Over-Produced Extracellular Polymeric Substances and Activated Antioxidant Enzymes Attribute to Resistance of Pb(II) for Algal–Bacterial Granular Sludge in Municipal Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthetic Wastewater and Algal–Bacterial Granular Sludge
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Analysis Methods
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
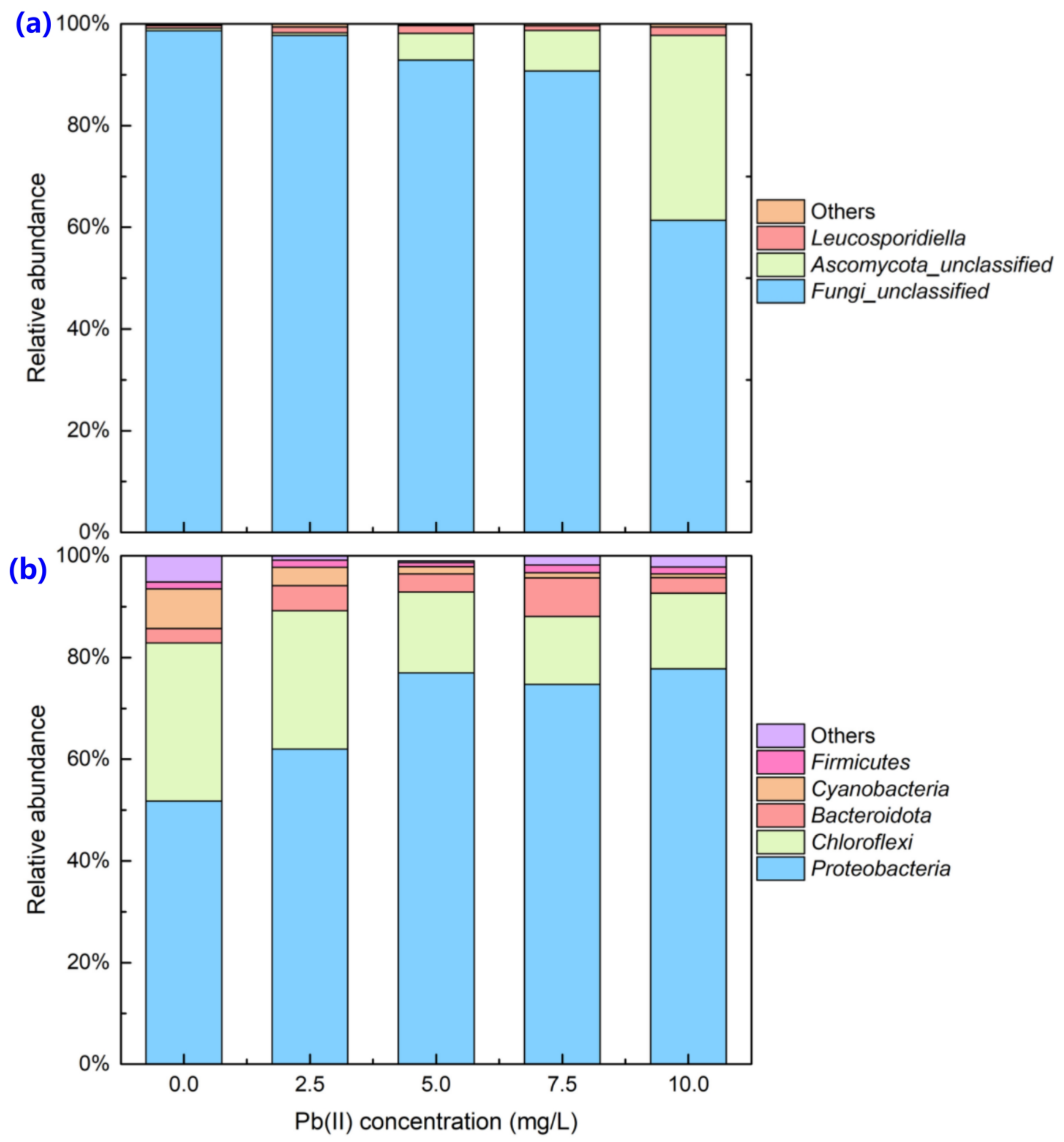
3.1. Changes in Microbial Communities
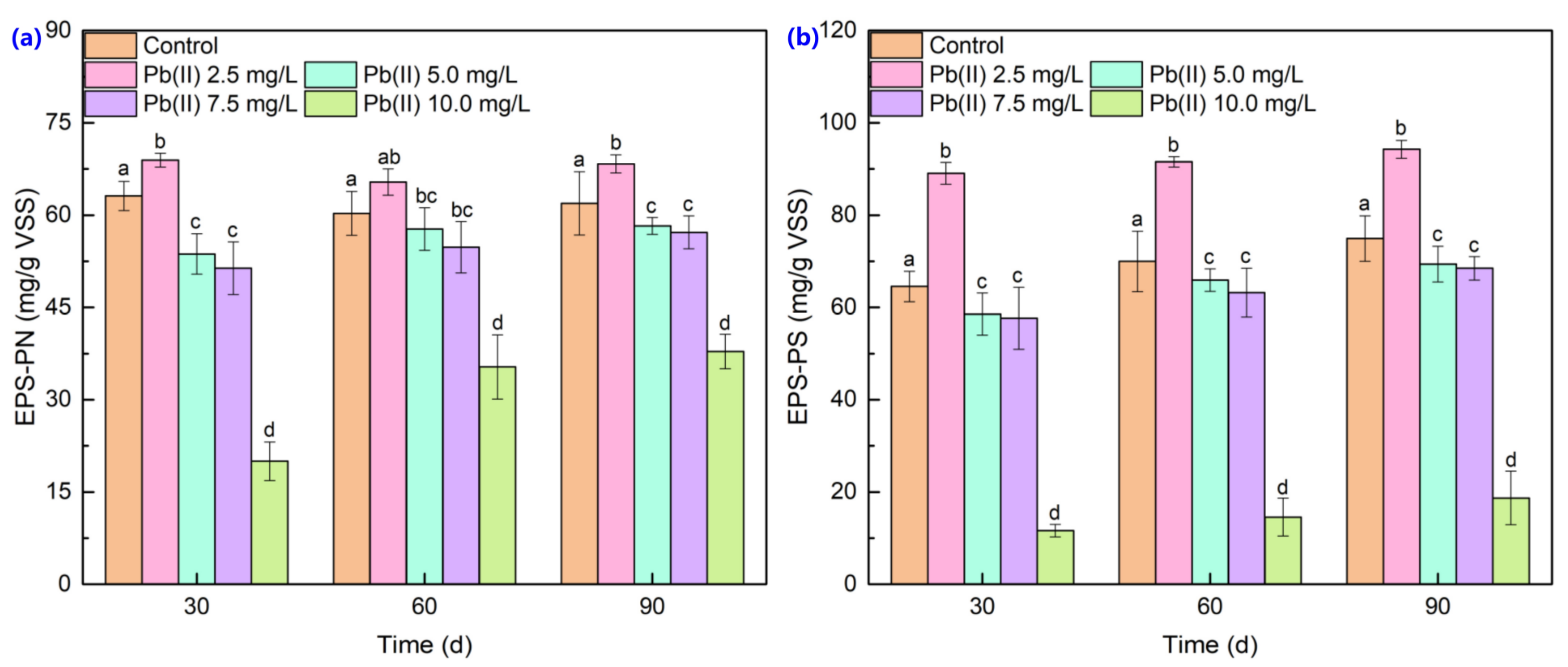
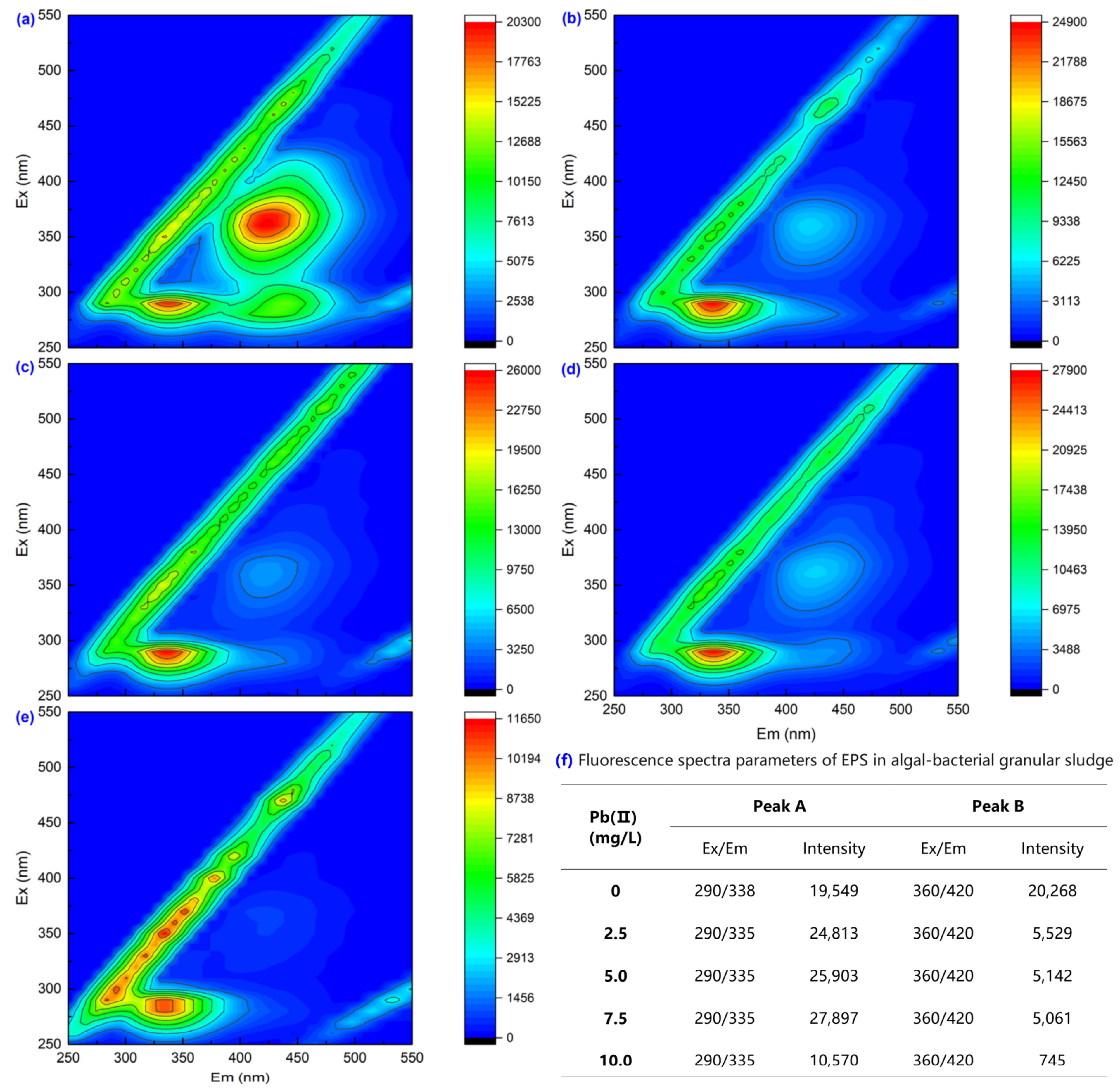
3.2. Extracellular Polymeric Substance Content
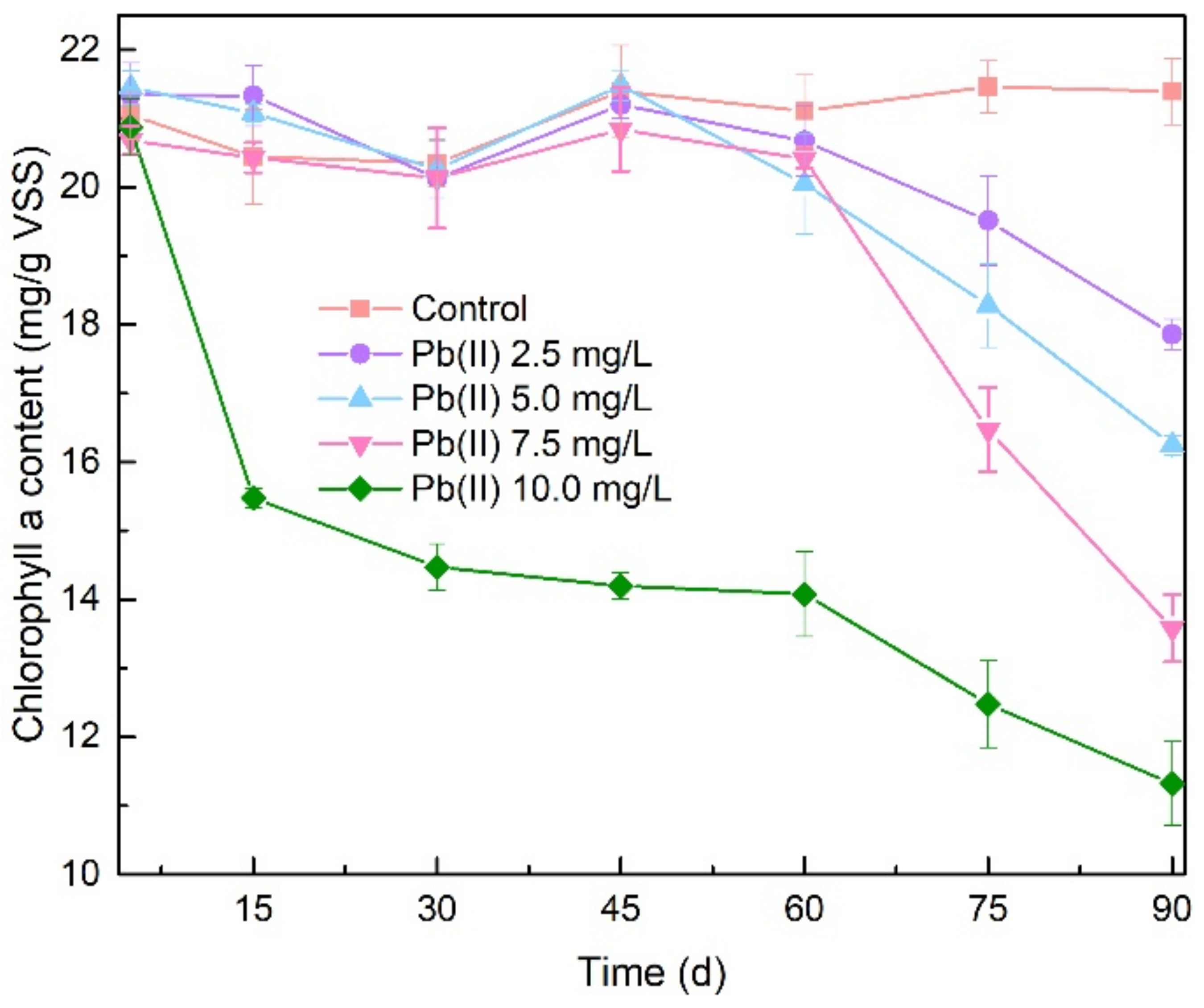
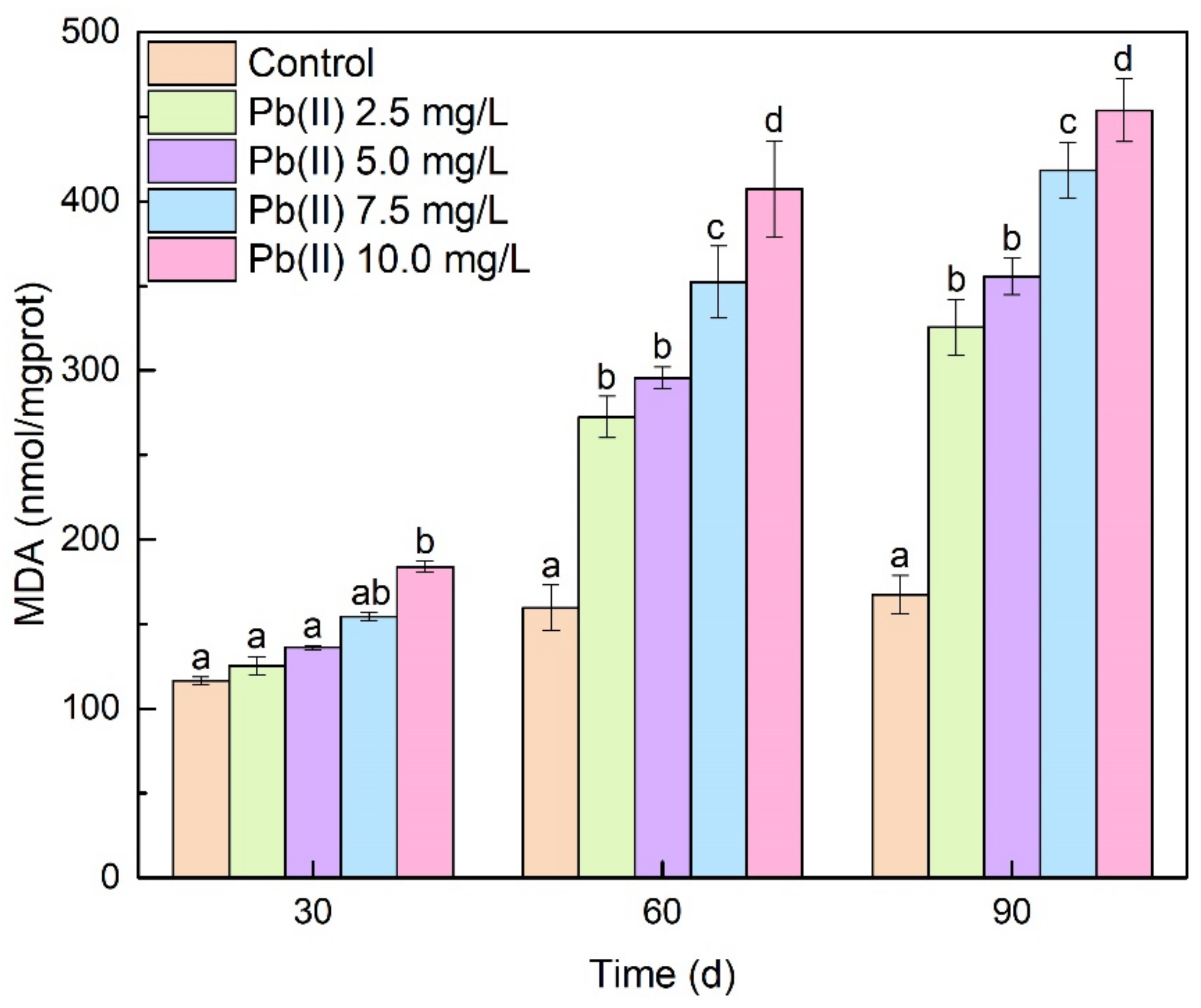
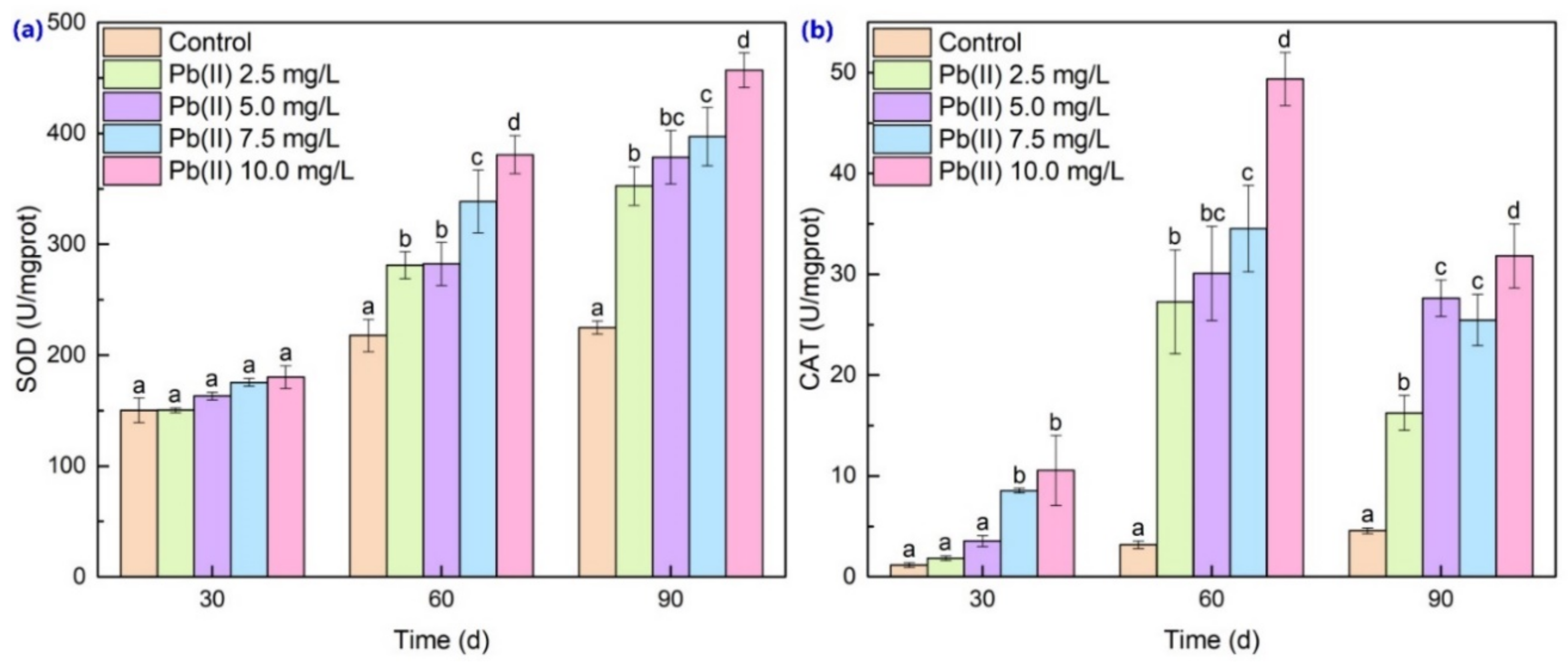
3.3. Antioxidant Enzyme Activities and MDA Content Analysis
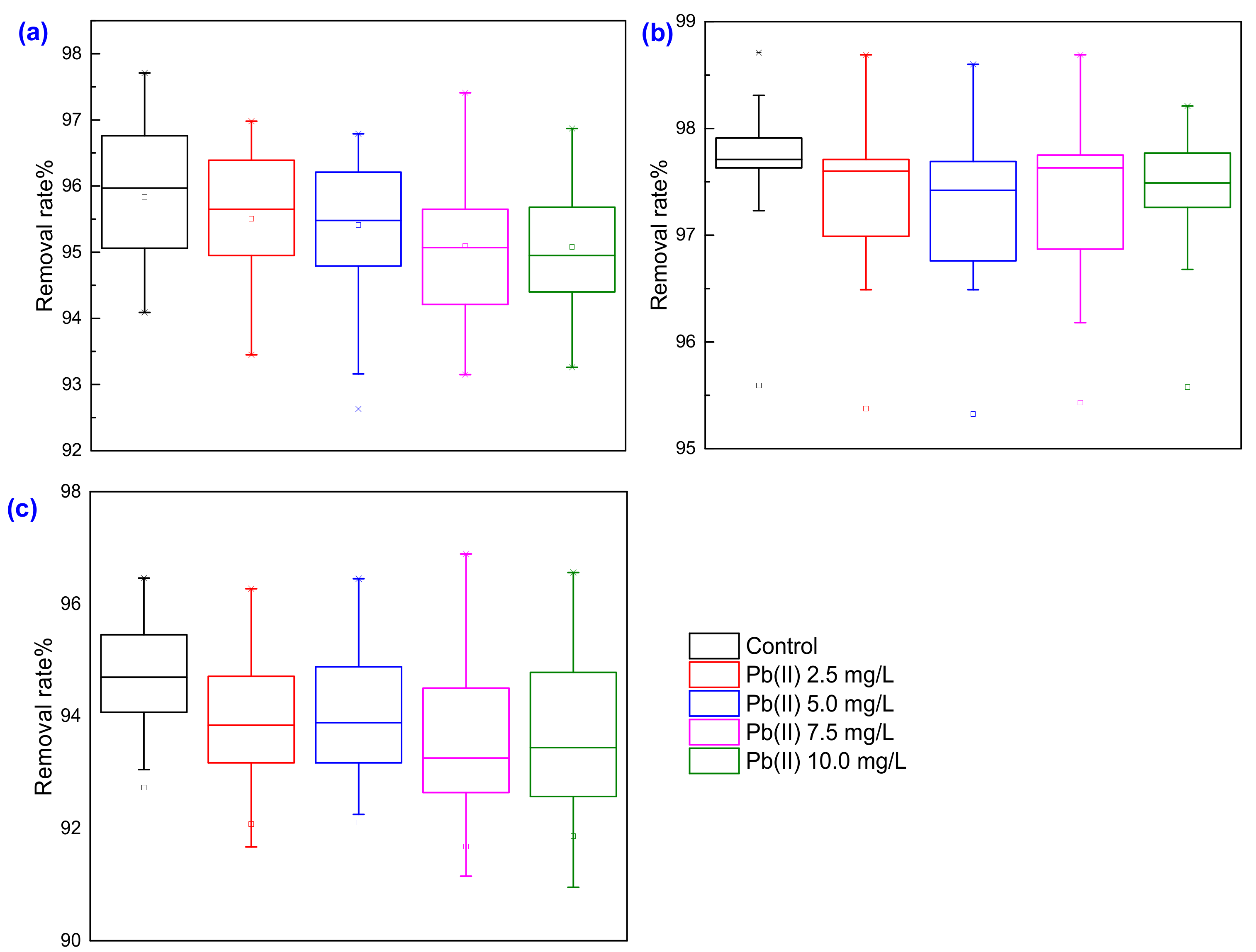
3.4. Performance in Treating Municipal Wastewater
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shrestha, R.; Ban, S.; Devkota, S.; Sharma, S.; Joshi, R.; Tiwari, A.P.; Kim, H.Y.; Joshi, M.K. Technological trends in heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Xi, S. The effects of heavy metals on human metabolism. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2020, 30, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda, K.N. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushwaha, A.; Hans, N.; Kumar, S.; Rani, R. A critical review on speciation, mobilization and toxicity of lead in soil-microbe-plant system and bioremediation strategies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, D.; Joshi, S.R. Study on bioremediation of Lead by exopolysaccharide producing metallophilic bacterium isolated from extreme habitat. Biotechnol. Rep. 2017, 16, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Dash, H.R.; Chakraborty, J. Genetic basis and importance of metal resistant genes in bacteria for bioremediation of contaminated environments with toxic metal pollutants. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 2967–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaszadeh, S.; Wan Alwi, S.R.; Webb, C.; Ghasemi, N.; Muhamad, I.I. Treatment of lead-contaminated water using activated carbon adsorbent from locally available papaya peel biowaste. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 118, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Nie, Q.; Ding, Y.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Shimizu, K.; Yuan, T. Pb(II) bioremediation using fresh algal-bacterial aerobic granular sludge and its underlying mechanisms highlighting the role of extracellular polymeric substances. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 444, 130452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 18918-2002; Discharge Standard of Pollutants for Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants. China Environment Press: Beijing, China, 2002.
- GB 5749-2022; Standards for Drinking Water Quality. State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Leung, P.T.Y.; Yi, A.X.; Ip, J.C.H.; Mak, S.S.T.; Leung, K.M.Y. Photosynthetic and transcriptional responses of the marine diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana to the combined effect of temperature stress and copper exposure. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, W.; Yang, L.; Joseph, S.; Shi, W.; Bian, R.; Zheng, J.; Li, L.; Shan, S.; Pan, G. Utilization of biochar produced from invasive plant species to efficiently adsorb Cd (II) and Pb (II). Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 317, 124011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhatib, R.; Maruthavanan, J.; Ghoshroy, S.; Steiner, R.; Sterling, T.; Creamer, R. Physiological and ultrastructural effects of lead on tobacco. Biol. Plant. 2012, 56, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.; Chen, C.W.; Haldar, D.; Tambat, V.S.; Kumar, P.; Tiwari, A.; Singhania, R.R.; Dong, C.-D.; Patel, A.K. Advancement in algal bioremediation for organic, inorganic, and emerging pollutants. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 317, 120840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Xiao, L.; Xu, A.; Mao, W.; Wu, Z.; Hicks, L.C.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, J. Silicon fertilization enhances the resistance of tobacco plants to combined Cd and Pb contamination: Physiological and microbial mechanisms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 255, 114816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, W.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, W.; Cui, F.; Lens PN, L.; Tay, J.H. Microalgal-bacterial consortia: From interspecies interactions to biotechnological applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 118, 109563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Zhang, M.; Gu, J.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y. A self-sustaining synergetic microalgal-bacterial granular sludge process towards energy-efficient and environmentally sustainable municipal wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2020, 179, 115884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, L.; Ji, B.; Hou, H.; Ma, Y. Microalgal-bacterial granular sludge process in non-aerated municipal wastewater treatment under natural day-night conditions: Performance and microbial community. Water 2021, 13, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purba LD, A.; Zahra, S.A.; Yuzir, A.; Iwamoto, K.; Abdullah, N.; Shimizu, K.; Lei, Z.; Hermana, J. Algal-bacterial aerobic granular sludge for real municipal wastewater treatment: Performance, microbial community change and feasibility of lipid recovery. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 333, 117374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ji, B.; Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Gu, J.; Liu, Y. Defensive responses of microalgal-bacterial granules to tetracycline in municipal wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 312, 123605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ji, B.; Cui, B.; Ma, Y.; Guo, D.; Liu, Y. Cadmium-effect on performance and symbiotic relationship of microalgal-bacterial granules. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 282, 125383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, G.; Hirayama, S.; Nguyen, B.V.; Lei, Z.; Shimizu, K.; Zhang, Z. Insight into Cr(VI) biosorption onto algal-bacterial granular sludge: Cr(VI) bioreduction and its intracellular accumulation in addition to the effects of environmental factors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 414, 125479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, Z.; Lee, D.-J. Enhanced biosorption of Cr(VI) from synthetic wastewater using algal-bacterial aerobic granular sludge: Batch experiments, kinetics and mechanisms. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 251, 117323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Cheah, W.Y.; Lai, S.H.; Ng, E.-P.; Khoo, K.S.; Show, P.L.; Ling, T.C. Symbiosis of microalgae and bacteria consortium for heavy metal remediation in wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, X.; Nuramkhaan, M.; Lei, Z.; Shimizu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Adachi, Y.; Lee, D.-J.; HwaTay, J. Rapid granulation of aerobic granular sludge: A mini review on operation strategies and comparative analysis. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 7, 100206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ji, B.; Zhang, M.; Gu, J.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y. Tetracycline-induced decoupling of symbiosis in microalgal-bacterial granular sludge. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; An, X.; De Philippis, R.; Ma, X.; Ye, C.; Chen, L. Identification of aqueous extracts from Artemisia ordosica and their allelopathic effects on desert soil algae. Chemoecology 2019, 29, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Cao, B.; Wang, D.; Ma, T.; Xia, H.; Yu, D. Influence of wastewater sludge treatment using combined peroxyacetic acid oxidation and inorganic coagulants re-flocculation on characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS). Water Res. 2016, 88, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbert, D.P.; Phipps, P.J.; Strange, R.E. Chapter III Chemical Analysis of Microbial Cells. Methods Microbiol. 1971, 5, 209–344. [Google Scholar]
- Raunkj, R.K.; Hvitved-Jacobsen, T.; Nielsen, P.H. Measurement of pools of protein, carbohydrate and lipid in domestic wastewater. Water Res. 1994, 28, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, Z.; Jin, Y.; He, M.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, C.; Niyungeko, C.; Arai, Y. Composition of microbial community in pig manure biochar-amended soils and the linkage to the heavy metals accumulation in rice at harvest. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 2189–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Ye, Y.; Hu, Y.; Shi, H. The variation in microbial community structure under different heavy metal contamination levels in paddy soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gong, L.; Gan, D.; Li, X.; Yao, J.; Wang, L.; Qu, J.; Cong, J.; Zhang, Y. Diversity, function and assembly of the Trifolium repens L. root-associated microbiome under lead stress. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouhend, A.S.; Milferstedt, K.; Hamelin, J.; Ansari, A.A.; Butler, C.; Carbajal-González, B.I.; Park, C. Growth progression of oxygenic photogranules and its impact on bioactivity for aeration-free wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, P.O.; Sinhor, V.; Crizel, M.G.; Pires, N.; Sanches Filho, P.J.; Picoloto, R.S.; Duarte, F.A.; Pereira CM, P.; Mesko, M.F. Bioremediation of chromium and lead in wastewater from chemistry laboratories promotes by cyanobacteria. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 19, 101161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventrella, A.; Catucci, L.; Piletska, E.; Piletsky, S.; Agostiano, A. Interactions between heavy metals and photosynthetic materials studied by optical techniques. Bioelectrochemistry 2009, 77, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, B.; Chang, C.; Lee, D. Fractionation of soluble microbial products (SMP) and soluble extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) from wastewater sludge. Environ. Technol. 2008, 29, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Hu, Y.; Xiong, F. Sorption of Cu(II) and Cd(II) by extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) from Aspergillus fumigatus. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2011, 65, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Li, M.-M.; Chen, T.-H.; Zhou, Y.-F.; Yue, Z.-B. Competitive adsorption of heavy metal by extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) extracted from sulfate reducing bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 163, 374–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, C.; Paul, W.; AL, J.; Karl, B. Fluorescence excitation−emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5701–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Wang, B.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Han, F.; Wang, X.; Du, B.; Wei, Q. Role of extracellular polymeric substances in biosorption of dye wastewater using aerobic granular sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 185, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Mangwani, N.; Das, S. Interaction of Pb(II) and biofilm associated extracellular polymeric substances of a marine bacterium Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes NP103. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 173, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.S.; Tuteja, N. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 48, 909–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Qin, L.; Yuan, B.; Liang, N. Time-dependent toxicity and health effects mechanism of cadmium to three green algae. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Dubey, R.S. Lead toxicity induces lipid peroxidation and alters the activities of antioxidant enzymes in growing rice plants. Plant Sci. 2003, 164, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yao, J.; Duran, R.; Liu, J.; Min, N.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, C.; Ma, B.; Pang, W.; et al. Toxic response of the freshwater green algae Chlorella pyrenoidosa to combined effect of flotation reagent butyl xanthate and nickel. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Li, M.; Teng, Z.; Qiu, B.; Huo, Y.; Zhang, K. Effects of Pb(II) and Cr(VI) stress on phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (Bacillus sp. Strain MRP-3): Oxidative stress and bioaccumulation potential. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S. Over-Produced Extracellular Polymeric Substances and Activated Antioxidant Enzymes Attribute to Resistance of Pb(II) for Algal–Bacterial Granular Sludge in Municipal Wastewater Treatment. Water 2023, 15, 3833. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213833
Yang J, Zhang Y, Wang S. Over-Produced Extracellular Polymeric Substances and Activated Antioxidant Enzymes Attribute to Resistance of Pb(II) for Algal–Bacterial Granular Sludge in Municipal Wastewater Treatment. Water. 2023; 15(21):3833. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213833
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Juanru, Yu Zhang, and Shulian Wang. 2023. "Over-Produced Extracellular Polymeric Substances and Activated Antioxidant Enzymes Attribute to Resistance of Pb(II) for Algal–Bacterial Granular Sludge in Municipal Wastewater Treatment" Water 15, no. 21: 3833. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213833




