Pollution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Metal Elements in Groundwater in the Ibinur Lake Basin of NW China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
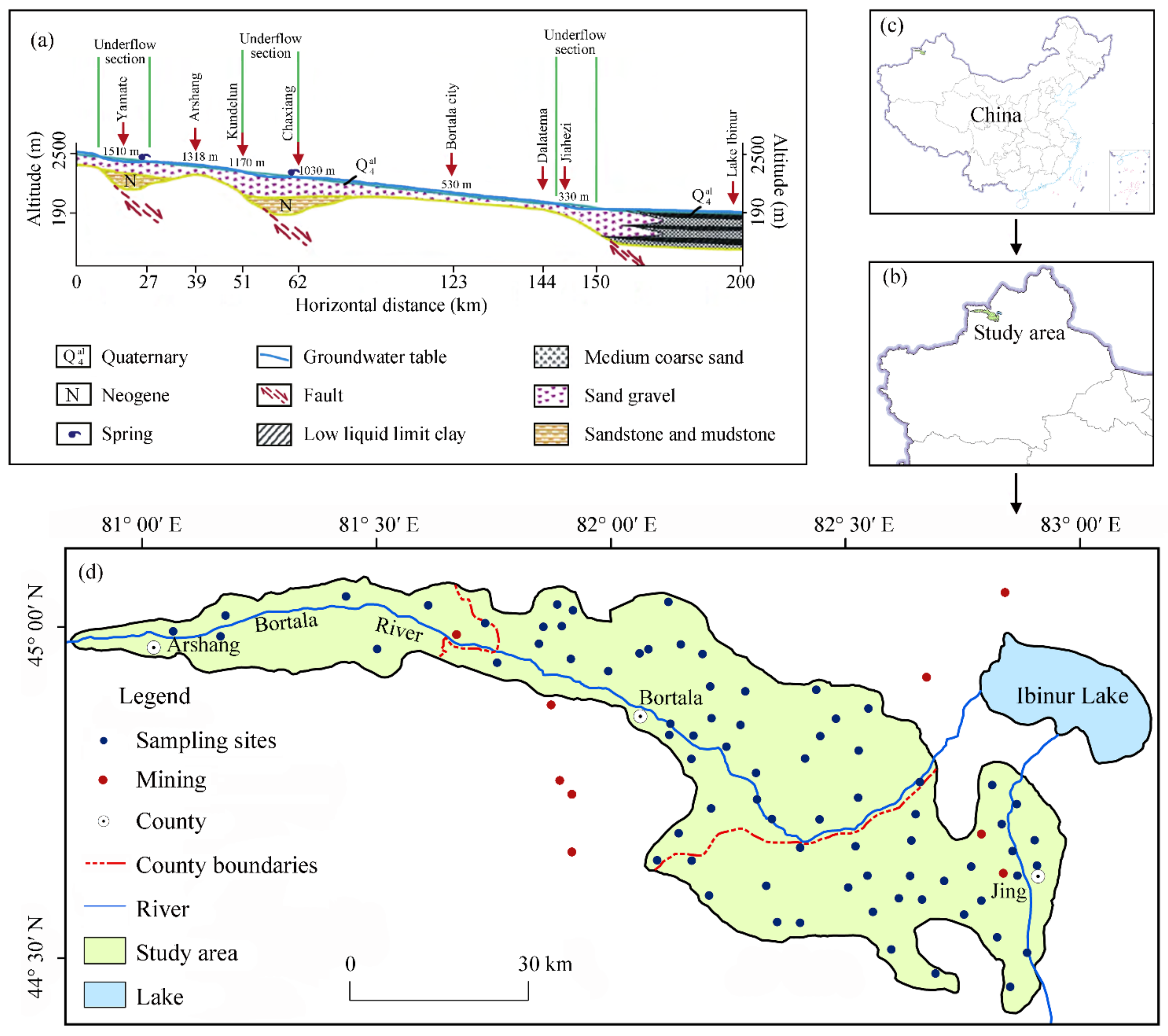
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Determination
2.3. Pollution Assessment
2.4. Potential Ecological Risk Assessment
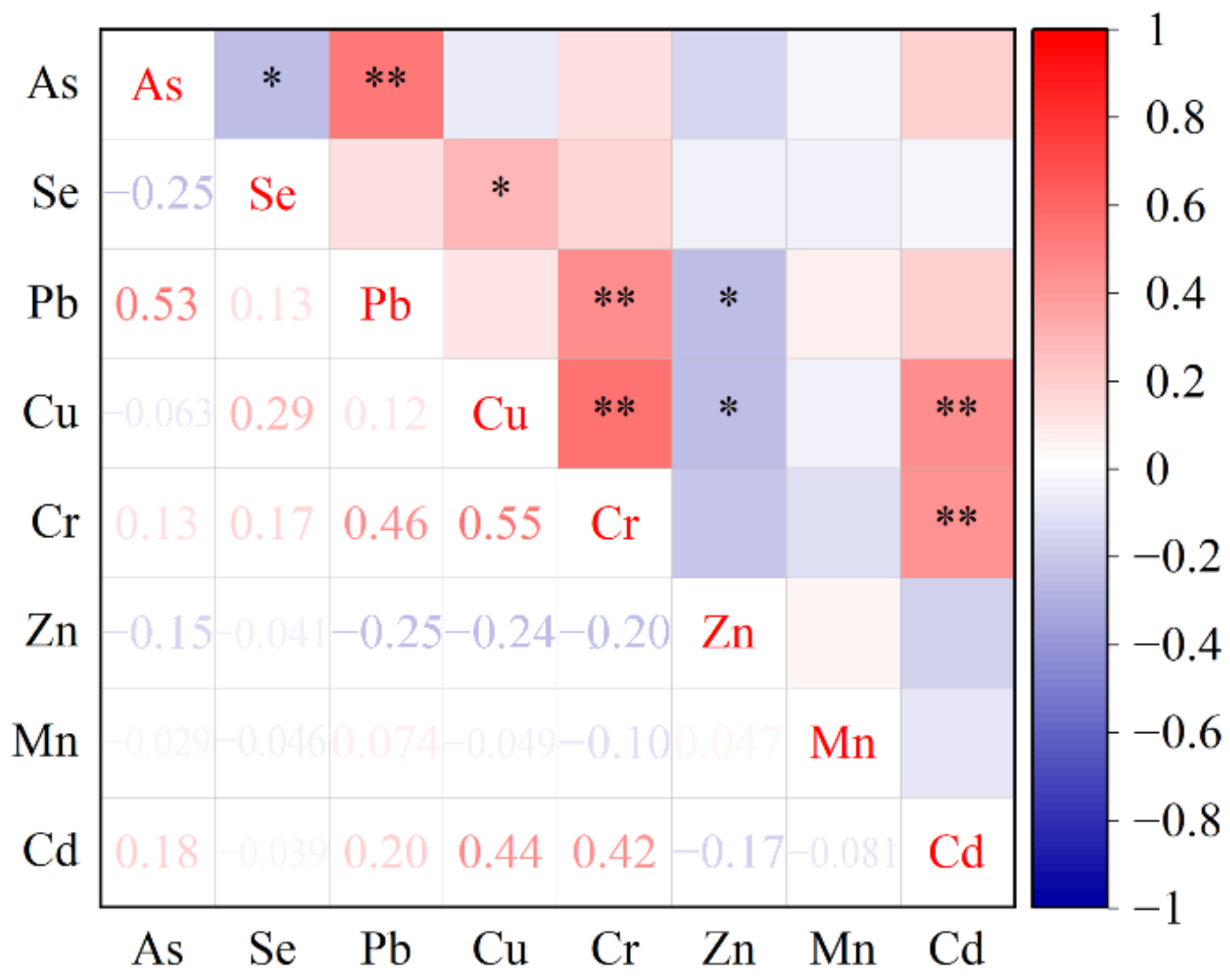
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Contents of Metals in Groundwater
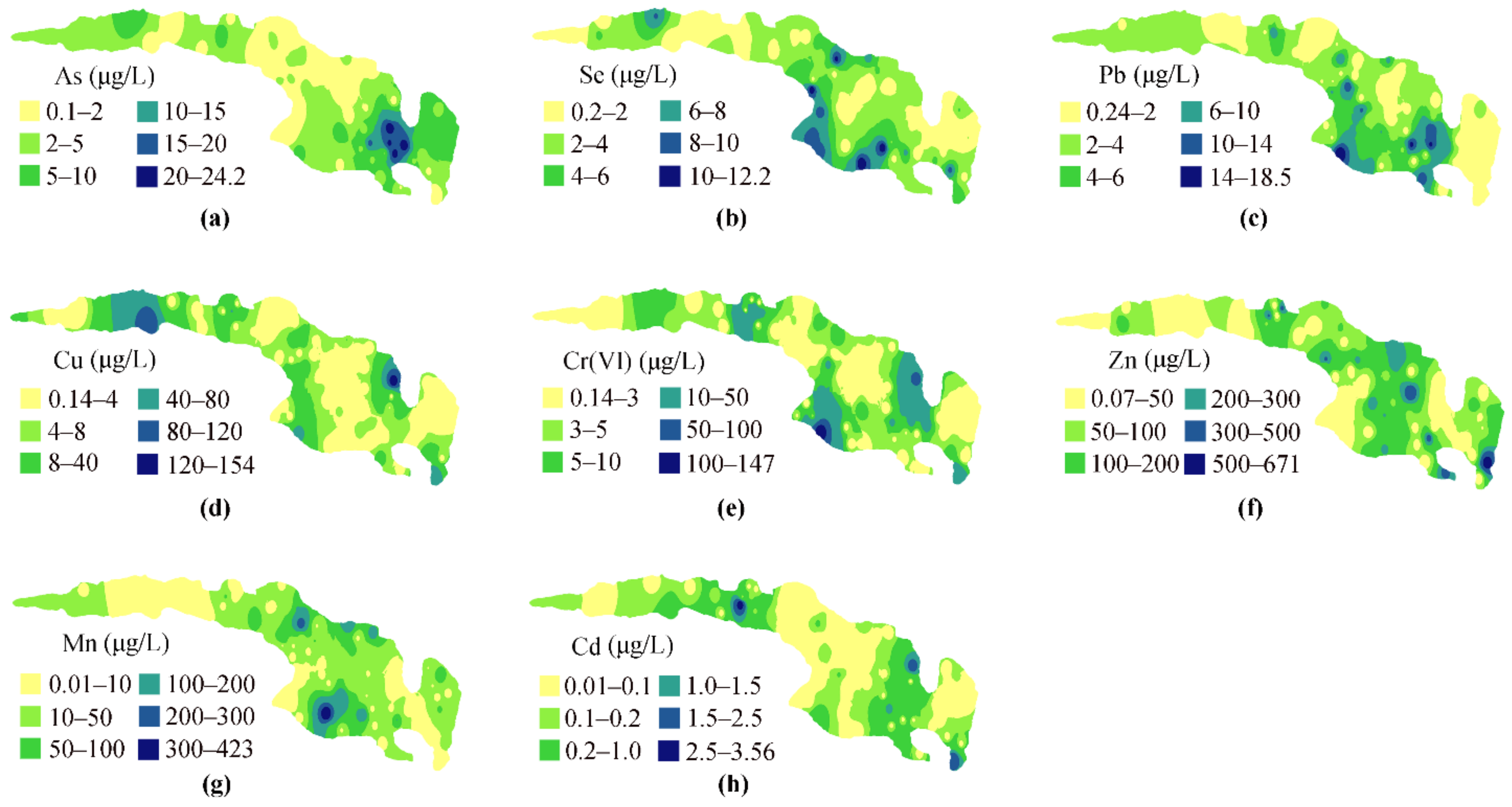
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Metal Contents
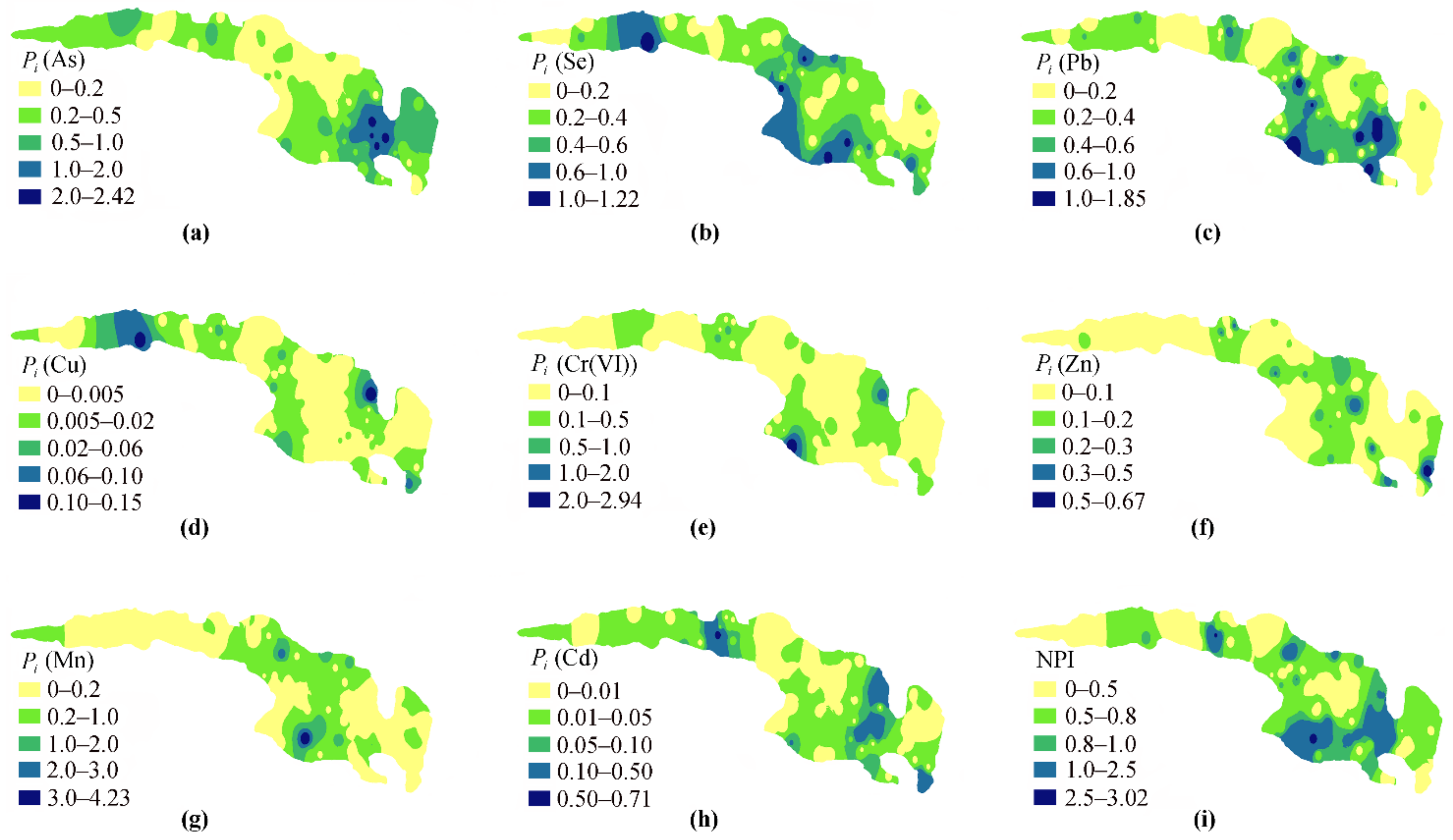
3.3. Pollution of Metals in Groundwater
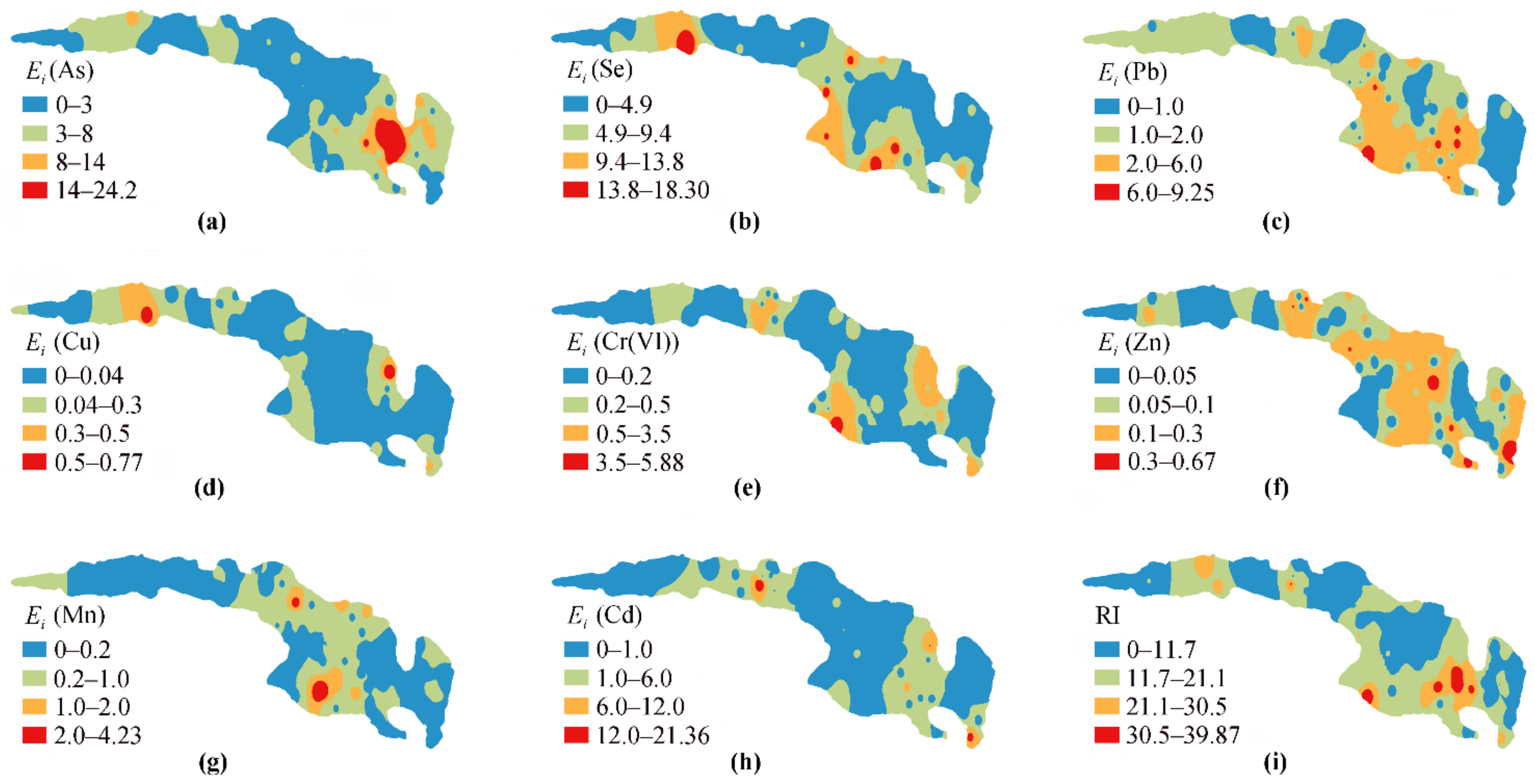
3.4. Ecological Risk of Metals in Groundwater
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramos, E.; Bux, R.K.; Medina, D.I.; Barrios-Piña, H.; Mahlknecht, J. Spatial and multivariate statistical analyses of human health risk associated with the consumption of heavy metals in groundwater of Monterrey Metropolitan Area, Mexico. Water 2023, 15, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, D.; Meng, X.; Wen, X.; Wu, J.; Yu, H.; Wu, M. Contamination characteristics, source identification, and source-specific health risks of heavy metal(loid)s in groundwater of an arid oasis region in Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 841, 156733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somalya, D.; Komal, S.; Navdeep, S. Water quality and health risk assessment of heavy metals in groundwater of Ranbir Singh Pura tehsil of Jammu and Kashmir, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1026–1044. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Karunanidhi, D.; Subramani, T.; Srinivasamoorthy, K. Sources and consequences of groundwater contamination. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxic. 2021, 80, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.; Wang, X.; Xia, D.; Zhu, J.; Yu, W.; Su, Y.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; Lei, Y.; et al. Improvement of ecological risk considering heavy metal in soil and groundwater surrounding electroplating factories. Processes 2022, 10, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarath, K.V.; Shaji, E.; Nandakumar, V. Characterization of trace and heavy metal concentration in groundwater: A case study from a tropical river basin of southern India. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139498–139511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojekunle, O.Z.; Awolokun, G.S.; Olatunde, A.K.; Adegoke, K.D.; Maxakato, N.W.; Balogun, M.A.; Afolabi, T.A. Environmental and health hazards of heavy metal concentrations in Ota and Agbara industrial areas, Ogun State, Nigeria. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobbina, S.J.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, L. Toxicity assessment due to sub-chronic exposure to individual and mixtures of four toxic heavy metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 294, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tian, W.; Zhang, X. Distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of metal elements for groundwater in the Ningxia region of China. Environ Sci. 2022, 43, 329–338. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Tan, Y.; Su, B.; Wang, L.; Liu, P. Environmental and health risks posed by heavy metal contamination of groundwater in the Sunan coal mine, China. Toxics 2022, 10, 390–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Jia, X.; Shao, M.; Niu, X.; Liu, J. Distributions of arsenic and other heavy metals, and health risk assessments for groundwater in the Guanzhong Plain Region of China. Environ. Res. 2019, 181, 108957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Su, Q.; Wang, S.; Gao, Z.; Liu, J. Spatial distribution and health risk assessment of dissolved heavy metals in groundwater of eastern China coastal zone. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 290, 118016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Liang, Y.; Li, J.; Zou, S.; Shen, H.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Z. Distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of metal elements in groundwater of Longzici Spring Area. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 4257–4266. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Zhao, Q.; Zheng, L.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Ren, M. Distribution, source and health risk assessment based on the Monte Carlo method of heavy metals in shallow groundwater in an area affected by mining activities, China. Ecotox. Environ. Safety 2021, 224, 112679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, X.; Chang, S.; Song, Y.; Lu, M.; Zhao, B.; Chen, H.; Gao, S.; Wang, L.; Cui, J.; et al. Source analysis and health risk assessment of heavy metals in groundwater of Shijiazhuang, a typical city in North China Plain. Environ Sci. 2022, 44, 4884–4895. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, Y.; Bai, F.; Yan, Z. Source analysis and health risk assessment of heavy metals in groundwater in the Oasis Belt of Ruoqiang County, Xinjiang. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2023, 43, 266–277. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Peng, H.; Hou, Q.; Peng, K.; Shi, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, M.; Huang, C.; Xu, L.; et al. Priority control factors for heavy metal groundwater contamination in peninsula regions based on source-oriented health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 894, 165062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hullysses, S.; Gerson, C.S.J.; Ricardo, C.; Juliana, M. Heavy metals and major anion content in groundwater of Tamoios coastal district (Rio de Janeiro/Brazil): Assessment of suitability for drinking purposes and human health risk. Inter. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 102, 7357–7379. [Google Scholar]
- Seyed, A.S.; Ali, M.; Rasoul, K.; Ahmad, Z. Distribution, exposure, and human health risk analysis of heavy metals in drinking groundwater of Ghayen County, Iran. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 13127–13144. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.; Guy, H.; Howden, N.J.K.; Ahmed, M.; Ismail, E. Carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic health risk assessment of heavy metals contamination in groundwater in the west of Minia area, Egypt. Human Eco. Risk Assess. 2022, 29, 571–596. [Google Scholar]
- Triassi, M.; Cerino, P.; Montuori, P.; Pizzolante, A.; Trama, U.; Nicodemo, F.; D’Auria, J.L.; De Vita, S.; De Rosa, E.; Limone, A. Heavy metals in groundwater of southern Italy: Occurrence and potential adverse effects on the environment and human health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, K.O.; Francis, O.O. Heavy metal contamination of groundwater: The example of boreholes around the Avindo-Sony sugar factory. J. Res. Sci. Engines 2022, 4, 104–107. [Google Scholar]
- Luiza, F.V.F.; Bruno, A.C.; Juliana, C.V.S.; Julio, C.J.S.; Nayara, H.M.; Fábio, K.; Valter, A.N.; Cassiana, C.M.; Kelly, M.P.O.; Alexeia, B. Metals and emerging contaminants in groundwater and human health risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 24581–24594. [Google Scholar]
- Hilary, I.O.; Thomas, O.A.; Sunday, C.I.; Eguakhide, A.; Henry, O.O.; Solomon, O. Spatial distribution of heavy metals in groundwater around automobile workshops in a popular Niger-Delta University town, Nigeria. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2023, 70, 79. [Google Scholar]
- John, K.N.; Henrietta, I.K.; Theresa, C.U.; Perpetua, O.C.; Genevieve, I.C.; Ephraim, O. Ecological and health risk assessment of radionuclides and heavy metals of surface and ground water of Ishiagu–Ezillo quarry sites of Ebonyi, Southeast Nigeria. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 10, 100307. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, A.U.; Sabir, M.I. Ecological risk assessment of ground water quality of two industrial zones of Karachi, Pakistan. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Tech. 2016, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emenike, P.C.; Tenebe, I.; Ogarekpe, N.; Omole, D.; Nnaji, C. Probabilistic risk assessment and spatial distribution of potentially toxic elements in groundwater sources in Southwestern Nigeria. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.; Gaagai, A.; Eid, M.H.; Szucs, P.; Hussein, H.; Elsherbiny, O.; Elsayed, S.; Khalifa, M.M.; Moghanm, F.S.; Moustapha, M.E.; et al. Groundwater quality and health risk assessment using indexing approaches, multivariate statistical analysis, artificial neural networks, and GIS techniques in El Kharga Oasis, Egypt. Water 2023, 15, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gao, M.; Jin, D.; Wang, T.; Yang, J. Assessment of groundwater quality and human health risk in the Aeolian-Sand Area of Yulin City, Northwest China. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Liu, F.; Zhou, X.; Pi, J.; Yin, W.; Li, F.; Huang, S.; Ma, F. Estimation of spatial distribution and health risk by arsenic and heavy metals in shallow groundwater around Dongting Lake plain using GIS mapping. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 128698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, D.; Wen, X.; Wu, J.; Wu, M.; Yu, H.; Zhang, C. Comprehensive probabilistic health risk assessment for exposure to arsenic and cadmium in groundwater. Environ. Manag. 2021, 67, 779–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, S. Estimation and spatiotemporal evolution of groundwater storage on the northern slope of the Tianshan Mountains over the past three decades. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2023, 78, 1744–1763. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Sun, J.; Aliya, B.; Li, L.; Hu, X.; Song, T. Ecological landscape pattern changes and security from 1990 to 2021 in Ebinur Lake Wetland Reserve, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xilinayi, D.; Alimujiang, K.; Rukeya, R.; Yimuranzi, A.; Wei, B. Assessment of water yield and water purification services in the arid zone of northwest China: The case of the Ebinur Lake Basin. Land 2023, 12, 533. [Google Scholar]
- HJ/T 164–2004; Technical Specifications for Environmental Monitoring of Groundwater. Environmental Science Press of China: Beijing, China, 2004. (In Chinese)
- GB/T 5750.6–2006; Standard Examination Method for Drinking Water-Metal Parameters. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2007. (In Chinese)
- Nemerow, N.L. Stream, Lake, Estuary, and Ocean Pollution; Van Nostrand Reinhold Publishing Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, X.; Ge, S.; Jiao, Z.; Zhan, W.; Wang, Y. Bioaccumulation and risk assessment of potential toxic elements in the soil-vegetable system as influenced by historical wastewater irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 279, 108197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osvaldo, J.B.R.; Sueli, Y.P.; Ana, E.S.A. Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater quality assessment using the water quality index and heavy-metal pollution index in the alluvial plain of Atibaia river-Campinas/SP, Brazil. Ground. Sustain. Develop. 2021, 15, 100661. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 14848–2017; Groundwater Quality Standard. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2017. (In Chinese)
- Håkanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sediment logical approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilleos, G.A. The Inverse Distance Weighted interpolation method and error propagation mechanism-creating a DEM from an analogue topographical map. J. Spat. Sci. 2011, 26, 283–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO (World Health Organization). Guidelines for drinking water quality: Fourth edition incorporating the first addendum. In WHO Library Cataloguing-In Publication Data Guidelines; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, R.; Xin, C.; Yu, S.; Li, X. Analysis of heavy metals sources in groundwater and assessment of health risks: An example from the southwest sub-basin of Shiqi River. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 796–806. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, A. Quantitative contributions of the major sources of heavy metals in soils to ecosystem and human health risks: A case study of Yulin, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 164, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Feng, C.; Zeng, G.; Gao, X.; Zhong, M.; Li, X.; Li, X.; He, X.; Fang, Y. Spatial distribution and source identification of heavy metals in surface soils in a typical coal mine city, Lianyuan, China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Cui, X.; Wang, X.; Hu, Q. Source identification and health risk assessment of heavy metals in groundwater of Yongqing County, Hebei Province. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2023, 39, 741–749. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.U.; Rai, N. Arsenic enrichment in the north Gangetic Plains of Laksar, Uttarakhand, India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 21, 100913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Y.; Han, S.; Liu, J.; Lu, H.; Bai, F.; Yan, Z. Migration and transformation mechanism of high arsenic groundwater in oasis belt in the middle part of northern piedmont of Tianshan Mountain. Earth Sci. 2023. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yang, F.; Ji, Y.; Zeng, Y. Distribution and co-enrichment genesis of arsenic, fluorine and iodine in groundwater of the oasis belt in the southern margin of Tarim Basin. Earth Sci. Front. 2022, 29, 99–114. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chao, B.; Luo, Y.; Wang, X. Stable carbon isotope signatures of high arsenic groundwater and their indicative significance in in Kuitun area of Xinjiang. Environ. Chem. 2024, 43, 1–10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Tuo, J.; Dai, S.; Rong, X.; Xing, X. Monitoring and analysis of arsenic content and valence state in rural drinking water from 2018 to 2020 in Aksu District. Chin. Endem. Dis. Control 2021, 36, 367–368. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, J.; Cao, Y. Distribution and co-enrichment of arsenic and fluorine in the groundwater of the Manas River Basin in Xinjiang. Arid Zone Res. 2023, 40, 1425–1437. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, J.; Han, S.; Hou, J.; Zeng, Y. Distribution and co-enrichment factors of arsenic and iodine in groundwater in the Shihezi area, Xinjiang. Environ. Chem. 2021, 40, 3464–3473. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
| Pollution Degree [37] | Pi | NPI | Ecological Risk Degree [41] | Ei | RI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pollution-free | Pi ≤ 1 | NPI < 1 | Low risk | Ei < 40 | RI ≤ 150 |
| Low pollution | 1 < Pi ≤ 2 | 1 ≤ NPI < 2.5 | Moderate risk | 40 < Ei ≤ 80 | 150 < RI ≤ 300 |
| Moderate pollution | 2 < Pi ≤ 3 | 2.5 ≤ NPI < 7 | High risk | 80 < Ei ≤ 160 | 300 < RI ≤ 600 |
| Heavy pollution | Pi > 3 | NPI ≥ 7 | Extremely high risk | 160 < Ei ≤ 320 | RI > 600 |
| Metals | As n = 59 | Se n = 67 | Pb n = 73 | Cu n = 75 | Cr(Ⅵ) n = 75 | Zn n = 75 | Mn n = 73 | Cd n = 29 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min (μg/L) | 1.08 | 0.27 | 0.24 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Max (μg/L) | 24.20 | 12.20 | 18.50 | 154.0 | 147.0 | 671.0 | 423.0 | 3.56 |
| Mean (μg/L) | 5.50 | 4.19 | 3.62 | 10.20 | 7.34 | 99.79 | 33.77 | 0.53 |
| Median (μg/L) | 3.18 | 3.19 | 1.85 | 1.45 | 1.89 | 46.7 | 5.65 | 0.17 |
| SD (μg/L) | 5.70 | 3.24 | 4.16 | 25.64 | 19.34 | 133.27 | 69.83 | 0.83 |
| CV | 1.04 | 0.77 | 1.15 | 2.51 | 2.63 | 1.34 | 2.07 | 1.58 |
| Skewness | 2.15 | 1.01 | 1.92 | 3.90 | 5.79 | 1.83 | 3.53 | 2.52 |
| Kurtosis | 4.24 | 0.16 | 3.03 | 16.63 | 38.48 | 4.03 | 15.16 | 6.33 |
| * National standard (μg/L) [40] | 10 | 10 | 10 | 1000 | 50 | 1000 | 100 | 5 |
| Standard-exceeding ratio (%) | 10.17 | 7.46 | 9.59 | 0 | 2.67 | 0 | 10.96 | 0 |
| ** Max. permissible level WHO (2017) (μg/L) [43] | 10 | 40 | 10 | 2000 | 50 | 5000 | 1000 | 5 |
| Statistics | Pi | NPI | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | Se | Pb | Cu | Cr(Ⅵ) | Zn | Mn | Cd | ||
| Min | 0.1080 | 0.0269 | 0.024 | 0.0001 | 0.0028 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0017 | 0.097 |
| Max | 2.42 | 1.22 | 1.85 | 0.15 | 2.94 | 0.67 | 4.23 | 0.71 | 3.02 |
| Mean | 0.56 | 0.42 | 0.36 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.1 | 0.34 | 0.11 | 0.67 |
| Statistics | Ei | RI | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | Se | Pb | Cu | Cr(Ⅵ) | Zn | Mn | Cd | ||
| Min | 0.10 | 0.40 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 2.31 |
| Max | 24.20 | 18.30 | 9.25 | 0.77 | 5.88 | 0.67 | 4.23 | 21.36 | 39.87 |
| Mean | 4.28 | 5.78 | 1.76 | 0.05 | 0.29 | 0.10 | 0.33 | 1.37 | 13.96 |
| Variables | As | Se | Pb | Cu | Cr(VI) | Zn | Mn | Cd | % of Variance | Cumulative % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | 0.381 | 0.233 | 0.652 | 0.687 | 0.809 | −0.477 | −0.117 | 0.653 | 30.242 | 30.242 |
| PC2 | 0.797 | −0.602 | 0.466 | −0.498 | −0.149 | −0.086 | 0.151 | −0.043 | 18.966 | 49.207 |
| PC3 | −0.033 | 0.513 | 0.397 | −0.057 | 0.007 | −0.015 | 0.690 | −0.396 | 13.228 | 62.435 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mamat, M.; Eziz, M.; Wang, L.; Subi, X.; Wang, N.; Hu, Y. Pollution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Metal Elements in Groundwater in the Ibinur Lake Basin of NW China. Water 2023, 15, 4071. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15234071
Mamat M, Eziz M, Wang L, Subi X, Wang N, Hu Y. Pollution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Metal Elements in Groundwater in the Ibinur Lake Basin of NW China. Water. 2023; 15(23):4071. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15234071
Chicago/Turabian StyleMamat, Muyassar, Mamattursun Eziz, Liling Wang, Xayida Subi, Ning Wang, and Yonglong Hu. 2023. "Pollution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Metal Elements in Groundwater in the Ibinur Lake Basin of NW China" Water 15, no. 23: 4071. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15234071
APA StyleMamat, M., Eziz, M., Wang, L., Subi, X., Wang, N., & Hu, Y. (2023). Pollution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Metal Elements in Groundwater in the Ibinur Lake Basin of NW China. Water, 15(23), 4071. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15234071







