Provenance Indication of Rare Earth Elements in Lake Particulates from Environmentally Sensitive Regions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
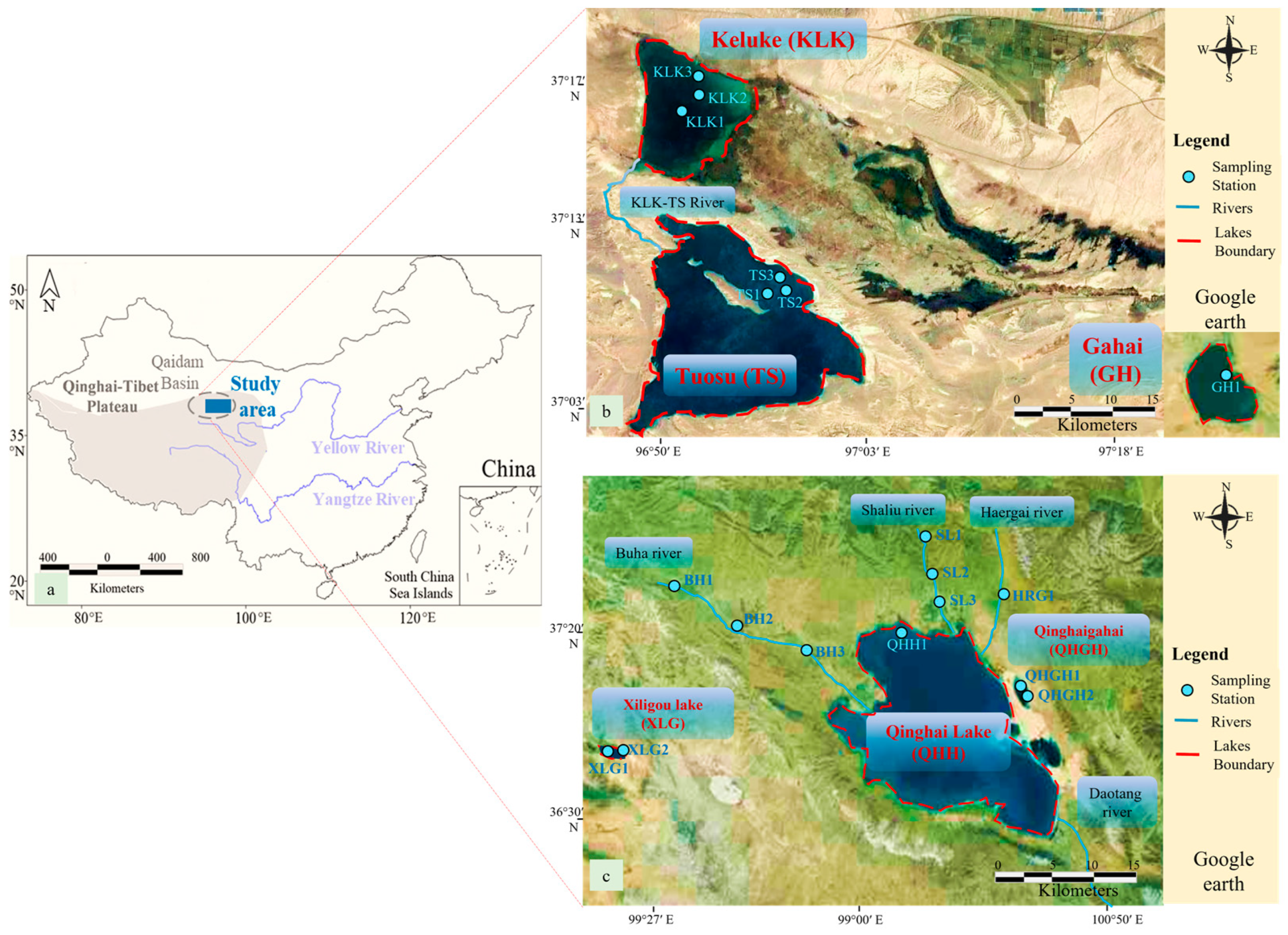
2. Study Area and Methodology
2.1. Hydrogeological Conditions
2.2. Sampling Design and REEs Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Particulate Matter Concentrations and Chemical Components in Two Regions
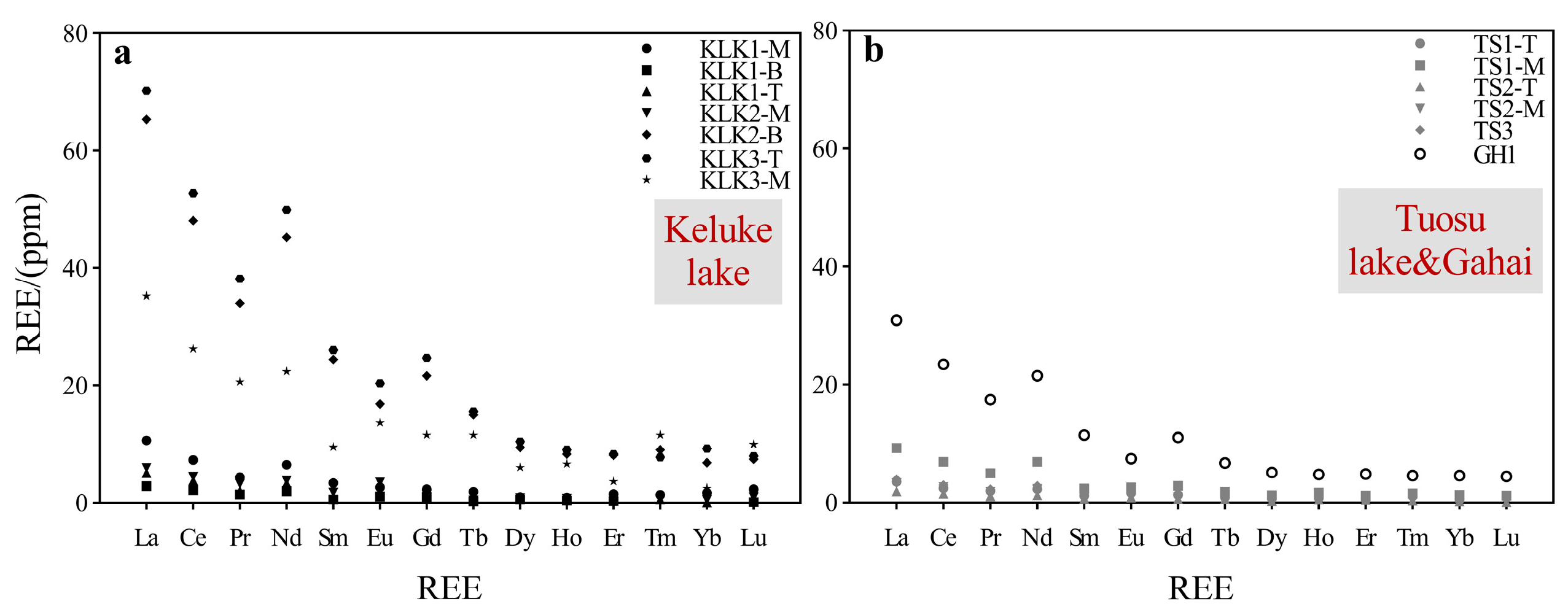
3.2. Region I: Distribution Characteristics of REEs
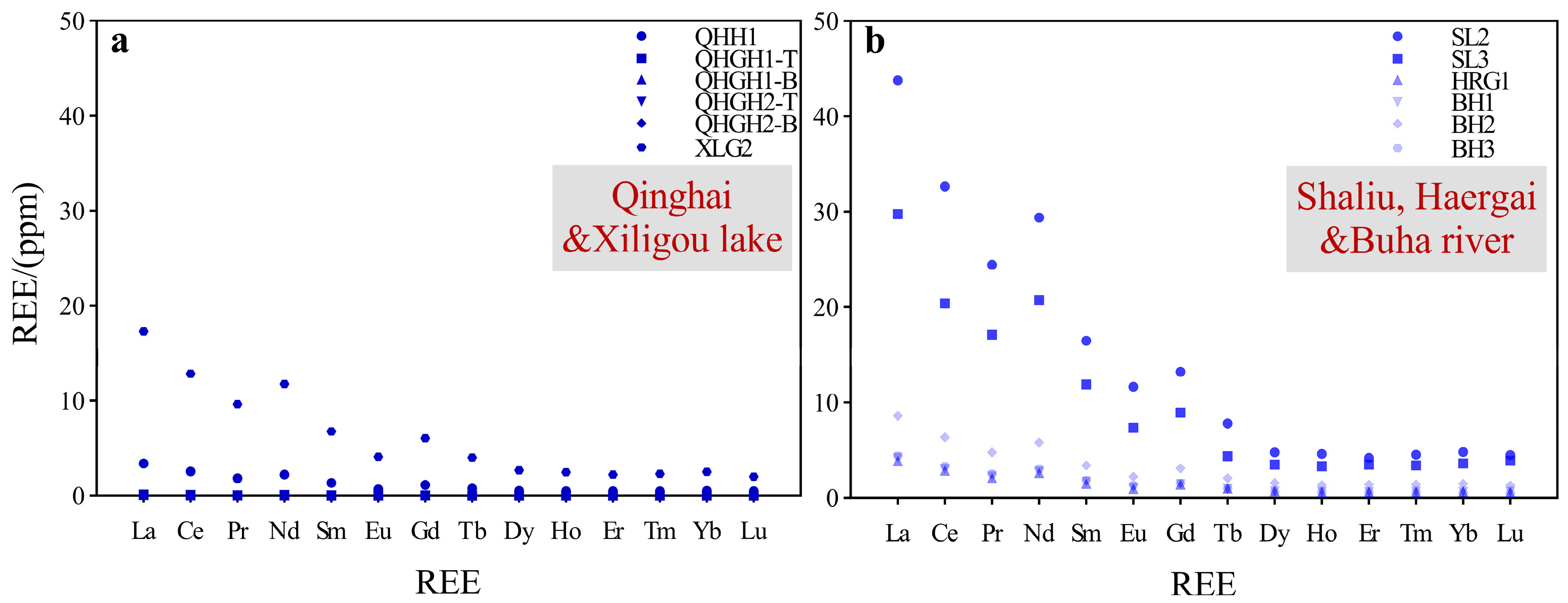
3.3. Region II: Distribution Characteristics of REEs
3.4. Region I vs. Region II
4. Discussion
4.1. Chondrite Standardized Partitioning Patterns
4.2. Parameter Ratio of REEs
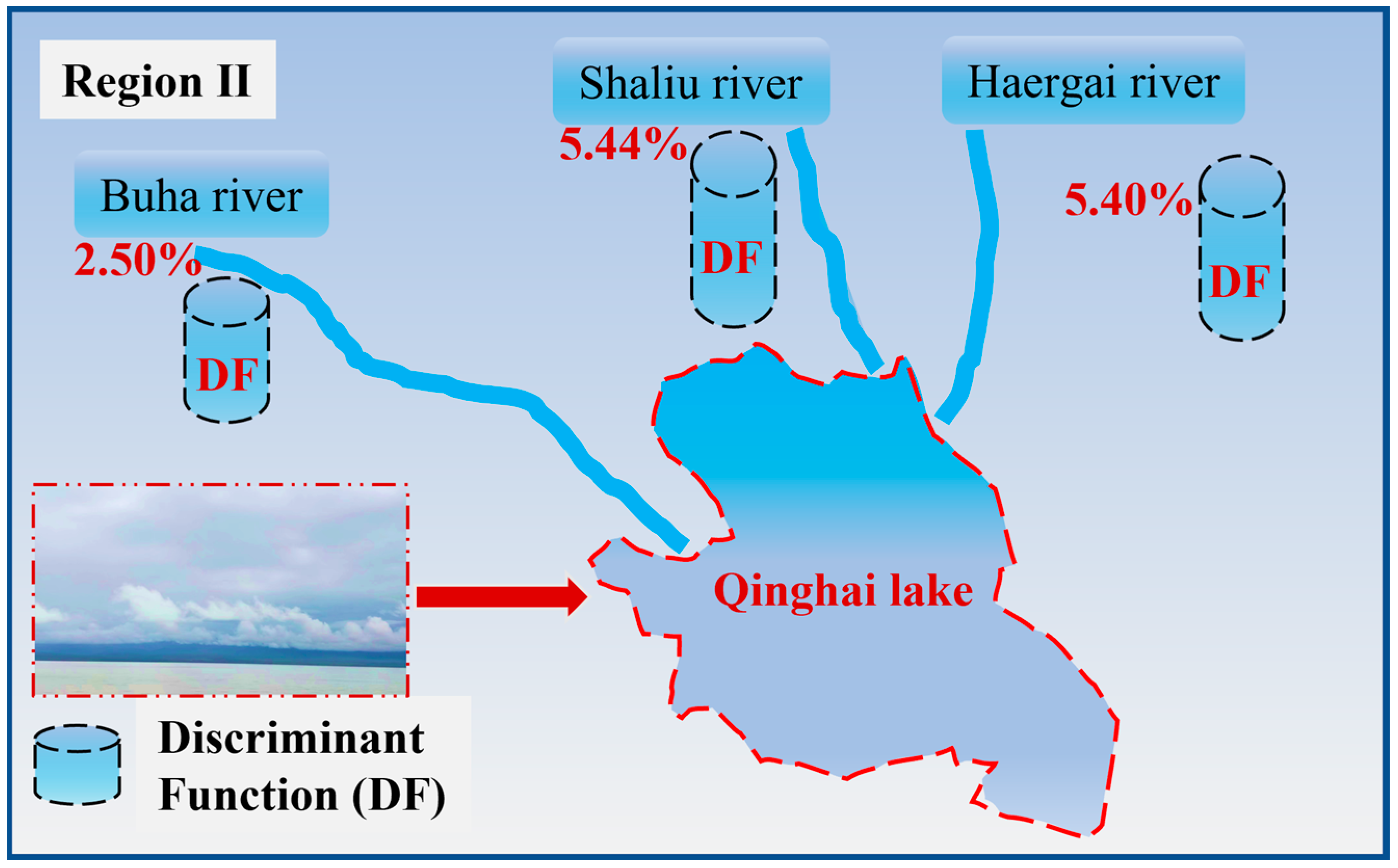
4.3. Discriminant Function in Region II
4.4. Indication of REEs
5. Conclusions
- The differences in REEs concentrations were relatively large in both regions, and the spatial distribution was heterogeneous. The ΣREE concentrations of lake particulate matter in Region I varied irregularly in depth, while the differences in ΣREE concentrations in Region II were correlated to the type and amount of particulate matter.
- There is no significant difference in ΣREE between the two regions, which are both characterized by relatively enriched LREE and lower HREE, but the degree of enrichment differs between the two regions.
- REEs partitioning is similar in the two regions, indicating that the source and formation of the particulate matter are consistent. Particulate matter in Region I predominantly originates from granite rocks undergoing weathering and transportation through rivers; the positive anomalies of Eu originate from the dissolution of Eu-rich minerals. Region II particulate matter is affected by chemical weathering and partial recycling of detrital material; the negative anomalies of Eu are inherited from the host rock. Diagenesis had no significant effect on the particulate rare earth elements, and different rivers contributed differently to Qinghai Lake.
- This study primarily provides a preliminary understanding of REEs in lake particles, assessing particle changes during the water-to-sediment process and their provenance indication. The solid speciation of REEs in particles is also an important part of future studies of the geochemical behavior of REEs, which is crucial for provenance studies.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pfalz, G.; Diekmann, B.; Freytag, J.C.; Biskaborn, B.K. Effect of temperature on carbon accumulation in northern lake systems over the past 21,000 years. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1233713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Huang, C.; Ma, N.; Zhang, Y. Improved landsat-based water and snow indices for extracting lake and snow cover/glacier in the Tibetan Plateau. Water 2020, 12, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nury, A.H.; Sharma, A.; Mehrotra, R.; Marshall, L.; Cordery, L. Projected changes in the Tibetan Plateau snowpack resulting from rising global temperatures. J. Geophys. Res. 2022, 127, e2021JD036201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, T.; Wang, J.; Schwalb, A.; Daut, G.; Plessen, B.; Zhu, L.; Mäusbacher, R.; Haberzettl, T. Precipitation dynamics on the Tibetan Plateau during the Late Quaternary—Hydroclimatic sedimentary proxies versus lake level variability. Glob. Planet. Change 2021, 205, 103594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinyemi, F.O.; Hutchinson, S.M.; Mîndrescu, M.; Rothwell, J.J. Lake sediment records of atmospheric pollution in the Romanian Carpathians. Quat. Int. 2013, 293, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maazallahi, M.; Khanehbad, M.; Moussavi-Harami, R.; Mahboubi, A.; Bajestani, M.S. Provenance analysis and maturity of the Rayen River sediments in Central Iran: Based on geochemical evidence. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinova, M.; Prokopčuk, N.; Tarasiuk, N. On the shapes of deep slopes of radiocesium vertical profiles in lake sediments. J. Environ. Radioact. 2023, 262, 107150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennwald, M.S.; Kipfer, R.; Imboden, D.M. Release of gas bubbles from lake sediment traced by noble gas isotopes in the sediment pore water. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 235, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worrall, F.; Pearson, D.G. The development of acidic groundwaters in coal-bearing strata: Part I. Rare earth element fingerprinting. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 1464–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krezoski, J.R. Sediment reworking and transport in eastern lake superior: In situ rare earth element tracer studies. J. Great Lakes Res. 1989, 15, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Han, X.; Ding, S.; Liang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Dong, L.L.; Zhang, H. Combining multiple methods for provenance discrimination based on rare earth element geochemistry in lake sediment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sojka, M.; Choiński, A.; Ptak, M.; Siepak, M. Causes of variations of trace and rare earth elements concentration in lakes bottom sediments in the Bory Tucholskie National Park, Poland. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slukovskii, Z.I.; Guzeva, A.V.; Dauvalter, V.A. Rare earth elements in surface lake sediments of Russian arctic: Natural and potential anthropogenic impact to their accumulation. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 142, 105325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.S.; Jiang, C.L.; Jiang, C.H.; Liu, F.; Zhu, Q.Y. Geochemical characteristics and migration patterns of rare earth elements in coal mining subsidence lakes under the influence of multiple factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Lin, C.; Yang, Q.; Yan, Y.; Huang, H.; Yu, R.; Cui, J.; Yan, Y. Distribution and source appointment of rare earth elements in offshore sediments of western Xiamen Bay, Southeast China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 201, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Sha, Z.; Wang, J.; Du, J.Z.; Hu, J.F.; Ma, Y.J. Historical changes in the major and trace elements in the sedimentary records of Lake Qinghai, Qinghai–Tibet Plateau: Implications for anthropogenic activities. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 2093–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Sha, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhong, Q.Q.; Fang, P.G.; Ma, Y.J.; Du, J.Z. Vertical distribution of radionuclides in Lake Qinghai, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, and its environmental implications. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Hao, L.; Li, S.; Wu, T.; Qin, Z.; Qiu, J. Geochemistry and petrography of the sediments from the marginal areas of Qinghai Lake, Northern Tibet Plateau, China: Implications for weathering and provenance. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 725553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spicer, R.A.; Su, T.; Valdes, P.J.; Farnsworth, A.; Wu, F.X.; Shi, G.; Spicer, T.E.; Zhou, Z. Why ‘the uplift of the Tibetan Plateau’ is a myth. Nat. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, nwaa091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; An, S.; Inouye, D.W.; Schwartz, M.D. Temperature and snowfall trigger alpine vegetation greenup on the world’s roof. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 3635–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, P.; Yun, H.; Jin, H.; Xu, X.; Jiang, G. Using stable isotopes to illuminate thermokarst lake hydrology in permafrost regions on the Qinghai-Tibet plateau, China. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2019, 30, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Zhu, L.; Ju, J.; Wang, J.; Ma, Q.; Kou, Q.A. Quantification of heat storage change-based evaporation behavior in middle–large-sized lakes in the inland of the Tibetan Plateau and their temporal and spatial variations. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.M.; Gu, X.F.; Yang, B.C.; Dang, X.Y.; Jiang, J.; You, X.Z. The Quaternary groundwater quality evaluation of Delingha Basin in Qinghai Province. Northwest. Geol. 2021, 54, 240–247. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, G.Y.; Yan, X.L.; Zhao, D.S.; Xiong, D.M. Petroleum geologic characteristics and exploration prospect of the Delingha fault-depression in the Qaidam Basin. Pet. Geol. Exper. 2006, 28, 500–503. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Ito, E. Possible orographic and solar controls of Late Holocene centennial-scale moisture oscillations in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L21705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Cheng, H.; Liu, W.G.; Mo, L.T.; Li, X.Z.; Ning, Y.F.; Ji, M.; Zong, B.Y.; Zhao, C. Geochemical and isotopic (U, Th) variations in lake waters in the Qinghai Lake Basin, Northeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China: Origin and paleoenvironmental implications. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, M.H.; Fang, X.M.; Wu, F.L.; Meng, Q.Q.; Zhang, Z.G.; Liu, X.M. Hydrochemical characteristics of the Hurleg Lake. Arid Land Geogr. 2015, 38, 44–51. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.; Zhang, J.W.; Wang, L.; Cui, X.L.; Ma, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.Z. Recent human impacts on sedimentary record: A case from Lake Tuosu. Quat. Sci. 2016, 36, 1456–1465. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Xu, H.Y.; Sun, Y.L.; Zhang, D.S.; Yang, Z.P. Lake-level change and water balance analysis at Lake Qinghai, west China during recent decades. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 1505–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; You, C.F.; Yu, J. Toward a Geochemical Mass Balance of Major Elements in Lake Qinghai, NE Tibetan Plateau: A Significant Role of Atmospheric Deposition. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 1901–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Yu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Shi, Y.; You, C.F. Constraints on Water Chemistry by Chemical Weathering in the Lake Qinghai Catchment, Northeastern Tibetan Plateau (China): Clues from Sr and its Isotopic Geochemistry. Hydrogeol. J. 2009, 17, 2037–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Pei, X.; Cao, C.; Chen, C.; Gong, Z.; Li, X.; Pang, J.; Liang, L.; Li, X.; Ning, Y.; et al. A novel tracer technique to quantify the lithogenic input flux of trace elements to Qinghai Lake. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 866314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Y.; Xia, D.S.; Liu, X.Y.; Liu, H.; Fan, Y.J.; Chen, P.Y.; Yu, Q. Application of magnetic susceptibility and heavy metal bioaccessibility to assessments of urban sandstorm contamination and health risks: Case studies from Dunhuang and Lanzhou, Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Hoff, J.; Gallup, C.D.; Richards, D.A.; Asmerom, Y. The half-lives of uranium-234 and thorium-230. Chem. Geol. 2000, 169, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.C.; Edwards, R.L.; Cheng, H.; Dorale, J.A.; Thomas, R.B.; Moran, S.B.; Weinstein, S.E.; Edmonds, H.N. Uranium and thorium isotopic and concentration measurements by magnetic sector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Chem. Geol. 2002, 185, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, P.; Li, X.Z.; Ning, Y.F.; Tan, L.C.; Edwards, R.L.; Yan, X.N.; Cheng, H. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of uranium isotopes in saline lake waters in the northeast of Qaidam Basin. Minerals 2020, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Fang, H.; He, G.; Jiang, H.; Wang, C. Effects of internal loading on phosphorus distribution in the Taihu Lake driven by wind waves and lake currents. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.B. Sedimentary Chronology Comparison of 210Pb, 137Cs and 239+240Pu in Different Water Environment. Master’s Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2021. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francke, A.; Dosseto, A.; Just, J.; Wagner, B.; Jones, B.G. Assessment of the controls on (234U/238U) activity ratios recorded in detrital lacustrine sediments. Chem. Geol. 2020, 550, 119698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Cao, C.; Li, X.; Pei, X.; Chen, C.; Liang, L.; Ning, Y.; Tan, L.; Edwards, R.L. Effects of ice freeze-thaw processes on U isotope compositions in saline lakes and their potential environmental implications. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 779954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Markovics, G.; Price, R.C. Chemical processes affecting alkalis and alkaline earths during continental weathering. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1980, 44, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Xu, Z.F.; Liu, C.Q. Rare-earth elements (REEs) of the suspended particulate matter in the upper reaches of the Xijiang River. Earth Environ. 2010, 38, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Li, X.X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.S. A study on the contents and species of rare earth elements in the water body in the Wuhan section of the Changjiang River. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1994, 49, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesson, K.H.; Berry, W.L.; Bird, D.A. Rare earth element concentrations and speciation in alkaline lakes from the western U.S.A. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1994, 21, 773–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Q.; Han, X.X.; Liang, T.; Guo, Q.J.; Li, J.; Ding, S.M. Discrimination of rare earth element geochemistry and co-occurrence in sediment from Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lake in China. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piper, D.Z. Rare earth elements in the sedimentary cycle: A summary. Chem. Geol. 1985, 14, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boynton, W.V. Cosmochemistry of the Rare Earth Elements: Meteorite Studies, 2nd ed.; Rare Earth Element Geochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; pp. 63–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, K.; Shazili, N.A. Rare earth elements in tropical surface water, soil and sediments of the Terengganu River Basin, Malaysia. J. Rare Earths 2009, 27, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laveuf, C.; Cornus, S. A review on the potentiality of rare earth elements to trace pedogenetic processes. Geoderma 2009, 154, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A.; Wesolowski, D.J.; Palmer, D.A. The aqueous geochemistry of the rare earth elements: IX. A potentiometric study of Nd3+ complexation with acetate in 0.1 molal NaCl solution from 25 °C to 225 °C. Chem. Geol. 2000, 167, 231–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soromotin, A.; Moskovchenko, D.; Khoroshavin, V.; Prikhodko, N.; Puzanov, A.; Kirillov, V.; Koveshnikov, M.; Krylova, E.; Krasnenko, A.; Pechkin, A. Major, trace and rare earth element distribution in water, suspended particulate matter and stream sediments of the Ob River Mouth. Water 2022, 14, 2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, T.; Leng, C.B.; Zhang, X.C.; Rehman, H.U. Geochemical attributes of magmatic apatite in the Kukaazi granite from western Kunlun orogenic belt, NW China: Implications for granite petrogenesis and Pb-Zn (-Cu-W) mineralization. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 204, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, M.S.; Ibranhim, S.; Samuding, K.; Kantasamy, N.; Rahman, S.A.; Hashim, A. Rare earth elements (REEs) as pollution indicator in sediment of Linggi River, Malaysia. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2019, 151, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwankam, F.N.; Eric, B.E.; Adama, A.; Bertrant, B.S.; Junior, A.N.R.; Ngwakfu, N.S.; Esue, M.F.; Ekumeli, M.H.; Ntube, N.M.; Agyingi, M.C. Geochemical characterisation of clastic sediments in Kompina (N’kapa Formation, NW Douala Basin, West Cameroon): Implication for provenance, paleoweathering and sediment maturity. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, B.L.; Li, X.Y. Runoff processes in the Qinghai Lake Basin, Northeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China: Insights from stable isotope and hydrochemistry. Quat. Int. 2015, 380–381, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Guo, H.M.; Pourret, O.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Z.X.; Zhang, W.M.; Liu, M.H. Distribution of rare earth elements in sediments of the North China Plain: A probe of sedimentation process. Appl. Geochem. 2021, 134, 105089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, M.R.; Araújo do Nascimento, C.W.; Biondi, C.M.; Agra Bezerra da Silva, Y.J.; Agra Bezerra da Silva, Y.J.; de Aguiar Accioly, A.M.; Montero, A.; Ugarte, O.M.; Estevez, J. Rare-earth-element geochemistry in soils developed in different geological settings of Cuba. Catena 2018, 162, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Site | Station | ΣREE | ΣLREE/ΣHREE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Keluke Lake | KLK1-M | 47.79 | 2.67 |
| KLK1-B | 12.60 | 3.97 | |
| KLK2-T | 22.08 | 3.57 | |
| KLK2-M | 28.62 | 3.76 | |
| KLK2-B | 319.71 | 2.73 | |
| KLK3-T | 350.42 | 2.77 | |
| KLK3-M | 191.01 | 2.01 | |
| Tuosu Lake | TS1-T | 19.61 | 1.93 |
| TS1-M | 45.85 | 2.56 | |
| TS2-T | 10.27 | 2.50 | |
| TS2-M | 16.33 | 3.08 | |
| TS3 | 21.84 | 2.25 | |
| Gahai Lake | GH1 | 158.14 | 2.43 |
| Site | Station | ΣREE | ΣLREE/ΣHREE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shaliu River | SL2 | 206.76 | 3.27 |
| SL3 | 141.69 | 3.12 | |
| Haergai River | HRG1 | 19.79 | 2.27 |
| Buha River | BH1 | 21.31 | 2.39 |
| BH2 | 44.81 | 2.29 | |
| BH3 | 22.50 | 2.72 | |
| Qinghai Lake | QHH1 | 16.93 | 2.50 |
| Qinghaigahai Lake | QHGH1-T | 0.66 | 2.39 |
| QHGH1-B | 0.51 | 2.39 | |
| QHGH2-T | 0.68 | 2.69 | |
| QHGH2-B | 0.85 | 2.30 | |
| Xiligou Lake | XLG2 | 86.74 | 2.57 |
| Site | Station | LaN/YbN | GdN/YbN | LaN/SmN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Keluke Lake | KLK1-M | 6.19 | 1.35 | 3.19 |
| KLK1-B | - | - | 5.06 | |
| KLK2-T | 129.14 | 48.01 | 4.67 | |
| KLK2-M | 11.57 | 2.59 | 3.39 | |
| KLK2-B | 9.53 | 3.16 | 2.67 | |
| KLK3-T | 7.58 | 2.67 | 2.69 | |
| KLK3-M | 14.03 | 4.60 | 3.71 | |
| Tuosu Lake | TS1-T | 6.97 | 2.57 | 2.95 |
| TS1-M | 7.10 | 2.18 | 3.86 | |
| TS2-T | 10.54 | 3.55 | 2.67 | |
| TS2-M | 6.30 | 1.76 | 3.61 | |
| TS3 | 7.21 | 2.63 | 2.79 | |
| Gahai Lake | GH1 | 6.74 | 2.41 | 2.70 |
| Site | Station | LaN/YbN | GdN/YbN | LaN/SmN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shaliu River | SL2 | 9.11 | 2.75 | 2.66 |
| SL3 | 8.27 | 2.48 | 2.50 | |
| Haergai River | HRG1 | 5.83 | 2.09 | 2.61 |
| Buha River | BH1 | 6.34 | 2.15 | 2.47 |
| BH2 | 5.89 | 2.11 | 2.54 | |
| BH3 | 7.82 | 2.74 | 2.35 | |
| Qinghai Lake | QHH1 | 6.55 | 2.18 | 2.53 |
| Qinghaigahai Lake | QHGH1-T | 8.66 | 3.27 | 2.24 |
| QHGH1-B | 7.84 | 3.89 | 2.18 | |
| QHGH2-T | 5.76 | 2.05 | 1.81 | |
| QHGH2-B | 5.15 | 2.38 | 2.16 | |
| Xiligou Lake | XLG2 | 6.91 | 2.42 | 2.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, L.; Li, L.; Cao, C.; Edwards, R.L. Provenance Indication of Rare Earth Elements in Lake Particulates from Environmentally Sensitive Regions. Water 2023, 15, 3700. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203700
Zhang P, Zhang Z, Liang L, Li L, Cao C, Edwards RL. Provenance Indication of Rare Earth Elements in Lake Particulates from Environmentally Sensitive Regions. Water. 2023; 15(20):3700. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203700
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Pu, Zhe Zhang, Lihua Liang, Lei Li, Chenyang Cao, and R. Lawrence Edwards. 2023. "Provenance Indication of Rare Earth Elements in Lake Particulates from Environmentally Sensitive Regions" Water 15, no. 20: 3700. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203700
APA StyleZhang, P., Zhang, Z., Liang, L., Li, L., Cao, C., & Edwards, R. L. (2023). Provenance Indication of Rare Earth Elements in Lake Particulates from Environmentally Sensitive Regions. Water, 15(20), 3700. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203700







