 | 0.7365 0.5424 0.4862 | 0.9928 0.9856 0.9853 | 0.0010 0.0000 0.0001 | 0.1363 0.0186 0.0595 | 0.0609 0.2628 0.3039 | |
| Squared Inverse | 152 | / | 0.0339 | 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 | 0.7427 0.5516 0.4965 | 0.9919 0.9838 0.9834 | 0.0010 0.0000 0.0001 | 0.1460 0.0213 0.0702 | 0.0652 0.1785 0.2333 | |
| Correlation | Equal | 5 | / | 0.4881 | 0.7687 0.5909 0.5796 | 0.6676 0.4457 0.3776 | 0.7756 0.6015 0.5928 | 0.3757 0.1412 0.1632 | 0.1499 0.0225 0.0725 | 0.3428 0.3025 0.3452 |
| Inverse | 67 | / | 0.0339 | 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 | 0.7197 0.5180 0.4588 | 0.9916 0.9832 0.9829 | 0.0010 0.0000 0.0001 | 0.1481 0.0219 0.0723 | 0.0662 0.2443 0.3136 | |
| Squared Inverse | 101 | / | 0.0373 | 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 | 0.7284 0.5306 0.4729 | 0.9921 0.9843 0.9840 | 0.0010 0.0000 0.0001 | 0.1432 0.0205 0.0635 | 0.0640 0.2359 0.2746 | |
| Spearman | Equal | 3 | / | 0.5559 | 0.6513 0.4242 0.4082 | 0.6004 0.3605 0.2819 | 0.6662 0.4438 0.4315 | 0.4508 0.2032 0.2098 | 0.1797 0.0323 0.1062 | 0.4113 0.2929 0.3173 |
| Inverse | 6 | / | 0.4542 | 0.6569 0.4315 0.4158 | 0.6158 0.3792 0.3030 | 0.6723 0.4520 0.4399 | 0.4359 0.4359 0.1791 | 0.1740 0.0303 0.0930 | 0.3977 0.3259 0.3532 | |
| Squared Inverse | 4 | / | 0.4780 | 0.6534 0.4270 0.4111 | 0.6373 0.4062 0.3333 | 0.6684 0.4468 0.4346 | 0.4392 0.1929 0.1848 | 0.1725 0.0298 0.0960 | 0.4004 0.3133 0.3516 | |
| Hamming | Equal | 3 | / | 0.4881 | 0.5071 0.2572 0.2366 | 0.9238 0.8534 0.8354 | 0.5241 0.2747 0.2587 | 0.5326 0.2837 0.2700 | 0.0737 0.0054 0.0232 | 0.4777 0.3612 0.3989 |
| Inverse | 5 | / | 0.0339 | 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 | 0.9678 0.9365 0.9288 | 0.9991 0.9983 0.9982 | 0.0010 0.0000 0.0001 | 0.0471 0.0022 0.0169 | 0.0210 0.2165 0.2718 | |
| Squared Inverse | 4 | / | 0.0441 | 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 | 0.9894 0.9790 0.9764 | 0.9997 0.9994 0.9994 | 0.0010 0.0000 0.0001 | 0.0275 0.0008 0.0114 | 0.0123 0.2746 0.3129 | |
| Jaccard | Equal | 3 | / | 0.5051 | 0.5119 0.2620 0.2416 | 0.9522 0.9066 0.8952 | 0.5282 0.2790 0.2631 | 0.5395 0.2910 0.2823 | 0.0583 0.0034 0.0233 | 0.4834 0.3731 0.4090 |
| Inverse | 3 | / | 0.0475 | 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 | 0.9703 0.9414 0.9342 | 0.9992 0.9984 0.9984 | 0.0010 0.0000 0.0001 | 0.0452 0.0020 0.0179 | 0.0202 0.2700 0.3193 | |
| Squared Inverse | 4 | / | 0.0201 | 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 | 0.9975 0.9942 0.9935 | 0.9999 0.9998 0.9998 | 0.0010 0.0000 0.0001 | 0.0156 0.0002 0.0078 | 0.0070 0.2347 0.2763 | |
| Cityblock | Equal | 4 | / | 0.4441 | 0.8309 0.6905 0.6819 | 0.7616 0.5801 0.5285 | 0.8364 0.6995 0.6929 | 0.3200 0.1024 0.1231 | 0.1288 0.0166 0.0529 | 0.2921 0.3097 0.3459 |
| Inverse | 5 | / | 0.0271 | 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 | 0.7373 0.5436 0.4875 | 0.9924 0.9848 0.9844 | 0.0010 0.0000 0.0001 | 0.1407 0.0198 0.0637 | 0.0628 0.2579 0.2991 | |
| Squared Inverse | 18 | / | 0.0237 | 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 | 0.7286 0.5308 0.4732 | 0.9922 0.9844 0.9840 | 0.0010 0.0000 0.0001 | 0.1424 0.0203 0.0636 | 0.0636 0.2245 0.2733 | |
| Seuclidean | Equal | 5 | / | 0.4542 | 0.7971 0.6353 0.6252 | 0.7683 0.5902 0.5399 | 0.8042 0.6467 0.6389 | 0.3537 0.1251 0.1434 | 0.1270 0.0161 0.0518 | 0.3215 0.3367 0.3586 |
| Inverse | 13 | / | 0.0271 | 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 | 0.7397 0.5471 0.4915 | 0.9918 0.9837 0.9834 | 0.0010 0.0000 0.0001 | 0.1460 0.0213 0.0688 | 0.0652 0.2176 0.2901 | |
| Squared Inverse | 23 | / | 0.0237 | 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 | 0.7707 0.5940 0.5442 | 0.9926 0.9852 0.9848 | 0.0010 0.0000 0.0001 | 0.1400 0.0196 0.0653 | 0.0625 0.2424 0.2879 | |
| R/R2/R2adj | RMSE/MSE/MAE |
|---|---|
| ALL | ALL |
| 0.9984 0.9968 0.9963 | 0.0152 2.3172 × 10−4 0.0051 |
| GWO: ×1 = 60 min, ×2 = 200 mg.L−1, ×3 = 0.1504 g.L−1, ×4 = 306,683 rpm, ×5 = 20 °C, ×6 = 4.7526 | |
| Predicted quantity of adsorbed phenol (mg.g−1) | 163.4230 |
| PSO: ×1 = 60 min, ×2 = 200 mg.L−1, ×3 = 0.1506 g.L−1, ×4 = 308.793 rpm, ×5 = 20 °C, ×6 = 4.7447 | |
| Predicted quantity of adsorbed phenol (mg.g−1) | 163.4230 |
| Experimental quantity of adsorbed phenol (mg.g−1) | 162.7543 |
| Error (mg.g−1) | 0.6687 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zamouche, M.; Chermat, M.; Kermiche, Z.; Tahraoui, H.; Kebir, M.; Bollinger, J.-C.; Amrane, A.; Mouni, L. Predictive Model Based on K-Nearest Neighbor Coupled with the Gray Wolf Optimizer Algorithm (KNN_GWO) for Estimating the Amount of Phenol Adsorption on Powdered Activated Carbon. Water 2023, 15, 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030493
Zamouche M, Chermat M, Kermiche Z, Tahraoui H, Kebir M, Bollinger J-C, Amrane A, Mouni L. Predictive Model Based on K-Nearest Neighbor Coupled with the Gray Wolf Optimizer Algorithm (KNN_GWO) for Estimating the Amount of Phenol Adsorption on Powdered Activated Carbon. Water. 2023; 15(3):493. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030493
Chicago/Turabian StyleZamouche, Meriem, Mouchira Chermat, Zohra Kermiche, Hichem Tahraoui, Mohamed Kebir, Jean-Claude Bollinger, Abdeltif Amrane, and Lotfi Mouni. 2023. "Predictive Model Based on K-Nearest Neighbor Coupled with the Gray Wolf Optimizer Algorithm (KNN_GWO) for Estimating the Amount of Phenol Adsorption on Powdered Activated Carbon" Water 15, no. 3: 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030493
APA StyleZamouche, M., Chermat, M., Kermiche, Z., Tahraoui, H., Kebir, M., Bollinger, J.-C., Amrane, A., & Mouni, L. (2023). Predictive Model Based on K-Nearest Neighbor Coupled with the Gray Wolf Optimizer Algorithm (KNN_GWO) for Estimating the Amount of Phenol Adsorption on Powdered Activated Carbon. Water, 15(3), 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030493








