Biological Invasions in Fresh Waters: Micropterus salmoides, an American Fish Conquering the World
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Ecological and Life-History Traits of M. salmoides
2.1. M. salmoides Traits in Native and Invaded Ecosystems
2.2. Traits Conferring Success on M. salmoides
3. Influences on Freshwater Biodiversity
3.1. Negative Associations with Native Fish Species: Predation and Competition
3.2. Non-Lethal Effects of Predation by Bass
3.3. Community-Wide Effects of M. salmoides
3.4. Factors Influencing Bass Predation Efficiency: Prey Naivety and Body Shape and the Predator–Prey Size Ratio
4. Influence of Environmental Variables on the Occurrence and Interactions of M. salmoides
4.1. Habitat Structural Complexity: The Effect of Vegetation and Coarse Woody Habitats
4.2. Effect of Turbidity on Predation by Sight
4.3. Anthropogenic Alteration of Freshwater Systems
4.4. The Influence of Climate Change
5. Socio-Economic Implications of Bass Introductions
6. Management Options
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ludsin, S.A.; Wolfe, A.D. Biological Invasion Theory: Darwin’s Contributions from The Origin of Species. BioScience 2001, 51, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polce, C.; Cardoso, A.C.; Deriu, I.; Gervasini, E.; Tsiamis, K.; Vigiak, O.; Zulian, G.; Maes, J. Invasive Alien Species of Policy Concerns Show Widespread Patterns of Invasion and Potential Pressure across European Ecosystems. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simberloff, D.; Martin, J.-L.; Genovesi, P.; Maris, V.; Wardle, D.A.; Aronson, J.; Courchamp, F.; Galil, B.; García-Berthou, E.; Pascal, M.; et al. Impacts of Biological Invasions: What’s What and the Way Forward. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernery, C.; Bellard, C.; Courchamp, F.; Brosse, S.; Gozlan, R.E.; Jarić, I.; Teletchea, F.; Leroy, B. Freshwater Fish Invasions: A Comprehensive Review. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2022, 53, 427–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubrock, P.; Bernery, C.; Cuthbert, R.; Liu, C.; Kourantidou, M.; Leroy, B.; Turbelin, A.; Kramer, A.; Verbrugge, L.; Diagne, C.; et al. What Is the Recorded Economic Cost of Alien Invasive Fishes Worldwide? Res. Sq. 2022, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozlan, R.E.; Britton, J.R.; Cowx, I.; Copp, G.H. Current Knowledge on Non-Native Freshwater Fish Introductions. J. Fish Biol. 2010, 76, 751–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, B.; Clavero, M.; Sánchez, M.I.; Vilà, M. Global Ecological Impacts of Invasive Species in Aquatic Ecosystems. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 22, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyl, O.L.F.; Schirrmann, M.K.; Hargrove, J.S.; Bodill, T.; Swartz, E.R. Invasion Status of Florida Bass Micropterus floridanus (Lesueur, 1822) in South Africa. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 42, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.; Runciman, B.; Pollard, S.; Grant, A. Biological Synopsis of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Can. Manuscr. Rep. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2009, 2884, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Page, L.M.; Burr, B.M. Field Guide to Freshwater Fishes: North America, North of Mexico (Peterson Field Guide Series), 2nd ed.; Houghton Mifflin Harcourt: Boston, MA, USA; New York, NY, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-0-547-24206-4. [Google Scholar]
- Robins, R.H.; Page, L.M.; Williams, J.D.; Randall, Z.S.; Sheehy, G.E. Fishes in the Freshwaters of Florida; University Press of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gelwick, F.P.; Gilliland, E.R.; Matthews, W.J. Introgression of the Florida Largemouth Bass Genome into Stream Populations of Northern Largemouth Bass in Oklahoma. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1995, 124, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratwicke, B.; Marshall, B.E. The Relationship between the Exotic Predators Micropterus salmoides and Serranochromis robustus and Native Stream Fishes in Zimbabwe. J. Fish Biol. 2001, 58, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamura, K. Performance as a Fish Predator of Largemouth Bass [Micropterus salmoides (Lacepède)] Invading Japanese Freshwaters: A Review. Ecol. Res. 2007, 22, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargrove, J.S.; Weyl, O.L.F.; Allen, M.S.; Deacon, N.R. Using Tournament Angler Data to Rapidly Assess the Invasion Status of Alien Sport Fishes (Micropterus spp.) in Southern Africa. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welcomme, R.L. A History of International Introductions of Inland Aquatic Species. ICES Mar. Sci. Symp. 1992, 194, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- CABI. Available online: https://www.cabi.org/ (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- Almeida, D.; Grossman, G.D. Regulated Small Rivers as ‘Nursery’ Areas for Invasive Largemouth Bass Micropterus salmoides in Iberian Waters. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2014, 24, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M.L.; Carlino, P.; Calizza, E.; Careddu, G.; Cicala, D.; Sporta Caputi, S.; Fiorentino, F.; Rossi, L. The Role of Alien Fish (the Centrarchid Micropterus salmoides) in Lake Food Webs Highlighted by Stable Isotope Analysis. Freshw. Biol. 2018, 63, 1130–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubrock, P.; Criado, A.; Monteoliva, A.; Monteoliva, J.; Santiago, T.; Inghilesi, A.; Tricarico, E. Control and Eradication Efforts of Aquatic Alien Fish Species in Lake Caicedo Yuso-Arreo. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2018, 9, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, M.; Motomura, Y. Feeding Habits of Largemouth Bass in a Non-Native Environment: The Case of a Small Lake with Bluegill in Japan. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1998, 52, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyl, O.L.F.; Hecht, T. A Successful Population of Largemouth Bass, Micropterus salmoides, in a Subtropical Lake in Mozambique. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1999, 54, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Frehse, F.A.; Hargrove, J.S.; Weyl, O.L.F.; Vitule, J.R.S. The Genetic Characteristics of Invasive Largemouth Bass in Southern Brazil. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2020, 36, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguy, L.; Long, J.M. Perceived Ecological Threats and Economic Benefits of Non-native Black Bass in the United States. Fisheries 2021, 46, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.M.; Seguy, L. Global Status of Non-Native Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides, Centrachidae) and Smallmouth Bass (Micropterus dolomieu, Centrarchidae): Disparate Views as Beloved Sportfish and Feared Invader. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2023, 31, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GISD Species Profile: Micropterus salmoides. Available online: http://www.iucngisd.org/gisd/species.php?sc=94 (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- Lowe, S.; Browne, M.; Boudjelas, S.; De Poorter, M. 100 of the World’s Worst Invasive Alien Species: A Selection from the Global Invasive Species Database. In Encyclopedia of Biological Invasions; Invasive Species Specialist Group: Auckland, New Zealand, 2000; pp. 1–11. ISBN 978-0-520-94843-3. [Google Scholar]
- Mayekiso, M.; Hecht, T. Conservation Status of the Anabantid Fish Sandelia bainsii in the Tyume River, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Wildl. Res.-24-Mon. Delayed Open Access 1988, 18, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Ellender, B.R.; Weyl, O.L.F.; Swartz, E.R. Invasion of a Headwater Stream by Non-Native Fishes in the Swartkops River System, South Africa. Afr. Zool. 2011, 46, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yi, S.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, S.; Fei, H. A Concise Review on Advancement of Micropterus salmoides Rhabdovirus (MSRV): Current Status and Challenges. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 30, 101551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.W.; Vitule, J.R.S. The Largemouth Bass Micropterus salmoides (Lacepède, 1802): Impacts of a Powerful Freshwater Fish Predator Outside of Its Native Range. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2019, 29, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubrock, P.J.; Bernery, C.; Cuthbert, R.N.; Liu, C.; Kourantidou, M.; Leroy, B.; Turbelin, A.J.; Kramer, A.M.; Verbrugge, L.N.H.; Diagne, C.; et al. Knowledge Gaps in Economic Costs of Invasive Alien Fish Worldwide. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, W.B.; Crossman, E.J. Freshwater Fishes of Canada. Fish. Res. Board Can. Bull. 1973, 184, 1–966. [Google Scholar]
- Budnik, R.R.; Steinhart, G.B.; Conroy, J.D.; Dillon, R.A.; Zweifel, R.D.; Ludsin, S.A. Effects of Hypoxia on Habitat Quality of Reservoir Largemouth Bass, Saugeye, and White Crappie. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2021, 150, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, F.N.; Ferreira, M.T. Influence of habitat structure on the fish prey consumption by largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides, in experimental tanks. Limnética 2006, 25, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, J.R.; Harper, D.M.; Oyugi, D.O. Is the Fast Growth of an Equatorial Micropterus salmoides Population Explained by High Water Temperature? Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2010, 19, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azami, K.; Takemoto, M.; Otsuka, Y.; Yamagishi, S.; Nakazawa, S. Meteorology and Species Composition of Plant Communities, Birds and Fishes before and after Initial Impoundment of Miharu Dam Reservoir, Japan. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 8, 81–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, M.-J.; Murphy, C.A.; García-Berthou, E. Temperature and Hydrologic Alteration Predict the Spread of Invasive Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giussani, G.; de Bernardi, R.; Ruffoni, T. Three Years of Experience in Biomanipulating a Small Eutrophic Lake: Lago Di Candia (Northern Italy). Hydrobiologia 1990, 200, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albright, M.F.; Harman, W.N.; Tibbits, W.T.; Gray, M.S.; Warner, D.M.; Hamway, R.J. Biomanipulation: A Classic Example in a Shallow Eutrophic Pond. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2004, 20, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuno, N.; Fujimoto, Y.; Shimada, T.; Shikano, S.; Kikuchi, E. Ontogenetic Dietary Shifts of Largemouth Bass Do Not Increase Trophic Position in a Shallow Eutrophic Lake in Japan. Ann. Limnol.-Int. J. Lim. 2016, 52, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baca, R.M.; Drenner, R.W. Do the Effects of Piscivorous Largemouth Bass Cascade to the Plankton? Hydrobiologia 1995, 316, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavero, M.; Hermoso, V.; Aparicio, E.; Godinho, F.N. Biodiversity in Heavily Modified Waterbodies: Native and Introduced Fish in Iberian Reservoirs. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 1190–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, D.; Almodóvar, A.; Nicola, G.G.; Elvira, B.; Grossman, G.D. Trophic Plasticity of Invasive Juvenile Largemouth Bass Micropterus salmoides in Iberian Streams. Fish. Res. 2012, 113, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, F.N.; Ferreira, M.T. Composition of Endemic Fish Assemblages in Relation to Exotic Species and River Regulation in a Temperate Stream. Biol. Invasions 2000, 2, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettoli, P.W.; Maceina, M.J.; Noble, R.L.; Betsill, R.K. Piscivory in Largemouth Bass as a Function of Aquatic Vegetation Abundance. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1992, 12, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahr, K.J.; Shoup, D.E. The Effects of Macrophyte Stem Density and Structural Complexity on Foraging Return of Invertivorous Juvenile Largemouth Bass. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2016, 36, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoda, H.; Mitsuo, Y. Variations in Piscivory of Invasive Largemouth Bass Micropterus salmoides Associated with Pond Environments. Limnology 2018, 19, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.C.O.; Ranåker, L.; Weinersmith, K.L.; Young, M.J.; Sih, A.; Conrad, J.L. Effects of Turbidity and an Invasive Waterweed on Predation by Introduced Largemouth Bass. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2014, 97, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.J.; Maceina, M.J. The Influence of Disparate Levels of Submersed Aquatic Vegetation on Largemouth Bass Population Characteristics in a Georgia Reservoir. J. Aquat. Plant Manag. 2002, 40, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka, H. Hypoxic Conditions Enhance Refuge Effect of Macrophyte Zone for Small Prey Fish from Piscivorous Predators. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2013, 20, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, J.F.; Stein, R.A. Predator-Prey Interaction between Largemouth Bass and Bluegills as Influenced by Simulated, Submersed Vegetation. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1982, 111, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, O. Optimal Foraging by Largemouth Bass in Structured Environments. Ecology 1984, 65, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.E.; Kaiser, H.; Weyl, O.L.F.; Dick, J.T.A. Habitat Simplification Increases the Impact of a Freshwater Invasive Fish. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2015, 98, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valley, R.D.; Bremigan, M.T. Effects of Macrophyte Bed Architecture on Largemouth Bass Foraging: Implications of Exotic Macrophyte Invasions. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2002, 131, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotceitas, V.; Colgan, P. Predator Foraging Success and Habitat Complexity: Quantitative Test of the Threshold Hypothesis. Oecologia 1989, 80, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Kitchell, J.F. The Trophic Cascade in Lakes; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996; ISBN 978-0-521-56684-1. [Google Scholar]
- Dibble, E.D.; Harrel, S.L. Largemouth Bass Diets in Two Aquatic Plant Communities. J. Aquat. Plant Manag. 1997, 35, 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- French, C.G.; Wahl, D.H. Influences of Dissolved Oxygen on Juvenile Largemouth Bass Foraging Behaviour. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2018, 27, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-K. Effects of Aquatic Macrophytes on Spatial Distribution and Feeding Habits of Exotic Fish Species Lepomis macrochirus and Micropterus salmoides in Shallow Reservoirs in South Korea. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, J.F.; Stein, R.A. Behavior of Fish Predators and Their Prey: Habitat Choice between Open Water and Dense Vegetation. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1989, 24, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sass, G.G.; Kitchell, J.F.; Carpenter, S.R.; Hrabik, T.R.; Marburg, A.E.; Turner, M.G. Fish Community and Food Web Responses to a Whole-lake Removal of Coarse Woody Habitat. Fisheries 2006, 31, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrenstorff, T.D.; Sass, G.G.; Helmus, M.R. The Influence of Littoral Zone Coarse Woody Habitat on Home Range Size, Spatial Distribution, and Feeding Ecology of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Hydrobiologia 2009, 623, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, J.J.; Sass, G.G. Largemouth Bass Nest Site Selection in Small, North Temperate Lakes Varying in Littoral Coarse Woody Habitat Abundances. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2011, 31, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaeta, J.W.; Sass, G.G.; Carpenter, S.R. Drought-Driven Lake Level Decline: Effects on Coarse Woody Habitat and Fishes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 71, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, Z.J.; Gaeta, J.W.; Carpenter, S.R. Coarse Woody Habitat, Lakeshore Residential Development, and Largemouth Bass Nesting Behavior. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2011, 31, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzoni, M.; Martin Dörr, A.J.; Erra, R.; Giovinazzo, G.; Mearelli, M.; Selvi, S. Growth and Reproduction of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides Lacépède, 1802) in Lake Trasimeno (Umbria, Italy). Fish. Res. 2002, 56, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.C.; Weyl, O.L.F. Age, Growth and Reproduction of Non-Native Largemouth Bass Micropterus salmoides (Lacépède, 1802) Populations in Two Temperate African Impoundments. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2017, 33, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.-M.; Oh, C.-W.; Lee, W.-O.; Na, J.-H. Population Biology of the Largemouth Bass, Micropterus salmoides from Goe-San Lake, Korea. J. Environ. Biol. 2013, 34, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beamish, C.A.; Booth, A.J.; Deacon, N. Age, Growth and Reproduction of Largemouth Bass, Micropterus salmoides, in Lake Manyame, Zimbabwe. Afr. Zool. 2005, 40, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, J.R.; Harper, D.M. Length–Weight Relationships of Fish Species in the Freshwater Rift Valley Lakes of Kenya. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2006, 22, 334–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, U.H.; Leal, M.E. Growth and Mortality of Black Bass, Micropterus salmoides (Pisces, Centrachidae; Lacapède, 1802) in a Reservoir in Southern Brazil. Braz. J. Biol. 2005, 65, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuno, N.; Chiba, Y.; Shindo, K.; Fujimoto, Y.; Shimada, T.; Shikano, S.; Kikuchi, E. Size-Dependent Ontogenetic Diet Shifts to Piscivory Documented from Stable Isotope Analyses in an Introduced Population of Largemouth Bass. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2012, 93, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinelli, A.; Scalici, M.; Gibertini, G. Diet and Reproduction of Largemouth Bass in a Recently Introduced Population, Lake Bracciano (Central Italy). Bull. Fr. Pêche Piscic. 2007, 385, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyle, P.B. Inland Fishes of California: Revised and Expanded; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-0-520-22754-5. [Google Scholar]
- Heidinger, R.C. Synopsis of Biological Data on the Largemouth Bass Micropterus salmoides (Lacepede) 1802; FAO Fisheries Synopses (FAO). no. 115; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Mulhollem, J.J.; Colombo, R.E.; Wahl, D.H. Effects of Heated Effluent on Midwestern US Lakes: Implications for Future Climate Change. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 78, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, K.C.; Cooke, S.J.; Suski, C.D.; Niezgoda, G.; Phelan, F.J.S.; Tinline, R.; Philipp, D.P. Assessment of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) Behaviour and Activity at Multiple Spatial and Temporal Scales Utilizing a Whole-Lake Telemetry Array. Hydrobiologia 2007, 582, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peat, T.B.; Gutowsky, L.F.G.; Doka, S.E.; Midwood, J.D.; Lapointe, N.W.R.; Hlevca, B.; Wells, M.G.; Portiss, R.; Cooke, S.J. Comparative Thermal Biology and Depth Distribution of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) and Northern Pike (Esox lucius) in an Urban Harbour of the Laurentian Great Lakes. Can. J. Zool. 2016, 94, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.; Kim, S.; An, K.-G. Distribution Pattern Prediction of an Invasive Alien Species Largemouth Bass Using a Maximum Entropy Model (MaxEnt) in the Korean Peninsula. J. Asia-Pac. Biodivers. 2018, 11, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosa, D.; Marr, S.M.; Wasserman, R.J.; Zengeya, T.A.; Weyl, O.L.F. An Evaluation of the Current Extent and Potential Spread of Black Bass Invasions in South Africa. Biol. Invasions 2019, 21, 1721–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, J.A.; Breck, J.E.; Bartell, S.M.; Kitchell, J.F. Evaluating the Constraints of Temperature, Activity and Consumption on Growth of Largemouth Bass. Environ. Biol. Fish. 1983, 9, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helser, T.E.; Lai, H.-L. A Bayesian Hierarchical Meta-Analysis of Fish Growth: With an Example for North American Largemouth Bass, Micropterus salmoides. Ecol. Model. 2004, 178, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. Search FishBase. Available online: https://www.fishbase.se/search.php (accessed on 9 April 2021).
- Bennett, G.W. The Growth of the Large Mouthed Black Bass, Huro salmoides (Lacépède), in the Waters of Wisconsin. Copeia 1937, 1937, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rypel, A.L. Climate–Growth Relationships for Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) across Three Southeastern USA States. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2009, 18, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchell, J.F. Food Web Management: A Case Study of Lake Mendota; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-1-4612-4410-3. [Google Scholar]
- Middaugh, C.R.; Foley, C.J.; Höök, T.O. Local and Lake-Scale Habitat Effects on Abundance, Lengths, and Diets of Age-0 Largemouth Bass and Bluegill in Indiana Temperate Lakes. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2013, 142, 1576–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, J.; Darling, J.A. Paradox Lost: Genetic Diversity and the Success of Aquatic Invasions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargrove, J.S.; Weyl, O.L.F.; Austin, J.D. Reconstructing the Introduction History of an Invasive Fish Predator in South Africa. Biol. Invasions 2017, 19, 2261–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, M.; Moyle, P.; Levine, R. Invasive Species Profiling? Exploring the Characteristics of Non-native Fishes across Invasion Stages in California. Freshw. Biol. 2004, 49, 646–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, F.; Elvira, B.; Collares-Pereira, M.J.; Moyle, P.B. Life-History Traits of Non-Native Fishes in Iberian Watersheds across Several Invasion Stages: A First Approach. Biol. Invasions 2008, 10, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowska, J.; Przybylski, M. Life-History Traits of Non-Native Freshwater Fish Invaders Differentiate Them from Natives in the Central European Bioregion. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2015, 25, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moor, I.J. Case Studies of the Invasion by Four Alien Fish Species (Cyprinus carpio, Micropterus salmoides, Oreochromis macrochir and O. mossambicus) of Freshwater Ecosystems in Southern Africa. Trans. R. Soc. S. Afr. 1996, 51, 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alofs, K.M.; Jackson, D.A. The Vulnerability of Species to Range Expansions by Predators Can Be Predicted Using Historical Species Associations and Body Size. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20151211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, D.M. Individual Variation in the Timing of Ontogenetic Niche Shifts in Largemouth Bass. Ecology 2003, 84, 1298–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, J.R.; Kitchell, J.F. Opportunistic Foraging by Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Am. Midl. Nat. 1987, 118, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzoni, M.; Corboli, M.; Dörr, A.J.M.; Giovinazzo, G.; Selvi, S.; Mearelli, M. Diets of Micropterus salmoides Lac. and Esox lucius l. in Lake Trasimeno (Umbria, Italy) and Their Diet Overlap. Bull. Fr. Pêche Piscic. 2002, 365–366, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassow, C.J.; Collier, A.; Hodgson, J.Y.S.; Buelo, C.D.; Hodgson, J.R. Filial Cannibalism by Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides): A Three-Decade Natural History Record from a Small Northern Temperate Lake. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2018, 33, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.C.; Hill, J.M.; Weyl, O.L.F. The Diet and Trophic Ecology of Non-Native Micropterus salmoides in Two South African Impoundments. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 44, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cathcart, C.N.; Dunker, K.J.; Quinn, T.P.; Sepulveda, A.J.; von Hippel, F.A.; Wizik, A.; Young, D.B.; Westley, P.A.H. Trophic Plasticity and the Invasion of a Renowned Piscivore: A Diet Synthesis of Northern Pike (Esox lucius) from the Native and Introduced Ranges in Alaska, U.S.A. Biol. Invasions 2019, 21, 1379–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abekura, K.; Hori, M.; Takemon, Y. Changes in Fish Community after Invasion and during Control of Alien Fish Populations in Mizoro-Ga-Ike, Kyoto City. Glob. Environ. Res. 2004, 8, 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.-H.; Paek, W.K.; An, K.-G. Exotic Species, Micropterus salmoides, as a Key Bioindicator Influencing the Reservoir Health and Fish Community Structure. J. Asia-Pac. Biodivers. 2016, 9, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volta, P.; Jeppesen, E.; Sala, P.; Galafassi, S.; Foglini, C.; Puzzi, C.; Winfield, I.J. Fish Assemblages in Deep Italian Subalpine Lakes: History and Present Status with an Emphasis on Non-Native Species. Hydrobiologia 2018, 824, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alofs, K.M.; Jackson, D.A.; Lester, N.P. Ontario Freshwater Fishes Demonstrate Differing Range-Boundary Shifts in a Warming Climate. Divers. Distrib. 2014, 20, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alofs, K.M.; Jackson, D.A. The Abiotic and Biotic Factors Limiting Establishment of Predatory Fishes at Their Expanding Northern Range Boundaries in Ontario, Canada. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 2227–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, L.M.; Phaneuf, D.J.; Abbott, J.K.; Fenichel, E.P. Per Trip Changes to the Economic Value of Ontario, Canada Anglers Fishing the Laurentian Great Lakes under Target Species Transitions. Hum. Dimens. Wildl. 2021, 26, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essington, T.E.; Hodgson, J.R.; Kitchell, J.F. Role of Satiation in the Functional Response of a Piscivore, Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2000, 57, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullerton, A.H.; Garvey, J.E.; Wright, R.A.; Stein, R.A. Overwinter Growth and Survival of Largemouth Bass: Interactions among Size, Food, Origin, and Winter Severity. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2000, 129, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornis, M.S.; Weidel, B.C.; Powers, S.M.; Diebel, M.W.; Cline, T.J.; Fox, J.M.; Kitchell, J.F. Fish Community Dynamics Following Dam Removal in a Fragmented Agricultural Stream. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 77, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embke, H.S.; Carpenter, S.R.; Isermann, D.A.; Coppola, G.; Beard, D.T., Jr.; Lynch, A.J.; Sass, G.G.; Feiner, Z.S.; Vander Zanden, M.J. Resisting Ecosystem Transformation through an Intensive Whole-Lake Fish Removal Experiment. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2022, 29, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, G.J.A.; Midway, S.R.; Wagner, T. Walleye Recruitment Success Is Less Resilient to Warming Water Temperatures in Lakes with Abundant Largemouth Bass Populations. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 75, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.; Sass, G.; Gaeta, J.; Hansen, G.; Isermann, D.; Lyons, J.; Jake, M.; Vander Zanden, J. Largemouth Bass Management in Wisconsin: Intraspecific and Interspecific Implications of Abundance Increases. In Black Bass Diversity: Multidisciplinary Science for Conservation; Tringali, M.D., Long, J.M., Birdsong, T.W., Allen, M.S., Eds.; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2015; pp. 193–206. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, C.J.; Isermann, D.A.; Whitlock, K.E.; Hansen, J.F. Assessing the Potential to Mitigate Climate-Related Expansion of Largemouth Bass Populations Using Angler Harvest. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 77, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoup, D.E.; Wahl, D.H. The Effects of Turbidity on Prey Selection by Piscivorous Largemouth Bass. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2009, 138, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dustin, D.L.; Vondracek, B. Nearshore Habitat and Fish Assemblages along a Gradient of Shoreline Development. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2017, 37, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olive, J.A.; Miranda, L.E.; Hubbard, W.D. Centrarchid Assemblages in Mississippi State-Operated Fishing Lakes. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2005, 25, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breeggemann, J.J.; Kaemingk, M.A.; DeBates, T.J.; Paukert, C.P.; Krause, J.R.; Letvin, A.P.; Stevens, T.M.; Willis, D.W.; Chipps, S.R. Potential Direct and Indirect Effects of Climate Change on a Shallow Natural Lake Fish Assemblage. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2016, 25, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenner, R.W.; Baca, R.M.; Gilroy, J.S.; Ernst, M.R.; Jensen, D.J.; Marshall, D.H. Community Responses to Piscivorous Largemouth Bass: A Biomanipulation Experiment. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2002, 18, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosher, B.T.; Newton, S.H.; Fine, M.L. The Spines of the Channel Catfish, Ictalurus punctatus, as an Anti-Predator Adaptation: An Experimental Study. Ethology 2006, 112, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoup, D.E.; Lane, W.D. Effects of Turbidity on Prey Selection and Foraging Return of Adult Largemouth Bass in Reservoirs. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2015, 35, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacheler, N.M.; Neal, J.W.; Noble, R.L. Diet Overlap between Native Bigmouth Sleepers (Gobiomorus dormitor) and Introduced Predatory Fishes in a Puerto Rico Reservoir. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2004, 13, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaBastille, A. Drastic Decline in Guatemala’s Giant Pied-Billed Grebe Population. Environ. Conserv. 1983, 10, 346–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoda, H.; Urano, T.; Ohira, M. Comparison of Food Habits between Native Amur Three-Lips (Opsariichthys uncirostris uncirostris) and Non-Native Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) in Lake Biwa, Japan. Ann. Limnol.-Int. J. Lim. 2015, 51, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Shindo, K.; Fujiwara, T.; Arita, K.; Saitoh, K.; Shimada, T. Success in Population Control of the Invasive Largemouth Bass Micropterus salmoides through Removal at Spawning Sites in a Japanese Shallow Lake. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2021, 12, 997–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, Y.; Yambe, H.; Takahashi, K.; Sato, S. Bile from Reproductively Mature Male Largemouth Bass Micropterus salmoides Attracts Conspecific Females and Offers a Practical Application to Control Populations. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2020, 11, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katano, O.; Nakamura, T.; Yamamoto, S. Prey Fish Selection by Far Eastern Catfish Silurus asotus and Largemouth Bass Micropterus salmoides. Fish. Sci. 2005, 71, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuki, H.; Awano, T.; Tsugeki, N.K.; Ishida, S.; Oda, H.; Makino, W.; Urabe, J. Historical Changes in the Ecosystem Condition of a Small Mountain Lake over the Past 60 Years as Revealed by Plankton Remains and Daphnia Ephippial Carapaces Stored in Lake Sediments. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, M.; Careddu, G.; Calizza, E.; Sporta Caputi, S.; Argenti, E.; Rossi, D.; Rossi, L.; Costantini, M.L. When Climate Change and Overexploitation Meet in Volcanic Lakes: The Lesson from Lake Bracciano, Rome’s Strategic Reservoir. Water 2023, 15, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calizza, E.; Rossi, L.; Careddu, G.; Sporta Caputi, S.; Costantini, M.L. A Novel Approach to Quantifying Trophic Interaction Strengths and Impact of Invasive Species in Food Webs. Biol. Invasions 2021, 23, 2093–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghetti, L.; Lorenzoni, M.; Carosi, A.; Natali, M. L’ittiofauna Alloctona del Lago Trasimeno: Impatti Ecologici e Ricadute Economiche Sull’attività di Pesca. 2018; 26p. Available online: https://www.isprambiente.gov.it/files2018/eventi/evento-conclusivo-progetto-life-u-savereds/GHETTI_Luciasavereds.pdf (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- Jorge, A.; Machado, M.G.; Alexandre, C.M.; da Silva, M.G.; Almeida, P.R.; Lança, M.J. Proximate Composition, Nutritional Lipid Quality, and Health Indices of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides Lacépède, 1802) from Several Mediterranean Reservoirs. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2022, 31, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambright, K.D. Experimental Analysis of Prey Selection by Largemouth Bass: Role of Predator Mouth Width and Prey Body Depth. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1991, 120, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowlin, W.H.; Drenner, R.W.; Guckenberger, K.R.; Lauden, M.A.; Alonso, G.T.; Fennell, J.E.; Smith, J.L. Gape Limitation, Prey Size Refuges and the Top–down Impacts of Piscivorous Largemouth Bass in Shallow Pond Ecosystems. Hydrobiologia 2006, 563, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maezono, Y.; Kobayashi, R.; Kusahara, M.; Miyashita, T. Direct and Indirect Effects of Exotic Bass and Bluegill on Exotic and Native Organisms in Farm Ponds. Ecol. Appl. 2005, 15, 638–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsumeda, T.; Takamura, N.; Nakagawa, M.; Kadono, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Mitsuhashi, H. Environmental and Biotic Characteristics to Discriminate Farm Ponds with and without Exotic Largemouth Bass and Bluegill in Western Japan. Limnology 2015, 16, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoda, H.; Mitsuo, Y.; Ohira, M.; Doi, M.; Senga, Y. Change of Fish Fauna in Ponds after Eradication of Invasive Piscivorous Largemouth Bass, Micropterus salmoides, in North-Eastern Japan. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2010, 20, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoda, H.; Mitsuo, Y.; Ohira, M.; Doi, M.; Senga, Y. Relationship between the Impact of Invasive Largemouth Bass and Environmental Conditions in Ponds. Res. Rep. Res. Educ. Cent. Inlandwater Environ. Shinshu Univ. 2010, 6, 133–141. [Google Scholar]
- Tsunoda, H.; Mitsuo, Y. Multiple Effects of Exotic Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) and Environmental Factors on Species Richness and Composition of Pond-Dwelling Fishes. Aquat. Living Resour. 2012, 25, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonekura, R.; Kita, M.; Yuma, M. Species Diversity in Native Fish Community in Japan: Comparison between Non-Invaded and Invaded Ponds by Exotic Fish. Ichthyol. Res. 2004, 2, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, M.; Piazzini, S.; Saveri, C. The Response of Amphibian Communities to Fish and Habitat Features in Mediterranean Permanent Ponds. Biologia 2014, 69, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, J.M.; Motta, P.J. Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) Switch Feeding Modalities in Response to Sensory Deprivation. Zoology 2012, 115, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, M.E.; Matthews, W.J. Algae-Grazing Minnows (Campostoma anomalum), Piscivorous Bass (Micropterus spp.), and the Distribution of Attached Algae in a Small Prairie-Margin Stream. Oecologia 1983, 60, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zweifel, R.D.; Hayward, R.S.; Rabeni, C.F. Bioenergetics Insight into Black Bass Distribution Shifts in Ozark Border Region Streams. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1999, 19, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saylor, R.K.; Lapointe, N.W.R.; Angermeier, P.L. Diet of Non-Native Northern Snakehead (Channa argus) Compared to Three Co-Occurring Predators in the Lower Potomac River, USA. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2012, 21, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenison, E.K.; Weldy, P.Y.; Williams, R.N. There Must Be Something in the Water: Assessing the Behavioral Responses of Rusty Crayfish (Orconectes rusticus) to Fish and Amphibian Predator Kairomones. J. Ethol. 2018, 36, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, J.M.; Weyl, O.L.F.; Esler, K.J.; Paxton, B.R.; Impson, N.D.; Dallas, H.F. Temperature Mediates the Impact of Non-Native Rainbow Trout on Native Freshwater Fishes in South Africa’s Cape Fold Ecoregion. Biol. Invasions 2018, 20, 2927–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, B.M.; Impson, D.; Rall, J. Present Status and Historical Changes in the Fish Fauna of the Berg River, South Africa. Trans. R. Soc. S. Afr. 2009, 64, 142–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Walt, J.A.; Weyl, O.L.F.; Woodford, D.J.; Radloff, F.G.T. Spatial Extent and Consequences of Black Bass (Micropterus Spp.) Invasion in a Cape Floristic Region River Basin. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2016, 26, 736–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Shen, L.; Zhou, Q.; Shao, J.; Xu, Q.Q.; Gorfine, H.; Zhang, H. Increasing Invasion Risk from the Northward Expansion of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) in China under Multiple Influences. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2023, 21, 835–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, T.; Miura, Y.; Krueger, D.; Sugiura, S. Utilizing Stomach Content and Faecal DNA Analysis Techniques to Assess the Feeding Behaviour of Largemouth Bass Micropterus salmoides and Bluegill Lepomis macrochirus. J. Fish Biol. 2014, 84, 1271–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.; Lee, C.; Takizawa, Y.; Chikaraishi, Y.; Oh, H.; Chang, K.; Jang, M.; Kim, H.; Lee, K.; Shin, K. Trophic Response to Ecological Conditions of Habitats: Evidence from Trophic Variability of Freshwater Fish. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 7250–7260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-K.; Kim, J.-C.; Lee, H.-J.; Kwon, H.-J.; Yun, J.-H. Microhabitat Characteristics Determine Fish Community Structure in a Small Stream (Yudeung Stream, South Korea). Proc. Natl. Inst. Ecol. Repub. Korea 2021, 2, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.-H.; Joo, G.-J.; Lucas, M.C. Diet of Introduced Largemouth Bass in Korean Rivers and Potential Interactions with Native Fishes. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2006, 15, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Z.; Shim, T.; Ki, S.J.; An, K.-G.; Jung, J. Prediction of Three-Dimensional Shift in the Distribution of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) under Climate Change in South Korea. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.; Jeppesen, E.; Ventura, M.; Buchaca, T.; Gim, J.-S.; Yoon, J.-D.; Kim, D.-H.; Joo, G.-J. Responses of Fish Assemblage Structure to Large-Scale Weir Construction in Riverine Ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 1334–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orrù, F.; Deiana, A.M.; Cau, A. Introduction and Distribution of Alien Freshwater Fishes on the Island of Sardinia (Italy): An Assessment on the Basis of Existing Data Sources: Alien Freshwater Fishes in Sardinia. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2010, 26, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Garrido, F.; Clavero, M.; Prenda, J. Jarabugo (Anaecypris hispanica) and freshwater blenny (Salaria fluviatilis): Habitat preferences and relationship with exotic fish species in the middle Guadiana basin. Limnética 2009, 28, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, F.N.; Ferreira, M.T.; Cortes, R.V. Composition and Spatial Organization of Fish Assemblages in the Lower Guadiana Basin, Southern Iberia. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 1997, 6, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaraz, C.; Carmona-Catot, G.; Risueño, P.; Perea, S.; Pérez, C.; Doadrio, I.; Aparicio, E. Assessing Population Status of Parachondrostoma arrigonis (Steindachner, 1866), Threats and Conservation Perspectives. Environ. Biol Fish 2015, 98, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilhéu, M.; da Silva, J.; Morais, M.; Matono, P.; Bernardo, J.M. Types of Dry-Season Stream Pools: Environmental Drivers and Fish Assemblages. Inland Waters 2020, 10, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.P.L.; Takemoto, R.M.; Vitule, J.R.S. Metazoan Parasites of Micropterus salmoides (Lacépède 1802) (Perciformes, Centrarchidae): A Review with Evidences of Spillover and Spillback. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sass, G.G.; Gille, C.M.; Hinke, J.T.; Kitchell, J.F. Whole-Lake Influences of Littoral Structural Complexity and Prey Body Morphology on Fish Predator–Prey Interactions. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2006, 15, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, L.A.V.; Ribeiro, V.M.; Freitas, M.O.; Kaufman, L.; Padial, A.A.; Vitule, J.R.S. Benthification, Biotic Homogenization behind the Trophic Downgrading in Altered Ecosystems. Ecosphere 2019, 10, e02757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.E.; Dick, J.T.A.; Weyl, O.L.F.; Robinson, T.B.; Richardson, D.M. Existing and Emerging High Impact Invasive Species Are Characterized by Higher Functional Responses than Natives. Biol. Lett. 2014, 10, 20130946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fine, M.L.; Mayo, M.S.; Newton, S.H.; Sismour, E.N. Largemouth Bass Predators Reduce Growth, Feeding and Movement in Juvenile Channel Catfish. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2011, 20, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, E.E.; Gilliam, J.F.; Hall, D.J.; Mittelbach, G.G. An Experimental Test of the Effects of Predation Risk on Habitat Use in Fish. Ecology 1983, 64, 1540–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, T.C.; Kelley, R.E.; Moore, P.A. Feeding in Fear: Indirect Effects of Predatory Fish on Macrophyte Communities Mediated by Altered Crayfish Foraging Behaviour. Freshw. Biol. 2018, 63, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, M.P.; Wahl, D.H. Foraging Modes of Predators and Behaviors of Prey Determine the Outcome of Multiple Predator Interactions. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2011, 140, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanLandeghem, M.M.; Carey, M.P.; Wahl, D.H. Turbidity-Induced Changes in Emergent Effects of Multiple Predators with Different Foraging Strategies. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2011, 20, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Cole, J.J.; Pace, M.L.; Batt, R.; Brock, W.A.; Cline, T.; Coloso, J.; Hodgson, J.R.; Kitchell, J.F.; Seekell, D.A.; et al. Early Warnings of Regime Shifts: A Whole-Ecosystem Experiment. Science 2011, 332, 1079–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanMiddlesworth, T.D.; McClelland, N.N.; Sass, G.G.; Casper, A.F.; Spier, T.W.; Lemke, M.J. Fish Community Succession and Biomanipulation to Control Two Common Aquatic Ecosystem Stressors during a Large-Scale Floodplain Lake Restoration. Hydrobiologia 2017, 804, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sih, A.; Bolnick, D.I.; Luttbeg, B.; Orrock, J.L.; Peacor, S.D.; Pintor, L.M.; Preisser, E.; Rehage, J.S.; Vonesh, J.R. Predator–Prey Naïveté, Antipredator Behavior, and the Ecology of Predator Invasions. Oikos 2010, 119, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carthey, A.J.R.; Blumstein, D.T. Predicting Predator Recognition in a Changing World. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2018, 33, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumstein, D.T.; Letnic, M.; Moseby, K.E. In Situ Predator Conditioning of Naive Prey Prior to Reintroduction. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20180058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steindler, L.A.; Blumstein, D.T.; West, R.; Moseby, K.E.; Letnic, M. Exposure to a Novel Predator Induces Visual Predator Recognition by Naïve Prey. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2020, 74, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.G.; Lima, S.L. Naiveté and an Aquatic–Terrestrial Dichotomy in the Effects of Introduced Predators. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2006, 21, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calizza, E.; Rossi, L.; Costantini, M.L. Predators and Resources Influence Phosphorus Transfer along an Invertebrate Food Web through Changes in Prey Behaviour. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, P. Effect of Body Form and Response Threshold on the Vulnerability of Four Species of Teleost Prey Attacked by Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1986, 43, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sismour, E.N.; Nellis, S.C.; Newton, S.H.; Mays, D.; Fine, M.L. An Experimental Study of Consumption of Channel Catfish Ictalurus punctatus by Largemouth Bass Micropterus salmoides When Alternative Prey Are Available. Cope 2013, 2013, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, S.A.; Friedman, S.T.; Wainwright, P.C. How Predation Shaped Fish: The Impact of Fin Spines on Body Form Evolution across Teleosts. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20151428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyle, J.A.; Keast, A. The Effect of Prey Morphology and Size on Handling Time in a Piscivore, the Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Can. J. Zool. 1987, 65, 1972–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katano, O.; Yamamoto, S.; Nakamura, T. Predation of Japanese Dace, Tribolodon hakonensis, by Largemouth Bass, Micropterus salmoides, in Experimental Aquaria. Ichthyol. Res. 2002, 4, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaeta, J.W.; Ahrenstorff, T.D.; Diana, J.S.; Fetzer, W.W.; Jones, T.S.; Lawson, Z.J.; McInerny, M.C.; Jr, V.J.S.; Zanden, M.J.V. Go Big or … Don’t? A Field-Based Diet Evaluation of Freshwater Piscivore and Prey Fish Size Relationships. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, J.E.; Stein, R.A.; Thomas, H.M. Assessing How Fish Predation and Interspecific Prey Competition Influence a Crayfish Assemblage. Ecology 1994, 75, 532–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huenemann, T.W.; Dibble, E.D.; Fleming, J.P. Influence of Turbidity on the Foraging of Largemouth Bass. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2012, 141, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, J.; Corcoran, J. Lateral Line Stimuli Can Override Vision to Determine Sunfish Strike Trajectory. J. Exp. Biol. 1993, 176, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didham, R.K.; Tylianakis, J.M.; Gemmell, N.J.; Rand, T.A.; Ewers, R.M. Interactive Effects of Habitat Modification and Species Invasion on Native Species Decline. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellender, B.; Weyl, O. A Review of Current Knowledge, Risk and Ecological Impacts Associated with Non-Native Freshwater Fish Introductions in South Africa. AI 2014, 9, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Fukushima, M.; Kameyama, S.; Fukushima, T.; Matsushita, B. How Do Dams Affect Freshwater Fish Distributions in Japan? Statistical Analysis of Native and Nonnative Species with Various Life Histories. Ecol. Res 2008, 23, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbold, B.; Moyle, P.B. Introduced Species and Vacant Niches. Am. Nat. 1986, 128, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nentwig, W. Biological Invasions: Why It Matters. In Biological Invasions; Nentwig, W., Ed.; Ecological Studies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 1–6. ISBN 978-3-540-36920-2. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, P.T.; Olden, J.D.; Vander Zanden, M.J. Dam Invaders: Impoundments Facilitate Biological Invasions into Freshwaters. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, L.; Bettoli, P.W. Largemouth Bass Natural History. In Largemouth Bass Aquaculture; 5M Publishing Ltd.: Sheffield, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-1-78918-086-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Navarro, A.; Gillingham, P.K.; Britton, J.R. Predicting Shifts in the Climate Space of Freshwater Fishes in Great Britain Due to Climate Change. Biol. Conserv. 2016, 203, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Meerhoff, M.; Holmgren, K.; González-Bergonzoni, I.; Teixeira-de Mello, F.; Declerck, S.A.J.; De Meester, L.; Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Bjerring, R.; et al. Impacts of Climate Warming on Lake Fish Community Structure and Potential Effects on Ecosystem Function. Hydrobiologia 2010, 646, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouizgane, A.; Farid, S.; Majdoubi, F.Z.; Droussi, M.; Guerriero, G.; Hasnaoui, M. Assessment of Climate Change Effects on Predation Activity and Growth of Largemouth Bass, Micropterus salmoides (Lacepede, 1802) by Water Temperature Variations. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2018, 30, 515–522. [Google Scholar]
- Deslauriers, D.; Chipps, S.R.; Breck, J.E.; Rice, J.A.; Madenjian, C.P. Fish Bioenergetics 4.0: An R-Based Modeling Application. Fisheries 2017, 42, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höök, T.O.; Foley, C.J.; Collingsworth, P.; Dorworth, L.; Fisher, B.; Hoverman, J.T.; LaRue, E.; Pyron, M.; Tank, J. An Assessment of the Potential Impacts of Climate Change on Freshwater Habitats and Biota of Indiana, USA. Clim. Change 2020, 163, 1897–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvira, B.; Almodóvar, A. Freshwater Fish Introductions in Spain: Facts and Figures at the Beginning of the 21st Century. J. Fish Biol. 2001, 59, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.J.; Hunt, K.M.; Ditton, R.B. Estimating the Economic Impacts of a Trophy Largemouth Bass Fishery: Issues and Applications. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2003, 23, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellender, B.R.; Woodford, D.J.; Weyl, O.L.F.; Cowx, I.G. Managing Conflicts Arising from Fisheries Enhancements Based on Non-Native Fishes in Southern Africa. J. Fish Biol. 2014, 85, 1890–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yang, H.; Xu, Z.; Li, X.; Leng, X. The Comparison of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) Fed Trash Fish and Formula Feeds: Growth, Flesh Quality and Metabolomics. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 966248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Deng, H.; Xu, Q.; Luo, K.; Zhou, J.; Gao, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, X. Effects of Tea Tree Essential Oil Supplementation in Low Fish Meal Diet on Growth, Lipid Metabolism, Anti-Oxidant Capacity and Immunity of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquac. Rep. 2022, 27, 101380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, G.L.; Sakmar, J.; Nicholls, A.; Litvak, M.K.; Hess, H.N.; Bruce, T.J.; Montague, H.R.; Kelly, A.M.; Roy, L.A.; Bernal, M.A.; et al. Effects of Temperature and Subspecies during Critical Early Life History Stages of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquaculture 2023, 570, 739350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, L.; Costantini, M.L.; Carlino, P.; di Lascio, A.; Rossi, D. Autochthonous and Allochthonous Plant Contributions to Coastal Benthic Detritus Deposits: A Dual-Stable Isotope Study in a Volcanic Lake. Aquat. Sci. 2010, 72, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, A.; Bronk, C.C.; Larson, B.; Taylor, S. The Impact of Predation Stress by Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) on the Growth and Development of Leopard Frog Tadpoles (Rana sphenocephala). J. Freshw. Ecol. 2008, 23, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Careddu, G.; Carlini, N.; Romano, A.; Rossi, L.; Calizza, E.; Sporta Caputi, S.; Costantini, M.L. Diet Composition of the Italian Crested Newt (Triturus carnifex) in Structurally Different Artificial Ponds Based on Stomach Contents and Stable Isotope Analyses. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2020, 30, 1505–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahel, F.J. Managing Freshwater Fish in a Changing Climate: Resist, Accept or Direct. Fisheries 2022, 47, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, A.J.; Rahel, F.J.; Limpinsel, D.; Sethi, S.A.; Engman, A.C.; Lawrence, D.J.; Mills, K.E.; Morrison, W.; Peterson, J.O.; Porath, M.T. Ecological and Social Strategies for Managing Fisheries Using the Resist-Accept-Direct (RAD) Framework. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2022, 29, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, J.C.; Haden, G.A.; O’Neill, M.; Pace, C. Effects of Flow Restoration and Exotic Species Removal on Recovery of Native Fish: Lessons from a Dam Decommissioning. Restor. Ecol. 2010, 18, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feiner, Z.S.; Shultz, A.D.; Sass, G.G.; Trudeau, A.; Mitro, M.G.; Dassow, C.J.; Latzka, A.W.; Isermann, D.A.; Maitland, B.M.; Homola, J.J.; et al. Resist-Accept-Direct (RAD) Considerations for Climate Change Adaptation in Fisheries: The Wisconsin Experience. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2022, 29, 346–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolding, J.; Van Zwieten, P. Sustainable Fishing of Inland Waters. J. Limnol. 2014, 73, 132–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutter, D.A.H.; Suski, C.D.; Philipp, D.P.; Klefoth, T.; Wahl, D.H.; Kersten, P.; Cooke, S.J.; Arlinghaus, R. Recreational Fishing Selectively Captures Individuals with the Highest Fitness Potential. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20960–20965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katano, O.; Sakano, H. A Fishing Method Using Live Bait and Its Effectiveness for the Eradication of Largemouth Bass, Micropterus salmoides. Jpn. J. Conserv. Ecol. 2010, 15, 183–191. [Google Scholar]
- Thresher, R.E.; Smith, R.; Cutajar, J. Optimizing the Impacts of an Invasive Species on the Threatened Endemic Biota of a Remote RAMSAR Site: Tilapia (Oreochromis iloticus) in Lake Kutubu, Papua New Guinea. Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 2661–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Ren, A.; Yu, L.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. An Environmental Impact Assessment of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) Aquaculture in Hangzhou, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shultz, A.; Luehring, M.; Ray, A.; Rose, J.D.; Croll, R.; Gilbert, J.; Price, M.; Graveen, J.; Chapman, L. Case Study: Applying the Resist–Accept–Direct Framework to an Ojibwe Tribe’s Relationship with the Natural World. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2022, 29, 392–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banha, F.; Diniz, A.; Anastácio, P.M. The Role of Anglers’ Perceptions and Habits in Biological Invasions: Perspectives from the Iberian Peninsula. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2017, 27, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
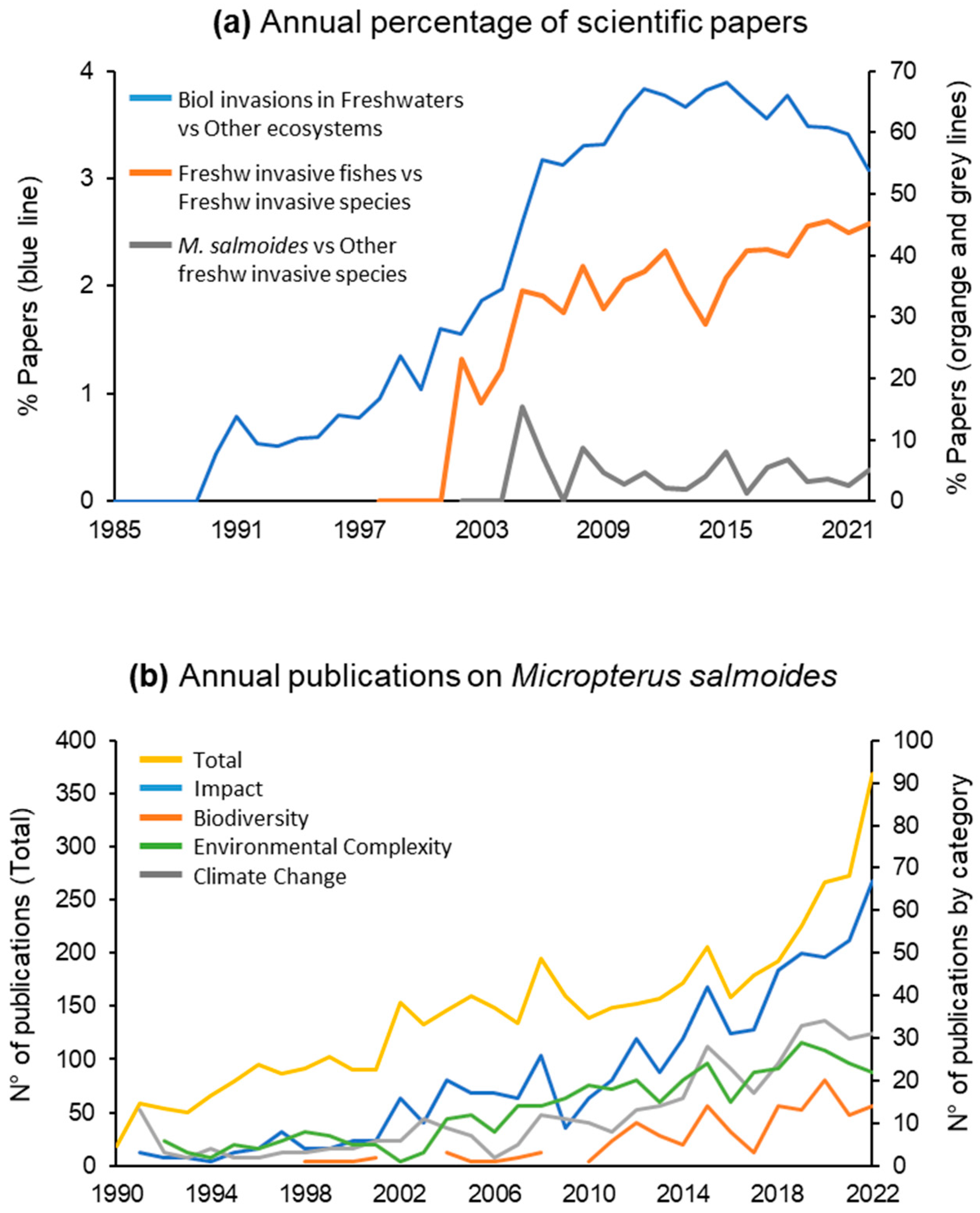

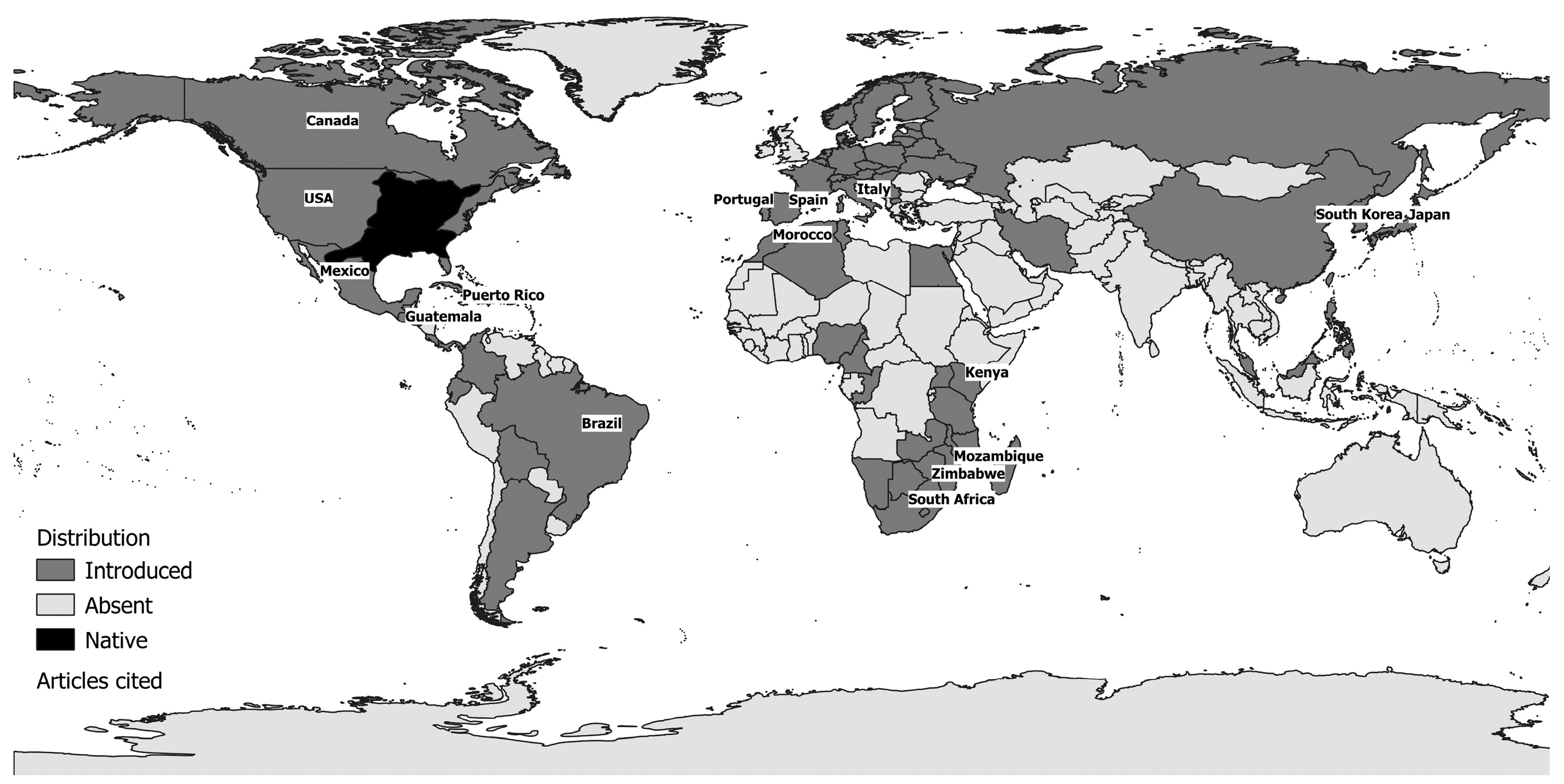
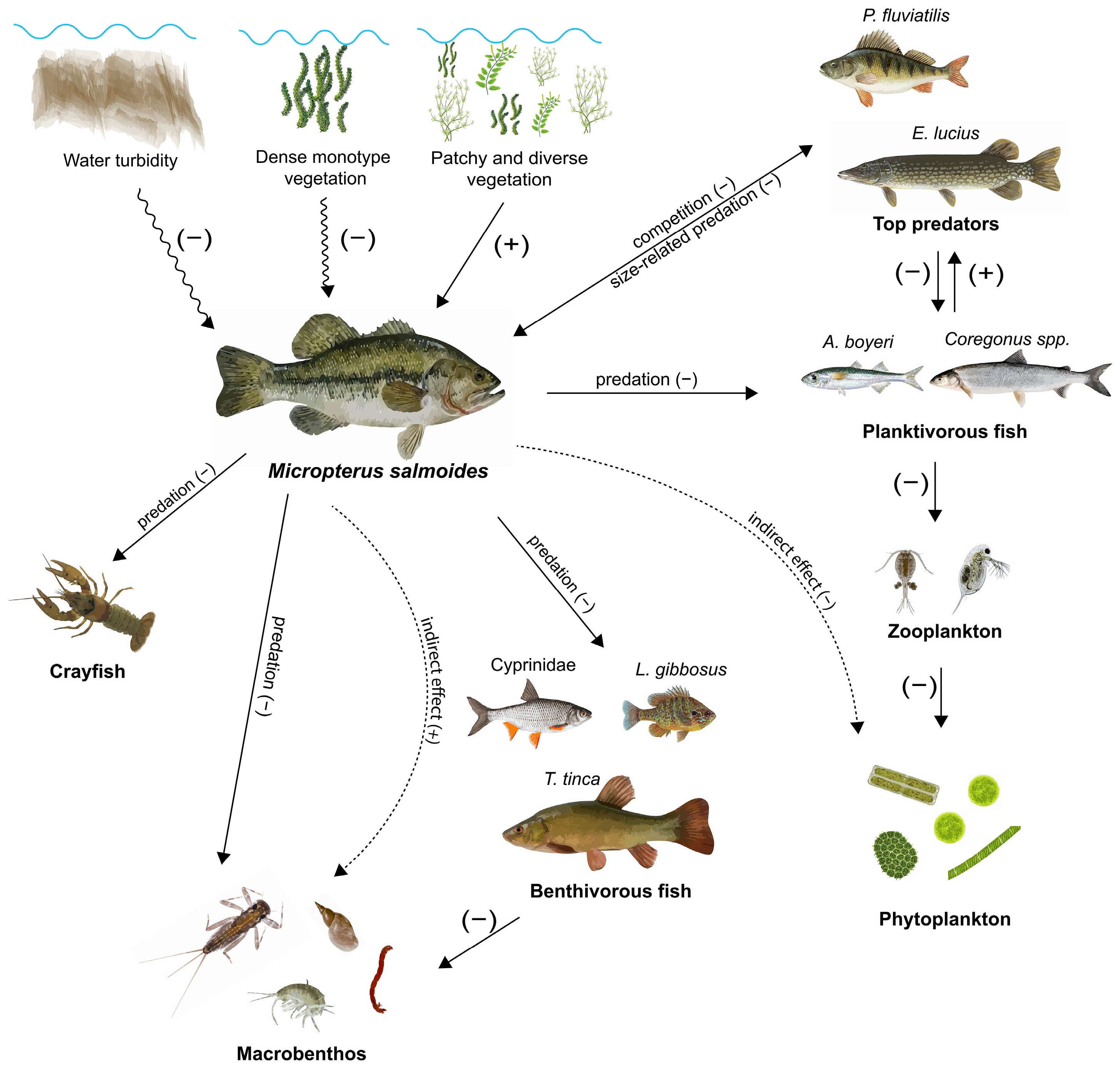
| Characteristics | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific name | Micropterus salmoides salmoides (Lacépède 1802) |
| Common names | Largemouth bass, Northern largemouth bass, Black bass |
| Native range | North America (St. Lawrence Lowlands, Great Lakes, Mississippi River basin, Quebec to Minnesota, South Carolina, Florida, part of New Mexico) |
| Non-native range | >50 countries around the world |
| Habitat | Predominantly warm [33,34,35,36,37,38], eutrophic [21,39,40,41,42], and lentic [9,37,43,44,45] waters. Submerged plants [9,19,21,33,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61], woody debris, or underwater structures [48,62,63,64,65,66]. |
| Age of sexual maturity | 3–5 y in Canada [33], 2–3 y in Italy [67], 1.3–2.3 y in South Africa [68] 2.0–2.4 y [69], 1 y in Zimbabwe [70], 0.9 y in Mozambique [22]. |
| Maximum life span | 15 y in Canada [33], 14 y in South Africa [68], 9 y in Zimbabwe [70], 8 y in South Korea [69], 7 y in Italy [67], 5 y in Mozambique [22]. |
| Mean length (min–max) * | 38.4 cm (10.2–54.4) in Canada [33]; NR (6.1–46.5) in Kenya [71]; NR (2.7–59.5) in South Africa [68]; 32.5 cm (22.0–53.7) in Zimbabwe [70]; 24.4 cm (10.0–47.8) in South Korea [69]; NR (21.0–46.6) in Brazil [72]; NR (up to 43.0 cm) in Japan [73]; 25.0 cm (13.8–42.9) in Italy [19,74]. |
| Micropterus salmoides Environments from the Cited Literature |
|---|
| Lakes and reservoirs |
| North America: Lake Opinicon-St. Lawrence [33,56], Ottawa system, Lake Simcoe-Great Lakes system [33], Ontario [33,95,105,106], Laurentian Great Lakes [79,107], Wisconsin (Paul Lake, Peter Lake [96,97,108], West Long Lake, Tuesday Lake [108], Trilby Lake [109], Lake Mason [110], McDermott and Sandy Beach [111], Little Rock Lake [62,63,64,65], Camp Lake [63], Lake Mendota [87], Bay Lake, Indian Lake, Alequash Lake, Little John Lake, Brandy Lake, Johnson Lake [66] and many others: [85,112,113,114]), Indiana (numerous lakes [88]), South Carolina (Par Pond [82]), Illinois (natural lakes: Forbes Lake, Lake Shelbyville, Lake Paradise, Pierce Lake, Lake Mingo, Lake Charleston; power plant cooling lakes: Clinton Lake, Newton Lake, Lake Coffeen [77] and others [115]), Michigan (Paul Lake [99], Big Crooked Lake and Camp Lake [55]), Minnesota [116], Mississippi [117], Nebraska (West Long Lake [118]), Texas (Balancing reservoir [42,119], Lake Conroe [46]), Virginia (Lake Chesdin and Lake Charles [120]), Ohio (Acton Lake, Burr Oak Lake, Pleasant Hill Lake [34], Knox Lake [109] and Ross Lake [52]), Oklahoma (Boomer Lake, Sooner Lake and Guthrie Lake [121], as well as lakes near Stillwater [47] and several reservoirs [12]), Puerto Rico (Carite Reservoir [122]) Central and South America: Guatemala (Lake Atitlán [123]), Brazil (Passauna, Piraquara, Capivari and Vossoroca reservoirs [23]). Africa: Kenya (Lake Naivasha [36,71], Lake Baringo [71]), Mozambique (Lake Chicamba [22]), and Zimbabwe (Lake Manyame [70]). Asia: Japan (Lake Biwa [51,124], Lake Izunuma [41,73], Lake Izunuma-Uchinuma [125,126], Lake Kawahara Oike [21], Lake Kizaki [127], Lake Hataya Ohnuma [128]), Miharu Dam Reservoir [37]), South Korea (Goe-San Lake [69], Masan, Gucheon and Yeongdeok reservoirs [103], and Nakdong River basin reservoirs [60]). Europe: Italy (Lake Bracciano [19,74,129,130], Lake Candia [39], Lake Trasimeno [67,98,131], Lake Mergozzo, Lake Maggiore, Lake Iseo, Lake Idro, Lake Garda [104]); and Spain and Portugal (several reservoirs [38,43], including Póvoa e Meadas, Monte Novo and Morgavel [132]). |
| Ponds |
| North America: (Moe Pond [40] and other ponds [133] in New York State, the Eagle Mountain Fish Hatchery [134] and U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Aquatic Ecosystem Research Facility [58] in Texas, and ponds near Stillwater in Oklahoma [47]. Asia: Japan (farm ponds in Saitama Prefecture [135], farm ponds in Hyogo Prefecture [136], farm ponds in Iwate Prefecture [48,124,137,138,139], ponds in Shiga Prefecture [140], and Mizoro-ga-ike Pond in Kyoto [102]. Europe: Italy (several permanent ponds in Cornocchia and Montagnola senese, Tuscany [141]). |
| Rivers |
| North America: California (Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta [49]), Florida (Hillsborough River [142]), Georgia (Chattahoochee River [50]), Oklahoma (Brier Creek [143], Maries River [144]), Missouri (Loose Creek [144]), Virginia and Maryland (Lower Potomac River [145]), Indiana (Blue River [146]), and Wisconsin (Big Spring Creek [110]). Africa: South Africa (Assegaaibos River, Amandel River [147], Berg River [147,148], Tyume River [28], Kubusi River [100]), Zimbabwe (Manyame River and other streams around Harare [13]), Blindekloof stream in the Swartkops River system [29], Olifants–Doorn River basin [149], and several other catchment areas [94]. Asia: China (Songhua-Liaohe Rivers, Haihe River, Huaihe River, Yellow River, Yangtze River, Pearl River, the Southeast, Southwest and Continental Basins [150]), Japan (Ezura River [151]), South Korea (various large South Korean rivers and their tributaries and small streams including Geum River [80,152,153,154,155], Han River [80,152,154,155], Nakdong River [60,80,152,154,155,156], and Yeongsan River [80,152,155]). Europe: Italy (several rivers in Sardinia [157]), Spain and Portugal (Bullaque River [44], River Jándula [18], Guadiana basin [35,158,159], the Raia tributary of the River Sorraia [45], Júcar River basin [160], and Degebe River basin [161]). |
| Brackish waters |
| North America: California [75]. Europe: Spain (Lake Caicedo Yuso-Arreo [20]). |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costantini, M.L.; Kabala, J.P.; Sporta Caputi, S.; Ventura, M.; Calizza, E.; Careddu, G.; Rossi, L. Biological Invasions in Fresh Waters: Micropterus salmoides, an American Fish Conquering the World. Water 2023, 15, 3796. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213796
Costantini ML, Kabala JP, Sporta Caputi S, Ventura M, Calizza E, Careddu G, Rossi L. Biological Invasions in Fresh Waters: Micropterus salmoides, an American Fish Conquering the World. Water. 2023; 15(21):3796. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213796
Chicago/Turabian StyleCostantini, Maria Letizia, Jerzy Piotr Kabala, Simona Sporta Caputi, Matteo Ventura, Edoardo Calizza, Giulio Careddu, and Loreto Rossi. 2023. "Biological Invasions in Fresh Waters: Micropterus salmoides, an American Fish Conquering the World" Water 15, no. 21: 3796. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213796





