Application of Gated Recurrent Unit Neural Network for Flood Extraction from Synthetic Aperture Radar Time Series
Abstract
:1. Introduction
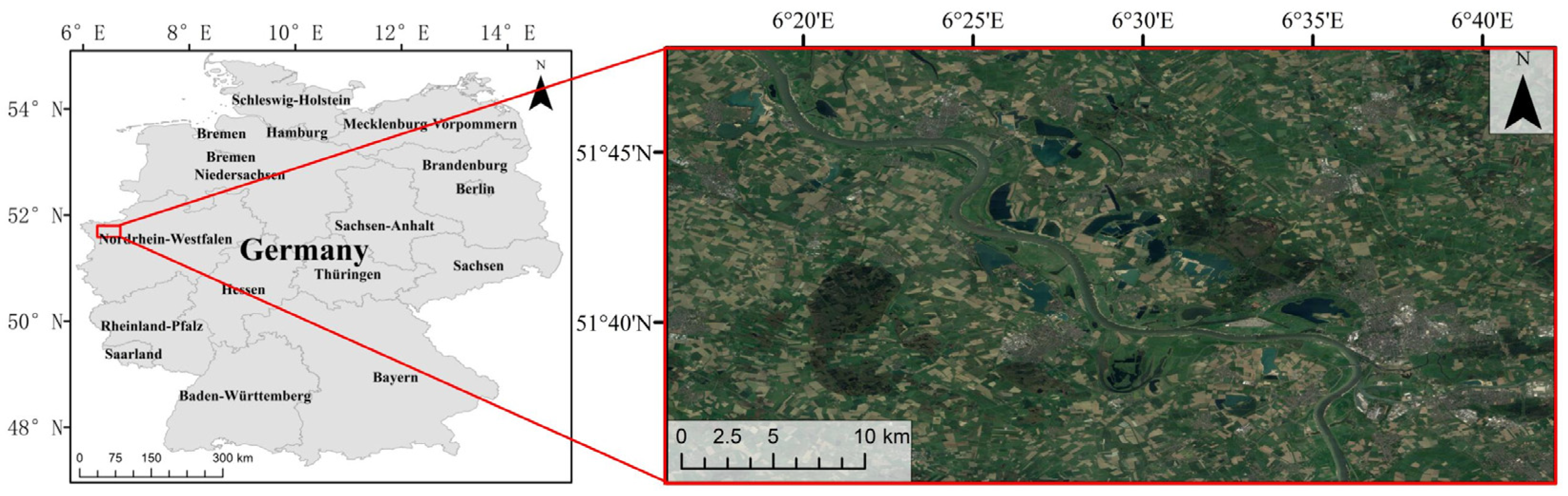
2. Site and Event
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Sentinel-1 Data
3.2. Data Preprocessing
3.3. Statistical Analysis of Time Series SAR Scattering Characteristics
3.4. GRU Neural Network Flood Area Identification
3.5. Flood Validation Data
4. Results
4.1. Evaluation Indicators
4.2. Comparison Method
4.3. Overall Accuracy Validation
4.4. Local Accuracy Validation
5. Discussion
5.1. SAR Image Outlier Detection
5.2. Accuracy of Flood Extraction
5.3. Strengths of the Method
5.4. Limitations and Potential Improvements
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pall, P.; Aina, T.; Stone, D.; Stott, P.; Nozawa, T.; Hilberts, A.; Lohmann, D.; Allen, M. Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Contribution to Flood Risk in England and Wales in Autumn 2000. Nature 2011, 470, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bioresita, F.; Puissant, A.; Stumpf, A.; Malet, J. A Method for Automatic and Rapid Mapping of Water Surfaces from Sentinel-1 Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Meng, Q. An Exploratory Study of Sentinel-1 SAR for Rapid Urban Flood Mapping on Google Earth Engine. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 113, 103002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, N.; Tuan, V.; Hang, L.; Hung, N.; The, D.; Dieu, D.; Anh, N.; Hackney, C. Hydrological/Hydraulic Modeling-Based Thresholding of Multi SAR Remote Sensing Data for Flood Monitoring in Regions of the Vietnamese Lower Mekong River Basin. Water 2020, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Wang, D.; Mao, K.; Anagnostou, E.; Hong, Y. Inundation Extent Mapping by Synthetic Aperture Radar: A Review. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, C.; Xu, L.; Wu, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, B. Multitemporal Water Extraction of Dongting Lake and Poyang Lake Based on an Automatic Water Extraction and Dynamic Monitoring Framework. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notti, D.; Giordan, D.; Calo, F.; Pepe, A.; Zucca, F.; Galve, J. Potential and Limitations of Open Satellite Data for Flood Mapping. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavalan, R. SAR Image Analysis Techniques for Flood Area Mapping—Literature Survey. Earth Sci. Inform. 2017, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; Heinila, K.; Huokuna, M.; Metsamaki, S.; Heilimo, J.; Sane, M. Satellite-Based Flood Mapping in the Boreal Region for Improving Situational Awareness. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2021, 15, e12744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVries, B.; Huang, C.; Armston, J.; Huang, W.; Jones, J.; Lang, M. Rapid and Robust Monitoring of Flood Events Using Sentinel-1 and Landsat Data on the Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matgen, P.; Hostache, R.; Schumann, G.; Pfister, L.; Hoffmann, L.; Savenije, H. Towards an Automated SAR-Based Flood Monitoring System: Lessons Learned from Two Case Studies. Phys. Chem. Earth 2011, 36, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulvirenti, L.; Pierdicca, N.; Chini, M.; Guerriero, L. An Algorithm for Operational Flood Mapping from Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Data Using Fuzzy Logic. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twele, A.; Cao, W.; Plank, S.; Martinis, S. Sentinel-1-Based Flood Mapping: A Fully Automated Processing Chain. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 2990–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chini, M.; Hostache, R.; Giustarini, L.; Matgen, P. A Hierarchical Split-Based Approach for Parametric Thresholding of SAR Images: Flood Inundation as a Test Case. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 6975–6988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, T.; Campanyà, J.; Naughton, O. A Methodology for Mapping Annual Flood Extent Using Multi-Temporal Sentinel-1 Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 282, 113273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Liu, D. A Local Thresholding Approach to Flood Water Delineation Using Sentinel-1 SAR Imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 159, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; Fatoyinbo, T.; Policelli, F. Flood Extent Mapping for Namibia Using Change Detection and Thresholding with SAR. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 035002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, D.; Giustarini, L.; Garcia-Pintado, J.; Cloke, H. Detection of Flooded Urban Areas in High Resolution Synthetic Aperture Radar Images Using Double Scattering. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 28, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinis, S.; Twele, A.; Voigt, S. Towards Operational near Real-Time Flood Detection Using a Split-Based Automatic Thresholding Procedure on High Resolution TerraSAR-X Data. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 9, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustarini, L.; Hostache, R.; Matgen, P.; Schumann, G.; Bates, P.; Mason, D. A Change Detection Approach to Flood Mapping in Urban Areas Using TerraSAR-X. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 2417–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinis, S.; Kersten, J.; Twele, A. A Fully Automated TerraSAR-X Based Flood Service. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 104, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldous, A.; Schill, S.; Raber, G.; Paiz, M.; Mambela, E.; Stevart, T. Mapping Complex Coastal Wetland Mosaics in Gabon for Informed Ecosystem Management: Use of Object-Based Classification. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 7, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chan, N.; Pan, B.; Ge, X.; Yang, H. Mapping Flood by the Object-Based Method Using Backscattering Coefficient and Interference Coherence of Sentinel-1 Time Series. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Liang, S.; He, X.; Ziegler, A.; Lin, P.; Pan, M.; Wang, D.; Zou, J.; Hao, D.; Mao, G.; et al. Rapid and Large-Scale Mapping of Flood Inundation via Integrating Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery with Unsupervised Deep Learning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 178, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, A.; Grimaldi, S.; Ramsankaran, R.; Pauwels, V.; Walker, J. Towards Operational SAR-Based Flood Mapping Using Neuro-Fuzzy Texture-Based Approaches. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 215, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sghaier, M.; Hammami, I.; Foucher, S.; Lepage, R. Flood Extent Mapping from Time-Series SAR Images Based on Texture Analysis and Data Fusion. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, O.; Anantrasirichai, N.; Achim, A.; Adams, B. River Planform Extraction from High-Resolution SAR Images via Generalized Gamma Distribution Superpixel Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 3942–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustarini, L.; Matgen, P.; Hostache, R.; Dostert, J. From SAR-based flood mapping to water level data assimilation into hydraulic models. In Proceedings of the Luxembourg Institute of Science & Technology, Edinburgh, UK, 24–27 September 2012; Neale, C., Maltese, A., Eds.; Volume 8531. [Google Scholar]
- Pulvirenti, L.; Pierdicca, N.; Chini, M.; Guerriero, L. Monitoring Flood Evolution in Vegetated Areas Using COSMO-SkyMed Data: The Tuscany 2009 Case Study. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 1807–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, S.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Pauwels, V.; Walker, J. Flood Mapping under Vegetation Using Single SAR Acquisitions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melancon, A.; Molthan, A.; Griffin, R.; Mecikalski, J.; Schultz, L.; Bell, J. Random Forest Classification of Inundation Following Hurricane Florence (2018) via L-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar and Ancillary Datasets. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Martinis, S.; Plank, S.; Ludwig, R. An Automatic Change Detection Approach for Rapid Flood Mapping in Sentinel-1 SAR Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 73, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.C.; Xue, D.J.; Li, C.R.; Zheng, J.; Li, W.Q. Study on new method for water area information extraction based on Sentinel—1 data. Yangtze River 2019, 50, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. Threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, V.; Kumar, V.; Matin, M.; Thapa, A.; Ellenburg, W.; Gupta, N.; Thapa, S. Flood Inundation Mapping- Kerala 2018; Harnessing the Power of SAR, Automatic Threshold Detection Method and Google Earth Engine. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.; Cao, B.; Park, E.; Yang, X.; Zhang, W.; Tarolli, P. Flood Monitoring in Rural Areas of the Pearl River Basin (China) Using Sentinel-1 SAR. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Deng, F.; Gong, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, W. Water Distribution Based on SAR and Optical Data to Improve Hazard Mapping. Environ. Res. 2023, 235, 116694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharrami, M.; Javanbakht, M.; Attarchi, S. Automatic Flood Detection Using Sentinel-1 Images on the Google Earth Engine. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisco, B. Mapping and monitoring surface water and wetlands with synthetic aperture radar. In Remote Sensing of Wetlands: Applications and Advances; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndikumana, E.; Minh, D.; Baghdadi, N.; Courault, D.; Hossard, L. Deep Recurrent Neural Network for Agricultural Classification Using Multitemporal SAR Sentinel-1 for Camargue, France. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anusha, N.; Bharathi, B. Flood Detection and Flood Mapping Using Multi-Temporal Synthetic Aperture Radar and Optical Data. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2020, 23, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, F.; Wan, L.; You, H. Flood Detection in Gaofen-3 SAR Images via Fully Convolutional Networks. Sensors 2018, 18, 2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, D.; Munoz, P.; Moftakhari, H.; Moradkhani, H. From Local to Regional Compound Flood Mapping with Deep Learning and Data Fusion Techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ji, J.; Xiong, Y.; Zhao, Q. FWENet: A Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Flood Water Body Extraction Based on SAR Images. Int. J. Digit Earth 2022, 15, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Wang, G.; Amankwah, S.; Wei, X.; Hu, Y.; Feng, A. Monitoring the Summer Flooding in the Poyang Lake Area of China in 2020 Based on Sentinel-1 Data and Multiple Convolutional Neural Networks. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Demir, I. U-Net-Based Semantic Classification for Flood Extent Extraction Using SAR Imagery and GEE Platform: A Case Study for 2019 Central US Flooding. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemni, E.; Bullock, J.; Belabbes, S.; Bromley, L. Fully Convolutional Neural Network for Rapid Flood Segmentation in Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konapala, G.; Kumar, S.; Ahmad, S. Exploring Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Diversity for Flood Inundation Mapping Using Deep Learning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 180, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhang, S.; Xue, B.; Zhao, T.; Wu, T. Cross-Modal Change Detection Flood Extraction Based on Convolutional Neural Network. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 117, 103197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Martinis, S.; Wieland, M. Urban Flood Mapping with an Active Self-Learning Convolutional Neural Network Based on TerraSAR-X Intensity and Interferometric Coherence. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 152, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.; Niculescu, S.; Bengoufa, S. Monitoring and Mapping Floods and Floodable Areas in the Mekong Delta (Vietnam) Using Time-Series Sentinel-1 Images, Convolutional Neural Network, Multi-Layer Perceptron, and Random Forest. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R.; Snoeij, P.; Geudtner, D.; Bibby, D.; Davidson, M.; Attema, E.; Potin, P.; Rommen, B.; Floury, N.; Brown, M.; et al. GMES Sentinel-1 Mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, M.; Dong, J.; Sarmah, S.; You, N.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, G.; Doughty, R.; Xiao, X. Identifying Floods and Flood-Affected Paddy Rice Fields in Bangladesh Based on Sentinel-1 Imagery and Google Earth Engine. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 166, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Wang, Z.; Mao, D.; Ren, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y. Rapid, Robust, and Automated Mapping of Tidal Flats in China Using Time Series Sentinel-2 Images and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 255, 112285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, S.; Devaraj, S.; Yarrakula, K. Mapping and Assessing Spatial Extent of Floods from Multitemporal Synthetic Aperture Radar Images: A Case Study over Adyar Watershed, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 63006–63021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.; Froger, J.; Minh, D. Multiscale Framework for Rapid Change Analysis from SAR Image Time Series: Case Study of Flood Monitoring in the Central Coast Regions of Vietnam. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, C.; Tian, B.; Wu, W.; Zhou, Y. Tide2Topo: A New Method for Mapping Intertidal Topography Accurately in Complex Estuaries and Bays with Time-Series Sentinel-2 Images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 200, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, D.; Bevington, J.; Dance, S.; Revilla-Romero, B.; Smith, R.; Vetra-Carvalho, S.; Cloke, H. Improving Urban Flood Mapping by Merging Synthetic Aperture Radar-Derived Flood Footprints with Flood Hazard Maps. Water 2021, 13, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, T.; Tu, Y.; Ren, Z.; Xu, B. Monitoring Post-Flood Recovery of Croplands Using the Integrated Sentinel-1/2 Imagery in the Yangtze-Huai River Basin. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloso, A.; Mermoz, S.; Bouvet, A.; Toan, T.; Planells, M.; Dejoux, J.; Ceschia, E. Understanding the Temporal Behavior of Crops Using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2-like Data for Agricultural Applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 199, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Chen, M.; Xie, X.; Zhang, C.; Mao, B.; Lei, G.; Wang, B.; Meng, X.; Guan, X.; Zhang, Y. Riparian Zone DEM Generation From Time-Series Sentinel-1 and Corresponding Water Level: A Novel Waterline Method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Li, J.; Chen, G.; Zhao, L.; Xiong, B.; Kuang, G. Improving Pixel-Based Change Detection Accuracy Using an Object-Based Approach in Multitemporal SAR Flood Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 3486–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, M.; Kilsby, C.; Moore, P. Multi-Temporal Synthetic Aperture Radar Flood Mapping Using Change Detection. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2018, 11, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amitrano, D.; Di Martino, G.; Iodice, A.; Riccio, D.; Ruello, G. Unsupervised Rapid Flood Mapping Using Sentinel-1 GRD SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3290–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cian, F.; Marconcini, M.; Ceccato, P. Normalized Difference Flood Index for Rapid Flood Mapping: Taking Advantage of EO Big Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 712–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangira, T.; Iannini, L.; Menenti, M.; van Niekerk, A.; Vekerdy, Z. Flood Extent Mapping in the Caprivi Floodplain Using Sentinel-1 Time Series. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 5667–5683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Bekaert, D.; Spaans, K.; Arikan, M. Recent Advances in SAR Interferometry Time Series Analysis for Measuring Crustal Deformation. Tectonophysics 2012, 514, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep Learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, O.; Kohne, T.; Zhan, E.; Cahill, B.; Yun, S.; Ross, Z.; Simons, M. Deep Learning-Based Damage Mapping With InSAR Coherence Time Series. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langkvist, M.; Karlsson, L.; Loutfi, A. A Review of Unsupervised Feature Learning and Deep Learning for Time-Series Modeling. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2014, 42, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordonez, F.; Roggen, D. Deep Convolutional and LSTM Recurrent Neural Networks for Multimodal Wearable Activity Recognition. Sensors 2016, 16, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.; Yunus, A.; Subramanian, S.; Avtar, R. Basin-Wide Flood Depth and Exposure Mapping from SAR Images and Machine Learning Models. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawaz, H.; Forestier, G.; Weber, J.; Idoumghar, L.; Muller, P. Deep Learning for Time Series Classification: A Review. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2019, 33, 917–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Wang, H.; Fan, J.; Ma, X. SAR Image Classification via Deep Recurrent Encoding Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 2255–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yeo, C.; Lau, C.; Lee, B. Leveraging Social Media News to Predict Stock Index Movement Using RNN-Boost. Data Knowl. Eng. 2018, 118, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, T.; Krauss, C. Deep Learning with Long Short-Term Memory Networks for Financial Market Predictions. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 270, 654–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagheer, A.; Kotb, M. Time Series Forecasting of Petroleum Production Using Deep LSTM Recurrent Networks. Neurocomputing 2019, 323, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutscher Wetterdienst. Klima und Umwelt. [WWW Document]. 2023. Available online: https://www.dwd.de/DE/klimaumwelt/klimaumwelt_node.html (accessed on 31 August 2023).
- WetterKontor. Wetter Düsseldorf. [WWW Document]. 2023. Available online: https://www.wetterkontor.de/wetter-vorhersage/deutschland/duesseldorf (accessed on 31 August 2023).
- Copernicus. The Copernicus Emergency Management Service Monitors the Extent and Impact of Floods in Southern and Western Germany. [WWW Document]. 2023. Available online: https://emergency.copernicus.eu/mapping/ems/copernicus-emergency-management-service-monitors-extent-and-impact-floods-southern-and-western (accessed on 23 May 2023).
- Parts-Iraola, P.; Nannini, M.; Scheiber, R.; De Zan, F.; Wollstadt, S.; Minati, F.; Vecchioli, F.; Costantini, M.; Borgstrom, S.; De Martino, P.; et al. Sentinel-1 assessment of the interferometric wide-swath mode. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 26–31 July 2015; pp. 5248–5251. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, I.; Cao, S.; Naeimi, V.; Paulik, C.; Wagner, W. Methods to Remove the Border Noise From Sentinel-1 Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Implications and Importance For Time-Series Analysis. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabel, D.; Bartalis, Z.; Wagner, W.; Doubkova, M.; Klein, J. Development of a Global Backscatter Model in Support to the Sentinel-1 Mission Design. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Lipton, Z.; Li, M.; Smola, A. Dive into Deep Learning; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023; pp. 244–249. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; DeVries, B.; Huang, C.; Lang, M.; Jones, J.; Creed, I.; Carroll, M. Automated Extraction of Surface Water Extent from Sentinel-1 Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhoff, R.; Kleuskens, M.; Winsemius, H.; Huizinga, H.; Brakenridge, G.; Bishop, C. Automated Global Water Mapping Based on Wide-Swath Orbital Synthetic-Aperture Radar. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Perrie, W.; Zhang, J.; Uhlhorn, E.; He, Y. High-Resolution Hurricane Vector Winds from C-Band Dual-Polarization SAR Observations. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschetti, G.; Iodice, A.; Riccio, D. A Canonical Problem in Electromagnetic Backscattering from Buildings. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 1787–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajnsek, I.; Jagdhuber, T.; Schcon, H.; Papathanassiou, K. Potential of Estimating Soil Moisture Under Vegetation Cover by Means of PolSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, D.; Dance, S.; Cloke, H. Floodwater Detection in Urban Areas Using Sentinel-1 and WorldDEM Data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2021, 15, 032003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, V.; Quang, N.; Hang, L. Optimizing Flood Mapping Using Multi-Synthetic Aperture Radar Images for Regions of the Lower Mekong Basin in Vietnam. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 54, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Satelite | Acquisition Date (yyyy/mm/dd) | Polarization | Instrument Mode | Pixel Size (m) | Orbit | Incident Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sentinel-1 A | 2020/09/18 | VV | IW | 10 × 10 | Descending | 35 |
| Sentinel-1 A | 2020/09/18 | VH | IW | 10 × 10 | Descending | 35 |
| Sentinel-1 A | 2020/10/07 | VV | IW | 10 × 10 | Descending | 43 |
| Sentinel-1 A | 2020/10/12 | VV | IW | 10 × 10 | Descending | 35 |
| Sentinel-1 A | 2020/10/19 | VV | IW | 10 × 10 | Descending | 43 |
| Sentinel-1 A | 2020/10/24 | VV | IW | 10 × 10 | Descending | 35 |
| Sentinel-1 A | 2020/11/05 | VV | IW | 10 × 10 | Descending | 35 |
| Sentinel-1 A | 2020/11/12 | VV | IW | 10 × 10 | Descending | 43 |
| Sentinel-1 A | 2020/11/17 | VV | IW | 10 × 10 | Descending | 35 |
| Sentinel-1 A | 2020/11/24 | VV | IW | 10 × 10 | Descending | 43 |
| Sentinel-1 A | 2020/11/29 | VV | IW | 10 × 10 | Descending | 35 |
| Sentinel-1 A | 2020/12/11 | VV | IW | 10 × 10 | Descending | 35 |
| Sentinel-1 A | 2020/12/18 | VV | IW | 10 × 10 | Descending | 43 |
| Sentinel-1 A | 2020/12/23 | VV | IW | 10 × 10 | Descending | 35 |
| Sentinel-1 A | 2020/12/30 | VV | IW | 10 × 10 | Descending | 43 |
| Sentinel-1 A | 2021/01/04 | VV | IW | 10 × 10 | Descending | 35 |
| Sentinel-1 A | 2021/01/11 | VV | IW | 10 × 10 | Descending | 43 |
| Sentinel-1 A | 2021/01/16 | VV | IW | 10 × 10 | Descending | 35 |
| Sentinel-1 A | 2021/01/23 | VV | IW | 10 × 10 | Descending | 43 |
| Sentinel-1 A | 2021/01/28 | VV | IW | 10 × 10 | Descending | 35 |
| Sentinel-1 A | 2021/02/09 | VV | IW | 10 × 10 | Descending | 35 |
| Sentinel-1 A | 2021/02/09 | VH | IW | 10 × 10 | Descending | 35 |
| Missed Alarm | False Alarm | Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GRU(Z-scores) | 8.45% | 9.79% | 99.20% |
| OTSU | 15.45% | 10.55% | 98.89% |
| SDWI | 16.14% | 7.32% | 99.01% |
| Z-score | 15.25% | 5.95% | 99.10% |
| Missed Alarm | False Alarm | Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GRU(Z-scores) | 6.84% | 7.14% | 97.65% |
| OTSU | 22.30% | 8.45% | 95.06% |
| SDWI | 12.35% | 6.18% | 96.96% |
| Z-score | 13.05% | 4.68% | 97.10% |
| Missed Alarm | False Alarm | Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GRU(Z-scores) | 8.99% | 6.94% | 94.57% |
| OTSU | 19.54% | 7.16% | 91.15% |
| SDWI | 18.34% | 3.41% | 92.70% |
| Z-score | 14.86% | 3.78% | 93.74% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Xie, C.; Tian, B.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Bian, S. Application of Gated Recurrent Unit Neural Network for Flood Extraction from Synthetic Aperture Radar Time Series. Water 2023, 15, 3779. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213779
Zhang M, Xie C, Tian B, Yang Y, Guo Y, Zhu Y, Bian S. Application of Gated Recurrent Unit Neural Network for Flood Extraction from Synthetic Aperture Radar Time Series. Water. 2023; 15(21):3779. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213779
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ming, Chou Xie, Bangsen Tian, Yanchen Yang, Yihong Guo, Yu Zhu, and Shuaichen Bian. 2023. "Application of Gated Recurrent Unit Neural Network for Flood Extraction from Synthetic Aperture Radar Time Series" Water 15, no. 21: 3779. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213779
APA StyleZhang, M., Xie, C., Tian, B., Yang, Y., Guo, Y., Zhu, Y., & Bian, S. (2023). Application of Gated Recurrent Unit Neural Network for Flood Extraction from Synthetic Aperture Radar Time Series. Water, 15(21), 3779. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213779






