Effect of Fe2+ on ANAMMOX Granular Sludge Cultured in a Biased Acidic Influent and Dynamic Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
0.066CH2O0.5N0.15 + 2.03H2O
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wastewater Feed and Sludge Source
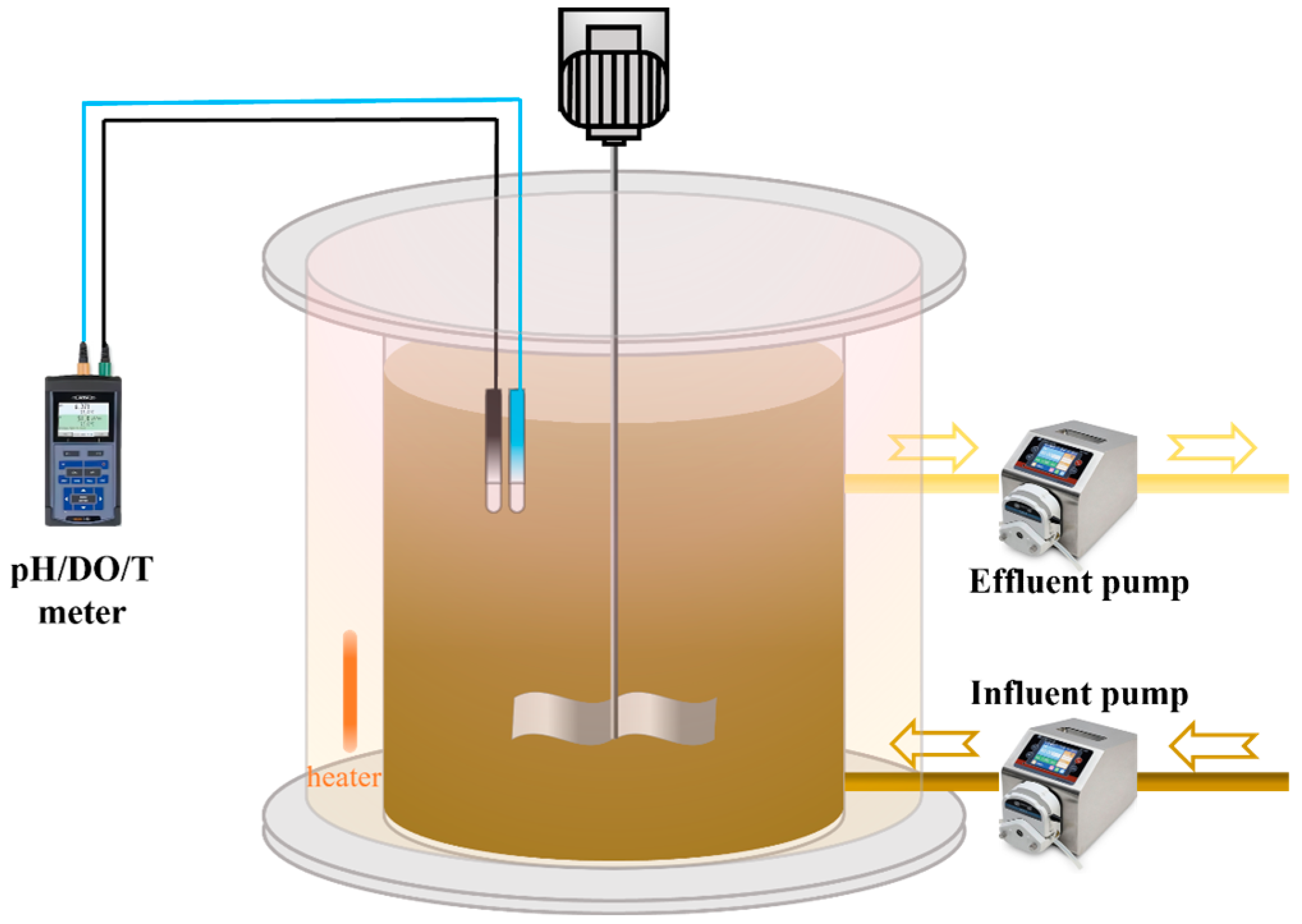
2.2. Reactor Configuration and Operation
2.3. Microbial Diversity
2.4. Influence of Different Fe2+ Concentrations on the Nitrogen Removal Effect
2.5. Analytical Methods
2.6. Calculation
3. Results and Discussion
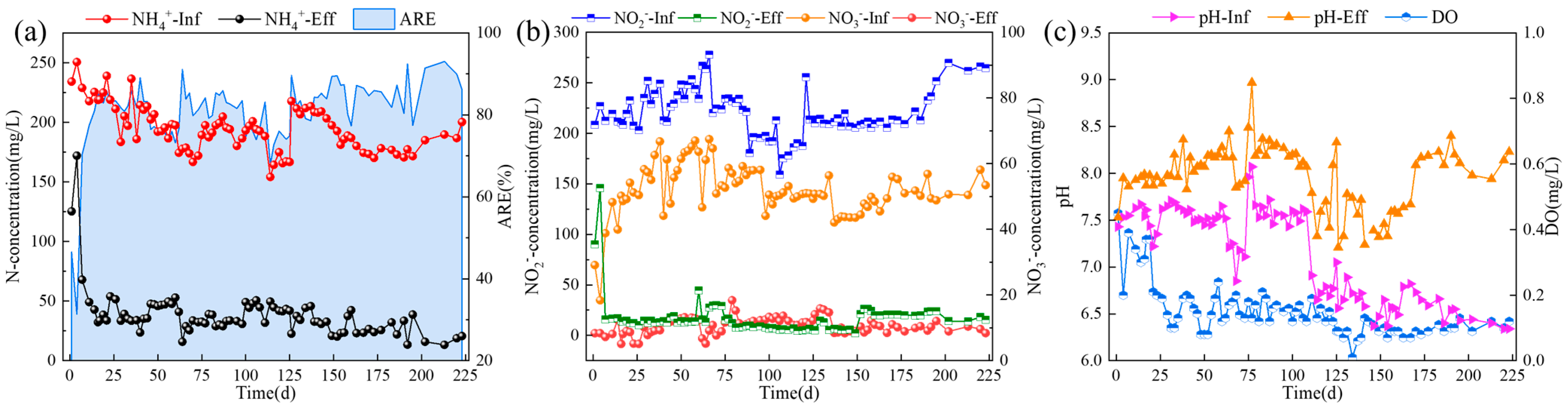
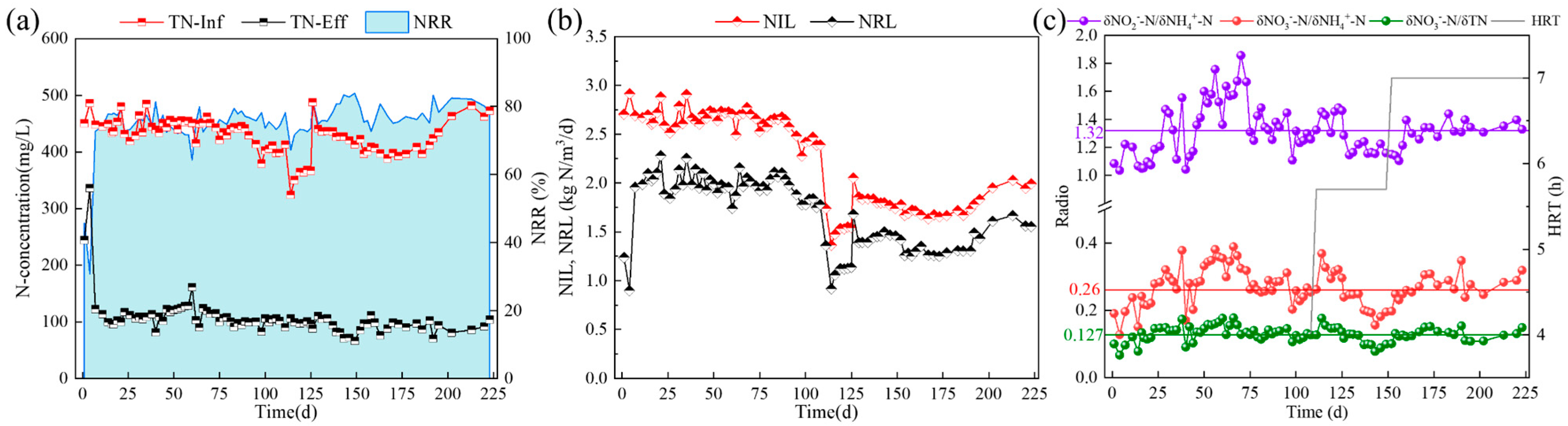
3.1. The Enrichment of ANAMMOX in CSTR by Gradual Reduction of pH
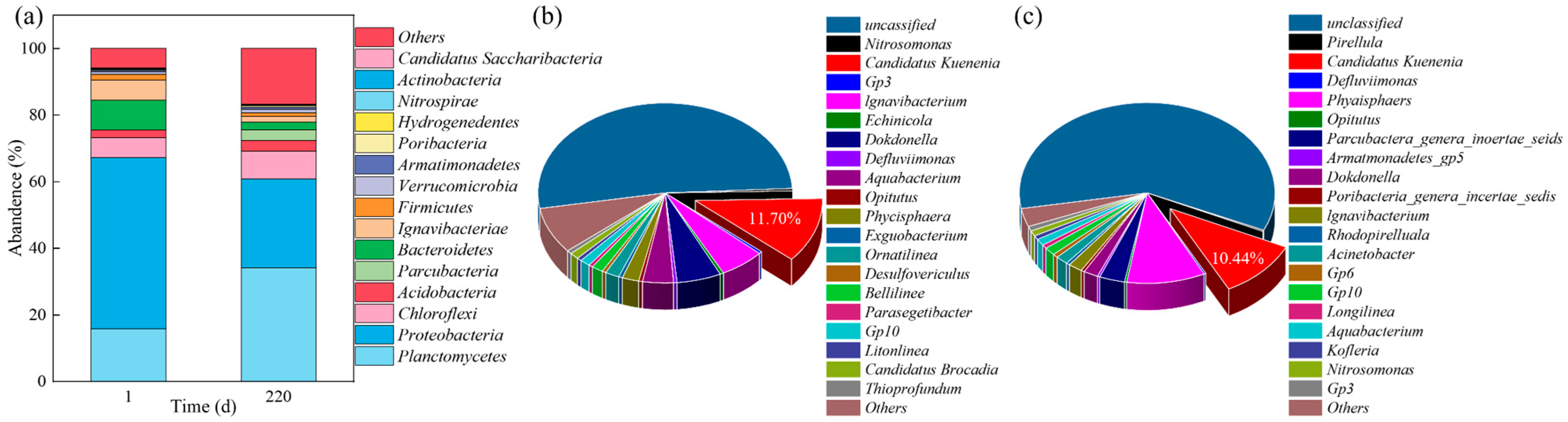
3.2. Microbial Diversity Analysis
3.3. Microbial Community Evolution at Phylum and Genus Level
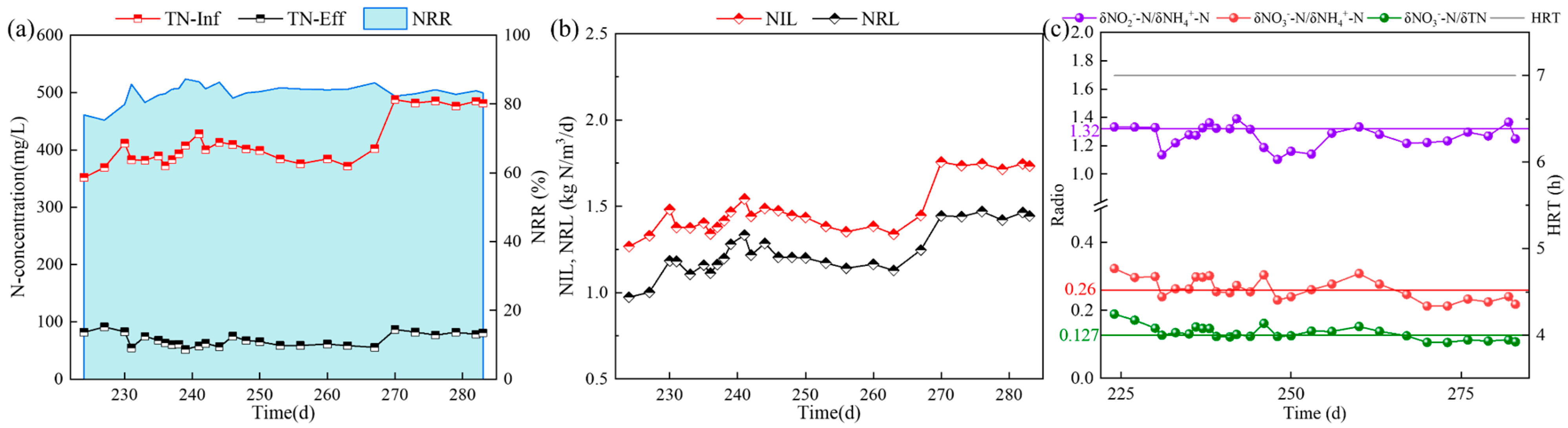
3.4. Influence of Different Fe2+ Concentrations on the Nitrogen Removal Effect
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Y.; Fang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Huang, J.; Ma, X.; He, K.; He, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhao, H. Microbial community and removal of nitrogen via the addition of a carrier in a pilot-scale duckweed-based wastewater treatment system. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 179, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Duan, L.; Mo, J.; Du, E.; Shen, J.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; He, C.; Zhang, F. Nitrogen deposition and its ecological impact in China: An overview. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2251–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Liang, H.; Yang, W.; Yang, T.; Chen, T.; Gao, D. The biochar/Fe-modified biocarrier driven simultaneous NDFO and Feammox to remove nitrogen from eutrophic water. Water Res. 2023, 243, 120280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, G.; Jeison, D.; Chamy, R. Nitrification with high nitrite accumulation for the treatment of wastewater with high ammonia concentration. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1371–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jianlong, W.; Ning, Y. Partial nitrification under limited dissolved oxygen conditions. Process Biochem. 2004, 39, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dongen, U.; Jetten, M.S.M.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. The SHARON®-Anammox® process for treatment of ammonium rich wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 44, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Wang, S.; Cao, S.; Miao, Y.; Jia, F.; Du, R.; Peng, Y. Biological nitrogen removal from sewage via anammox: Recent advances. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Bian, Y.; Yang, F.; Xu, J.; Qiu, F. Achieving partial nitrification: A strategy for washing NOB out under high DO condition. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 347, 119186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, F.; Hidaka, T.; Nakagawa, A.; Yorozu, H.; Tsuno, H. Removal of high concentration ammonia from wastewater by a combination of partial nitrification and anammox treatment. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 1485–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strous, M.; Heijnen, J.J.; Kuenen, J.G.; Jetten, M.S.M. The sequencing batch reactor as a powerful tool for the study of slowly growing anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing microorganisms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 50, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Peng, L.; Mao, N.; Geng, J.; Ren, H.; Xu, K. Effects of Fe3+ on microbial communities shifts, functional genes expression and nitrogen transformation during the start-up of Anammox process. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, D.; He, Y.; Yue, H.; Yang, S. Effects of Fe(ii) on microbial communities, nitrogen transformation pathways and iron cycling in the anammox process: Kinetics, quantitative molecular mechanism and metagenomic analysis. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 68005–68016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ren, L.; Yao, Z.; Wan, X.; Lu, P.; Zhang, X. Removal of Nitrogen Oxide Based on Anammox through Fe(II)EDTA Absorption. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 7247–7255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jin, Y. Effects of Fe(II) on N2O emissions from anammox reactors. Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 63, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Yang, K.; Sun, Y.; Tian, J.; Lv, B. Nitrate removal by a novel autotrophic denitrifier (Microbacterium sp.) using Fe(II) as electron donor. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Niftrik, L.; Geerts, W.J.C.; van Donselaar, E.G.; Humbel, B.M.; Yakushevska, A.; Verkleij, A.J.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Strous, M. Combined structural and chemical analysis of the anammoxosome: A membrane-bounded intracytoplasmic compartment in anammox bacteria. J. Struct. Biol. 2008, 161, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schalk, J.; de Vries, S.; Kuenen, J.G.; Jetten, M.S.M. Involvement of a Novel Hydroxylamine Oxidoreductase in Anaerobic Ammonium Oxidation. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 5405–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Walsh, K.; Webb, R.; Rijpstra, W.I.; van de Pas-Schoonen, K.; Verbruggen, M.J.; Hill, T.; Moffett, B.; Fuerst, J.; Schouten, S.; et al. Candidatus “Scalindua brodae”, sp. nov., Candidatus “Scalindua wagneri”, sp. nov., Two New Species of Anaerobic Ammonium Oxidizing Bacteria. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 26, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirpus, I.E.Y.; de Been, M.; Op den Camp, H.J.M.; Strous, M.; Le Paslier, D.; Kuenen, G.J.; Jetten, M.S.M. A new soluble 10kDa monoheme cytochrome c-552 from the anammox bacterium Candidatus “Kuenenia stuttgartiensis”. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 252, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spang, A.; Poehlein, A.; Offre, P.; Zumbrägel, S.; Haider, S.; Rychlik, N.; Nowka, B.; Schmeisser, C.; Lebedeva, E.V.; Rattei, T.; et al. The genome of the ammonia-oxidizing Candidatus Nitrososphaera gargensis: Insights into metabolic versatility and environmental adaptations. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 3122–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H.-w.; Wu, C.; Bi, W.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, X. Simultaneous Fe(III) reduction and ammonia oxidation process in Anammox sludge. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 64, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Cai, X.; Wang, Z.; Xia, S. Enhancement and mechanisms of iron-assisted anammox process. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhou, X.; Qing, K.; Cao, W.; Zhang, Y. Novel insight into the inhibitory effects and mechanisms of Fe(II)-mediated multi-metabolism in anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox). Water Res. 2023, 242, 120291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Chen, J.-b.; Wu, X.-x.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, S.-q. Rapid discrimination of Panax notogeinseng of different grades by FT-IR and 2DCOS-IR. J. Mol. Struct. 2016, 1124, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilcreas, F.W. Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1966, 56, 387–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, S.; Peng, Y. Stable nitrogen removal in the novel continuous flow anammox system under deteriorated partial nitrification: Significance and superiority of the anaerobic-oxic-anoxic–oxic operation mode. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 361, 127693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Chen, H.; Gao, X.; Zhang, J. Achieving PN through the selective recovery of AOB activity in inactivated nitrifying bacteria: Combined aerobic starvation and FA. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 116004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Bian, Y.; Yang, F.; Liao, M.; Xu, J.; Qiu, F. Influencing factors on the activity of an enriched Nitrospira culture with granular morphology. Environ. Technol. 2023. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.-j.; Zheng, P.; Mahmood, Q.; Chen, J.-w. Start-up and inhibition analysis of the Anammox process seeded with anaerobic granular sludge. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 36, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamchoi, N.; Nitisoravut, S. Anammox enrichment from different conventional sludges. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 2225–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, J.-M.; Su, Q.; Ma, Y.; Valverde-Pérez, B.; Domingo-Félez, C.; Jensen, M.M.; Smets, B.F. The pH dependency of N-converting enzymatic processes, pathways and microbes: Effect on net N2O production. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 1623–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, R.; Cao, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Peng, Y. Flexible Nitrite Supply Alternative for Mainstream Anammox: Advances in Enhancing Process Stability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6353–6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, F.; Wang, S.-N.; Li, K.-Y.; Dong, J.-Y.; Xu, R.-Z.; Zhang, L.-L.; Xie, W.-M.; Cao, J.-S. Formation of microbial products by activated sludge in the presence of a metabolic uncoupler o-chlorophenol in long-term operated sequencing batch reactors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, S.; Yu, D.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Bi, C.; Zhen, J.; Yuan, M. Achieving deep-level nutrient removal via combined denitrifying phosphorus removal and simultaneous partial nitrification-endogenous denitrification process in a single-sludge sequencing batch reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 289, 121690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Teeseling, M.C.F.; Mesman, R.J.; Kuru, E.; Espaillat, A.; Cava, F.; Brun, Y.V.; VanNieuwenhze, M.S.; Kartal, B.; van Niftrik, L. Anammox Planctomycetes have a peptidoglycan cell wall. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodha, T.; Narvekar, S.; Karodi, P. Classification of uncultivated anammox bacteria and Candidatus Uabimicrobium into new classes and provisional nomenclature as Candidatus Brocadiia classis nov. and Candidatus Uabimicrobiia classis nov. of the phylum Planctomycetes and novel family Candidatus Scalinduaceae fam. nov to accommodate the genus Candidatus Scalindua. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 44, 126272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Martínez, A.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Rodelas, B.; Abbas, B.; Martinez-Toledo, M.; van Loosdrecht, M.; Osorio, F.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J. 454-Pyrosequencing Analysis of Bacterial Communities from Autotrophic Nitrogen Removal Bioreactors Utilizing Universal Primers: Effect of Annealing Temperature. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 892013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, R.; Peng, Z.; Zhai, H.; Zhang, H. Effect of Fe (II) in low-nitrogen sewage on the reactor performance and microbial community of an ANAMMOX biofilter. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.U.; Rehman, M.U.; Zahoor, M.; Shah, A.B.; Zekker, I. Biodegradation of Brown 706 Dye by Bacterial Strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Water 2021, 13, 2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, M.; Naeem, M.; Zahoor, M.; Hanafiah, M.M.; Oyekanmi, A.A.; Ullah, R.; Farraj, D.A.A.; Elshikh, M.S.; Zekker, I.; Gulfam, N. Biological Degradation of the Azo Dye Basic Orange 2 by Escherichia coli: A Sustainable and Ecofriendly Approach for the Treatment of Textile Wastewater. Water 2022, 14, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.U.; Zahoor, M.; Rehman, M.U.; Shah, A.B.; Zekker, I.; Khan, F.A.; Ullah, R.; Albadrani, G.M.; Bayram, R.; Mohamed, H.R.H. Biological Mineralization of Methyl Orange by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Water 2022, 14, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, Y.; Kurahashi, M.; Sakiyama, Y.; Ohuchi, M.; Yokota, A.; Harayama, S. Phycisphaera mikurensis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from a marine alga, and proposal of Phycisphaeraceae fam. nov., Phycisphaerales ord. nov. and Phycisphaerae classis nov. in the phylum Planctomycetes. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 55, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
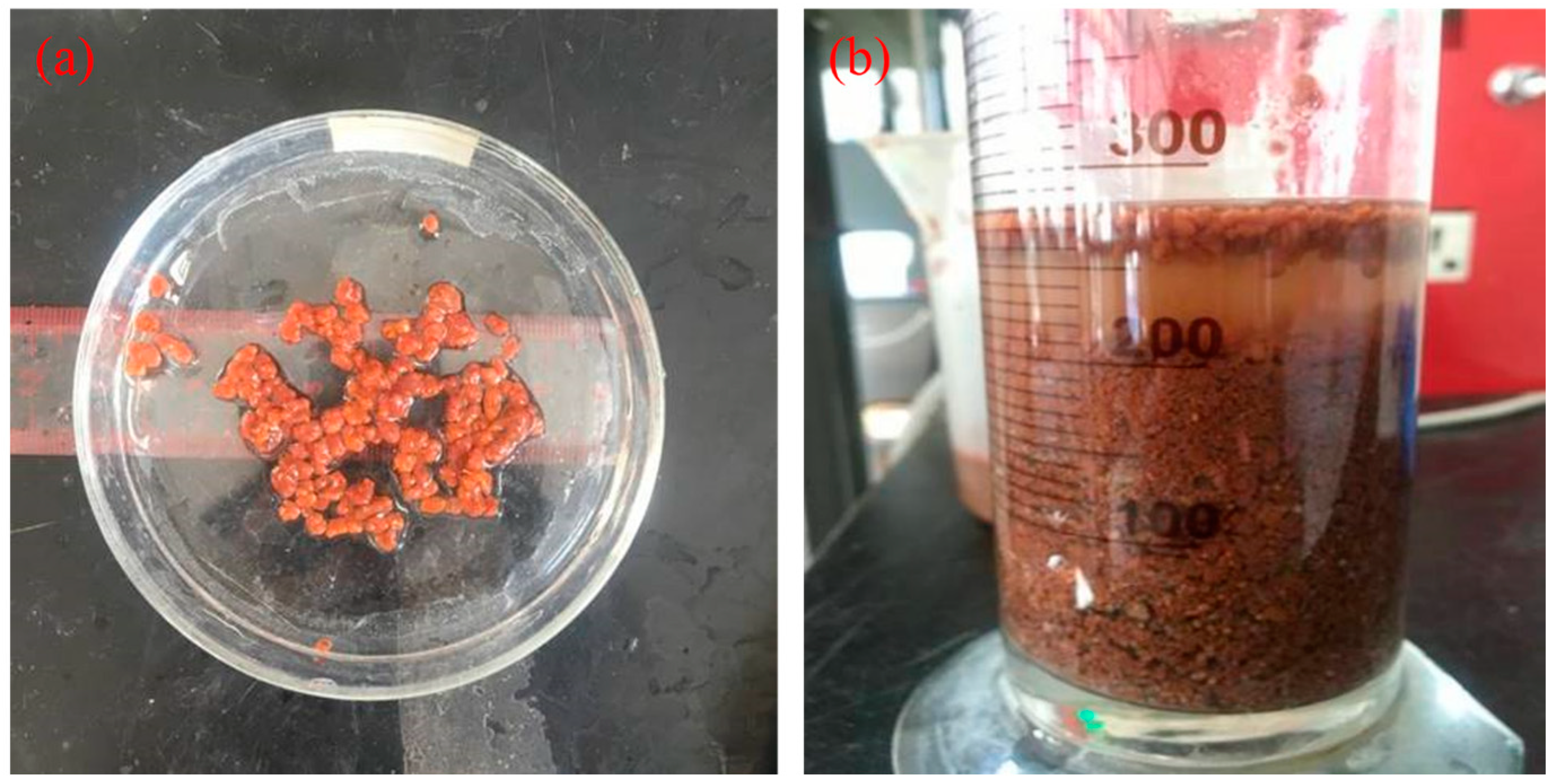


| Time/ (d) | HRT/ (h) | pH | rpm/ (r/min) | NH4+-N/ (mg/L) | NO2−-N/ (mg/L) | NO3−-N/ (mg/L) | PO43−-P/ (mg/L) | Trace Element/ (ml/L) | DO/ (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1–31 | 4.0 | 7.50–7.70 | 20 | 180–250 | 200–250 | 5–12 | 10 | 1 | 0.30 |
| 32–73 | 4.0 | 7.10–7.50 | 30 | 165–240 | 210–280 | 5–13 | 10 | 1 | 0.16 |
| 74–108 | 4.0 | 7.10–7.50 | 40 | 180–205 | 155–235 | 10–18 | 10 | 1 | 0.15 |
| 109–152 | 5.7 | 6.50–7.50 | 40 | 150–220 | 175–255 | 8–16 | 10 | 1 | 0.11 |
| 153–223 | 7.0 | 6.30–6.50 | 40 | 170–200 | 205–270 | 8–12 | 10 | 1 | 0.09 |
| Time/(d) | Fe2+/(mg/L) | HRT/(h) | rpm/(r/min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 224–243 | 10 | 7.00 | 40 |
| 244–263 | 20 | 7.00 | 40 |
| 264–283 | 30 | 7.00 | 40 |
| Sample | OTU | Simpson | Shannon | ACE | Chao1 | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| day1 | 962 | 0.11 | 3.58 | 1322 | 1238.07 | 1.00 |
| day220 | 1729 | 0.03 | 4.26 | 24967.40 | 12446.44 | 0.97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, K.; Bian, Y.; Jiang, S.; Fu, S.; Kang, J.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Yang, W. Effect of Fe2+ on ANAMMOX Granular Sludge Cultured in a Biased Acidic Influent and Dynamic Environment. Water 2023, 15, 3762. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213762
Fu K, Bian Y, Jiang S, Fu S, Kang J, Li X, Li Z, Yang W. Effect of Fe2+ on ANAMMOX Granular Sludge Cultured in a Biased Acidic Influent and Dynamic Environment. Water. 2023; 15(21):3762. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213762
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Kunming, Yihao Bian, Shan Jiang, Sibo Fu, Jia Kang, Xiaodan Li, Zirui Li, and Wenbing Yang. 2023. "Effect of Fe2+ on ANAMMOX Granular Sludge Cultured in a Biased Acidic Influent and Dynamic Environment" Water 15, no. 21: 3762. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213762





