The Future of Cyanobacteria Toxicity in Estuaries Undergoing Pulsed Nutrient Inputs: A Case Study from Coastal Louisiana
Abstract
:1. Introduction
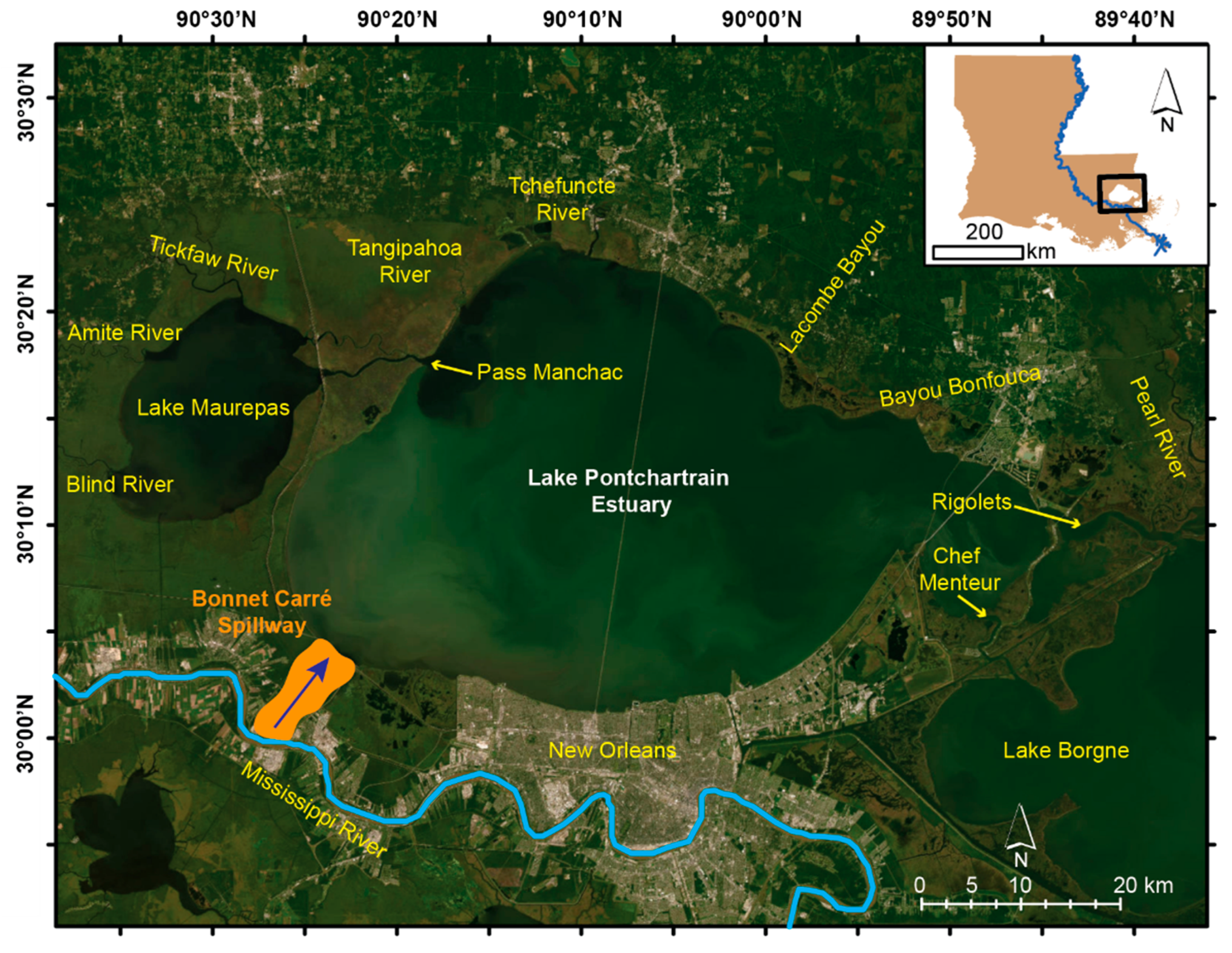
2. Focus Region: The Lake Pontchartrain Estuary (LPE)
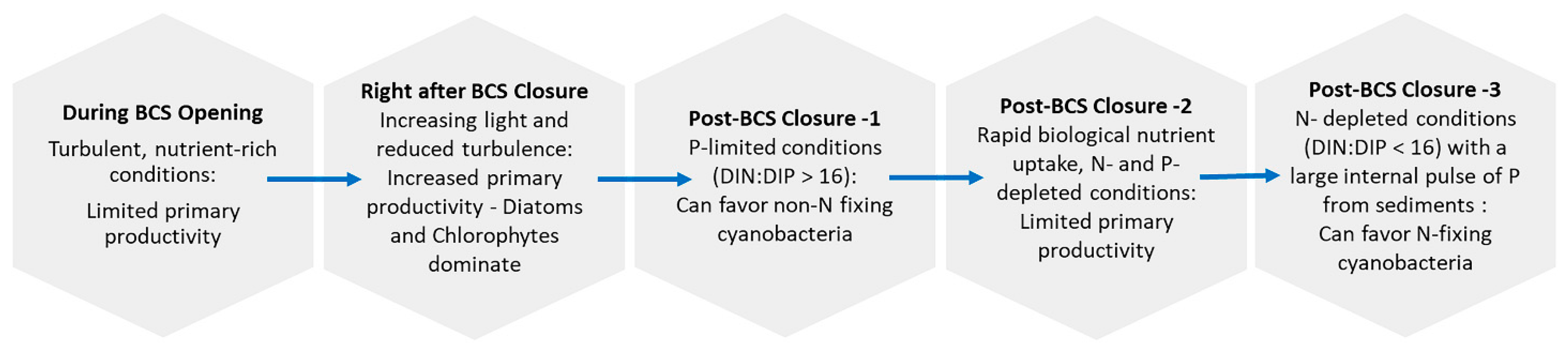
3. Environmental and Biological Drivers Supporting cyanoHABs
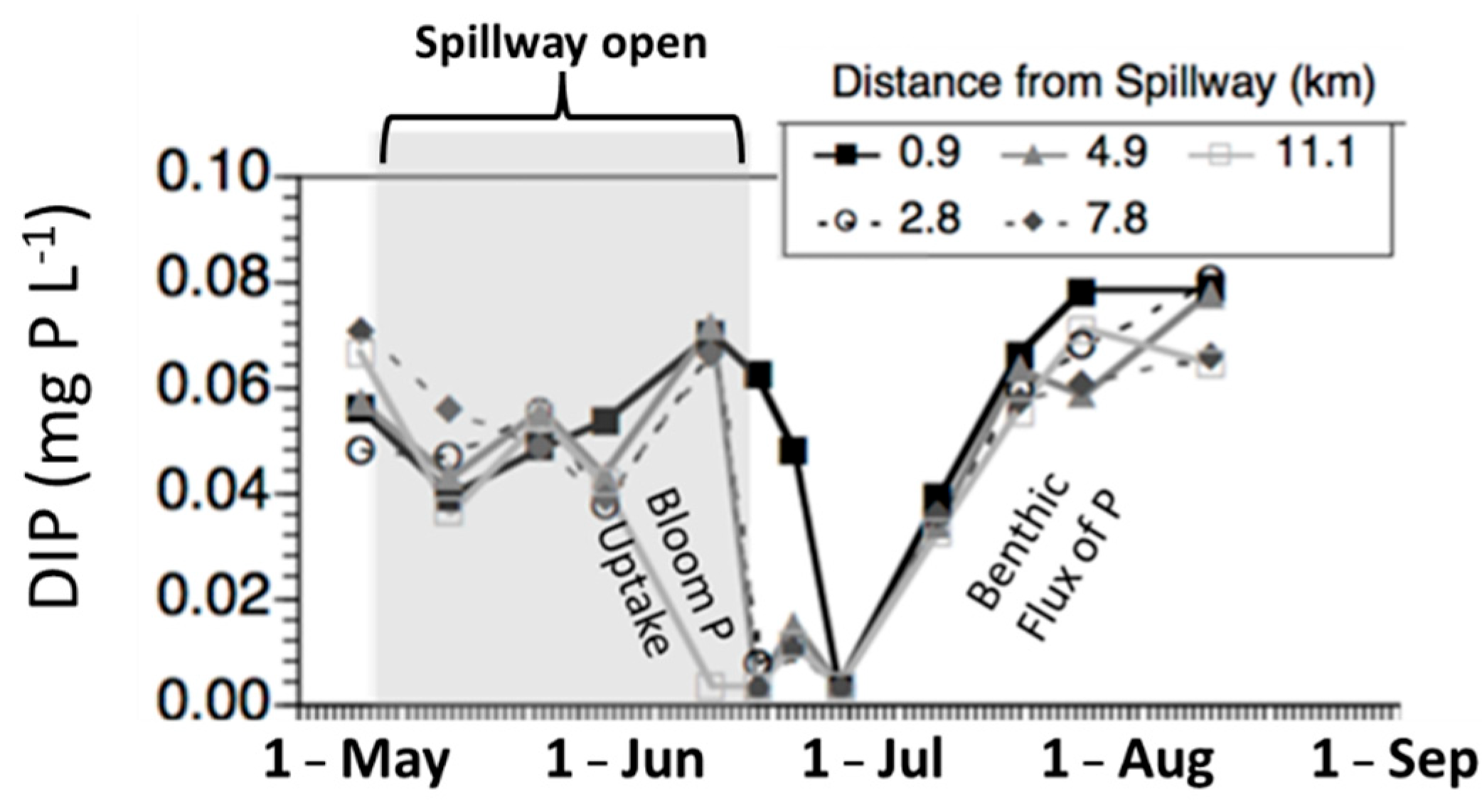
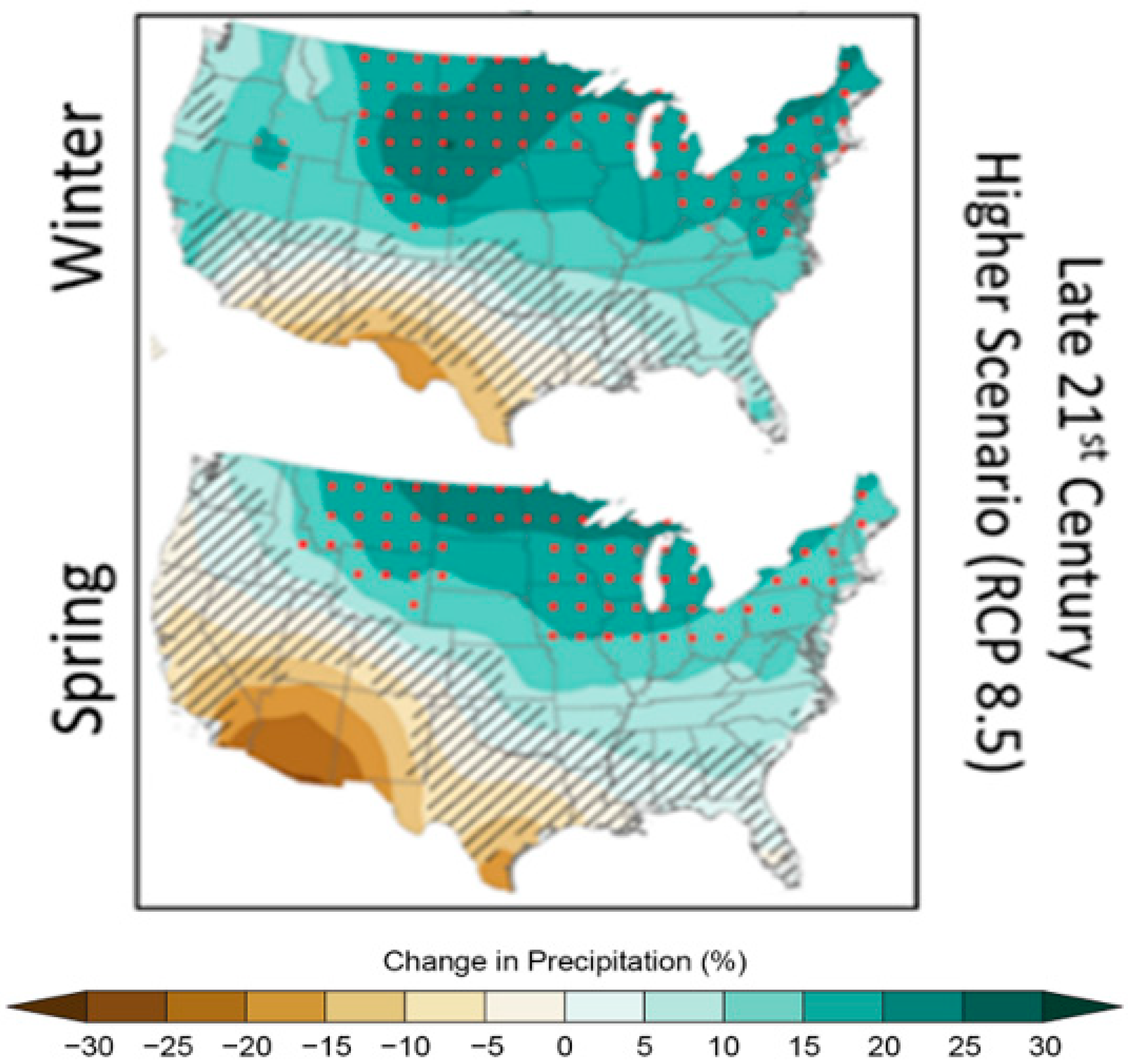
4. Pathways for Nutrient Transport into Systems of Interest
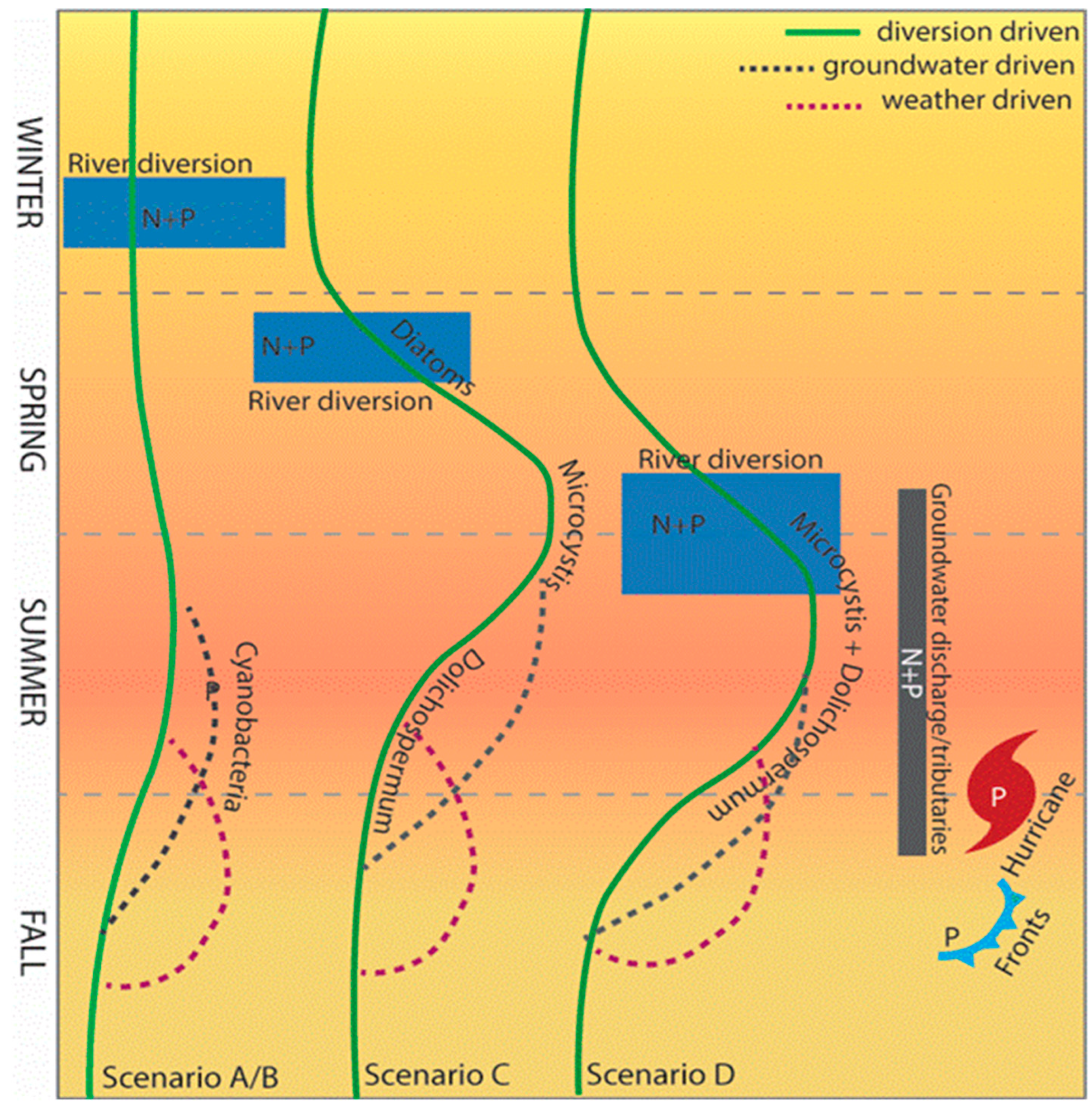
5. Forecasting to Anticipate Human Exposure: Variations in Cyanobacteria Species, Toxin Type, and Modality as Functions of Growth Stimuli
6. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, D.M.; Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M. Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: Nutrient sources, composition, and consequences. Estuaries 2002, 25, 704–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Hall, N.S.; Calandrino, E.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a world experiencing anthropogenic and climatic-induced change. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Anglada, L.V.; Hilborn, E.D.; Backer, L.C. Harmful algal blooms (HABs) and public health: Progress and current challenges. Toxins 2016, 7, 4437–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Hall, N.S.; Peierls, B.L.; Rossignol, K.L. Evolving Paradigms and Challenges in Estuarine and Coastal Eutrophication Dynamics in a Culturally and Climatically Stressed World. Estuaries Coasts 2014, 37, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilan, B.A.; Pearson, L.A.; Muenchhoff, J.; Moffitt, M.C.; Dittmann, E. Environmental conditions that influence toxin biosynthesis in cyanobacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1239–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Cruz, A.A.; Hiskia, A.; Kaloudis, T.; Chernoff, N.; Hill, D.; Antoniou, M.G.; He, X.; Loftin, K.; O’Shea, K.; Zhao, C.; et al. A review on cylindrospermopsin: The global occurrence, detection, toxicity and degradation of a potent cyanotoxin. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 1979–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugger, M.; Lenoir, S.; Berger, C.; Ledreux, A.; Druart, J.-C.; Humbert, J.-F.; Guette, C.; Bernard, C. First report in a river in France of the benthic cyanobacterium Phormidium favosum producing anatoxin-a associated with dog neurotoxicosis. Toxicon 2005, 45, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mez, K.; Beattie, K.A.; Codd, G.A.; Hanselmann, K.; Hauser, B.; Naegeli, H.; Preisig, H.R. Identification of a microcystin in benthic cyanobacteria linked to cattle deaths on alpine pastures in Switzerland. Eur. J. Phycol. 1997, 32, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Fulton, R.S.; Moisander, P.H.; Dyble, J. Harmful Freshwater Algal Blooms, with an Emphasis on Cyanobacteria. Sci. World J. 2001, 1, 139109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, M.A.B.; Rodrigues, R.A.M.; Schlüter, L.; Podduturi, R.; Jørgensen, N.O.G.; Calijuri, M.C. Influence of Environmental Factors on Occurrence of Cyanobacteria and Abundance of Saxitoxin-Producing Cyanobacteria in a Subtropical Drinking Water Reservoir in Brazil. Water 2021, 13, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, A.M.; Anderson, E.J.; Beletsky, D.; Boland, S.; Bosch, N.S.; Bridgeman, T.B.; Chaffin, J.D.; Cho, K.; Confesor, R.; Daloğlu, I.; et al. Record-setting algal bloom in Lake Erie caused by agricultural and meteorological trends consistent with expected future conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6448–6452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.; Cho, K.H.; Lee, H.; Kang, T.; Kim, J.H. The relative importance of water temperature and residence time in predicting cyanobacteria abundance in regulated rivers. Water Res. 2017, 124, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giani, A.; Taranu, Z.E.; von Rückert, G.; Gregory-Eaves, I. Comparing key drivers of cyanobacteria biomass in temperate and tropical systems. Harmful Algae 2020, 97, 101859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adyasari, D.; Montiel, D.; Mortazavi, B.; Dimova, N. Storm-Driven Fresh Submarine Groundwater Discharge and Nutrient Fluxes From a Barrier Island. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 679010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.G.; Swarzenski, P.W. An investigation of submarine groundwater—Borne nutrient fluxes to the west Florida shelf and recurrent harmful algal blooms. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, A.M. Study role of climate change in extreme threats to water quality. Nature 2016, 535, 349–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.C.; Bargu, S.; Dash, P.; Rabalais, N.N.; Sutor, M.; Morrison, W.; Walker, N.D. Evaluating the potential risk of microcystins to blue crab (Callinectes sapidus) fisheries and human health in a eutrophic estuary. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riekenberg, J.; Bargu, S.; Twilley, R. Phytoplankton Community Shifts and Harmful Algae Presence in a Diversion Influenced Estuary. Estuaries Coasts 2015, 38, 2213–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargu, S.; Skaggs, B.; Boudreaux, M.; Hammond, C.N.; Snow, C.; Aw, T.G.; Stumpf, R. Water Quality and Toxic Cyanobacteria in Oligohaline Estuary Beaches during the Longest Mississippi River Basin Flood Event in 2019. Estuaries Coasts 2023, 46, 1865–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, P.; Walker, N.D.; Mishra, D.R.; Hu, C.; Pinckney, J.L.; D’Sa, E.J. Estimation of cyanobacterial pigments in a freshwater lake using OCM satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3409–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, E.D.; Smith, E.A.; Bargu, S.; White, J.R. Will Mississippi River diversions designed for coastal restoration cause harmful algal blooms? Ecol. Eng. 2016, 91, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, E.D.; White, J.R.; Smith, E.A.; Bargu, S.; Li, C. Estuarine ecosystem response to three large-scale Mississippi River flood diversion events. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 458–460, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.R.; Fulweiler, R.W.; Li, C.Y.; Bargu, S.; Walker, N.D.; Twilley, R.R.; Green, S.E. Mississippi River Flood of 2008: Observations of a Large Freshwater Diversion on Physical, Chemical, and Biological Characteristics of a Shallow Estuarine Lake. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5599–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dortch, Q.; Parsons, M.L.; Rabalais, N.N.; Turner, R.E. What is the threat of harmful algal blooms in Louisiana coastal waters? In Recent Research in Coastal Louisiana: Natural System Function and Response to Human Influence; Rozas, L.P., Nyman, J.A., Proffitt, C.E., Rabalais, N.N., Reed, D.J., Turner, R.E., Eds.; Louisiana Sea Grant Publication: Lafayette LA, USA, 1998; pp. 134–144. [Google Scholar]
- Dortch, Q.; Peterson, T.D.; Achee, S.; Furr, K.L. Phytoplankton, cyanobacterial blooms, and N2 fixation in years with and without Mississippi River diversions. In Nitrogen Loading into Lake Pontchartrain; Turner, R.E., Justic, D., Rabalais, N.N., Dortch, Q., Eds.; Lake Pontchartrain Basin Foundation: Metairie, LA, USA, 2001; pp. 4.1–4.26. [Google Scholar]
- Mize, S.V.; Demcheck, D.K. Water quality and phytoplankton communities in Lake Pontchartrain during and after the Bonnet Carré Spillway opening, April to October 2008, in Louisiana, USA. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2009, 29, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabalais, N.N. Consequences of Mississippi River diversion for Louisiana coastal restoration. Natl. Wetl. Newsl. 2005, 27, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.; Mendenhall, W.; Atilla, N.; Morrison, W.; Rabalais, N.N. Cyanobacteria in eutrophied fresh to brackish lakes in Barataria estuary, Louisiana. In Cynobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms: State of the Science and Research Needs; Hudnell, H.K., Ed.; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 308–309. [Google Scholar]
- Preece, E.P.; Hardy, F.J.; Moore, B.C.; Bryan, M. A review of microcystin detections in Estuarine and Marine waters: Environmental implications and human health risk. Harmful Algae 2017, 61, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shingai, Q.K.; Wilkinson, G.M. Microcystin as a biogeochemical cycle: Pools, fluxes, and fates of the cyanotoxin in inland waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2023, 8, 406–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibelings, B.W.; Backer, L.C.; Kardinaal, W.E.A.; Chorus, I. Current approaches to cyanotoxin risk assessment and risk management around the globe. Harmful Algae 2014, 40, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyraite, G.; Kataržytė, M.; Overlingė, D.; Vaičiūtė, D.; Jonikaitė, E.; Schernewski, G. Skip the Dip—Avoid the Risk? Integrated Microbiological Water Quality Assessment in the South-Eastern Baltic Sea Coastal Waters. Water 2020, 12, 3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.E.; Dortch, Q.; Rabalais, N.N. Inorganic nitrogen transformations at high loading rates in an oligohaline estuary. Biogeochemistry 2004, 68, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.E.; Dortch, Q.; Justic, D.; Swenson, E.M. Nitrogen loading into an urban estuary: Lake Pontchartrain (Louisiana, U.S.A.). Hydrobiologia 2002, 487, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Li, C.; White, J.R.; Bargu, S.; Milan, B.; Bentley, S. Numerical Experiments on Variation of Freshwater Plume and Leakage Effect From Mississippi River Diversion in the Lake Pontchartrain Estuary. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2020, 125, e2019JC015282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, C.; Bargu, S.; Hammond, C.N.; Hiatt, M.; White, J.R. Effect of Mississippi River discharge plume on temporal and spatial variability of toxic cyanobacteria in an oligohaline estuary. Hydrobiologia 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyrou, M.E.; Bianchi, T.S.; Lambert, C.D. Transport and fate of dissolved organic carbon in the Lake Pontchartrain esutary, Louisiana, U.S.A. Biogeochemistry 1997, 38, 207–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis, R.S.; Powell, G.L. Hydrography, mixing characteristics, and residence times of Gulf of Mexico estuaries. In Biogeochemistry of Gulf of Mexico Estuaries; Bianchi, T.S., Pennock, J.R., Twilley, R.R., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 29–61. [Google Scholar]
- Luketina, D. Simple Tidal Prism Models Revisited. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1998, 46, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Walker, N.; Hou, A.; Georgiou, I.; Roberts, H.; Laws, E.; McCorquodale, J.A.; Weeks, E.; Li, X.; Crochet, J. Circular plumes in Lake Pontchartrain estuary under wind straining. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 80, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, I.; McCorquodale, J.A. Stratification and Circulation in Lake Pontchartrain. In Estuarine and Coastal Modeling (2001); American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2012; pp. 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, C.C.; Ibelings, B.W.; Hoffmann, E.P.; Hamilton, D.P.; Brookes, J.D. Eco-physiological adaptations that favour freshwater cyanobacteria in a changing climate. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1394–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Blooms Like It Hot. Science 2008, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marc, B.; Renato, M.; Simone De, O.; Mauro, M.; Beatriz, B. Dynamics of a toxic cyanobacterial bloom (Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii) in a shallow reservoir in the semi-arid region of northeast Brazil. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1999, 20, 285–297. [Google Scholar]
- Dokulil, M.T.; Teubner, K. Cyanobacterial dominance in lakes. Hydrobiologia 2000, 438, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlik-Skowrońska, B.; Kalinowska, R.; Skowroński, T. Cyanotoxin diversity and food web bioaccumulation in a reservoir with decreasing phosphorus concentrations and perennial cyanobacterial blooms. Harmful Algae 2013, 28, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taranu, Z.E.; Pick, F.R.; Creed, I.F.; Zastepa, A.; Watson, S.B. Meteorological and Nutrient Conditions Influence Microcystin Congeners in Freshwaters. Toxins 2019, 11, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jos, A.; Cameán, A.M. Freshwater Algal Toxins: Monitoring and Toxicity Profile. Toxins 2020, 12, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Haas, L. Calculating age and residence time in the tidal York River using three-dimensional model experiments. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 61, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiatt, M.; Castañeda-Moya, E.; Twilley, R.; Hodges, B.R.; Passalacqua, P. Channel-Island Connectivity Affects Water Exposure Time Distributions in a Coastal River Delta. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 2212–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safak, I.; Wiberg, P.L.; Richardson, D.L.; Kurum, M.O. Controls on residence time and exchange in a system of shallow coastal bays. Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 97, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, N.S.; Paerl, H.W.; Peierls, B.L.; Whipple, A.C.; Rossignol, K.L. Effects of climatic variability on phytoplankton community structure and bloom development in the eutrophic, microtidal, New River Estuary, North Carolina, USA. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 117, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peierls, B.L.; Hall, N.S.; Paerl, H.W. Non-monotonic Responses of Phytoplankton Biomass Accumulation to Hydrologic Variability: A Comparison of Two Coastal Plain North Carolina Estuaries. Estuaries Coasts 2012, 35, 1376–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloern, J.E. Turbidity as a control on phytoplankton biomass and productivity in estuaries. Cont. Shelf Res. 1987, 7, 1367–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Justic, D.; Lane, R.R.; Day, J.W.; Cable, J.E. Hydrodynamic response of the Breton Sound estuary to pulsed Mississippi River inputs. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 95, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umgiesser, G.; Ferrarin, C.; Cucco, A.; De Pascalis, F.; Bellafiore, D.; Ghezzo, M.; Bajo, M. Comparative hydrodynamics of 10 Mediterranean lagoons by means of numerical modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2014, 119, 2212–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, Y.; Bargu, S.; White, J.R. Temporally-displaced Mississippi River spring flood pulse shows muted aquatic ecosystem response in estuarine waters: A climate change warning for coastal foodwebs. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USACE. Bonnet Carre Spillway Operations. Available online: https://www.mvn.usace.army.mil/Missions/MississippiRiver-Flood-Control/Bonnet-Carre-Spillway-Overview/Historic-Operation-of-Bonnet-Carre/ (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Dodds, W.K. Nutrients, eutrophication and harmful algal blooms along the freshwater to marine continuum. WIREs Water 2019, 6, e1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Monroy, V.H.; Lenaker, P.; Twilley, R.R.; Delaune, R.D.; Lindau, C.W.; Nuttle, W.; Habib, E.; Fulweiler, R.W.; Castañeda-Moya, E. Denitrification in coastal Louisiana: A spatial assessment and research needs. J. Sea Res. 2010, 63, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.; Lv, T.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Han, C.; Yu, W.; Yan, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhao, H.; Zuo, Z.; et al. The spatiotemporal characteristics of water quality and phytoplankton community in a shallow eutrophic lake: Implications for submerged vegetation restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, L.V.; Thompson, J.K. Changing restoration rules: Exotic bivalves interact with residence time and depth to control phytoplankton productivity. Ecosphere 2012, 3, art117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, S.F.; Denise, L.B.; Roger, I.E.N.; Kemp, W.M.; Mark, L. Effects of oyster population restoration strategies on phytoplankton biomass in Chesapeake Bay: A flexible modeling approach. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 336, 43–61. [Google Scholar]
- Leruste, A.; Malet, N.; Munaron, D.; Derolez, V.; Hatey, E.; Collos, Y.; De Wit, R.; Bec, B. First steps of ecological restoration in Mediterranean lagoons: Shifts in phytoplankton communities. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 180, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Rabalais, N.N.; Turner, R.E. Effects of Mississippi River water on phytoplankton growth and composition in the upper Barataria estuary, Louisiana. Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 1831–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissel, B.; Gaçe, A.; Fry, B. Tracing river influences on phytoplankton dynamics in two Louisiana estuaries. Ecology 2005, 86, 2751–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Wu, S.; Wu, X.; Lv, X.; Sivakumar, B.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Gao, A.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Impacts of a large river-to-lake water diversion project on lacustrine phytoplankton communities. J. Hydrol. 2020, 587, 124938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconer, I.R. Potential impact on human health of toxic cyanobacteria. Phycologia 1996, 35, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconer, I.R.; Humpage, A.R. Health Risk Assessment of Cyanobacterial (Blue-green Algal) Toxins in Drinking Water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2005, 2, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceballos-Laita, L.; Marcuello, C.; Lostao, A.; Calvo-Begueria, L.; Velazquez-Campoy, A.; Bes, M.T.; Fillat, M.F.; Peleato, M.-L. Microcystin-LR Binds Iron, and Iron Promotes Self-Assembly. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4841–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vézie, C.; Rapala, J.; Vaitomaa, J.; Seitsonen, J.; Sivonen, K. Effect of Nitrogen and Phosphorus on Growth of Toxic and Nontoxic Microcystis Strains and on Intracellular Microcystin Concentrations. Microb. Ecol. 2002, 43, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargu, S.; White, J.R.; Li, C.; Czubakowski, J.; Fulweiler, R.W. Effects of freshwater input on nutrient loading, phytoplankton biomass, and cyanotoxin production in an oligohaline estuarine lake. Hydrobiologia 2011, 661, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.; Hulot, F.D. Population Dynamics of Harmful Cyanobacteria. In Harmful Cyanobacteria; Huisman, J., Matthijs, H.C.P., Visser, P.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 143–176. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrão-Filho, A.d.S.; Soares, M.C.S.; de Freitas Magalhães, V.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. Biomonitoring of cyanotoxins in two tropical reservoirs by cladoceran toxicity bioassays. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, M. Present and future opportunities in the use of atomic force microscopy to address the physico-chemical properties of aquatic ecosystems at the nanoscale level. Int. Aquat. Res. 2022, 14, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Struewing, I.; Wymer, L.; Tettenhorst, D.R.; Shoemaker, J.; Allen, J. Use of qPCR and RT-qPCR for monitoring variations of microcystin producers and as an early warning system to predict toxin production in an Ohio inland lake. Water Res. 2020, 170, 115262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Caraco, N.F.; Correll, D.L.; Howarth, R.W.; Sharpley, A.N.; Smith, V.H. Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorous and nitrogen. Ecol. Appl. 1998, 8, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, E.Y.; Kim, G.; Primeau, F.; Moore, W.S.; Cho, H.-M.; DeVries, T.; Sarmiento, J.L.; Charette, M.A.; Cho, Y.-K. Global estimate of submarine groundwater discharge based on an observationally constrained radium isotope model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 8438–8444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecher, A.L.; Kessler, J.; Sparrow, K.; Garcia-Tigreros Kodovska, F.; Dimova, N.; Murray, J.; Tulaczyk, S.; Paytan, A. Methane transport through submarine groundwater discharge to the North Pacific and Arctic Ocean at two Alaskan sites. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, S344–S355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecher, A.L.; Mackey, K.; Kudela, R.; Ryan, J.; Fisher, A.; Murray, J.; Paytan, A. Nutrient Loading through Submarine Groundwater Discharge and Phytoplankton Growth in Monterey Bay, CA. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6665–6673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, W.S. The Effect of Submarine Groundwater Discharge on the Ocean. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2009, 2, 59–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel, D.; Lamore, A.; Stewart, J.; Dimova, N. Is Submarine Groundwater Discharge (SGD) Important for the Historical Fish Kills and Harmful Algal Bloom Events of Mobile Bay? Estuaries Coasts 2019, 42, 470–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanial, V.; Moore, W.S.; Shiller, A.M. Does a bottom-up mechanism promote hypoxia in the Mississippi Bight? Mar. Chem. 2021, 235, 104007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, A.H.; David, C.H.; Famiglietti, J.S. Continental patterns of submarine groundwater discharge reveal coastal vulnerabilities. Science 2016, 353, 705–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; White, J.R.; DeLaune, R.D. Diverted Mississippi River sediment as a potential phosphorus source affecting coastal Louisiana water quality. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2012, 27, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, E.D.; Nguyen, N.T.; White, J.R. Changes in estuarine sediment phosphorus fractions during a large-scale Mississippi River diversion. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, E.D.; Nguyen, N.T.; Bargu, S.; White, J.R. Internal loading of phosphorus from sediments of Lake Pontchartrain (Louisiana, USA) with implications for eutrophication. Hydrobiologia 2012, 684, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.M.; Reddy, K.R.; James, R.T. Internal Nutrient Loads from Sediments in a Shallow, Subtropical Lake. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2005, 21, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibler, S.R.; Tester, P.A.; Kunkel, K.E.; Moore, S.K.; Litaker, R.W. Effects of ocean warming on growth and distribution of dinoflagellates associated with ciguatera fish poisoning in the Caribbean. Ecol. Model. 2015, 316, 194–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.K.; Mantua, N.J.; Salathé, E.P. Past trends and future scenarios for environmental conditions favoring the accumulation of paralytic shellfish toxins in Puget Sound shellfish. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayhoe, K.; Wuebbles, D.J.; Easterling, D.R.; Fahey, D.W.; Doherty, S.; Kossin, J.; Sweet, W.; Vose, R.; Wehner, M. Our changing climate. In Impacts, Risks, and Adaptation in the United States: Fourth National Climate Assessment; Reidmiller, D.R., Avery, C.W., Easterling, D.R., Kunkel, K.E., Lewis, K.L.M., Maycock, T.K., Stewart, B.C., Eds.; U.S. Global Change Research Program: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; Volume 2, pp. 72–144. [Google Scholar]
- González Vilas, L.; Spyrakos, E.; Torres Palenzuela, J.M.; Pazos, Y. Support Vector Machine-based method for predicting Pseudo-nitzschia spp. blooms in coastal waters (Galician rias, NW Spain). Prog. Oceanogr. 2014, 124, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raine, R.; McDermott, G.; Silke, J.; Lyons, K.; Nolan, G.; Cusack, C. A simple short range model for the prediction of harmful algal events in the bays of southwestern Ireland. J. Mar. Syst. 2010, 83, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, R.P.; Litaker, R.W.; Lanerolle, L.; Tester, P.A. Hydrodynamic accumulation of Karenia off the west coast of Florida. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 189–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roiha, P.; Westerlund, A.; Nummelin, A.; Stipa, T. Ensemble forecasting of harmful algal blooms in the Baltic Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2010, 83, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bargu, S.; Hiatt, M.; Maiti, K.; Miller, P.; White, J.R. The Future of Cyanobacteria Toxicity in Estuaries Undergoing Pulsed Nutrient Inputs: A Case Study from Coastal Louisiana. Water 2023, 15, 3816. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213816
Bargu S, Hiatt M, Maiti K, Miller P, White JR. The Future of Cyanobacteria Toxicity in Estuaries Undergoing Pulsed Nutrient Inputs: A Case Study from Coastal Louisiana. Water. 2023; 15(21):3816. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213816
Chicago/Turabian StyleBargu, Sibel, Matthew Hiatt, Kanchan Maiti, Paul Miller, and John R. White. 2023. "The Future of Cyanobacteria Toxicity in Estuaries Undergoing Pulsed Nutrient Inputs: A Case Study from Coastal Louisiana" Water 15, no. 21: 3816. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213816
APA StyleBargu, S., Hiatt, M., Maiti, K., Miller, P., & White, J. R. (2023). The Future of Cyanobacteria Toxicity in Estuaries Undergoing Pulsed Nutrient Inputs: A Case Study from Coastal Louisiana. Water, 15(21), 3816. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213816







