Reconstruction of Snow Cover in Kaidu River Basin via Snow Grain Size Gap-Filling Based on Machine Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Preprocessing
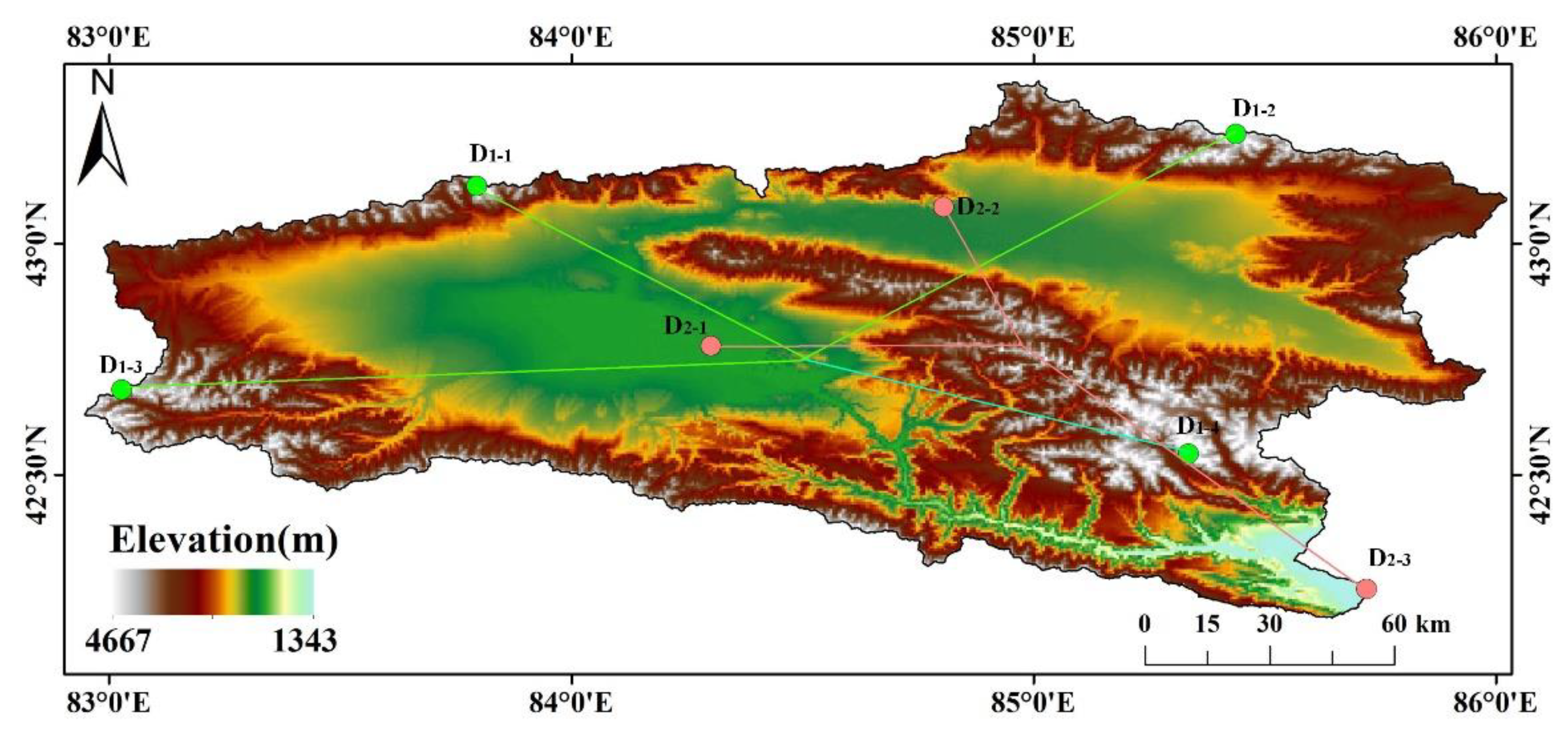
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Satellite Remote Sensing Data
2.3. Geographic Data
2.4. Ground Observation
3. Methodology
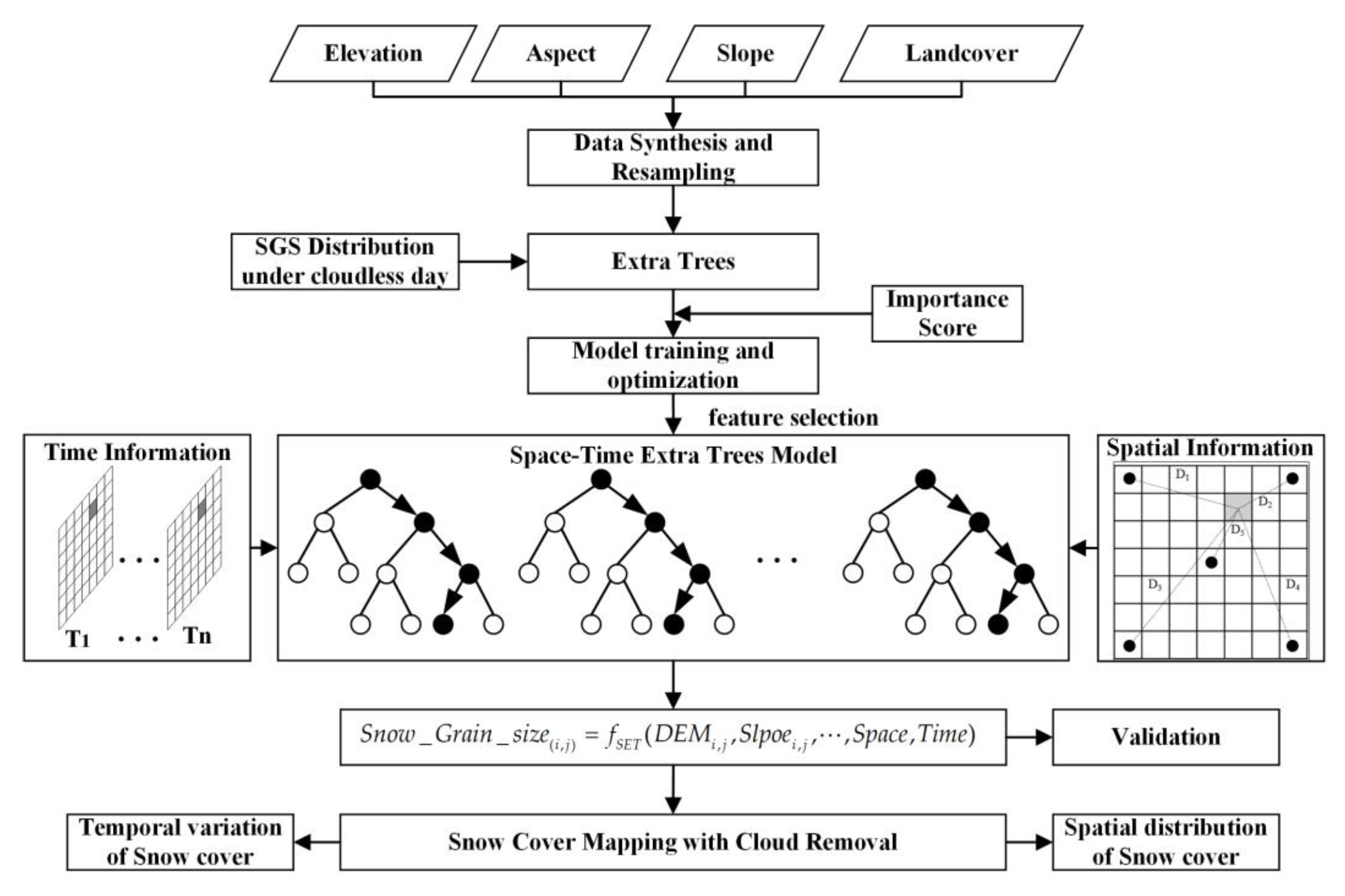
3.1. Construction of Space–Time Extra Trees Model
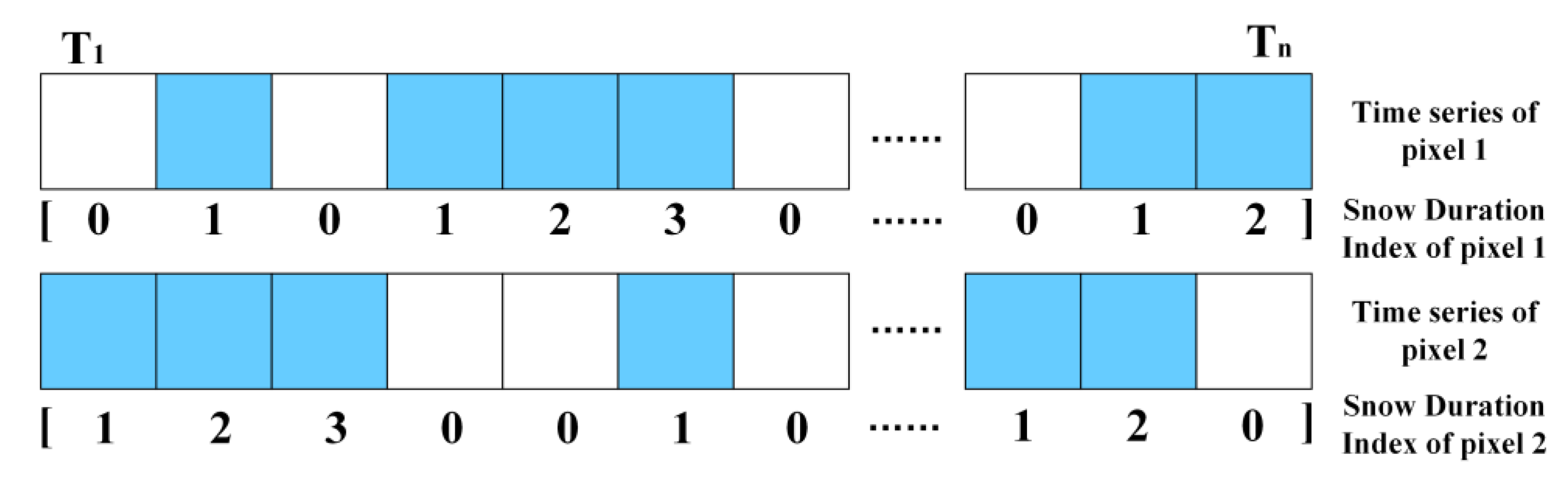
3.2. Design of Temporal and Spatial Dimensional Information
3.3. Applicability Evaluation and Factor Optimization of the Model
3.4. Snow Recognition of Landsat
3.5. Metrics for Evaluating the Accuracy of Snow after Cloud Removal
4. Results
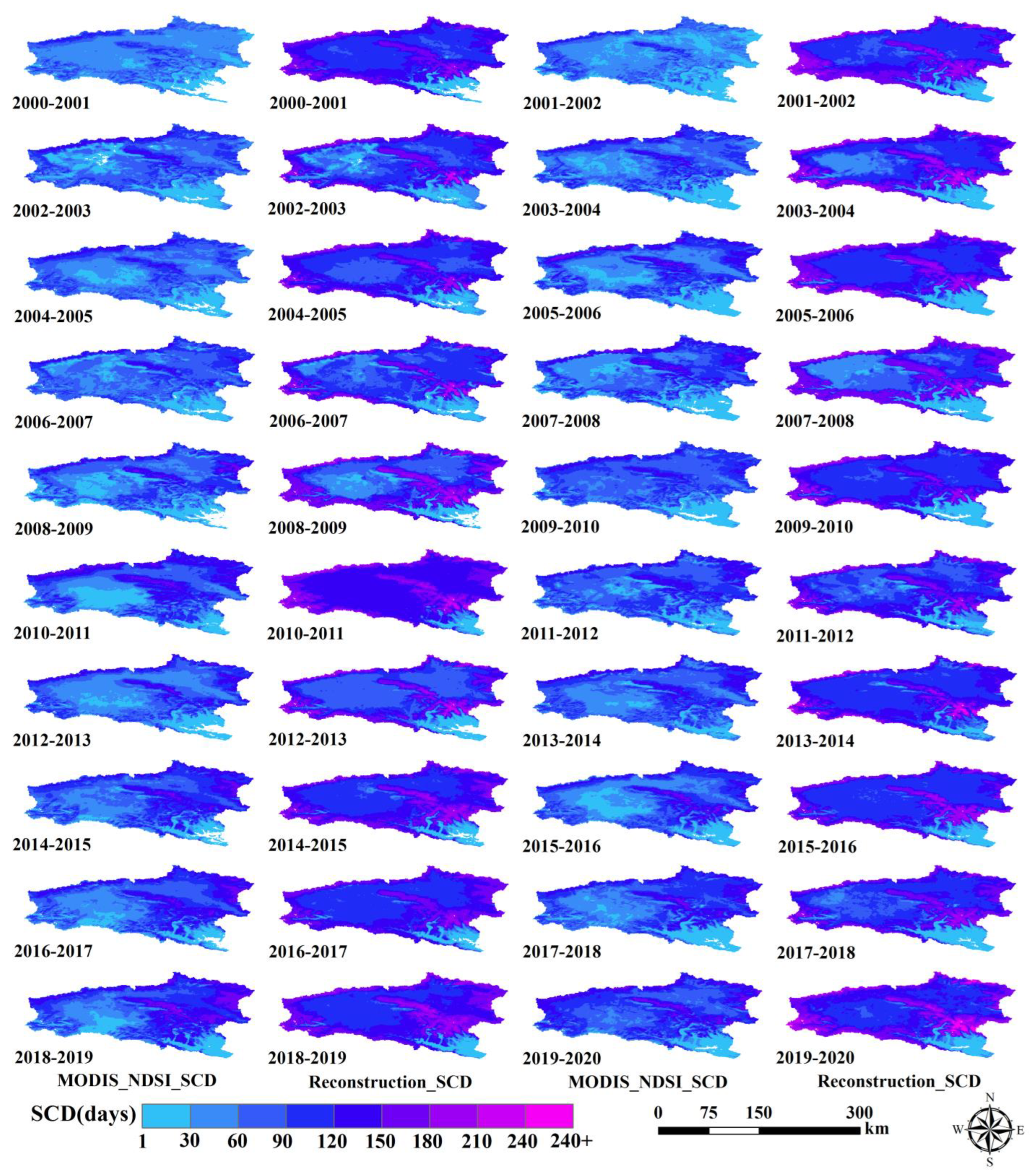
4.1. Mapping of Snow Cover Reconstruction
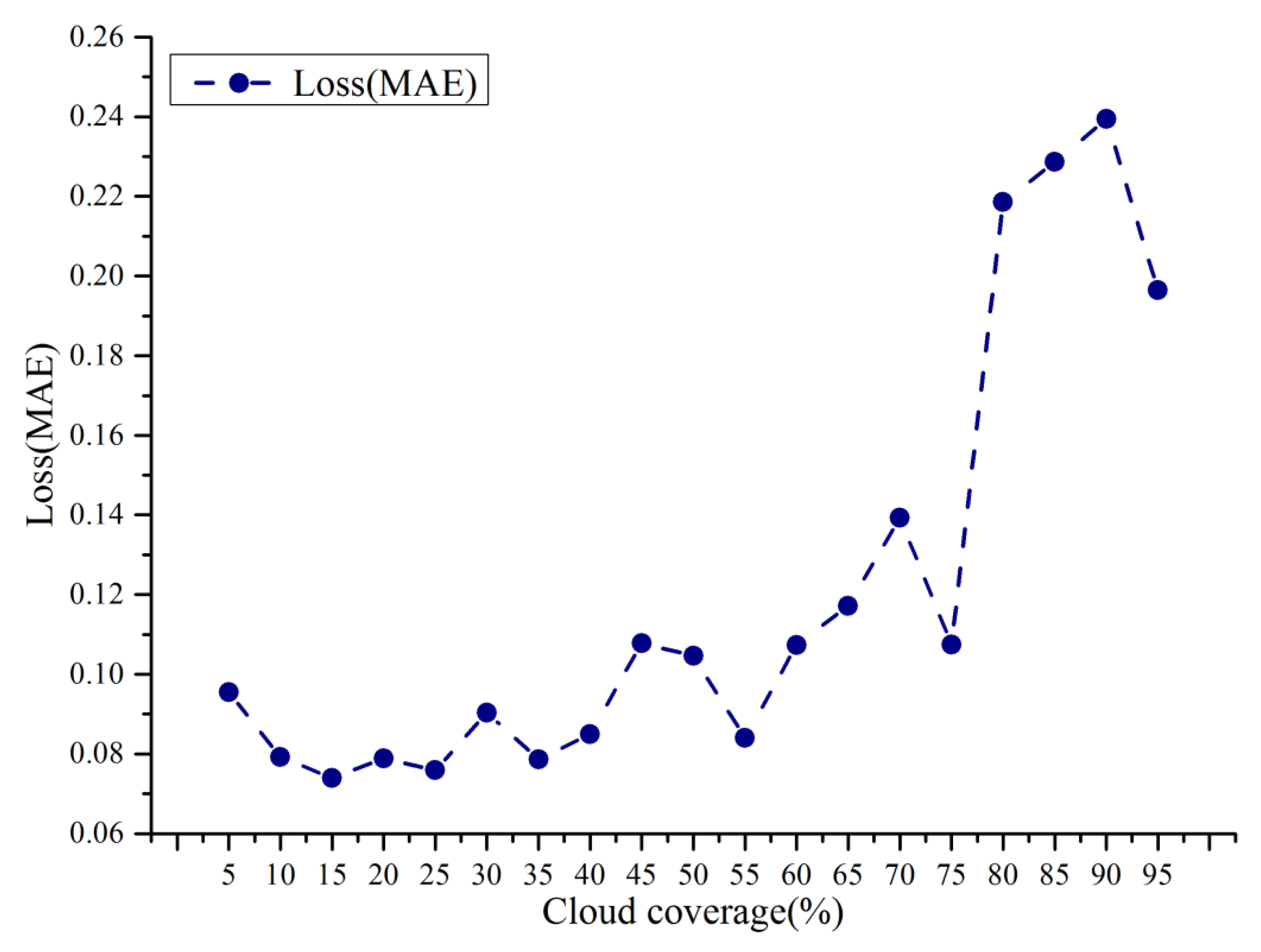
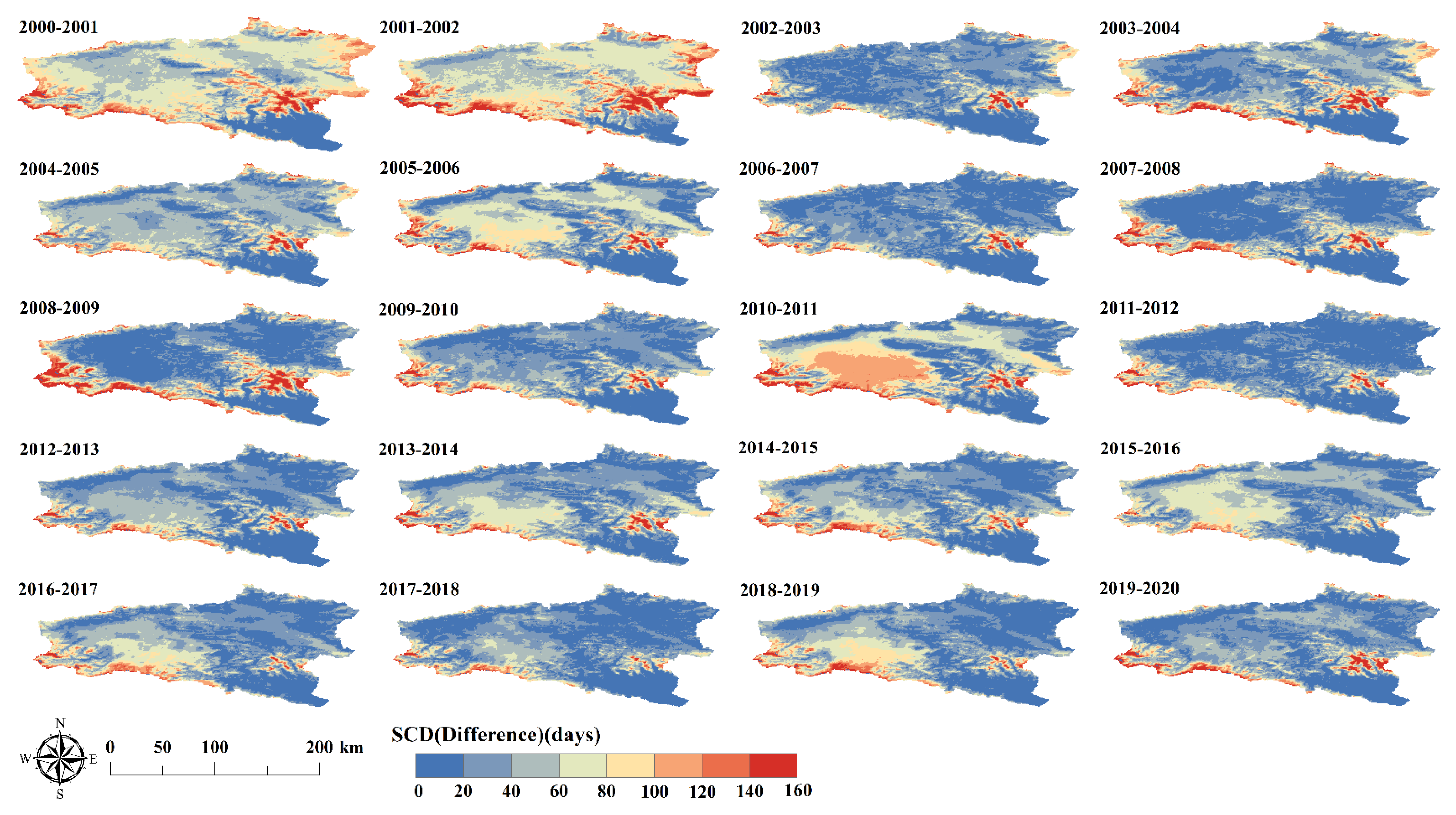
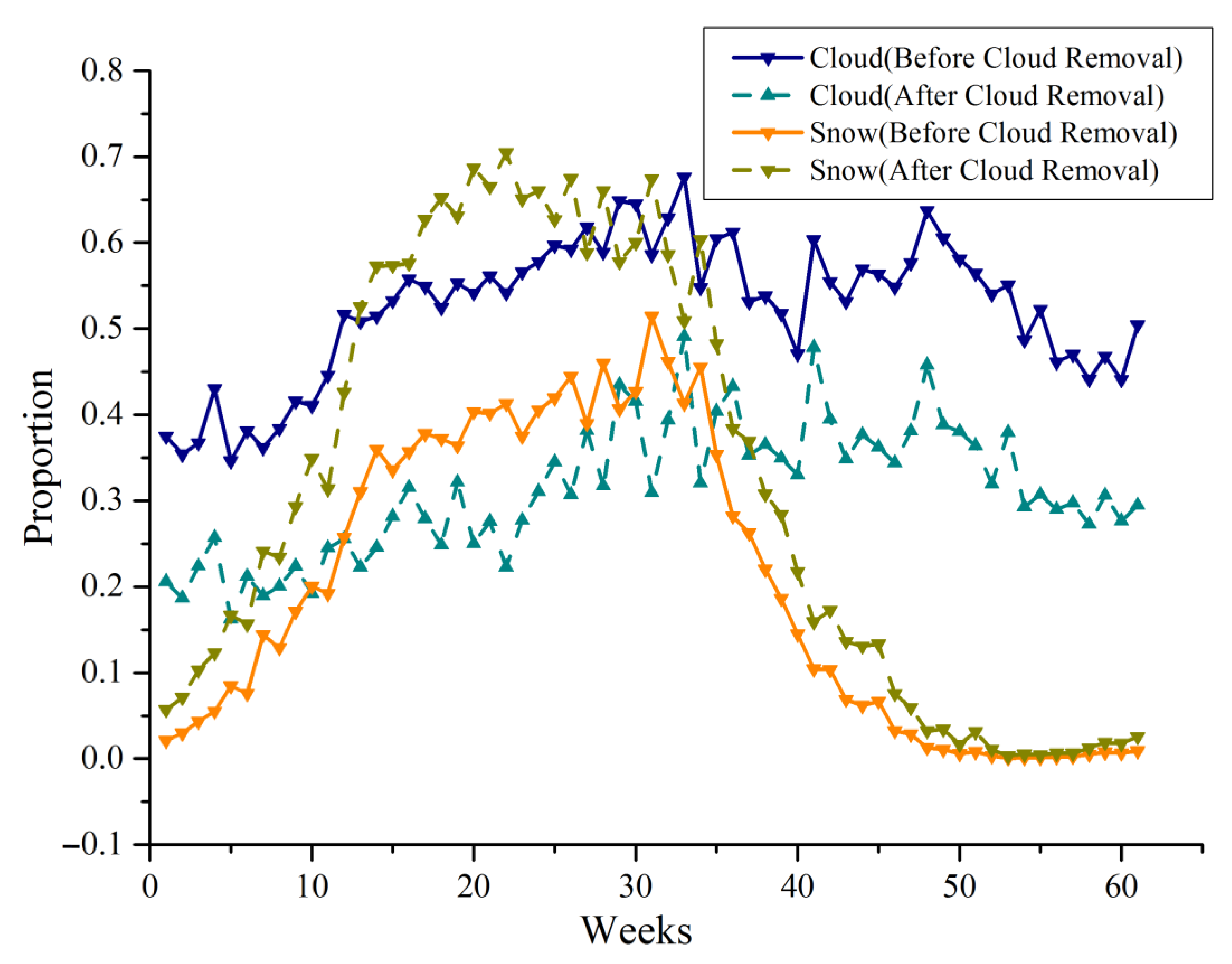
4.2. Accuracy of Snow Reconstruction and Cloud Coverage Variations
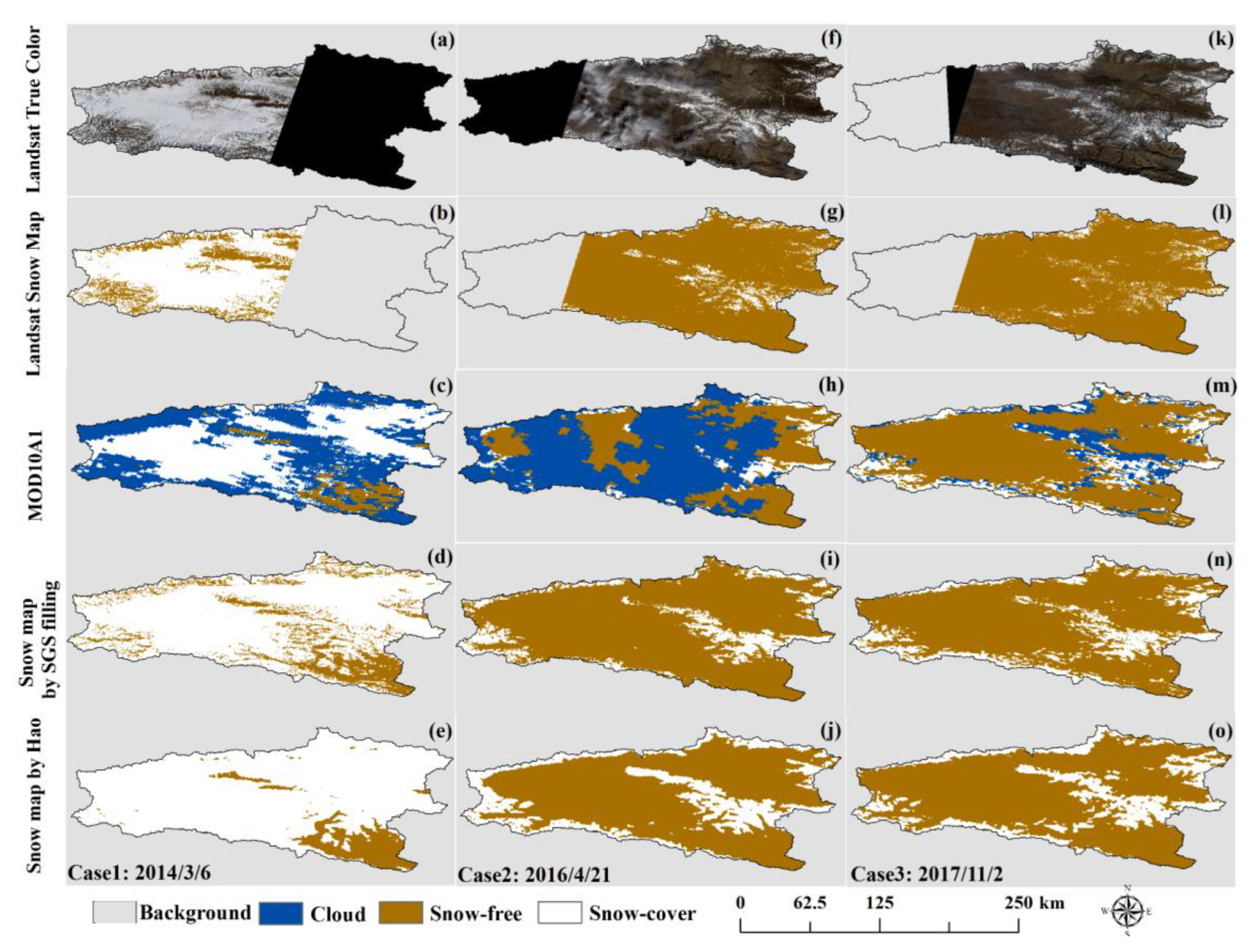
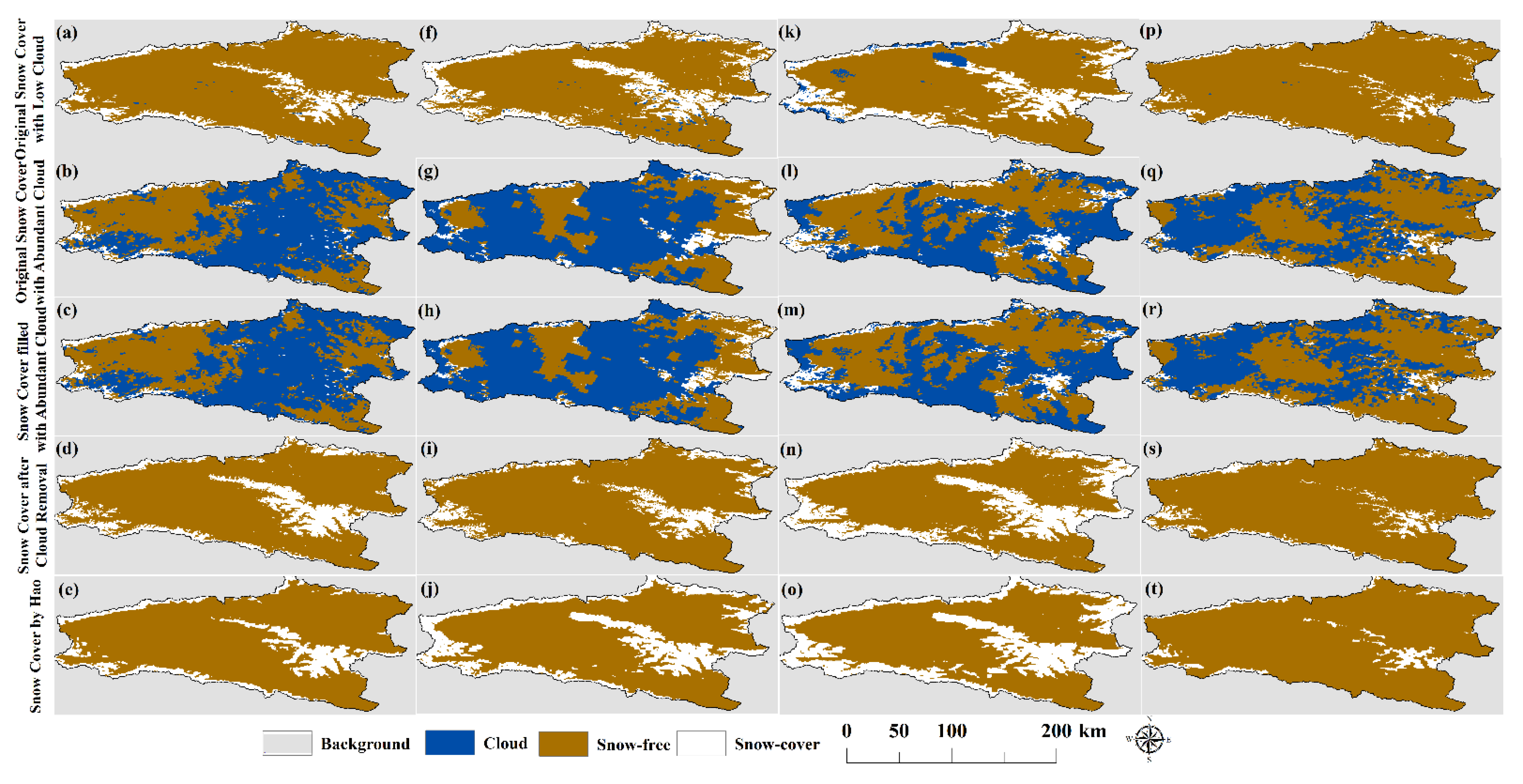
4.3. Validation of Individual Snow Cover Mapping
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, S.X.; Woodcock, C.E. Improvement and expansion of the Fmask algorithm: Cloud, cloud shadow, and snow detection for Landsats 4-7, 8, and Sentinel 2 images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Li, Q.; Nie, W.; Ye, C. A depth information-based method to enhance rainfall-induced landslide deformation area identification. Measurement 2023, 219, 113288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A.; Salomonson, V.V. Development of methods for mapping global snow cover using moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 54, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Su, F.; Yang, D.; Tong, K.; Meng, F.; Kan, B. Spatiotemporal variation of snow cover over the Tibetan Plateau based on MODIS snow product, 2001–2014. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 708–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, G.; Che, T.; Yan, W.; Ye, M.; Ma, N. Ground-based evaluation of MODIS snow cover product V6 across China: Implications for the selection of NDSI threshold. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2712–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Ba, Z.; Liang, J. A procedure for 3D simulation of seismic wave propagation considering source-path-site effects: Theory, verification and application. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 51, 2925–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Li, A.; Liu, Q.; Huang, C. Cloud and snow discrimination for CCD images of HJ-1A/B constellation based on spectral signature and spatio-temporal context. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, J.; Meng, X.; Zhou, B.; Fang, G.; Spencer, B.F. Discrimination Between Dry and Water Ices by Full Polarimetric Radar: Implications for China’s First Martian Exploration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 61, 5100111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jing, Y.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. The recent developments in cloud removal approaches of MODIS snow cover product. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 2401–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Z.; Du, L.; Lu, X.; Chen, J.; Cao, Z. Smoothed Lv Distribution Based Three-Dimensional Imaging for Spinning Space Debris. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5113813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gafurov, A.; Bárdossy, A. Cloud removal methodology from MODIS snow cover product. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 1361–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Chen, J.; Sun, Q.; Li, Z.; Tan, W.; Wei, Y. Reconstructing of High-Spatial-Resolution Three-Dimensional Electron Density by Ingesting SAR-Derived VTEC Into IRI Model. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4508305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Menzel, L. Producing cloud-free MODIS snow cover products with conditional probability interpolation and meteorological data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Meng, X.; Zhang, L. An integrated framework for the spatio–temporal–spectral fusion of remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 7135–7148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Deng, J.; Xie, H.; Liang, T. Spatio-temporal change of snow cover and its response to climate over the Tibetan Plateau based on an improved daily cloud-free snow cover product. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 169–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Wang, L.; Keim, B.D.; Konsoer, K.; Yin, Z.; Liu, M.; Zheng, W. Spatial and wavelet analysis of precipitation and river discharge during operation of the Three Gorges Dam, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Gao, X.G.; Chu, W.; Sorooshian, S. Estimation of daily cloud-free, snow-covered areas from MODIS based on variational interpolation. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, 9523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggio, L.; Gimona, A. Sequence-based mapping approach to spatio-temporal snow patterns from MODIS time-series applied to Scotland. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 34, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Fu, W.X.; Shen, H.F.; Huang, C.L.; Zhang, L.P. Monitoring snow cover variability (2000–2014) in the Hengduan Mountains based on cloud-removed MODIS products with an adaptive spatio-temporal weighted method. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yu, B.; Wu, J.; Kang, E.L.; Xu, M.; Wang, S.; Klein, A.; Chen, Y. Improving MODIS snow products with a HMRF-based spatio-temporal modeling technique in the Upper Rio Grande Basin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 568–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Guo, H.; Xie, P.Y.; Wang, J.; Hao, X.H. A Condi-tional Probability Interpolation Method Based on a Space-Time Cube for MODIS Snow Cover Products Gap Filling. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, W.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, P.; Wang, H.; Chen, S. Binary and Fractional MODIS Snow Cover Mapping Boosted by Machine Learning and Big Landsat Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4305714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; He, T.; Liang, S.; Zhao, T. Improving Fractional Snow Cover Retrieval from Passive Micwave Data Using a Radiative Transfer Model and Machine Learning Method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 4304215. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y. Extraction of snow cover from high-resolution remote sensing imagery using deep learing on a smll dataset. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 11, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shean, D. Improving Mountain Snow and Land Cover Mapping Using Very-High-Resolution (VHR) Optical Satellite Images and Random Forest Machine Learning Models. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Huang, X.; Li, X.; Liang, T. MODIS fractional snow cover mapping using machine learning technology in a mountainous area. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, M.; Lin, H.; Liu, J.; Li, Y. Satellite Image for Cloud and Snow Recognition Based on Lightweight Feature Map Attention Network. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, B. Quantifying the effects of climate variability and human activities on runoff for Kaidu River Basin in arid region of northwest China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 111, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiyan, C.; Yaning, C.; Weihong, L.; Xinming, H.; Yupeng, L.; Qifei, Z. Identifying evaporation fractionation and streamflow components based on stable isotopes in the Kaidu River Basin with mountain–oasis system in north-west China. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 2423–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domine, F.; Albert, M.; Huthwelker, T.; Jacobi, H.W.; Kokhanovsky, A.A.; Lehning, M.; Picard, G.; Simpson, W.R. Snow physics as relevant to snow photochemistry. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 171–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.M.; Wang, N.L. Progress in the research on snow grain size retrieved from remote Sensing. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2011, 33, 539–545. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Feng, X.; Xiao, P.; Ye, N.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, Y. Snow grain-size estimation over mountainous areas from modis imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 15, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Cheng, C.; Qi, P.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. Retrieval of Snow Grain Size and Albedo Using Two Radiative Transfer Models. Acta Opt. Sin. 2020, 40, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Hao, X.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Zhao, H.; Gao, Y.; Shao, D.; Zhong, X.; Li, H. Retrieval and analysis of spatiotemporal variation of snow black carbon and snow grain size in Northern Xinjiang based on MODIS data. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2019, 41, 1192–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.H.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, P.; Huang, C.L. The measurement and retrieval of the spectral reflectance of different snow grain size on Northern Xinjiang, China. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2013, 33, 190–195. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, W.P. Snow Grain and Snow Fraction Retrieval Algorithm based on Asymptotic Radiative Transfer Model. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2017, 32, 64–70. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L.; Chen, S. Cloud removal method for snow cover products based on denoising autoencoder artificial neural network. J. Nanjing Univ. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2023, 15, 169–179. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, M.; Liang, T. AMSR2 snow depth downscaling algorithm based on a multifactor approach over the Tibetan Plateau, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Ma, N.; Zhang, Y. Development of a fine-resolution snow depth product based on the snow cover probability for the Tibetan Plateau: Validation and spatial–temporal analyses. J. Hydrol. 2022, 604, 127027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Tian, W.; Liu, Q.; Ma, G.; Kan, X.; Chu, Y. Downscaling snow depth mapping by fusion of microwave and optical remote-sensing data based on deep learning. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Xiao, L.; Wang, J.; Tian, W.; Tan, H. Snow cover mapping for mountainous areas by fusion of MODIS L1B and geographic data based on stacked denoising auto-encoders. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2018, 57, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurts, P.; Ernst, D.; Wehenkel, L. Extremely randomized trees. Mach. Learn. 2006, 63, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, B.; Ma, C.; Wang, T. WRF-CMAQ-MOS Studies Based on Extremely Randomized Trees. Acta Meteorol. Sin 2018, 76, 779–789. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, W. Research on Fault Early Warning Algorithm of Reheater in Thermal Power Plant Based on Extreme Random Tree. J. Shanghai Univ. Electr. Power 2020, 36, 445–450. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Lyapustin, A.; Sun, L.; Peng, Y.; Xue, W.; Sun, T.; Cribb, M. Reconstructing 1-km-resolution high-quality PM2. 5 data records from 2000 to 2018 in China: Spatiotemporal variations and policy implications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Ma, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Tian, W.; Kan, X. Accelerated decline of snow cover in China from 1979 to 2018 observed from space. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozier, J. Spectral signature of alpine snow cover from the Landsat Thematic Mapper. Remote Sens. Environ. 1989, 28, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.G.; Barnett, A.C. Validation of daily MODIS snow cover maps of the Upper Rio Grande River Basin for the 2000–2001 snow year. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Huang, G.; Zheng, Z.; Sun, X.; Ji, W.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Wang, X. Development and validation of a new MODIS snow-cover-extent product over China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 1937–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Properties | Variable Description |
|---|---|
| Numerical Range | 0–1000 μm (0: Snow-free, Others: Snow) |
| Data Format | GeoTiff |
| Space Scope | 82.33° E~88.12° E; 42.03° N~44.37° N |
| Spatial Resolution | 0.005° (500 m) |
| Time Range | 27 February 2000~7 May 2020 |
| Time Resolution | Daily |
| Channel 1 | Channel 2 | Image Classification |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | Cloud |
| 0 | 1 | Snow-free |
| 1~1000 μm | 0 | Snow-cover |
| 1 | 1 | None |
| Ground True | Snow | Snow-Free | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Snow Reconstruction | |||
| Snow | TP | FP | |
| Snow-free | FN | TN | |
| The Value Interval for Kappa | The Consistency Level of the Image |
|---|---|
| 0 < Kappa ≤ 0.20 | Very low consistency |
| 0.20 < Kappa ≤ 0.40 | General consistency |
| 0.40 < Kappa ≤ 0.60 | Medium consistency |
| 0.60 < Kappa ≤ 0.80 | High consistency |
| 0.80 < Kappa ≤ l | Almost complete consistency |
| Methods | RMSE (μm) | MAE (μm) |
|---|---|---|
| Classification and Regression Tree, CART | 68.048 | 49.934 |
| K-Nearest Neighbor, KNN | 57.108 | 42.516 |
| Random Forest, RF | 55.822 | 41.692 |
| Ridge Regression, RR | 57.054 | 45.048 |
| Support Vector Regression, SVR | 56.710 | 42.880 |
| Denoising Autoencoder Artificial Neural Network, DAANN | 54.186 | 40.852 |
| Space–Time Extra Randomized Trees | 52.751 | 40.109 |
| Accuracy (%) | Case 1: 6 March 2014 | Case 2: 21 April 2016 | Case 3: 2 November 2017 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Reconstruction | After Reconstruction | Before Reconstruction | After Reconstruction | Before Reconstruction | After Reconstruction | |
| OA | 64.15 | 81.03 | 38.26 | 88.45 | 77.46 | 85.23 |
| Precision | 65.28 | 82.86 | 4.38 | 35.74 | 82.48 | 88.53 |
| Recall | 85.79 | 95.28 | 34.24 | 65.16 | 81.24 | 86.68 |
| F1-Score | 74.14 | 88.64 | 7.77 | 46.16 | 81.86 | 87.60 |
| Kappa | 17.79 | 32.84 | 6.83 | 86.74 | 81.46 | 86.93 |
| Hydrological Year | Trainable Days | Un-Trainable Days | SCD of MODIS | SCD of Reconstructed Snow | SCD of the Station |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000–2001 | 216 | 149 | 46 | 104 | 159 |
| 2001–2002 | 244 | 121 | 22 | 83 | 111 |
| 2002–2003 | 234 | 131 | 3 | 3 | 16 |
| 2003–2004 | 252 | 114 | 44 | 72 | 78 |
| 2004–2005 | 229 | 136 | 59 | 103 | 144 |
| 2005–2006 | 246 | 119 | 58 | 108 | 148 |
| 2006–2007 | 243 | 122 | 29 | 40 | 49 |
| 2007–2008 | 248 | 118 | 31 | 39 | 29 |
| 2008–2009 | 227 | 138 | 58 | 75 | 110 |
| 2009–2010 | 225 | 140 | 67 | 90 | 127 |
| 2010–2011 | 256 | 109 | 78 | 142 | 173 |
| 2011–2012 | 238 | 127 | 69 | 77 | 89 |
| 2012–2013 | 236 | 129 | 39 | 74 | 124 |
| 2013–2014 | 250 | 115 | 69 | 99 | 137 |
| 2014–2015 | 225 | 140 | 63 | 87 | 116 |
| 2015–2016 | 215 | 150 | 35 | 94 | 134 |
| 2016–2017 | 231 | 134 | 64 | 96 | 141 |
| 2017–2018 | 229 | 136 | 54 | 92 | 146 |
| 2018–2019 | 228 | 137 | 53 | 94 | 136 |
| 2019–2020 | 221 | 144 | 85 | 122 | 146 |
| Mean days | 234.65 | 130.45 | 51.30 | 84.7 | 115.65 |
| Snow Cover Data | Annual Average Accuracy (%) | Average Annual Coverage (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OA | Precision | Recall | F1 | Snow | Cloud | Snow-Free | |
| MODIS Snow | 93.69 | 82.54 | 86.67 | 84.55 | 21.52 | 52.46 | 26.02 |
| Reconstructed snow | 92.96 | 83.91 | 89.02 | 86.39 | 33.84 | 34.41 | 31.75 |
| Accuracy (%) | Validation Day 1 | Validation Day 2 | Validation Day 3 | Validation Day 4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Our’s | Hao’s | Our’s | Hao’s | Our’s | Hao’s | Our’s | Hao’s | |
| OA | 92.89 | 94.43 | 86.99 | 92.58 | 91.44 | 89.45 | 95.77 | 94.96 |
| Precision | 70.12 | 75.23 | 87.55 | 78.54 | 80.34 | 69.02 | 73.13 | 63.72 |
| Recall | 90.40 | 87.65 | 54.69 | 91.52 | 90.84 | 96.62 | 76.21 | 65.80 |
| F1-Score | 78.98 | 80.97 | 67.32 | 84.53 | 85.27 | 80.52 | 74.64 | 64.75 |
| Kappa | 74.78 | 77.72 | 59.74 | 79.69 | 79.26 | 73.56 | 72.33 | 62.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, L.; Ma, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Kan, X. Reconstruction of Snow Cover in Kaidu River Basin via Snow Grain Size Gap-Filling Based on Machine Learning. Water 2023, 15, 3726. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213726
Zhu L, Ma G, Zhang Y, Wang J, Kan X. Reconstruction of Snow Cover in Kaidu River Basin via Snow Grain Size Gap-Filling Based on Machine Learning. Water. 2023; 15(21):3726. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213726
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Linglong, Guangyi Ma, Yonghong Zhang, Jiangeng Wang, and Xi Kan. 2023. "Reconstruction of Snow Cover in Kaidu River Basin via Snow Grain Size Gap-Filling Based on Machine Learning" Water 15, no. 21: 3726. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213726





