NaOH-Activated Natural Glauconite for Low-Cost Adsorption of Congo Red Dye
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Glauconite Activation
2.3. Instrumentations/Characterizations
2.4. Preparation of Adsorbate
2.5. Adsorption Studies
2.6. Adsorption Isotherms
2.7. Adsorption Mechanisms and Kinetics
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Adsorbent Characterization
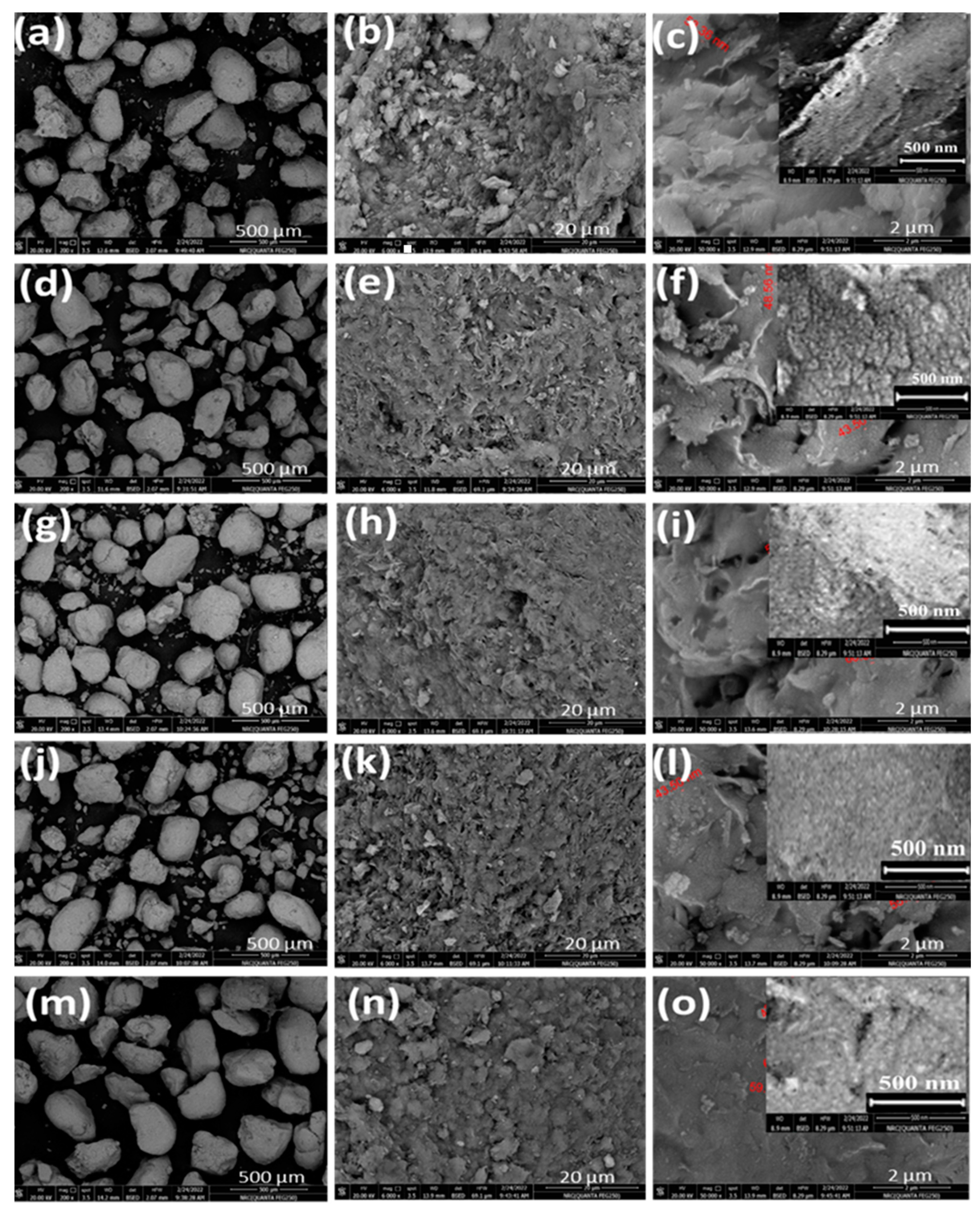
3.1.1. Morphological Study
3.1.2. Functional Groups and Crystallographic Structures
3.2. Adsorption of Congo Red
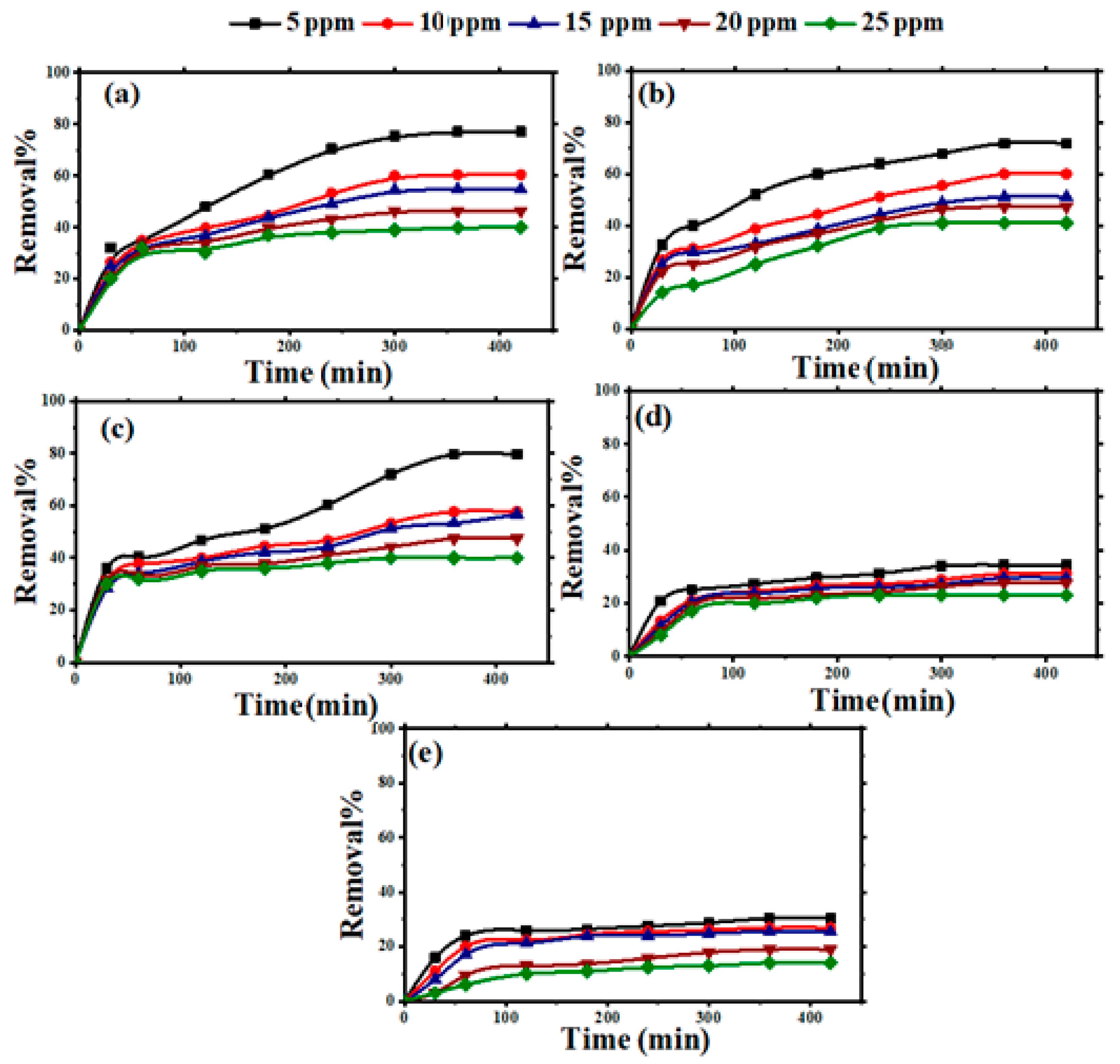
3.2.1. Effects of Starting Dye Concentration
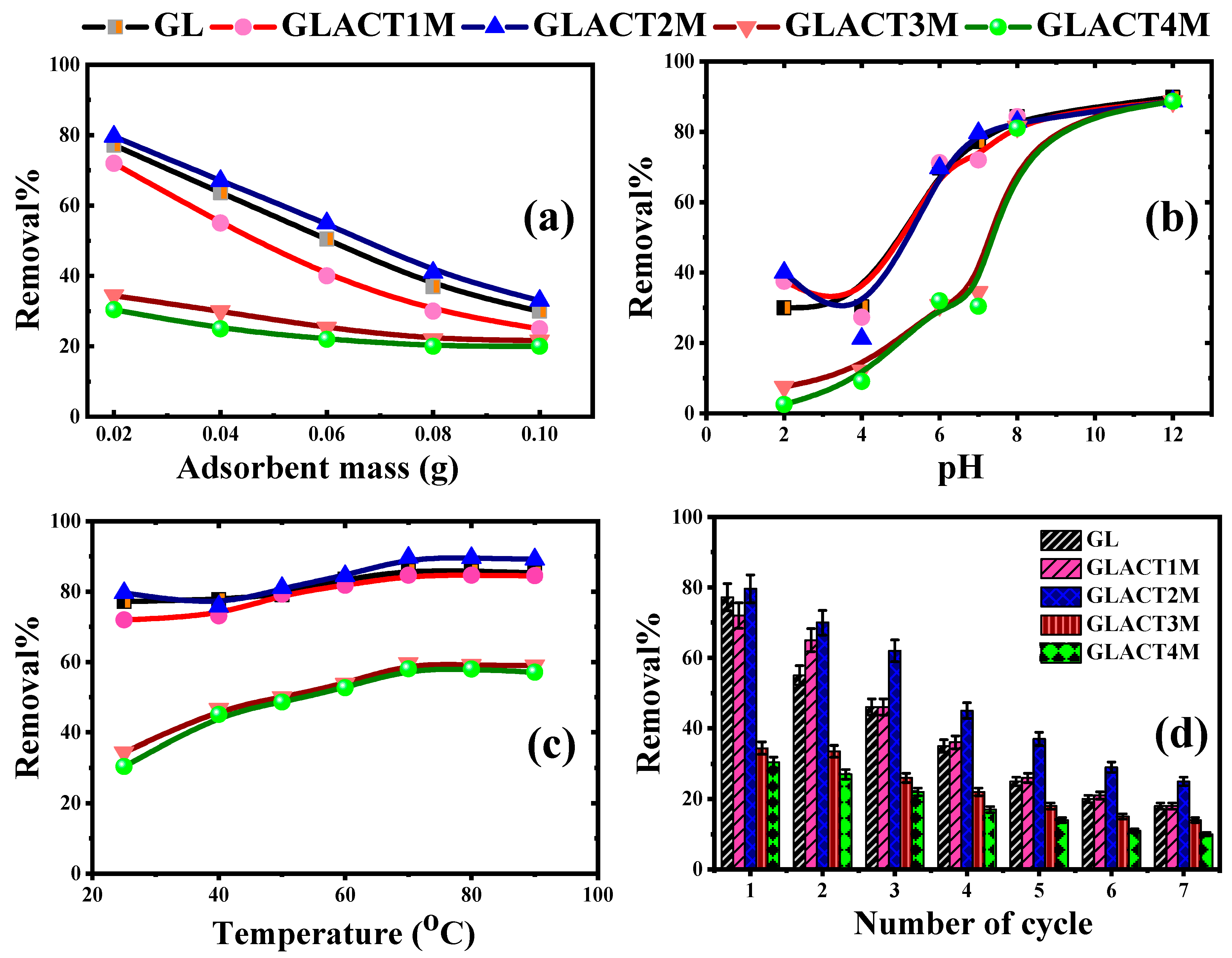
3.2.2. Effects of Adsorbent Doses
3.2.3. Effects of Solution pH
3.2.4. Effects of Adsorption Temperatures
3.2.5. Reusability of Adsorbents
3.3. Adsorption Equilibrium Isotherms
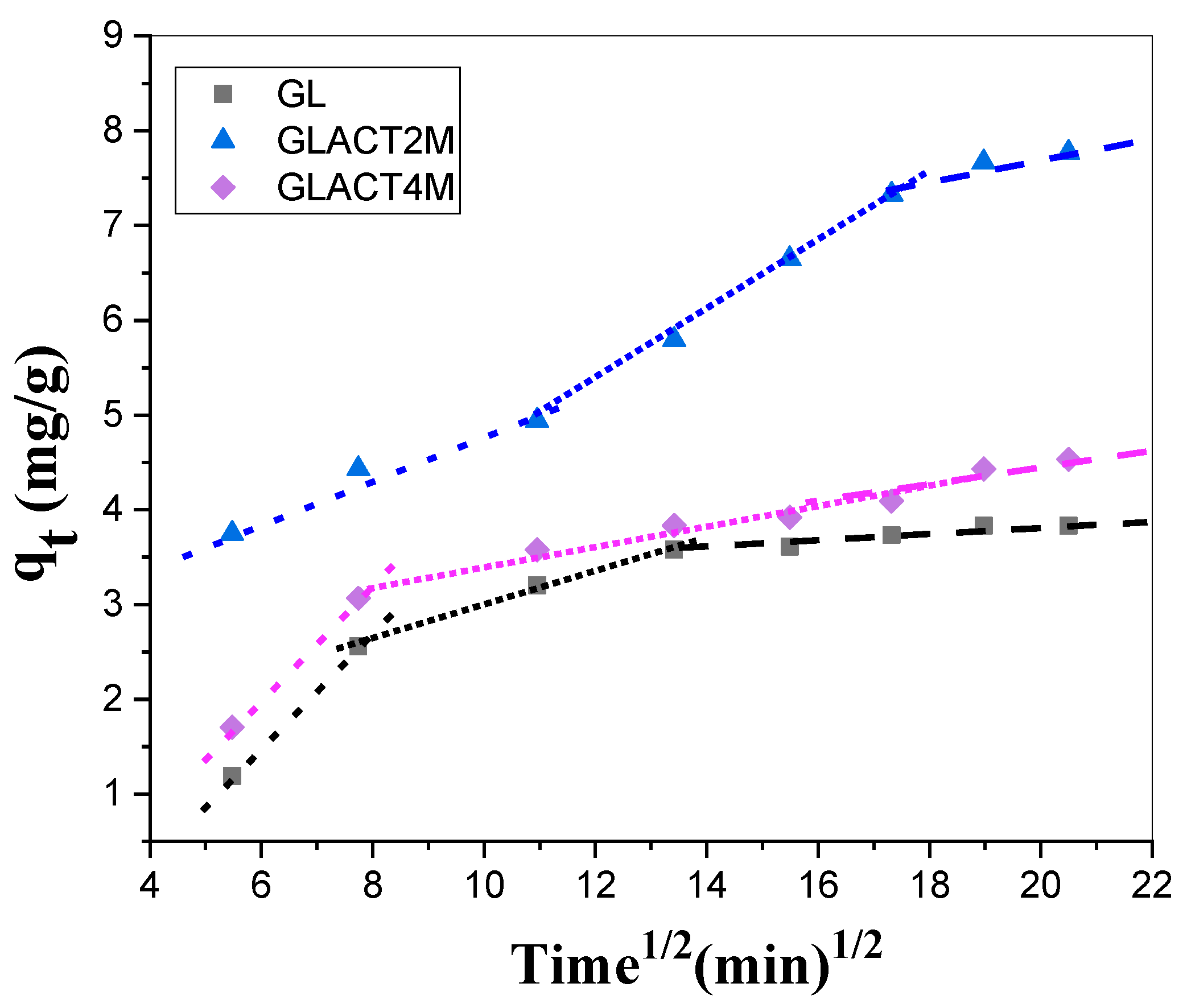
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics and Sorption Mechanisms
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruiz-Santoyo, V.; Andrade-Espinoza, B.A.; Romero-Toledo, R.; Anaya-Esparza, L.M.; Villagrán, Z.; Guerra-Contreras, A. Use of Nanostructured Photocatalysts for Dye Degradation: A Review. Period. Polytech. Chem. Eng. 2022, 66, 367–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, C.G.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H.; Affandi, N.A.; Nga, J.L.H.; Vijayan, V. Photocatalytic treatment of detergent-contaminated wastewater: A short review on current progress. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 39, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathoure, A.K.; Dhatwalia, V.K. Toxicity and Waste Management Using Bioremediation; Engineering Science Reference; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay, R.; Bhaduri, D.; Sarkar, B.; Rusmin, R.; Hou, D.; Khanam, R.; Sarkar, S.; Biswas, J.K.; Vithanage, M.; Bhatnagar, A. Clay–polymer nanocomposites: Progress and challenges for use in sustainable water treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 383, 121125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustapha, S.; Ndamitso, M.; Abdulkareem, A.; Tijani, J.; Shuaib, D.; Ajala, A.; Mohammed, A. Application of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles immobilized on clay in wastewater treatment: A review. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varjani, S.; Rakholiya, P.; Shindhal, T.; Shah, A.V.; Ngo, H.H. Trends in dye industry effluent treatment and recovery of value added products. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 39, 101734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, D.A.; Scholz, M. Textile dye wastewater characteristics and constituents of synthetic effluents: A critical review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1193–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamd, A.; Shaban, M.; Al Mohamadi, H.; Dryaz, A.R.; Ahmed, S.A.; Al-Ola, K.A.A.; El-Mageed, H.R.A.; Soliman, N.K. Novel Wastewater Treatment by Using Newly Prepared Green Seaweed–Zeolite Nanocomposite. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 11044–11056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Advantages and disadvantages of techniques used for wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, F.; Abukhadra, M.R.; Shaban, M. Removal of safranin dye from water using polypyrrole nanofiber/Zn-Felayered double hydroxide nanocomposite (Ppy NF/Zn-Fe LDH) of enhanced adsorption and photocatalytic properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghabaee, S.; Behin, J.; Ansari, M.; Rajabi, L. Synthesis and characterization maleate-alumoxane nanoparticles for removal of reactive yellow 84 dye from aqueous solution. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 2061–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behin, J.; Farhadian, N. Response surface methodology and artificial neural network modeling of reactive red 33 decolorization by O3/UV in a bubble column reactor. Adv. Environ. Technol. 2016, 1, 33–44. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, S.; Gupta, B.; Srivastava, S.K.; Gupta, A.K. Recent advances on the removal of dyes from wastewater using various adsorbents: A critical review. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 4497–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhou, H.; Liu, G.; Qiao, J.; Wang, J.; Lu, H.; Yang, L.; Wu, Y. Methylene blue adsorption onto swede rape straw (Brassica napus L.) modified by tartaric acid: Equilibrium, kinetic and adsorption mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 125, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.; Gao, X.; Seliem, M.K.; Mobarak, M.; Dong, R.; Wang, X.; Fu, K.; Li, Q.; Li, Z. Efficient adsorption of anionic azo dyes on porous heterostructured MXene/biomass activated carbon composites: Experiments, characterization, and theoretical analysis via advanced statistical physics models. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imessaoudene, A.; Cheikh, S.; Hadadi, A.; Hamri, N.; Bollinger, J.-C.; Amrane, A.; Tahraoui, H.; Manseri, A.; Mouni, L. Adsorption Performance of Zeolite for the Removal of Congo Red Dye: Factorial Design Experiments, Kinetic, and Equilibrium Studies. Separations 2023, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Extross, A.; Waknis, A.; Tagad, C.V.V.; Gedam, P.D. Pathak. Adsorption of congo red using carbon from leaves and stem of water hyacinth: Equilibrium, kinetics, thermodynamic studies. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 1607–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, P.K.; Poonia, V.; Kumar, R.; Kataria, N.; Sharma, P.; Lamba, J.; Bhattacharya, P. Congo red dye removal using modified banana leaves: Adsorption equilibrium, kinetics, and reusability analysis. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 23, 101005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubangakene, N.O.; Elwardany, A.; Fujii, M.; Sekiguchi, H.; Elkady, M.; Shokry, H. Biosorption of Congo Red dye from aqueous solutions using pristine biochar and ZnO biochar from green pea peels. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 189, 636–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortada, W.I.; Nabieh, K.A.; Abdelghany, A.M. Efficient and Low-Cost Surfactant-Assisted Solid Phase Extraction Procedure For Removal Of Methylene Blue Using Natural Dolomite. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Asim, M.; Khan, T.A. Low cost adsorbents for the removal of organic pollutants from wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 113, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, A. Perspectives on green fabrication and sustainable utilization of adsorption materials for wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 187, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Wang, L.; Fu, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, H. Iron redox cycling in layered clay minerals and its impact on contaminant dynamics: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 159003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G. Sorption and reduction of hexavalent uranium by natural and modified silicate minerals: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 2441–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, D.; Hamd, A.; Soliman, N.K.; Elzanaty, A.M.; Alanazi, A.M.; Shaban, M.; El-Sayed, R.; Ahmed, S.A. Polyaniline/Glauconite Nanocomposite Adsorbent for Congo Red Dye from Textile Wastewater. Separations 2022, 9, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, C.; Kumari, N.; Jindal, R.; Gautam, R. Application of Efficient Naturally Occurring Clay Mineral for Fuchsin Basic Dye Removal. In Advances in Functional and Smart Materials; Prakash, C., Singh, S., Krolczyk, G., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, F.; Hassaballa, S.; Shaban, M.; Ahmed, A.M. Highly Efficient Photocatalyst Fabricated from the Chemical Recycling of Iron Waste and Natural Zeolite for Super Dye Degradation. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altowyan, A.S.; Shaban, M.; Faidey, Z.M.; Abdelkarem, K.; Al-Dossari, M.; Abd El-Gawaad, N.S.; Kordy, M.G.M. Design and Characterization of Zeolite/Serpentine Nanocomposite Photocatalyst for Solar Hydrogen Generation. Materials 2022, 15, 6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennifer, E.C.; Ifedi, O.P. Modification of natural bentonite clay using cetyl trimethyl-ammonium bromide and its adsorption capability on some petrochemical wastes. Chem. Int. 2019, 5, 269–273. [Google Scholar]
- Awwad, A.; Amer, M.; Al-aqarbeh, M.M. TiO2-kaolinite nanocomposite prepared from the Jordanian Kaolin clay: Adsorption and thermodynamics of Pb (II) and Cd (II) ions in aqueous solution. Chem. Int. 2020, 6, 168–178. [Google Scholar]
- Kausar, A.; Sher, F.; Hazafa, A.; Javed, A.; Sillanpää, M.; Iqbal, M. Biocomposite of sodium-alginate with acidified clay for wastewater treatment: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 1272–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasadi, A.; Khaili, F.; Awwad, A.M. Adsorption of Cu (II), Ni (II) and Zn (II) ions by nano kaolinite: Thermodynamics and kinetics studies. Chem. Int. 2019, 5, 226–258. [Google Scholar]
- Zehhaf, A.; Benyoucef, A.; Quijada, C.; Taleb, S.; Morallon, E. Algerian natural montmorillonites for arsenic (III) removal in aqueous solution. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selby, D. U-Pb zircon geochronology of the Aptian/Albian boundary implies that the GL-O international glauconite standard is anomalously young. Cretac. Res. 2009, 30, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobeih, M.M.; El-Shahat, M.F.; Osman, A.; Zaid, M.A.; Nassar, M.Y. Glauconite clay-functionalized chitosan nanocomposites for efficient adsorptive removal of fluoride ions from polluted aqueous solutions. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 25567–25585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, O.; Osman, H.H.; Sayed, S.A.; Shalabi, M.E.H. The removal of uranium and thorium from their aqueous solutions via glauconite. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 53, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrushka, I.M.; Gumnitskii, Y.M.; Malovanyi, M.S. External diffusion kinetics of the adsorption of anionic red 8C dye on glauconite. Theor. Found Chem. Eng. 2013, 47, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, J.; Hao, C.M.; Huang, T.C.P. The removal of metals and ammonium by natural glauconite. Environ. Int. 1987, 13, 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Younes, H.; El-Etriby, H.K.; Mahanna, H. High removal efficiency of reactive yellow 160 dye from textile wastewater using natural and modified glauconite. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 5659–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikova, L.A.; Bel’chinskaya, L.I.; Krupskaya, V.V.; Roessner, F.; Zhabin, A.V. In Effect of acid and alkaline treatment on physicalchemical properties of surface of natural glauconite. Sorpt. Chromatogr. Process. 2015, 15, 730–740. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption isotherm models: Classification, physical meaning, application and solving method. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.A.; Vemparala, B.; Madras, G. Adsorption kinetics of dyes and their mixtures with Co3O4–ZrO2 composites. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2684–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Liu, Y.; Tan, X.; Wang, S.; Zeng, G.; Zheng, B.; Li, T.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, W. Effect of porous zinc–biochar nanocomposites on Cr (VI) adsorption from aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 35107–35115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, M.Y.; Ahmed, I.S.; Raya, M.A. A facile and tunable approach for synthesis of pure silica nanostructures from rice husk for the removal of ciprofloxacin drug from polluted aqueous solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 282, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar, S.; Mishra, D.; Agrawal, A.; Sahu, K.K. Physical and chemical characterization and recovery of potash fertilizer from glauconitic clay for agricultural application. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 143, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Jin, Q.; Wang, X.; Yang, J. Adsorption studies of a water soluble dye, Reactive Red MF-3B, using sonication-surfactant-modified attapulgite clay. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 143, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, K.; Youssef, M.; El-Rahiem, F.A.; Hassan, M. Dye removal using some surface modified silicate minerals. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2014, 24, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indhu, S.; Muthukumaran, K. Removal and recovery of reactive yellow 84 dye from wastewater and regeneration of functionalised Borassus flabellifer activated carbon. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3111–3121. [Google Scholar]
- Younes, H.; Mahanna, H.; El-Etriby, H.K. Fast adsorption of phosphate (PO4−) from wastewater using glauconite. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 80, 1643–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.S.; El Kammar, A.M.; Guda, A.M.; Boulos, T.R.; Saleh, A. Characterization and mineral beneficiation of Egyptian glauconite for possible industrial use. Part. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oghenejohoh, K.; Ohimor, E. Effect of sodium hydroxide concentration on the physical properties of zeolite produced from local clay found in Nigeria’s Niger Delta. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2011, 56, 445–452. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, Y.C. Optimization of parameters for adsorption of methylene blue on a low-cost activated carbon. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.S.; Soliman, N.; Abdelrheem, D.A.; Ramadan, A.A.; Elghandour, A.H.; Ahmed, S.A. Adsorption of Cd2+ and Cr3+ ions from aqueous solutions by using residue of Padina gymnospora waste as promising low-cost adsorbent. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevim, F.; Lacin, O.; Ediz, E.F.; Demir, F. Adsorption capacity, isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies on adsorption behavior of malachite green onto natural red clay. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2021, 40, e13471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, M.; Demirbaş, Ö.; Çelikçapa, S.; Doğan, M. Sorption of acid red 57 from aqueous solution onto sepiolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 116, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Zafar, S.; Buzdar, A.R.; Azhar, M.F.; Hassan, W.; Aziz, A. Use of citrus sinensis leaves as a bioadsorbent for removal of congo red dye from aqueous solution. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2018, 27, 4679–4688. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.I.; Zafar, S.; Khan, M.A.; Mumtaz, F.; Prapamonthon, P.; Buzdar, A.R. Bougainvillea glabra leaves for adsorption of congo red from wastewater. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2018, 27, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar]
- Arnata, I.W.; Suprihatin, S.; Fahma, F.; Richana, N.; Sunarti, T.C. Adsorption of anionic congo red dye by using cellulose from sago frond. Poll Res. 2019, 38, 43–53. [Google Scholar]
- Hamzeh, Y.; Ashori, A.; Azadeh, E.; Abdulkhani, A. Removal of Acid Orange 7 and Remazol Black 5 reactive dyes from aqueous solutions using a novel biosorbent. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2012, 32, 1394–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellaoui, L.; Guedidi, H.; Knani, S.; Reinert, L.; Duclaux, L.; Ben Lamine, A. Application of statistical physics formalism to the modeling of adsorption isotherms of ibuprofen on activated carbon. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2015, 387, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raval, N.P.; Kumar, M. Geogenic arsenic removal through core–shell based functionalized nanoparticles: Groundwater in-situ treatment perspective in the post–COVID anthropocene. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.V.; Porkodi, K. Mass transfer, kinetics and equilibrium studies for the biosorption of methylene blue using Paspalum notatum. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, N.F.; Barbosa, C.M.; Rodríguez-Díaz, J.M.; Duarte, M.M. Removal of naphthenic acids using activated charcoal: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 1405–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J., Jr.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. 1963, 89, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Khan, A.; Anwar, N.; Naeem, M. A comparative study of the adsorption of congo red dye on rice husk, rice husk char and chemically modified rice husk char from aqueous media. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2020, 34, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustus, E.N.; Samuel, A.S.; Nimibofa, A.; Donbebe, W. Removal of congo red from aqueous solutions using fly ash modified with hydrochloric acid. Br. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2017, 20, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litefti, K.; Freire, M.S.; Stitou, M.; González-Álvarez, J. Adsorption of an anionic dye (Congo red) from aqueous solutions by pine bark. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
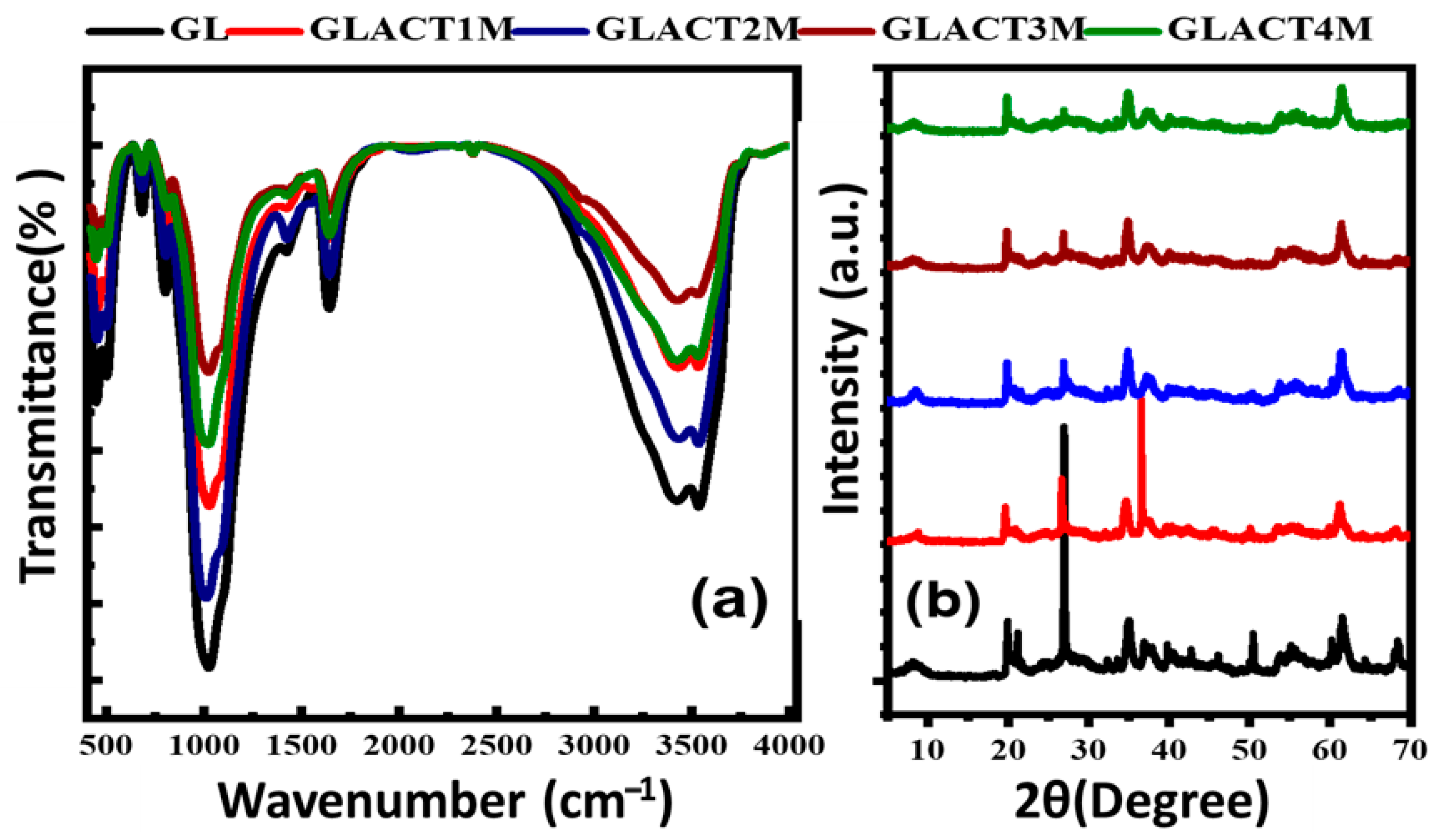

| Peak Position (cm−1) | Functional Group | Ref. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GL | GLACT1M | GLACT2M | GLACT3M | GLACT4M | ||
| 445–498 | 450–488 | 450–496 | 450–496 | 445–496 | Si–O–Fe & Si–O–Mg | [35,39,46,47,48,49] |
| 680 | 681 | 681 | 681 | 680 | OH or Si–O bond | |
| 800 | 794 | 803 | 802 | 809 | Al Fe–OH | |
| 1023 | 1025 | 1009 | 1022 | 1018 | Si–O–Si | |
| 1421 | 1421–1555 | 1424 | 1423–1514 | 1422 | C–H | |
| 1640 | 1640 | 1641 | 1640 | 1641 | H–O–H & C = O | |
| 3422–3533 | 3420–3532 | 3430–3533 | 3425–3530 | 3424–3531 | O–H and/or N–H | |
| Langmuir Isotherm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorbent | Qo (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | RL | R2 |
| GL | 13.2 | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.9725 |
| GLACT1M | 13.1 | 0.22 | 0.14 | 0.9850 |
| GLACT2M | 11.9 | 0.33 | 0.11 | 0.9687 |
| GLACT3M | 11.7 | 0.05 | 0.43 | 0.9430 |
| GLACT4M | 5.1 | 0.15 | 0.21 | 0.9302 |
| Freundlich Isotherm | ||||
| Adsorbent | 1/n | Kf | R2 | |
| GL | 2.4172 | 3.59 | 0.9916 | |
| GLACT1M | 2.2048 | 3.13 | 0.9951 | |
| GLACT2M | 2.7400 | 3.87 | 0.9501 | |
| GLACT3M | 1.3716 | 0.75 | 0.9703 | |
| GLACT4M | 2.0240 | 0.93 | 0.8202 | |
| Temkin Isotherm | ||||
| Adsorbent | B (J/mol) | KT (L/mole) | R2 | |
| GL | 2.7463 | 3.0359 | 0.9552 | |
| GLACT1M | 2.8728 | 2.2784 | 0.9823 | |
| GLACT2M | 2.3737 | 4.4942 | 0.9257 | |
| GLACT3M | 2.4943 | 0.5774 | 0.9599 | |
| GLACT4M | 1.2315 | 1.2086 | 0.8078 | |
| Adsorbent | Conditions | Reference | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dye | Co (mg/L) | Dose (g/L) | pH | Time (min) | Qm (mg/g) | R% | ||
| Chemically modified rice husk char | CR | 80 | 0.5 | 7 | 10–50 | 2.04 | 90% | [65] |
| Fly ash modified with 1 M, 3 M, 4 M HCl | CR | 25–100 | 0.2 | 7 | 60 | 0.004, 0.74, 0.06 | [66] | |
| Phosphate-modified kaolinite | CR | 25–300 | 0.1 | 3–8 | 5–600 | - | 65% | [10] |
| Thermally activated GL | RY160 | 10–80 | 1 | 1 | 180 | - | 64% | [39] |
| Acetic acid-activated GL | RY160 | 10–80 | 1 | 1 | 180 | - | 81% | [39] |
| GL/Polyaniline composite | CR | 5–25 | 0.02 | 7 | 420 | 14.1 | 86% | [25] |
| Pinus pinaster bark | CR | 5 | 10 | 2 | 10,080 (7 days) | 1.6 | 100 | [67] |
| GL | CR | 5–25 | 0.02 | 7 | 360 | 13.2 | 79.6% | Present study |
| GLACT1M | 13.1 | |||||||
| GLACT2M | 11.9 | |||||||
| GLACT3M | 11.7 | |||||||
| GLACT4M | 5.1 | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamd, A.; Salah, D.; Alyafei, H.F.; Soliman, N.K.; El-Reedy, A.A.M.; Elzanaty, A.M.; Al-Saeedi, S.I.; Al-Ghamdi, A.; Shaban, M.; El-Sayed, R.; et al. NaOH-Activated Natural Glauconite for Low-Cost Adsorption of Congo Red Dye. Water 2023, 15, 3753. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213753
Hamd A, Salah D, Alyafei HF, Soliman NK, El-Reedy AAM, Elzanaty AM, Al-Saeedi SI, Al-Ghamdi A, Shaban M, El-Sayed R, et al. NaOH-Activated Natural Glauconite for Low-Cost Adsorption of Congo Red Dye. Water. 2023; 15(21):3753. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213753
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamd, Ahmed, Doaa Salah, Huda Fadol Alyafei, Nofal K. Soliman, Ahmed A. M. El-Reedy, Ali M. Elzanaty, Sameerah I. Al-Saeedi, Azza Al-Ghamdi, Mohamed Shaban, Refat El-Sayed, and et al. 2023. "NaOH-Activated Natural Glauconite for Low-Cost Adsorption of Congo Red Dye" Water 15, no. 21: 3753. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213753






